Domestic policy of Vladimir Putin
 |
|---|
The domestic policies of Vladimir Putin concerns the internal Russian policies of Vladimir Putin during his tenure as President of Russia, as well as the effects of Putinism and the Putin legislative program within Russia. He previously served as president from 2000 to 2008, and has held the position since 2012.
Background
Putin's domestic policies, especially early in his first presidency, were aimed at creating a strict "vertical of power". On 13 May 2000, he issued a decree dividing the 89 federal subjects of Russia between 7 federal districts overseen by representatives named by himself in order to facilitate federal administration. Putin also pursued a policy of enlargement of federal subjects: their number was reduced from 89 in 2000 to the present 83 after the autonomous okrugs of Russia were merged with their parent subjects.

According to Stephen White, Russia under the presidency of Putin made it clear that it had no intention of establishing a "second edition" of the American or British political system, but rather a system that was closer to Russia's own traditions and circumstances.[1] Putin's administration has often been described as a "sovereign democracy".[2] First proposed by Vladislav Surkov in February 2006, the term quickly gained currency within Russia and arguably unified various political elites around it. According to its proponents, the government's actions and policies ought above all to enjoy popular support within Russia itself and not be determined from outside the country.[3][4]
In July 2000, according to a law proposed by him and approved by the Federal Assembly of Russia, Putin gained the right to dismiss heads of the federal subjects. In 2004, the direct election of governors by popular vote was ended. This was seen by Putin as a necessary move to stop separatist tendencies and get rid of those governors who were connected with organised crime.[5] The measure proved to be temporary: in 2012, as proposed by Putin's successor Dmitry Medvedev, the direct election of governors was re-introduced.[6] Along with the return of elected governors, Medvedev's reforms also simplified the registration of political parties and reduced the number of signatures required by non-parliamentary parties and independent candidates to participate in elections,[6] thus reverting or further loosening the restrictions imposed by previous Putin-endorsed legislation. Notably, the tough electoral legislation has been among the government actions effected under Putin's presidency that have been criticised by many independent Russian media outlets and Western commentators as anti-democratic.[7][8]
During his first term in office, Putin moved to curb the political ambitions of some of the Yeltsin-era oligarchs, resulting in the exile or imprisonment of such people as Boris Berezovsky, Vladimir Gusinsky, Mikhail Khodorkovsky; other oligarchs soon joined Putin's camp.[citation needed]
Putin presided over an intensified fight with organised crime and terrorism that resulted in two times lower murder rates by 2011,[9] as well as significant reduction in the numbers of terrorist acts by the late 2000s (decade).[10]
Putin succeeded in codifying land law and tax law and promulgated new codes on labour, administrative, criminal, commercial and civil procedural law.[11] Under Medvedev's presidency, Putin's government implemented some key reforms in the area of state security, the Russian police reform and the Russian military reform.
Economic, industrial, and energy policies

Under the first Putin administration the economy made real gains of an average 7% per year (2000: 10%, 2001: 5.1%, 2002: 4.7%, 2003: 7.3%, 2004: 7.2%, 2005: 6.4%, 2006: 8.2%, 2007: 8.5%),[12] making it the 7th largest economy in the world in purchasing power. Russia's nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP) increased 6 fold, climbing from 22nd to 10th largest in the world. In 2007, Russia's GDP exceeded that of Russian SFSR in 1990, meaning it has overcome the devastating consequences of the 1998 financial crisis and preceding recession in the 1990s.[13]
During Putin's first term of eight years in office, industry grew by 76%, investments increased by 125%,[13] and agricultural production and construction increased as well. Real incomes more than doubled and the average monthly salary increased sevenfold from $80 to $640.[14][15] From 2000 to 2006 the volume of consumer credit increased 45 times[16][17] and the middle class grew from 8 million to 55 million. The number of people living below the poverty line decreased from 30% in 2000 to 14% in 2008.[13][18]
In 2001, Putin, who has advocated liberal economic policies, introduced a flat tax rate of 13%;[19][20] the corporate rate of tax was also reduced from 35 percent to 24 percent;[19] Small businesses also get better treatment. The old system with high tax rates has been replaced by a new system where companies can choose either a 6-percent tax on gross revenue or a 15-percent tax on profits.[19] The overall tax burden is lower in Russia than in most European countries.[21]
A central concept in Putin's economic thinking was the creation of so-called National champions, vertically integrated companies in strategic sectors that are expected not only to seek profit, but also to "advance the interests of the nation". Examples of such companies include Gazprom, Rosneft and United Aircraft Corporation.[22]
Before the Putin era, in 1998, over 60% of industrial turnover in Russia was based on barter and various monetary surrogates. The use of such alternatives to money has now fallen out of favour, boosting economic productivity significantly. Besides raising wages and consumption, Putin's government has received broad praise also for eliminating this problem.[23]
Some oil revenue went to the stabilization fund established in 2004. The fund accumulated oil revenue, allowing Russia to repay all of the Soviet Union's debts by 2005. In early 2008, it was split into the Reserve Fund (designed to protect Russia from possible global financial shocks) and the National Welfare Fund, whose revenues will be used for a pension reform.[13]
Inflation remained a problem however, as between 1999–2007 it was kept at the forecast ceiling only twice, and in 2007 the inflation exceeded that of 2006, continuing an upward trend at the beginning of 2008.[13] The Russian economy is still commodity-driven despite its growth. Payments from the fuel and energy sector in the form of customs duties and taxes accounted for nearly half of the federal budget's revenues. The large majority of Russia's exports are made up of raw materials and fertilizers,[13] although exports as a whole accounted for only 8.7% of the GDP in 2007, compared to 20% in 2000.[24]
In December 2011, after 15 years of negotiations, Russia finally joined the World Trade Organisation. The accession to WTO was expected to be ratified by Russian Parliament in the spring of 2012.

To boost the market share of locally produced vehicles and support the Russia's automotive industry, the government under Putin implemented several protectionist measures and launched programs to attract foreign producers into the country. In late 2005, the government enacted legislation to create special economic zones (SEZ) with the aim of encouraging investments by foreign automotive companies. The benefits of operating in the special economic zones include tax allowances, abolishment of asset and land taxes and protection against changes in the tax regime. Some regions also provide extensive support for large investors (over $100 million.) These include Saint Petersburg/Leningrad Oblast, Kaluga Oblast and Kaliningrad Oblast.[25] Under Putin as President and Premier, most of the world's largest automotive companies opened plants in Russia, including Ford Motor Company, Toyota, General Motors, Nissan, Hyundai Motor, Suzuki, Magna International, Scania and MAN SE.
In 2005, Putin initiated an industry consolidation programme to bring the main aircraft producing companies under a single umbrella organization, the United Aircraft Corporation (UAC). The aim was optimize production lines and minimise losses. The programme was divided in three parts: reorganization and crisis management (2007–2010), evolution of existing projects (2010–2015) and further progress within the newly created structure (2015–2025).[26]
The UAC, one of the so-called national champions and comparable to EADS in Europe, enjoyed considerable financial support from the Russian government, and injected money to the companies it had acquired to improve their financial standing. The deliveries of civilian aircraft increased to 6 in 2005, and in 2009 the industry delivered 15 civilian aircraft, worth 12.5 billion roubles, mostly to domestic customers.[27] Since then Russia has successfully tested the fifth generation jet fighter, Sukhoi PAK FA, and started the commercial production of the regional airliner Sukhoi Superjet 100, as well as started developing a number of other major projects.
In a similar fashion, Putin created the United Shipbuilding Corporation in 2007, which led to the recovery[citation needed] of shipbuilding in Russia. Since 2006, much efforts were put into consolidation and development of the Rosatom Nuclear Energy State Corporation, which led to the renewed construction of nuclear power plants in Russia as well as a vast activity of Rosatom abroad, buying huge shares in world's leading uranium production companies and building nuclear power plants in many countries, including Iran, China, Vietnam and Belarus.[citation needed] In 2007, the Russian Nanotechnology Corporation was established, aimed to boost the science and technology and high-tech industry in Russia.[28]
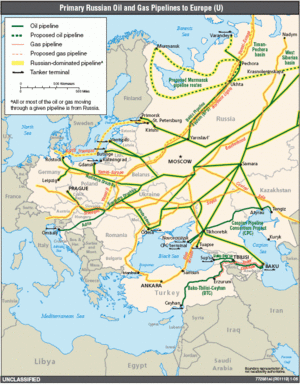
In the decade following 2000, energy in Russia helped transform the country, especially oil and gas energy. This transformation promoted Russia's well-being and international influence, and the country was frequently described in the media as an energy superpower.[29] Putin oversaw growing taxation of oil and gas exports which helped finance the budget, while the oil industry of Russia, production, and exports all significantly grew.
Putin sought to increase Russia's share of the European energy market by building submerged gas pipelines bypassing Ukraine and the New Europe (the countries which were often seen as non-reliable transit partners by Russia, especially following Russia-Ukraine gas disputes of the late 2000s (decade)). The pipeline projects backed by Putin include the Blue Stream from Russia to Turkey (build on the Black Sea bed), Nord Stream from Russia to Germany (the longest sub-sea pipeline in the world, built through the Baltic Sea) and the planned South Stream from Russia to the Balkans and Italy (via the Black Sea). Russia also undermined the rival pipeline project Nabucco by buying the Turkmen gas and redirecting it into Russian pipelines.
On the other hand, Russia diversified its export markets by building the Trans-Siberian oil pipeline to the markets of China, Japan and Korea, as well as the Sakhalin–Khabarovsk–Vladivostok gas pipeline in the Russian Far East. Russia has built LNG plant on Sakhalin and is building another one in Primorye, aiming to increase the overseas gas exports. Meanwhile, in the Gulf of Finland Russia has built a major Ust-Luga port connected to the Baltic Pipeline System-II, which allowed to export oil without transit through the ports of the Baltic states. The share of processed oil slowly grows with major oil refineries being built in Tatarstan and other regions of Russia.
Putin also presided over resuming the construction of major hydropower plants, such as the Bureya Dam and the Boguchany Dam, as well as the restoration of the nuclear industry of Russia, with some 1 trillion rubles ($42.7 billion) allocated from the federal budget to nuclear power and industry development before 2015.[30] A large number of nuclear power stations and units are currently being constructed by the state corporation Rosatom in Russia and abroad.
Arctic policy

Putin has sought to increase Russian military and economic presence in the Arctic. In August 2007, a Russian expedition named Arktika 2007, led by Artur Chilingarov, planted a Russian flag on the seabed below the North Pole to underline Russia's 2001 claim submission.[31] In June 2008 General Vladimir Shamanov announced that Russia would increase the operational radius of its Northern Fleet submarines.[32] and in July 2011, Defense Minister Anatoly Serdyukov announced plans for two brigades to be stationed in the Arctic.[33]
A construction program of floating nuclear power plants will provide power to Russian Arctic coastal cities and gas rigs. A 21,500-ton barge with twin 35-megawatt reactors, the Akademik Lomonosov, will go into operation in 2012.[34][35] The Prirazlomnoye field, an offshore oilfield in the Pechora Sea that will include up to 40 wells, is currently under construction and drilling is expected to start in early 2012. It will have the world's first ice-resistant oil platform and will also be the first offshore Arctic platform.[36][37]
In August 2011 Rosneft, a Russian government-operated oil company, signed a deal with ExxonMobil to receive oil assets in exchange for the joint development of Russian Arctic resources by both companies.[38] The agreement includes a $3.2 billion hydrocarbon exploration of the Kara and Black seas,[39] as well as joint development of ice-resistant drilling platforms and other Arctic technologies.[40] "The scale of the investment is very large. It’s scary to utter such huge figures" said Putin on signing the deal.[38]
Environmental policy

In 2004, President Putin signed the Kyoto Protocol treaty designed to reduce greenhouse gases.[41] However Russia did not face mandatory cuts, because the Kyoto Protocol limits emissions to a percentage increase or decrease from 1990 levels and Russia's greenhouse-gas emissions fell well below the 1990 baseline due to a drop in economic output after the breakup of the Soviet Union.[42]
Putin personally supervises and/or promotes a number of protection programmes for rare and endangered animals in Russia:
- The Amur Tiger Programme[43]
- The White Whale Programme[44]
- The Polar Bear Programme[45]
- The Snow Leopard Programme[46]
Religions policy
Orthodox Christianity, Islam, Buddhism and Judaism, defined by law as Russia's traditional religions and a part of Russia's "historical heritage"[47] enjoyed limited state support in the Putin era. The vast construction and restoration of churches, started in 1990s, continued under Putin, and the state allowed the teaching of religion in schools (parents are provided with a choice for their children to learn the basics of one of the traditional religions or secular ethics). His approach to religious policy has been characterised as one of support for religious freedoms, but also the attempt to unify different religions under the authority of the state.[48] In 2012, Putin was honored in Bethlehem and a street was named after him.[49]

Putin regularly attends the most important services of the Russian Orthodox Church on the main Orthodox Christian holidays. He established a good relationship with Patriarchs of the Russian Church, the late Alexy II of Moscow and the current Kirill of Moscow. As President, he took an active personal part in promoting the Act of Canonical Communion with the Moscow Patriarchate, signed 17 May 2007 that restored relations between the Moscow-based Russian Orthodox Church and the Russian Orthodox Church Outside Russia after the 80-year schism.[50]
Putin and United Russia enjoy high electoral support in the national republics of Russia, in particular in the Muslim-majority republics of Povolzhye and the North Caucasus.
Under Putin, the Hasidic FJCR became increasingly influential within the Jewish community, partly due to the influence of Federation-supporting businessmen mediated through their alliances with Putin, notably Lev Leviev and Roman Abramovich.[51][52] According to the JTA, Putin is popular amongst the Russian Jewish community, who see him as a force for stability. Russia's chief rabbi, Berel Lazar, said Putin "paid great attention to the needs of our community and related to us with a deep respect."[53]
Military development
The resumption of long-distance flights of Russia's strategic bombers was followed by the announcement by Russian Defense Minister Anatoliy Serdyukov during his meeting with Putin on 5 December 2007, that 11 ships, including the aircraft carrier Kuznetsov, would take part in the first major navy sortie into the Mediterranean since Soviet times.[54] The sortie was to be backed up by 47 aircraft, including strategic bombers.[55]

While from the early 2000s (decade) Russia started pumping more money into its military and defence industry, it was only in 2008 that the full-scale Russian military reform began, aimed to modernize Russian Armed Forces and made them significantly more effective. The reform was largely carried by Defense Minister Anatoly Serdyukov during Medvedev's Presidency, under supervision of both Putin, as the Head of Government, and Medvedev, as the Commander-in-Chief of the Russian Armed Forces.
Key elements of the reform included reducing the armed forces to a strength of one million; reducing the number of officers; centralising officer training from 65 military schools into 10 'systemic' military training centres; creating a professional NCO corps; reducing the size of the central command; introducing more civilian logistics and auxiliary staff; elimination of cadre-strength formations; reorganising the reserves; reorganising the army into a brigade system; reorganising air forces into an air base system instead of regiments.[56]
The number of Russia's military districts was reduced to just 4. The term of draft service was reduced from two years to one, which put an end to the old harassment traditions in the army, since all conscripts became very close by draft age. The gradual transition to the majority professional army by the late 2010s was announced, and a large programme of supplying the Armed Forces with new military equipment and ships was started. The Russian Space Forces were replaced on 1 December 2011 with the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces.
In spite of Putin's call for major investments in strategic nuclear weapons, these will fall well below the New START limits due to the retirement of aging systems.[57]
References and notes
- ^ White, Stephen (2010). "Classifying Russia's Politics". In White, Stephen (ed.). Developments in Russian Politics 7. New York: Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-230-22449-0.
- ^ R. Sakwa, Putin: Russia's Choice, 2008, p. 42-43
- ^ Sovereignty is a Political Synonym of Competitiveness Vladislav Surkov, public appearance, 7 February 2006
- ^ Our Russian Model of Democracy is Titled «Sovereign Democracy» Vladislav Surkov, briefing, 28 June 2006.
- ^ "''Президентское фильтрование'' губернаторов оценили политики". Radiovesti.ru. Retrieved 2012-05-07.
- ^ a b "State Duma Approves Liberal Political Reforms". RIA Novosti. 28 February 2012. Retrieved 2012-05-07.
- ^ Kramer, Andrew E. (22 April 2007). "50% Good News Is the Bad News in Russian Radio". The New York Times. Russia. Retrieved 2011-09-24.
- ^ Masha Lipman, Anders Aslund (2 December 2004). "Russian Media Criticism of Vladimir Putin: Evidence and Significance". Carnegieendowment.org. Retrieved 2010-03-02.
- ^ "Несмотря на двукратное снижение числа убийств, на фоне европейских показателей оно остается крайне высоким". Demoscope.ru. Retrieved 2012-05-07.
- ^ "МВД рапортует: количество терактов снизилось в 15 раз". Finmarket.ru. Retrieved 2012-05-07.
- ^ Sharlet, Robert (2005). "In Search of the Rule of Law". In White, Gitelman, Sakwa (ed.). Developments in Russian Politics. Vol. 6. Duke University Press. ISBN 0-8223-3522-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". Imf.org. 14 September 2006. Retrieved 2011-12-09.
- ^ a b c d e f "Russia's economy under Vladimir Putin: achievements and failures". En.rian.ru. Retrieved 2013-06-22.
- ^ "Russians weigh Putin's protégé". Moscow. Associated Press. 3 May 2008. Retrieved 2008-12-29.
- ^ Putin's Economy – Eight Years On. Russia Profile, 15 August 2007. Retrieved 23 April 2008
- ^ "РОЗНИЧНЫЙ ПОДХОД. Российские банки борются за частников". Vtbmagazine.ru. Archived from the original on June 19, 2006. Retrieved 2010-03-02.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Ежегодно объем потребительского кредитования в России удваивается". Bank.samaratoday.ru. Retrieved 2010-03-02.
- ^ "Основные Социально-Экономические Индикаторы Уровня Жизни Населения". Gks.ru. Archived from the original on February 18, 2012. Retrieved 2010-03-02.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Daniel Mitchell Russia's Flat-Tax Miracle. The Heritage Foundation. 24 March 2003.
- ^ "Putin Advocates Strong Russia, Liberal Economy; President Surprisingly Candid In First State of Nation Address". Encyclopedia.com. 9 July 2000. Retrieved 2010-03-02.[dead link]
- ^ "A Comparative Study of Taxation in Russia and Other CIS, East European and OECD Countries". Papers.ssrn.com. 9 April 2004. Retrieved 2010-03-02.
- ^ Goldman, Marshall I. (2008). "Chapter 5". Petrostate: Putin, Power and the New Russia. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-534073-0.
- ^ Iikka. Korhonen et al. The challenges of the Medvedev era. Bank of Finland's Institute for Economies in Transition, 24 June 2008.
- ^ Rosstat Confirms Record GDP Growth Kommersant. Retrieved 5 May 2008.
- ^ Krkoska, Libor; Spencer, Alan (2008). "Automotive Industry in Russia: Impact of foreign investments in car assembly plants on suppliers' entry" (PDF). European Bank for Reconstruction and Development.
- ^ Zvereva, Polina (11 October 2009). "State-sponsored consolidation". Russia & CIS Observer. 3 (26).
- ^ "Annual Report 2009" (PDF). United Aircraft Corporation. 2010.
- ^ Future Vision The Wall Street Journal
- ^ Russia, China in Deal On Refinery, Not Gas by Jacob Gronholt-Pedersen. The Wall Street Journal, 22 September 2010
- ^ Russia builds nuclear power stations all over the world at amur.kp.ru
- ^ William J. Broad (19 February 2008). "Russia's Claim Under Polar Ice Irks American". The New York Times. Retrieved 2011-07-27.
- ^ Adrian Blomfield (11 June 2008). "Russia plans Arctic military build-up". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 2011-07-27.
- ^ Mia Bennett (4 July 2011). "Russia, Like Other Arctic States, Solidifies Northern Military Presence". Foreign Policy Association. Retrieved 2011-07-27.
- ^ Richard Galpin (22 September 2010). "The struggle for Arctic riches". BBC News. Retrieved 2011-08-28.
- ^ Peter Fairley (2 July 2010). "Russia Launches Floating Nuclear Power Plant". IEEE Spectrum. Retrieved 2011-08-28.
- ^ "Gazprom starts towing of Prirazlomnoye platform to field". iStockAnalyst. 25 August 2011. Retrieved 2011-08-28.[dead link]
- ^ "Prirazlmonaya sea platform to be delivered to offshore oil field". ITAR-TASS. 26 August 2011. Retrieved 2011-08-28.
- ^ a b Andrew Kramer (30 August 2011). "Exxon Reaches Arctic Oil Deal With Russians". The New York Times. Retrieved 2011-09-05.
- ^ Melodie Warner (30 August 2011). "Exxon Mobil, Rosneft To Jointly Develop Hydrocarbon Resources Globally". The Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on May 23, 2012. Retrieved 2011-09-05.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Roger Howard (4 September 2011). "How Arctic oil could break new ground". The Guardian. Retrieved 2011-09-05.
- ^ The New York Times. 6 November 2004. Retrieved 20 April 2008.
- ^ Tony Johnson. "G8's Gradual Move toward Post-Kyoto Climate Change Policy". Council on Foreign Relations. Retrieved 2010-03-02.
- ^ THE AMUR TIGER PROGRAMME premier.gov.ru Archived 2012-07-18 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ THE WHITE WHALE PROGRAMME premier.gov.ru Archived 2012-06-13 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ THE POLAR BEAR PROGRAMME premier.gov.ru Archived 2012-06-13 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ THE SNOW LEOPARD PROGRAMME premier.gov.ru Archived 2012-06-13 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Bell, I (2002). Eastern Europe, Russia and Central Asia. ISBN 978-1-85743-137-7. Retrieved 27 December 2007.
- ^ A religion for the nation or a nation for the religion: Putin's third way for Russia, Beth Admiraal, in Russian Nationalism and the National Reassertion of Russia, edited by Marlène Laruelle, (Routledge, 2009)
- ^ "Bethlehem street named after Putin". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 2012-06-27. Retrieved 2013-06-22.
- ^ "he President of Russia attended the ceremonial signing of the Act on Canonical Communion that was held in the Cathedral of Christ the Saviour" (Press release). Embassy of Russia in Ottawa. 17 May 2007. Archived from the original on 2 October 2008. Retrieved 2008-10-02. Archived by WebCite at www.webcitation.org/5bGjBVfm6
- ^ No love lost, Yossi Mehlman, Haaretz, 11 December 2005
- ^ Phyllis Berman Lea Goldman, (September 15, 2003). "Cracked De Beers". Forbes
- ^ Krichevksy, Lev (10 October 2011). ""In Putin's return, Russian Jews see stability". Jewish Telegraphic Agency". Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 2013-06-22.
- ^ Beginning of Meeting with Defense Minister Anatoliy Serdyukov, 5 December 2007, Kremlin.ru
- ^ Guy Faulconbridge Russian navy to start sorties in Mediterranean. Reuters. 5 December 2007.
- ^ "Military reform to change army structure. What about its substance?". RIA Novosti. 17 October 2008. Retrieved 2012-05-07.
- ^ Kristensen, Hans M. "New START Data Released: Nuclear Flatlining." FAS, 3 October 2012.
