Solar eclipse of January 27, 2055
| Solar eclipse of January 27, 2055 | |
|---|---|
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | 1.155 |
| Magnitude | 0.6932 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 69°30′N 112°12′W / 69.5°N 112.2°W |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 17:54:05 |
| References | |
| Saros | 122 (60 of 70) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9630 |
A partial solar eclipse will occur on Wednesday, January 27, 2055. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. It will be visible across North America.
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 2054–2058
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
The partial solar eclipses on March 9, 2054 and September 2, 2054 occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set, and the partial solar eclipses on May 22, 2058 and November 16, 2058 occur in the next lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2054 to 2058 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 117 | August 3, 2054 Partial |
−1.4941 | 122 | January 27, 2055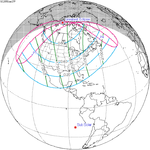 Partial |
1.155 | |
| 127 | July 24, 2055 Total |
−0.8012 | 132 | January 16, 2056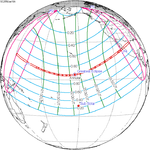 Annular |
0.4199 | |
| 137 | July 12, 2056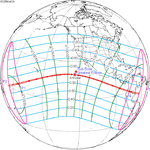 Annular |
−0.0426 | 142 | January 5, 2057 Total |
−0.2837 | |
| 147 | July 1, 2057 Annular |
0.7455 | 152 | December 26, 2057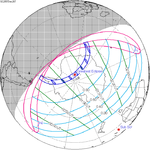 Total |
−0.9405 | |
| 157 | June 21, 2058 Partial |
1.4869 | ||||
Tritos
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of February 28, 2044
- Followed: Solar eclipse of December 27, 2065
Tzolkinex
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of December 16, 2047
- Followed: Solar eclipse of March 11, 2062
References
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.




