Normorphine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Normorphine |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.712 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
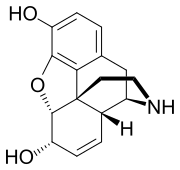
| Formula | C16H17NO3 |
| Molar mass | 271.311 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Normorphine is an opiate analogue, the N-demethylated derivative of morphine, that was first described in the 1950s[1] when a large group of N-substituted morphine analogues were characterized for activity.
Normorphine has relatively little opioid activity in its own right,[2][3] but is a useful intermediate which can be used to produce both opioid antagonists such as nalorphine, and also potent opioid agonists such as N-phenethylnormorphine.[4] It is also produced as a major metabolite of morphine,[5] with its formation from morphine catalysed by the liver enzymes CYP3A4 and CYP2C8.[6]
Normorphine is a controlled substance listed under the Single Convention On Narcotic Drugs 1961 and the laws in various states implementing it; for example, in the United States it is a Schedule I Narcotic controlled substance, with an ACSCN of 9313 and an annual aggregate manufacturing quota of 18 grammes in 2013, unchanged from the prior year.
References
- ^ Journal of the American Chemistry Society 75,4963 (1953)
- ^ Fraser HF, Wikler A, Van Horn GD, Eisenman AJ, Isbell H. Human pharmacology and addiction liability of normorphine. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 1958 Mar;122(3):359-69. PMID 13539761
- ^ Lasagna L, De Kornfeld TJ. Analgesic potency of normorphine in patients with postoperative pain. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 1958 Nov;124(3):260-3. PMID 13588540
- ^ Daniel Lednicer. Central Analgetics. (1982), p146. ISBN 0-471-08314-3
- ^ Yeh SY. Urinary excretion of morphine and its metabolites in morphine-dependent subjects. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 1975 Jan;192(1):201-10. PMID 235634
- ^ Projean D, Morin PE, Tu TM, Ducharme J. Identification of CYP3A4 and CYP2C8 as the major cytochrome P450 s responsible for morphine N-demethylation in human liver microsomes. Xenobiotica. 2003 Aug;33(8):841-54. PMID 12936704
