2024 United Kingdom general election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 650 seats in the House of Commons. 326 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 2024 United Kingdom general election is scheduled for Thursday, 4 July 2024. It will determine the composition of the House of Commons, which determines the government of the United Kingdom. Significant constituency boundary changes will be in effect – the first such changes since those implemented at the 2010 general election. It will be the first UK general election in which voter identification is required to vote in person in Great Britain.[h] The general election will be the first since Brexit on 31 January 2020, which was a major issue in the previous election; it will also be the first to take place under the Dissolution and Calling of Parliament Act 2022.
Discussion around the campaign has been focused on the prospect of a change in government, as the opposition Labour Party led by Keir Starmer has significant leads in opinion-polling over the governing Conservative Party led by the prime minister, Rishi Sunak. Projections four weeks before the vote indicated a landslide victory for Labour that would surpass the one achieved by Tony Blair at the 1997 general election, while comparisons have been made in the media to the 1993 Canadian federal election, due to the prospect of a potential Conservative wipeout.
Background
Political background of the Conservatives before the election
 2024 United Kingdom general election (4 July) | |
|---|---|
| Parties | |
| Campaign | |
| Overview by country | |
| Outcome | |
| Related | |
| |
The Conservatives under Boris Johnson won a landslide victory at the 2019 general election and the new government passed the Brexit withdrawal agreement.[1][2] The COVID-19 pandemic saw the government institute public health restrictions, including limitations on social interaction, that Johnson and some of his staff were later found to have broken. The resulting political scandal (Partygate), one of many in a string of controversies[3][4] that characterised Johnson's premiership, damaged his personal reputation. The situation escalated with the Chris Pincher scandal in July 2022, leading to Johnson's resignation.[5] He resigned as an MP the following year[6] after an investigation unanimously found that he had lied to Parliament.[7]
Liz Truss won the resultant leadership election and succeeded Johnson in September.[8][9] Truss announced large-scale tax cuts and borrowing in a mini-budget on 23 September, which was widely criticised and – after it rapidly led to financial instability – largely reversed.[10] She resigned in October, making her the shortest-serving prime minister in British history.[11] Rishi Sunak was elected unopposed to succeed Truss in October.[12][13]
During his premiership Sunak has been credited with improving the economy and stabilising national politics following the premierships of his predecessors,[14] although many of his pledges and policy announcements have ultimately been unfulfilled.[15][16] He has not averted further unpopularity for the Conservatives who, by the time of Sunak's election, had been in government for 12 years. Public opinion in favour of a change in government was reflected in the Conservatives' poor performance at the 2022, 2023 and 2024 local elections.[17]
Political background of other parties before the election
Keir Starmer won the Labour Party's 2020 leadership election, succeeding Jeremy Corbyn.[18] Under his leadership, Starmer has repositioned the party away from the left and toward the political centre.[19][20] He has emphasised the importance of eliminating antisemitism within the party, which had been a controversial issue during Corbyn's leadership. The political turmoil from the Conservative scandals and government crises led to Labour having a significant lead in polling over the Conservatives, often by very wide margins, since late 2021, coinciding with the start of the Partygate scandal.[3][4] During the 2023 local elections, Labour gained more than 500 councillors and 22 councils, becoming the largest party in local government for the first time since 2002.[21] Labour made further gains in the 2024 local elections, including winning the West Midlands mayoral election.[22]
Ed Davey, who previously served in the Cameron–Clegg coalition government, won the Liberal Democrat's 2020 leadership election, succeeding Jo Swinson, who lost her seat in the previous general election.[23] Davey prioritised defeating the Conservatives and ruled out working with them following the election.[24] The Liberal Democrats made gains in local elections: in the 2024 local elections, the Liberal Democrats finished second for the first time in a local election cycle since 2009.[25]
Like the Conservatives, the Scottish National Party (SNP) suffered political turmoil and saw a decrease in their popularity in opinion polling, with multiple party leaders and First Ministers (Nicola Sturgeon, Humza Yousaf and John Swinney) and the Operation Branchform police investigation. Sturgeon claimed occupational burnout was the reason for her resignation,[26] while Yousaf resigned amid a government crisis following his termination of a power-sharing agreement with the Scottish Greens.[27] When Swinney assumed the leadership after being elected unopposed to succeed Yousaf, the SNP had been in government for 17 years.[28]
Changes to the composition of the House of Commons before the election
This table relates to the composition of the House of Commons after the 2024 UK general election and summarises the changes in party affiliation that took place during the 2024–present Parliament.
| Affiliation | Members | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elected in 2024[29] |
Current[30] | Difference | ||
| Labour[i] | 411[j] | 402 | ||
| Conservative | 121 | 121 | ||
| Liberal Democrats | 72 | 72 | ||
| Independent | 6 | 15[k] | ||
| SNP | 9 | 9 | ||
| Sinn Féin | 7 | 7 | ||
| DUP | 5 | 5 | ||
| Reform UK | 5 | 5 | ||
| Green (E&W) | 4 | 4 | ||
| Plaid Cymru | 4 | 4 | ||
| SDLP | 2 | 2 | ||
| Alliance | 1 | 1 | ||
| TUV | 1 | 1 | ||
| UUP | 1 | 1 | ||
| Speaker | 1 | 1 | ||
| Vacant | 0 | 0 | ||
| Total | 650 | 650 | ||
| Total voting[l] | 639 | 639 | ||
| Majority of voting | 181 | 165[34] | ||
For full details of changes during the 2024–present Parliament, see By-elections and Defections, suspensions and resignations.
The results of the 2019 general election are given above, alongside the numbers in the House of Commons at dissolution on 30 May 2024. Seat counts changed through 23 by-elections and a number of defections and suspensions of members from their party that took place throughout the 2019–2024 parliament. There were no vacant seats at dissolution.
Date of the election
Originally the next election was scheduled to take place on 2 May 2024 under the Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011.[m] At the 2019 general election, in which the Conservatives won a majority of 80 seats, the party's manifesto contained a commitment to repeal the Fixed-term Parliaments Act.[36] In December 2020, the government duly published a draft Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011 (Repeal) Bill, later retitled the Dissolution and Calling of Parliament Act 2022.[37][38] This entered into force on 24 March 2022. Thus, the prime minister can again request the monarch to dissolve Parliament and call an early election with 25 working days' notice. Section 4 of the Act provided: "If it has not been dissolved earlier, a Parliament dissolves at the beginning of the day that is the fifth anniversary of the day on which it first met." The Electoral Commission confirmed that the 2019 Parliament would, therefore, have to be dissolved, at the latest, by 17 December 2024, and that the next general election had to take place no later than 28 January 2025.[39][40]
With no election date fixed in law, there was speculation as to when the prime minister, Rishi Sunak, would call an election. On 18 December 2023, Sunak told journalists that the election would take place in 2024 rather than January 2025.[41] On 4 January, he first suggested the general election would probably be in the second half of 2024.[42] Throughout 2024, political commentators and MPs expected the election to be held in the autumn.[43][44][45] On 22 May 2024, following much speculation through the day,[46][47][48] Sunak officially announced the election would be held on 4 July with the dissolution of the Parliament on 30 May.[49]
The deadline for candidate nominations was 7 June 2024, with ongoing political campaigning for four weeks until polling day on 4 July. On the day of the election, polling stations across the country will be open from 7 am, and will close at 10 pm. The date chosen for the 2024 general election made it the first to be held in July since the 1945 general election. A total of 4,515 candidates were nominated, more than in any previous general election.[50]
Timetable
| Date | Day | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 22 May | Wednesday | Prime Minister Rishi Sunak requests a dissolution of parliament from King Charles III and announces the date of polling day for the general election as 4 July. |
| 24 May | Friday | Last sitting day of business. Parliament prorogued. |
| 25 May | Saturday | Beginning of pre-election period (also known as purdah).[53] |
| 30 May | Thursday | Dissolution of parliament and official start of the campaign. Royal Proclamation issued dissolving the 2019 Parliament, summoning the 2024 Parliament and setting the date for its first meeting.[54] |
| 7 June | Friday | Nominations of candidates close (4 pm). Publication of statement of persons nominated, including notice of poll and situation of polling stations (5 pm). |
| 13 June | Thursday | Deadline to register to vote at 11:59 pm in Northern Ireland. |
| 18 June | Tuesday | Deadline to register to vote at 11:59 pm in Great Britain. |
| 19 June | Wednesday | Deadline to apply for a postal vote. |
| 26 June | Wednesday | Deadline to register for a proxy vote at 5 pm. Exemptions applied for emergencies. |
| 4 July | Thursday | Polling Day – polls open from 7 am to 10 pm. |
| 4–5 July | Thursday–Friday | Results announced for most or all constituencies. |
| 5 July | Friday | End of pre-election period (also known as purdah). |
| 9 July | Tuesday | First meeting of the new Parliament of the United Kingdom, for the formal election of Speaker of the House of Commons. Over the next few days, MPs will be sworn in. |
| 17 July | Wednesday | State Opening of Parliament and King's Speech. |
Electoral system
General elections in the United Kingdom are organised using first-past-the-post voting. The Conservative Party, which won a majority at the 2019 general election, included pledges in its manifesto to remove the 15-year limit on voting for British citizens living abroad, and to introduce a voter identification requirement in Great Britain.[55][56] These changes were included in the Elections Act 2022.[57]
Boundary reviews

The Periodic Review of Westminster constituencies, which proposed reducing the number of constituencies from 650 to 600, commenced in 2011 but temporarily stopped in January 2013. Following the 2015 general election, each of the four parliamentary boundary commissions of the United Kingdom recommenced their review process in April 2016.[58][59][60] The four commissions submitted their final recommendations to the Secretary of State on 5 September 2018[61][62] and made their reports public a week later.[63][64][65][61] However, the proposals were never put forward for approval before the calling of the general election held on 12 December 2019, and in December 2020 the reviews were formally abandoned under the Schedule to the Parliamentary Constituencies Act 2020.[66] A projection by psephologists Colin Rallings and Michael Thrasher of how the 2017 votes would have translated to seats under the 2018 boundaries suggested the changes would have been beneficial to the Conservatives and detrimental to Labour.[67][68]
In March 2020, Cabinet Office minister Chloe Smith confirmed that the 2023 Periodic Review of Westminster constituencies would be based on retaining 650 seats.[69][70] The previous relevant legislation was amended by the Parliamentary Constituencies Act 2020[71] and the four boundary commissions formally launched their 2023 reviews on 5 January 2021.[72][73][74][75] They were required to issue their final reports prior to 1 July 2023.[66] Once the reports had been laid before Parliament, Orders in Council giving effect to the final proposals had to be made within four months, unless "there are exceptional circumstances". Prior to the Parliamentary Constituencies Act 2020, boundary changes could not be implemented until they were approved by both Houses of Parliament. The boundary changes were approved at a meeting of the Privy Council on 15 November 2023[76] and came into force on 29 November 2023,[77] meaning that the election will be contested on these new boundaries.[78]
Notional 2019 results
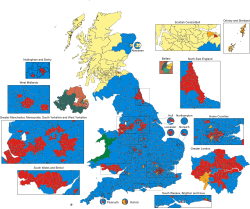
The election will be contested under new constituency boundaries established by the 2023 Periodic Review of Westminster constituencies. Consequently, media outlets tend to report seat gains and losses as compared to notional results. These are the results if all votes cast in 2019 were unchanged, but regrouped by new constituency boundaries.[79] Notional results in the UK are always estimated, usually with the assistance of local election results, because vote counts at parliamentary elections in the UK do not yield figures at any level more specific than that of the whole constituency.[80]
In England, seats will be redistributed towards Southern England, away from Northern England, due to the different rates of population growth. North West England and North East England will lose two seats each whereas South East England will gain seven seats and South West England will gain three seats.[81] Based on historical voting patterns, this is expected to help the Conservatives.[82] Based on these new boundaries, different parties would have won several constituencies with unchanged names but changed boundaries in 2019. For example, the Conservatives would have won Wirral West and Leeds North West instead of the Labour Party, but Labour would have won Pudsey and Heywood & Middleton instead of the Conservatives. Westmorland and Lonsdale, the constituency represented by former Liberal Democrat leader Tim Farron, is now notionally a Conservative seat.
In Scotland, 57 MPs will be elected, down from the 59 in 2019, with the following notional partisan composition of Scotland's parliamentary delegation:[83] The Scottish National Party would remain steady on 48 seats, despite two of its constituencies being dissolved. The Scottish Conservatives' seat count of six would likewise remain unchanged. Scottish Labour would have retained Edinburgh South, the sole constituency they won in 2019. Had the 2019 general election occurred with the new boundaries in effect, the Scottish Liberal Democrats would have only won two seats (Edinburgh West and Orkney and Shetland), instead of the four they did win that year, as the expanded electorates in the other two would overcome their slender majorities.
Under the new boundaries, Wales will lose eight seats, electing 32 MPs instead of the 40 it elected in 2019. Welsh Labour would have won 18 instead of the 22 MPs it elected in 2019, and the Welsh Conservatives 12 instead of 14. Due to the abolition and merging of rural constituencies in West Wales, Plaid Cymru would have only won two seats instead of four. Nonetheless, the boundary changes are expected to cause difficulty for the Conservatives as more pro-Labour areas are added to some of their safest seats.[84]
In Northern Ireland, the notional results are identical to the actual results of the 2019 general election in Northern Ireland.
| Party | MPs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 actual result | 2019 notional result | Change | ||
| Conservative | 365 | 372 | ||
| Labour | 202 | 200 | ||
| SNP | 48 | 48 | ||
| Liberal Democrats | 11 | 8 | ||
| DUP | 8 | 8 | ||
| Sinn Féin | 7 | 7 | ||
| Plaid Cymru | 4 | 2 | ||
| SDLP | 2 | 2 | ||
| Green (E&W) | 1 | 1 | ||
| Alliance | 1 | 1 | ||
| Speaker | 1 | 1 | ||
Postal vote delays
The weekend before the election, City of Edinburgh Council, Fife Council, and East Lothian Council[85] in Scotland had to set up emergency polling stations and hand deliver postal ballots after reports of voters not receiving their ballots.[86][87] Fife council had to issues over 200 replacement ballots on 29 June.[88] The SNP's Stephen Flynn raised concerns that due to the timing of the election many families in Scotland would be on holiday and unable to cast their votes in person.[89]
Some areas of England were also affected. Peter Holt, the chief executive of Uttlesford District Council, took responsibility for the delay in North West Essex blaming "human error" but warned that close results in the area could be challenged,[90] although a spokesperson for Rishi Sunak denied this.[91]
By Monday 1 July, three days before polling day, it was reported that thousands of postal votes across over 90 constituencies were affected.[91] Postal affairs minister Kevin Hollinrake criticised Royal Mail for their handling of votes, urging them "to do all they can" to get ballots out of sorting offices and delivered on time. Royal Mail blamed the government for the issue, saying ballots were being delivered "as soon as they arrive in [their] network".[89]
Campaign

Discussion around the campaign has been focused on the prospect of a change in government, as the opposition Labour Party led by Keir Starmer has significant leads in opinion-polling over the governing Conservative Party led by the prime minister, Rishi Sunak. Projections four weeks before the vote indicated a landslide victory for Labour that would surpass the one achieved by Tony Blair at the 1997 general election, while comparisons have been made in the media to the 1993 Canadian federal election, due to the prospect of a potential Conservative wipeout.[92][93]
On the afternoon of 22 May 2024, Sunak announced that he had asked the King to call a general election for 4 July 2024, surprising his own MPs.[94] The calling of the election was welcomed by all major parties.[95][96][97]
Sunak's announcement took place during heavy rain at a lectern outside 10 Downing Street, without the use of any shelter from the rain.[98] The D:Ream song "Things Can Only Get Better" (frequently used by the Labour Party in its successful 1997 campaign) was being played loudly in the background by the political activist Steve Bray as Sunak announced the date of the general election.[99] This led to the song reaching number two on UK's iTunes Charts.[100][101]
22–29 May
At the beginning of the campaign, Labour had a significant lead in polling over the Conservatives.[17][102] Polling also showed Labour doing well against the Scottish National Party (SNP) in Scotland.[103] Davey has been noted, with praise and criticism, for his campaign stunts.[104] When visiting Windermere, Davey fell off a paddleboard, while campaigning to highlight the issue of sewage discharges into rivers and lakes.[105] A couple of days later, Davey won media attention when going down a Slip 'N Slide, while drawing attention to deteriorating mental health among children. When asked about these stunts, Davey said: "Politicians need to take the concerns and interests of voters seriously but I'm not sure they need to take themselves seriously all the time and I'm quite happy to have some fun".[106]
On 23 May, Sunak said that before the election there would be no flights to Rwanda for those seeking asylum.[107] Immigration figures were published for 2023 showing immigration remained at historically high levels, but had fallen compared to 2022.[108] Nigel Farage initially said that he would not stand as a candidate in the election, while his party Reform UK said it would stand in 630 seats across England, Scotland and Wales.[109] Farage later announced on 3 June that, contrary to his statement earlier in the campaign, he would stand for Parliament in Clacton, and that he had resumed leadership of Reform UK, taking over from Richard Tice. He also predicted that Labour would win the election.[110]
Davey launched the Liberal Democrat campaign in Cheltenham in Gloucestershire.[111] The SNP campaign launch the same day was overshadowed over a dispute around leader John Swinney's support for Michael Matheson and developments in Operation Branchform.[112] Starmer launched the Labour Party campaign in Gillingham at the Priestfield Stadium, home of Gillingham Football Club.[113]
On 24 May, the Conservatives proposed setting up a Royal Commission to consider a form of mandatory national service.[114] It would be made up of two streams for 18-year-olds to choose from, either 'community volunteering' by volunteering with organisations such as the NHS, fire service, ambulance, search and rescue, and critical local infrastructure, or 'military training' in areas like logistics and cyber security.[115]
Former Labour leader Jeremy Corbyn announced on 24 May he was running as an independent in Islington North against a Labour candidate, and was thus expelled from the party.[116]
On 27 May, Starmer made a keynote speech on security and other issues.[117][118]
On 28 May, the Conservatives pledged a "Triple Lock Plus" where the personal income tax allowance for pensioners would always stay higher than the state pension.[119] Labour criticised the policy as being uncosted.[120] Davey went paddleboarding on Lake Windermere in the marginal constituency of Westmorland and Lonsdale, highlighting the release of sewage in waterways.[121] He pledged to abolish Ofwat and introduce a new water regulator to tackle the situation, in addition to proposing a ban on bonuses for chief executives of water companies.[122] Starmer was in West Sussex and emphasised his small town roots in his first big campaign speech.[123]
On 29 May, Labour's Shadow Health Secretary Wes Streeting promised a 18-week NHS waiting target within five years of a Labour government.[124] Labour also pledged to double number of NHS scanners in England. On the same day Starmer denied that Diane Abbott had been blocked as a candidate amid differing reports.[125] Abbott had been elected as a Labour MP, but had been suspended from the parliamentary party for a brief period. There was controversy about further Labour Party candidate selections, with several candidates on the left of the party being excluded.[126] Abbott said she had been barred from standing as a Labour Party candidate at the election, but Starmer later said she would be "free" to stand as a Labour candidate.[127]
30 May – 5 June
On 30 May, both the Conservatives and Labour ruled out any rise in value-added tax.[128] The SNPs Màiri McAllan claimed that only the SNP offered Scotland a route back into the European Union, making Pro-Europeanism part of the party's campaign.[129] Reform UK proposed an immigration tax on British firms who employ foreign workers.[130] Carla Denyer and Adrian Ramsay launched the Green Party campaign in Bristol.[131] Rhun ap Iorwerth launched the Plaid Cymru campaign in Bangor.[132] George Galloway launched the Workers Party of Britain campaign in Ashton-under-Lyne.[133]
Labour promised to cut net migration by improving training for British workers.[134]
On 31 May, the Conservatives announced new 'pride in places' pledges, including new rules to tackle anti-social behaviour, rolling out the hot-spot policing programme to more areas, and more town regeneration projects. The Conservatives also unveiled plans for fly-tippers to get points on their driving licences.[135]
On 3 June, Sunak pledged to tackle what he called the "confusion" over the legal definition of sex by proposing amending the Equality Act.[136] Labour focused on national security, with Starmer reaffirming his commitment to a "nuclear deterrent triple lock", including building four new nuclear submarines.[110] A YouGov poll conducted on the same day put Labour on course for the party's biggest election victory in history, beating Tony Blair's 1997 landslide.[137]
On 4 June, Farage launched his campaign in Clacton.[138] He announced the previous day that he intends Reform UK to be the Official Opposition following the election as opposed to the Conservatives, saying that the Conservatives are incapable of being the Opposition due to "spending most of the last five years fighting each other rather than fighting for the interests of this country".[139]
6–12 June
On 6 June, the Greens announced plans to invest an extra £50 billion a year for the NHS by raising taxes on the top 1% of earners.[140] Social care has been a campaign issue.[141] The Conservatives announced a policy on expanding child benefit for higher-earners.[142] Labour also announced communities will be given powers to transform derelict areas into parks and green spaces. Labour's countryside protection plan would also include the planting new national forests, taskforces for tree-planting and flood resilience, new river pathways, and a commitment to revive nature.[143] Green spaces would be a requirement in the development of party's new housing and town plans.[144]
Sunak and Starmer attended D-Day commemorations on 6 June, the 80th anniversary. Sunak was widely criticised for leaving events early to do an interview with ITV, including by veterans.[145] Starmer met with Volodymyr Zelenskyy and King Charles III during the D-Day commemorations, and said that Sunak "has to answer for his actions".[146][147] Sunak apologised the next day[148] and apologised again on 10 June.[149] He made a third apology on 12 June.[150]
Farage was among those critical of Sunak over his leaving the D-Day events,[151] saying on 7 June that Sunak did not understand "our culture". Conservative and Labour politicians criticised these words as being a racist attack on Sunak, which Farage denied.[152] Douglas Ross announced he would stand down as the leader of the Scottish Conservatives after the election.[153]
On 10 June, Labour pledged 100,000 new childcare places and more than 3,000 new nurseries as part of its childcare plan.[154]
The Liberal Democrat manifesto For a Fair Deal was released on 10 June,[155][156] which included commitments on free personal care in England,[157] investment in the NHS including more GPs, increased funding for education and childcare (including a tutoring guarantee for children from low-income families), increased funding for public services, tax reforms, reaching net zero by 2045 (5 years before the current government target of 2050), investing in green infrastructure, innovation, training and skills across the UK to boost economic growth, and removing the two-child limit on tax and benefits.[158] The Liberal Democrats also offered a lifelong skills grant, giving adults £5,000 to spend on improving their skills.[159] The party wants electoral reform, and pledged to introduce proportional representation for electing MPs, and local councillors in England, and cap donations to political parties.[160][161]
Sunak launched the Conservative manifesto Clear Plan. Bold Action. Secure Future. on 11 June, addressing the economy, taxes, welfare, expanding free childcare, education, healthcare, environment, energy, transport, community, and crime.[162][163] They pledged to lower taxes, increase education and NHS spending, deliver 92,000 more nurses and 28,000 more doctors, introduce a new model of National Service, continue to expand apprenticeships and vocational training, simplify the planning system to speed up infrastructure projects (digital, transport and energy), and to treble Britain's offshore wind capacity and support solar energy. The manifesto includes a pledge to abolish Stamp Duty on homes worth up to £425,000 for first time buyers and expand the Help to Buy scheme.[164] The Conservatives also pledged a recruitment of 8,000 new police officers and a rollout of facial recognition technology.[165] Much of what has been proposed is already incorporated in the 2024 budget.[166][167][168]
On 6 June, the Green Party of England and Wales announced plans to invest an extra £50 billion a year for the NHS by raising taxes on the top 1% of earners.[140] The GPEW manifesto Real Hope. Real Change. was released on 12 June, which pledged more taxes on the highest earners, generating £70 billion a year to help tackle climate change and the NHS. They also pledged increased spending for public services, free personal care in England, renationalisation of railways, water and energy, a green society, a wealth tax, a carbon tax, and a windfall tax on the profit of banks.[169][170]
On 12 June, Conservative minister Grant Shapps said in a radio interview that voters should support the Conservatives so as to prevent Labour winning "a super-majority", meaning a large majority (the UK Parliament does not have any formal supermajority rules). This was interpreted by journalists as a possible and surprising admission of defeat.[171][172][173] It paralleled social media advertising by the Conservatives that also focused on urging votes not to give Starmer a large majority.[174]
13–19 June
On 13 June, Starmer launched the Labour Party manifesto Change, which focused on economic growth, planning system reforms, infrastructure, clean energy, healthcare, education, childcare, crime, and strengthening workers' rights.[175][176] It pledged a new publicly owned energy company and National Wealth Fund, a "Green Prosperity Plan", rebuilding the NHS and reducing patient waiting times, free breakfast clubs in primary schools, investing in green infrastructure, innovation, training and skills across the UK to boost economic growth, and renationalisation of the railway network.[177] It includes wealth creation and 'pro-business and pro-worker' policies.[178] The manifesto also pledged to give votes to 16 year olds, reform the House of Lords, and to tax private schools, with money generated going into improving state education.[179][180][181] The party guaranteed giving all areas of England devolution powers, in areas such as integrated transport, planning, skills, and health.[182][183]
On 17 June, Farage and Tice launched the Reform UK manifesto, which they called a "contract" (Our Contract with You). It pledged to lower taxes, lower immigration, increase funding for public services, reform the NHS and decrease its waiting lists to 'zero', bring utilities and critical national infrastructure under 50% public ownership (the other 50% owned by pension funds), replace the House of Lords with a more democratic second chamber, and to replace first-past-the-post voting with a system of proportional representation.[184] It also pledged to accelerate transport infrastructure in coastal regions, Wales, the North, and the Midlands.[185][186] The party also wants to freeze non-essential immigration and recruit 40,000 new police officers.[187] Reform UK are the only major party to oppose the current net zero target made by the government.[188] Instead, it pledged to support the environment with more tree planting, more recycling and less single-use plastics.[189][190][191] Farage predicted Labour would win the election, but said he was planning to campaign for the next election.[192]
Labour's Shadow Chancellor Rachel Reeves claimed Labour's green plans would create over 650,000 jobs.[193][194] The Liberal Democrats offered more cost-of-living help for rural communities.[195] Davey highlighted his manifesto pledge to build 380,000 new homes a year, 150,000 of which would be social homes.[196] On 18 June, Labour pledged hundreds of new banking hubs, to ''breathe life'' into high streets.[197][198]
On 19 June, both the SNP and Sinn Féin released their manifestos. The SNP leader John Swinney said a vote for his party would "intensify" the pressure to secure a second Scottish independence referendum, with other pledges in the SNP manifesto including boosting NHS funding, scrapping the two-child limit on benefits, calling for an immediate ceasefire in the Gaza Strip, scrapping the Trident defence programme, re-joining the European Union, transitioning to a green economy attracting more foreign migrants,[199] tackling drug deaths and devolving broadcasting powers.[200] The Sinn Féin manifesto called for greater devolution to Northern Ireland and for the UK and Irish governments to set a date for a referendum on the unification of Northern Ireland with the Republic of Ireland.[201] Galloway launched the Workers Party manifesto, with promises to improve "poverty pay" and provide more social housing.[202] It pledged the renationalisation of utility companies, free school meals for all children without means testing, free adult education, and to hold a referendum on the continued existence of the monarchy and proportional representation for elections.[203]
David TC Davies, the Secretary of State for Wales, told a BBC interview the polls were "clearly pointing at a large Labour majority", but added that he believed there was "no great optimism" from voters.[204] A potentially large Labour majority was also acknowledged by Chancellor Jeremy Hunt and Secretary of State for Work and Pensions Mel Stride.[205] Alison McGarry, the Labour chair of Islington North, resigned from the Labour Party after being spotted campaigning for Corbyn; she resigned rather than face expulsion for breaking the party's rules on campaigning for a rival candidate.[206]
20–26 June
On 20 June, the parties focused on housing. Labour pledged action to protect renters with new legal protections for tenants. It would immediately ban Section 21 "no-fault" evictions, as part of plans to reform the private rented sector in England.[207] Labour also pledged to reform planning laws and build 1.5 million homes to spread homeownership.[208] The Conservatives offered stronger legal protections for tenants, including banning Section 21 "no-fault" evictions.[209] They said they would build 1.6 million new homes, prioritising brownfield development, while protecting the countryside.[210] The Liberal Democrats offered more protections for tenants, additional social housing, and more garden cities.[211][212]
Also on 20 June, the Alliance Party in Northern Ireland launched their manifesto.[213] Its core policies include reforming the political institutions, dedicated funding for integrated education, a Green New Deal to decarbonise Northern Ireland's economy, childcare reforms, and lowering the voting age to 16.[214]
On 21 June, in a BBC Panorama interview with Nick Robinson, Farage repeated comments he had made previously claiming that the West and NATO provoked Russia's invasion of Ukraine. He was criticised for this by Sunak and Starmer.[215] He also stated that Reform UK would lower the tax burden to encourage people into work.[216] Farage stated in another interview that he would remove university tuition fees if he won power for those studying science, technology, engineering, medicine or maths. Reform UK have already pledged to scrap interest on student loans and to extend the loan capital repayment periods to 45 years.[217] Farage also declared his ambition for Reform UK to replace the Conservatives as the biggest right-wing party in Parliament.[218]
The Conservatives pledged a review of licensing laws and planning rules aimed at boosting pubs, restaurants and music venues.[219] Labour framed its 10-year science and R&D budget plans as part of its industrial strategy, with an aim of boosting workforce and regional development.[220][221] Labour and the Liberal Democrats also focused on water pollution and improving England's water quality.[222][223]
On 24 June, Labour focused on NHS dentistry and health.[224] Labour also pledged to hold a knife crime summit every year and halve incidents within a decade.[225] The Greens pledged to end 'dental deserts' with £3 billion for new NHS contracts.[226]
The Liberal Democrats launched a mini-manifesto for carers.[227] It pledged to establish an independent living taskforce to help people live independently in their own homes, a new care worker's minimum wage to raise their pay by £2 an hour, and a new National Care Agency. Sunak launched the Scottish Conservatives' manifesto.[228] Starmer discussed a proposed Football Governance Bill,[229] which will establish the new Independent Football Regulator.[230] The Conservatives and Liberal Democrats have also committed to introducing an Independent Football Regulator.[231] The Liberal Democrats pledged to establish a series of "creative enterprise zones" across the UK to regenerate cultural output.[232]
On 26 June, Alex Salmond launched the Alba Party manifesto. It pledged to increase funding for public services, increase NHS staffing, provide an annual £500 payment to households receiving the council tax reduction at a cost of £250 million, increase the Scottish Child Payment, reducing fuel bills, a new Scottish clean energy public company, and Scottish Independence.[233]
Starmer pledged GP reforms, including the training of thousands more GPs, updating the NHS App, and bringing back the 'family doctor'.[234] Labour would also trial new "neighbourhood health centres".[235] The Social Democratic and Labour Party also launched their manifesto on 26 June in Northern Ireland.[236] It pledges a 'Marshall Plan' to tackle health, institutional reform, stronger environmental protection with an independent Environmental Protection Agency, and improving NI's financial settlement.[237]
27 June – present
On 27 June, Labour pledged to reform careers advice and work experience in schools for one million pupils, committing to deliver two weeks' worth of quality work experience for every young person, and recruit more than thousands of new careers advisers.[238] This is part of the party's wider plan to establish a "youth guarantee" of access to training, an apprenticeship or support to find work for all 18 to 21-year-olds.[239][240]
On 27 June, Channel 4 News reported that their reporter working under cover inside the Reform UK campaign in Clacton, alleged homophobic, racist and Islamophobic comments had been made by two Reform UK party campaigners.[241][242] These included an individual calling Sunak a "Paki" and another calling the LGBT flag "degenerate".[243][242] Sunak responded that hearing the racist slur against him "hurts and it makes me angry".[244] Farage described the anti-gay comments as "vulgar, drunk and wrong"[245] and condemned the other individual's racist comments. They were removed as party candidates.[246] On 30 June, one candidate defected to the Conservatives over a perceived lack of leadership from Reform UK on the issue.[247][248]
On 29 June, the Liberal Democrats called for an 'emergency NHS budget' to hire more GPs.[249] Starmer hosted a major campaign rally,[250] and stated in The Guardian "if you vote Labour on Thursday, the work of change begins. We will launch a new national mission to create wealth in every community. We’ll get to work on repairing our public services with an immediate cash injection, alongside urgent reforms. And we will break with recent years by always putting country before party."[251][252]
The Greens announced a 'Charter for Small Business', which pledged £2 billion per year in grant funding for local authorities, regional mutual banks for investment in decarbonisation and local economic sustainability, and increasing annual public subsidies for rail and bus travel to £10 billion.[253][254] They also pledged free bus travel for under-18s.[255] The Northern Ireland Conservatives had their manifesto launched by Northern Ireland Secretary Chris Heaton-Harris.[256]
On 30 June, the Liberal Democrats pledged to double funding for Bereavement Support Payments, and to spend £440 million a year on support for bereaved families.[257] Sunak visited Machzike Hadath Synagogue in North London, highlighting antisemitism.[258]
On 1 July, Davey did a bungee jump in Eastbourne, a "Blue Wall" constituency, asking people to "take the plunge" and vote Liberal Democrat.[259]
Betting scandal
During the general election campaign, allegations were made that illicit bets were placed by political party members and police officers, some of whom may have had insider knowledge of the date of the general election before Sunak publicly announced when it would be held.[260]
The allegations started with a report in The Guardian saying that Conservative candidate and Parliamentary Private Secretary to the Prime Minister, Craig Williams, had placed a £100 bet on 19 May 2024 that the election would be in July, three days before Sunak announced the general election to the public. In response, the Gambling Commission opened an inquiry into alleged betting offences relating to the day of the election. Later, further allegations, or admissions of political betting, were made involving police officers, Conservative members, a Labour member, and a Liberal Democrat member.
Foreign Secretary David Cameron condemned Williams for making the bet, saying it was a "very foolish decision".[261] Sunak said on 20 June that he was "incredibly angry to learn of these allegations" and that "it's right that they're being investigated properly by the relevant law enforcement authorities".[262] Sunak and the Conservative Party faced criticism from Starmer and Davey after the scandal came to light.[263][264] Davey, whilst admitting that he had bet on the outcome of elections, also called for a review of gambling laws.[265]
Media coverage
Broadcasters listed by order of line-up announcement date.
Sky News
On 23 May, Sky News announced that its election night coverage would be hosted by Kay Burley and Sophy Ridge, with analysis from Andy Burnham and Ruth Davidson.[266] They will be joined by Beth Rigby, Trevor Phillips, Ed Conway and Sam Coates.[267]
Channel 4 News
On 24 May, Channel 4 announced that its coverage would be hosted by Krishnan Guru-Murthy and Emily Maitlis, with analysis from Alastair Campbell and Rory Stewart.[266][268] Nadine Dorries was announced as part of the lineup on 25 June.[269]
BBC News
On 28 May, BBC News announced that its coverage would be hosted by Clive Myrie and Laura Kuenssberg, with analysis from Sir John Curtice, Jeremy Vine and Reeta Chakrabarti.[266][270]
ITV News
On 10 June, ITV News announced their election night coverage would be hosted by Tom Bradby, assisted by Robert Peston, Anushka Asthana and Paul Brand alongside election analysts Professors Jane Green and Colin Rallings.[271] They will be joined by Nicola Sturgeon, George Osborne and Ed Balls.[272]
CNN International
On 24 June, CNN International announced that Richard Quest and Isa Soares would host election night coverage for the network alongside results analyst Anna Stewart; Salma Abdelaziz and Clare Sebastian will report live from London-based constituencies and Max Foster will host the later hours of coverage with Nic Robertson reporting from Downing Street.[273]
GB News
On 25 June, GB News announced that Camilla Tominey and Stephen Dixon would anchor their election night coverage; they will be joined remotely by Patrick Christys and Michelle Dewberry from a watch party in Essex, and results analysis will be provided by Christopher Hope, Tom Harwood, Gloria De Piero and Matthew Goodwin.[272]
Debates and interviews
Debates
| ← 2019 debates | 2024 |
|---|
The Conservatives challenged Keir Starmer to six televised debates.[274] Labour announced that it would not agree to such a proposal, and offered two head-to-head debates—one shown on the BBC, and one shown on ITV; a spokesperson said both networks would offer the greatest audience, and the prospect of any debates on smaller channels would be rejected as it would not be a "valuable use of campaign time". Liberal Democrat leader Ed Davey declared his wish to be included in "any televised debates".[275] Starmer confirmed he would take part in a "leaders' event" hosted by Sky News, in which he would take questions from an audience in Grimsby, and that negotiations were undergoing for Rishi Sunak to also attend.[276]
On 29 May, it was announced that the first leaders' debate would be hosted by ITV News and titled "Sunak v Starmer: The ITV Debate" with Julie Etchingham as moderator, on Tuesday 4 June.[277] Key topics were the cost of living crisis, the National Health Service (NHS), young people, immigration and tax policy.[278] Sunak asserted that Labour would cost households £2000 more in tax, which Starmer denied. Sunak claimed this figure was calculated by "independent Treasury officials". Fact checkers disputed the sum, noting it was based on assumptions made by political appointees and that the figure was over a 4-year period. On 5 June, the BBC reported that James Bowler, the Treasury permanent secretary, wrote that "civil servants were not involved in the [...] calculation of the total figure used" and that "any costings derived from other sources or produced by other organisations should not be presented as having been produced by the Civil Service".[279] The Office for Statistics Regulation also criticised the claim on the grounds that it was presented without the listener knowing it was a sum over 4 years.[280] A YouGov snap poll after the debate indicated that 46% of debate viewers thought Sunak had performed better, and 45% believed Starmer had performed better.[281] A Savanta poll published the next day, however, favoured Starmer 44% to Sunak 39%.[282] The debate was watched by 5.37 million viewers, making it the most-viewed programme of the week.[283]
An STV debate hosted by Colin Mackay took place on 3 June, which included Douglas Ross, Anas Sarwar, John Swinney and Alex Cole-Hamilton.[284] Another debate between these leaders (also including Lorna Slater) took place on 11 June, on BBC Scotland, hosted by Stephen Jardine.
A BBC debate hosted by Mishal Husain took place on 7 June, which included Nigel Farage, Carla Denyer, Rhun ap Iorwerth, Daisy Cooper, Stephen Flynn, Angela Rayner and Penny Mordaunt.[285] The debate included exchanges between Mordaunt and Rayner over tax, and all the attendees criticised Sunak leaving the D-Day events early; Farage called Sunak's actions "disgraceful" and said veterans had been deserted, Cooper said it was "politically shameful" and Mordaunt said Sunak's choice to leave prematurely had been "completely wrong".[286][287] After the seven-way debate, a snap poll found that viewers considered Farage had won, followed by Rayner, but that Flynn, Denyer and Cooper scored best on doing a good job.[288] Another debate between these leaders took place on 13 June, with Julie Etchingham as moderator.[289] The debate included further exchanges between Mordaunt and Rayner over tax.[290]
On 12 June Sky News hosted a town hall-style leaders' event in Grimsby hosted by Beth Rigby, including Starmer and Sunak, where they took questions from both Rigby and the audience.[291] The debate covered various topics, including the NHS, the economy, immigration, and their future plans in government. Starmer started the event by saying he was putting the country ahead of his party, bringing Labour "back into the service of working people". He went on to attack the Conservatives on tax policy, saying that "the Tories are in no position to lecture anyone about tax rises". When questioned by Rigby over supporting Jeremy Corbyn in the previous election, Starmer that he was "certain that we would lose the 2019 election".[292][293] Sunak adopted a defensive stance, saying that "it [hadn't] been an easy 18 months" and was questioned over his early exit from the 80th D-Day anniversary events, as well as the Rwanda asylum plan.[294] 64% of those questioned by YouGov immediately following the debate said that Starmer had performed better, compared to 36% who said Sunak had performed better.[295]
Channel 4 News hosted a debate on 18 June with all seven of the main parties focusing solely on the issues of immigration and law and order.[296] On 24 June, a The Sun/Talk event hosted by Harry Cole titled Never Mind the Ballots: Election Showdown was attended by Sunak and Starmer.[n]
Other BBC debates included three Question Time specials, two hosted by Fiona Bruce on 20 and 28 June, and one hosted by Bethan Rhys Roberts on 24 June. The first of the two hosted by Bruce featured four separate half-hour question and answer sessions with Sunak, Starmer, Davey and Swinney; the second of the two hosted by Bruce featured the same format with Ramsay and Farage; the programme hosted by Rhys Roberts featured the same format with ap Iorwerth. There was a BBC Cymru Wales debate on 21 June;[297] and a debate between Sunak and Starmer hosted by Husain took place on 26 June.[298] There was also a BBC debate on 27 June involving the five largest Northern Irish political parties.[297]
| 2024 United Kingdom general election debates in Northern Ireland | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Organiser | Host | Format | Venue | Viewing figures (millions) |
P Present I Invited S Surrogate NI Not invited A Absent N No debate | ||||||||||||
| DUP | Sinn Féin | SDLP | UUP | Alliance | ||||||||||||||
| 23 June[314] [author missing] | UTV | Vicki Hawthorne | Debate | UTV HQ, City Quays 2, Belfast[315] | TBA | P Robinson |
S Finucane |
P Eastwood |
S Butler |
P Long | ||||||||
| 27 June[297] | BBC Northern Ireland | Tara Mills | Debate | Broadcasting House, Belfast | TBA | P Robinson |
S Hazzard |
P Eastwood |
S Butler |
P Long | ||||||||
Interviews
In addition to the debates, the BBC and ITV broadcast programmes in which the leaders of the main parties were interviewed at length.[316][317]
Sunak's Tonight interview drew substantial coverage in the week prior to broadcast, as Sunak controversially departed the D-Day commemorations early to attend; it was later revealed that the interview slot had been chosen by Sunak and his team, from a range of options offered by ITN.[318]
Endorsements
Newspapers, organisations, and individuals have endorsed parties or individual candidates for the election.
Candidates
There are 4515 candidates standing, which constitutes a record number. This is a mean of 6.95 candidates per constituency. No seat has fewer than five people contesting it; Sunak's Richmond and Northallerton seat has the most candidates, with thirteen.[319]
A record number of Conservative MPs are not standing for re-election, including former prime minister Theresa May and former cabinet ministers Sajid Javid, Dominic Raab, Matt Hancock, Ben Wallace, Nadhim Zahawi, Kwasi Kwarteng and Michael Gove.[320]
In March 2022, Labour abandoned all-women shortlists, citing legal advice that continuing to use them for choosing parliamentary candidates would be an unlawful practice under the Equality Act 2010, since the majority of Labour MPs were now women.[321]
In March 2024, Reform UK announced an electoral pact with the Northern Irish unionist party TUV.[322][323] The TUV applied to run candidates as "TUV/Reform UK" on ballot papers, but this was rejected by the Electoral Office.[324] Farage unilaterally ended this deal by endorsing two competing candidates from the Democratic Unionist Party on 10 June.[325] Reform UK also announced a pact with the Social Democratic Party (SDP), a minor socially conservative party, in some seats.[326]
The below table shows all parties standing in at least 14 seats:
| Parties[327] | Number of candidates[328] | |
|---|---|---|
| Conservative Party | 635 | |
| Labour Party | 631 | |
| Liberal Democrats | 630 | |
| Reform UK | 609 | |
| Green Party of England and Wales | 574 | |
| Workers Party of Britain | 152 | |
| Social Democratic Party | 122 | |
| Scottish National Party | 57 | |
| Co-operative Party | 48[v] | |
| Scottish Greens | 44 | |
| Heritage Party | 41 | |
| Trade Unionist and Socialist Coalition | 40 | |
| Plaid Cymru | 32 | |
| Yorkshire Party | 27 | |
| Rejoin EU | 26 | |
| UKIP | 24 | |
| Christian Peoples Alliance | 22 | |
| Official Monster Raving Loony Party | 22 | |
| Alba Party | 19 | |
| Alliance Party of Northern Ireland | 18 | |
| Social Democratic and Labour Party | 18 | |
| Ulster Unionist Party | 17 | |
| Democratic Unionist Party | 16 | |
| Party of Women | 16 | |
| Scottish Family Party | 16 | |
| Communist Party of Britain | 14 | |
| Sinn Féin | 14 | |
| Traditional Unionist Voice | 14 | |
There are additionally
- 37 other parties with more than one candidate standing,
- 36 candidates who are the only candidates of the group they are representing
- 459 independent candidates
- the Speaker.
A more complete list can be found here.
Opinion polling
| Opinion polling for UK general elections |
|---|
| 2010 election |
| Opinion polls |
| 2015 election |
| Opinion polls • Leadership approval |
| 2017 election |
| Opinion polls • Leadership approval |
| 2019 election |
| Opinion polls • Leadership approval |
| 2024 election |
| Opinion polls • Leadership approval |
Discussion around the campaign has been focused on the prospect of a change in government. Under Rishi Sunak's leadership, the Conservatives performed poorly at the 2022 and 2023 local elections, where Labour and the Liberal Democrats made gains from Conservatives, often by very wide margins. The parties made further gains in the 2024 local elections.
Under Keir Starmer's leadership, the Labour Party suffered losses in the 2021 local elections but since the end of 2021, the party has consistently polled ahead of the Conservatives, often by very wide margins, including the highest poll lead of any party in over 20 years amid the government crisis during the Truss premiership.[329][330] During the 2022 local elections, Labour gained 108 seats (22 in England, 20 in Scotland, and 66 in Wales).[331] During the 2023 local elections, the Labour Party gained more than 500 councillors and 22 councils, becoming the largest party in local government for the first time since 2002.[332] Labour made further gains in the 2024 local elections and had a greater number of successful candidates than the Conservatives.[333]
Under Ed Davey's leadership, the Liberal Democrats have made gains in local elections alongside Labour, with both parties making gains in the 2023 local elections and made further gains in the 2024 local elections, where the Liberal Democrats finished second for the first time in a local election cycle since 2009.[334]
A YouGov poll conducted on the same day revealed Labour to be on course for the party's biggest election victory in history, beating Tony Blair's 1997 landslide. The poll indicated Labour could win 422 seats, while the Conservatives were projected to win 140 seats.[335] Halfway through the campaign, psephologist John Curtice summarised the polls as having shown little change in the first two weeks of the campaign, but that they had then shown some clear shifts. Specifically, both the Conservatives and Labour had shown a decline of a few percentage points, leaving the gap between them unchanged, while Reform UK and the Liberal Democrats had both shown an increase, with one YouGov poll published 13 June attracting attention for showing Reform UK one point above the Conservative Party.[336][337]
Graphical summaries
Projections
"Others" figure includes the Speaker as well as the various political parties in Northern Ireland unless otherwise stated.
Four weeks before the vote
Halfway through the campaign, psephologist John Curtice said that the polls had shown little change in the first two weeks of the campaign, but that they had since shown some clear shifts, attributing these in part to the assumption of Reform UK leadership by Farage. Specifically, both the Conservatives and Labour had shown a few percentage points decline, leaving the gap between them unchanged, while Reform UK and the Liberal Democrats had both shown a few percentage points increase, with one YouGov poll published 13 June attracting attention for showing Reform UK above the Conservative Party.[338][339]
| Source | Date | Con | Lab | Lib Dems | SNP | Plaid | Green | Reform | Others | Overall result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Economist[340] | 7 June | 182 | 394 | 22 | 24 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 19 | Labour majority 138 |
| Electoral Calculus[341] | 7 June | 76 | 472 | 60 | 16 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 20 | Labour majority 294 |
| ElectionMapsUK[342] | 8 June | 101 | 451 | 59 | 13 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 19 | Labour majority 252 |
| Financial Times[343] | 7 June | 139 | 443 | 32 | 14 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 19 | Labour majority 236 |
| New Statesman[344][345] | 8 June | 86 | 456 | 64 | 20 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 19 | Labour majority 262 |
| YouGov[346] | 3 June | 140 | 422 | 48 | 17 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 19 | Labour majority 194 |
Two weeks before the vote
| Source | Date | Con | Lab | Lib Dems | SNP | Plaid | Green | Reform | Others | Overall result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Economist [347] | 20 June | 184 | 383 | 23 | 28 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 19[n 1] | Labour majority 116 |
| Electoral Calculus[348] | 21 June | 76 | 457[n 2] | 66 | 22 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 2 | Labour majority 264 |
| Financial Times[349] | 19 June | 97 | 459 | 51 | 21 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 19[n 1] | Labour majority 268 |
| The New Statesman[350] | 20 June | 101 | 437 | 63 | 22 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 19[n 1] | Labour majority 224 |
| YouGov[351] | 19 June | 108 | 425 | 67 | 20 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 0 | Labour majority 198 |
| Ipsos[352] | 18 June | 115 | 453 | 38 | 15 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 1[n 2] | Labour majority 256 |
| Savanta[353][354] | 19 June | 53 | 516 | 50 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Labour majority 380 |
| The New Statesman[355] | 22 June | 96 | 435 | 63 | 24 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 1 | Labour majority 238 |
One week before the vote
| Source | Date | Con | Lab | Lib Dems | SNP | Plaid | Green | Reform | Others | Overall result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Economist[356] | 27 June | 117 | 429 | 42 | 23 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 19[n 1] | Labour majority 208 |
| Electoral Calculus[357] | 26 June | 60 | 450[n 2] | 71 | 24 | 4 | 4 | 18 | 19[n 3] | Labour majority 250 |
| Financial Times[358] | 28 June | 91 | 459 | 64 | 13 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 19[n 1] | Labour majority 268 |
| ElectionMapsUK[359] | 27 June | 80 | 453 | 71 | 17 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 19[n 1] | Labour majority 256 |
| The New Statesman[360] | 29 June | 90 | 436 | 68 | 23 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 19[n 1] | Labour majority 222 |
| ElectionMapsUK[361] | 1 July | 81 | 453 | 69 | 17 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 19 | Labour majority 256 |
See also
- 2020s in United Kingdom political history
- 2024 in politics and government
- 2024 United Kingdom general election in England
- 2024 United Kingdom general election in Northern Ireland
- 2024 United Kingdom general election in Scotland
- 2024 United Kingdom general election in Wales
- List of target seats in the 2024 United Kingdom general election
- Elections in the United Kingdom
- List of general elections in the United Kingdom
Notes
- ^ Figures below show state of the Commons at dissolution on 30 May 2024.
- ^ Stephen Flynn led the SNP in the House of Commons at dissolution.
- ^ Sinn Féin are abstentionists from Parliament. Michelle O'Neill leads Sinn Féin in Northern Ireland.
- ^ Liz Saville Roberts led Plaid Cymru in the House of Commons at dissolution.
- ^ Neale Hanvey led Alba in the House of Commons at dissolution.
- ^ Caroline Lucas was the Green Party's sole MP in the House of Commons at dissolution.
- ^ Richard Tice was the leader at the time of the dissolution of Parliament, while Lee Anderson was their sole MP. Farage became leader on 3 June 2024.
- ^ In Northern Ireland, voter ID was already required at elections before it was introduced in the rest of the UK.
- ^ Includes 43 MPs sponsored by the Co-operative Party, who are designated Labour and Co-operative.[31]
- ^ Some media sources, such as BBC News, listed Labour's total as 412, by including the Speaker (who, to demonstrate his neutrality, had resigned his Labour Party membership on taking office).
- ^ Nine were elected as Labour MPs but seven of these have been suspended from the parliamentary party until December 2024. A further MP, Mike Amesbury, was suspended on 27 October 2024. Rosie Duffield resigned from the Labour Party on 28 September 2024. Five Independent MPs form the Independent Alliance technical group.
- ^ In the current (2024–present) Parliament, the seven members of Sinn Féin follow a policy of abstentionism. They do not swear into the house, and do not take part in its formal processes (doing so would also compel a by-election).[32] The Speaker and deputy speakers (two Conservative and one Labour) by convention exercise only a casting vote.[33]
- ^ The Fixed-term Parliaments Act automatically scheduled general elections for the first Thursday in May of the fifth year after the previous general election.[35] The previous election was held in December 2019.
- ^ Not a debate.
- ^ Debate took place in Gilbert Scott Building's Bute Hall.
- ^ Not a debate: Sunak and Starmer separately answered questions from the studio audience.
- ^ This debate was focused solely on the issues of immigration and law and order.
- ^ Not a debate: the party leaders were each separately asked questions by the studio audience.
- ^ Not a debate: the party leaders were both separately asked questions.
- ^ Not a debate.
- ^ Not a debate: the party leaders will both separately be asked questions by the studio audience.
- ^ In electoral pact with the Labour Party, all candidates are also standing for the Labour Party
References
- ^ Henley, Jon (13 December 2019). "Boris Johnson wins huge majority on promise to 'get Brexit done'". The Guardian. Retrieved 23 June 2024.
- ^ "Brexit: Boris Johnson signs withdrawal agreement in Downing Street". BBC News. 24 January 2020. Retrieved 23 June 2024.
- ^ a b James, Liam; Middleton, Joe; Dalton, Jane (11 January 2023). "Boris Johnson's biggest scandals: a timeline". The Independent. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ a b "Party claims the latest in a string of controversies for Boris Johnson". Richmond and Twickenham Times. 12 January 2022. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ Amos, Owen (7 July 2022). "Boris Johnson resigns: Five things that led to the PM's downfall". BBC News. Archived from the original on 7 July 2022. Retrieved 7 July 2022.
- ^ Meredith, Sam (7 July 2022). "UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson resigns". CNBC. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ "Privileges committee clerk performed 'hilarious' impersonation of Boris Johnson". The Telegraph. 30 August 2023.
- ^ Middleton, Alia (28 May 2023). "United Kingdom: political developments and data in 2022". European Journal of Political Research. 62: 528. doi:10.1111/2047-8852.12401.
- ^ Allen, Nicholas (6 January 2023). "Those who wear the crown wield the knife: the brutality of recent takeover reshuffles". The Political Quarterly. 94 (1): 36. doi:10.1111/1467-923X.13229.
- ^ Marsh, David (22 June 2023). "Britain's failed attempt at monetary and fiscal exceptionalism". The Economist's Voice. 20 (1): 119–130. doi:10.1515/ev-2023-0021.
- ^ "Liz Truss resigns as UK prime minister". BBC News. 20 October 2022. Archived from the original on 20 October 2022. Retrieved 20 October 2022.
- ^ "Rishi Sunak: A quick guide to the UK's new prime minister". BBC News. 24 October 2022. Archived from the original on 18 January 2024. Retrieved 4 June 2024.
- ^ "Rishi Sunak vows to fix Liz Truss's mistakes in first speech as PM". BBC News. 25 October 2022. Archived from the original on 25 October 2022. Retrieved 4 June 2024.
- ^ Seldon, Anthony; Meakin, Jonathan; Thoms, Illias; Egerton, Tom (2024). The Impossible Office?: The History of the British Prime Minister—Revised and Updated. Cambridge University Press. pp. 398–400. ISBN 978-1-009-42977-1.
- ^ Reuben, Anthony (17 June 2024). "Rishi Sunak's five promises: What progress has he made?". BBC News. Archived from the original on 17 June 2024. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ^ Brown, Faye (5 October 2023). "What is the new Advanced British Standard replacing A-Levels?". Sky News. Archived from the original on 11 June 2024. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ^ a b "Explore our prediction model for Britain's looming election". The Economist. 15 April 2024. Archived from the original on 28 May 2024. Retrieved 28 May 2024.
- ^ Lynch, David (4 April 2020). "Labour leadership: Keir Starmer will lead the party after Jeremy Corbyn's exit". Oxford Mail. Newsquest Media Group. Archived from the original on 6 April 2020. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- ^ Nicholas Cecil. "Sir Keir Starmer to declare Labour is 'party of the centre-ground' once again". Evening Standard. Archived from the original on 10 October 2022. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- ^ Webber, Esther; Courea, Eleni; Casalicchio, Emilio; Rea, Ailbhe (27 September 2022). "'No Drama Starmer': Is the UK Labour Party quietly marching back to power?". Politico. Archived from the original on 5 May 2023. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- ^ Joshua Nevett (5 May 2023). "Local elections 2023: Labour eyes power after crushing Tory losses". BBC News. Archived from the original on 5 May 2023. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- ^ Seddon, Paul (4 May 2024). "Seven takeaways from the local elections". BBC News. Archived from the original on 6 June 2024. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ^ "Sir Ed Davey wins Liberal Democrats leadership election". BBC News. 27 August 2020. Retrieved 27 August 2020.
- ^ Read, Jonathon (13 July 2020). "Ed Davey says he is 'anti-Conservative' and will work with Keir Starmer to oust Boris Johnson". The New European. Archived from the original on 26 July 2020. Retrieved 26 July 2020.
- ^ "Britain's Conservatives trounced in local elections as Labour makes gains". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 5 May 2024.
- ^ "Nicola Sturgeon says time is right to resign as Scotland's first minister". BBC News. 15 February 2023. Retrieved 15 February 2023.
- ^ "Scotland's first minister Humza Yousaf resigns". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 29 April 2024.
- ^ "John Swinney wins SNP leadership unopposed". BBC News. 6 May 2024. Retrieved 6 May 2024.
- ^ "UK General election 2024 Results". BBC News. Retrieved 26 October 2024.
- ^ Cracknell, Richard; Baker, Carl; Pollock, Loui (26 July 2024). "General election 2024 results – House of Commons Library". UK Parliament. Retrieved 10 August 2024.
- ^ "About: Members of Parliament". Co-operative Party. Retrieved 10 May 2024.
- ^ Kelly, Conor (19 August 2019). "Understanding Sinn Féin's Abstention from the UK Parliament". E-International Relations. Retrieved 16 December 2019.
- ^ Boothroyd, David. "House of Commons: Tied Divisions". United Kingdom Election Results. Archived from the original on 6 March 2008. Retrieved 3 June 2024.
- ^ Zodgekar, Ketaki; Baker, Finn (5 July 2024). "How big is the Labour government's majority?". Retrieved 24 July 2024.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011: Section 1". legislation.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 4 February 2024. Retrieved 23 May 2024.
- ^ Kettle, Martin (12 December 2019). "If the exit poll is right, this election will transform British politics". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 23 May 2024. Retrieved 13 December 2019.
- ^ "Government to fulfil manifesto commitment and scrap Fixed-term Parliaments Act". gov.uk. 1 December 2020. Archived from the original on 5 December 2020. Retrieved 6 December 2020.
- ^ "Boris Johnson pushes for power to call election at any time". BBC News. 12 May 2021. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ "Electoral administration bulletin" (PDF). Electoral Commission. 22 March 2023. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 May 2024. Retrieved 26 March 2023.
- ^ Bloom, Dan (17 March 2023). "London Playbook: Strikes hope — Budget fallout — Labour's election prep". Politico. Archived from the original on 26 March 2023. Retrieved 26 March 2023.
- ^ "Rishi Sunak confirms election will be next year, despite legal right to wait until January 2025". Politics.co.uk. 18 December 2023. Retrieved 17 June 2024.
- ^ Stacey, Kiran (4 January 2024). "Rishi Sunak indicates he will not call election until second half of 2024". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 17 June 2024.
- ^ Riley-Smith, Ben (5 May 2024). "No 10 'shelves plan for summer general election'". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Retrieved 1 July 2024.
Downing Street has shelved plans for a general election this summer, The Telegraph understands, with an autumn vote now widely expected after Tory local election defeats.
- ^ Parker, George; Strauss, Delphine; Pickard, Jim (23 April 2024). "Summer or autumn? Rishi Sunak's election date dilemma". Financial Times. Retrieved 1 July 2024.
Sunak's aides insist they are still "planning for an autumn election" and most Tory MPs remain convinced the prime minister will play it long, hoping for a revival in economic and political fortunes later in the year.
- ^ Stewart, Heather; Mason, Rowena (22 May 2024). "Why has the UK PM called a general election, what's at stake and what happens now?". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 1 July 2024.
Many observers had expected the poll to be held in the autumn – perhaps in October or November
- ^ Brown, Faye (23 May 2024). "General election called for 4 July, as Rishi Sunak says 'now is the moment for Britain to choose its future'". Sky News. Archived from the original on 22 May 2024. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ Crerar, Pippa (22 May 2024). "Rishi Sunak will call general election for July in surprise move – sources". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 23 May 2024. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Rishi Sunak expected to announce summer general election shortly". BBC. 22 May 2024. Archived from the original on 22 May 2024. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Rishi Sunak announces 4 July vote in Downing Street statement". BBC News. Archived from the original on 8 June 2024. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ Moss, Neil (10 June 2024). "Record number of candidates standing at election". BBC News. Archived from the original on 10 June 2024. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ^ "All the key General Election dates and deadlines". The Independent. Archived from the original on 23 May 2024. Retrieved 23 May 2024.
- ^ "Timetable for a UK Parliamentary general election on 4 July 2024". Electoral Commission. 2024. Archived from the original on 25 May 2024. Retrieved 25 May 2024.
- ^ "General election guidance 2024". Gov.uk. Archived from the original on 23 May 2024. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "Orders Approved and Business Transacted" (PDF). Privy Council Office. 30 May 2024. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 May 2024. Retrieved 31 May 2024.
- ^ "Our Plan | Conservative Manifesto 2019". Conservative Party. Archived from the original on 16 December 2019. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- ^ "The 2019 Conservative manifesto half-time analysis". Institute for Government. 19 December 2021. Retrieved 2 July 2024.
- ^ "Greater protections for voters as government's Elections Bill achieves Royal Assent". GOV.UK. Retrieved 2 July 2024.
- ^ "Boundary review launched". Boundary Commission for England. 24 February 2016. Archived from the original on 26 December 2016. Retrieved 30 October 2019.
- ^ "2018 Review of Westminster Parliamentary constituencies". Boundary Commission for Scotland. Archived from the original on 30 October 2019. Retrieved 30 October 2019.
- ^ "2018 Review". Boundary Commission for Wales. Archived from the original on 27 September 2019. Retrieved 30 October 2019.
- ^ a b "2018 Review". Boundary Commission for Northern Ireland. 16 February 2016. Archived from the original on 8 July 2018. Retrieved 17 September 2018.
- ^ "Towards final recommendations (and beyond)". Boundary Commission for England. Archived from the original on 8 July 2018. Retrieved 8 July 2018.
- ^ "2018 Review". Boundary Commission for England. Archived from the original on 10 September 2018. Retrieved 17 September 2018.
- ^ "2018 Review of Westminster Constituencies". Boundary Commission for Scotland. Archived from the original on 30 October 2019. Retrieved 17 September 2018.
- ^ "2018 Review of Parliamentary constituencies". Boundary Commission for Wales. Archived from the original on 18 October 2016. Retrieved 17 September 2018.
- ^ a b "Parliamentary Constituencies Act 2020". Archived from the original on 6 August 2021.
- ^ Jones, Ian [@ian_a_jones] (10 September 2018). "New constituency boundaries could have given the Tories a majority of 16 at the last election (projection: Rallings/Thrasher)" (Tweet). Retrieved 30 October 2019 – via Twitter.
- ^ "New parliamentary map would have given Tories a majority of 16 at last election". ITV News. 10 September 2018. Archived from the original on 8 October 2019. Retrieved 30 October 2019.
- ^ "Correspondence with Chloe Smith MP" (PDF). Parliament of the United Kingdom. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 September 2020. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- ^ Proctor, Kate (26 March 2020). "MPs no longer to get automatic vote on constituency boundary plans". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 21 February 2024. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- ^ "Parliamentary Constituencies Act". legislation.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 21 February 2024. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- ^ "2023 Review launched". Boundary Commission for England. Archived from the original on 5 January 2021. Retrieved 7 January 2021.
- ^ "2023 Review of UK Parliament Constituencies". Boundary Commission for Scotland. Archived from the original on 5 January 2021. Retrieved 7 January 2021.
- ^ "2023 Review". Boundary Commission for Wales. Archived from the original on 5 January 2021. Retrieved 7 January 2021.
- ^ "2023 Review: Electoral Quota and Allocation of Constituencies Announced". Boundary Commission for Northern Ireland. 5 January 2021. Archived from the original on 5 January 2021. Retrieved 7 January 2021.
- ^ "List of Business – 15th November 2023" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 November 2023. Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- ^ "The Parliamentary Constituencies Order 2023", legislation.gov.uk, The National Archives, SI 2023/1230, retrieved 20 November 2023
- ^ Baston, Lewis (10 June 2023). "Lewis Baston: With Boris Johnson gone, who will win Uxbridge & South Ruislip?". On London. Archived from the original on 11 June 2023. Retrieved 11 June 2023.
- ^ "2023 Boundary Review – Notional Election Results (GE2019)". Sayers Insights. 2023. Archived from the original on 3 February 2024. Retrieved 14 September 2023.
- ^ a b "General election: Labour would need record swing to win". BBC News. 16 January 2024. Archived from the original on 23 May 2024. Retrieved 23 May 2024.
- ^ "Boundary review: Winners and losers from proposed changes". BBC News. 8 June 2021. Archived from the original on 3 December 2023. Retrieved 6 October 2023.
- ^ "Tories could gain most from new election map". BBC News. 8 November 2022. Archived from the original on 21 September 2023. Retrieved 6 October 2023.
- ^ Media, P. A. (8 November 2022). "Scotland to lose two Commons seats in latest Boundary Commission proposals". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 23 May 2024. Retrieved 6 October 2023.
- ^ "Map of Welsh MPs seats redrawn as number to be cut to 32". BBC News. 28 June 2023. Archived from the original on 23 May 2024. Retrieved 6 October 2023.
- ^ Dewar, Caitlyn (29 June 2024). "Third council sets up emergency postal vote centre amid nationwide delays". STV News. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ O'Hare, Paul (28 June 2024). "Councils open emergency voting booths after postal ballot delay". BBC Scotland News. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ "What is my council doing to deal with postal vote delays?". BBC News. 28 June 2024. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ "Postal voters without packs urged to contact councils". BBC News. 1 July 2024. Retrieved 1 July 2024.
- ^ a b Culbertson, Alix (2 July 2024). "Royal Mail blames government for general election postal ballot delays". Sky News. Retrieved 2 July 2024.
- ^ Knight, Matt; Godfrey-Evans, Henry (28 June 2024). "Uttlesford postal vote delays: Council chief 'mortified' by error". BBC News. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ a b Ross, Madeleine; Gibbons, Amy; Hymas, Charles (1 July 2024). "Royal Mail criticised for failing to deliver postal votes before election". The Telegraph. Retrieved 2 July 2024.
- ^ Walker, Peter (20 February 2024). "Another Canada 93? Tory Sunak critics fear extinction-level election result". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 15 June 2024. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- ^ Hunt, Wayne (1 June 2024). "Can the Tories avoid the fate of Canada's Conservatives?". The Spectator. Archived from the original on 14 June 2024. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- ^ "How Rishi Sunak sprung general election surprise on Tories". BBC News. 23 May 2024. Archived from the original on 26 May 2024. Retrieved 27 May 2024.
- ^ Rogers, Alexandra. "Sir Keir Starmer says election is 'moment country has been waiting for' as he declares 'it is time for change'". Sky News. Retrieved 24 June 2024.
- ^ "People are crying out for change – Ed Davey". BBC News. Archived from the original on 22 May 2024. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ Picheta, Rob (22 May 2024). "UK PM Rishi Sunak calls surprise July vote as his party seeks to defy dire polls". CNN. Retrieved 2 July 2024.
- ^ Constable, Oli. "General Election: Sunak jokes about avoiding cold after soggy speech". BBC. Archived from the original on 28 May 2024. Retrieved 28 May 2024.
- ^ Mitchell, Archie (22 May 2024). "Rishi Sunak's election announcement drowned out by Blair's 1997 theme tune by D:Ream". The Independent. Archived from the original on 23 May 2024. Retrieved 23 May 2024.
- ^ Barber, Nicholas. "D:Ream's Things Can Only Get Better: The unlikely pop song that became a defining British political anthem". www.bbc.com. Retrieved 28 June 2024.
- ^ "'Never again': D:Ream ban Labour from using Things Can Only Get Better". PA Media. 31 May 2024. Archived from the original on 2 June 2024.
The band members expressed regret at letting Tony Blair use the track for his general election victory celebrations in 1997, saying they were accused of "having blood on their hands" after the UK got involved with the war in Iraq.
- ^ "General election 2024: Polling guru crunches the numbers... in 60 seconds". BBC News. 26 May 2024. Archived from the original on 29 May 2024. Retrieved 29 May 2024.
- ^ Grant, Cameron (28 May 2024). "Balance Tips in Labour's Favour Among Scottish Voters". True North. Archived from the original on 28 May 2024. Retrieved 29 May 2024.
- ^ Miller, Hannah (31 May 2024). "Lib Dems aim to grab attention with campaign stunts". BBC News. Archived from the original on 15 June 2024. Retrieved 31 May 2024.
- ^ Rawlinson, Kevin (28 May 2024). "Stunts, sewage and serious messaging: Lib Dems hope to capitalise on outrage at water pollution". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 15 June 2024. Retrieved 1 June 2024.
- ^ Patrick, Holly (31 May 2024). Ed Davey rides rubber ring on waterslide as Lib Dems campaign about children's mental health. The Independent. Archived from the original on 1 June 2024. Retrieved 1 June 2024.
- ^ Seddon, Paul; Casciani, Dominic (23 May 2024). "No Rwanda flights before election, says Rishi Sunak". BBC News. Archived from the original on 23 May 2024. Retrieved 23 May 2024.
- ^ "ONS estimates net migration down by 10% in 2023 but still historically high at +685,000". Electronic Immigration Network. 23 May 2024. Archived from the original on 24 May 2024. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ Geiger, Chas (23 May 2024). "Nigel Farage rules out standing for Reform UK in general election". BBC News. Archived from the original on 23 May 2024. Retrieved 23 May 2024.
- ^ a b "General election live: Nigel Farage to stand in election and become leader of Reform UK". BBC News. Archived from the original on 3 June 2024. Retrieved 3 June 2024.
- ^ "General Election: Liberal Democrats leader, Sir Ed Davey, launches party's election campaign in Cheltenham". Sky News. Archived from the original on 24 May 2024. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ Learmonth, Andrew (24 May 2024). "General Election: Swinney's campaign launch overshadowed by Matheson and Branchform". The Herald. Archived from the original on 24 May 2024. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ Boddy, Robert (23 May 2024). "Labour launches election campaign in Kent". Kent Online. Archived from the original on 2 June 2024. Retrieved 2 June 2024.
- ^ McKiernan, Jennifer; McGarvey, Emily (25 May 2024). "Conservatives plan to bring back mandatory National Service". BBC News. Archived from the original on 27 May 2024. Retrieved 27 May 2024.
- ^ "National service explained: Rishi Sunak unveils Conservative election plan". BBC News. 26 May 2024. Retrieved 1 July 2024.
- ^ Watson, Iain; Geiger, Chas (24 May 2024). "Corbyn confirms he will stand against Labour". BBC News. Archived from the original on 27 May 2024. Retrieved 27 May 2024.
- ^ "General election latest: Sir Keir Starmer to make personal pledge in first major campaign speech as parties clash over security". Sky News. Archived from the original on 27 May 2024. Retrieved 27 May 2024.
- ^ Maddox, David (27 May 2024). "General election latest: Starmer to aim speech at undecided voters as he insists he changed Labour". The Independent. Archived from the original on 27 May 2024. Retrieved 27 May 2024.
- ^ "General election: Tories announce 'Triple Lock Plus' pension allowance". BBC News. 27 May 2024. Archived from the original on 27 May 2024. Retrieved 28 May 2024.
- ^ Chaplain, Chloe (27 May 2024). "Tories pledge 'triple lock plus' tax cut for pensioners in challenge to Labour". i (newspaper). Archived from the original on 8 June 2024. Retrieved 29 May 2024.
- ^ "Going, going, gone: Ed Davey takes a dip in Windermere". BBC News. Archived from the original on 28 May 2024. Retrieved 28 May 2024.
- ^ Savage, Claudia (28 May 2024). "Sir Ed Davey takes the plunge as he reveals Lib Dem plan to tackle sewage crisis". Evening Standard. Archived from the original on 28 May 2024. Retrieved 28 May 2024.
- ^ "Starmer emphasises small town roots in first big campaign speech". BBC News. 28 May 2024. Archived from the original on 29 May 2024. Retrieved 29 May 2024.
- ^ "Labour promises to hit 18-week NHS waiting target within five years". BBC News. 28 May 2024. Archived from the original on 28 May 2024. Retrieved 29 May 2024.
- ^ "Keir Starmer denies Diane Abbott barred from standing for Labour". BBC News. 29 May 2024. Archived from the original on 29 May 2024. Retrieved 29 May 2024.
- ^ "I see no reason why Diane Abbott can't stand for Labour – Angela Rayner". 30 May 2024. Archived from the original on 30 May 2024. Retrieved 30 May 2024.
- ^ Brown, Faye (31 May 2024). "Diane Abbott 'free' to stand for Labour at general election, Sir Keir Starmer says". Sky News.
- ^ "Labour and Tories rule out VAT rise after election". BBC News. 30 May 2024. Archived from the original on 30 May 2024. Retrieved 30 May 2024.
- ^ "Only SNP offering route back to EU – McAllan". BBC News. 30 May 2024. Archived from the original on 30 May 2024. Retrieved 30 May 2024.
- ^ "Reform UK would bring in immigration tax on firms". BBC News. 30 May 2024. Archived from the original on 30 May 2024. Retrieved 30 May 2024.
- ^ "Greens challenge 'timid' Labour in election launch". BBC News. 30 May 2024. Archived from the original on 9 June 2024. Retrieved 30 May 2024.
- ^ "Plaid Cymru the only party putting Wales first – Rhun ap Iorwerth". BBC News. 30 May 2024. Archived from the original on 30 May 2024. Retrieved 30 May 2024.
- ^ "George Galloway launches Workers Party campaign with attack on Labour". BBC News. 1 June 2024. Archived from the original on 3 June 2024. Retrieved 3 June 2024.
- ^ "Sir Keir Starmer promises cut to net migration under Labour". BBC News. 2 June 2024. Archived from the original on 2 June 2024. Retrieved 2 June 2024.
- ^ "Fly-tippers to get points on driving licence, Tories promise". BBC News. 30 May 2024. Retrieved 1 July 2024.
- ^ "Lib Dems photobomb prime minister while campaigning in Oxford". Sky News. Archived from the original on 3 June 2024. Retrieved 3 June 2024.
- ^ Zakir-Hussain, Maryam (3 June 2024). "General Election polls – latest: Labour set to win more seats than Blair in 1997, shock YouGov forecast says". The Independent. Archived from the original on 3 June 2024. Retrieved 3 June 2024.
- ^ "Nigel Farage to run as Reform UK candidate in Clacton". BBC. Archived from the original on 3 June 2024. Retrieved 3 June 2024.
- ^ "Nigel Farage to run as Reform UK candidate in Clacton". BBC. Archived from the original on 4 June 2024. Retrieved 4 June 2024.
- ^ a b "Greens call for extra £50bn a year to 'nurse NHS back to health'". BBC News. 6 June 2024. Archived from the original on 6 June 2024. Retrieved 6 June 2024.
- ^ Samuel, Mithran (22 May 2024). "What the 2024 general election means for social care". Community Care. Archived from the original on 6 June 2024. Retrieved 6 June 2024.
- ^ "Conservatives vow to let high earners keep more in child benefits". BBC News. 6 June 2024. Archived from the original on 10 June 2024. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ^ Harvey, Fiona; Horton, Helena (6 June 2024). "Communities will be given right to turn eyesores into parks, says Labour". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ "Labour unveils plans for new housing on 'grey belt'". BBC News. 19 April 2024. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ "Furious veterans unimpressed with Sunak's apology for skipping D-Day event". The Independent. 7 June 2024. Archived from the original on 7 June 2024. Retrieved 8 June 2024.
- ^ "Starmer: Sunak has to answer for his own actions". BBC News. 7 June 2024. Archived from the original on 8 June 2024. Retrieved 8 June 2024.
- ^ Sigsworth, Tim (7 June 2024). "Zelensky shares D-Day video featuring Starmer with no sign of missing Sunak". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Archived from the original on 9 June 2024. Retrieved 8 June 2024.
- ^ "PM apologises for leaving D-Day commemorations early". BBC News. 7 June 2024. Archived from the original on 7 June 2024. Retrieved 7 June 2024.
- ^ "Harder to have own home under Tories, Sunak tells BBC". Archived from the original on 10 June 2024. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ^ Cherry, Stephen (12 June 2024). "Rishi Sunak's D-Day apology reveals the limits of saying sorry". New Statesman. Retrieved 17 June 2024.
- ^ "Farage and Mordaunt criticise Sunak's 'completely wrong' decision to leave D-Day early, in heated election debate". LBC. Archived from the original on 8 June 2024. Retrieved 8 June 2024.
- ^ "Nigel Farage defends claim Sunak 'doesn't understand our culture'". Archived from the original on 10 June 2024. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ^ "Douglas Ross to resign as leader of Scottish Conservatives". Archived from the original on 10 June 2024. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ^ "Labour pledges 100,000 new childcare places". BBC News. 10 June 2024. Archived from the original on 10 June 2024. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ^ "Lib dem manifesto to pledge £9bn NHS and care 'rescue package'". Archived from the original on 10 June 2024. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ^ "Liberal Democrat manifesto: 11 key policies explained". BBC News. 10 June 2024. Archived from the original on 12 June 2024. Retrieved 12 June 2024.
- ^ "Liberal Democrats pledge free personal care". BBC News. 3 June 2024. Retrieved 2 July 2024.
- ^ "Lib Dem manifesto: 11 key policies explained". BBC News. 10 June 2024. Archived from the original on 12 June 2024. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- ^ Walker, Peter; correspondent, Peter Walker Senior political (15 June 2024). "What each party promises voters in its UK general election manifesto". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 15 June 2024.
{{cite news}}:|last2=has generic name (help) - ^ "Liberal Democrat Party manifesto". Local Government Association.
- ^ Holl-Allen, Genevieve (3 June 2024). "Lib Dem manifesto 2024: Ed Davey's policies for the general election". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Retrieved 17 June 2024.
- ^ "Rishi Sunak: Tory manifesto will include tax cuts". Archived from the original on 10 June 2024. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ^ "Conservative manifesto 2024: summary of the key policies". thetimes.com. Archived from the original on 11 June 2024. Retrieved 11 June 2024.
- ^ Gutteridge, Nick (17 May 2024). "Conservative Party manifesto 2024: Rishi Sunak's policies for the general election". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Archived from the original on 11 June 2024. Retrieved 12 June 2024.
- ^ "Conservatives plan to recruit 8,000 new police officers". BBC News. 9 June 2024. Retrieved 15 June 2024.
- ^ "Spring Budget 2024 (HTML)". GOV.UK. Retrieved 16 June 2024.
- ^ "The Spring Budget 2024: What you need to know". Prime Minister's Priorities. Retrieved 16 June 2024.
- ^ "UK Budget 2024: All the highlights". Politico. 6 March 2024. Retrieved 16 June 2024.
- ^ Walker, Peter; correspondent, Peter Walker Senior political (12 June 2024). "More tax, better housing: key takeaways from the Green party manifesto". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 15 June 2024. Retrieved 12 June 2024.
{{cite news}}:|last2=has generic name (help) - ^ "Green Party manifesto 2024: Key policies analysed". BBC News. 12 June 2024. Retrieved 17 June 2024.
- ^ "Tories seem to admit defeat as minister pleads: Don't give Starmer a 'super majority'". Archived from the original on 13 June 2024. Retrieved 12 June 2024.
- ^ Maidment, Jack; Gibbons, Amy. "Labour 'super-majority' would put UK in 'dangerous place', Defence Secretary warns". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 12 June 2024. Retrieved 12 June 2024.
- ^ "Why Grant Shapps is warning about a Labour 'super-majority'". Archived from the original on 12 June 2024. Retrieved 12 June 2024.
- ^ Adu, Aletha; Waterson, Jim (12 June 2024). "Tories fighting to prevent Labour winning 'supermajority', says Shapps". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 13 June 2024. Retrieved 12 June 2024.
- ^ "Labour manifesto 2024: Find out how Labour will get Britain's future back". The Labour Party. 23 May 2024. Archived from the original on 13 June 2024. Retrieved 12 June 2024.
- ^ "Labour launches manifesto for change". Community Trade Union. 13 June 2024. Retrieved 2 July 2024.
- ^ Reid, Jenni (13 June 2024). "Britain's Labour Party pledges 'wealth creation' as it targets landslide election victory". CNBC. Archived from the original on 13 June 2024. Retrieved 13 June 2024.
- ^ "Starmer launches Labour's pro-business, pro-worker manifesto with £7.35bn of new taxes". Yahoo News. 13 June 2024. Archived from the original on 13 June 2024. Retrieved 13 June 2024.
- ^ "Manifesto checker: What are the Labour, Conservatives', Liberal Democrats', Greens' and Plaid Cymru's key pledges?". Sky News. Archived from the original on 11 June 2024. Retrieved 13 June 2024.
- ^ Mason, Rowena (13 June 2024). "Change and growth: five key takeaways from the Labour manifesto launch". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 13 June 2024.
- ^ Gibbons, Amy; Sigsworth, Tim (16 May 2024). "Labour Party manifesto 2024: Keir Starmer's election promises". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Retrieved 13 June 2024.
- ^ Rayner, Keir Starmer and Angela (17 June 2024). "Keir Starmer and Angela Rayner: Labour will empower local leaders". thetimes.com. Retrieved 17 June 2024.
- ^ "Labour manifesto 2024: 12 key policies analysed". BBC News. 13 June 2024. Retrieved 17 June 2024.
- ^ Penna, Dominic (30 May 2024). "Reform UK manifesto: Nigel Farage's key policies at a glance". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Retrieved 15 June 2024.
- ^ "Policies Reform UK". Reform UK. Retrieved 17 June 2024.
- ^ Anderson, Elizabeth (2 July 2024). "Election 2024 manifestos: Parties' pledges on growth and the economy". inews.co.uk. Retrieved 2 July 2024.
- ^ "All of Farage's Reform UK pledges on immigration – and how the Tories compare". i (newspaper). 14 June 2024. Retrieved 17 June 2024.
- ^ Webb, Caitlin (17 June 2024). "Reform UK manifesto: scrap net zero and reform planning". Local Government Chronicle (LGC). Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ Piper, Elizabeth; James, William. "Nigel Farage promises tighter borders and tax cuts in election 'contract'". Reuters.
- ^ "UK election updates from June 16: Reform UK launches manifesto". Financial Times. Retrieved 17 June 2024.
- ^ Sandford, Daniel (17 June 2024). "Reform UK manifesto 2024: 11 key policies analysed". BBC News. Retrieved 17 June 2024.
- ^ "Nigel Farage says Reform's 'real ambition' is the next general election". Sky News. Retrieved 17 June 2024.
- ^ "A dash for growth: the shadow chancellor prepares for government". Financial Times. Retrieved 17 June 2024.
- ^ Stacey, Kiran; correspondent, Kiran Stacey Political (16 June 2024). "Labour's green plans will create 650,000 jobs, says Rachel Reeves". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 17 June 2024.
{{cite news}}:|last2=has generic name (help) - ^ Henderson, Guy (18 June 2024). "Lib Dem leader Sir Ed Davey promises Devon fuel relief". Devon Live. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ^ "Sandcastles and wheelbarrows: Ed Davey continues his colourful Lib Dem campaign". ITV.com.
- ^ "Labour plans to open 350 banking hubs across Britain". aol.co.uk.
- ^ Shaw, Vicky (17 June 2024). "Labour sets out plans for hundreds of new banking hubs". Evening Standard. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ^ Johnson, Simon; Sanderson, Daniel (19 June 2024). "SNP manifesto 2024: John Swinney's election policies at a glance". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Retrieved 23 June 2024.
- ^ "SNP manifesto: Key policies analysed". BBC News. 19 June 2024. Retrieved 20 June 2024.
- ^ "Sinn Féin election manifesto: Key policies analysed". BBC News. 19 June 2024. Retrieved 20 June 2024.
- ^ "Workers Party makes pay and housing pledges in election manifesto". BBC News. BBC. 19 June 2024. Retrieved 19 June 2024.
- ^ Hurst, Pat (19 June 2024). "George Galloway's Workers Party manifesto at a glance". Evening Standard. Retrieved 20 June 2024.
- ^ "David TC Davies: Polls point to big Labour majority, says top Tory". BBC News. 19 June 2024. Retrieved 20 June 2024.
- ^ "Jeremy Hunt: Labour government would need effective opposition". BBC News. 19 June 2024. Retrieved 20 June 2024.
- ^ "Labour's Islington North chairman who 'hid in bush when spotted campaigning for Corbyn' quits". The Telegraph. 20 June 2024. Retrieved 20 June 2024.
- ^ Callaghan, David (21 June 2024). "Labour launches stinging attack on letting agents and landlords". The Negotiator. Retrieved 21 June 2024.
- ^ Stein, Joshua (13 June 2024). "Labour manifesto promises infrastructure and planning overhaul". Construction News. Retrieved 21 June 2024.
- ^ "Housing: Parties battle over help for first-time buyers and renters". BBC News. 20 June 2024. Retrieved 21 June 2024.
- ^ "The challenges faced by the Conservative election manifesto promise to increase the national housing target". planningresource.co.uk. Retrieved 21 June 2024.
- ^ Robertson, Ben (20 June 2024). "Election 2024: What the party manifestos mean for landlords & home owners". Norton Insurance. Retrieved 21 June 2024.
- ^ "2024 election manifestos: party pledges on housing". National Housing Federation. Retrieved 21 June 2024.
- ^ "Alliance Party manifesto: Key policies analysed". BBC News. 20 June 2024. Retrieved 23 June 2024.
- ^ Young, David (20 June 2024). "Alliance Party's General Election manifesto at a glance". Evening Standard. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ "West provoked Ukraine war, Nigel Farage says". BBC News. 21 June 2024. Retrieved 21 June 2024.
- ^ Walker, Peter; correspondent, Peter Walker Senior political (21 June 2024). "Nigel Farage claims Russia was provoked into Ukraine war". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 21 June 2024.
{{cite news}}:|last2=has generic name (help) - ^ "Our Contract with You" (PDF). Reform UK. 17 June 2024. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ^ "Free university, cannabis, replacing the Tories: Nigel Farage answers your questions". ITV News.
- ^ "Tories to focus on pubs and clubs in first 100 days of government". BBC News. 21 June 2024. Retrieved 23 June 2024.
- ^ Jones, Frances (21 June 2024). "Labour 10-year R&D budgets to be part of industrial strategy". Research Professional News. Retrieved 23 June 2024.
- ^ Pardo, Santiago Bedoya (18 June 2024). "NCUB: Labour's manifesto pledges will boost UK R&D and tackle the skills crisis". The Accountant. Retrieved 23 June 2024.
- ^ "Labour and the Liberal Democrats step up campaigns against sewage dumping". BBC News. 21 June 2024. Retrieved 23 June 2024.
- ^ "Sir Ed Davey splashes in Sheringham for election campaign". BBC News. 22 June 2024. Retrieved 25 June 2024.
- ^ "Labour promises 100,000 extra child dental appointments". BBC News. 11 June 2024. Retrieved 24 June 2024.
- ^ Hymas, Charles (24 June 2024). "Starmer to hold annual summit on knife crime for 'grieving families'". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Retrieved 24 June 2024.
- ^ Savage, Claudia (24 June 2024). "Greens pledges to end 'dental deserts' with £3bn for new NHS contract". Evening Standard. Retrieved 24 June 2024.
- ^ "Liberal Democrats launch mini-manifesto for carers". www.shropshirestar.com. 24 June 2024. Retrieved 24 June 2024.
- ^ Meighan, Craig (24 June 2024). "Scottish Tory manifesto pledges to 'reverse years of SNP incompetence'". STV News. Retrieved 25 June 2024.
- ^ EFL (24 June 2024). "Sir Keir Starmer visits Northampton Town to discuss Football Governance Bill". EFL. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ^ "Football Governance Bill: Legislation for independent football regulator being introduced". BBC Sport. 18 March 2024. Retrieved 25 June 2024.
- ^ EFL (24 June 2024). "Sir Keir Starmer visits Northampton Town to discuss Football Governance Bill". EFL. Retrieved 25 June 2024.
- ^ "Lib Dems pledge 'creative enterprise zones' and European links in manifesto arts promise". The Stage. Retrieved 25 June 2024.
- ^ "Alba Party is 'natural home' for supporters of independence, declares Alex Salmond". The National. 26 June 2024. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ^ Dex, Robert (25 June 2024). "Labour pledges to end 8am scramble for GP appointments by training more doctors". Evening Standard. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ^ Lind, Sofia (13 June 2024). "Labour to 'reform' general practice with new 'neighbourhood health centres'". Pulse Today. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ^ "SDLP taking aim at South Down as party launches election manifesto". BelfastTelegraph.co.uk. 26 June 2024. ISSN 0307-1235. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ "SDLP manifesto: Key policies analysed". BBC News. 26 June 2024. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ Savage, Claudia (26 June 2024). "Labour pledges to 'turbocharge' careers advice for one million pupils". Evening Standard. Retrieved 27 June 2024.
- ^ Newsroom, Labour (26 June 2024). "Labour's Pledge to Boost Work Experience and Careers Advice – Sector Reaction". FE News. Retrieved 27 June 2024.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Brett-Harding, Will (25 June 2024). "How do election manifestos compare to the local growth evidence?". What Works Growth. Retrieved 27 June 2024.
- ^ "Exclusive: Undercover inside Reform's campaign – evidence of homophobia and canvasser's racism". Channel 4 News. 27 June 2024.
- ^ a b "Reform UK campaigners caught making racist slurs". BBC News. 27 June 2024. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ Smout, Alistair; MacAskill, Andrew (29 June 2024). "Rishi Sunak hurt and angry over Reform volunteer's racial slur". The Sydney Morning Herald.
- ^ Mason, Rowena; Stacey, Kiran (28 June 2024). "Nigel Farage 'has questions to answer' over Reform racism, says Rishi Sunak". The Guardian.
- ^ "Reform UK activist's racial slur hurts, says Sunak". BBC News. 28 June 2024.
- ^ "Nigel Farage criticizes racist remarks by Reform UK worker. But he later called it a 'stitch-up'". AP News. 28 June 2024. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ Gibbons, Amy; Hardaker, Daniel (30 June 2024). "Reform candidate defects to Tories amid racism row". The Telegraph.
- ^ Mansfield, Mark (30 June 2024). "Reform UK candidate drops out and backs Tories amid racism row". Nation.Cymru. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ "Lib Dems demand 'emergency NHS budget' to hire more GPs". www.gponline.com. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ "Election latest: Elton John backs Labour and Starmer in general election; Sunak gives very personal speech at London temple". Sky News. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ "Election latest: Elton John backs Labour and Starmer in general election; Sunak gives very personal speech at London temple". Sky News. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ Starmer, Keir (29 June 2024). "Labour needs a clear mandate. If you want change, vote for it". The Observer. ISSN 0029-7712. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ Corry, Paul (28 June 2024). "Greens launch Charter for Small Business". Green Party. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ Lill, Dominic (18 June 2024). "Manifestos for Small Businesses: Key Takeaways | Talk Business". Talk Business | Entrepreneur & Business Advice. Retrieved 2 July 2024.
- ^ James, Rhiannon (28 June 2024). "Greens set out charter for small businesses to help high streets thrive". Evening Standard. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ "Chris Heaton Harris launches NI Conservatives manifesto". BBC News. 29 June 2024. Retrieved 1 July 2024.
- ^ Staff, A. O. L. (30 June 2024). "Lib Dems pledge to spend £440 million a year on support for bereaved families". www.aol.co.uk. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ Durrant, Will (30 June 2024). "Sunak describes antisemitism as 'sickness' in pitch to London's Jewish community". Evening Standard. Retrieved 1 July 2024.
- ^ "Lib Dems plunge head first into final week of campaign". BBC News. 1 July 2024. Retrieved 1 July 2024.
- ^ Martin, Daniel. "Sunak refuses to say whether aide who bet on election date knew it would be in July". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 14 June 2024. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- ^ Weaver, Matthew (13 June 2024). "David Cameron says Rishi Sunak aide's bet on election date was 'very foolish'". The Guardian. Retrieved 23 June 2024.
- ^ Francis, Sam (20 June 2024). "Rishi Sunak 'incredibly angry' over alleged election betting". BBC News. Retrieved 23 June 2024.
- ^ Courea, Eleni (23 June 2024). "Fourth Tory official subject to investigation in election date betting scandal". The Guardian. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ^ "'Proper' to wait for result of betting probe, says Sunak amid ongoing scandal". The Independent. 24 June 2024. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ^ Whannel, Kate (26 June 2024). "Ed Davey calls for gambling law review after election bet row". BBC News. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ^ a b c Clarke, Naomi (28 May 2024). "Laura Kuenssberg, Emily Maitlis and Kay Burley among TV election night hosts". Evening Standard. Archived from the original on 29 May 2024. Retrieved 29 May 2024.
- ^ "Election Night Live on Sky News". skygroup.sky. 23 May 2024. Archived from the original on 29 May 2024. Retrieved 29 May 2024.
- ^ "Channel 4 firms up General Election coverage with heavyweight analysis, announces Rest is Politics deal | Channel 4". Channel 4. 24 May 2024. Archived from the original on 29 May 2024. Retrieved 29 May 2024.
- ^ Singleton, David (25 June 2024). "C4 signs Nadine Dorries for election night coverage". Broadcast. Retrieved 28 June 2024.
- ^ "Clive Myrie and Laura Kuenssberg to host BBC election night coverage". BBC News. 28 May 2024. Archived from the original on 28 May 2024. Retrieved 28 May 2024.
- ^ "ITV announces General Election night plans". ITV. 10 June 2024.
- ^ a b Ponsford, Dominic (17 June 2024). "Election 2024: How broadcasters are covering UK general election". Press Gazette. Retrieved 19 June 2024.
- ^ "CNN International to bring special multi-platform coverage of the 2024 UK election". Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ Frayne, James (23 May 2024). "How Starmer could throw away a 20-point lead". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Archived from the original on 23 May 2024. Retrieved 23 May 2024.
- ^ Francis, Sam (24 May 2024). "Starmer agrees to TV election debates with Sunak". BBC News. Archived from the original on 9 June 2024. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "General election latest – Starmer agrees to take part in Sky News leader's special event". Sky News. 24 May 2024. Archived from the original on 6 June 2024. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ McIntosh, Steven (29 May 2024). "General election debate: ITV to host Rishi Sunak and Keir Starmer head-to-head". BBC News. Archived from the original on 29 May 2024. Retrieved 29 May 2024.
- ^ "General election 2024: Sunak and Starmer clash over tax in first debate". BBC News. 4 June 2024. Archived from the original on 8 June 2024. Retrieved 8 June 2024.
- ^ "Keir Starmer says Rishi Sunak had 'back against the wall' and lied in debate". BBC News. 4 June 2024. Archived from the original on 5 June 2024. Retrieved 6 June 2024.
- ^ "Rishi Sunak defends £2,000 tax claim after widespread criticism". BBC News. 6 June 2024. Archived from the original on 8 June 2024. Retrieved 8 June 2024.
- ^ Smith, Matthew (4 June 2024). "General election 2024: ITV debate snap poll". YouGov. Archived from the original on 4 June 2024. Retrieved 4 June 2024.
- ^ "Election latest: Sunak not taking questions amid talk of Tory battle to succeed him – as Dragon joins Starmer at brewery". Archived from the original on 6 June 2024. Retrieved 6 June 2024.
- ^ a b c "Weekly top 50 shows: 03 Jun 2024 – 09 Jun 2024". BARB. Retrieved 20 June 2024.
- ^ a b Scott, Kevin (29 May 2024). "Scottish party leaders to take part in STV General Election debate". STV News. Archived from the original on 31 May 2024. Retrieved 2 June 2024.
- ^ "The key figures who took part in BBC election debate". BBC News. 7 June 2024. Archived from the original on 8 June 2024. Retrieved 8 June 2024.
- ^ "Seven takeaways from multi-party BBC election debate". BBC News. 7 June 2024. Archived from the original on 8 June 2024. Retrieved 8 June 2024.
- ^ "Mordaunt says Sunak's decision to leave D-Day event was 'wrong'". BBC News. 7 June 2024. Archived from the original on 8 June 2024. Retrieved 8 June 2024.
- ^ "More in Common Snap Poll – Post BBC Seven Party Debate". moreincommon.org.uk. Archived from the original on 8 June 2024. Retrieved 8 June 2024.
- ^ "ITV announces further election debate | Press Centre". Archived from the original on 1 June 2024. Retrieved 31 May 2024.
- ^ "General election live 2024: Parties clash over NHS and education in ITV debate". BBC News. Archived from the original on 13 June 2024. Retrieved 13 June 2024.
- ^ "Be in the audience for our general election leaders event". Sky News. Archived from the original on 31 May 2024. Retrieved 2 June 2024.
- ^ "Starmer: 'I knew we'd lose 2019 election with Corbyn'". BBC News. 12 June 2024. Retrieved 15 June 2024.
- ^ "Jeremy Corbyn accuses Keir Starmer of rewriting history". BBC News. 13 June 2024. Retrieved 15 June 2024.
- ^ "Election latest: Rishi Sunak questioned on 'catalogue of broken promises' – as Sir Keir Starmer likened to 'political robot'". Sky News. Archived from the original on 12 June 2024. Retrieved 12 June 2024.
- ^ "Sir Keir Starmer performed best overall in Sky News leaders' event, poll suggests". Sky News. Archived from the original on 12 June 2024. Retrieved 12 June 2024.
- ^ "Watch Channel 4 News' live debate – 'The UK Decides: Immigration, Law and Order'". Channel 4 News. 18 June 2024. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "BBC announces Network TV Election Debates and Question Time Leaders' Special". BBC Media Centre. 2 June 2024. Archived from the original on 2 June 2024. Retrieved 2 June 2024.
- ^ "BBC general election debate live: Fiery Sunak slates Starmer on small boats as Labour leader blasts PM's 'Truss pledges'". The Independent. 26 June 2024. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ^ "Salford revealed as host of first Sunak v Starmer live TV election debate".
- ^ Goldbart, Max (5 June 2024). "General Election Debate Ratings Revealed: Rishi Sunak & Keir Starmer's Face-Off Watched By Less Than 5M". Deadline. Archived from the original on 9 June 2024. Retrieved 5 June 2024.
- ^ "The BBC Election Debate - How to watch on TV and BBC iPlayer".
- ^ Clarke, Naomi (8 June 2024). "BBC multi-party General Election debate watched by 3.2m viewers on average". Evening Standard via MSN. Archived from the original on 11 June 2024. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ^ "BBC Scotland debate: Key exchanges as party leaders clash".
- ^ "Key moments from Sunak and Starmer's grilling in Grimsby".
- ^ "ITV confirms line up for second dock10 General Election debate".
- ^ Clarke, Naomi (14 June 2024). "ITV General Election debate watched by 2.1 million viewers on average". Evening Standard via MSN. Archived from the original on 15 June 2024. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- ^ a b "ITV Cymru Wales announces General Election coverage plans". ITV News. 6 June 2024. Archived from the original on 7 June 2024. Retrieved 7 June 2024.
- ^ "Colchester's Firstsite hosts Channel 4 election debate".
- ^ "University venue for flagship BBC Question Time Leaders' debate".
- ^ "Sunak defends betting response, as Starmer denies Corbyn support — as it happened".
- ^ a b "Additional Question Time Leaders' Special and scheduling changes to BBC Panorama interviews". BBC News. 18 June 2024. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ^ "Nottingham Trent University to host final head-to-head General Election Debate tonight between Sir Keir Starmer and Rishi Sunak".
- ^ "Final Election 2024 Leaders' Special Question Time".
- ^ https://x.com/utv/status/1804187115686678732?t=nxYbb_VhejmyUegAMOvQeA&s=19
- ^ "Brexit fall-out, finances and a unified Ireland dominate leaders' TV debate".
- ^ "BBC News – Election 2024, The Panorama Interviews with Nick Robinson". BBC. Retrieved 28 June 2024.
- ^ "The ITV Election Interviews". ITV. Retrieved 28 June 2024.
- ^ Waterson, Jim (12 June 2024). "From Partygate to Post Office to D-day: five ways ITV has shaken up the election". The Guardian. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ^ "2024 UK general election candidate summary". democracyclub.org.uk. 12 June 2024.
- ^ "Rishi Sunak warned he has 'six months' to get a grip as rebellions grow". The Independent. London. 28 November 2022. Retrieved 7 December 2022.
- ^ Rogers, Alexandra (7 March 2022). "Exclusive: Labour Drops All-Women Shortlists For Next General Election". HuffPost. Archived from the original on 26 March 2022. Retrieved 26 March 2022.
- ^ Crisp, James (16 March 2024). "Reform strikes election pact with hardline Northern Ireland party". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 16 March 2024. Retrieved 17 March 2024.
- ^ "TUV conference: Jim Allister announces partnership with Reform UK". BBC News. 16 March 2024. Archived from the original on 23 May 2024. Retrieved 16 March 2024. ;"The future of DUP big hitters could now lie in Jim Allister's hands". Belfast Telegraph. 16 March 2024. Archived from the original on 16 March 2024. Retrieved 16 March 2024.
- ^ "Northern Ireland general election: 136 candidates to stand". Archived from the original on 9 June 2024. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ^ "Nigel Farage endorses DUP candidates despite TUV-Reform alliance". BBC News. Archived from the original on 10 June 2024. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ^ SDP (22 October 2022). "Reform UK and SDP Agree General Election Pact". SDP. Archived from the original on 22 October 2022. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ^ "Who can I vote for in the UK 2024 general election?". BBC News. 6 June 2024. Archived from the original on 15 June 2024. Retrieved 12 June 2024.
- ^ "Open candidate information for UK elections". Democracy Club Candidates. Archived from the original on 1 June 2024. Retrieved 13 June 2024.
- ^ Beth Mann (21 October 2022). "Britons now think that Labour will win a majority at the next election". YouGov. Archived from the original on 9 July 2023. Retrieved 9 July 2023.
- ^ "Labour surge to 33-point lead over the Conservatives in new poll". ITV News. 29 September 2022. Archived from the original on 25 March 2023. Retrieved 9 July 2023.
- ^ "Election results 2022: How the parties performed in maps and charts". BBC News. 7 May 2022. Archived from the original on 7 May 2022. Retrieved 8 May 2022.
- ^ Joshua Nevett (5 May 2023). "Local elections 2023: Labour eyes power after crushing Tory losses". BBC News. Archived from the original on 5 May 2023. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- ^ Seddon, Paul (4 May 2024). "Seven takeaways from the local elections". BBC News. Archived from the original on 6 June 2024. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ^ "Britain's Conservatives trounced in local elections as Labour makes gains". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 16 May 2024. Retrieved 5 May 2024.
- ^ Zakir-Hussain, Maryam (3 June 2024). "General Election polls – latest: Labour set to win more seats than Blair in 1997, shock YouGov forecast says". The Independent. Archived from the original on 3 June 2024. Retrieved 3 June 2024.
- ^ "John Curtice on the Farage effect". BBC News. 14 June 2024. Archived from the original on 15 June 2024. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- ^ "Reform now 1pt ahead of the Tories, although this is still within the margin of error | YouGov". yougov.co.uk. Archived from the original on 15 June 2024. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- ^ "John Curtice on the Farage effect". BBC News. 14 June 2024. Archived from the original on 15 June 2024. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- ^ "Reform now 1pt ahead of the Tories, although this is still within the margin of error | YouGov". yougov.co.uk. Archived from the original on 15 June 2024. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- ^ "The Economist's UK general election forecast". The Economist. Archived from the original on 7 June 2024. Retrieved 7 June 2024.
- ^ "General Election Prediction". Archived from the original on 7 June 2024. Retrieved 7 June 2024.
- ^ "General Election Nowcast — Election Maps UK". Archived from the original on 10 June 2024. Retrieved 7 June 2024.
- ^ "Predict the UK general election result". Archived from the original on 3 June 2024. Retrieved 7 June 2024.
- ^ "Model update / How would the UK vote if the election was held today?". Britain Elects on X. 7 June 2024. Archived from the original on 9 June 2024. Retrieved 7 June 2024.
- ^ "Who will win the 2024 UK general election?". 23 May 2024. Archived from the original on 6 June 2024. Retrieved 7 June 2024.
- ^ "General Election 2024: Tory wipeout and 12 ministers at risk of losing seats, YouGov poll suggests". Archived from the original on 8 June 2024. Retrieved 7 June 2024.
- ^ "The Economist's UK general election forecast". The Economist. Retrieved 20 June 2024.
- ^ "General Election Prediction". electoralcalculus.co.uk. Retrieved 23 June 2024.
- ^ "Predict the UK general election result". Retrieved 20 June 2024.
- ^ Walker, Ben (23 May 2024). "Who will win the 2024 UK general election?". State of the Nation. Retrieved 20 June 2024.
- ^ "Second YouGov 2024 election MRP shows Conservatives on lowest seat total in history | YouGov". yougov.co.uk. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ "Ipsos MRP". Ipsos MRP. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ^ Riley-Smith, Ben (10 June 2024). "Sunak to lose seat in Tory wipeout, major poll predicts". The Telegraph.
- ^ "Savanta's first MRP of election campaign predicts Labour on for majority of 382 - Savanta". savanta.com. 19 June 2024. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ Walker, Ben. "Who will win the 2024 UK general election?". New Statesman. Retrieved 23 June 2024.
- ^ "UK general election forecast". The Economist. Retrieved 27 June 2024.
- ^ "MRP Poll June 2024". electoralcalculus.co.uk. Retrieved 27 June 2024.
- ^ "Predict the UK general election result". ig.in.ft.com. 24 June 2024. Retrieved 30 June 2024.
- ^ "General Election Nowcast". Election Maps UK. Retrieved 27 June 2024.
- ^ "Who will win the 2024 UK general election?". The New Statesman. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ "General Election Nowcast". Election Maps UK. Retrieved 2 July 2024.
External links
Great Britain manifestos
- Alba Party
- Conservative Party
- Labour Party
- Liberal Democrat
- Green Party of England & Wales
- Reform UK
- Scottish National Party
- Plaid Cymru English Welsh
- Workers Party
- Scottish Greens
- Social Democratic Party






