Bromopride
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral, IM, IV |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50 to 75% (oral) 78% (intramuscular) |
| Protein binding | 40% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 4 to 5 hours |
| Excretion | Renal, 10 to 14% unchanged |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.021.675 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
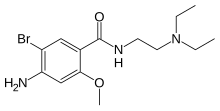
| Formula | C14H22BrN3O2 |
| Molar mass | 344.253 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Bromopride (INN) is a dopamine antagonist with prokinetic properties widely used as an antiemetic, closely related to metoclopramide. It is not available in the United States.
Bromopride appears to be safe and effective for use in pregnancy.[1]
Indications
[edit]Bromopride is indicated in the treatment of nausea and vomiting, including postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV); gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD/GORD); and as preparation for endoscopy and radiographic studies of the gastrointestinal tract. The manufacturer also claims it is valuable in, among other indications, hiccups and gastrointestinal adverse effects of radiation therapy.
Adverse effects
[edit]Bromopride is generally well tolerated; the most common adverse effects of its use are somnolence and fatigue. Bromopride may rarely cause extrapyramidal symptoms and, as with metoclopramide, may increase prolactin levels.[2]
Chemistry
[edit]Bromopride is a substituted benzamide, closely related to metoclopramide.[3] It is identical to metoclopramide except for the presence of a bromine atom where metoclopramide has a chlorine substituent.
Availability
[edit]Bromopride is not available in the United States or the United Kingdom. It is marketed in Brazil by Sanofi-Synthélabo under the trade name Digesan, by LIBBS under the name Plamet, and as a generic drug.
References
[edit]- ^ Araújo JR (1981). "Evaluation of bromopride in nausea and vomiting of pregnancy". J Bras Ginecol (in Portuguese). 91 (4): 283–5.
- ^ "Bula do Profissional de Saúde: Bromoprida". Bulário Eletrônico da Anvisa (in Portuguese). Brazilian National Health Surveillance Agency. April 11, 2006. Archived from the original on September 28, 2007. Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- ^ Brodie RR, Chasseaud LF, Darragh A, Lambe RF, Rooney L, Taylor T (1986). "Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of the anti-emetic agent bromopride". Biopharm Drug Dispos. 7 (3): 215–22. doi:10.1002/bdd.2510070302. PMID 3730521.
