Solar eclipse of May 30, 1965
| Solar eclipse of May 30, 1965 | |
|---|---|
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | −0.4225 |
| Magnitude | 1.0544 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 315 s (5 min 15 s) |
| Coordinates | 2°30′S 133°48′W / 2.5°S 133.8°W |
| Max. width of band | 198 km (123 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 21:17:31 |
| References | |
| Saros | 127 (55 of 82) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9432 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on Sunday, May 30, 1965. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from northwestern Northland Region in New Zealand on May 31st (Monday), and Manuae in Cook Islands, Manuae and Motu One in French Polynesia, and Peru on May 30th (Sunday).
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses of 1964–1967
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
The partial solar eclipses on January 14, 1964 and July 9, 1964 occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1964 to 1967 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 117 | June 10, 1964 Partial |
−1.1393 | 122 | December 4, 1964 Partial |
1.1193 | |
| 127 | May 30, 1965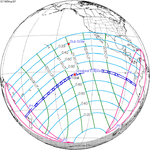 Total |
−0.4225 | 132 | November 23, 1965 Annular |
0.3906 | |
| 137 | May 20, 1966 Annular |
0.3467 | 142 | November 12, 1966 Total |
−0.33 | |
| 147 | May 9, 1967 Partial |
1.1422 | 152 | November 2, 1967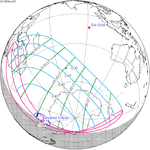 Total (non-central) |
1.0007 | |
Saros 127
This eclipse is a part of Saros series 127, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 82 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on October 10, 991 AD. It contains total eclipses from May 14, 1352 through August 15, 2091. There are no annular or hybrid eclipses in this set. The series ends at member 82 as a partial eclipse on March 21, 2452. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of totality was produced by member 31 at 5 minutes, 40 seconds on August 30, 1532. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit.[2]
| Series members 46–68 occur between 1801 and 2200: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 46 | 47 | 48 |
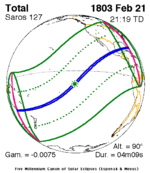 February 21, 1803 |
 March 4, 1821 |
 March 15, 1839 |
| 49 | 50 | 51 |
 March 25, 1857 |
 April 6, 1875 |
 April 16, 1893 |
| 52 | 53 | 54 |
 April 28, 1911 |
 May 9, 1929 |
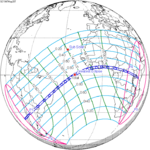 May 20, 1947 |
| 55 | 56 | 57 |
 May 30, 1965 |
 June 11, 1983 |
 June 21, 2001 |
| 58 | 59 | 60 |
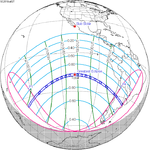 July 2, 2019 |
 July 13, 2037 |
 July 24, 2055 |
| 61 | 62 | 63 |
 August 3, 2073 |
 August 15, 2091 |
 August 26, 2109 |
| 64 | 65 | 66 |
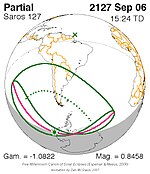 September 6, 2127 |
 September 16, 2145 |
 September 28, 2163 |
| 67 | 68 | |
 October 8, 2181 |
 October 19, 2199 | |
Inex series
This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Inex series members between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
 July 10, 1907 (Saros 125) |
 June 19, 1936 (Saros 126) |
 May 30, 1965 (Saros 127) |
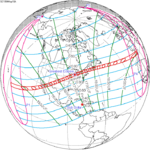 May 10, 1994 (Saros 128) |
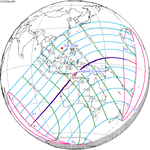 April 20, 2023 (Saros 129) |
 March 30, 2052 (Saros 130) |
 March 10, 2081 (Saros 131) |
||
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| 22 eclipse events between January 5, 1935 and August 11, 2018 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January 4–5 | October 23–24 | August 10–12 | May 30–31 | March 18–19 |
| 111 | 113 | 115 | 117 | 119 |
 January 5, 1935 |
 August 12, 1942 |
 May 30, 1946 |
 March 18, 1950 | |
| 121 | 123 | 125 | 127 | 129 |
 January 5, 1954 |
 October 23, 1957 |
 August 11, 1961 |
 May 30, 1965 |
 March 18, 1969 |
| 131 | 133 | 135 | 137 | 139 |
 January 4, 1973 |
 October 23, 1976 |
 August 10, 1980 |
 May 30, 1984 |
 March 18, 1988 |
| 141 | 143 | 145 | 147 | 149 |
 January 4, 1992 |
 October 24, 1995 |
 August 11, 1999 |
 May 31, 2003 |
 March 19, 2007 |
| 151 | 153 | 155 | ||
 January 4, 2011 |
 October 23, 2014 |
 August 11, 2018 | ||
References
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ "NASA - Catalog of Solar Eclipses of Saros 127". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.




