Newly industrialized country
The category of newly industrialized country (NIC) is a socioeconomic classification applied to several countries around the world by political scientists and economists.
NICs are countries whose economies have not yet reached First World status but have, in a macroeconomic sense, outpaced their developing counterparts. Another characterization of NICs is that of nations undergoing rapid economic growth (usually export-oriented). Incipient or ongoing industrialization is an important indicator of a NIC. In many NICs, social upheaval can occur as primarily rural, agricultural populations migrate to the cities, where the growth of manufacturing concerns and factories can draw many thousands of laborers.
NICs usually share some other common features, including:
- Increased social freedoms and civil rights.
- Strong political leaders.
- A switch from agricultural to industrial economies, especially in the manufacturing sector.
- An increasingly open-market economy, allowing free trade with other nations in the world.
- Large national corporations operating in several continents.
- Strong capital investment from foreign countries.
- Political leadership in their area of influence.
- Lowered poverty rates.
NICs often receive support from international organizations such as the WTO and other internal support bodies. However, as environmental, labor and social standards tend to be significantly weaker in NICs, many fair trade supporters have advocated standards for importing their products and criticized the outsourcing of jobs to NICs.
Historical context
The term began to be used circa 1970 when the Four Asian Tigers[1] of Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea and Taiwan rose to global prominence as NICs in the 1970s and 80s, with exceptionally fast industrial growth since the 1960s; all four regions have since graduated into advanced economies and high-income economies. There is a clear distinction between these countries and the nations now considered to be NICs. In particular, the combination of an open political process, high GNI per capita and a thriving, export-oriented economic policy has shown that these countries have now not only reached but surpassed the ranks of many developed countries. All four economies are classified as High-income economies by the World Bank and Advanced economies by the IMF and CIA. All of them also possess Human Development Index over 0.9, equal to Western European countries. South Korea in particular, is the only OECD member and a "full democracy" in Asia along with Japan. Japan is a parliamentary constitutional monarchy.
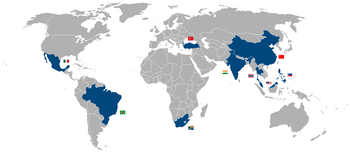
Current NIC countries
The following table presents the list of countries consistently considered NICs in each continent by different authors and experts.[2][3][4][5] Turkey, and South Africa are classified as developed countries by the CIA.[6] Turkey is a founding member of the OECD since 1961 and Mexico joined in 1994. The G8+5 group is composed by G8 members plus China, India, Brazil, Mexico and South Africa.
| Continent | Country | GDP (PPP) (Millions of USD, 2008 IMF)[7] |
GDP per capita (USD, 2008 IMF)[8] |
GDP per capita (PPP) (USD, 2008 IMF)[9] |
Income equality (GINI) 2006[10] | Human Development Index (HDI, 2007)[11] |
List of countries by GDP (real) growth rate | List of countries by GDP (real) growth rate per capita |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Africa | 492,684 | 5,693 | 10,119 | 57.8 | 0.683 (medium) | 4.50 | 4.92 | |
| North America | 1,548,007 | 12,235 | 14,560 | 46.3 | 0.854 (high) | 3.00 | 3.30 | |
| South America | 1,981,207 | 8,197 | 10,326 | 54 | 0.813 (high) | 5.70 | 4.50 | |
| Asia | 7,916,429 | 3,315 | 5,963 | 44.7 | 0.772 (medium) | 11.10 | 9.95 | |
| 3,288,345 | 1,016 | 2,762 | 32.5 | 0.612 (medium) | 9.70 | 7.02 | ||
| 384,119 | 8,141 | 14,072 | 49.2 | 0.829 (high) | 5.40 | 3.65 | ||
| 320,384 | 1,866 | 3,546 | 44.5 | 0.751 (medium) | 7.50 | 7.40 | ||
| 546,095 | 4,115 | 8,225 | 42 | 0.783 (medium) | 4.40 | 3.93 | ||
| Europe | 915,184 | 10,472 | 13,138 | 38 | 0.806 (high) | 5.20 | 4.10 |
According to Goldman Sachs review of emerging economies, by 2050 the largest economies in the world will be as follows: China, USA, India, Brazil, and Mexico.[12]
For China and India, the immense population of these two nations (each with over 1.1 billion people as of January 2009) means that per capita income will remain low even if either economy surpasses that of the United States in overall GDP. When GDP per capita is calculated according to Purchasing Power Parity (PPP), this takes into account the lower costs of living in each newly industrialized country.
Brazil, China, India, Mexico and South Africa meet annually with the G8 countries to discuss financial topics and climate change, due to their economic importance in today's global market and environmental impact, in a group known as G8+5.[13] This group is expected to be expanded to G14 by adding Egypt alongside the five forementioned countries.[14] Once the group goes in affect, Egypt could soon be classified as a NIC.
Other NIC countries
Each author set a list of countries accordingly to the methods or type of economic analysis. This sometimes results in a country being mentioned as NIC in a particular work, but that is rarely considered as such by the other authors. This is the case of nations such as Egypt, Indonesia and Russia.[2]
Brief economic analysis
NICs usually benefit from comparatively low labor costs, which translates into lower input prices for suppliers. As a result, it is often easier for producers in NICs to outperform and outproduce factories in developed countries, where the cost of living is higher, and labor unions and other organizations have more political sway.
This comparative advantage is often criticized by advocates of the fair trade movement.
Issues
Economic freedom is not always associated with political freedom in nations such as the People's Republic of China, where Internet censorship and other abuses of civil rights are common. The case is diametrically opposite in the case of the other Asian giant, India, which has been a liberal democracy throughout its post-colonial history. Other NICs vary between these two opposing examples. The Chinese government has responded to these accusations by arguing that China's increasing standard of living has provided a utilitarian social benefit that outweighs the detrimental effect of individual violations.
India faces different types of issues compared to China. While China's economy has greatly benefited due to foreign investment by wealthy neighbors such as Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan, four of the nine nations neighboring India are classified as Least Developed Countries. India is the newly industrialized country with 27.5% of the population living under the national poverty line. [15] South Africa faces an influx of immigrants from countries such as Zimbabwe.
References
- ^ Japan and the Newly Industrialized Economies
- ^ a b c d e f Paweł Bożyk (2006). "Newly Industrialized Countries". Globalization and the Transformation of Foreign Economic Policy. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. p. 164. ISBN 0-75-464638-6.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Mauro F. Guillén (2003). "Multinationals, Ideology, and Organized Labor". The Limits of Convergence. Princeton University Press. pp. 126 (Table 5.1). ISBN 0-69-111633-4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j David Waugh (3rd edition 2000). "Manufacturing industries (chapter 19), World development (chapter 22)". Geography, An Integrated Approach. Nelson Thornes Ltd. pp. 563, 576–579, 633, and 640. ISBN 0-17-444706-X.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|year=(help) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j N. Gregory Mankiw (4th Edition 2007). Principles of Economics. ISBN 0-32-422472-9.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|year=(help) - ^ CIA World Factbook
- ^ IMF World Economic Outlook Database, April 2009. GDP-PPP figures of selected NIC countries for 2007 and 2008.
- ^ IMF World Economic Outlook Database, April 2009. Nominal GDP per capita figures of selected NIC countries for 2007 and 2008.
- ^ IMF World Economic Outlook Database, April 2009. GDP-PPP per capita figures of selected NIC countries for 2007 and 2008.
- ^ See List of countries by income equality for Gini reference. The higher the figure, the higher the inequality.
- ^ United Nations report [1]
- ^ [2]
- ^ G8 Structure and activities
- ^ " France invites Egypt to join G14"
- ^ Poverty estimates for 2004-05, Planning commission, Government of India, March 2007.
15. The Planning Commission, Government of India
