Buk missile system
| 9K37 Buk NATO reporting name: SA-11 Gadfly, SA-17 Grizzly | |
|---|---|
 Buk-M1-2 air defence system in 2010 | |
| Type | Medium range SAM system |
| Place of origin | Soviet Union |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1979–present |
| Used by | See list of present and former operators |
| Wars | See combat service |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Almaz-Antey:
|
| Variants | 9K37 "Buk", 9K37M, 9K37M1 "Buk-M1", 9K37M1-2 "Buk-M1-2", 9K37M1-2A, 9K317 "Buk-M2", "Buk-M3" naval: 3S90 (M-22), 3S90M, 3S90E1, 3S90M1 |
The Buk missile system (Template:Lang-ru; “beech” (tree), /bʊk/) is a family of self-propelled, medium-range surface-to-air missile systems developed by the Soviet Union and its successor state, the Russian Federation, and designed to fight cruise missiles, smart bombs, fixed- and rotary-wing aircraft, and unmanned aerial vehicles.[2]
The Buk missile system is the successor to the NIIP/Vympel 2K12 Kub (NATO reporting name SA-6 "Gainful").[3] The first version of Buk adopted into service carried the GRAU designation 9K37 and was identified in the west with the NATO reporting name "Gadfly" as well as the US Department of Defense designation SA-11.
With the integration of a new missile the Buk-M1-2 and Buk-M2 systems also received a new NATO reporting name Grizzly and a new DoD designation SA-17. In 2013, the latest incarnation "Buk-M3" was scheduled for production.[4]
A naval version of the system, designed by MNIIRE Altair (currently part of GSKB Almaz-Antey) for the Russian Navy, according to Jane's Missiles & Rockets, received the GRAU designation 3S90M1 and will be identified with the NATO reporting name Gollum and a DoD designation SA-N-7C. The naval system was scheduled for delivery in 2014.[5]
Development
Development of the 9K37 "Buk" was started on 17 January 1972 at the request of the Central Committee of the CPSU.[6] The development team comprised many of the same institutions that had developed the previous 2K12 "Kub" (NATO reporting name "Gainful", SA-6). These included the Tikhomirov Scientific Research Institute of Instrument Design (NIIP) as the lead designer and the Novator design bureau, which were responsible for the development of the missile armament.[6] In addition to the land-based missile system a similar system was to be produced for the naval forces, the result being the 3S90 "Uragan" (Template:Lang-ru; hurricane) which also carries the SA-N-7 and "Gadfly" designations.[7]
| Kub | Kvadrat | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kub-M1 | Kub-M | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kub-M3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buk | Uragan | Shtil | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buk-M1 | Buk-1 (Kub-M4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buk-M1-2 | Gang Gange | Buk-M1-2A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buk-M2 | Ural | Buk-M2E | Buk-M2EK | Ezh | Shtil | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buk-M3 | Export Version | Soviet or Russian Version | Smerch | Shtil-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Buk missile system was designed to surpass the 2K12 Kub in all parameters, and its designers, including its chief designer Ardalion Rastov, visited Egypt in 1971 to see Kub in operation.[8] Both the Kub and Buk used self-propelled launchers developed by Ardalion Rastov. As a result of this visit, the developers came to the conclusion that each Buk transporter erector launcher (TEL) should have its own fire control radar, rather than being reliant on one central radar for the whole system as in Kub.[8] The result of this move from TEL to transporter erector launcher and radar (TELAR) was a system able to shoot at multiple targets from multiple directions at the same time.
During 1974 the developers determined that although the Buk missile system is the successor to the Kub missile system, both systems could share some interoperability. The result of this decision was the 9K37-1 Buk-1 system.[6] Interoperability between Buk TELAR and Kub TEL meant an increase in the number of fire control channels and available missiles for each system, as well as faster entry of Buk system components into service. The Buk-1 was adopted into service in 1978 following completion of state trials, while the complete Buk missile system was accepted into service in 1980[8] after state trials took place between 1977 and 1979.[6]
| External images | |
|---|---|
The naval variant of the 9K37 "Buk", the 3S-90 "Uragan," was developed by the Altair design bureau under the direction of chief designer G.N. Volgin.[9] The 3S-90 used the same 9M38 missile as the 9K37, though the launcher and associated guidance radars were exchanged for naval variants. After the 9S-90 system was tested, between 1974 and 1976 on the Kashin-class destroyer Provorny, it was accepted into service in 1983 on the Project 956 Sovremenny-class destroyers.[9]
No sooner had the 9K37 "Buk" entered service than the Central Committee of the CPSU authorised the development of a modernised 9K37 which would become the 9K37M1 Buk-M1, adopted into service in 1983.[6] The modernisation improved the performance of the system radars, its "probability of kill" and its resistance to electronic countermeasures (ECM). Additionally a non-cooperative threat classification system was installed, relying on analysis of returned radar signals to purportedly identify and clearly distinguish civilian aircraft from potential military targets in the absence of IFF.[8]

Another modification to the Buk missile system was started in 1992 with work carried out between 1994 and 1997 to produce the 9K37M1-2 Buk-M1-2,[6] which entered service in 1998.[10] This modification introduced a new missile, the 9M317, which offered greater kinematic performance over the previous 9M38, which could still be used by the Buk-M1-2. Such sharing of the missile type caused a transition to a different GRAU designation, 9K317, which has been used independently for all later systems. The previous 9K37 series name was also preserved for the complex, as was the "Buk" name. The new missile, as well as a variety of other modifications, allowed the system to shoot down ballistic missiles and surface targets, as well as enlarging the "performance and engagement envelope" (zone of danger for potential attack) for more traditional targets like aircraft and helicopters.[6] The 9K37M1-2 Buk-M1-2 also received a new NATO reporting name distinguishing it from previous generations of the Buk system; this new reporting name was the SA-17 Grizzly. The export version of the 9K37M1-2 system is called "Ural" (Template:Lang-ru)

The introduction of the 9K37M1-2 system for the land forces also marked the introduction of a new naval variant, the "Ezh", which carries the NATO reporting name SA-N-7B 'Grizzly' (9M317 missile). was exported under the name "Shtil" and carries a NATO reporting name of SA-N-7C 'Gollum' (9M317E missile), according to Jane's catalogue.[7] The 9K317 incorporates the 9M317 missile to replace the 9M38 used by the previous system. A further development of the system was unveiled as a concept at EURONAVAL 2004, a vertical launch variant of the 9M317, the 9M317ME, which is expected to be exported under the name 3S90E "Shtil-1". Jane's also reported that in the Russian forces it would have a name of 3S90M "Smerch" (Template:Lang-ru, English translation: 'tornado').[9][11][12]
The Buk-M1-2 modernisation — based on a previous more advanced developmental system referred to as the 9K317 "Buk-M2" —[6] featured new missiles and a new third-generation phased array fire control radar allowing targeting of up to four targets while tracking a further 24. A new radar system with a fire control radar on a 24 m extending boom reputedly enabled more accurate targeting of low-altitude planes.[13] This new generation of Buk missile systems was stalled due to poor economic conditions after the fall of the Soviet Union. The system was presented as a static display at the 2007 MAKS Airshow.
In October 2007, Russian General Nikolai Frolov, commander of the Russian Ground Forces air defense, declared that the army would receive the brand-new Buk-M3 to replace the Buk-M1. He stipulated that the M3 would feature advanced electronic components and enter into service in 2009.[14] The upgraded Buk-M3 TELAR will have a seven rollers tracked chassis and 6 missiles in launch tubes.[15]
Description

A standard Buk battalion consists of a command vehicle, target acquisition radar (TAR) vehicle, six transporter erector launcher and radar (TELAR) vehicles and three transporter erector launcher (TEL) vehicles. A Buk missile battery consists of two TELAR and one TEL vehicle.

The Buk-M1-2 TELAR uses the GM-569 chassis designed and produced by JSC MMZ (Mytishchi).[16] TELAR superstructure is a turret containing the fire control radar at the front and a launcher with four ready-to-fire missiles on top. Each TELAR is operated by a crew of four and is equipped with chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear (CBRN) protection. The radar fitted to each TELAR, referred to as the 'Fire Dome' by NATO, is a monopulse type radar and can begin tracking at the missile's maximum range (32 km/20 mi) and can track aircraft flying at between 15 m and 22 km (50 to 72,000 ft) altitudes.[citation needed] It can guide up to three missiles against a single target. The 9K37 system supposedly has much better ECCM characteristics (i.e., is more resistant to ECM and jamming) than the 3M9 Kub system that it replaces.[citation needed] While the early Buk had a day radar tracking system 9Sh38 (similar to that used on Kub, Tor and Osa missile system), its current design can be fitted with a combined optical tracking system with a thermal camera and a laser range-finder for passive tracking of the target. The 9K37 system can also utilise the same 1S91 Straight Flush 25 kW G/H band continuous wave radar as the 3M9 "Kub" system.
The 9S35 radar of the original Buk TELAR uses a mechanical scan of a Cassegrain antenna reflector, where the Buk-M2 TELAR design used a PESA, for tracking and missile guidance.

The 9K37 utilises the 9S18 "Tube Arm" or 9S18M1 (which carries the NATO reporting name "Snow Drift") (Template:Lang-ru; dome) target acquisition radar in combination with the 9S35 or 9S35M1 "Fire Dome" H/I band tracking and engagement radar which is mounted on each TELAR. The Snow Drift target acquisition radar has a maximum detection range of 85 km (53 mi) and can detect an aircraft flying at 100 m (330 ft) from 35 km (22 mi) away and even lower flying targets at ranges of around 10–20 km (6–12 mi). Snow Drift is mounted on a chassis similar to that of the TELAR, as is the command vehicle. The control post which coordinates communications between the surveillance radar(s) and the launchers is able to communicate with up to six TELs at once.[citation needed]

The TEL reload vehicle for the Buk battery resembles the TELAR, but instead of a radar they have a crane for the loading of missiles. They are capable of launching missiles directly but require the cooperation of a Fire Dome–equipped TELAR for missile guidance. A reload vehicle can transfer its missiles to a TELAR in around 13 minutes and can reload itself from stores in around 15 minutes.
Also, the Buk-M2 featured a new vehicle like TELAR but with radar atop of a telescopic lift and without missiles, called a target acquisition radar (TAR) 9S36. This vehicle could be used together with two TELs 9A316 to attack up to four targets, missile guidance in forested or hilly regions.
The mobile simulator SAM Buk-M2E was shown at MAKS-2013. A self-propelled fire simulator installation JMA 9A317ET SAM "Buk-M2E", based on the mobile, is designed for training and evaluating the combat crew in the war environment to detect, capture, lock on to ("maintain") and defeat targets. A computer information system fully records all actions of the crew to a "black box" to allow objective assessment of the consistency of the crew's actions and results.[17]
All vehicles of the Buk-M1 (Buk-M1-2) missile system use an Argon-15A computer, as does the Zaslon radar (the first Soviet-made airborne digital computer, designed in 1972 by the Soviet Research Institute of Computer Engineering (NICEVT, currently NII Argon). It is produced at a Kishinev plant originally named "50 Years of the USSR".[18][19] The vehicles of Buk-M2 (Buk-M2E) missile system use a slightly upgraded version of Argon-A15K. This processor is also used in such military systems as anti-submarine defense Korshun and Sova, airborne radars for MiG-31 and MiG-33, mobile tactical missile systems Tochka, Oka and Volga. Currently,[when?] Argons are upgraded with the Baget series of processors by NIIP.[citation needed]
Basic missile system specifications
- Target acquisition range (by TAR 9S18M1, 9S18M1-1)
- Range: 140 kilometres (87 miles)
- Altitude: 60 meters – 25 kilometers (197 feet – 15.5 miles)
- Firing groups in one division: up to 6 (with one command post)
- Firing groups operating in a sector
- 90° in azimuth, 0–7° and 7–14° in elevation
- 45° in azimuth, 14–52° in elevation
- Radar mast lifting height (for TAR 9S36): 21 meters
- Reloading of 4 missiles by TEL from itself: around 15 minutes
- Combat readiness time: no more than 5 minutes
- Kill probability (by one missile): 90–95%
- Target engagement zone
- Aircraft
- Altitude: 15 meters – 25 kilometers (50 feet – 15.5 miles)
- Range: 3–42 kilometres (2–26 miles)
- Tactical ballistic missiles
- Altitude: 2.0–16 kilometres (1.2–9.9 miles)
- Range: 3–20 kilometres (1.9–12.4 miles)
- Sea targets: up to 25 kilometres (16 miles)
- Land targets: up to 15 kilometres (9.3 miles)
- Aircraft
Chance to destroy aircraft 0,7-0,93 maneuvering the aircraft 0.6 (for 1 missile 9M38). In '92, the system has proven the ability to destroy Scud missile R-17 and rocket MLRS caliber of 0.3 meters.[20]
Operation
The Buk is a mobile, radar-guided surface-to-air missile (SAM) missile system with all four main components — acquisition and targeting radars, a command element, missile launchers, and a logistics element — mounted on tracked vehicles. This allows the system to move with other military forces and relocate to make it a more difficult target to find than a fixed SAM system.
- The acquisition radar component (several variants have differing capabilities) allows the system to identify, track and target selected targets.
- The command component is intended to discern "friendly" military aircraft from foes (IFF), prioritize multiple targets, and pass radar targeting information to the missile launchers.
- The missile launcher component can carry a variety of missiles (as listed below) and may be able to engage more than one target simultaneously.
- The logistics component carries additional (reload) missiles and provides other supplies and parts for the system and the operators.
In general, the system identifies potential targets (radar), selects a particular target (command), fires a missile (launcher) at the target, and resupplies the system (logistics). The missiles require a radar lock to initially steer the missile to the target until the missile's on-board radar system takes over to provide final course corrections. A proximity fuse aboard the missile determines when it will detonate, creating an expanding fragmentation pattern of missile components and warhead to intercept and destroy the target. A proximity fuse improves the "probability of kill" given the missile and target closure rates, which can be more than 3,000 km/h (1,900 mph) (or more than 900 m/s (3,000 ft/s)).
Alternatively, the command component may be able to remotely detonate the missile, or the on-board contact fuse will cause the warhead to detonate. The most capable radar, assuming it has a line of sight (no terrain between the radar and the target), can track targets (depending on size) as low as 30 m (98 ft) and as far as 140 km (87 mi). The most capable missile can hit targets as far as 50 km (31 mi) and more than 24,000 m (79,000 ft) in altitude. Since the introduction of the Buk in the 1970s, the capabilities of its system components have evolved, which has led to different nomenclature and nicknames for the components' variants. The Buk has also been adapted for use on naval vessels.
Integration with higher level command posts
The basic command post of the Buk missile system is 9С510 (9K317 Buk-M2), 9S470M1-2 (9K37M1-2 Buk-M1-2) and 9S470 (Buk-M1) vehicles, organizing the Buk system into a battery. It is capable of linking with various higher level command posts (HLCPs). As an option, with the use of HLCP, the Buk missile system may be controlled by an upper level command post system 9S52 Polyana-D4, integrating it with S-300V/S-300VM into an air defence brigade.[21][22] Also, it may be controlled by an upper-level command-post system 73N6ME «Baikal-1ME» together with 1-4 units of PPRU-M1 (PPRU-M1-2), integrating it with SA-19 "Grison" (9K22 Tunguska) (6-24 units total) into an air defence brigade, as well as SA-10/20 and SA-5 Gammon and SA-2 Guideline and SA-3 Goa and Air Force.[23][24] With the use of the mobile command center Ranzhir or Ranzhir-M (GRAU designations 9S737, 9S737М) the Buk missile system allows creation of mixed groups of air defense forces, including Tor, Tungushka, Strela-10, and Igla.[25] "Senezh" [26] is another optional command post for a free mixing of any systems. In addition to mixing their potential, each of the air defense system with the aid of Senezh[27][28][29] can become part of another air defense system (missile's / radar's / targeting information). And do not lose quality. The system works automatically.[30] But for the full realization of all functions, a Senezh-control system need various other monitoring systems for air defense and air force. Otherwise a Senezh system will work as a command center, but not within a free association.
3S90 "Uragan" / M-22

The 3S90 "Uragan" (Template:Lang-ru; hurricane) is the naval variant of the 9K37 "Buk" and has the NATO reporting name "Gadfly" and US DoD designation SA-N-7, it also carries the designation M-22. The export version of this system is known as "Shtil" (Template:Lang-ru; still). The 9М38 missiles from the 9K37 "Buk" are also used on the 3S90 "Uragan". The launch system is different with missiles being loaded vertically onto a single arm trainable launcher, this launcher is replenished from an under-deck magazine with a 24 round capacity, loading takes 12 seconds to accomplish.[9] The Uragan utilises the MR-750 Top Steer D/E band as a target acquisition radar (naval analogue of the 9S18 or 9S18M1) which has a maximum detection range of 300 km (190 mi) depending on the variant. The radar performing the role of the 9S35 the 3R90 Front Dome H/I band tracking and engagement radar with a maximum range of 30 km (19 mi).
Operation 1974 (replacement of on a ship air defenses) has been tested on the new ship in 1980. It was adopted in 1983.[31]
3S90 "Ezh"
The modernised version of the 3S90m is the 9K37M1-2 (or 9K317E) "Ezh", which carries the NATO reporting name "Grizzly" or SA-N-12 and the export designation "Shtil". It uses the new 9M317 missile.
In 1997, India signed a contract for the three Project 1135.6 frigates with "Shtil". Later, when the decision was made to modernize it with a new package of hardware & missiles, the name changed to "Shtil-1".
3S90M "Shtil-1"
In 2004, the first demonstration module of the new 9M317ME missile was presented by Dolgoprudniy Scientific and Production Plant for the upgraded 3S90M "Shtil-1" naval missile system (jointly with 'Altair'). Designed primary for the export purpose, its latest variant used a vertical launch missile which is fired from under-deck silos clustered into groups of twelve, twenty-four or thirty-six. The first Shtil-1 systems were installed into ships exported to India and China.[32][33] Old systems Uragan, Ezh and Shtil could be upgraded to Shtil-1 by replacing the launcher module inside the ship.
The reaction time is 5–10 seconds (Shtil-1).[34] The interval between starts is less 2 seconds. To protect against boats, helicopters, aircraft, anti-ship missiles.[35]
Missiles
| 9М38 | |
|---|---|
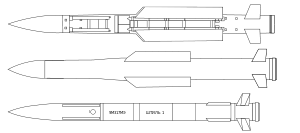 Comparison of 9M38M1, 9M317 and 9M317ME surface-to-air missiles of the Buk missile system | |
| Type | Surface-to-air missile |
| Place of origin | Soviet Union |
| Production history | |
| Variants | 9М38, 9М38M1, 9M317 |
| Specifications (9М38, 9M317) | |
| Mass | 690 kg, (1521 Lbs) 715 kg,(1576 Lbs) |
| Length | 5.55 m (18'-3") |
| Diameter | 0.4 m (15 3/4") (wingspan 0.86 m)(2'-10") |
| Warhead | Frag-HE |
| Warhead weight | 70 kg,(154.3 Lbs) |
Detonation mechanism | Radar proximity fuse |
| Propellant | Solid propellant rocket |
Operational range | 30 kilometres (19 mi) |
| Flight altitude | 14,000 metres (46,000 ft) |
| Maximum speed | Mach 3 |
Guidance system | Semi-active radar homing |
Launch platform | See system composition |
9М38 and 9М38M1 missile
The 9M38 uses a single-stage X-winged design without any detachable parts; its exterior design is similar to the American Tartar and Standard surface-to-air missile series, which led to the half-serious nickname of Standardski.[36] The design had to conform to strict naval dimension limitations, allowing the missile to be adapted for the M-22 SAM system in the Soviet Navy. Each missile is 5.55 m (18.2 ft) long, weighs 690 kg (1,520 lb) and carries a relatively large 70 kg (150 lb) warhead which is triggered by a radar proximity fuze. In the forward compartment of the missile, a semi-active homing radar head (9E50, Template:Lang-ru), autopilot equipment, power source and warhead are located. The homing method chosen was proportional navigation. Some elements of the missile were compatible with the Kub's 3M9; for example, its forward compartment diameter (33 cm), which was less than the rear compartment diameter.

The 9M38 surface-to-air missile utilizes a two-mode solid-fuel rocket engine with total burn time of about 15 seconds; the combustion chamber is reinforced by metal. For the purpose of reducing the centering dispersion while in flight, the combustion chamber is located close to the center of the missile and includes a longer gas pipe. The 9M38 is capable of readiness without inspection for at least 10 years of service. The missile is delivered to the army in the 9Ya266 (9Я266) transport container.
The 9М38M1 missile uses active homing when approaching the goal.[37]
9M317 missile
The 9M317 missile was developed as a common missile for the Russian Ground Force's Air Defence Forces (PVO) (using Buk-M1-2) as well as for ship-based PVO of the Russian Navy (Ezh). Its exterior design bears a resemblance to the Vympel R-37 air-to-air missile.
The unified multi-functional 9M317 (export designation 9M317E) can be used to engage aerodynamic, ballistic, above-water and radio contrast targets from both land and sea. Examples of targets include tactical ballistic missiles, strategic cruise missiles, anti-ship missiles, tactical, strategic and army aircraft and helicopters. It was designed by OJSC Dolgoprudny Scientific Production Plant (DNPP). The maximum engagable target speed was 1200 m/s[38] and it can tolerate an acceleration overload of 24G. It was first used with Buk-M1-2 system of the land forces and the Shtil-1 system of the naval forces.
In comparison with 9M38M1, the 9M317 has a larger defeat area, which is up to 45 km of range and 25 km of altitude and of lateral parameter, and a larger target classification. Externally the 9M317 differs from the 9M38M1 by a smaller wing chord. It uses the inertial correction control system with semi-active radar homing, utilising the proportional navigation (PN) targeting method.
The semi-active missile homing radar head (used in 9E420, Template:Lang-ru) as well as 9E50M1 for the 9M38M1 missile (9E50 for 9M38) and 1SB4 for Kub missile (Template:Lang-ru) was designed by MNII Agate (Zhukovskiy) and manufactured by MMZ at Ioshkar-Ola.
The 9M317 missile uses active homing when approaching the goal.[39][40]
9M317M and 9M317A missile development projects
Currently, several modernized versions are in development, including the 9M317M / 9M317ME, and active radar homing (ARH) missile 9M317A / 9M317MAE.
The lead developer, NIIP, reported the testing of the 9M317A missile within Buk-M1-2A "OKR Vskhod" (Sprout in English) in 2005.[41] The range is reported as being up to 50 km (31 mi), maximum altitude around 25 km (82,000 ft) and maximum target speed around Mach 4. The weight of the missile has increased slightly to 720 kg (1587 lb).
The missile's Vskhod development program for the Buk-M1-2A was completed in 2011. This missile could increase the survival capability and firing performance of the Buk-M1-2A using its ability to hit targets over the horizon.[42]
In 2011, Dolgoprudny NPP completed preliminary trials of the new autonomous target missile system OKR Pensne (pince-nez in English) developed from earlier missiles.[42]
9M317ME missile
The weight of the missile is 581 kg, including the 62 kg blast fragmentation warhead initiated by a dual-mode radar proximity fuze. Dimensions of the hull are 5.18 m length; 0.36 m maximum diameter. Range is 2.5–32 km in a 3S90M "Shtil-1" naval missile system. Altitude of targets from 15 m up to 15 km (and from 10 m to 10 km against other missiles). 9M317ME missiles can be fired at 2-second intervals, while its reaction (readiness) time is up to 10 s.
The missile was designed to be single-staged, inertial guidance, radio control mid-course update and terminal semi-active radar homing.[32]
The tail surfaces have a span of 0.82 m when deployed after the missile leaves the launch container by a spring mechanism. Four gas-control vanes operating in the motor efflux turn the missile towards the required direction of flight. After the turnover manoeuvre, they are no longer used and subsequent flight controlled via moving tail surfaces. A dual-mode solid-propellant rocket motor provides the missile with a maximum speed of Mach 4.5.[43]
Comparison
| Missile (GRAU designation) |
3M9 | 9М38 | 9М38 9М38M1 |
9М38 9М38M1 9М38M2/9M317 |
9M317 | 9M317ME |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| System (GRAU and NATO designation) |
2K12 "Kub" (SA-6) |
9K37 "Buk" (SA-11) |
9K37M "Buk-M1" (SA-11) |
9K37M1-2 "Buk-M1-2" (SA-17) |
9K317E "Buk-M2E"[44] (SA-17) |
3S90M/3S90E "M-22[45] "/"Shtil-1"[32] (SA-N-12) |
| Introduced | 1967[46] | adopted by 1980[47] is used from 1978[48] | 1983[citation needed] is used from 1979[49] | 1998[50] | development is completed 1988,[51][52][53][54] produced from 2007 | 1983 / first seen in 2004[34] |
| Missiles per TEL | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 12/24/36 |
| Missile weight | 599 kg (1321 lb) |
690 kg (1521 lb) |
690 kg (1521 lb) |
9М38M1: – 690 kg (1521 lb); 9M317: – 710–720 kg (1565–1587 lb) |
710–720 kg (1565–1587 lb) |
581 kg |
| Range | 8(6)–22 km (2–15 miles)[46] |
3,5–25 (30) km (3–19 miles) |
3,3–35 km (2–22 miles)[55] |
9М38M1: – 3–42 km (2–26 miles); 9M317: 3–50 km (2–31 miles) |
3–50(M2),[56] 45(M2E)[57] km (2–31(29) miles) |
(M-22=25 km)/3,5-32[58] up to 50 km (taking into account the use against large targets (ships))[59] |
| Range of altitude | 100–7000 m [46] |
25–18000 (20000) m (100-46,000 ft)[47] |
15–22000 m (100-72,000 ft)[55] |
15–25000 m (100-82,000 ft)[60] |
15 of M2E[24] 10 of M2[61]–25000 m (to-82,000 ft) |
(M-22=10)5[62]–15000 m |
| Missile speed (Mach) |
2.8 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4.5 (For M-22 average speed of 1000 m / s) |
| Maximum target speed (Mach) |
2 | 800 m/s[47] | 4 | 4 | to meet (M2E - aerodynamic up to 1100[38] m/s, of ballistic 1200 m/s), pursuing 300–400 m/s[56] | 830 m/s[59]/? |
| Maximum maneuverability (G) (for missiles). |
19/? | 19[63] | 20 | 24[64] | For missiles (24[38]). For target (10[40]). | up to 19/? |
| Simultaneous fire |
1–2 ("Kub"M4/"Buk-1" ) | (2) max 6[49] 18[65] | (2) 18[65] | 22[65][66] 6 old/12 update 1997[64] | 24[24][67] | 2-12[62] (For Shtil-1 directs to 3 missiles simultaneously at each target)[58] |
Other variants
Original design tree
- 9K37-1 'Buk-1' – First Buk missile system variant accepted into service, incorporating a 9A38 TELAR within a 2K12M3 Kub-M3 battery.
- 9K37 'Buk'- The completed Buk missile system with all new system components, back-compatible with 2K12 Kub.
- 9K37M1 'Buk-M1' – An improved variant of the original 9K37 which entered into service with the then Soviet armed forces.
- 9K37M1-2 'Buk-M1-2' ('Gang' for export markets) – An improved variant of the 9K37M1 'Buk-M1' which entered into service with the Russian armed forces.
- 9K317 'Ural' (9K37M2) – initial design of Buk-M2 which entered into service with the Russian armed forces
- 9K317E 'Buk-M2E' - revised design for export markets[68]



- 9K37M1-2A 'Buk-M1-2A' - redesign of Buk-M1-2 for the use of 9M317A missile
- 'Buk-M2EK'[69] – A wheeled variant of Buk-M2 on MZKT-6922 chassis exported to Venezuela and Syria.
- 9K317M 'Buk-M3' (9K37M3) – A zenith-rocket division of it has 36 target channels in total.
Naval version design tree
- 3S90/M-22 'Uragan' (SA-N-7 "Gadfly") – Naval version of the 9K37 Buk missile system with 9M38/9M38M1 missile.
- 3S90 "Ezh" (SA-N-7B/SA-N-12 'Grizzly') – Naval version of the 9K37M1-2 with 9M317 missile.
- 3S90 "Shtil" (SA-N-7C 'Gollum') – Naval export version of the 9K37M1-2 with 9M317E missile.
- 3S90E "Shtil-1" (SA-N-12 'Grizzly') – Naval export version with 9M317ME missile.
- 3S90M "Smerch" (SA-N-12 'Grizzly') – Possible naval version with 9M317M missile.
Copies
 Belarus – In May on the MILEX-2005 exposition in Minsk, Belarus presented their own modification of 9K37 Buk, called Buk-MB.[70] On 26 June 2013 an exported version of Buk-MB was displayed on a military parade in Baku. It included the new 80K6M Ukrainian-build radar on an MZKT chassis (instead the old 9S18M1) and the new Russian-build missile 9M317 (as in Buk-M2).[71]
Belarus – In May on the MILEX-2005 exposition in Minsk, Belarus presented their own modification of 9K37 Buk, called Buk-MB.[70] On 26 June 2013 an exported version of Buk-MB was displayed on a military parade in Baku. It included the new 80K6M Ukrainian-build radar on an MZKT chassis (instead the old 9S18M1) and the new Russian-build missile 9M317 (as in Buk-M2).[71] People's Republic of China
People's Republic of China
- HQ-16 (Hongqi-16) - Co-developed by China and Russia,[72][73] believed to be based on either the SA-11 or SA-17.[72] Credited with a range of 40 km. Also known as the HQ-16A.[73]
- HHQ-16 - Naval variant of the HQ-16 with a range of 35 to 75 km.[72][73]
- LY-80 - Export version of the HQ-16[74]
- HQ-16B - Improved Chinese development of the HQ-16. Reportedly has improved rocket motor and wings, and a range of 70 km.[73]
 Iran – Ra'ad (Thunder) Medium Ranged Surface-to-Air Missile System using Ta'er 2 missiles. It has very similar layout to wheeled Buk-M2EK 9M317. It was shown during 2012 military parade.[75]
Iran – Ra'ad (Thunder) Medium Ranged Surface-to-Air Missile System using Ta'er 2 missiles. It has very similar layout to wheeled Buk-M2EK 9M317. It was shown during 2012 military parade.[75]
System composition
| Complex (GRAU and NATO designation) |
9K37 "Buk" (SA-11) |
9K37-1 "Buk-1" (SA-11) |
9K37M1 "Buk-M1" (SA-11) |
9K37M1-2 "Buk-M1-2" (SA-17) |
9K317E "Buk-M2E" |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Command Post | 9S470 | N/A | 9S470M1 | 9S470M1-2 | 9S510 |
| Surveillance Radar (SURN, SOTs or TAR) |
9S18 Kupol | 1S91M3 | 9S18M1 Kupol-M1 | 9S18М1-1 | 9S112, 9S36 |
| TELAR | 9А310, 9А38 |
9A38 | 9A310M1 | 9A310M1-2 | 9A317 |
| TEL | 9А39 | 2P25M3 | 9A39M1 | 9A39M1, 9A39M1-2 |
9A316 |
9K37 Buk


- Upper level CP (PBU of the zrbr – zenith-rocket brigade) from the structure of ASU Polyana-D4
- 4 × zrdn (zenith-rocket division)
- CP 9S470
- SOTs 9S18 Kupol range up to 120 km (45 km at a height 30 meters).[76]
- 3 × zrbat (zenith-rocket battery)
- 2 × TELAR 9А310
- 1 × TEL 9А39
- Technical service division
- Сommunication service platoon
- 4 × zrdn (zenith-rocket division)
2K12M4 Kub-M4 (9K37-1 Buk-1)
- 1 × SURN 1S91M3 (from the structure of 2K12M3 Kub-M3)
- 4 × TEL 2P25M3 (from the structure of 2K12M3 Kub-M3)
- 1 × TELAR 9A38 (from the structure of 9K37 Buk)
9K37M1 Buk-M1 (Ganges)
Technical service division
- 9V95M1E – mobile automatized control and test station vehicle based on a ZiL-131 with a trailer
- 9V883, 9V884, 9V894 – repair and technical service vehicles based on Ural-43203-1012
- 9V881E – technical service workshop based on Ural-43203-1012
- 9T229 – transporter vehicle for 8 missiles or 6 containers with missiles based on a KrAZ-255Б
- 9T31M – autocrane
- MTO-ATG-M1 – technical service workshop based on ZiL-131
Preparing to fight (inversely) - 5 min. Translation in battle mode, not for the first time in battle (after moving to another place) - no more than 20 seconds.[77] During the exercise, "Defense 92" (1992) SAM family of "Buk" conducted successful firing at targets on the basis of ballistic missile R-17 Elbrus, and on the basis of MLRS rockets "Smerch" (caliber 0.3 meters).[78]
9K37M1-2 Buk-M1-2 (Ural)
A command post vehicle 9S470M1-2 may take control over 4 batteries, each has 1 TELAR 9A310M1-2 with 1 × TEL 9A39M1/9A39M1-2 or 2 batteries, each has 1 target acquisition radar 9S18М1-1 and 2 x TELs 9A39M1
Additionally, the TELAR 9A310M1-2 may take control over the Kub vehicles – just the TEL 2P25 or the self-propelled unit of reconnaissance and guidance 1S91 with a TEL 2P25. In this configuration complex can simultaneously fire two goals instead of one.[64]
Probability of hitting of one rocket is:[66] - Statically flying aircraft - 0.7–0.9; - Maneuvering aircraft with overdrive to 7–8 G - 0.5–0.7; - Tactical ballistic missiles - 0.5–0.7; - Anti-radar missiles - 0.6–0.8; - Cruise missiles - 0.6–0.8.
The composition:[64] command post 9S470M1-2 6 self-propelled fire units 9A310M1-2 can perform all combat functions,[64] including identification of the state of the owner of the object detected.[77] 3 launchers (can fire, transporting and loading of other launchers) installation 9A39M1, target detection station 9S18M1, machine of maintenance 9V881M1-2 with caravan ZIP 9T456, workshop of maintenance SPA-M1, machine of repair and maintenance.
The maximum range of fire against ballistic missiles is 20 km, and the maximum target speed is 1200 m / s.[79] Its capacity of protecting against ballistic missiles are comparable with that of the Patriot PAC-2.[80] However, the height is less.[77] Preparing to fight (inversely) - 5 min.[79] Translation in battle mode, not for the first time in battle (after moving to another place) - no more than 20 seconds.[77] The range for engaging targets on land is 15 km, 25 km on the water.[81] The capture distance of targets with RCS = 5 m² - 40 km.[64] It automatically provides a high resistance to interference and work in several different combat modes, detection range of the locator of early detection 160 km.[77]
Technical service division
- Technical service vehicle MTO 9V881M1-2 with a trailer ZIP 9T456
- Technical service workshop MTO AGZ-M1
- Technical service and maintenance vehicles MRTO: MRTO-1 9V883M1, MRTO-2 9V884M1, MRTO-3 9V894M1
- Transport vehicle (TM) 9T243 with a technological equipment set KTO 9T3184
- Automated control and test mobile station AKIPS 9V95M1
- Workshop vehicle for the missile maintenance 9T458
- Unified compressor station UKS-400V
- Mobile power plant PES-100-T/400-AKP1
9K317 Buk-M2
There was an experimental 9А320 TEL (with 8 missiles).
Some works were conducted to utilize a wheeled vehicles for Buk-M2-1 on a KrAZ-260 chassis, but they were not completed.[82]
Developed in 1988.[83] Accepted for service in 2008.
The structure of the Buk-M2[24][61][84]
- Fighting means
- Anti-aircraft missiles: 9М317
- Self-propelled firing installation: 9А317 and 9А318 (towed), has everything for self-War, reaction time - 5 sec, range to 20 km (reflecting surface=1–2m2 height - 3 km), 18–20 km (rs=1-2m2, height - 10–15m), range of work in the system -5 to + 85 degrees for missile guidance (to search for up to 70 if alone)[38]
- Installation of charging 9А317 and 9А318 or shooting teams 9С510: 9А316 and 9А320;[85]
- Management tools
Command post 9С510, reaction time 2 seconds.
- Radar of targets detection (all directions - 360°) 9С18М1-3, range to 160 km (1-2m2)
Radar of illumination and guidance of missiles or radar of targets detection of range ±60° 9С36.
- 9S36-1 (if derrick is raised as much as possible) range to 120 km (reflecting surface=1–2m2 height - 3 km), 30-35 km (rs=1-2m2, height - 10–15m) [61]
Translation in battle mode for the first time in battle-not more than 5 minutes, but 10–15 minutes when using derrick in which the radar of 9S36-1. Translation in battle mode, not for the first time in battle (after moving to another place) - no more than 20 seconds.[61]
The probability of hitting targets one missile is: (data from the developer and several other sources)
- Aircraft of tactical aviation - 0.9–0.95
- Tactical ballistic missiles - 0.6–0.7 maximum speed of ballistic targets 1200 m / s.
- Cruise missiles - 0.7–0.8
- Hovering helicopters - 0.3–0.4[67]
- Helicopter - 0.7–0.8[61]
- Anti-radiation missile - 0.5–0.7.[56]
The minimum rs to 0.05 square meters. Day-and-night passive optical system for target detection, thermal imager with minimal radiation (9А317 and 9А318)[86] The system operates in a mountainous area without glare.[38]
The normal range of a ballistic missile to intercept with the use Buk is up to 200 km[87]
Buk-M3
This article may require copy editing for grammar, style, cohesion, tone, or spelling. (July 2016) |
The 9K317M 'Buk-M3' (9K37M3) is the latest production version. The Buk-M3 is based on completely new hardware.[88][89] The new Buk-M3 has 36 target channels and features advanced electronic components. Specifications include a maximum target speed of 3,000 m/s (11,000 km/h; 6,700 mph), altitude range of 0.015–35 km (49–114,829 ft) and distance of 2.5–70 km (1.6–43.5 mi). Extensive trials were began in 2015,[90] with the first deliveries planned for 2016.[91][92] (2 into 2016).[93] Probability of hitting the target with one missile: aircraft - 0.95; Tactical ballistic missiles - 0.7; Cruise missiles - 0.8. Increased efficiency against electronic countermeasures and manoeuvring targets.[94] The more compact missiles increase carrying capacity to six missiles.[95] The missile's new HE-fragmentation warhead can more easily penetrate armor.[96] The complex is highly mobile, designed against air, ground and sea targets (the destroyer).[97]
Missile speed of 1,550 m / s. The missile maneuvers and air rudders and by reactive rudders[98] The interval between shots one second in any direction. Targeting by commands or only active homing, or in combination. Thermal Radar works on any targets at any time in any weather. The system is easy to destroy the MGM-140 ATACMS.[99] Photo of the launcher
Radar of illumination and guidance of missiles or radar of targets detection of range ±60° 9S36. The goal at a height of 7–10 meters can be detected at distances of up to 35 km, goal type AGM-158A "JASSM" at a height of 20 m, RCS in the range of 0.1m at a distance of 17 – 18 km.[100] The radar sees targets at a height of 5 meters, in practical shooting demonstrate an ability destroy anti-ship missiles with a flight height of 5 meters.[99]
In June 2016, the "Almaz-Antey" announced successful trials of a new anti-aircraft complex of medium-range "Buk-M3". Firing at the Kapustin Yar in the Astrakhan region was carried out on a ballistic target, which was made by the missile-target. The first brigade set of the SAM "Buk-M3" handed over to the military in 2016.[101][102]
Already in active duty.[103]
Service history
Combat service
- Abkhaz authorities claimed that Buk air defense system was used to shoot down four Georgian drones at the beginning of May 2008.[104]
- Analysts concluded that Georgian Buk missile systems were responsible for downing four Russian aircraft—three Sukhoi Su-25 close air support aircraft and a Tupolev Tu-22M strategic bomber—in the 2008 South Ossetia war.[105] U.S. officials have said Georgia's SA-11 Buk-1M was certainly the cause of the Tu-22M's loss and contributed to the losses of the three Su-25s.[106] According to some analysts, the loss of four aircraft is surprising and a heavy toll for Russia given the small size of Georgia's military.[107][108] Some have also pointed out, that Russian electronic counter-measures systems were apparently unable to jam and suppress enemy SAMs in the conflict[109] and that Russia was, surprisingly, unable to come up with effective countermeasures against missile systems it had designed.[105] Georgia bought these missile systems from Ukraine which had an inquiry to determine if the purchase was illegal.[110]
- The system was used in the downing of the Boeing 777-200ER Malaysia Airlines Flight 17, on 17 July 2014, in eastern Ukraine, which resulted in 298 fatalities.[111][112] Evidence included missile fragments found on site including pieces of warhead stuck in the wreckage as well as non-explosive parts of the missile parts with serial number remnants.[113] Missile fragments were recovered from the bodies of the flight crew.[114] According to one analysis, the launcher belonged to the Russian 53rd Anti-Aircraft Rocket Brigade.[115]
Operators


Current operators

 Egypt – Buk-M1 and Buk-M2 versions[121]
Egypt – Buk-M1 and Buk-M2 versions[121] Finland – In 1996 Finland started operating the missile systems that they received from Russia as debt payment.[122] Due to concerns about susceptibility to electronic warfare, Finland has accelerated the plans to replace the missile system with NASAMS 2.[123][124][125]
Finland – In 1996 Finland started operating the missile systems that they received from Russia as debt payment.[122] Due to concerns about susceptibility to electronic warfare, Finland has accelerated the plans to replace the missile system with NASAMS 2.[123][124][125] Georgia[126]
Georgia[126] India[127]
India[127] Iran - Raad with Taer-2 missiles, copy locally produced from Buk M1-2 obtained.
Iran - Raad with Taer-2 missiles, copy locally produced from Buk M1-2 obtained. North Korea[128]
North Korea[128] People's Republic of China[129] – Improved variant as the HQ-16, a navalized VLS system. Joint People's Republic of China/Russian project to upgrade the naval 9K37M1-2 system 'Shtil' (SA-N-12).
People's Republic of China[129] – Improved variant as the HQ-16, a navalized VLS system. Joint People's Republic of China/Russian project to upgrade the naval 9K37M1-2 system 'Shtil' (SA-N-12). Russia – more than 430 9К37 and 9К317 as of 2016.[130][131][132][133] Replacement of complex 9К37 with the newer 9К317 Buk M2 is planned to be completed by 70% or more by 2020.[134][135][136] 1 battalion of Buk-M3 was delivered in 2016.[137]
Russia – more than 430 9К37 and 9К317 as of 2016.[130][131][132][133] Replacement of complex 9К37 with the newer 9К317 Buk M2 is planned to be completed by 70% or more by 2020.[134][135][136] 1 battalion of Buk-M3 was delivered in 2016.[137] Syria[138] 8 complexes 9К317E Buk-M2E delivered from Russian Federation in 2011 (Stockholm International Peace Research Institute – Arms Transfers Database) for Land Forces + 10/8[139] Buk-M2E for Air Defence.[140] + 20 Buk-M1-2s.[141]
Syria[138] 8 complexes 9К317E Buk-M2E delivered from Russian Federation in 2011 (Stockholm International Peace Research Institute – Arms Transfers Database) for Land Forces + 10/8[139] Buk-M2E for Air Defence.[140] + 20 Buk-M1-2s.[141] Venezuela – Buk-M2EK Received[142] (20 ordered).[143]
Venezuela – Buk-M2EK Received[142] (20 ordered).[143]
Former operators
See also
References
- ^ "Big Russian flotilla led by Admiral Kuznetsov carrier heads for Syrian port". DEBKAfile. 21 August 2008. Retrieved 23 March 2010.
- ^ "Russian mobile surface-to-air missile systems". RIA Novosti. 8 February 2007. Retrieved 18 November 2008.
- ^ "What the Russian papers say". RIA Novosti. 28 August 2007. Retrieved 18 November 2008.
- ^ "Russian Troops to Start Getting Advanced Air Defense Systems in 2016". RIA Novosti. 28 December 2013. Retrieved 29 December 2013.
- ^ "Russian Navy to receive first Shtil SAM systems in 2014". IHS Jane's Missiles & Rockets. 6 November 2013. Retrieved 29 December 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "9K37 Buk (SA-11 Gadfly)". Vestnik PVO (in Russian). 17 November 2004. Retrieved 20 August 2008.
- ^ a b c d "Chief Designer Ardalion Rastov". milparade.udm.ru. 31 August 1998. Archived from the original on 23 January 2009. Retrieved 23 August 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d "M-22 Uragan (SA-N-7 Gadfly)". Vestnik PVO (pvo.guns.ru) (in Russian). 17 November 2004. Retrieved 17 November 2008.
- ^ "Air defense missile complex (ADMC) "Buk-М1-2"". OJSC NIIP. 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ "Smerch/Shtil-1/-2 (SA-N-12 'Grizzly') (Russian Federation), Defensive weapons". Jane's Strategic Weapon Systems. 11 February 2010. Retrieved 21 August 2011.
- ^ "Smerch/Shtil-1/-2 (SA-N-7B/C or SA-N-12 'Grizzly') (Russian Federation), Defensive weapons". Jane's Strategic Weapon Systems. 11 March 2011. Retrieved 21 August 2011.
- ^ "Зенитный ракетный комплекс "Бук-М2Э"". OJSC NIIP (Russian). 2005. Archived from the original on 27 September 2008. Retrieved 23 August 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Russia to boost Ground Forces air defense – commander". RIA Novosti. 21 September 2007. Retrieved 19 November 2008.
- ^ "New variant of TELAR for Buk-M3 missile system was presented in Moscow" (in Russian). military-informant.com. 21 August 2013. Retrieved 3 October 2013.
- ^ "GM 569, 579, 577, 567 (Buk) for ADMC "Buk-M1-2" and "Buk-M2"". JSC MMZ (in Russian). 2011. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ "Mobile simulator SAM Buk-M2E shown at MAKS-2013". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ The MiG-31 Foxhound: One of the World's Greatest Interceptors at Aircraft InFormation.info
- ^ Argon-15 at www.computer-museum.ru
- ^ "topwar.ru > Версия для печати > Армейский самоходный зенитный ракетный комплекс "Бук"". Retrieved 29 September 2016.
- ^ Template:Ru icon KSA KP zrbr 9S52M Polyana-D4M at Missile Technology Information System of BGTU Voenmeh
- ^ Template:Ru icon ASU sg zrk 9S52M1 Polyana-D4M1 at Missile Technology Information System of BGTU Voenmeh
- ^ Template:Ru icon ASU Baikal-1ME at Missile Technology Information System of BGTU Voenmeh
- ^ a b c d Main defense product range at JSC «Concern «Almaz-Antey» website
- ^ Template:Ru icon UBCP 9S737M at Missile Technology Information System of BGTU Voenmeh
- ^ Template:Ru icon Senezh-M1E at OKB Peleng website
- ^ "34Л6 "СЕНЕЖ-М1Э"". Pvo.guns.ru. 18 July 2006. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "Автоматизированная Система Управления". Pvo.guns.ru. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "ВКО". Old.vko.ru. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "АСУ Сенеж-М1Э". Arms-expo.ru. 22 May 2015. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "М-22 "Ураган"". Pvo.guns.ru. 22 May 2009. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ a b c Template:Ru icon Russian Anti-Aircraft Missiles & Systems by Peter F. Berezovsky
- ^ Russia moves to vertical-launch Shtil by Miroslav Gyürösi, Jane's Missiles and Rockets, 18 November 2004
- ^ a b "Штиль-1 с ЗУР 9М317МЭ". Pvo.guns.ru. 22 May 2009. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ «Штиль» от «Авиационного оборудования». rostec.ru (in Russian). 3 July 2013. Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ^ Compare to Concordski
- ^ "9К37М1 "Бук-М1" - зенитный ракетный комплекс малой дальности". Army.lv. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ a b c d e "Зенитный ракетный комплекс средней дальности 9К317 "Бук-М2" | Ракетная техника". Rbase.new-factoria.ru. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "Уникальный зенитный комплекс средней дальности "Бук-2М" » Военное обозрение". Topwar.ru. 15 December 2011. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ a b Юрьевна, Сизова Ирина. Многоцелевой зенитный ракетный комплекс средней дальности «Бук-М2». www.niip.ru (in Russian). Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ^ Template:Ru icon Annual statement of the OJSC Tikhomirov Scientific Research Institute of Instrument Design in 2005
- ^ a b "2011 Financing Statement of the OJSC DNPP". ZAO SCRIN (in Russian). Dolgoprudny Scientific Production Plant. 2012. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ Batch 2 Of Three Project 1135.6 Frigates Being Readied, Pakistan Defence, 14 April 2011
- ^ "Russia forces USA out from its traditional arms markets". Pravda.Ru. 16 May 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2012.
- ^ "Комплекс M-22 Ураган | Ракетная техника". Rbase.new-factoria.ru. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ a b c "Зенитный ракетный комплекс 2К12 Куб". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ a b c "Зенитный ракетный комплекс 9К37 Бук". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ "ЗРК БУК- обзор". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ a b "-1". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ "Buk-M2E Air Defence Missile System - Army Technology". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ "В Индонезии устроили презентацию российского комплекса "Бук-М2Э" - ОРУЖИЕ РОССИИ Информационное агентство". Arms-expo.ru. 22 May 2015. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "ЗРК "Бук-М2Э" » Военное обозрение". Topwar.ru. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "-2, - "-2"". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ "ЗРК "Бук-М2Э"". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ a b "Зенитный ракетный комплекс 9К37 Бук-М1". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ a b c "Зенитный ракетный комплекс средней дальности 9К317 "Бук-М2"". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ Основная продукция военного назначения (in Russian). Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ a b ""Штиль-1" - Алмаз-Антей". Almaz-antey.ru. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ a b «Штиль» - российский зенитно-ракетный комплекс, модульные комплекты которого поступят на вооружение ВМФ России в 2014 году (in Russian). 23 September 2013. Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ^ "Buk-M1-2 - Almaz Antey Corp". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ a b c d e Template:Ru icon ZRK SD 9K317 "Buk-M2" at Missile Technology Information System of BGTU Voenmeh
- ^ a b "Корабельный зенитный ракетный комплекс "Штиль-1" | Ракетная техника". Rbase.new-factoria.ru. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "ЗРК "Бук"-Зенитная ракета 9М38". Pvo.guns.ru. 20 July 2000. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f "Зенитный ракетный комплекс Бук-М1-2 (Урал)". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ a b c Vasily N. Ya, Gurinovitch AL, anti-aircraft missile systems, page 251
- ^ a b Сизова Ирина Юрьевна. "Зенитный ракетный комплекс "Бук-М1-2"". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ a b Multichannel middle-range ADMC «Buk-М2E» at NIIP website
- ^ "Russia to exhibit Buk-M2 air defense system at LAAD 2007". RIA Novosti. 17 April 2007. Retrieved 20 August 2008.
- ^ Russia celebrates the Day of military drivers, 29 May 2010 Template:Ru icon
- ^ Army prepares to test upgraded BUK missile system, Charter'97, 11.10.2005
- ^ Template:Ru iconBuk-MB on a military parade in Baku, Voenno-politicheskoe obozrenie, 26 June 2013
- ^ a b c Schwartz, Paul (August 2015). Russia’s Contribution to China’s Surface Warfare Capabilities (PDF) (Report). Center for Strategic and International Studies. p. 28. Retrieved 9 October 2016.
- ^ a b c d Fisher, Richard D. Jr.; Gibson, Neil (7 September 2016). "China develops longer-range HQ-16 SAM variant". janes.com. Retrieved 10 October 2016.
- ^ Blasko, Dennis (2012). The Chinese Army Today (2nd ed.). Routledge. p. 163. ISBN 9780415783224.
- ^ "Iran tests new anti-air missile defense: Guard". The Daily Star Newspaper - Lebanon. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ "ЗРК "Бук"-Станция обнаружения и целеуказания". Pvo.guns.ru. 20 July 2000. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ a b c d e "RusArmy.com -". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ "ЗРК "Бук-М1"". Pvo.guns.ru. 21 July 2000. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ a b Бук-М1-2 - Алмаз-Антей. www.almaz-antey.ru (in Russian). Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ^ http://rbase.new-factoria.ru/sites/default/files/missile/c300v/s-300vm-envel.jpg
- ^ ЗРК "Бук-М1-2"/ (экспорт. "Урал"). pvo.guns.ru (in Russian). Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ^ Template:Ru icon History of the testings on Emba firing range
- ^ "Дальность "Бук-М3" достигла 70 км, по ряду параметров он превзошел С-300". Retrieved 29 September 2016.
- ^ "Зенитно-ракетный комплекс "Бук-М2" принят на вооружение в башкирской бригаде ПВО". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ "Зенитный ракетный комплекс "Бук-М2Э" | Армейский вестник". army-news.ru (in Russian). 6 January 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ^ ""Бук" и "Тунгуска": опции совершенства". www.oborona.ru. Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ^ Источник: комплекс ПВО "Бук-М3" примут на вооружение до конца года (in Russian). Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ^ "ANTIAIRCRAFT MISSILE SYSTEM 9К317М "BUK-M3"". Nevskii-bastion.ru. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ МОСКВА, ОРУЖИЕ РОССИИ www.arms-expo.ru 12 (22 May 2015). "До конца 2015 года комплекс ПВО "Бук-М3" будет принят на вооружение - ОРУЖИЕ РОССИИ Информационное агентство". Arms-expo.ru. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "НИИП им. Тихомирова: госиспытания Т-50 начнутся в марте-апреле | РИА Новости". Ria.ru. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "Новейший зенитно-ракетный комплекс "Бук-М3" начнет поступать в войска с 2016 года". Russian.rt.com. 31 December 2013. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "ВЗГЛЯД / Минобороны: Поступление ЗРК "Бук-М3" в войска ожидается в 2016 году". Vz.ru. 28 December 2013. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ askof. "В этом году Минобороны получит несколько комплектов ЗРК "Тор-М2" и "Бук-М3"". Retrieved 29 September 2016.
- ^ Имя *. "Бук-М3 самоходный ЗРК | огнестрельное оружие России". Rus-guns.com. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ The Russian-made Buk-M3 air defense system will use new cutting-edge missile - Armyrecognition.com, 27 December 2015
- ^ ""Бук-М3" против ATACMS: почему российские ракеты превосходят американский комплекс". 6 January 2016. Retrieved 29 September 2016.
- ^ http://www.oborona.ru/includes/periodics/priority/2016/0629/174618663/detail.shtml
- ^ http://army-news.ru/2015/06/buk-m3-vyvedet-armejskuyu-pvo-na-novyj-uroven/
- ^ a b http://tvzvezda.ru/news/forces/content/201601060753-g1ze.htm
- ^ Даманцев, Евгений. ""Бук-М3" выведет армейскую ПВО на новый уровень - Армейский вестник". Retrieved 29 September 2016.
- ^ "Rogozin told the Russian anti-aircraft missiles of the new generation". LNRMedia. 6 August 2016.
- ^ https://sputniknews.com/military/201610211046578106-russia-buk-systems/
- ^ https://rg.ru/2016/10/24/pervyj-divizion-zrk-buk-m3-prishel-v-vojska.html
- ^ "SA-11 'Gadfly' Used to Down Georgian Drones". Abkhaz FM, Civil Georgia (in Georgian). The Georgian Times. 6 May 2008.
- ^ a b "Air Defense: Russia Takes A Beating Over Georgia". StrategyWorld.com. 14 August 2008. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ Georgian Military Folds Under Russian Attack By David A. Fulghum, Douglas Barrie, Robert Wall and Andy Nativi, AW&ST, 15 August 2008
- ^ War Reveals Russia's Military Might and Weakness By Vladimir Isachenkov, Associated Press, 18 August 2008
- ^ Georgia war shows Russian army strong but flawed, Reuters, 20 August 2008
- ^ Russian Army's weaknesses exposed during war in Georgi, Nikita Petrov, RIA Novosti), 9 September 2008
- ^ "Yushchenko may have to answer for illegal arms sales to Georgia" (in Russian (English Translation)). Voice of Russia. 26 October 2010. Retrieved 27 October 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ Gregory Katz and Matthew Knight (17 July 2014). "Buk Missile Suspected in Malaysia Plane Disaster". ABC News. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 18 July 2014. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "MH17 Ukraine disaster: Dutch Safety Board blames missile". 13 October 2015. Retrieved 29 September 2016 – via www.bbc.co.uk.
- ^ "Evidence proving that flight MH-17 was taken down by a BUK missile". rtlnieuws. 19 March 2015. Retrieved 9 April 2015.
- ^ "Bodies of MH17 victims 'contain missile fragments', SBU says". Ukraine Today. 19 December 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
Some of the bodies of the passengers of Malaysia Airlines Flight MH17, which crashed in Donetsk on July 17, contain metal fragments that indicate the plane was shot down by a surface-to-air missile, Ukraine's SBU security service said on Friday
- ^ Oliphant, Roland (3 May 2016). "'Russian army supplied MH17 missile', report claims". The Telegraph. Retrieved 10 May 2016.
- ^ "ForcesDZ • Afficher le sujet - Buk-M2E [SA-17 Grizzly]". www.forcesdz.com. Retrieved 29 November 2016.
- ^ "Azerbaijan to demonstrate "BUK" anti-aircraft missile complex". News.Az. 20 June 2013. Retrieved 23 June 2013.
- ^ "Tikhomirov Instrument Research Institute 9K37 Buk (SA-11 'Gadfly') low to high-altitude surface-to-air missile system". Jane's Information Group. 20 March 2008. Retrieved 4 August 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "The "BUK" Ground Force Air Defense System". State Company "Ukroboronservice". Ukraine. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ Source: Military Balance 2016, page 206
- ^ "Egyptian President Reinforces Friendship with Russia – Kommersant Moscow". Kommersant.com. Retrieved 20 February 2012.
- ^ Video of Buk firing, Finnish Defence Forces website [dead link]
- ^ "Pääkaupunkiseudun ilmasuojassa paljastui aukko". Suomen Kuvalehti (in Finnish). Pekka Ervasti. 3 June 2008. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ "Finland Updating Its Air Defense Systems". Defense Industry Daily. 10 September 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ "BUK M1 -ilmatorjuntajärjestelmä löytyy edelleen myös Suomesta – video". YLE (in Finnish). 23 July 2014. Retrieved 2 August 2014.
- ^ "Armament of the Georgian Army". Geo-army.ge. Archived from the original on 9 March 2012. Retrieved 20 February 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Project 15 D Dehli Class Destroyer". globalsecurity.org. 10 August 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ Армия Ким Чен Ира, Анатолий Цыганок. ПОЛИТ.РУ, 16 October 2006
- ^ New HQ-16 surface to air missile ready for action: PLA, China Military News, 28 September 2011
- ^ Source: Military Balance 2016, page 190
- ^ Source: Military Balance 2016, page 195
- ^ Source: Military Balance 2016, page 197
- ^ Source: Military Balance 2016, page 199
- ^ "Buk-M2 goes on combat duty for anti-aircraft defence". Rambler News (in Russian). 30 November 2011. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ "Russian Land Forces will dismiss the old defense technology modernization programs". Lenta.ru (in Russian). 28 February 2011. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ Moscow Defense Brief № 1, 2011
- ^ http://bmpd.livejournal.com/2198822.html
- ^ "9K37 Buk". Jane's Information Group. 17 November 2008. Retrieved 19 November 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "Trade Registers". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ "Чем будет воевать Сирия в случае агрессии стран западной коалиции?". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ The International Institute For Strategic Studies IISS The Military Balance 2012. — Nuffield Press, 2012. — С. 349 с
- ^ "Russian Photos (updated on regular basis) - Page 3675". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ SIPRI Arms Transfers Database. Information generated: 09 March 2014.
Sources
- What is a buk missile? at The Wall Street Journal
- V. Tikhomirov Scientific Research Institute of Instrument Design Website (Russian manufacturer of Buk)
- "SA-11 GADFLY (9K37M1 BUK-M1)". Federation of American Scientists. 20 June 2000.
- Buk-M1-2 air defense missile system has no equals in terms of combat employment, Yevgeny Pigin, Gennady Kaufman, Military Parade, 1998.
- "SA-11 Gadfly / 9K37M1 Buk". warfare.be. 2004–2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- Buk SA-11 Gadfly. Prospects for Buk-M1-2 air defense missile system at enemyforces.com
Russian sources
- Template:Ru icon Ulyanovsk Mechanical Plant
- Template:Ru icon 9K37-1 Buk-1 (SA-11 Gadfly) · TELAR 9A38 · 9K37 Buk (SA-11 Gadfly) · CP 9S470 · SURN 9S18 Kupol (NATO classification – Tube Arm) · TELAR 9A310 · TEL 9A39 · Buk-M1 (export name – Gang) · Buk-M1-2 (export name – Ural) · Comparison table of technical specifications of Buk, Buk-M1, Buk-M1-2 · Closing article for Buk · Photos of Buk-M1 in Finnish Army · M-22 Uragan (SA-N-7 Gadfly) · 9M38 · 9M317 at Vestnik PVO website
