Korean conflict: Difference between revisions
Jack Upland (talk | contribs) →Current situation: Uncited and unverified |
Jerryzhu2004 (talk | contribs) Added "2017" year for clarity |
||
| Line 142: | Line 142: | ||
In 2017, the incoming U.S. President [[Donald Trump]] abandoned the policy of "strategic patience" associated with the preceding Obama administration. |
In 2017, the incoming U.S. President [[Donald Trump]] abandoned the policy of "strategic patience" associated with the preceding Obama administration. |
||
In March, it was reported that the South Korean government had increased the rewards to [[North Korean defector]]s who brought classified information or military equipment with them.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://asiancorrespondent.com/2017/03/south-korea-govt-pay-defectors-north-korea-secrets/#8jmylFYF6gcExTYD.97|title=South Korea: Government to pay defectors for North Korea secrets|publisher=Asian Correspondent|date=5 March 2017|deadurl=no|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20170306132526/https://asiancorrespondent.com/2017/03/south-korea-govt-pay-defectors-north-korea-secrets/#8jmylFYF6gcExTYD.97|archivedate=6 March 2017|df=}}</ref> |
In March 2017, it was reported that the South Korean government had increased the rewards to [[North Korean defector]]s who brought classified information or military equipment with them.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://asiancorrespondent.com/2017/03/south-korea-govt-pay-defectors-north-korea-secrets/#8jmylFYF6gcExTYD.97|title=South Korea: Government to pay defectors for North Korea secrets|publisher=Asian Correspondent|date=5 March 2017|deadurl=no|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20170306132526/https://asiancorrespondent.com/2017/03/south-korea-govt-pay-defectors-north-korea-secrets/#8jmylFYF6gcExTYD.97|archivedate=6 March 2017|df=}}</ref> |
||
On July 4, 2017, North Korea successfully conducted its first test of an [[intercontinental ballistic missile]] (ICBM), named [[Hwasong-14]].<ref name="NYT July 4">{{cite news |title=North Korea Claims Success in Long-Range Missile Test |first1=Sang-hun |last1=Choe |first2= |last2= |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2017/07/04/world/asia/north-korea-missile-test-icbm.html |newspaper=The New York Times |location=New York |date=July 4, 2017 |accessdate=July 4, 2017 |page= |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20170704065145/https://www.nytimes.com/2017/07/04/world/asia/north-korea-missile-test-icbm.html |archivedate=July 4, 2017 |deadurl=no |df= }}</ref> It conducted another test on 28 July.<ref name="NYT Jul 29">{{cite news |title=North Korea Launches Ballistic Missile, the Pentagon Says |first1=Sang-hun |last1=Choe |first2=Eileen |last2=Sullivan |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2017/07/28/world/asia/north-korea-ballistic-missile.html |newspaper=The New York Times |location=New York |date=July 28, 2017 |accessdate=July 28, 2017 |page= |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20170728175029/https://www.nytimes.com/2017/07/28/world/asia/north-korea-ballistic-missile.html |archivedate=July 28, 2017 |deadurl=no |df= }}</ref> On August 5, 2017, the UN imposed further sanctions which were met with defiance from the North Korean government.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-40846959|title=North Korea vows to retaliate against US over sanctions|website=BBC News|deadurl=no|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20170810082250/http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-40846959|archivedate=2017-08-10|df=}}</ref> |
On July 4, 2017, North Korea successfully conducted its first test of an [[intercontinental ballistic missile]] (ICBM), named [[Hwasong-14]].<ref name="NYT July 4">{{cite news |title=North Korea Claims Success in Long-Range Missile Test |first1=Sang-hun |last1=Choe |first2= |last2= |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2017/07/04/world/asia/north-korea-missile-test-icbm.html |newspaper=The New York Times |location=New York |date=July 4, 2017 |accessdate=July 4, 2017 |page= |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20170704065145/https://www.nytimes.com/2017/07/04/world/asia/north-korea-missile-test-icbm.html |archivedate=July 4, 2017 |deadurl=no |df= }}</ref> It conducted another test on 28 July.<ref name="NYT Jul 29">{{cite news |title=North Korea Launches Ballistic Missile, the Pentagon Says |first1=Sang-hun |last1=Choe |first2=Eileen |last2=Sullivan |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2017/07/28/world/asia/north-korea-ballistic-missile.html |newspaper=The New York Times |location=New York |date=July 28, 2017 |accessdate=July 28, 2017 |page= |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20170728175029/https://www.nytimes.com/2017/07/28/world/asia/north-korea-ballistic-missile.html |archivedate=July 28, 2017 |deadurl=no |df= }}</ref> On August 5, 2017, the UN imposed further sanctions which were met with defiance from the North Korean government.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-40846959|title=North Korea vows to retaliate against US over sanctions|website=BBC News|deadurl=no|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20170810082250/http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-40846959|archivedate=2017-08-10|df=}}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 12:17, 23 March 2018
| Korean conflict | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 The Korean DMZ, viewed from the north. | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
| ||||||||
| This article is part of a series on |
 |
|---|
|
|
 |
|---|
|
|
The Korean conflict is based on the division between the Democratic People's Republic of Korea in the north and the Republic of Korea in the south, both of which claim to be the government of the entire peninsula. During the Cold War, North Korea was backed by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist states, and South Korea was backed by the United States and its allies. The division of Korea occurred at the end of World War II in 1945, and tensions erupted into the Korean War in 1950. When the war ended, the country was devastated, but the division remained. North and South Korea continued a military standoff with periodic clashes. The cold civil war survived the collapse of the Eastern Bloc of 1989 to 1991.
The US maintains a military presence in the South to help deter any potential attack from the North. In 1997, U.S. President Bill Clinton described the division of Korea as the "Cold War's last divide".[1] In 2002, U.S. President George W Bush described North Korea as a member of an "Axis of Evil".[2][3] Facing increasing isolation, North Korea has developed missile and nuclear capabilities.
Background
Korea was annexed by the Empire of Japan in 1910. In the following decades during the Japanese occupation of Korea, nationalist and radical groups emerged, mostly in exile, to struggle for independence. Divergent in their outlooks and approaches, these groups failed to unite in one national movement.[4][5] Based in China, the Korean Provisional Government failed to obtain widespread recognition.[6] The many leaders agitating for Korean independence included the conservative and U.S.-educated Syngman Rhee, who lobbied the U.S. government, and the Communist Kim Il-sung, who fought a guerrilla war against the Japanese from neighboring Manchuria to the north of Korea.[7]
Following the end of the occupation, many high-ranking Koreans were accused of collaborating with Japanese imperialism.[8] An intense struggle between various figures and political groups aspiring to lead Korea ensued.[9]
Division of Korea

On August 9, 1945, in the closing days of World War II, the Soviet Union declared war on Japan and advanced into Korea. Though the Soviet declaration of war had been agreed by the Allies at the Yalta Conference, the US government became concerned at the prospect of all of Korea falling under Soviet control. The US government therefore requested Soviet forces halt their advance at the 38th parallel north, leaving the south of the peninsula, including the capital, Seoul, to be occupied by the US. This was incorporated into General Order No. 1 to Japanese forces after the surrender of Japan on August 15. On August 24, the Red Army entered Pyongyang and established a military government over Korea north of the parallel. American forces landed in the south on September 8 and established the United States Army Military Government in Korea.[10]
The Allies had originally envisaged a joint trusteeship which would usher Korea towards independence, but most Korean nationalists wanted independence immediately.[11] Meanwhile, the wartime co-operation between the Soviet Union and the US deteriorated as the Cold War took hold. Both occupying powers began promoting into positions of authority Koreans aligned with their side of politics and marginalizing their opponents. Many of these emerging political leaders were returning exiles with little popular support.[12][13] In North Korea, the Soviet Union supported Korean Communists. Kim Il-sung, who from 1941 had served in the Soviet Army, became the major political figure.[14] Society was centralized and collectivized, following the Soviet model.[15] Politics in the South were more tumultuous, but the strongly anti-Communist Syngman Rhee, who had been educated in the United States, was positioned as the most prominent politician.[16] The rival leaders, Kim Koo and Lyuh Woon-hyung, were assassinated.[9]
As a result, two antagonistic states emerged, with diametrically opposed political, economic, and social systems. In South Korea, a general election was held on May 10, 1948. The Republic of Korea (or ROK) was established with Syngman Rhee as President, and formally replaced the US military occupation on August 15. In North Korea, the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (or DPRK) was declared on September 9, with Kim Il-sung, as prime minister. Soviet occupation forces left the DPRK on December 10, 1948. US forces left the ROK the following year, though the US Korean Military Advisory Group remained to train the Republic of Korea Army.[17] The new regimes even adopted different names for Korea: the North choosing Choson, and the South Hanguk.[18]
Both opposing governments considered themselves to be the government of the whole of Korea (as they do to this day), and both saw the division as temporary.[19][20] Kim Il-sung lobbied Stalin and Mao for support in a war of reunification. Syngman Rhee repeatedly expressed his desire to conquer the North.[21][22] In 1948 North Korea, which had almost all of the generators, turned off the electricity supply to the South.[23] In the lead-up to the outbreak of war, there were frequent clashes along the 38th parallel, especially at Kaesong and Ongjin, initiated by both sides.[24][25]
Throughout this period there were uprisings in the South, such as the Jeju Uprising and the Yeosu–Suncheon Rebellion, that were brutally suppressed. In all, over one hundred thousand lives were lost in fighting across Korea before the Korean War began.[26]
Korean War

By 1950, North Korea had clear military superiority over the South. The Soviet occupiers had armed it with surplus weaponry and provided training. Many troops returning to North Korea were battle-hardened from their participation in the Chinese Civil War, which had just ended.[27][28] Kim Il-sung expected a quick victory, predicting that there would be pro-Communist uprisings in the South and that the US would not intervene.[29] Rather than perceiving the conflict as a civil war, however, the West saw it in Cold War terms as Communist aggression, related to recent events in China and Eastern Europe.[30]
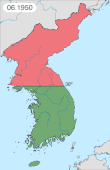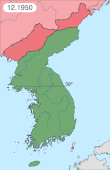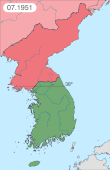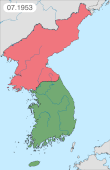
North Korea invaded the South on June 25, 1950, and swiftly overran most of the country. In September 1950 United Nations force, led by the United States, intervened to defend the South, and following the Incheon Landing and breakout from the Busan Perimeter, rapidly advanced into North Korea. As they neared the border with China, Chinese forces intervened on behalf of North Korea, shifting the balance of the war again. Fighting ended on July 27, 1953, with an armistice that approximately restored the original boundaries between North and South Korea.[22]
Korea was devastated. More than one million civilians and soldiers had been killed. Seoul was in ruins, having changed hands four times.[31] Almost every substantial building in North Korea had been destroyed.[32][33] As a result, North Koreans developed a deep-seated enmity towards the US.[31]
Armistice
Negotiations for an armistice began on July 10, 1951, as the war continued. The main issues were the establishment of a new demarcation line and the exchange of prisoners. After Stalin died, the Soviet Union brokered concessions which led to an agreement on July 27, 1953.[34]
Syngman Rhee opposed the armistice because it left Korea divided. As negotiations drew to a close, he attempted to sabotage the arrangements for the release of prisoners, and led mass rallies against the armistice.[35] He refused to sign the agreement, but reluctantly agreed to abide by it.[36]
The armistice inaugurated an official ceasefire but did not lead to a peace treaty.[37] It established the Korean Demilitarized Zone (DMZ), a buffer zone between the two sides, that intersected the 38th parallel but did not follow it.[36] Despite its name, the border was, and continues to be, one of the most militarized in the world.[31]
North Korea has announced that it will no longer abide by the armistice at least six times, in the years 1994, 1996, 2003, 2006, 2009, and 2013.[38][39]
Continuing conflict during the Cold War

After the war, the Chinese forces left, but US forces remained in the South. Sporadic conflict continued between North and South Korea. On October 1, 1953, the United States and South Korea signed a defense treaty.[40] In 1958, the United States stationed nuclear weapons in South Korea.[41] In 1961, North Korea signed mutual defense treaties with the USSR and China.[42] During this period, North Korea was described by former CIA director Robert Gates to be the "toughest intelligence target in the world".[43] Alongside the military confrontation, there has been a propaganda war, including balloon propaganda campaigns.
The opposing regimes aligned themselves with opposing sides in the Cold War. Both sides received recognition as the legitimate government of Korea from the opposing blocs.[44][45]
North Korea presented itself as a champion of orthodox Communism, distinct from the Soviet Union and China. The regime developed the doctrine of Juche or self-reliance, which included extreme military mobilization.[46] In response to the threat of nuclear war, it constructed extensive facilities underground and in the mountains.[47][23] The Pyongyang Metro opened in the 1970s, with the capacity to double as bomb shelter.[48] Until the early 1970s, North Korea was economically the equal of the South.[49]
South Korea became a strongly anti-Communist military dictatorship and was heavily involved in the Vietnam War.[50] North Korea's occupation left behind a guerrilla movement that persisted in Cholla provinces.[31]
Tensions between North and South escalated in the late 1960s with a series of low-level armed clashes known as the Korean DMZ Conflict. In 1966, Kim declared "liberation of the south" to be a "national duty".[51] In 1968, North Korean commandos launched the Blue House Raid, an unsuccessful attempt to assassinate the South Korean President Park Chung-hee. Shortly after, the US spy ship Pueblo was captured by the North Korean navy.[52] The Americans saw the crisis in terms of the global confrontation with Communism, but rather than orchestrating the incident the Soviet government was concerned by it.[53] Kim was, however, inspired by Communist successes in the Vietnam War.[54]
In 1969, North Korea shot down a US EC-121 spy plane over the Sea of Japan, killing all 31 crew on board, which constitutes the largest single loss of US aircrew during the Cold War.[55] In 1969, Korean Air Lines YS-11 was hijacked and flown to North Korea. Similarly, in 1970, the hijackers of Japan Airlines Flight 351 were given asylum in North Korea.[56] In response to the Blue House Raid, the South Korean government set up a special unit to assassinate Kim Il-sung, but the mission was aborted in 1972.[57]
In 1974 a North Korean sympathizer attempted to assassinate President Park and killed his wife, Yuk Young-soo.[58] In 1976, the axe murder incident led to the death of two US Army officers in the DMZ and threatened to trigger a wider war.[59][60] In the 1970s, North Korea kidnapped a number of Japanese citizens.[56]
In 1976, in now-declassified minutes, US Deputy Secretary of Defense William Clements told Henry Kissinger that there had been 200 raids or incursions into North Korea from the South, though not by the U.S. military.[61] Details of only a few of these incursions have become public, including raids by South Korean forces in 1967 that had sabotaged about 50 North Korean facilities.[62]
In the 1970s, both North and South began building up their military capacity.[63] It was discovered that North Korea had dug tunnels under the DMZ which could accommodate thousands of troops.[64] Alarmed at the prospect of US disengagement, South Korea began a secret nuclear weapons program which was strongly opposed by Washington.[65]
In 1977, US President Jimmy Carter proposed the withdrawal of troops from South Korea. There was a widespread backlash in America and in South Korea, and critics argued that this would allow the North to capture Seoul. Carter postponed the move, and his successor Ronald Reagan reversed the policy, increasing troop numbers to forty-three thousand.[66] After Reagan supplied the South with F-16 fighters, and after Kim Il-sung visited Moscow in 1984, the USSR recommenced military aid and co-operation with the North.[67]
Unrest in the South came to a head with the Gwangju Uprising in 1980. The dictatorship equated dissent with North Korean subversion. On the other hand, some young protesters viewed the US as complicit in political repression and identified with the North's nationalist propaganda.[68][69]
In 1983 North Korea carried out the Rangoon bombing, a failed assassination attempt against South Korean President Chun Doo-hwan while he was visiting Burma.[70] The bombing of Korean Air Flight 858 in 1987, in the lead up to the Seoul Olympics, led to the US government placing North Korea on its list of terrorist countries.[71][72]
The end of the Cold War
As the Cold War ended, North Korea lost the support of the Soviet Union and plunged into an economic crisis. With the death of Leader Kim Il-sung in 1994,[73] there were expectations that the North Korean government could collapse and the peninsula would be reunified.[74][75]
In response to its increased isolation, North Korea redoubled its efforts to develop nuclear weapons and intercontinental ballistic missiles. In 1994, US President Bill Clinton considered bombing the Yongbyon nuclear reactor. He was advised that if war broke out, it could cost 52,000 US and 490,000 South Korean military casualties in the first three months, as well as a large number of civilian casualties.[76][77] Instead, in 1994, the US and North Korea signed an Agreed Framework which aimed to freeze North Korea's nuclear program. In 1998, South Korean President Kim Dae-jung initiated the Sunshine Policy which aimed to foster better relations with the North.[78] However, in the aftermath of the September 11 attacks, U.S. President George W Bush denounced the policy, and in 2002 branded North Korea as a member of an "Axis of Evil".[2][3] Six-party talks involving North and South Korea, the United States, Russia, Japan, and China commenced in 2003 but failed to achieve a resolution. In 2006, North Korea announced it had successfully conducted its first nuclear test.[79] The Sunshine Policy was formally abandoned by South Korean President Lee Myung-bak after his election in 2007.[80]
At the start of the twenty first century, it was estimated that the concentration of firepower in the area between Pyongyang and Seoul was greater than that in central Europe during the Cold War.[81] The North's Korean People's Army was numerically twice the size of South Korea's military and had the capacity to devastate Seoul with artillery and missile bombardment. South Korea's military, however, was assessed as being technically superior in many ways.[82][83] US forces remained in South Korea and carried out annual military exercises with South Korean forces, including Key Resolve, Foal Eagle, and Ulchi-Freedom Guardian. These have been routinely denounced by North Korea as acts of aggression.[84][85][86] Between 1997 and 2016, the North Korea government accused other governments of declaring war against it 200 times.[87] Analysts have described the US garrison as a tripwire ensuring American military involvement, but some have queried whether sufficient reinforcements would be forthcoming.[88]
During this period, two North Korean submarines were captured after being stranded on the South Korean coast, one near Gangneung in 1996 and one near Sokcho in 1998. In December 1998, the South Korean navy sank a North Korean semi-submersible in the Battle of Yeosu. In 2001, the Japanese Coast Guard sank a North Korean spy ship in the Battle of Amami-Ōshima.
Conflict intensified near the disputed maritime boundary known as the Northern Limit Line in the Yellow Sea. In 1999 and 2002, there were clashes between the navies of North and South Korea, known as the First and Second battle of Yeonpyeong. On March 26, 2010, a South Korean naval vessel, the ROKS Cheonan, sank, near Baengnyeong Island in the Yellow Sea and a North Korean torpedo was blamed. On November 23, 2010, in response to a joint military exercise, North Korea fired artillery at South Korea's Greater Yeonpyeong island in the Yellow Sea, and South Korea returned fire.
In 2013, amidst tensions about its missile program, North Korea forced the temporary shutdown of the jointly operated Kaesong Industrial Region.[89] The zone was shut again in 2016.[90] A South Korean parliamentarian was convicted of plotting a campaign of sabotage to support the North in 2013 and jailed for 12 years.[91] In 2014, according to the New York Times, US President Barack Obama ordered the intensification of cyber and electronic warfare to disrupt North Korea's missile testing.[92] However, this account has been disputed by analysts from the Nautilus Institute.[93]
In 2016, in the face of protests, South Korea decided to deploy the US THAAD anti-missile system.[94] After North Korea's fifth nuclear test in September 2016, it was reported that South Korea had developed a plan to raze Pyongyang if there were signs of an impending nuclear attack from the North.[95] As South Korea was convulsed by scandal, North Korea enthusiastically supported the removal of President Park Geun-hye, intensifying leaflet drops.[96] In turn, Park's supporters accused the opposition Liberty Korea Party of basing its logo on Pyongyang's Juche Tower.[97]
Current situation
In 2017, the incoming U.S. President Donald Trump abandoned the policy of "strategic patience" associated with the preceding Obama administration.
In March 2017, it was reported that the South Korean government had increased the rewards to North Korean defectors who brought classified information or military equipment with them.[98]
On July 4, 2017, North Korea successfully conducted its first test of an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM), named Hwasong-14.[99] It conducted another test on 28 July.[100] On August 5, 2017, the UN imposed further sanctions which were met with defiance from the North Korean government.[101] Following the sanctions, Trump warned that North Korean nuclear threats "will be met with fire, fury and frankly power, the likes of which the world has never seen before". In response, North Korea announced that it was considering a missile test in which the missiles would land near the US territory of Guam.[102][103]
On August 29, North Korea fired another missile.[104] Days later with tensions still high, North Korea conducted their sixth nuclear test on September 3.[105] The test was met with international condemnation and resulted in further economic sanctions being taken against North Korea.[106] Just over two weeks after their previous test, North Korea launched another missile.[107]
In October, it was reported that North Korea hackers had stolen classified South Korean military data the year before, including a plan for the killing of Kim Jong-un. According to cybersecurity experts, North Korea maintains an army of hackers trained to disrupt enemy computer networks and steal both money and sensitive data. In the past decade, it has been blamed for numerous cyber-attacks and other hacking attacks in South Korea and elsewhere.[108]
On November 28, North Korea launched another missile, which, according to analysts, would be capable of reaching anywhere in the United States.[109] The test resulted in the United Nations placing further sanctions on the country.[110]
In January 2018, the Seoul–Pyongyang hotline was reopened after almost two years.[111]
Later in January, a international meeting was co-hosted by Canada and the USA regarding ways to increase the effectiveness of the sanctions on North Korea.[112] The co-chairs (Canadian Foreign Minister Freeland and U.S. Secretary of State Tillerson) issued a summary that emphasized the urgency of persuading North Korea to denuclearize and emphasizing the need for sanctions to create conditions for a diplomatic solution.[113]
In February, North Korea sent an unprecedented high-level delegation to the Winter Olympics in South Korea, headed by Kim Yo-jong, sister of Kim Jong-un, and President Kim Yong-nam, which passed on an invitation to President Moon to visit the North.[114]
See also
- History of North Korea
- History of South Korea
- Korean reunification
- North Korea–South Korea relations
- North Korea–United States relations
- List of border incidents involving North Korea
References
- ^ Hyung Gu Lynn (2007). Bipolar Orders: The Two Koreas since 1989. Zed Books. p. 3.
- ^ a b Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea's Place in the Sun: A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. p. 504. ISBN 0-393-32702-7.
- ^ a b Bluth, Christoph (2008). Korea. Cambridge: Polity Press. p. 112. ISBN 978-07456-3357-2.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. pp. 31–37. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea's Place in the Sun: A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 156–60. ISBN 0-393-32702-7.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea's Place in the Sun: A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 159–60. ISBN 0-393-32702-7.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. pp. 35–36, 46–47. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. pp. 48–49. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ a b Robinson, Michael E (2007). Korea's Twentieth-Century Odyssey. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. p. 103. ISBN 978-0-8248-3174-5.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 50. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 59. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. pp. 50–51, 59. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea's Place in the Sun: A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 194–95. ISBN 0-393-32702-7.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 56. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 68. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. pp. 66, 69. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea's Place in the Sun: A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 255–56. ISBN 0-393-32702-7.
- ^ Bluth, Christoph (2008). Korea. Cambridge: Polity Press. p. 178. ISBN 978-07456-3357-2.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 72. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea's Place in the Sun: A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 505–06. ISBN 0-393-32702-7.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea's Place in the Sun: A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 249–58. ISBN 0-393-32702-7.
- ^ a b Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 71. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ a b Robinson, Michael E (2007). Korea's Twentieth-Century Odyssey. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. p. 120. ISBN 978-0-8248-3174-5.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea's Place in the Sun: A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 247–53. ISBN 0-393-32702-7.
- ^ Stueck, William W. (2002), Rethinking the Korean War: A New Diplomatic and Strategic History, Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, p. 71, ISBN 0-691-11847-7
- ^ Jager, Sheila Miyoshi (2013). Brothers at War – The Unending Conflict in Korea. London: Profile Books. p. 4. ISBN 978-1-84668-067-0.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 73. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Robinson, Michael E (2007). Korea's Twentieth-Century Odyssey. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. pp. 114–15. ISBN 978-0-8248-3174-5.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. pp. 72, 77–78. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 86. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ a b c d Robinson, Michael E (2007). Korea's Twentieth-Century Odyssey. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. p. 119. ISBN 978-0-8248-3174-5.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea's Place in the Sun: A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 297–98. ISBN 0-393-32702-7.
- ^ Jager, Sheila Miyoshi (2013). Brothers at War – The Unending Conflict in Korea. London: Profile Books. pp. 237–42. ISBN 978-1-84668-067-0.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. pp. 81–82. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Jager, Sheila Miyoshi (2013). Brothers at War – The Unending Conflict in Korea. London: Profile Books. pp. 278–81. ISBN 978-1-84668-067-0.
- ^ a b Bluth, Christoph (2008). Korea. Cambridge: Polity Press. p. 20. ISBN 978-07456-3357-2.
- ^ Hyung Gu Lynn (2007). Bipolar Orders: The Two Koreas since 1989. Zed Books. p. 8.
- ^ "Chronology of major North Korean statements on the Korean War armistice". News. Yonhap. 2009-05-28. Archived from the original on 2013-03-10.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "North Korea ends peace pacts with South". BBC News. 2013-03-08. Archived from the original on 2013-03-10.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 206. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea's Place in the Sun: A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. p. 493. ISBN 0-393-32702-7.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 208. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Oberdorfer, Don; Carlin, Robert (2014). The Two Koreas: A Contemporary History. Basic Books. p. 48. ISBN 9780465031238.
- ^ Wertz, Daniel; Oh, JJ; Kim, Insung (2015). The DPRK Diplomatic Relations (PDF) (Report). National Committee on North Korea. p. 1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-12-28.
{{cite report}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Oberdorfer, Don; Carlin, Robert (2014). The Two Koreas: A Contemporary History. Basic Books. p. 123. ISBN 9780465031238.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. pp. 93, 95–97. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea's Place in the Sun: A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. p. 497. ISBN 0-393-32702-7.
- ^ Springer, Chris (2003). Pyongyang: the hidden history of the North Korean capital. Entente Bt. p. 125. ISBN 978-963-00-8104-7.
- ^ Robinson, Michael E (2007). Korea's Twentieth-Century Odyssey. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. p. 148. ISBN 978-0-8248-3174-5.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. pp. 107, 116. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Jager, Sheila Miyoshi (2013). Brothers at War – The Unending Conflict in Korea. London: Profile Books. p. 366. ISBN 978-1-84668-067-0.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 99. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Jager, Sheila Miyoshi (2013). Brothers at War – The Unending Conflict in Korea. London: Profile Books. p. 371. ISBN 978-1-84668-067-0.
- ^ Oberdorfer, Don; Carlin, Robert (2014). The Two Koreas: A Contemporary History. Basic Books. pp. 50–51. ISBN 9780465031238.
- ^ Larson, George A. ] (2001). Cold war shoot downs: Part two. Challenge Publications Inc.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ a b Bluth, Christoph (2008). Korea. Cambridge: Polity Press. p. 47. ISBN 978-07456-3357-2.
- ^ Hyung Gu Lynn (2007). Bipolar Orders: The Two Koreas since 1989. Zed Books. p. 158.
- ^ Oberdorfer, Don; Carlin, Robert (2014). The Two Koreas: A Contemporary History. Basic Books. pp. 42–45. ISBN 9780465031238.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 210. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Oberdorfer, Don; Carlin, Robert (2014). The Two Koreas: A Contemporary History. Basic Books. pp. 59–66. ISBN 9780465031238.
- ^ "Minutes of Washington Special Actions Group Meeting, Washington, August 25, 1976, 10:30 a.m." Office of the Historian, U.S. Department of State. 25 August 1976. Archived from the original on 25 September 2012. Retrieved 12 May 2012.
Clements: I like it. It doesn't have an overt character. I have been told that there have been 200 other such operations and that none of these have surfaced. Kissinger: It is different for us with the War Powers Act. I don't remember any such operations.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Lee Tae-hoon (7 February 2011). "S. Korea raided North with captured agents in 1967". The Korea Times. Archived from the original on 1 October 2012. Retrieved 12 May 2012.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Oberdorfer, Don; Carlin, Robert (2014). The Two Koreas: A Contemporary History. Basic Books. pp. 47–49, 54–55. ISBN 9780465031238.
- ^ Oberdorfer, Don; Carlin, Robert (2014). The Two Koreas: A Contemporary History. Basic Books. pp. 45–47. ISBN 9780465031238.
- ^ Oberdorfer, Don; Carlin, Robert (2014). The Two Koreas: A Contemporary History. Basic Books. pp. 55–59. ISBN 9780465031238.
- ^ Jager, Sheila Miyoshi (2013). Brothers at War – The Unending Conflict in Korea. London: Profile Books. pp. 396–413. ISBN 978-1-84668-067-0.
- ^ Oberdorfer, Don; Carlin, Robert (2014). The Two Koreas: A Contemporary History. Basic Books. pp. 122–23. ISBN 9780465031238.
- ^ Jager, Sheila Miyoshi (2013). Brothers at War – The Unending Conflict in Korea. London: Profile Books. pp. 417–24. ISBN 978-1-84668-067-0.
- ^ Oberdorfer, Don; Carlin, Robert (2014). The Two Koreas: A Contemporary History. Basic Books. pp. 98–103. ISBN 9780465031238.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 147–48. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 165. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Bluth, Christoph (2008). Korea. Cambridge: Polity Press. pp. 46–47. ISBN 978-07456-3357-2.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. pp. 173–76. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea's Place in the Sun: A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. p. 509. ISBN 0-393-32702-7.
- ^ Hyung Gu Lynn (2007). Bipolar Orders: The Two Koreas since 1989. Zed Books. p. 93.
- ^ Jager, Sheila Miyoshi (2013). Brothers at War – The Unending Conflict in Korea. London: Profile Books. p. 439. ISBN 978-1-84668-067-0.
- ^ Oberdorfer, Don; Carlin, Robert (2014). The Two Koreas: A Contemporary History. Basic Books. p. 247. ISBN 9780465031238.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 178. ISBN 0-415-23749-1.
- ^ Bluth, Christoph (2008). Korea. Cambridge: Polity Press. p. 1. ISBN 978-07456-3357-2.
- ^ South Korea Formally Declares End to Sunshine Policy Archived 2012-04-12 at the Wayback Machine, Voice of America Archived 2012-05-14 at the Wayback Machine, 18 November 2010
- ^ Bluth, Christoph (2008). Korea. Cambridge: Polity Press. p. vi. ISBN 978-07456-3357-2.
- ^ Bluth, Christoph (2008). Korea. Cambridge: Polity Press. pp. 138–43. ISBN 978-07456-3357-2.
- ^ Hyung Gu Lynn (2007). Bipolar Orders: The Two Koreas since 1989. Zed Books. pp. 142–43.
- ^ "Backgrounder: How DPRK has condemned U.S.-S. Korea joint military exercises". Xinhua. 22 August 2016. Archived from the original on 23 August 2016.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea's Place in the Sun: A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 488–89, 494–96. ISBN 0-393-32702-7.
- ^ Oberdorfer, Don; Carlin, Robert (2014). The Two Koreas: A Contemporary History. Basic Books. pp. 61, 213. ISBN 9780465031238.
- ^ Byrne, Leo (8 July 2016). "China, North Korea criticize new U.S. sanctions". NK News. Archived from the original on 8 July 2016.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Bluth, Christoph (2008). Korea. Cambridge: Polity Press. pp. 144–45. ISBN 978-07456-3357-2.
- ^ K .J. Kwon (16 September 2013). "North and South Korea reopen Kaesong Industrial Complex". CNN. Archived from the original on 28 January 2014. Retrieved 17 January 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "South Korea to Halt Work at Joint Industrial Park With North". NBC News. 10 February 2016. Archived from the original on 10 February 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Leftist lawmaker gets 12-year prison term for rebellion plot". Yonhap News Agency. 17 February 2014. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Sanger, David E; Broad, William J (4 March 2017). "Trump Inherits a Secret Cyberwar Against North Korean Missiles". New York Times. Archived from the original on 6 March 2017.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Schiller, Markus; Hayes, Peter (9 March 2017). "Did cyber attacks slow down North Korea's missile progress?". NK News. Archived from the original on 9 March 2017.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Ahn, JH (22 August 2016). "S.Korea to review possible new sites for THAAD deployment". NK News. Archived from the original on 22 August 2016.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "S. Korea unveils plan to raze Pyongyang in case of signs of nuclear attack". Yonhap News Agency. 11 September 2015. Archived from the original on 18 September 2016.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ O'Carroll, Chad (10 February 2017). "Graphic, pro-North Korea leaflets found in downtown Seoul". NK News. Archived from the original on 10 February 2017.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Ahn, JH (14 February 2017). "New South Korean party accused of using Pyongyang's Juche Tower as logo". NK News. Archived from the original on 16 February 2017.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "South Korea: Government to pay defectors for North Korea secrets". Asian Correspondent. 5 March 2017. Archived from the original on 6 March 2017.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Choe, Sang-hun (July 4, 2017). "North Korea Claims Success in Long-Range Missile Test". The New York Times. New York. Archived from the original on July 4, 2017. Retrieved July 4, 2017.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Choe, Sang-hun; Sullivan, Eileen (July 28, 2017). "North Korea Launches Ballistic Missile, the Pentagon Says". The New York Times. New York. Archived from the original on July 28, 2017. Retrieved July 28, 2017.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "North Korea vows to retaliate against US over sanctions". BBC News. Archived from the original on 2017-08-10.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "North Korea considering firing missiles at Guam, per state media". 8 August 2017. Archived from the original on 8 August 2017.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Atom: Nordkorea legt detaillierten Plan für Raketenangriff Richtung Guam vor - WELT". DIE WELT. Archived from the original on 2017-10-12. Retrieved 2017-08-10.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Kim 'Guided' North Korean Missile Test". skynews.com.au. 30 August 2017. Archived from the original on 29 August 2017.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Collins, Pádraig (3 September 2017). "North Korea nuclear test: what we know so far". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 3 September 2017. Retrieved 4 September 2017.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ McGeough, Paul (12 September 2017). "North Korea: Sanctions tighten screws on regime but China, Russia get their way". The Sydney Morning Herald. Archived from the original on 12 September 2017. Retrieved 13 September 2017.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Pyongyang fires missile through Japan's airspace into Pacific Ocean". RT International. Archived from the original on 14 September 2017. Retrieved 15 September 2017.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Sang-hun, Choe (10 October 2017). "North Korean Hackers Stole U.S.-South Korean Military Plans, Lawmaker Says". New York Times. Archived from the original on 12 October 2017.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ North Korea’s Longest Missile Test Yet Archived 2017-11-28 at the Wayback Machine, David Wright, All Things Nuclear, Union of Concerned Scientists.
- ^ "Security Council Tightens Sanctions on Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Unanimously Adopting Resolution 2397 (2017)". United Nations. 22 December 2017. Archived from the original on 24 December 2017. Retrieved 24 December 2017.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Kim, Hyung-Jin (3 January 2018). "North Korea reopens cross-border communication channel with South Korea". Chicago Tribune. AP. Archived from the original on 4 January 2018. Retrieved 5 January 2018.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Canada and United States to co-host Vancouver Foreign Ministers' Meeting on Security and Stability on Korean Peninsula". Global Affairs Canada. Office of the Minister of Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 6 January 2018. Retrieved 6 January 2018.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Co-chairs’ summary of the Vancouver Foreign Ministers’ Meeting on Security and Stability on the Korean Peninsula Archived 2018-01-27 at the Wayback Machine, 16 January 2018.
- ^ Ji, Dagyum (12 February 2018). "Delegation visit shows N. Korea can take "drastic" steps to improve relations: MOU". NK News.
External links
- Korean War
- Revolution-based civil wars
- Civil wars involving the states and peoples of Asia
- History of Korea
- History of North Korea
- History of South Korea
- Foreign relations of South Korea
- Foreign relations of North Korea
- Territorial disputes of South Korea
- Territorial disputes of North Korea
- Korea–United States relations
- Korea–Soviet Union relations
- North Korea–South Korea border
- Partition (politics)
- Aftermath of the Korean War
- Allied occupation of Korea
- Ongoing conflicts
- North Korea–South Korea relations
- North Korea–United States relations
- Government of North Korea
- Military history of North Korea
- Nuclear program of North Korea