Solar eclipse of May 6, 1883
| Solar eclipse of May 6, 1883 | |
|---|---|
 An artist's depiction of the total solar eclipse, observed from Caroline Atoll, Caroline Islands. | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | −0.425 |
| Magnitude | 1.0634 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 358 s (5 min 58 s) |
| Coordinates | 8°06′S 144°36′W / 8.1°S 144.6°W |
| Max. width of band | 229 km (142 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 21:53:49 |
| References | |
| Saros | 136 (30 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9241 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on May 6, 1883. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The path of totality fell across the southern Pacific Ocean with no major landfall. Partiality was visible from far eastern Australia at sunrise, and New Zealand, as well as western South America and southern Mexico near sunset. This eclipse is a member of Solar Saros 136, and its maximum duration was 5 minutes and 58.24 seconds.
Observations
An expedition of American astronomers traveled from Peru to Caroline Island aboard the USS Hartford to observe the total solar eclipse. A French expedition also observed the eclipse from Caroline, and the United States Navy mapped the atoll.[1] Johann Palisa, a member of the expedition, discovered an asteroid later that year which he named Carolina "in remembrance of his visit to [the] island."[2]
Related eclipses
Saros 136
This eclipse is a part of Saros series 136, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 71 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on June 14, 1360. It contains annular eclipses from September 8, 1504 through November 12, 1594; hybrid eclipses from November 22, 1612 through January 17, 1703; and total eclipses from January 27, 1721 through May 13, 2496. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on July 30, 2622. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of annularity was produced by member 9 at 32 seconds on September 8, 1504, and the longest duration of totality was produced by member 34 at 7 minutes, 7.74 seconds on June 20, 1955. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s descending node of orbit.[3]
| Series members 26–47 occur between 1801 and 2200: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 26 | 27 | 28 |
 March 24, 1811 |
 April 3, 1829 |
 April 15, 1847 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
 April 25, 1865 |
 May 6, 1883 |
 May 18, 1901 |
| 32 | 33 | 34 |
 May 29, 1919 |
 June 8, 1937 |
 June 20, 1955 |
| 35 | 36 | 37 |
 June 30, 1973 |
 July 11, 1991 |
 July 22, 2009 |
| 38 | 39 | 40 |
 August 2, 2027 |
 August 12, 2045 |
 August 24, 2063 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 |
 September 3, 2081 |
 September 14, 2099 |
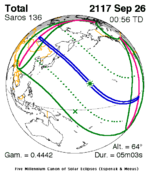 September 26, 2117 |
| 44 | 45 | 46 |
 October 7, 2135 |
 October 17, 2153 |
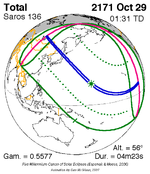 October 29, 2171 |
| 47 | ||
 November 8, 2189 | ||
Notes
- ^ Bryan, E.H. (1942). American Polynesia and the Hawaiian Chain. Honolulu: Tongg Publishing Company.
- ^ Schmadel, L.D. (2000). Dictionary of Minor Planet Names (4th ed.). Berlin: Springer-Verlag Telos. ISBN 3-540-66292-8.
- ^ "NASA - Catalog of Solar Eclipses of Saros 136". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.
References
- NASA graphic
- The Total Solar Eclipse of 16th April, 1893. Report on Results Obtained with the Slit Spectroscopes, by E. H. Hills, 1894, The Royal Society.
- Scientific American: The Solar Eclipse Of May 6, 1883, Professor C. S. Hastings, of the Johns Hopkins University, also includes many interesting details in his account of the trip
- The total solar eclipse of May 6, 1883, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 44, p. 180 [1]
- Some of the Meteorological Results of the Total Solar Eclipse of May 6, 1883, Nature 31, 601–601 (30 April 1885) [2]




