From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Epipregnanolone
Names
IUPAC name
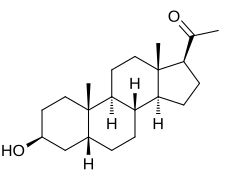
3β-Hydoxy-5β-pregnan-20-one
Preferred IUPAC name
1-[(1S ,3aS ,3bR ,5aR ,7S ,9aS ,9bS ,11aS )-7-Hydroxy-9a,11a-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H -cyclopenta[a ]phenanthren-1-yl]ethan-1-one
Other names
3β,5β-Tetrahydroprogesterone
Identifiers
ChemSpider
UNII
InChI=1S/C21H34O2/c1-13(22)17-6-7-18-16-5-4-14-12-15(23)8-10-20(14,2)19(16)9-11-21(17,18)3/h14-19,23H,4-12H2,1-3H3/t14-,15+,16+,17-,18+,19+,20+,21-/m1/s1
Key: AURFZBICLPNKBZ-GRWISUQFSA-N
CC(=O)[C@H]1CC[C@@H]2[C@@]1(CC[C@H]3[C@H]2CC[C@H]4[C@@]3(CC[C@@H](C4)O)C)C
Properties
C 21 H 34 O 2
Molar mass
−1
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Chemical compound
Epipregnanolone , also known as 3β-hydroxy-5β-pregnan-20-one , 3β,5β-tetrahydroprogesterone , or 3β,5β-THP , is an endogenous neurosteroid .[ 1] negative allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor and reverses the effects of potentiators like allopregnanolone .[ 2] [ 3] biosynthesized from progesterone by the actions of 5β-reductase and 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase , with 5β-dihydroprogesterone as the intermediate in this two-step transformation.[ 2]
Epipregnanolone is not a progestogen itself, but via metabolization into other steroids, behaves indirectly as one.[ 4]
The sulfate of epipreganolone, epipregnanolone sulfate , is a negative allosteric modulator of the NMDA [ 5] GABAA receptors [ 6] TRPM3 channel activator .[ 7] [ 8]
Chemistry
See also
References
^ Neurosteroids and Brain Function ISBN 978-0-08-054423-6 ^ a b Abraham Weizman (1 February 2008). Neuroactive Steroids in Brain Function, Behavior and Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Novel Strategies for Research and Treatment ISBN 978-1-4020-6854-6 ^ Jan Egebjerg; Arne Schousboe; Povl Krogsgaard-Larsen (4 October 2001). Glutamate and GABA Receptors and Transporters: Structure, Function and Pharmacology ISBN 978-0-7484-0881-8 ^ Beyer, C.; González-Flores, O.; Ramı́rez-Orduña, J.M.; González-Mariscal, G. (1999). "Indomethacin Inhibits Lordosis Induced by Ring A-Reduced Progestins: Possible Role of 3α-Oxoreduction in Progestin-Facilitated Lordosis". Hormones and Behavior . 35 (1): 1–8. doi :10.1006/hbeh.1998.1457 . ISSN 0018-506X . PMID 10049597 . ^ Norman G. Bowery (19 June 2006). Allosteric Receptor Modulation in Drug Targeting ISBN 978-1-4200-1618-5 ^ Park-Chung M, Malayev A, Purdy RH, Gibbs TT, Farb DH (1999). "Sulfated and unsulfated steroids modulate gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor function through distinct sites". Brain Res . 830 (1): 72–87. doi :10.1016/s0006-8993(99)01381-5 . PMID 10350561 . ^ Issues in Pharmacology, Pharmacy, Drug Research, and Drug Innovation: 2011 Edition ISBN 978-1-4649-6342-1 ^ Advances in Glutamic Acid Research and Application: 2013 Edition: ScholarlyBrief ISBN 978-1-4816-7049-4
Ionotropic
GABAA Tooltip γ-Aminobutyric acid A receptor
Positive modulators (abridged; see here for a full list): α-EMTBL Alcohols (e.g., drinking alcohol , 2M2B )Anabolic steroids Avermectins (e.g., ivermectin )Barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbital )Benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam )Bromide compounds (e.g., potassium bromide )Carbamates (e.g., meprobamate )Carbamazepine Chloralose Chlormezanone Clomethiazole Dihydroergolines (e.g., ergoloid (dihydroergotoxine) )Etazepine Etifoxine Fenamates (e.g., mefenamic acid )Flavonoids (e.g., apigenin , hispidulin )Fluoxetine Flupirtine Imidazoles (e.g., etomidate )Kava constituents (e.g., kavain )Lanthanum Loreclezole Monastrol Neuroactive steroids (e.g., allopregnanolone , cholesterol , THDOC )Niacin Niacinamide Nonbenzodiazepines (e.g., β-carbolines (e.g., abecarnil ), cyclopyrrolones (e.g., zopiclone ), imidazopyridines (e.g., zolpidem ), pyrazolopyrimidines (e.g., zaleplon ))Norfluoxetine Petrichloral Phenols (e.g., propofol )Phenytoin Piperidinediones (e.g., glutethimide )Propanidid Pyrazolopyridines (e.g., etazolate )Quinazolinones (e.g., methaqualone )Retigabine (ezogabine) ROD-188 Skullcap constituents (e.g., baicalin )Stiripentol Sulfonylalkanes (e.g., sulfonmethane (sulfonal) )Topiramate Valerian constituents (e.g., valerenic acid )Volatiles /gases (e.g., chloral hydrate , chloroform , diethyl ether , paraldehyde , sevoflurane )Negative modulators: 1,3M1B 3M2B 11-Ketoprogesterone 17-Phenylandrostenol α3IA α5IA (LS-193,268) β-CCB β-CCE β-CCM β-CCP β-EMGBL Anabolic steroids Amiloride Anisatin β-Lactams (e.g., penicillins , cephalosporins , carbapenems )Basmisanil Bemegride Bicyclic phosphates (TBPS , TBPO , IPTBO )BIDN Bilobalide Bupropion CHEB Chlorophenylsilatrane Cicutoxin Cloflubicyne Cyclothiazide DHEA DHEA-S Dieldrin (+)-DMBB DMCM DMPC EBOB Etbicyphat FG-7142 (ZK-31906) Fiproles (e.g., fipronil )Flavonoids (e.g., amentoflavone , oroxylin A )Flumazenil Fluoroquinolones (e.g., ciprofloxacin )Flurothyl Furosemide Golexanolone Iomazenil (123 I) IPTBO Isopregnanolone (sepranolone) L-655,708 Laudanosine Lindane MaxiPost Morphine Morphine-3-glucuronide MRK-016 Naloxone Naltrexone Nicardipine Nonsteroidal antiandrogens (e.g., apalutamide , bicalutamide , enzalutamide , flutamide , nilutamide )Oenanthotoxin Pentylenetetrazol (pentetrazol) Phenylsilatrane Picrotoxin (i.e., picrotin , picrotoxinin and dihydropicrotoxinin )Pregnenolone sulfate Propybicyphat PWZ-029 Radequinil Ro 15-4513 Ro 19-4603 RO4882224 RO4938581 Sarmazenil SCS Suritozole TB-21007 TBOB TBPS TCS-1105 Terbequinil TETS Thujone U-93631 Zinc ZK-93426 GABAA -ρ Tooltip γ-Aminobutyric acid A-rho receptor
Metabotropic
GABAB Tooltip γ-Aminobutyric acid B receptor
PR Tooltip Progesterone receptor
Agonists
Testosterone derivatives: Progestins: 6,6-Difluoronorethisterone 6,6-Difluoronorethisterone acetate 17α-Allyl-19-nortestosterone Allylestrenol Altrenogest Chloroethynylnorgestrel Cingestol Danazol Desogestrel Dienogest Ethinylandrostenediol
Ethisterone Ethynerone Etonogestrel Etynodiol Etynodiol diacetate Gestodene Gestrinone Levonorgestrel Levonorgestrel esters (e.g., levonorgestrel butanoate )Lynestrenol Lynestrenol phenylpropionate Metynodiol Metynodiol diacetate Norelgestromin Norethisterone (norethindrone) Norethisterone esters (e.g., norethisterone acetate , norethisterone enanthate )Noretynodrel Norgesterone Norgestimate Norgestrel Norgestrienone Norvinisterone Oxendolone Quingestanol Quingestanol acetate Tibolone Tigestol Tosagestin ; Anabolic–androgenic steroids: 11β-Methyl-19-nortestosterone 11β-Methyl-19-nortestosterone dodecylcarbonate 19-Nor-5-androstenediol 19-Nor-5-androstenedione 19-Nordehydroepiandrosterone Bolandiol Bolandiol dipropionate Bolandione Dimethisterone Dienedione Dienolone Dimethandrolone Dimethandrolone buciclate Dimethandrolone dodecylcarbonate Dimethandrolone undecanoate Dimethyldienolone Dimethyltrienolone Ethyldienolone Ethylestrenol (ethylnandrol) Methyldienolone Metribolone (R-1881) Methoxydienone (methoxygonadiene) Mibolerone Nandrolone Nandrolone esters (e.g., nandrolone decanoate , nandrolone phenylpropionate )Norethandrolone Normethandrone (methylestrenolone, normethandrolone, normethisterone) RU-2309 Tetrahydrogestrinone Trenbolone (trienolone) Trenbolone esters (e.g., trenbolone acetate , trenbolone enanthate )Trendione Trestolone Trestolone acetate MixedSPRMs Tooltip Selective progesterone receptor modulators ) Antagonists
mPR Tooltip Membrane progesterone receptor PAQR Tooltip Progestin and adipoQ receptor )