Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe | |
|---|---|
 Goethe in 1828, by Joseph Karl Stieler | |
| Born | 28 August 1749 Free Imperial City of Frankfurt, Holy Roman Empire |
| Died | 22 March 1832 (aged 82) Weimar, Grand Duchy of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, German Confederation |
| Occupation | Poet, novelist, playwright, natural philosopher, diplomat, civil servant |
| Nationality | German |
| Alma mater | |
| Literary movement | |
| Notable works | Faust; The Sorrows of Young Werther; Wilhelm Meister's Apprenticeship; Elective Affinities; "Prometheus"; Zur Farbenlehre; Italienische Reise; West–östlicher Divan |
| Spouse | |
| Children | 5 (4 died young)
|
| Relatives | Cornelia Schlosser (sister) Christian August Vulpius (brother-in-law) |
| Signature | |
 | |
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (/ˈɡɜːtə/, also US: /ˈɡɜːrtə, ˈɡeɪtə, -ti/ GURT-ə, GAYT-ə, -ee;[1][2] German: [ˈjoːhan ˈvɔlfɡaŋ fɔn ˈɡøːtə] ;[2] 28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German writer and statesman. His works include: four novels; epic and lyric poetry; prose and verse dramas; memoirs; an autobiography; literary and aesthetic criticism; and treatises on botany, anatomy, and colour. In addition, numerous literary and scientific fragments, more than 10,000 letters, and nearly 3,000 drawings by him have survived. He is considered the greatest German literary figure of the modern era.[3]
A literary celebrity by the age of 25, Goethe was ennobled by the Duke of Saxe-Weimar, Karl August, in 1782 after taking up residence in Weimar in November 1775 following the success of his first novel, The Sorrows of Young Werther (1774). He was an early participant in the Sturm und Drang literary movement. During his first ten years in Weimar, Goethe became a member of the Duke's privy council, sat on the war and highway commissions, oversaw the reopening of silver mines in nearby Ilmenau, and implemented a series of administrative reforms at the University of Jena. He also contributed to the planning of Weimar's botanical park and the rebuilding of its Ducal Palace.[4][a]
Goethe's first major scientific work, the Metamorphosis of Plants, was published after he returned from a 1788 tour of Italy. In 1791 he was made managing director of the theatre at Weimar, and in 1794 he began a friendship with the dramatist, historian, and philosopher Friedrich Schiller, whose plays he premiered until Schiller's death in 1805. During this period Goethe published his second novel, Wilhelm Meister's Apprenticeship; the verse epic Hermann and Dorothea, and, in 1808, the first part of his most celebrated drama, Faust. His conversations and various shared undertakings throughout the 1790s with Schiller, Johann Gottlieb Fichte, Johann Gottfried Herder, Alexander von Humboldt, Wilhelm von Humboldt, and August and Friedrich Schlegel have come to be collectively termed Weimar Classicism.
The German philosopher Arthur Schopenhauer named Wilhelm Meister's Apprenticeship one of the four greatest novels ever written,[5][b] while the American philosopher and essayist Ralph Waldo Emerson selected Goethe as one of six "representative men" in his work of the same name (along with Plato, Emanuel Swedenborg, Montaigne, Napoleon, and Shakespeare). Goethe's comments and observations form the basis of several biographical works, notably Johann Peter Eckermann's Conversations with Goethe (1836).
Life
Early life
Goethe's father, Johann Caspar Goethe, lived with his family in a large house (today the Goethe House) in Frankfurt, then an Imperial Free City of the Holy Roman Empire. Though he had studied law in Leipzig and had been appointed Imperial Councillor, he was not involved in the city's official affairs.[6] Johann Caspar married Goethe's mother, Catharina Elizabeth Textor at Frankfurt on 20 August 1748, when he was 38 and she was 17.[7] All their children, with the exception of Johann Wolfgang and his sister, Cornelia Friederica Christiana, who was born in 1750, died at early ages.

His father and private tutors gave Goethe lessons in all the common subjects of their time, especially languages (Latin, Greek, French, Italian, English and Hebrew). Goethe also received lessons in dancing, riding and fencing. Johann Caspar, feeling frustrated in his own ambitions, was determined that his children should have all those advantages that he had not.[6]
Although Goethe's great passion was drawing, he quickly became interested in literature; Friedrich Gottlieb Klopstock and Homer were among his early favorites. He had a lively devotion to theater as well and was greatly fascinated by puppet shows that were annually arranged in his home; this is a recurrent theme in his literary work Wilhelm Meister's Apprenticeship.
He also took great pleasure in reading works on history and religion. He writes about this period:
I had from childhood the singular habit of always learning by heart the beginnings of books, and the divisions of a work, first of the five books of Moses, and then of the 'Aeneid' and Ovid's 'Metamorphoses'. ... If an ever busy imagination, of which that tale may bear witness, led me hither and thither, if the medley of fable and history, mythology and religion, threatened to bewilder me, I readily fled to those oriental regions, plunged into the first books of Moses, and there, amid the scattered shepherd tribes, found myself at once in the greatest solitude and the greatest society.[8]
Goethe became also acquainted with Frankfurt actors.[9] Among early literary attempts, he was infatuated with Gretchen, who would later reappear in his Faust and the adventures with whom he would concisely describe in Dichtung und Wahrheit.[10] He adored Caritas Meixner (1750–1773), a wealthy Worms trader's daughter and friend of his sister, who would later marry the merchant G. F. Schuler.[11]
Legal career

Goethe studied law at Leipzig University from 1765 to 1768. He detested learning age-old judicial rules by heart, preferring instead to attend the poetry lessons of Christian Fürchtegott Gellert. In Leipzig, Goethe fell in love with Anna Katharina Schönkopf and wrote cheerful verses about her in the Rococo genre. In 1770, he anonymously released Annette, his first collection of poems. His uncritical admiration for many contemporary poets vanished as he became interested in Gotthold Ephraim Lessing and Christoph Martin Wieland. Already at this time, Goethe wrote a good deal, but he threw away nearly all of these works, except for the comedy Die Mitschuldigen. The restaurant Auerbachs Keller and its legend of Faust's 1525 barrel ride impressed him so much that Auerbachs Keller became the only real place in his closet drama Faust Part One. As his studies did not progress, Goethe was forced to return to Frankfurt at the close of August 1768.
Goethe became severely ill in Frankfurt. During the year and a half that followed, because of several relapses, the relationship with his father worsened. During convalescence, Goethe was nursed by his mother and sister. In April 1770, Goethe left Frankfurt in order to finish his studies at the University of Strasbourg.
In Alsace, Goethe blossomed. No other landscape has he described as affectionately as the warm, wide Rhine area. In Strasbourg, Goethe met Johann Gottfried Herder. The two became close friends, and crucially to Goethe's intellectual development, Herder kindled his interest in Shakespeare, Ossian and in the notion of Volkspoesie (folk poetry). On 14 October 1772 Goethe held a gathering in his parental home in honour of the first German "Shakespeare Day". His first acquaintance with Shakespeare's works is described as his personal awakening in literature.[12]
On a trip to the village Sessenheim, Goethe fell in love with Friederike Brion, in October 1770,[13][14] but, after ten months, terminated the relationship in August 1771.[15] Several of his poems, like "Willkommen und Abschied", "Sesenheimer Lieder" and "Heidenröslein", originate from this time.
At the end of August 1771, Goethe acquired the academic degree of the Lizenziat (Licentia docendi) in Frankfurt and established a small legal practice. Although in his academic work he had expressed the ambition to make jurisprudence progressively more humane, his inexperience led him to proceed too vigorously in his first cases, and he was reprimanded and lost further ones. This prematurely terminated his career as a lawyer after only a few months. At this time, Goethe was acquainted with the court of Darmstadt, where his inventiveness was praised. From this milieu came Johann Georg Schlosser (who was later to become his brother-in-law) and Johann Heinrich Merck. Goethe also pursued literary plans again; this time, his father did not have anything against it, and even helped. Goethe obtained a copy of the biography of a noble highwayman from the German Peasants' War. In a couple of weeks the biography was reworked into a colourful drama. Entitled Götz von Berlichingen, the work went directly to the heart of Goethe's contemporaries.
Goethe could not subsist on being one of the editors of a literary periodical (published by Schlosser and Merck). In May 1772 he once more began the practice of law at Wetzlar. In 1774 he wrote the book which would bring him worldwide fame, The Sorrows of Young Werther. The outer shape of the work's plot is widely taken over from what Goethe experienced during his Wetzlar time with Charlotte Buff (1753–1828)[16] and her fiancé, Johann Christian Kestner (1741–1800),[16] as well as from the suicide of the author's friend Karl Wilhelm Jerusalem (1747–1772); in it, Goethe made a desperate passion of what was in reality a hearty and relaxed friendship.[17] Despite the immense success of Werther, it did not bring Goethe much financial gain because copyright laws at the time were essentially nonexistent. (In later years Goethe would bypass this problem by periodically authorizing "new, revised" editions of his Complete Works.)[18]
Early years in Weimar

In 1775, Goethe was invited, on the strength of his fame as the author of The Sorrows of Young Werther, to the court of Karl August, Duke of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, who would become Grand Duke in 1815. (The Duke at the time was 18 years of age, to Goethe's 26.) Goethe thus went to live in Weimar, where he remained for the rest of his life and where, over the course of many years, he held a succession of offices, becoming the Duke's friend and chief adviser.[19][20]
In 1776, Goethe formed a close relationship to Charlotte von Stein, an older, married woman. The intimate bond with von Stein lasted for ten years, after which Goethe abruptly left for Italy without giving his companion any notice. She was emotionally distraught at the time, but they were eventually reconciled.[21]
Goethe, aside from official duties, was also a friend and confidant to the Duke, and participated fully in the activities of the court. For Goethe, his first ten years at Weimar could well be described as a garnering of a degree and range of experience which perhaps could be achieved in no other way. In 1779, Goethe took on the War Commission of the Grand Duchy of Saxe-Weimar, in addition to the Mines and Highways commissions. In 1782, when the chancellor of the Duchy's Exchequer left his office, Goethe agreed to act in his place for two and a half years; this post virtually made him prime minister and the principal representative of the Duchy.[3] Goethe was ennobled in 1782 (this being indicated by the "von" in his name).
As head of the Saxe-Weimar War Commission, Goethe participated in the recruitment of mercenaries into the Prussian and British military during the American Revolution. The author W. Daniel Wilson claims that Goethe engaged in negotiating the forced sale of vagabonds, criminals, and political dissidents as part of these activities.[22]
Italy

Goethe's journey to the Italian peninsula and Sicily from 1786 to 1788 was of great significance in his aesthetic and philosophical development. His father had made a similar journey during his own youth, and his example was a major motivating factor for Goethe to make the trip. More importantly, however, the work of Johann Joachim Winckelmann had provoked a general renewed interest in the classical art of ancient Greece and Rome. Thus Goethe's journey had something of the nature of a pilgrimage to it. During the course of his trip Goethe met and befriended the artists Angelica Kauffman and Johann Heinrich Wilhelm Tischbein, as well as encountering such notable characters as Lady Hamilton and Alessandro Cagliostro (see Affair of the Diamond Necklace).
He also journeyed to Sicily during this time, and wrote intriguingly that "To have seen Italy without having seen Sicily is to not have seen Italy at all, for Sicily is the clue to everything." While in Southern Italy and Sicily, Goethe encountered, for the first time genuine Greek (as opposed to Roman) architecture, and was quite startled by its relative simplicity. Winckelmann had not recognized the distinctness of the two styles.
Goethe's diaries of this period form the basis of the non-fiction Italian Journey. Italian Journey only covers the first year of Goethe's visit. The remaining year is largely undocumented, aside from the fact that he spent much of it in Venice. This "gap in the record" has been the source of much speculation over the years.
In the decades which immediately followed its publication in 1816, Italian Journey inspired countless German youths to follow Goethe's example. This is pictured, somewhat satirically, in George Eliot's Middlemarch.
Weimar

In late 1792, Goethe took part in the Battle of Valmy against revolutionary France, assisting Duke Karl August of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach during the failed invasion of France. Again during the Siege of Mainz he assisted Carl August as a military observer. His written account of these events can be found within his Complete Works.
In 1794, Friedrich Schiller wrote to Goethe offering friendship; they had previously had only a mutually wary relationship ever since first becoming acquainted in 1788. This collaborative friendship lasted until Schiller's death in 1805.

In 1806, Goethe was living in Weimar with his mistress Christiane Vulpius, the sister of Christian A. Vulpius, and their son Julius August Walter von Goethe. On 13 October, Napoleon's army invaded the town. The French "spoon guards", the least disciplined soldiers, occupied Goethe's house:
The 'spoon guards' had broken in, they had drunk wine, made a great uproar and called for the master of the house. Goethe's secretary Riemer reports: 'Although already undressed and wearing only his wide nightgown... he descended the stairs towards them and inquired what they wanted from him.... His dignified figure, commanding respect, and his spiritual mien seemed to impress even them.' But it was not to last long. Late at night they burst into his bedroom with drawn bayonets. Goethe was petrified, Christiane raised a lot of noise and even tangled with them, other people who had taken refuge in Goethe's house rushed in, and so the marauders eventually withdrew again. It was Christiane who commanded and organized the defense of the house on the Frauenplan. The barricading of the kitchen and the cellar against the wild pillaging soldiery was her work. Goethe noted in his diary: "Fires, rapine, a frightful night... Preservation of the house through steadfastness and luck." The luck was Goethe's, the steadfastness was displayed by Christiane.[23]
Days afterward, on 19 October 1806, Goethe legitimized their 18-year relationship by marrying Christiane in a quiet marriage service at the Jakobskirche in Weimar. They had already had several children together by this time, including their son, Julius August Walter von Goethe (1789–1830), whose wife, Ottilie von Pogwisch (1796–1872), cared for the elder Goethe until his death in 1832. August and Ottilie had three children: Walther, Freiherr von Goethe (1818–1885), Wolfgang, Freiherr von Goethe (1820–1883) and Alma von Goethe (1827–1844). Christiane von Goethe died in 1816. Johann reflected, "There is nothing more charming to see than a mother with her child in her arms, and there is nothing more venerable than a mother among a number of her children."[24]

Later life
After 1793, Goethe devoted his endeavours primarily to literature. By 1820, Goethe was on amiable terms with Kaspar Maria von Sternberg. In 1823, having recovered from a near fatal heart illness, the 74-year-old Goethe fell in love with the teenaged Ulrike von Levetzow whom he wanted to marry, but because of the opposition of her mother he never proposed. Their last meeting in Carlsbad on 5 September 1823 inspired him to the famous Marienbad Elegy which he considered one of his finest works.[25] During that time he also developed a deep emotional bond with the Polish pianist Maria Agata Szymanowska.[26]
In 1821 Goethe's friend Carl Friedrich Zelter introduced him to the 12-year-old Felix Mendelssohn. Goethe, now in his seventies, was greatly impressed by the child, leading to perhaps the earliest confirmed comparison with Mozart in the following conversation between Goethe and Zelter:
"Musical prodigies ... are probably no longer so rare; but what this little man can do in extemporizing and playing at sight borders the miraculous, and I could not have believed it possible at so early an age." "And yet you heard Mozart in his seventh year at Frankfurt?" said Zelter. "Yes", answered Goethe, "... but what your pupil already accomplishes, bears the same relation to the Mozart of that time that the cultivated talk of a grown-up person bears to the prattle of a child."[27]
Mendelssohn was invited to meet Goethe on several later occasions,[28] and set a number of Goethe's poems to music. His other compositions inspired by Goethe include the overture Calm Sea and Prosperous Voyage (Op. 27, 1828), and the cantata Die erste Walpurgisnacht (The First Walpurgis Night, Op. 60, 1832).[29]
Death

In 1832, Goethe died in Weimar of apparent heart failure. His last words, according to his doctor Carl Vogel, were, Mehr Licht! (More light!), but this is disputed as Vogel was not in the room at the moment Goethe died.[30] He is buried in the Ducal Vault at Weimar's Historical Cemetery.
Eckermann closes his famous work, Conversations with Goethe, with this passage:
The morning after Goethe's death, a deep desire seized me to look once again upon his earthly garment. His faithful servant, Frederick, opened for me the chamber in which he was laid out. Stretched upon his back, he reposed as if asleep; profound peace and security reigned in the features of his sublimely noble countenance. The mighty brow seemed yet to harbour thoughts. I wished for a lock of his hair; but reverence prevented me from cutting it off. The body lay naked, only wrapped in a white sheet; large pieces of ice had been placed near it, to keep it fresh as long as possible. Frederick drew aside the sheet, and I was astonished at the divine magnificence of the limbs. The breast was powerful, broad, and arched; the arms and thighs were elegant, and of the most perfect shape; nowhere, on the whole body, was there a trace of either fat or of leanness and decay. A perfect man lay in great beauty before me; and the rapture the sight caused me made me forget for a moment that the immortal spirit had left such an abode. I laid my hand on his heart – there was a deep silence – and I turned away to give free vent to my suppressed tears.
The first production of Richard Wagner's opera Lohengrin took place in Weimar in 1850. The conductor was Franz Liszt, who chose the date 28 August in honour of Goethe, who was born on 28 August 1749.[31]
Literary work

Overview
The most important of Goethe's works produced before he went to Weimar were Götz von Berlichingen (1773), a tragedy that was the first work to bring him recognition, and the novel The Sorrows of Young Werther (German: Die Leiden des jungen Werthers) (1774), which gained him enormous fame as a writer in the Sturm und Drang period which marked the early phase of Romanticism. Indeed, Werther is often considered to be the "spark" which ignited the movement, and can arguably be called the world's first "best-seller." During the years at Weimar before he met Schiller he began Wilhelm Meister's Apprenticeship, wrote the dramas Iphigenie auf Tauris (Iphigenia in Tauris), Egmont, Torquato Tasso, and the fable Reineke Fuchs.[citation needed]
To the period of his friendship with Schiller belong the conception of Wilhelm Meister's Journeyman Years (the continuation of Wilhelm Meister's Apprenticeship), the idyll of Hermann and Dorothea, the Roman Elegies and the verse drama The Natural Daughter. In the last period, between Schiller's death, in 1805, and his own, appeared Faust Part One, Elective Affinities, the West-Eastern Diwan (a collection of poems in the Persian style, influenced by the work of Hafez), his autobiographical Aus meinem Leben: Dichtung und Wahrheit (From My Life: Poetry and Truth) which covers his early life and ends with his departure for Weimar, his Italian Journey, and a series of treatises on art. His writings were immediately influential in literary and artistic circles.[32][citation needed]
Goethe was fascinated by Kalidasa's Abhijñānaśākuntalam, which was one of the first works of Sanskrit literature that became known in Europe, after being translated from English to German.[33]

Details of selected works
The short epistolary novel, Die Leiden des jungen Werthers, or The Sorrows of Young Werther, published in 1774, recounts an unhappy romantic infatuation that ends in suicide. Goethe admitted that he "shot his hero to save himself": a reference to Goethe's own near-suicidal obsession with a young woman during this period, an obsession he quelled through the writing process. The novel remains in print in dozens of languages and its influence is undeniable; its central hero, an obsessive figure driven to despair and destruction by his unrequited love for the young Lotte, has become a pervasive literary archetype. The fact that Werther ends with the protagonist's suicide and funeral—a funeral which "no clergyman attended"—made the book deeply controversial upon its (anonymous) publication, for on the face of it, it appeared to condone and glorify suicide. Suicide is considered sinful by Christian doctrine: suicides were denied Christian burial with the bodies often mistreated and dishonoured in various ways; in corollary, the deceased's property and possessions were often confiscated by the Church.[34] However, Goethe explained his use of Werther in his autobiography. He said he "turned reality into poetry but his friends thought poetry should be turned into reality and the poem imitated." He was against this reading of poetry.[35] Epistolary novels were common during this time, letter-writing being a primary mode of communication. What set Goethe's book apart from other such novels was its expression of unbridled longing for a joy beyond possibility, its sense of defiant rebellion against authority, and of principal importance, its total subjectivity: qualities that trailblazed the Romantic movement.
The next work, his epic closet drama Faust, was completed in stages. The first part was published in 1808 and created a sensation. Goethe finished Faust Part Two in the year of his death, and the work was published posthumously. Goethe's original draft of a Faust play, which probably dates from 1773–74, and is now known as the Urfaust, was also published after his death.[36]
The first operatic version of Goethe's Faust, by Louis Spohr, appeared in 1814. The work subsequently inspired operas and oratorios by Schumann, Berlioz, Gounod, Boito, Busoni, and Schnittke as well as symphonic works by Liszt, Wagner, and Mahler. Faust became the ur-myth of many figures in the 19th century. Later, a facet of its plot, i.e., of selling one's soul to the devil for power over the physical world, took on increasing literary importance and became a view of the victory of technology and of industrialism, along with its dubious human expenses. In 1919, the world premiere complete production of Faust was staged at the Goetheanum.

Goethe's poetic work served as a model for an entire movement in German poetry termed Innerlichkeit ("introversion") and represented by, for example, Heine. Goethe's words inspired a number of compositions by, among others, Mozart, Beethoven (who idolised Goethe),[37] Schubert, Berlioz and Wolf. Perhaps the single most influential piece is "Mignon's Song" which opens with one of the most famous lines in German poetry, an allusion to Italy: "Kennst du das Land, wo die Zitronen blühn?" ("Do you know the land where the lemon trees bloom?").
He is also widely quoted. Epigrams such as "Against criticism a man can neither protest nor defend himself; he must act in spite of it, and then it will gradually yield to him", "Divide and rule, a sound motto; unite and lead, a better one", and "Enjoy when you can, and endure when you must", are still in usage or are often paraphrased. Lines from Faust, such as "Das also war des Pudels Kern", "Das ist der Weisheit letzter Schluss", or "Grau ist alle Theorie" have entered everyday German usage.
Some well-known quotations are often incorrectly attributed to Goethe. These include Hippocrates' "Art is long, life is short", which is echoed in Goethe's Faust and Wilhelm Meister's Apprenticeship.
Scientific work
As to what I have done as a poet,... I take no pride in it... But that in my century I am the only person who knows the truth in the difficult science of colours—of that, I say, I am not a little proud, and here I have a consciousness of a superiority to many.
— Johann Eckermann, Conversations with Goethe
Although his literary work has attracted the greatest amount of interest, Goethe was also keenly involved in studies of natural science.[38] He wrote several works on morphology, and colour theory. Goethe also had the largest private collection of minerals in all of Europe. By the time of his death, in order to gain a comprehensive view in geology, he had collected 17,800 rock samples.
His focus on morphology and what was later called homology influenced 19th century naturalists, although his ideas of transformation were about the continuous metamorphosis of living things and did not relate to contemporary ideas of "transformisme" or transmutation of species. Homology, or as Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire called it "analogie", was used by Charles Darwin as strong evidence of common descent and of laws of variation.[39] Goethe's studies (notably with an elephant's skull lent to him by Samuel Thomas von Soemmerring) led him to independently discover the human intermaxillary bone, also known as "Goethe's bone", in 1784, which Broussonet (1779) and Vicq d'Azyr (1780) had (using different methods) identified several years earlier.[40] While not the only one in his time to question the prevailing view that this bone did not exist in humans, Goethe, who believed ancient anatomists had known about this bone, was the first to prove its existence in all mammals. The elephant's skull that led Goethe to this discovery, and was subsequently named the Goethe Elephant, still exists and is displayed in the Ottoneum in Kassel, Germany.
During his Italian journey, Goethe formulated a theory of plant metamorphosis in which the archetypal form of the plant is to be found in the leaf – he writes, "from top to bottom a plant is all leaf, united so inseparably with the future bud that one cannot be imagined without the other".[41] In 1790, he published his Metamorphosis of Plants.[42][43] As one of the many precursors in the history of evolutionary thought, Goethe wrote in Story of My Botanical Studies (1831):
The ever-changing display of plant forms, which I have followed for so many years, awakens increasingly within me the notion: The plant forms which surround us were not all created at some given point in time and then locked into the given form, they have been given... a felicitous mobility and plasticity that allows them to grow and adapt themselves to many different conditions in many different places.[44]
Goethe's botanical theories were partly based on his gardening in Weimar.[45]
Goethe also popularized the Goethe barometer using a principle established by Torricelli. According to Hegel, "Goethe has occupied himself a good deal with meteorology; barometer readings interested him particularly... What he says is important: the main thing is that he gives a comparative table of barometric readings during the whole month of December 1822, at Weimar, Jena, London, Boston, Vienna, Töpel... He claims to deduce from it that the barometric level varies in the same proportion not only in each zone but that it has the same variation, too, at different altitudes above sea-level".[46]
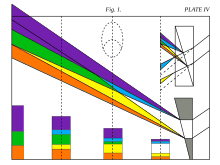
In 1810, Goethe published his Theory of Colours, which he considered his most important work. In it, he contentiously characterized colour as arising from the dynamic interplay of light and darkness through the mediation of a turbid medium.[47] In 1816, Schopenhauer went on to develop his own theory in On Vision and Colours based on the observations supplied in Goethe's book. After being translated into English by Charles Eastlake in 1840, his theory became widely adopted by the art world, most notably J. M. W. Turner.[48] Goethe's work also inspired the philosopher Ludwig Wittgenstein, to write his Remarks on Colour. Goethe was vehemently opposed to Newton's analytic treatment of colour, engaging instead in compiling a comprehensive rational description of a wide variety of colour phenomena. Although the accuracy of Goethe's observations does not admit a great deal of criticism, his aesthetic approach did not lend itself to the demands of analytic and mathematical analysis used ubiquitously in modern Science. Goethe was, however, the first to systematically study the physiological effects of colour, and his observations on the effect of opposed colours led him to a symmetric arrangement of his colour wheel, 'for the colours diametrically opposed to each other... are those which reciprocally evoke each other in the eye. (Goethe, Theory of Colours, 1810).[49] In this, he anticipated Ewald Hering's opponent colour theory (1872).[50]
Goethe outlines his method in the essay The experiment as mediator between subject and object (1772).[51] In the Kurschner edition of Goethe's works, the science editor, Rudolf Steiner, presents Goethe's approach to science as phenomenological. Steiner elaborated on that in the books The Theory of Knowledge Implicit in Goethe's World-Conception[52] and Goethe's World View,[53] in which he characterizes intuition as the instrument by which one grasps Goethe's biological archetype—The Typus.
Novalis, himself a geologist and mining engineer, expressed the opinion that Goethe was the first physicist of his time and 'epoch-making in the history of physics', writing that Goethe's studies of light, of the metamorphosis of plants and of insects were indications and proofs 'that the perfect educational lecture belongs in the artist's sphere of work'; and that Goethe would be surpassed 'but only in the way in which the ancients can be surpassed, in inner content and force, in variety and depth—as an artist actually not, or only very little, for his rightness and intensity are perhaps already more exemplary than it would seem'. [54]
Eroticism
Many of Goethe's works, especially Faust, the Roman Elegies, and the Venetian Epigrams, depict erotic passions and acts. For instance, in Faust, the first use of Faust's power after signing a contract with the devil is to seduce a teenage girl. Some of the Venetian Epigrams were held back from publication due to their sexual content. Goethe clearly saw human sexuality as a topic worthy of poetic and artistic depiction, an idea that was uncommon in a time when the private nature of sexuality was rigorously normative.[55]
In a conversation on April 7, 1830 Goethe stated that pederasty is an "aberration" that easily leads to "animal, roughly material" behavior. He continued, "Pederasty is as old as humanity itself, and one can therefore say, that it resides in nature, even if it proceeds against nature....What culture has won from nature will not be surrendered or given up at any price."[56] On another occasion he wrote: "I like boys a lot, but the girls are even nicer. If I tire of her as a girl, she'll play the boy for me as well".[57]

Religion and politics
Goethe was a freethinker who believed that one could be inwardly Christian without following any of the Christian churches, many of whose central teachings he firmly opposed, sharply distinguishing between Christ and the tenets of Christian theology, and criticizing its history as a "hodgepodge of fallacy and violence".[58][59] His own descriptions of his relationship to the Christian faith and even to the Church varied widely and have been interpreted even more widely, so that while Goethe's secretary Eckermann portrayed him as enthusiastic about Christianity, Jesus, Martin Luther, and the Protestant Reformation, even calling Christianity the "ultimate religion,"[60] on one occasion Goethe described himself as "not anti-Christian, nor un-Christian, but most decidedly non-Christian,"[61] and in his Venetian Epigram 66, Goethe listed the symbol of the cross among the four things that he most disliked.[62] According to Nietzsche, Goethe had "a kind of almost joyous and trusting fatalism" that has "faith that only in the totality everything redeems itself and appears good and justified."[63]
Born into a Lutheran family, Goethe's early faith was shaken by news of such events as the 1755 Lisbon earthquake and the Seven Years' War. Goethe's preoccupation with and reverence for Spinoza are well known and documented in the history of Western thought.[64][65] He was one of the central figures in a great flowering of a highly influential Neo-Spinozism[66][67][68] which occurred in German philosophy and literature of the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries.[69][70]—that was the first remarkable Spinoza revival in history.[71] Like Lessing and Herder, in many respects, Goethe was a devoted Spinozist.[72][73][74][75][76] He was also a pantheist, like some other prominent Spinozists such as Flaubert and Albert Einstein. His later spiritual perspective incorporated elements of pantheism (heavily influenced by Spinoza's thought),[64][65][77] humanism, and various elements of Western esotericism, as seen most vividly in part 2 of Faust. Like Heinrich Heine, Nietzsche mentions in his writings frequently Goethe and Spinoza as a pair.[78] A year before his death, in a letter to Sulpiz Boisserée, Goethe wrote that he had the feeling that all his life he had been aspiring to qualify as one of the Hypsistarians, an ancient Jewish-pagan sect of the Black Sea region who, in his understanding, sought to reverence, as being close to the Godhead, what came to their knowledge of the best and most perfect.[79] Goethe's unorthodox religious beliefs led him to be called "the great heathen" and provoked distrust among the authorities of his time, who opposed the creation of a Goethe monument on account of his offensive religious creed.[80] August Wilhelm Schlegel considered Goethe "a heathen who converted to Islam."[80]
Politically, Goethe described himself as a "moderate liberal."[81][82][83] He was critical of the radicalism of Bentham and expressed sympathy for the prudent liberalism of François Guizot.[84] At the time of the French Revolution, he thought the enthusiasm of the students and professors to be a perversion of their energy and remained skeptical of the ability of the masses to govern.[85] Goethe sympathized with the American Revolution and later wrote a poem in which he declared "America, you're better off than our continent, the old."[86][87] He did not join in the anti-Napoleonic mood of 1812, and he distrusted the strident nationalism which started to be expressed.[88] The medievalism of the Heidelberg Romantics was also repellent to Goethe's eighteenth-century ideal of a supra-national culture.[89]
Goethe was a Freemason, joining the lodge Amalia in Weimar in 1780, and frequently alluded to Masonic themes of universal brotherhood in his work,[90] he was also attracted to the Bavarian Illuminati a secret society founded on 1 May 1776.[91][90] Although often requested to write poems arousing nationalist passions, Goethe would always decline. In old age, he explained why this was so to Eckermann:
How could I write songs of hatred when I felt no hate? And, between ourselves, I never hated the French, although I thanked God when we were rid of them. How could I, to whom the only significant things are civilization [Kultur] and barbarism, hate a nation which is among the most cultivated in the world, and to which I owe a great part of my own culture? In any case this business of hatred between nations is a curious thing. You will always find it more powerful and barbarous on the lowest levels of civilization. But there exists a level at which it wholly disappears, and where one stands, so to speak, above the nations, and feels the weal or woe of a neighboring people as though it were one's own.[92]
Influence

Goethe had a great effect on the nineteenth century. In many respects, he was the originator of many ideas which later became widespread. He produced volumes of poetry, essays, criticism, a theory of colours and early work on evolution and linguistics. He was fascinated by mineralogy, and the mineral goethite (iron oxide) is named after him.[93] His non-fiction writings, most of which are philosophic and aphoristic in nature, spurred the development of many thinkers, including Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, Schopenhauer, Søren Kierkegaard, Friedrich Nietzsche, Ernst Cassirer, and Carl Jung.[citation needed] Along with Schiller, he was one of the leading figures of Weimar Classicism. Schopenhauer cited Goethe's novel Wilhelm Meister's Apprenticeship as one of the four greatest novels ever written, along with Tristram Shandy, La Nouvelle Héloïse and Don Quixote.[5] Nietzsche wrote, "Four pairs it was that did not deny themselves to my sacrifice: Epicurus and Montaigne, Goethe and Spinoza, Plato and Rousseau, Pascal and Schopenhauer. With these I must come to terms when I have long wandered alone; they may call me right and wrong; to them will I listen when in the process they call each other right and wrong."[94]
Goethe embodied many of the contending strands in art over the next century: his work could be lushly emotional, and rigorously formal, brief and epigrammatic, and epic. He would argue that Classicism was the means of controlling art, and that Romanticism was a sickness, even as he penned poetry rich in memorable images, and rewrote the formal rules of German poetry. His poetry was set to music by almost every major Austrian and German composer from Mozart to Mahler, and his influence would spread to French drama and opera as well. Beethoven declared that a "Faust" Symphony would be the greatest thing for art. Liszt and Mahler both created symphonies in whole or in large part inspired by this seminal work, which would give the 19th century one of its most paradigmatic figures: Doctor Faustus.


The Faust tragedy/drama, often called Das Drama der Deutschen (the drama of the Germans), written in two parts published decades apart, would stand as his most characteristic and famous artistic creation. Followers of the twentieth century esotericist Rudolf Steiner built a theatre named the Goetheanum after him—where festival performances of Faust are still performed.
Goethe was also a cultural force. During his first meeting with Napoleon in 1808, the latter famously remarked: "Vous étes un homme (You are a man)!"[95] The two discussed politics, the writings of Voltaire, and Goethe's Sorrows of Young Werther, which Napoleon had read seven times and ranked among his favorites.[96][97] Goethe came away from the meeting deeply impressed with Napoleon's enlightened intellect and his efforts to build an alternative to the corrupt old regime.[96][98] Goethe always spoke of Napoleon with the greatest respect, confessing that "nothing higher and more pleasing could have happened to me in all my life" than to have met Napoleon in person.[99]
Germaine de Staël, in De l'Allemagne (1813), presented German Classicism and Romanticism as a potential source of spiritual authority for Europe, and identified Goethe as a living classic.[100] She praised Goethe as possessing "the chief characteristics of the German genius" and uniting "all that distinguishes the German mind."[100] Staël's portrayal helped elevate Goethe over his more famous German contemporaries and transformed him into a European cultural hero.[100] Goethe met with her and her partner Benjamin Constant, with whom he shared a mutual admiration.[101]
In Victorian England, Goethe exerted a profound influence on George Eliot, whose partner George Henry Lewes wrote a Life of Goethe.[102] Eliot presented Goethe as "eminently the man who helps us to rise to a lofty point of observation" and praised his "large tolerance", which "quietly follows the stream of fact and of life" without passing moral judgments.[102] Matthew Arnold found in Goethe the "Physician of the Iron Age" and "the clearest, the largest, the most helpful thinker of modern times" with a "large, liberal view of life."[103]

It was to a considerable degree due to Goethe's reputation that the city of Weimar was chosen in 1919 as the venue for the national assembly, convened to draft a new constitution for what would become known as Germany's Weimar Republic. Goethe became a key reference for Thomas Mann in his speeches and essays defending the republic.[104] He emphasized Goethe's "cultural and self-developing individualism", humanism, and cosmopolitanism.[104]
The Federal Republic of Germany's cultural institution, the Goethe-Institut is named after him, and promotes the study of German abroad and fosters knowledge about Germany by providing information on its culture, society and politics.
The literary estate of Goethe in the Goethe and Schiller Archives was inscribed on UNESCO's Memory of the World Register in 2001 in recognition of its historical significance.[105]
Goethe's influence was dramatic because he understood that there was a transition in European sensibilities, an increasing focus on sense, the indescribable, and the emotional. This is not to say that he was emotionalistic or excessive; on the contrary, he lauded personal restraint and felt that excess was a disease: "There is nothing worse than imagination without taste". Goethe praised Francis Bacon for his advocacy of science based on experiment and his forceful revolution in thought as one of the greatest strides forward in modern science.[106] However, he was critical of Bacon's inductive method and approach based on pure classification.[107] He said in Scientific Studies:
We conceive of the individual animal as a small world, existing for its own sake, by its own means. Every creature is its own reason to be. All its parts have a direct effect on one another, a relationship to one another, thereby constantly renewing the circle of life; thus we are justified in considering every animal physiologically perfect. Viewed from within, no part of the animal is a useless or arbitrary product of the formative impulse (as so often thought). Externally, some parts may seem useless because the inner coherence of the animal nature has given them this form without regard to outer circumstance. Thus...[not] the question, What are they for? but rather, Where do they come from?[108]

Goethe's scientific and aesthetic ideas have much in common with Denis Diderot, whose work he translated and studied.[109][110] Both Diderot and Goethe exhibited a repugnance towards the mathematical interpretation of nature; both perceived the universe as dynamic and in constant flux; both saw "art and science as compatible disciplines linked by common imaginative processes"; and both grasped "the unconscious impulses underlying mental creation in all forms."[109][110] Goethe's Naturanschauer is in many ways a sequel to Diderot's interprète de la nature.[110]
His views make him, along with Adam Smith, Thomas Jefferson, and Ludwig van Beethoven, a figure in two worlds: on the one hand, devoted to the sense of taste, order, and finely crafted detail, which is the hallmark of the artistic sense of the Age of Reason and the neo-classical period of architecture; on the other, seeking a personal, intuitive, and personalized form of expression and society, firmly supporting the idea of self-regulating and organic systems. George Henry Lewes celebrated Goethe's revolutionary understanding of the organism.[109]
Thinkers such as Ralph Waldo Emerson would take up many similar ideas in the 1800s. Goethe's ideas on evolution would frame the question that Darwin and Wallace would approach within the scientific paradigm. The Serbian inventor and electrical engineer Nikola Tesla was heavily influenced by Goethe's Faust, his favorite poem, and had actually memorized the entire text. It was while reciting a certain verse that he was struck with the epiphany that would lead to the idea of the rotating magnetic field and ultimately, alternating current.[111]
Works
See Johann Wolfgang von Goethe bibliography
Books about, or featuring, Goethe
include:
- The Life of Goethe by George Henry Lewes
- Goethe: The History of a Man by Emil Ludwig
- Goethe by Georg Brandes. Authorized translation from the Danish (2nd ed. 1916) by Allen W. Porterfield, New York, Crown publishers, 1936. "Crown edition, 1936." Title Wolfgang Goethe
- Goethe: his life and times by Richard Friedenthal
- Lotte in Weimar: The Beloved Returns by Thomas Mann
- Conversations with Goethe by Johann Peter Eckermann
- Goethe's World: as seen in letters and memoirs ed. by Berthold Biermann
- Goethe: Four Studies by Albert Schweitzer
- Goethe Poet and Thinker by E.M. Wilkinson and L.A. Willoughby
- Goethe and his Publishers by Siegfried Unseld
- Goethe by T.J. Reed
- Goethe. A Psychoanalytic Study, by Kurt R. Eissler
- The Life of Goethe. A Critical Biography by John Williams
- Goethe: The Poet and the Age (2 Vols.), by Nicholas Boyle
- Goethe's Concept of the Daemonic: After the Ancients, by Angus Nicholls
- Goethe and Rousseau: Resonances of their Mind, by Carl Hammer, Jr.
- Doctor Faustus of the popular legend, Marlowe, the Puppet-Play, Goethe, and Lenau, treated historically and critically. – A parallel between Goethe and Schiller. – An historic outline of German Literature , by Louis Pagel
- Goethe and Schiller, Essays on German Literature, by Hjalmar Hjorth Boyesen
- Goethe-Wörterbuch (Goethe Dictionary, abbreviated GWb). Herausgegeben von der Berlin-Brandenburgischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, der Akademie der Wissenschaften in Göttingen und der Heidelberger Akademie der Wissenschaften. Stuttgart. Kohlhammer Verlag; ISBN 978-3-17-019121-1
See also
- Young Goethe in Love (2010)
- Dora Stock – her encounters with the 16-year-old Goethe.
- Goethe Basin
- Johann-Wolfgang-von-Goethe-Gymnasium
- W. H. Murray – author of misattributed quotation "Until one is committed ..."
- Nature (Tobler essay), essay often mis-attributed to Goethe
Awards named after him
References
Footnotes
- ^ In 1998, both of these sites, together with nine others, were designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site under the name Classical Weimar.[4]
- ^ The others Schopenhauer named were Tristram Shandy, La Nouvelle Héloïse, and Don Quixote.[5]
Citations
- ^ "Goethe". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Merriam-Webster.
- ^ a b Wells, John (2008). Longman Pronunciation Dictionary (3rd ed.). Pearson Longman. ISBN 978-1-4058-8118-0.
- ^ a b Nicholas Boyle, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe at the Encyclopædia Britannica
- ^ a b "Classical Weimar UNESCO Justification". Justification for UNESCO Heritage Cites. UNESCO. Retrieved 7 June 2012.
- ^ a b c Schopenhauer, Arthur (January 2004). The Art of Literature. Retrieved 22 March 2015.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ a b Herman Grimm: Goethe. Vorlesungen gehalten an der Königlichen Universität zu Berlin. Vol. 1. J.G. Cotta'sche Buchhandlung Nachfolger, Stuttgart / Berlin 1923, p. 36
- ^ Catharina was the daughter of Johann Wolfgang Textor, sheriff (Schultheiß) of Frankfurt, and Anna Margaretha Lindheimer.
- ^ von Goethe, Johann Wolfgang. The Autobiography of Goethe: truth and poetry, from my own life, Volume 1 (1897), translated by John Oxenford, pp. 114, 129
- ^ Valerian Tornius: Goethe – Leben, Wirken und Schaffen. Ludwig-Röhrscheid-Verlag, Bonn 1949, p. 26
- ^ Emil Ludwig: Goethe – Geschichte eines Menschen. Vol. 1. Ernst-Rowohlt-Verlag, Berlin 1926, pp. 17–18
- ^ Karl Goedeke: Goethes Leben. Cotta / Kröner, Stuttgart around 1883, pp. 16–17
- ^ "Originally speech of Goethe to the Shakespeare's Day by University Duisburg". Uni-duisburg-essen.de. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ Herman Grimm: Goethe. Vorlesungen gehalten an der Königlichen Universität zu Berlin. Vol. 1. J. G. Cotta'sche Buchhandlung Nachfolger, Stuttgart / Berlin 1923, p. 81
- ^ Karl Robert Mandelkow, Bodo Morawe: Goethes Briefe. 2. edition. Vol. 1: Briefe der Jahre 1764–1786. Christian Wegner, Hamburg 1968, p. 571
- ^ Valerian Tornius: Goethe – Leben, Wirken und Schaffen. Ludwig-Röhrscheid-Verlag, Bonn 1949, p. 60
- ^ a b Mandelkow, Karl Robert (1962). Goethes Briefe. Vol. 1: Briefe der Jahre 1764–1786. Christian Wegner Verlag. p. 589
- ^ Mandelkow, Karl Robert (1962). Goethes Briefe. Vol. 1: Briefe der Jahre 1764–1786. Christian Wegner Verlag. pp. 590–92
- ^ See Goethe and his Publishers
- ^ Hume Brown, Peter (1920). Life of Goethe. pp. 224–25.
- ^ "Goethe und Carl August – Freundschaft und Politik" by Gerhard Müller, in Th. Seemann (ed.): Anna Amalia, Carl August und das Ereignis Weimar. Jahrbuch der Klassik Stiftung Weimar 2007. Göttingen: Wallstein Verlag, pp. 132–64 (in German)
- ^ Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Wilson, W. Daniel (1999). Das Goethe-Tabu [The Goethe Taboo: Protest and Human Rights in Classical Weimar] (in German). Munich: Deutsche Taschenbuch Verlag (dtv). pp. 49–57, also the entire book. ISBN 978-3-423-30710-9.; "The Goethe Case by W. Daniel Wilson" – The New York Review of Books.
- ^ Safranski, Rüdiger (1990). Schopenhauer and the Wild Years of Philosophy. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-79275-3.
- ^ Chamberlain, Alexander (1896). The Child and Childhood in Folk Thought: (The Child in Primitive Culture), p. 385. MacMillan.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Goethe's third summer".
- ^ Briscoe, J. R. (Ed.). (2004). New historical anthology of music by women (Vol. 1). Indiana University Press. pp. 126–27.
- ^ Todd 2003, p. 89.
- ^ Mercer-Taylor 2000, pp. 41–42, 93.
- ^ Todd 2003, pp. 188–90, 269–70.
- ^ Carl Vogel: "Die letzte Krankheit Goethe's". In: Journal der practischen Heilkunde (1833).
- ^ Grove's Dictionary of Music and Musicians, 5th ed., 1954
- ^ See, generally Schiller, F. (1877). Correspondence between Schiller and Goethe, from 1794 to 1805 (Vol. 1). G. Bell.
- ^ Baumer, Rachel Van M.; Brandon, James R. (1993) [1981]. Sanskrit Drama in Performance. Motilal Banarsidass. p. 9. ISBN 978-81-208-0772-3.
- ^ "The Stigma of Suicide – A history". Pips Project. Archived from the original on 6 October 2007. See also: "Ophelia's Burial".
- ^ Goethe, Johann Wolfgang von; Goethe, Johann Wolfgang von; Goethe, Johann Wolfgang von; Oxenford, John; Morrison, Alexander James William (27 July 1848). "The auto-biography of Goethe. Truth and poetry: from my own life". London, H. G. Bohn – via Internet Archive.
- ^ Goethe's Plays, by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, translated into English with introductions by Charles E. Passage, Publisher Benn Limited, 1980, ISBN 0-510-00087-8, 978-0-510-00087-5
- ^ Wigmore, Richard (2 July 2012). "A meeting of genius: Beethoven and Goethe, July 1812". Gramophone. Haymarket. Retrieved 6 July 2012.
- ^ "Johann Wolfgang von Goethe". The Nature Institute. Retrieved 28 August 2008.
- ^ Darwin, C.R. (1859). On the origin of species by means of natural selection, or the preservation of favoured races in the struggle for life (1st ed.). John Murray.
- ^ K. Barteczko and M. Jacob (1999). "A re-evaluation of the premaxillary bone in humans". Anatomy and Embryology. 207 (6): 417–37. doi:10.1007/s00429-003-0366-x. PMID 14760532.
- ^ Goethe, J.W. Italian Journey. Robert R Heitner. Suhrkamp ed., vol. 6.
- ^ Versuch die Metamorphose der Pflanzen zu Erklären. Library of Congress. Retrieved 2 January 2018.
- ^ Magnus, Rudolf; Schmid, Gunther (2004). Metamorphosis of Plants. ISBN 978-1-4179-4984-7. Retrieved 28 August 2008.
- ^ Frank Teichmann (tr. Jon McAlice) "The Emergence of the Idea of Evolution in the Time of Goethe" first published in Interdisciplinary Aspects of Evolution, Urachhaus (1989)
- ^ Balzer, Georg (1966). Goethe als Gartenfreund. München: F. Bruckmann KG.
- ^ Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, Hegel's Philosophy of Nature: Encyclopaedia of the Philosophical Sciences (1830), part 2 translated by A.V. Miller, illustrated, reissue, reprint Oxford University Press, 2005 ISBN 0-19-927267-0, 978-0-19-927267-9, Google Books
- ^ Aristotle wrote that colour is a mixture of light and dark, since white light is always seen as somewhat darkened when it is seen as a colour. (Aristotle, On Sense and its Objects, III, 439b, 20 ff.: "White and black may be juxtaposed in such a way that by the minuteness of the division of its parts each is invisible while their product is visible, and thus colour may be produced.")
- ^ Bockemuhl, M. (1991). Turner. Taschen, Koln. ISBN 978-3-8228-6325-1.
- ^ Goethe, Johann (1810). Theory of Colours, paragraph No. 50.
- ^ "Goethe's Color Theory". Retrieved 28 August 2008.
- ^ "The Experiment as Mediator between Subject and Object". Archived from the original on 10 November 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2014.
- ^ "The Theory of Knowledge Implicit in Goethe's World Conception". 1979. Retrieved 28 August 2008.
- ^ "Goethe's World View". Retrieved 28 August 2008.
- ^ 'Goethe's Message of Beauty in Our Twentieth Century World', (Friedrich) Frederick Hiebel, RSCP California. ISBN 0-916786-37-4
- ^ Outing Goethe and His Age; edited by Alice A. Kuzniar.[page needed]
- ^ Goethe, Johann Wolfgang (1976). Gedenkausgabe der Werke, Briefe und Gespräche. Zürich : Artemis Verl. p. 686. Retrieved 27 April 2016.
- ^ Bullough, V.L. (1990). History in adult human sexual behavior with children and adolescents in Western societies (Pedophilia: Biosocial Dimensions ed.). Springer-Verlag New York Inc. p. 72. ISBN 978-1-4613-9684-0. Retrieved 27 April 2016.
- ^ The phrase Goethe uses is "Mischmasch von Irrtum und Gewalt", in his "Zahme Xenien" IX, Goethes Gedichte in Zeitlicher Folge, Insel Verlag 1982 ISBN 3-458-14013-1, p. 1121
- ^ Arnold Bergsträsser, "Goethe's View of Christ", Modern Philology, Vol. 46, No. 3 (Feb. 1949), pp. 172–202; M. Tetz, "Mischmasch von Irrtum und Gewalt. Zu Goethes Vers auf die Kirchengeschichte", Zeitschrift für Theologie und Kirche 88 (1991) pp. 339–63
- ^ Goethe, Johann Wolfgang von; Eckermann, Johann Peter; Soret, Frédéric Jacob (1850). Conversations of Goethe with Eckermann and Soret, Vol. II, pp. 423–24. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ Boyle 1992, 353[incomplete short citation]
- ^ Thompson, James (1895). Venetian Epigrams. Retrieved 17 July 2014. Venetian Epigrams, 66, ["Wenige sind mir jedoch wie Gift und Schlange zuwider; Viere: Rauch des Tabacks, Wanzen und Knoblauch und †."]. The cross symbol he drew has been variously understood as meaning Christianity, Christ, or death.
- ^ Friedrich Nietzsche, The Will to Power, § 95
- ^ a b Goethe, Johann Wolfgang von: Letters from Italy, 1786–1788. Translated from the German by W. H. Auden and Elizabeth Mayer (New York: Penguin Books, 1995). Goethe: "For many years I did not dare look into a Latin author or at anything which evoked an image of Italy. If this happened by chance, I suffered agonies. Herder often used to say mockingly that I had learned all my Latin from Spinoza, for that was the only Latin book he had ever seen me reading. He did not realize how carefully I had to guard myself against the classics, and that it was sheer anxiety which drove me to take refuge in the abstractions of Spinoza."
- ^ a b Johann Peter Eckermann: "Goethe found such a point of view early in Spinoza, and he gladly recognizes how much the views of this great thinker have been in keeping with the needs of his youth. He found himself in him, and so he could fix himself to him in the most beautiful way." [Original in German: "Einen solchen Standpunkt fand Goethe früh in Spinoza, und er erkennet mit Freuden, wie sehr die Ansichten dieses großen Denkers den Bedürfnissen seiner Jugend gemäß gewesen. Er fand in ihm sich selber, und so konnte er sich auch an ihm auf das schönste befestigen."] (Gespräche mit Goethe in den letzten Jahren seines Lebens, 1831)
- ^ Danzel, Theodor Wilhelm: Über Goethes Spinozismus. Ein Beitrag zur tieferen Würdigung des Dichters und Forschers. (Hamburg: Johann August Meißner, 1843)
- ^ Schneege, Gerhard: Zu Goethes Spinozismus. (Breslau: Druck von O. Gutsmann, 1910)
- ^ Lindner, Herbert: Das Problem des Spinozismus im Schaffen Goethes und Herders. (Weimar: Arion, 1960)
- ^ Warnecke, Friedrich: Goethe, Spinoza und Jacobi. (Weimar: Hermann Böhlaus Nachfolger, 1908)
- ^ Timm, Hermann: Gott und die Freiheit: Studien zur Religionsphilosophie der Goethezeit, Band 1: Die Spinozarenaissance. (Frankfurt am Main: Vittorio Klostermann, 1974)
- ^ Gálik, Marián (1975), "Two Modern Chinese Philosophers on Spinoza (Some Remarks on Sino-German Spinoza's 'Festschrift')". Oriens Extremus 22(1): 29–43: "The Germans, however, were the first to manifest serious interest in him. Their first great philosopher Leibniz went to seek his advice and his counsel; they were the only ones to invite him to lecture at their university. Even though Leibniz concealed him from the world, the Germans revealed him to the world. The generation of their greatest philosophers and poets from the second half of the 18th and the first half of the 19th centuries grew up under his influence. Goethe read him together with Charlotte von Stein, and even read him together with her in Latin. To Hegel, Spinoza was "der Mittelpunkt der modernen Philosophie"."
- ^ Johann von Goethe: "...Happily, I had already prepared if not fully cultivated myself on this side, having in some degree appropriated the thoughts and mind of an extraordinary man, and though my study of him had been incomplete and hasty, I was yet already conscious of important influences derived from this source. This mind, which had worked upon me thus decisively, and which was destined to affect so deeply my whole mode of thinking, was Spinoza. After looking through the world in vain, to find a means of development for my strange nature, I at last fell upon the Ethics of this philosopher. Of what I read out of the work, and of what I read into it, I can give no account. Enough that I found in it a sedative for my passions, and that a free, wide view over the sensible and moral world, seemed to open before me. [...] The all-composing calmness of Spinoza was in striking contrast with my all-disturbing activity; his mathematical method was the direct opposite of my poetic humour and my way of writing, and that very precision which was thought ill-adapted to moral subjects, made me his enthusiastic disciple, his most decided worshipper." (The Autobiography of Goethe: Truth and Poetry: From My Own Life, 1848) [Translated from the German by John Oxenford; London: George Bell and Sons, 1897]
- ^ Melamed, S. M.: Spinoza and Buddha: Visions of a Dead God. (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1933). S. M. Melamed (1933): "Not only Goethe's poetry but his science is Spinozistically motivated. Convinced of the oneness of nature, he approached it with a certainty to discover in it oneness, and his discovery of the os intermaxtllare in man, which influenced the development of comparative anatomy, is one of the by-products of his Spinozistic sentiments. In his theory of the metamorphosis of the plants, which he expounded scientifically and poetically, he also expressed a good deal of Spinozism. Spinoza enabled him to read the various pages of nature as one book. Goethe respected Kant and may be described as a Kant scholar, but he was a Spinoza adherent. His world-picture is Spinozistic and not Kantian."
- ^ Bollacher, Martin: Der junge Goethe und Spinoza. Studien zur Geschichte des Spinozismus in der Epoche des Sturm und Drang. (Tübingen: Niemeyer, 1968)
- ^ Bell, David: Spinoza in Germany from 1670 to the Age of Goethe. (London: University of London, Institute of Germanic Studies, 1984)
- ^ Guidorizzi, Ernesto: L'orizzonte. Da Spinoza a Goethe. La poesia dell'infinito. (Napoli: Edizioni Scientifiche Italiane, 1991)
- ^ Jungmann, Albert: Goethes Naturphilosophie zwischen Spinoza und Nietzsche. Studien zur Entwicklung von Goethes Naturphilosophie bis zur Aufnahme von Kants «Kritik der Urteilskraft». (Frankfurt am Main: Peter Lang, 1989)
- ^ Yovel, Yirmiyahu, 'Nietzsche and Spinoza: Enemy-Brothers,'. In: Spinoza and Other Heretics, Vol. 2: The Adventures of Immanence. (Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1989). Yirmiyahu Yovel: "Speaking of his 'ancestors', Nietzsche at various times gives several lists, but he always mentions Spinoza and Goethe—and always as a pair. This is no accident, for Nietzsche sees Goethe as incorporating Spinoza and as anticipating his own “Dionysian” ideal."
- ^ Lletter to Boisserée dated 22 March 1831 quoted in Peter Boerner, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe 1832/1982: A Biographical Essay. Bonn: Inter Nationes, 1981 p. 82
- ^ a b Krimmer, Elisabeth; Simpson, Patricia Anne (2013). Religion, Reason, and Culture in the Age of Goethe. Boydell & Brewer. p. 99.
- ^ Eckermann, Johann Peter (1901). Conversations with Goethe. M.W. Dunne. p. 320.
'Dumont,' returned Goethe, 'is a moderate liberal, just as all rational people are and ought to be, and as I myself am.'
- ^ Selth, Jefferson P. (1997). Firm Heart and Capacious Mind: The Life and Friends of Etienne Dumont. University Press of America. pp. 132–33.
- ^ Mommsen, Katharina (2014). Goethe and the Poets of Arabia. Boydell & Brewer. p. 70.
- ^ Peter Eckermann, Johann (1901). Conversations with Goethe. M.W. Dunne. pp. 317–319.
- ^ McCabe, Joseph. 'Goethe: The Man and His Character'. p. 343
- ^ Unseld, Siegfried (1996). Goethe and His Publishers. University of Chicago Press. pp. 36–37.
- ^ Gemünden, Gerd (1998). Framed Visions: Popular Culture, Americanization, and the Contemporary German and Austrian Imagination. University of Michigan Press. pp. 18–19.
- ^ Unseld, Siegfried (1996). Goethe and His Publishers. University of Chicago Press. p. 212.
- ^ Richards, David B. (1979). Goethe's Search for the Muse: Translation and Creativity. John Benjamins Publishing. p. 83.
- ^ a b Beachy, Robert (2000). "Recasting Cosmopolitanism: German Freemasonry and Regional Identity in the Early Nineteenth Century". Eighteenth-Century Studies. 33 (2): 266–74. doi:10.1353/ecs.2000.0002. JSTOR 30053687.
- ^ Schüttler, Hermann (1991). Die Mitglieder des Illuminatenordens, 1776–1787/93. Munich: Ars Una. pp. 48–49, 62–63, 71, 82. ISBN 978-3-89391-018-2.
- ^ Will Durant (1967). The Story of Civilization Volume 10: Rousseau and Revolution. Simon&Schuster. p. 607.
- ^ Webmineral.com. Retrieved 21 August 2009,
- ^ Nietzsche, Friedrich: The Portable Nietzsche. (New York: The Viking Press, 1954)
- ^ Friedenthal, Richard (2010). Goethe: His Life & Times. Transaction Publishers. p. 389.
- ^ a b Broers, Michael (2014). Europe Under Napoleon. I.B. Tauris. p. 4.
- ^ Swales, Martin (1987). Goethe: The Sorrows of Young Werther. CUP Archive. p. 100.
- ^ Merseburger, Peter (2013). Mythos Weimar: Zwischen Geist und Macht. Pantheon. pp. 132–33.
- ^ Ferber, Michael (2008). A Companion to European Romanticism. John Wiley & Sons. p. 450.
- ^ a b c Gillespie, Gerald Ernest Paul; Engel, Manfred (2008). Romantic Prose Fiction. John Benjamins Publishing. p. 44.
- ^ Wood, Dennis (2002). Benjamin Constant: A Biography. Routledge. p. 185.
- ^ a b Röder-Bolton, Gerlinde (1998). George Eliot and Goethe: An Elective Affinity. Rodopi. pp. 3–8.
- ^ Connell, W.F. (2002). The Educational Thought and Influence of Matthew Arnold. Routledge. p. 34.
- ^ a b Mundt, Hannelore (2004). Understanding Thomas Mann. Univ of South Carolina Press. pp. 110–11.
- ^ "The literary estate of Goethe in the Goethe and Schiller Archives". UNESCO Memory of the World Programme. Retrieved 29 September 2017.
- ^ Richter, Simon J. (2007). Goethe Yearbook 14. Harvard University Press. pp. 113–14.
- ^ Amrine, F.R.; Zucker, Francis J. (2012). Goethe and the Sciences: A Reappraisal. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 232.
- ^ Scientific Studies, Suhrkamp ed., vol. 12, p. 121; trans. Douglas Miller
- ^ a b c Roach, Joseph R. (1993). The Player's Passion: Studies in the Science of Acting. University of Michigan Press. pp. 165–66.
- ^ a b c Fellows, Otis Edward (1981). Diderot Studies. Librairie Droz. pp. 392–94.
- ^ Seifer, Marc J. (1998) "Wizard: The Life and Times of Nikola Tesla: Biography of a Genius", Citadel Press, pp. 22, 308
Sources
- Mercer-Taylor, Peter (2000). The Life of Mendelssohn. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-63972-9.
- Todd, R. Larry (2003). Mendelssohn – A Life in Music. Oxford, England; New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-511043-2.
External links
- Goethe on In Our Time at the BBC
- "Goethe and the Science of the Enlightenment" In Our Time, BBC Radio 4 discussion with Nicholas Boyle and Simon Schaffer (February 10, 2000).
- Johann Wolfgang von Goethe at Find a Grave
- Works by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe at Project Gutenberg
- Works by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe at Faded Page (Canada)
- Works by or about Johann Wolfgang von Goethe at the Internet Archive
- Works by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)

- "Works by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe". Zeno.org (in German).
- At the Linda Hall Library, Goethe's:
- Works by and about Johann Wolfgang von Goethe in University Library JCS Frankfurt am Main: Digital Collections Judaica
- Free scores of Johann Wolfgang von Goethe's texts in the Choral Public Domain Library (ChoralWiki)
- Goethe in English at Poems Found in Translation
- Poems of Goethe set to music, lieder.net
- Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
- 1749 births
- 1832 deaths
- 18th-century German dramatists and playwrights
- 18th-century German novelists
- 18th-century German philosophers
- 19th-century German dramatists and playwrights
- 19th-century German novelists
- 19th-century German philosophers
- Color scientists
- Enlightenment philosophers
- German autobiographers
- German Freemasons
- German-language poets
- German poets
- German travel writers
- German untitled nobility
- Leipzig University alumni
- Members of the Bavarian Academy of Sciences
- Members of the Zentrale Dombauverein zu Köln von 1842
- Natural philosophers
- Pantheists
- Writers from Frankfurt
- People from Weimar
- Romantic poets
- Sturm und Drang
- University of Strasbourg alumni
- Spinozists
- Neo-Spinozism
