Solar eclipse of June 30, 1973: Difference between revisions
removed false info |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
With a maximum eclipse of 7 minutes and 3.55 seconds, this was the last total solar eclipse that exceeds 7 minutes in [[Solar Saros 136|this series]]. There will not be a longer total solar eclipse until [[Solar eclipse of June 25, 2150|June 25, 2150]]. |
With a maximum eclipse of 7 minutes and 3.55 seconds, this was the last total solar eclipse that exceeds 7 minutes in [[Solar Saros 136|this series]]. There will not be a longer total solar eclipse until [[Solar eclipse of June 25, 2150|June 25, 2150]]. |
||
The greatest eclipse occurred in the [[Agadez]] area in the northwest of Niger not far from Algeria inside the Sahara Desert somewhat 40 km east of the small mountain of |
The greatest eclipse occurred in the [[Agadez]] area in the northwest of Niger not far from Algeria inside the Sahara Desert somewhat 40 km east of the small mountain of Ebenenanoua at 18.8 N and 5.6 E and occurred at 11:38 UTC. |
||
The umbral portion of the path started near the border of [[Guyana]] and the [[Brazil]]ian state [[Roraima]], passed northern [[Surinam (Dutch colony)|Dutch Guiana]] (today's [[Suriname]]), headed into the Atlantic, included one of the [[Portuguese Cape Verde]] (today's [[Cape Verde]]) Islands, which was [[Santo Antão, Cape Verde|Santo Antão]], [[Nouadhibou]] and Nouakchott and other parts of Central Mauritania, northern Mali, the southernmost of Algeria, the middle and southeastern Niger, the middle of Chad, the Sudan including Darfur and parts that are now in the South Sudan including Kodok, a part of the northernmost Uganda, a part of northern Kenya, the southernmost of Somalia, and the [[Alphonse Group]] of British [[Seychelles]] (today's Seychelles). |
The umbral portion of the path started near the border of [[Guyana]] and the [[Brazil]]ian state [[Roraima]], passed northern [[Surinam (Dutch colony)|Dutch Guiana]] (today's [[Suriname]]), headed into the Atlantic, included one of the [[Portuguese Cape Verde]] (today's [[Cape Verde]]) Islands, which was [[Santo Antão, Cape Verde|Santo Antão]], [[Nouadhibou]] and Nouakchott and other parts of Central Mauritania, northern Mali, the southernmost of Algeria, the middle and southeastern Niger, the middle of Chad, the Sudan including Darfur and parts that are now in the South Sudan including Kodok, a part of the northernmost Uganda, a part of northern Kenya, the southernmost of Somalia, and the [[Alphonse Group]] of British [[Seychelles]] (today's Seychelles). |
||
Revision as of 22:36, 21 March 2024
| Solar eclipse of June 30, 1973 | |
|---|---|
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | −0.0785 |
| Magnitude | 1.0792 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 424 s (7 min 4 s) |
| Coordinates | 18°48′N 5°36′E / 18.8°N 5.6°E |
| Max. width of band | 256 km (159 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 11:38:41 |
| References | |
| Saros | 136 (35 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9450 |
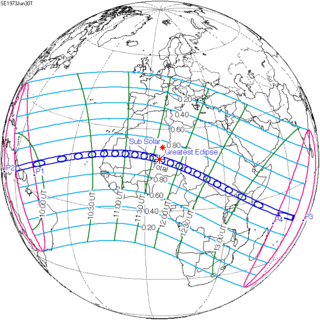
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on Saturday, June 30, 1973.[1] A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.
With a maximum eclipse of 7 minutes and 3.55 seconds, this was the last total solar eclipse that exceeds 7 minutes in this series. There will not be a longer total solar eclipse until June 25, 2150.
The greatest eclipse occurred in the Agadez area in the northwest of Niger not far from Algeria inside the Sahara Desert somewhat 40 km east of the small mountain of Ebenenanoua at 18.8 N and 5.6 E and occurred at 11:38 UTC.
The umbral portion of the path started near the border of Guyana and the Brazilian state Roraima, passed northern Dutch Guiana (today's Suriname), headed into the Atlantic, included one of the Portuguese Cape Verde (today's Cape Verde) Islands, which was Santo Antão, Nouadhibou and Nouakchott and other parts of Central Mauritania, northern Mali, the southernmost of Algeria, the middle and southeastern Niger, the middle of Chad, the Sudan including Darfur and parts that are now in the South Sudan including Kodok, a part of the northernmost Uganda, a part of northern Kenya, the southernmost of Somalia, and the Alphonse Group of British Seychelles (today's Seychelles).
Observations
This eclipse was observed by a group of scientists, which included Donald Liebenberg, from the Los Alamos National Laboratory. They used two airplanes to extend the apparent time of totality by flying along the eclipse path in the same direction as the Moon's shadow as it passed over Africa. One of the planes was a prototype (c/n 001) of what was later to become the Concorde, which has a top speed of almost 1,300 miles per hour (2,100 km/h) (Mach 2). This enabled scientists from Los Alamos, the Paris Observatory, the Kitt Peak National Observatory, Queen Mary University of London, the University of Aberdeen and CNRS to extend totality to more than 74 minutes; nearly 10 times longer than is possible when viewing a total solar eclipse from a stationary location.[2] The Concorde was specially modified with rooftop portholes for the mission, and is currently on display with the Solar Eclipse mission livery at Musée de l’air et de l’espace.[3] The data gathered resulted in three papers published in Nature[4] and a book.[5]
The eclipse was also observed by a charter flight from Mount San Antonio College in Southern California. The DC-8 with 150 passengers intercepted the eclipse at 35,000 feet (11,000 m) just off the east coast of Africa and tracked the eclipse for three minutes. The passengers rotated seats every 20 seconds so that each passenger had three 20 second opportunities at the window to observe and take pictures. A separate observation opportunity was provided on a specialized commercial cruise by the S.S. Canberra, which traveled from New York City to the Canary Islands and Dakar, Senegal, observing 5 minutes and 44 seconds of totality out in the Atlantic between those two stops in Africa.[6][7] That cruise's passengers included notables in the scientific community such as Neil Armstrong, Scott Carpenter, Isaac Asimov, Walter Sullivan, and the then 15-years old Neil deGrasse Tyson.[8][9]
Related eclipses
Eclipses in 1973
- An annular solar eclipse on Thursday, 4 January 1973.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on Thursday, 18 January 1973.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on Friday, 15 June 1973.
- A total solar eclipse on Saturday, 30 June 1973.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on Sunday, 15 July 1973.
- A partial lunar eclipse on Monday, 10 December 1973.
- An annular solar eclipse on Monday, 24 December 1973.
Solar eclipses of 1971–1974
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[10]
The partial solar eclipses on February 25, 1971 and August 20, 1971 occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1971 to 1974 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 116 | July 22, 1971 Partial |
1.513 | 121 | January 16, 1972 Annular |
−0.9365 | |
| 126 | July 10, 1972 Total |
0.6872 | 131 | January 4, 1973 Annular |
−0.2644 | |
| 136 | June 30, 1973 Total |
−0.0785 | 141 | December 24, 1973 Annular |
0.4171 | |
| 146 | June 20, 1974 Total |
−0.8239 | 151 | December 13, 1974 Partial |
1.0797 | |
Saros 136
This eclipse is a part of Saros series 136, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 71 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on June 14, 1360. It contains annular eclipses from September 8, 1504 through November 12, 1594; hybrid eclipses from November 22, 1612 through January 17, 1703; and total eclipses from January 27, 1721 through May 13, 2496. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on July 30, 2622. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of annularity was produced by member 9 at 32 seconds on September 8, 1504, and the longest duration of totality was produced by member 34 at 7 minutes, 7.74 seconds on June 20, 1955. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s descending node of orbit.[11]
| Series members 26–47 occur between 1801 and 2200: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 26 | 27 | 28 |
 March 24, 1811 |
 April 3, 1829 |
 April 15, 1847 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
 April 25, 1865 |
 May 6, 1883 |
 May 18, 1901 |
| 32 | 33 | 34 |
 May 29, 1919 |
 June 8, 1937 |
 June 20, 1955 |
| 35 | 36 | 37 |
 June 30, 1973 |
 July 11, 1991 |
 July 22, 2009 |
| 38 | 39 | 40 |
 August 2, 2027 |
 August 12, 2045 |
 August 24, 2063 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 |
 September 3, 2081 |
 September 14, 2099 |
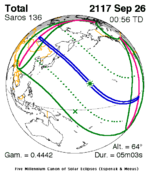 September 26, 2117 |
| 44 | 45 | 46 |
 October 7, 2135 |
 October 17, 2153 |
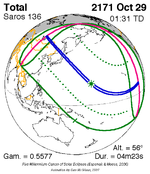 October 29, 2171 |
| 47 | ||
 November 8, 2189 | ||
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.
| 22 eclipse events between September 12, 1931 and July 1, 2011 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| September 11–12 | June 30–July 1 | April 17–19 | February 4–5 | November 22–23 |
| 114 | 116 | 118 | 120 | 122 |
 September 12, 1931 |
 June 30, 1935 |
 April 19, 1939 |
 February 4, 1943 |
 November 23, 1946 |
| 124 | 126 | 128 | 130 | 132 |
 September 12, 1950 |
 June 30, 1954 |
 April 19, 1958 |
 February 5, 1962 |
 November 23, 1965 |
| 134 | 136 | 138 | 140 | 142 |
 September 11, 1969 |
 June 30, 1973 |
 April 18, 1977 |
 February 4, 1981 |
 November 22, 1984 |
| 144 | 146 | 148 | 150 | 152 |
 September 11, 1988 |
 June 30, 1992 |
 April 17, 1996 |
 February 5, 2000 |
 November 23, 2003 |
| 154 | 156 | |||
 September 11, 2007 |
 July 1, 2011 | |||
Notes
- ^ Hatherill, Chris (March 9, 2016). "When Astronomers Chased a Total Eclipse in a Concorde".
- ^ Mulkin, Barb (1981). "In Flight: The Story of Los Alamos Eclipse Missions" (PDF). Los Alamos National Laboratory. p. 42. Retrieved 2010-07-14.
- ^ Chris Hatherill (9 March 2016). "When Astronomers Chased a Total Eclipse in a Concorde". Motherboard. Vice.
- ^ Hatherill, Chris (9 March 2016). "When Astronomers Chased a Total Eclipse in a Concorde". Vice. Retrieved 10 March 2016.
- ^ Léna, Pierre (2015). Racing the Moon's Shadow with Concorde 001. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-21729-1. Retrieved 10 March 2016.
- ^ Stewart Leber, Bay (July 12, 1973). "Voyage to Darkness". Honolulu Star-Ledger. Honolulu. Retrieved February 12, 2020.
- ^ Sullivan, Walter (July 1, 1973). "Rare Eclipse Sweeps Across Width of Africa". The New York Times. New York. Retrieved February 12, 2020.
- ^ Asimov, Isaac (April 1, 1980). In Joy Still Felt. Doubleday. ISBN 9780385155441.
- ^ DeGrasse Tyson, Neil (May 1, 2004). The Sky is Not the Limit. Prometheus Books. ISBN 9781616141202.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ "NASA - Catalog of Solar Eclipses of Saros 136". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.