Gurjar
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (August 2015) |
| Regions with significant populations | |
|---|---|
| India • Pakistan • Afghanistan | |
| Languages | |
| Gujari • Punjabi • Urdu • Hindi | |
| Religion | |
| Hinduism • Islam • Sikhism |
Gurjar or Gujjar is a pastoral agricultural ethnic group with populations in India and Pakistan and a small number in northeastern Afghanistan.[1] Alternative spellings include Gurjara, Gojar, Gūjar, Gurjjara, and Gūrjara.[2][3] Although they are able to speak the language of the country where they live, Gurjars have their own language, known as Gujari. They variously follow Hinduism, Islam, and Sikhism.[1][4] The Gurjars are classified as Other Backward Class (OBC) in some states in India; however, Gujjars in Jammu and Kashmir and parts of Himachal Pradesh are categorised as a Scheduled Tribe.[5][6][7] Hindu Gurjars today are assimilated into several varnas.
History
Origin
Historians and Anthropologists differ on issue of Gurjar origin.[8]General Cunningham identifies the Gujjars with Kushanas (Indo-Scythian people) of eastern tartars. He explains that 'Korso' and 'Kushan' written on the coins of Kushana King Kanishka is same as Gorsi and Kusane clans of Gurjars respectively.[9][10] He further adds that Gujars came to India in the 3rd wave of migration around the mid third century CE. Ibbeston also supports Indo-Scythians descend of Gurjars. K.S.Singh also support the theory on the basis that beside Jats, Gurjars are the only race of foreign origin in north west part of Indian subcontinent who are known to have been powerful during early centuries of Christian era.[9]
James Compbell, too, agrees on the central Asian origin of Gurjars but link them with the Khazar people (Huna people) of Armenia and north Medra, who occupied prominent position in 6th century CE in Europe and Asia border Area.Bhandarkar also traces Gujars from Khazar people of white Huna stock. He explains that Khazar people left imprints of their name en-route their migration in form of Gurjistans. He locates three such Gurjistans, one in central Asia, the other two in Hazara region of undivided Punjab and near Ghazini. He further mentions two Gurjar kingdoms, one in western Rajasthan (9th century CE) and one in Jaipur territory (Al-beruni's Gujarat province) and believes that when Xuan Xang visited India, Gujars got Hinduised and assimilated into ranks of warriors.[9]
V.A.Smith believes Gujars to be a branch of the white Hunas or allied groups. Grierson, too, points out that Gurjars migrated along with Hunas and other allied Groups in about 6th century CE.Dr.BhagwanLal is of the opinion that Gurjars and Hunas came to India in two different waves at different times, Huna between 200BCE and 500CE, while Gujjars established themselves in Indian subcontinent between 400 CE and 600 CE.[9]
Thus, historians who supports foreign origin of Gujars believe that they entered Indian subcontinent from North-west Indian Frontier and established themselves in the Indus region, Hazara, undivided Punjab, Kashmir and Rajasthan.[9]
Some scholars contradict the foreign origin of Gurjars.[11] Vaidya points out that that Gurjars are purely Aryan, their nasal index being 66.9, based on the anthropological reports of Sir H. Risely. G.H.Ojha, K.M.Munshi and A.N. Bhardwaj also support Indo-Aryan origin of Gurjars. Baij Nath Puri, too, points out that Gurjars were the original Indo-Aryan people of Rajasthan, partly from the Mount Abu region.[9]
It has been suggested that the Gurjars, along with people from northwestern India, merged with the Hephthalites and formed the Rajput clan.[12]
Linguistic theories
According to scholars such as Baij Nath Puri, the Mount Abu (ancient Arbuda Mountain) region of present-day Rajasthan had been abode of the Gurjars during medieval period.[13] The association of the Gurjars with the mountain is noticed in many inscriptions and epigraphs including Tilakamanjari of Dhanpala.[14] These Gurjars migrated from the Arbuda mountain region and as early as in the 6th century A.D., they set up one or more principalities in Rajasthan and Gujarat. Whole or a larger part of Rajasthan and Gujarat had been long known as Gurjaratra (country ruled or protected by the Gurjars) or Gurjarabhumi (land of the Gurjars) for centuries prior to the Mughal period.[15]
In Sanskrit texts, the ethnonym has sometimes been interpreted as "destroyer of the enemy": gur meaning "enemy" and ujjar meaning "destroyer").[16][17]
In its survey of The People of India, the Anthropological Survey of India (AnSI) – a government-sponsored organisation – noted that
The Gurjars/Gujjars were no doubt a remarkable people spread from Kashmir to Gujarat and Maharashtra, who gave an identity to Gujarat, established kingdoms, entered the Rajput groups as the dominant lineage of Badgujar, and survive today as a pastoral and a tribal group with both Hindu and Muslim segments.[18]
Irawati Karve, the Indologist and historian, believed that the Gurjars position in society and the caste system generally varied from one linguistic area of India to another. In Maharashtra, Karve thought that they were probably absorbed by the Rajputs and Marathas but retained some of their distinct identity. She based her theories on analysis of clan names and tradition, noting that while most Rajputs claim their origins to lie in the mythological Chandravansh or Suryavansh dynasties, at least two of the communities in the region claimed instead to be descended from the Agnivansh.[18][a]
A 2009 study conducted by Tribal Research and Cultural Foundation, under the supervision of Gurjar scholar Javaid Rahi, claimed that the word "Gojar" has a Central Asian Turkic origin, written in romanized Turkish as Göçer. The study claimed that according to the new research, the Gurjar race "remained one of the most vibrant identity of Central Asia in BC era and later ruled over many princely states in northern India for hundred of years."[19]
Gurjar rulers
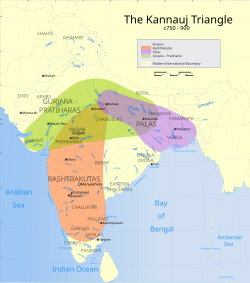
According to some historical accounts, the kingdom with capital at Bhinmal (or Srimal) was established by the Gurjars. A minor kingdom of Bharuch was the offshoot of this Kingdom.[20] In 640–41 CE, the Chinese traveller Xuanzang (Hieun Tsang) described the kingdoms of Su-la-cha (identified with Saurashtra) and Kiu-che-lo (identified with Gurjara) in his writings. He stated that the Gurjaras ruled a rich and populous kingdom with capital at Bhinmal (Pilo-mo-lo).[21] According to his expositor, M. Vivien de St. Martin, Su-la-cha represents the modern Gujarat, and Kiu-che-lo (Gurjjara), "the country of the Gujars", represents the region between Anhilwara and the Indus River, i.e. Sindh region.[22]
D. B. Bhandarkar also believed that Gurjara-Pratiharas were a clan of Gurjars.[23]
Dasrath Sharma believed that although some sections of the Pratiharas (i.e., the one to which Mathanadeva belonged) were Gurjars by caste, the Pratiharas of Kannauj were not Gurjars and there was no Gurjara empire in Northern India in 8th and 9th century,[24][25] though from the work of other historians it has been known that Kannauj was capital of Gurjara-Pratihara.[26][27][28]
Chavdas, also known as Gurjar Chapas, was also one of the ruling clans of Gurjars.[29]
British rule
In the 18th century, several Gurjar chieftains and small kings were in power. During the reign of Rohilla Nawab Najib-ul-Daula, Dargahi Singh, the Gurjar chieftain of Dadri possessed 133 villages at a fixed revenue of Rs.29,000.[30] A fort at Parlchhatgarh in Meerut District, also known as Qila Parikishatgarh, is ascribed to a Gurjar Raja Nain Singh.[31]
During the revolt of 1857, the Gujars of Chundrowli rose against the British, under the leadership of Damar Ram. The Gujars of Shunkuri village, numbering around three thousand, joined the rebel sepoys. According to British records, the Gurjars plundered gunpowder and ammunition from the British and their allies.[32] In Delhi, the Metcalfe House was sacked by the Gurjar villagers from whom the land was taken to erect the building.[33] The British records claim that the Gujars carried out several robberies. Twenty Gujars were reported to have been beheaded by Rao Tula Ram for committing dacoities in July 1857.[34] In September 1857, the British were able to enlist the support of many Gujars at Meerut.[35] The colonial authors always used the code word "turbulent" for the castes who were generally hostile to British rule. They cited proverbs that appear to evaluate the caste in an unfavorable light. The British ethnographer, William Crooke, described that Gurjars seriously impeded the operations of the British Army before Delhi.[36] Reporter Meena Radhakrishna believe that the British classified the Gurjars along with others as "criminal tribes" because of their active participation in the revolt of 1857, and also because, they considered these tribes to be prone to criminality in the absence of legitimate means of livelihood.[37]
Demographics
Gurjars are mainly concentrated in the Indo-Gangetic plains, the Himalayan region, and eastern parts of Afghanistan, although the Gurjar diaspora is found in other places as well. A majority of Gurjars follow Hinduism and Islam, though small Gurjar communities following other religions exist.
India
In India, the Gurjars are found mainly in Rajasthan, Gujarat, Delhi, Haryana, Punjab, western Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, northern Madhya Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh and the Maharashtra. The semi-nomadic Muslim Gujjar groups are found in the states of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and northwestern Uttar Pradesh.[38] The name for the state of Gujarat has derived from "Gurjar".[39]
Afghanistan

Small pockets of Gurjars are found in Afghanistan's northeastern region, particularly in and around the Nuristan province. According to the Naval Postgraduate School:
They roam with their herds, usually of cows, from the high Himalayas in India to the Hindu Kush of Afghanistan, although rarely are they seen in Afghanistan anymore, as Pakistan has hindered their passage through its territory and most preferred to stay within India. Some in India remain Hindu, although further west many are Muslim. Often they can be recognized by their avoidance of others, and their brightly hennaed beards. They are proud, fierce, and loyal. Their traditions are millennia old, and they have preserved them well in the face of great adversity. They are somewhat related to Nuristanis, although exactly how is a subject of conjecture. Similar to Nuristanis, some genetic root gives many Gujjars a distinctly European appearance, up to and including blond hair and blue eyes.[1]
Culture
Today, the Gurjars are classified under the Other Backward Class (OBC) category in some states in India.[40] However, in Jammu and Kashmir and parts of Himachal Pradesh, they are designated as a Scheduled Tribe under the Indian government's reservation program of positive discrimination. Hindu Gurjars today are assimilated into several varnas.[41]
Gujari (or Gojri), classified under Rajasthani,[42] has traditionally been the primary language of the Gurjars.
Haryana
The Gurjar community in Haryana has set elaborate guidelines for solemnizing marriages and holding other functions.[43] In a mahapanchayat ("the great panchayat"), the Gurjar community decided that those who sought dowry would be excommunicated from the society.[44]
Rajasthan

Songs pertaining to Krishna and Gurjars were documented in Gurjar-inhabited areas during the British Raj, the connection being that Nand Mihir, the foster-father of Krishna, is claimed to be a Gurjar.[45] Radha, the consort of Krishna, was also a Gurjar.[46]
The Rajasthani Gurjars worship the Sun God, Devnarayan (an avatar of Vishnu), Shiva and Bhavani.[47][48]
In Rajasthan, some members of the Gurjar community resorted to violent protests over the issue of reservation in 2006 and 2007. During the 2003 election to the Rajasthan assembly, the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) promised them ST status.[49] However, the party failed to keep its promise after coming to the power, resulting in protests by the Gurjars in September 2006.[50]
In May 2007, during violent protests over the reservation issue, the members of the Gurjar community clashed with the police twenty six people (including two policemen).[51] Subsequently, the Gurjars protested violently, under various groups including the Gurjar Sangarsh Samiti,[52] Gurjar Mahasabha[53] and the Gurjar Action Committee.[54] The protestors blocked roads and set fire to two police stations and some vehicles.[55] Presently, the Gurjars in Rajasthan are classified as Other Backward Classes (OBCs).[56]
On 5 June 2007 the Gurjar rioted over their desire to be added to the central list of tribes who are given preference in India government job selection as well as placement in the schools sponsored by the states of India. This preference is given under a system designed to help India's poor and disadvantaged citizens. However, other tribes on the list oppose this request as it would make it harder to obtain the few positions already set aside.[57]
In December 2007, the Akhil Bhartiya Gurjar Mahasabha ("All-India Gurjar Council") stated that the community would boycott BJP, which is in power in Rajasthan.[58] But now in 2009 all Gurjars were supporting BJP so that they can be politically benefitted.Kirori Singh Bainsla fought and lost at BJP ticket. In early 2000s (decade), the Gurjar community in Dang region of Rajasthan was also in news for the falling sex ratio, unavailability of brides, and the resulting polyandry.[59][60]
Madhya Pradesh
Presently, the Gurjars in Madhya Pradesh are classified as Other Backward Classes (OBCs).[61]
Gujarat and Maharashtra
A few scholars believe that the Leva Kunbis (or Kambis) of Gujarat, a section of the Patidars, are possibly of Gurjar origin.[62][63][64] However, several others state that the Patidars are Kurmis or Kunbis (Kanbis);[65][66] the National Commission for Backward Classes of India lists Leva Patidars (or Lewa Petidars) as a sub-caste of Kunbis/Kurmis. Dode Gujars and Dore Gujars are listed as separate caste in Maharashtra and Gurjars are included in OBC list in Gujarat but Patidars are not.[67]
A community using Gurjar and Gurjarpadhye as their surnames resides in the coastal Konkan region of Maharashtra, inhabiting Pangre, Hasol, and other villages in Ratnagiri District. Originally bearing the name "Gurjarpadhye", many now prefer to call themselves Gurjar. The community may have been living in the Konkan region for at least three centuries, although this estimate may be inaccurate. The community is a sub-caste of the larger Karhade Brahmin group[68] and speaks the Marathi language.
Himachal Pradesh
As of 2001[update], the Gurjars in parts of Himachal Pradesh were classified as a Scheduled Tribe.[69] [70]
Jammu and Kashmir
In the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir (J&K), the concentration of Muslim Gurjars is observed in the districts of Rajouri and Poonch, followed by, Ananatnag, Udhampur and Doda districts.[71] It is believed that Gurjars migrated to Jammu and Kashmir from Gujarat (via Rajasthan) and Hazara district of NWFP.[72] Another group called Bakarwal (or Bakerwal) belongs to the same ethnic stock as the Gurjars, and inter-marriages freely take place among them.[citation needed]
As of 2001[update], the Gurjars and the Bakarwals in Jammu and Kashmir were classified as Scheduled Tribes.[69] According to the 2001 Census of India, Gurjar is the most populous scheduled tribe in J&K, having a population of 763,806. Around 99.3 per cent population of Gurjar and Bakarwal in J&K follow Islam.[71]
The Gurjars of Jammu and Kashmir in 2007 demanded to treat this tribal community as a linguistic minority in the State and provide constitutional safeguards to their language Gojri. They also impressed upon the state government to take up the matter with Delhi for inclusion of Gojri in the list of official languages of India.[73][74]
In 2002, some Gurjars and Bakarwals in J&K demanded a separate state (Gujaristan) for Gurjar and Bakarwal communities, under the banner of All India Gurjar Parishad.[75]
Van Gujjars
The Van Gujjars ("forest Gujjars") are found in the Shivalik hills area of North India. The Van Gujjars follow Islam, and they have their own clans, similar to the Hindu gotras.[76] They are a pastoral semi-nomadic community, practising transhumance. In the winter season, the Van Gujjars migrate with their herds to the Shiwalik foothills, and in summer, they migrate to pastures high up in the mountains. The Van Gujjars have had conflicts with the forest authorities, who prohibited human and livestock populations inside a reserved park, and blamed the Van Gujjar community for poaching and timber smuggling.[76] After the creation of the Rajaji National Park (RNP), the Van Gujjars in Deharadun were asked to shift to a resettlement colony at Pathari near Hardwar. In 1992, when the Van Gujjars returned to the foothills, the RNP authorities tried to block them from the park area. The community fought back and finally the forest authorities had to relent.[77] Later, a community forest management (CFM) programme aiming to involve the Van Gujjars in forest management was launched.[citation needed]
See also
- Gujrat
- List of Gurjar clans
- List of Gurjars
- History of Gujarat
- Tribal Research and Cultural Foundation
References
Notes
Citations
- ^ a b c "Nuristan". Program for Culture & Conflict Studies. Naval Postgraduate School. October 2009. Retrieved 4 November 2013.
- ^ Jean-Philippe Platteau (2010). Culture, Institutions, and Development: New Insights Into an Old Debate.
- ^ Randeep Ramesh in Delhi (29 May 2007). "Rajasthan hit by riots over caste system | World news". theguardian.com. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
- ^ Singh, David Emmanuel (2012). Islamization in Modern South Asia: Deobandi Reform and the Gujjar Response. Walter de Gruyter. pp. 48 and 51.
- ^ S. P. Agrawal, J. C. Aggarwal (1991). Educational and Social Uplift of Backward Classes: At what Cost and How? : Mandal Commission and After, Part 1. Concept Publishing Company. p. 175. ISBN 9788170223399.
- ^ Census India. "List of notified Scheduled Tribes" (PDF). Census India, Govt. of India. Retrieved 13 January 2016.
- ^ Page, Jeremy (30 May 2008). "India's Gujjar caste fight for a downgrade". The Times. Retrieved 1 December 2009.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|subscription=ignored (|url-access=suggested) (help) - ^ "Gurjara-Pratihara Dynastyrv". Britannica Concise. Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 31 May 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f Sahni, Bindu (2015). "Migration and Settlement Pattern of Gujjars in the 19th Century Himachal Pradesh". Global Journal of engineering, science, and social science studies. 1: 19.
- ^ Sir Alexander Cunningham (1871). Four Reports Made During the Years, 1862-63-64-65. Government Central Press. pp. 73–.
- ^ Parishad, Bharatiya Gurjar (1996). Gurjara aura Unakā Itihāsa meṃ Yogadāna Vishaya para Prathama Itihāsa Sammelana. The Packard Humanities Institute. pp. 34–65. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ Kurbanov, Aydogdy (2010). "The Hephthalites: Archaeological and Historican Analysis" (PDF). p. 243. Retrieved 11 January 2013.
As a result of the merging of the Hephthalites and the Gujars with population from northwestern India, the Rajputs (from Sanskrit "rajputra" – "son of the rajah") formed.
- ^ Kulbhushan Warikoo; Sujit Som. Gurjars of Jammu and Kashmir. Indira Gandhi Rashtriya Manav Sangrahalaya.
Dr. B. N. Puri who wrote a thesis Gurjar Pratihar at oxford university states that the Gurjars were local people ..
- ^ Sudarśana Śarmā (2002). Tilakamañjarī of Dhanapāla: a critical and cultural study. Parimal Publications. p. 214.
- ^ Ramesh Chandra Majumdar; Achut Dattatrya Pusalker; A. K. Majumdar; Dilip Kumar Ghose; Vishvanath Govind Dighe; Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan (1977). The History and Culture of the Indian People: The classical age. Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan. p. 153.
- ^ Warikoo, Kulbhushan; Som, Sujit (2000). Gurjars of Jammu and Kashmir. Indira Gandhi Rashtriya Manav Sangrahalaya. p. 4.
"Gurjar" is a sanskrit word which has been explained thus: Gur+Ujjar;'Gur' means 'enemy' and 'ujjar' means 'destroyer'. The word means "Destroyer of the enemy".
- ^ Parishada, Bhāratīya Gurjara (1993). Gurjara aura Unakā Itihāsa meṃ Yogadāna Vishaya para Prathama …, Volume 2. Bharatiya Gurjar Parisha. p. 27.
Sanskrit Dictionary Compiled by Pandit Radha Kant (Shakabada 1181) explains: Gurjar=Gur (enemy)+Ujar(destroyer)
- ^ a b c Kumar Suresh Singh; B. V. Bhanu; Anthropological Survey of India (2004). People of India: Maharashtra. Popular Prakashan. p. xxviii. ISBN 81-7991-101-2, ISBN 978-81-7991-101-3.
- ^ "www.dailyexcelsior.com". Daily Excelsior. Retrieved 29 June 2009.[dead link]
- ^ Malabari, Behramji Merwanji; Krishnalal M. Jhaveri (1998). Gujarat and the Gujaratis: Pictures of Men and Manners Taken from Life. Asian Educational Services. p. 2. ISBN 81-206-0651-5.
- ^ Campbell, James MacNabb; Reginald Edward Enthoven (1901). Gazetteer of the Bombay Presidency. Govt. Central Press. p. 2. ISBN 81-206-0651-5.
- ^ "Juzr or Jurz". Persian Texts in Translation. The Packard Humanities Institute. Archived from the original on 29 September 2007. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ Bhandarkar, Devadatta Ramakrishna (1989). Some Aspects of Ancient Indian Culture. Asian Educational Services. p. 64. ISBN 81-206-0457-1.
- ^ Majumdar, Ramesh Chandra (2002) [1976]. Readings in Political History of India, Ancient, Mediaeval, and Modern. B.R. Pub. Corp (on behalf of Indian Society for Prehistoric and Quaternary Studies), D.K. Publishers' Distributors. p. 209.
But he refused to believe that the Imperial Pratiharas of Kanauj were also Gujars in this sense.
- ^ Imperial Gazetteer of India, vol. 2. Digital South Asia Library. p. 320. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
But whatever our theories regarding the infusion of Gujar blood among the Rajputs, there was certainly no Gurjara (Gujar) empire in Northern India
- ^ Kulke, Hermann; Rothermund, Dietmar (2004). A history of India (4th, illustrated ed.). Routledge, 2004. 432 pages. ISBN 0-415-32920-5. ISBN 978-0-415-32920-0.
In 9th century the Gurjara pratiharas kings, Bhoja (836–885) and Mahendrapala (885–910), proved to be more powerful than their contemporaries of the other two dynasties whom they defeated several times. Kanauj then emerged as the main focus of power in India.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|nopp=ignored (|no-pp=suggested) (help) - ^ Majumdar, Ramesh Chandra; Samiti, Bhāratīya Itihāsa (1954) [1954]. The History and Culture of the Indian People: The classical age. G. Allen & Unwin, original from-the University of Michigan.
Rajasekharan, the great poet and playwright at the Gurjara-pratihara court of Kannauj.
- ^ Chopra, Pran Nath (2003). A comprehensive history of ancient India. Sterling Publishers Pvt. Ltd. p. 196. ISBN 81-207-2503-4. ISBN 978-81-207-2503-4.
Al-Masudi who visited his (Gurjara mahipala) court, also refers to the great power and resources of the Gurjara pratihara rules of Kannauj.
- ^ Chintaman Vinayak Vaidya (1979). History of mediaeval Hindu India, Volume 1. Cosmo Publications. p. 355.
- ^ Uttar Pradesh District Gazetteers. Govternment of Uttar Pradesh. 1993. p. 152.
- ^ "Tourist Places". District Administration Meerut. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ Agha Humayun Amin (January 2000). "The Delhi Campaign". Defence Journal. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ Sen, Geeti; Ashis Banerjee (2001). The Human Landscape. Orient Longman. p. 236. ISBN 81-250-2045-4.
- ^ Jivanlala (Jeewan Lal), Munshi (1974) [1898]. "Narrative Of Munshi Jeewan Lal". In Charles Metcalfe, 1st Baron Metcalfe (ed.). Two Native Narratives of the Mutiny in Delhi. Seema Publications (original publisher: A. Constable & Co). pp. 10–27. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: numeric names: editors list (link) - ^ C.R. Bijoy (February 2003). The Adivasis of India – A History of Discrimination, Conflict, and Resistance. People's Union for Civil Liberties.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ Everyday life in South Asia By Diane P. Mines, Sarah Lamb, Published by Indiana University Press, 2002, pp.206
- ^ Meena Radhakrishna (16 July 2006). "Dishonoured by history". folio: Special issue with the Sunday Magazine. The Hindu. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ Chib, Sukhdev Singh (1977). Himachal Pradesh. Light & Life Publishers. p. 99.
- ^ Gujrat Government. "Gujrat state official site".
The State took its name from the Gujara, the land of the Gujjars, who ruled the area during the 700s and 800s.
- ^ Page, Jeremy (30 May 2008). "India's Gujjar caste fight for a downgrade". The Times. Retrieved 1 December 2009.
- ^ Sharma, R. S. (2003). Early medieval Indian society: a study in feudalisation. Orient Longman Private Limited. p. 207. ISBN 81-250-2523-5. Retrieved 30 November 2009.
It would be wrong to think that all foreigners were accepted as kshatriya and Rajputs for, in course of time, the Gujar people broke up into brahmans, banias, potters, goldsmiths, not to speak of herdsmen and cultivators (kunbis), who were looked upon as sudras.
- ^ Dr. R.P. Khatana. "Gujari Language and Identity in Jammu and Kashmir". Kashmir News Network: Language Section (koshur.org). Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ Chattar Pal Tanwar (3 August 2003). "Anti-dowry campaign renewed before marriage season". The Tribune, Chandigarh. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ Parmindar Singh (29 June 2003). "No band, no dhol, and just 11 baratis". The Tribune, Chandigarh. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ J. Kennedy (1907). The child Krishna, Christianity and the Gujars. Royal Asiatic Society.
- ^ Taran Singh (1992). Guru Nanak, his mind and art. Bahri Publications. p. 142. ISBN 81-7034-066-7. ISBN 978-81-7034-066-9.
- ^ Daniel Neuman; Shubha Chaudhuri; Komal Kothari (2007). Bards, ballads and boundaries: an ethnographic atlas of music traditions in West Rajasthan. Seagull. ISBN 1905422075, ISBN 978-1-905422-07-4.
Devnarayan is worshipped as an avatar or incarnation of Vishnu. This epic is associated with the Gujar caste
- ^ Indian studies: past & present, Volume 11. Today & Tomorrow's Printers & Publishers. 1970. p. 385.
The Gujars of Punjab, North Gujarat and Western Rajasthan worship Sitala and Bhavani
- ^ "Gujjar of Rajasthan and ST Status". Countercurrents.org ! News. 6 June 2008. Retrieved 24 June 2009.
- ^ "Gujjar community goes berserk in Rajasthan". Yahoo! News. 5 September 2006. Retrieved 31 May 2007. [dead link]
- ^ "Gujjar unrest: CPI(M) demands judicial probe". The Hindu. 30 May 2007. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ "Talks between Rajasthan Government, Gujjars collapse". Zee News. 30 May 2007. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ "Gujjars seek resignation of Minister Kalulal Gujjar". Deccan Herald. 30 May 2007. Archived from the original on 29 September 2007. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ "Four dead in Gujjar-police clash in Rajasthan". The Times of India. 29 May 2007. Archived from the original on 13 January 2009. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Impoverished villagers burn police stations, vehicles in India". Pravda.ru. 29 May 2007. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ "Central List Of Other Backward Classes: Rajasthan". National Commission for Backward Classes. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ "The Race to the Bottom of India's Ladder". Time Magazine. 5 June 2007. Retrieved 26 August 2007.
- ^ "Gurjar community 'threatens' to boycott BJP". The Hindu. 31 December 2007. Retrieved 31 December 2007.
- ^ Manipadma Jena (3 August 2003). "Men without women". The Hindu. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ Astrid Lobo Gajiwala (7 February 2005). "Diminishing returns". The National Catholic Reporter. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ "Central List Of Other Backward Classes: Madhya Pradesh". National Commission for Backward Classes. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ B K., Mohapatra; R. Trivedi; A. K. Mehta; J. M. Vyas; V. K. Kashyap (June 2004). "Genetic Diversity at 15 Fluorescent-Labeled Short Tandem Repeat Loci in the Patel and Other Communities of Gujarat, India". American Journal of Forensic Medicine and Pathology. 25 (2): 108–112. doi:10.1097/01.paf.0000114137.01885.01. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
They are a section of the Kambi who address themselves as Patidar, and probably they are Gujjar in origin.
- ^ "Buldhana: Castes". Buldhana District Gazetteer. Gazetteers Department, Cultural Affairs Department of Government of Maharashtra. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ Panjabi, Kewalram Lalchand (1977). The Indomitable Sardar. Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan. p. 4.
Vallabhbhai Patel belonged to the famous clan of Leva Gujar Patidars who played a notable role in the history of Gujarat. They were Gujars who came from Punjab and had occupied the rich charotar land between Mahi and Tapi rivers.
- ^ "Culture and Traditions". Patidar Samaj. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ Pocock, David Francis (1972). Kanbi and Patidar: A Study of the Patidar Community of Gujarat. Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-823175-X.
- ^ "Central List of Other Backward Classes". National Commission for Backward Classes. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ Saraswati, Baidyanath (1977). Brahmanic Ritual Traditions in the Crucible of Time. Indian Institute of Advanced Study. p. 45.
- ^ a b "List of Scheduled Tribes". Census of India: Government of India. 7 March 2007. Retrieved 27 November 2012.
- ^ http://www.peoplegroupsindia.com/profiles/gujjar/
- ^ a b "Jammu & Kashmir Data Highlights: The Scheduled Tribes". Census of India 2001. Office of the Registrar General, India. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ Kapoor, A. K.; M. K. Raha; D. Basu; Satwanti Kapoor (1994). Ecology and man in the Himalayas. M. D. Publications. pp. 43–44. ISBN 978-81-85880-16-7.
- ^ "Meri News". Meri News. Retrieved 16 April 2009.
- ^ "Kashmir Watch". Kashmir Watch. Retrieved 16 April 2009.
- ^ "Gujjars, Bakerwals demand Gujaristan in J&K". Indian Express. 29 July 2002. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ a b Radhakrishna Rao (4 September 2000). "Outside the jungle book". Business Line. The Hindu. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
- ^ Gooch, Pernille (1998). At the Tail of the Buffalo: Van Gujjar pastoralists between the forest and the world arena. Dept. of Sociology, Lund University. ISBN 91-89078-53-5.
Further reading
- Rawat, Ajay Singh (1993), Man and Forests: The Khatta and Gujjar Settlements of Sub-Himalayan Tarai, Indus Publishing, ISBN 978-81-85182-97-1
- Singh, David Emmanuel (2012), Islamization in Modern South Asia: Deobandi Reform and the Gujjar Response, Walter de Gruyter, ISBN 978-1-61451-246-2
- Hāṇḍā, Omacanda (1998), Textiles, Costumes, and Ornaments of the Western Himalaya, Indus Publishing, pp. 257-, ISBN 978-81-7387-076-7
External links
- Use dmy dates from March 2013
- Gurjar
- Ethnic groups in India
- Ethnic groups in Afghanistan
- Social groups of Pakistan
- Social groups of Rajasthan
- Social groups of Jammu and Kashmir
- Social groups of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
- Social groups of Uttar Pradesh
- Social groups of Madhya Pradesh
- Social groups of Haryana
- Social groups of Punjab, Pakistan
- Social groups of Punjab, India
- Social groups of Himachal Pradesh
- Ethnic groups in Kunar Province
- Hindu dynasties
- Hindu communities
- Punjabi tribes
- Hindkowan tribes
- Demographic history of India
- Pastoralists
- Suryavansha
- Scheduled Tribes of Jammu and Kashmir
- Scheduled Tribes of Himachal Pradesh
- Indian castes
