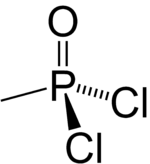
Methylphosphonyl dichloride
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methylphosphonic dichloride | |
| Other names
Methanephosphonic dichloride
Methanephosphonic acid dichloride Methylphosphonyl dichloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.578 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH3Cl2OP | |
| Molar mass | 132.91 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.468 g/mL at 20 °C |
| Melting point | 28 to 34 °C (82 to 93 °F; 301 to 307 K) |
| Boiling point | 163 °C (325 °F; 436 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Very Toxic |
| Flash point | >110 °C |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
26 ppm/4h by inhalation (rat) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Methyl phosphonic dichloride is an organophosphorus compound. It has a number of potential uses but is most notable as being a precursor to several chemical weapons agents. It is a white crystalline solid, with a low melting point. It hydrolyzes readily and must be handled with care as it is exceedingly toxic.[citation needed]
Synthesis and reactions
Methyl phosphonic dichloride is produced by oxidation of methyldichlorophosphine, e.g. with sulfuryl chloride:[1]
- MePCl2 + SO2Cl2 → MeP(O)Cl2 + SOCl2
It can also be produced from a range of methyl-phosphonates (e.g. dimethyl methylphosphonate) via chlorination with thionyl chloride. Various amines can be used to catalyse this process.[2] It reacts with hydrogen fluoride or sodium fluoride to produce methylphosphonyl difluoride, which is used in the production of sarin and soman nerve agents.
References
- ^ Svara, J.; Weferling, N.; Hofmann, T. "Phosphorus Compounds, Organic," In 'Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2008. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_545.pub2.
- ^ Maier, Ludwig (1990). "ORGANIC PHOSPHORUS COMPOUNDS 90.l A CONVENIENT, ONE-STEP SYNTHESIS OF ALKYL- AND ARYLPHOSPHONYL DICHLORIDES". Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Silicon and the Related Elements. 47 (3–4): 465–470. doi:10.1080/10426509008038002.
