Mactan–Cebu International Airport: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
| [[Korean Air]] | [[Gimhae International Airport|Busan]], [[Incheon International Airport|Seoul–Incheon]] |
| [[Korean Air]] | [[Gimhae International Airport|Busan]], [[Incheon International Airport|Seoul–Incheon]] |
||
| [[Orenair]] | '''Seasonal Charter:''' [[Sheremetyevo International Airport|Moscow-Sheremetyevo]]<ref>{{cite news|title=PH Embassy hosts launch of Moscow-Cebu charter flights|url=http://www.gov.ph/2014/10/23/ph-embassy-hosts-launch-of-moscow-cebu-charter-flights/|accessdate=24 October 2014 |newspaper=Department of Foreign Affairs - Philippines Official webpage|date=24 October 2014}}</ref> |
| [[Orenair]] | '''Seasonal Charter:''' [[Sheremetyevo International Airport|Moscow-Sheremetyevo]]<ref>{{cite news|title=PH Embassy hosts launch of Moscow-Cebu charter flights|url=http://www.gov.ph/2014/10/23/ph-embassy-hosts-launch-of-moscow-cebu-charter-flights/|accessdate=24 October 2014 |newspaper=Department of Foreign Affairs - Philippines Official webpage|date=24 October 2014}}</ref> |
||
| [[Philippine Airlines]] | [[Ninoy Aquino International Airport|Manila]], [[Chūbu Centrair International Airport|Nagoya–Centrair]],<ref>http://airlineroute.net/2014/08/29/pr-cebngo-dec14/</ref> [[Kansai International Airport|Osaka–Kansai]], [[Incheon International Airport|Seoul–Incheon]], [[Narita International Airport|Tokyo–Narita]] |
| [[Philippine Airlines]] | [[Ninoy Aquino International Airport|Manila]], [[Los Angeles International Airport|Los Angeles]] (begins March 15, 2016,<ref>{{cite news|title=PAL to launch Cebu-Los Angeles direct flights in 2016|url=http://www.rappler.com/business/industries/171-aviation-tourism/101767-philippine-airlines-cebu-los-angeles-direct-flights-soon|accessdate=6 August 2015|publisher=Rappler|date=6 August 2015}}</ref> [[Chūbu Centrair International Airport|Nagoya–Centrair]],<ref>http://airlineroute.net/2014/08/29/pr-cebngo-dec14/</ref> [[Kansai International Airport|Osaka–Kansai]], [[Incheon International Airport|Seoul–Incheon]], [[Narita International Airport|Tokyo–Narita]]<br>'''Charter:''' [[Nanning Wuxu International Airport|Nanning]]<ref>http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2015-07/26/c_134448499.htm</ref> |
||
| Philippine Airlines<br>{{nowrap|operated by [[PAL Express]]}} | [[Bacolod–Silay International Airport|Bacolod]], [[Bancasi Airport|Butuan]], [[Laguindingan International Airport|Cagayan de Oro]], [[Francisco Bangoy International Airport|Davao]], [[Iloilo International Airport|Iloilo]], [[Ninoy Aquino International Airport|Manila]], [[Daniel Z. Romualdez Airport|Tacloban]] |
| Philippine Airlines<br>{{nowrap|operated by [[PAL Express]]}} | [[Bacolod–Silay International Airport|Bacolod]], [[Bancasi Airport|Butuan]], [[Laguindingan International Airport|Cagayan de Oro]], [[Francisco Bangoy International Airport|Davao]], [[Iloilo International Airport|Iloilo]], [[Ninoy Aquino International Airport|Manila]], [[Daniel Z. Romualdez Airport|Tacloban]] |
||
| [[SilkAir]] | [[Singapore Changi Airport|Singapore]]{{Ref|1|1}} |
| [[SilkAir]] | [[Singapore Changi Airport|Singapore]]{{Ref|1|1}} |
||
Revision as of 07:57, 6 August 2015
Mactan–Cebu International Airport Tugpahanang Pangkalibutan sa Mactan–Sugbo (Cebuano) Paliparang Pandaigdig ng Mactan–Cebu (Tagalog) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| File:Mactan Cebu Airport Logo.png | |||||||||||
 Exterior of Mactan–Cebu International Airport | |||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||
| Operator | Mactan–Cebu International Airport Authority | ||||||||||
| Serves | Metro Cebu | ||||||||||
| Location | Lapu-Lapu Airport Road, Ibo, Lapu-Lapu City, Metro Cebu, Philippines | ||||||||||
| Hub for | AirAsia Zest Cebu Pacific PAL Express Philippine Airlines | ||||||||||
| Built | 1956 | ||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 11 m / 36 ft | ||||||||||
| Website | mactancebuairport.com | ||||||||||
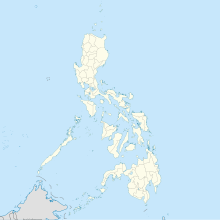
| Map | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Statistics (2014) | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
2014 MCIAA Statistcs | |||||||||||
Mactan–Cebu International Airport (Cebuano: Tugpahanang Pangkalibutan sa Mactan–Sugbo, Filipino: Paliparang Pandaigdig ng Mactan–Cebu) (IATA: CEB, ICAO: RPVM) located in Central Visayas region, is the second busiest airport of the Philippines and one of the top 20 airports in the ASEAN region in 2011.[citation needed] It is located in Lapu-Lapu City on Mactan Island, part of Metro Cebu. The airport is managed by the Mactan–Cebu International Airport Authority. It covers an area of 797 hectares (1,970 acres).
It has a single 3,300-meter (10,800 ft) runway that was built by the United States in 1956 as an emergency airport for Strategic Air Command bombers and was known as the Mactan Air Base.[1] The runway is complemented by a full-length taxiway that it shares with the current Mactan Air Base of the Philippine Air Force.
Mactan–Cebu International Airport was chosen as the most viable location for the world's largest aircraft, Antonov 225, to safely land when considering the combination of onward land transportation, sea freight, and airport capacity. The arrival of the aircraft in Lapu-Lapu City marked the very first time that the aircraft landed in the Philippines.
History
The runway was built by the United States Air Force in 1956 as an emergency airport for Strategic Air Command bombers and it was known as the Mactan Air Base.[1] It remained a spartan outpost until the Vietnam War in the 1960s when it became a base for a C-130 unit of the U.S. Air Force.[1]
In the mid-1960s, the civilian airport was opened, to replace the Lahug Airport (now the site of Cebu IT Park), which could no longer be expanded due to safety and physical problems. The airport was later expanded to the current Mactan–Cebu International Airport (MCIA).
On August 20, 2008, the Mactan–Cebu International Airport Authority (MCIAA) announced that about 300 million Philippine pesos will be spent for the terminal expansion program to address the increasing volume of passenger traffic. MCIAA former general manager Danilo Augusto Francia said the program also includes the establishment of a second passenger terminal in the Mactan–Cebu International Airport.[2] In 2009, former general manager Francia announced for the public bidding for the construction of the new generation terminal to service only international flight.
In 2010, the newly elected Philippine President, Benigno Aquino III selected Nigel Paul Villarete as the new General Manager of the Mactan–Cebu International Airport (MCIA)[3] and Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of MCIAA. Mr. Villarete prioritized the completion of the terminal expansion[4] and the completion of the unfinished administration building.[5]


Following Typhoon Haiyan (Yolanda), one of the biggest typhoons ever recorded and one of the most destructive typhoons in the Philippines, the airport was used as a center for air operations for the relief effort. The airport is centrally located in the Visayas which was the region most affected by the storm, especially the Eastern Visayas islands of Leyte and Samar. The Cebu airport was relatively unaffected by the storm while the airports of the Eastern Visayas were unusable immediately after.
On April 23, 2014, the Department of Transportation and Communications awarded the operations and maintenance of MCIA to a consortium of the Philippine Megawide Construction Corporation and Bangalore-based GMR Infrastructure. The consortium won with a bid of 17.5 billion Philippine pesos. MCIAA will turn over to the private consortium the operations and maintenance of the airport starting October 2014.[6] The new terminal building to be designed by local architects[7] is expected to be completed by 2018.[8]
Terminals, airlines and destinations
The existing terminal houses both domestic and international operations and has an annual capacity of 4.5 million passengers.[9]
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| AirAsia | Kuala Lumpur[10] |
| AirAsia Zest | Davao, Manila, Seoul–Incheon |
| Air Busan | Busan |
| Asiana Airlines | Seoul–Incheon |
| Cathay Pacific | Hong Kong |
| Cebgo | Cagayan de Oro, Davao, Manila, Puerto Princesa |
| Cebu Pacific | Bacolod, Busuanga, Butuan, Cagayan de Oro, Camiguin, Caticlan, Clark, Davao, Dipolog, Dumaguete, General Santos, Hong Kong, Iloilo, Kalibo, Legazpi, Manila, Ozamiz, Pagadian, Puerto Princesa, Siargao, Singapore, Surigao, Tacloban, Tandag, Tokyo–Narita,[11] Zamboanga Charter: Busan, Seoul–Incheon |
| China Airlines | Charter: Taipei–Taoyuan[12] |
| Jeju Air | Seoul–Incheon |
| Jin Air | Seoul–Incheon |
| Korean Air | Busan, Seoul–Incheon |
| Orenair | Seasonal Charter: Moscow-Sheremetyevo[13] |
| Philippine Airlines | Manila, Los Angeles (begins March 15, 2016,[14] Nagoya–Centrair,[15] Osaka–Kansai, Seoul–Incheon, Tokyo–Narita Charter: Nanning[16] |
| Philippine Airlines operated by PAL Express | Bacolod, Butuan, Cagayan de Oro, Davao, Iloilo, Manila, Tacloban |
| SilkAir | Singapore1 |
| Tigerair | Singapore1 |
- Notes
- ^1 : This flight may make a stop between Cebu and the listed destination. However, the airline does not have rights to transport passengers solely between Cebu and the intermediate stop.
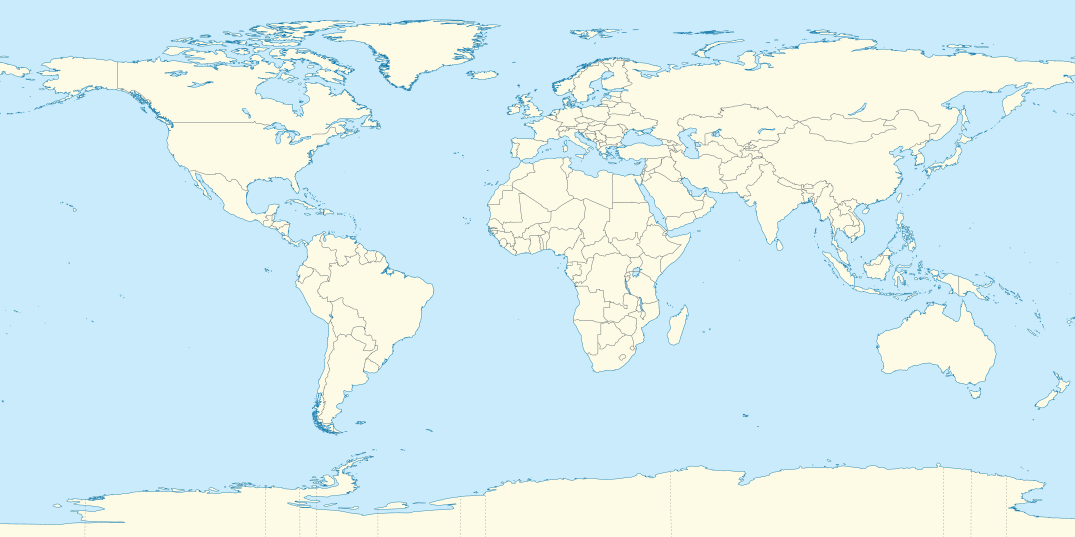
| Destinations maps |
|---|
Destinations around the world
|
| Cargo Airlines |
|---|
| 2GO (Air) |
| FedEx Express |
| Pacific East Asia Cargo Airlines |
| Tri-MG Intra Asia Airlines |
| TransGlobal Airways |
Incidents/Accidents
On December 11, 1994, Philippine Airlines Flight 434 was flying on its second leg of the Ninoy Aquino International Airport – Mactan–Cebu International Airport – New Tokyo International Airport (now Narita International Airport) route when a bomb on board exploded, killing a passenger. The airliner was able to make an emergency landing. Authorities later found out that Ramzi Yousef planted the bomb on the airliner to test the bomb for his Project Bojinka plot. His project was discovered in Manila after an apartment fire on the night of January 5 and the morning of January 6, 1995.
Ramzi Yousef was on board Flight 434 from Manila when he planted the bomb beneath a vacant seat. He used a fake identity thus he was able to pass through security in Manila. Yousef set the time for the bomb to blow off when the airplane was already in its Cebu–Tokyo leg. Yousef got off the plane during the stopover in Cebu from Manila.
References
- ^ a b c "Mactan–Benito Ebuen Air Base". Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 22 July 2013.
- ^ Mactan–Cebu airport to set aside P300-M for expansion
- ^ Positive News Media, "P-Noy names four Cebuanos to Mactan airport board", http://www.allvoices.com/s/event-6803478/aHR0cDovL3Bvc2l0aXZlbmV3c21lZGlhLm5ldC9hbTIvcHVibGlzaC9CdXNpbmVzc18xOS9QLU5veV9uYW1lc19mb3VyX0NlYnVhbm9zX3RvX01hY3Rhbl9haXJwb3J0X2JvYXJkLnNodG1s
- ^ http://www.passengerterminaltoday.com, news, "Expanded Mactan–Cebu to open in November," http://www.passengerterminaltoday.com/news.php?NewsID=27172
- ^ Gregg M. Rubio/FPL (The Freeman), November 03, 2010, "Villarete to finish MCIAA administrative building despite corruption tag," http://www.philstar.com/Article.aspx?articleId=626707&publicationSubCategoryId=107
- ^ http://www.philstar.com/business/2014/04/23/1314907/megawide-gmr-remits-p16.1-b-payment-cebu-airport-project
- ^ http://www.mb.com.ph/megawide-gmr-airport-design-reflects-cebu-culture/
- ^ http://asia.nikkei.com/Business/Business-Briefs/PhilippineIndia-consortium-to-overhaul-Cebu-airport-by-2018
- ^ http://ppp.gov.ph/?p=7469
- ^ ABS-CBN News.com, May 4, 2014, "AirAsia to mount KL–Cebu direct flights", http://www.abs-cbnnews.com/business/05/04/14/airasia-mount-kl-cebu-direct-flights
- ^ "Cebu Pacific to launch direct Cebu-Tokyo flights". www.cebupacificair.com. Cebu Pacific. 27 October 2014. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ http://airlineroute.net/2014/12/09/ciae-ceb-jan15/
- ^ "PH Embassy hosts launch of Moscow-Cebu charter flights". Department of Foreign Affairs - Philippines Official webpage. 24 October 2014. Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- ^ "PAL to launch Cebu-Los Angeles direct flights in 2016". Rappler. 6 August 2015. Retrieved 6 August 2015.
- ^ http://airlineroute.net/2014/08/29/pr-cebngo-dec14/
- ^ http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2015-07/26/c_134448499.htm
External links
- Mactan-Cebu International Airport
- Mactan–Cebu International Airport Authority
- Mactan Cebu International Airport - Flight Status and Updates for Travelers to and from cebu
- Template:WAD
- Current weather for RPVM at NOAA/NWS
- Airport information for CEB / RPVM at Great Circle Mapper. Source: DAFIF (effective October 2006).
- Accident history for CEB / RPVM at Aviation Safety Network