Djibouti: Difference between revisions
A Werewolf (talk | contribs) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
==Politics== |
==Politics== |
||
{{Ref improve section|date=May 2010}} |
{{Ref improve section|date=May 2010}} djibouti is a funny word |
||
{{Main|Politics of Djibouti}} |
{{Main|Politics of Djibouti}} |
||
Djibouti is a [[Semi-presidential republic|semi-presidential]] [[republic]], with [[executive power]] in the central government, and [[legislative power]] in both the government and parliament. The parliamentary party system is dominated by the [[People's Rally for Progress]] (RPP) and the President who currently is [[Ismail Omar Guelleh]]. The country's current constitution was approved in September 1992. Djibouti is a [[Dominant-party system|one party dominant state]] with the People's Rally for Progress in power. Other parties are allowed, but the main opposition, [[Union for a Presidential Majority]], boycotted the 2005 and 2008 elections leaving all of the legislative seats to the RPP. (''See [[Elections in Djibouti]].'') |
Djibouti is a [[Semi-presidential republic|semi-presidential]] [[republic]], with [[executive power]] in the central government, and [[legislative power]] in both the government and parliament. The parliamentary party system is dominated by the [[People's Rally for Progress]] (RPP) and the President who currently is [[Ismail Omar Guelleh]]. The country's current constitution was approved in September 1992. Djibouti is a [[Dominant-party system|one party dominant state]] with the People's Rally for Progress in power. Other parties are allowed, but the main opposition, [[Union for a Presidential Majority]], boycotted the 2005 and 2008 elections leaving all of the legislative seats to the RPP. (''See [[Elections in Djibouti]].'') |
||
Revision as of 21:40, 31 March 2011
The article's lead section may need to be rewritten. (October 2010) |
Republic of Djibouti جمهورية جيبوتي Jumhūriyyat Jībūtī République de Djibouti Jamhuuriyadda Jabuuti Gabuutih Ummuuno | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Unité, Égalité, Paix" (translation) "Unity, Equality, Peace" | |
| Anthem: Djibouti | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Djibouti |
| Official languages | Arabic and French[1] |
| Demonym(s) | Djiboutian |
| Government | Semi-presidential republic |
| Ismail Omar Guelleh | |
| Dileita Mohamed Dileita | |
| Independence from France | |
• Date | June 27, 1977 |
| Area | |
• Total | 23,200 km2 (9,000 sq mi) (149th) |
• Water (%) | 0.09 (20 km² / 7.7 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2009 estimate | 864,000[2] (160th) |
• 2009 census | 818,159 |
• Density | 37.2/km2 (96.3/sq mi) (168th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2010 estimate |
• Total | 2.101 billion[3] |
• Per capita | 2,549[3] |
| GDP (nominal) | 2010 estimate |
• Total | 1.128 billion[3] |
• Per capita | 1,369[3] |
| Gini (2009) | 40.0 medium |
| HDI (2007) | Error: Invalid HDI value (155th) |
| Currency | Franc (DJF) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (EAT) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (not observed) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | 253 |
| ISO 3166 code | DJ |
| Internet TLD | .dj |
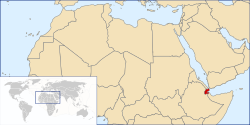
Djibouti ([جيبوتي Jībūtī] Error: {{Lang-xx}}: text has italic markup (help), French: Djibouti, [Jabuuti] Error: {{Lang-xx}}: text has italic markup (help), Afar: Gabuuti), officially the Republic of Djibouti ([جمهورية جيبوتي Jumhūriyyat Jībūtī] Error: {{Lang-xx}}: text has italic markup (help), French: République de Djibouti, [Jamhuuriyadda Jabuuti] Error: {{Lang-xx}}: text has italic markup (help), Afar: Gabuutih Ummuuno), is a country in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Eritrea in the north, Ethiopia in the west and south, and Somalia in the southeast. The remainder of the border is formed by the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden at the east. Djibouti, which had a population of 818,159 at the 2009 census,[5] is one of the least populous countries in Africa.[6] The predominant religion in Djibouti is Islam, with a 94% majority, with the remaining 6% practicing Christianity. In the 19th century, Djibouti, then known as French Somaliland (French: Côte Française des Somalis), was acquired by France through various treaties with Somali sultans.[7] In 1967 the name was changed to the French Territory of the Afars and the Issas (French: Territoire Français des Afars et des Issas). The territory was declared an independent nation in 1977, and changed its name to the Republic of Djibouti. Djibouti joined the United Nations on September 20, 1977.[8][9] While Djibouti is an independent state, it maintains deep French relations, and through various military and economic agreements with France, it receives continued security and economic assistance.[10]
History
The history of Djibouti goes back thousands of years to a time when populations in the area traded hides and skins for the perfumes and spices of ancient Egypt, India and China. Through close contacts with the adjacent Arabian Peninsula for more than 1,000 years, the Somali and Afar ethnic groups in the region became among the first populations on the continent to embrace Islam.[11]

From 1862 to 1894, the land on the north side of the Gulf of Tadjoura was called Obock, and was ruled by Somali Sultans. France first gained a foothold in the region through various treaties signed between 1883 and 1887.[12] In 1894, Léonce Lagarde established a permanent French administration in the city of Djibouti and named the region French Somaliland (Côte française des Somalis). It lasted from 1896 until 1967, when it was renamed the French Territory of the Afars and the Issas.[13]
In 1958, on the eve of neighboring Somalia's independence in 1960, a referendum was held in Djibouti to decide whether or not to join the Somali Republic or to remain with France. The referendum turned out in favour of a continued association with France, partly due to a combined yes vote by the sizable Afar ethnic group and resident Europeans.[14] There was also widespread vote rigging, with the French expelling thousands of Somalis before the referendum reached the polls.[15] The majority of those who voted no were Somalis who were strongly in favour of joining a united Somalia as had been proposed by Mahmoud Harbi, Vice President of the Government Council. Harbi was killed in a plane crash two years later. Djibouti finally gained its independence from France in 1977 and Hassan Gouled Aptidon, a French-groomed Somali who campaigned for a yes vote in the referendum of 1958, eventually wound up as the nation's first president (1977–1991).[14]
Djibouti is a Somali, Afar and Muslim country, which regularly takes part in Islamic affairs. It is also a member of the Arab League, as well as the African Union and the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD).
Politics
This section needs additional citations for verification. (May 2010) |
djibouti is a funny word
Djibouti is a semi-presidential republic, with executive power in the central government, and legislative power in both the government and parliament. The parliamentary party system is dominated by the People's Rally for Progress (RPP) and the President who currently is Ismail Omar Guelleh. The country's current constitution was approved in September 1992. Djibouti is a one party dominant state with the People's Rally for Progress in power. Other parties are allowed, but the main opposition, Union for a Presidential Majority, boycotted the 2005 and 2008 elections leaving all of the legislative seats to the RPP. (See Elections in Djibouti.) The government is seen as being controlled by the Somali Issa Dir clan who enjoy the support of the Somali clans, especially the Isaaq who is also the clan of the current presidents wife and the clan of many ministers and government officials are Isaaq and the Gadabuursi Dir who are the third most prominent Somali clan in Djibouti politics. The country has recently come out of a decade-long civil war, with the government and the Front for the Restoration of Unity and Democracy (FRUD) signing a peace treaty in 2000. Two FRUD members are part of the current cabinet.
Djibouti's second president, Guelleh, succeeded Hassan Gouled Aptidon in office in 1999.[16] Despite elections of the 1990s being described as "generally fair", Guelleh was sworn in for his second and final six-year term as president after a one-man election on 8 April 2005. He took 100% of the votes in a 78.9% turnout.
The prime minister, who follows the council of ministers ('cabinet'), is appointed by the President. The parliament – the Chambre des Députés – consists of 52 members who are selected every five to nine years.
In 2001, the Djiboutian government leased the former French military base Camp Lemonnier to the United States Central Command for operations related to Combined Joint Task Force Horn of Africa (CJTF-HOA). In 2009, Central Command transitioned responsibilities in Africa to AFRICOM.
France's 13th Demi-Brigade of the Foreign Legion is based in Djibouti, but not in Djibouti City.
In February 2011 protesters in Djibouti joined the Arab world protests, demanding that President Guelleh step down.
Geography

Djibouti lies in Northeast Africa on the Gulf of Aden at the southern entrance to the Red Sea. It has 314 km (195 mi) of coastline and shares a 113 km (70 mi) border with Eritrea, 337 km (209 mi) with Ethiopia and 58 km (36 mi) with Somalia (total 506 km (314 mi)*). It lies between latitudes 10° and 13°N, and longitudes 41° and 44°E.
The country is mainly a stony semidesert, with scattered plateaus and highlands. It has an area of 8,900 square miles (23,051 km2).
Regions and districts

Djibouti is sectioned into five regions and one city. It is further subdivided into eleven districts.
The regions and city are:
- Ali Sabieh Region (Région d'Ali Sabieh)
- Arta Region (Région d'Arta)
- Dikhil Region (Région de Dikhil)
- Djibouti (city) (Ville de Djibouti)
- Obock Region (Région d'Obock)
- Tadjourah Region (Région de Tadjourah))
Economy
The economy of Djibouti is based on service activities connected with the country's strategic location[17] and status as a free trade zone in northeast Africa. Two-thirds of the inhabitants live in the capital city, the remainder being mostly nomadic herders. Scant rainfall limits crop production to fruits and vegetables, and most food must be imported.

In April 2005, the United Nations World Food Programme warned that 30,000 people in Djibouti face serious food shortages following three years of poor rains.[18]
Djibouti provides services as both a transit port for the region and an international transshipment and refueling center. It has few natural resources and little industry. The nation is, therefore, heavily dependent on foreign assistance to help support its balance of payments and to finance development projects. Salt Investment, a Djiboutian company, is overseeing a $70 million operation to industrialize the collection of Djibouti’s plentiful salt in the Region Lake Asal.
There are gold miners from India, geothermal experts from Iceland, Turkish hotel managers, Saudi oil engineers, French bankers and American military contractors. Investors from Dubai have leased the country's port, in an effort to develop the area as a gateway to the region. Saudi investors are reportedly exploring the possibility of linking the Horn of Africa with the Arabian Peninsula via an 18-mile long oversea bridge referred to as the Bridge of the Horns. Tarek bin Laden, half brother of Osama bin Laden, has been linked to the project.
An unemployment rate of 40% to 50% continues to be a major problem. Inflation is not a concern, however, because of the fixed tie of the franc to the U.S. dollar. Per capita consumption dropped an estimated 35% over the last seven years because of recession, civil war, and a high population growth rate (including immigrants and refugees). The secession of Eritrea from Ethiopia has been beneficial to Djibouti, as the Port of Djibouti is now serving as landlocked Ethiopia's primary link to the sea. Faced with a multitude of economic difficulties, the government has fallen into arrears on long-term external debt and has been struggling to meet the stipulations of foreign aid donors.[1]
Demographics


The population consists of two major ethnic groups: the Somali and the Afar. The Somali clan component in Djibouti is mainly composed of the Issas, who form the majority, and the Gadabuursi. Both are subclans of the Dir. The Issas form part of the Madoobe Dir while the Gadabuursi are part of the Madaluug Dir. The remainder of the population consists of Europeans (mostly French and Italians), Arabs and Ethiopians. Although French and Arabic are the official languages, Somali and Afar are widely spoken.[1] The bulk of Djibouti's people are urban residents; the remainder are pastoralists.
Health
The life expectancy at birth is about 60 for both females and males.[19] Fertility is at 2.79 children per woman.[19] In the country there are about 18 doctors per 100,000 persons.[20]
According to a 2005 World Health Organization estimate, about 93.1% of Djibouti's women and girls have undergone female genital cutting,[21] a pre-marital custom mainly endemic to Northeast Africa and parts of the Near East that has its ultimate origins in Ancient Egypt.[22][23] Although legally proscribed in 1994, the procedure is still widely practiced, as it is deeply ingrained in the local culture.[24] Encouraged and performed by women in the community, circumcision is primarily intended to deter promiscuity and to offer protection from assault.[24][25] About 94% of Djibouti's male population has also reportedly undergone male circumcision.[26]
Religion

Djibouti's population is predominantly Muslim. Islam is observed by 94% of Djibouti's population (about 740,000) (2010 estimate), while the remaining six percent follow Christianity.[27]
Every town and village in Djibouti has a mosque where people go to worship.[citation needed] Tombs of their former religious leaders and those considered holy are known as sacred spaces. The most famous sacred space for Islam in Djibouti is the tomb of Sheikh Abu Yazid, which is found in the Goda Mountains.[citation needed] In addition to the Islamic calendar, Muslims in Djibouti also recognize New Year's Day (January 1) and Labor Day (May 1) as holidays.[citation needed]
The Republic of Djibouti names Islam as the sole state religion, the Constitution of 1992 provides for the equality of citizens of all faiths (Art. 1) as well as the freedom to practise any religion (Art. 11). Djibouti's Family Code (Code de la Famille) of 2002 prohibits Muslim women from marrying non-Muslim men, unless the men convert to Islam. Marriage, divorce and inheritance are handled by the Family Court which applies the Family Code and has jurisdiction over Muslims, while non-Muslims must instead turn to civil courts. According to the International Religious Freedom Report 2008, while Muslim Djiboutians have the legal right to convert to another faith or marry outside of Islam, "converts may face negative societal, tribal, and familial attitudes towards their decision" and often face pressure to revert to Islam.[28]
Between 7,000 and 8,000 Catholics live in Djibouti, of which some 300 are local Djiboutians, the rest being foreigners [citation needed]. The Christian population largely consists of foreign-born or expatriate residents. [citation needed] Djibouti has a Catholic diocese, 4 Catholic priests all of whom are foreigners – as well as about 40 Catholic missionaries. [citation needed]
Culture

Djiboutian attire reflects the region's hot and arid climate. When not dressed in western clothing such as jeans and t-shirts, men typically wear the macawiis, which is a sarong-like garment worn around the waist. Among nomads, many wear a loosely wrapped white cotton robe called a tobe that goes down to about the knee, with the end thrown over the shoulder (much like a Roman toga).
Women typically wear the dirac, which is a long, light, diaphanous voile dress made of cotton or polyester that is worn over a full-length half-slip and a bra. Married women tend to sport head-scarves referred to as shash, and also often cover their upper body with a shawl known as garbasaar. Unmarried or young women, however, do not always cover their heads. Traditional Arabian garb such as the male jellabiya (jellabiyaad in Somali) and the female jilbāb is also commonly worn. For some occasions such as festivals, women may adorn themselves with specialized jewelry and head-dresses similar to those worn by the Berber tribes of the Maghreb.[29]
A lot of Djibouti's original art is passed on and preserved orally, mainly through song. Many examples of Islamic, Ottoman, and French influences can also be noted in the local buildings, which contain plasterwork, carefully constructed motifs and calligraphy.
Education
Education in Djibouti is strongly influenced by France.[30] Although the government effort resulted in an increase in enrollment during the 1990s, the education system is still below people’s expectations and the needs of a developing nation.[31] There are 81 public primary schools, 24 registered private primary schools, 12 secondary schools and two vocational schools in Djibouti.[30][32] Female gross enrollment rate was at 21.9% and male gross enrollment rate was at 29.0% in 2007.[33]
See also
References
- ^ a b c "Djibouti". World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 2007-09-06. Retrieved 2007-09-18.
- ^ Department of Economic and Social Affairs
Population Division (2009). "World Population Prospects, Table A.1" (PDF). 2008 revision. United Nations. Retrieved 2009-03-12.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); line feed character in|author=at position 42 (help) - ^ a b c d "Djibouti". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 2010-04-21.
- ^ Human Development Report 2009. The United Nations. Retrieved 5 October 2009.
- ^ "Communication Officielle des Resultats du Recensement Général de la Population". Ministère de l'Economie, des Finances et de la Planification, Djibouti. 2010. Retrieved 18 February 2011.
- ^ World Bank country data Djibouti (2009) (number rounded)
- ^ [1]
- ^ [2]
- ^ United Nations member states
- ^ [3]
- ^ A Country Study: Somalia from The Library of Congress
- ^ Hugh Chisholm (ed.), The encyclopædia britannica: a dictionary of arts, sciences, literature and general information, Volume 25, (At the University press: 1911), p.383.
- ^ Worldstatesmen.org
- ^ a b Barrington, Lowell, After Independence: Making and Protecting the Nation in Postcolonial and Postcommunist States, (University of Michigan Press: 2006), p.115
- ^ Kevin Shillington, Encyclopedia of African history, (CRC Press: 2005), p.360.
- ^ "DJIBOUTI: Guelleh sworn in for second presidential term". Retrieved December 4, 2005.
- ^ Brass, Jennifer N. 2008. "Djibouti's unusual resource curse" Journal of Modern African Studies. 46, 4: 523-545.
- ^ Djibouti drought threatens 30,000 with grave food shortages, 29 April 2005, World Food Programme. Retrieved August 4, 2007.
- ^ a b https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/dj.html
- ^ "IRIN | Country Profile | Djibouti". Irinnews.org. Retrieved 2010-06-20.
- ^ Prevalence of FGM
- ^ Rose Oldfield Hayes (1975). "Female genital mutilation, fertility control, women's roles, and the patrilineage in modern Sudan: a functional analysis". American Ethnologist. 2 (4): 617–633. doi:10.1525/ae.1975.2.4.02a00030.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Herbert L. Bodman, Nayereh Esfahlani Tohidi, Women in Muslim societies: diversity within unity, (Lynne Rienner Publishers: 1998), p. 41.
- ^ a b DJIBOUTI: Women fight mutilation
- ^ Suzanne G. Frayser, Thomas J. Whitby, Studies in human sexuality: a selected guide, (Libraries Unlimited: 1995), p. 257.
- ^ Male Circumcision and AIDS: The Macroeconomic Impact of a Health Crisis
- ^ CIA World Factbook (2010) – Djibouti
- ^ United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. "[accessed 13 December 2009 Immigration and Refugee Board of Canada, "Djibouti: Situation and treatment of Christians, including instances of discrimination or violence; effectiveness of recourse available in cases of mistreatment; problems that a Muslim can face if he or she converts to Christianity or marries a Christian (2000–2009)", 5 August 2009". Unhcr.org. Retrieved 2010-06-20.
- ^ "Image of Djibouti women in head-dresses". Retrieved April 5, 2008.
- ^ a b "Hare, Harry (2007) ICT in Education in Djibouti, World Bank".
- ^ "Hare, Harry (2007) ICT in Education in Djibouti, World Bank".
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|url=(help) - ^ "http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/scr/2009/cr09203.pdf" (PDF).
{{cite web}}: External link in|title= - ^ "Human Development Report 2009 - Djibouti". Hdrstats.undp.org. Retrieved 2010-06-20.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
Further reading
- Djibouti's Unusual Resource Curse Jennifer N. Brass
- Djibouti: Pawn of the Horn of Africa Robert Saint-Veran
- Historical Dictionary of Djibouti Daoud A. Alwan
- Naval Strategy East of Suez: The Role of Djibouti Charles W
External links
- Government
- General information
- Djibouti from al-Bab
- Country Profile from BBC News
- "Djibouti". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Djibouti from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Djibouti at Curlie
- DjibNet directory, mostly in French
 Wikimedia Atlas of Djibouti
Wikimedia Atlas of Djibouti
- News media
- Travel
- Djibouti
- African countries
- Arabic-speaking countries
- Countries bordering the Red Sea
- Former colonies of France
- French-speaking countries
- Gulf of Aden
- Horn of Africa
- Least Developed Countries
- Member states of La Francophonie
- Member states of the African Union
- Member states of the Arab League
- Member states of the Organisation of the Islamic Conference
- Republics
- States and territories established in 1977