Solar eclipse of September 30, 1913
Appearance
| Solar eclipse of September 30, 1913 | |
|---|---|
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | −1.1005 |
| Magnitude | 0.8252 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 61°00′S 11°36′E / 61°S 11.6°E |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 4:45:49 |
| References | |
| Saros | 152 (7 of 70) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9311 |
A partial solar eclipse occurred on September 30, 1913. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 1910–1913
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
The partial solar eclipse on August 31, 1913 occurs in the next lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1910 to 1913 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 117 | May 9, 1910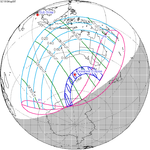 Total |
−0.9437 | 122 | November 2, 1910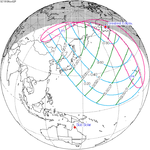 Partial |
1.0603 | |
| 127 | April 28, 1911 Total |
−0.2294 | 132 | October 22, 1911 Annular |
0.3224 | |
| 137 | April 17, 1912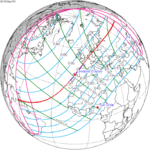 Hybrid |
0.528 | 142 | October 10, 1912 Total |
−0.4149 | |
| 147 | April 6, 1913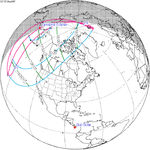 Partial |
1.3147 | 152 | September 30, 1913 Partial |
−1.1005 | |
References
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
External links
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC




