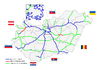
Highways in Hungary
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Hungarian. (January 2019) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|

Controlled-access highways in Hungary are dual carriageways, grade separated with controlled-access, designed for high speeds. The legislation amendments defined two types of highways: motorways (Hungarian: autópálya) and expressways (Hungarian: autóút).
The main differences are that motorways have emergency lanes and the maximum allowed speed limit is 130 km/h (81 mph), while expressways may be built without them and the speed limit is 110 km/h (68 mph).
According to the Állami Autópályakezelő Zrt. ("State Motorway Management Plc."), the total length of the Hungarian motorway system was 1,646 kilometers in 2020.[1] The construction of the Hungarian motorway system started in 1964 with M7, which finished in 1975 between Budapest and the Lake Balaton. The total length of the system reached 200 km in 1980, 500 km in 1998 and 1000 km in 2007.
The Hungarian motorway network currently comprises 13 motorways, 13 expressways, of which 18 of them are at least partially operational, and 12 (M1, M5, M7, M15, M19, M25, M30, M31, M35, M43, M51 and M70) have been completed as of October 2021.
Highway system
Motorways and Expressways
The following is a list of all existing and/or under construction highways in Hungary.
Motorways in Hungary (![]() ; in Hungarian: autópálya), are defined as two-lane motorways in each direction, with emergency lane. The speed limit is 130 km/h or 80 mph.
Expressways (
; in Hungarian: autópálya), are defined as two-lane motorways in each direction, with emergency lane. The speed limit is 130 km/h or 80 mph.
Expressways (![]() ; in Hungarian: autóút) are defined as dual carriageways with lower standards than that of a motorway, but with the same restrictions. Speed limit is 110 km/h or 70 mph.
Road signs are white shield on blue and the abbreviation for both types of highways is M.
; in Hungarian: autóút) are defined as dual carriageways with lower standards than that of a motorway, but with the same restrictions. Speed limit is 110 km/h or 70 mph.
Road signs are white shield on blue and the abbreviation for both types of highways is M.
| Sign | E-roads | Class | Route | Planned total length (km) |
In use | U/C (km)[2] |
Map | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| From | Via | To | (km)[2] | % | ||||||
| Biatorbágy ( |
Törökbálint ( |
Budaörs ( |
109 | 77 | 71% | 0 |  | |||
| Budapest | Budaörs ( |
Hegyeshalom |
171 | 171 | 100% | N/A |  | |||
| Dunakeszi ( |
Vác – Rétság | Hont–Parassapuszta |
68 | 30 | 44% | 0 |  | |||
| Budapest ( |
Gödöllő ( |
Beregdaróc |
307 | 280 | 91% | 0 |  | |||
| Budapest | Vecsés ( |
Nagykereki |
223 | 130 | 58% | 0 |  | |||
| Budapest | Gyál ( |
Röszke |
173 | 173 | 100% | N/A |  | |||
| Budapest ( |
Budafok-Tétény ( |
Ivándárda |
212 | 193 | 91% | 19 |  | |||
| Budapest | Törökbálint ( |
Letenye ( |
233 | 233 | 100% | N/A |  | |||
| Balatonfőkajár ( |
Sárbogárd ( |
Abony ( |
163 | 8 | 5% | 0 |  | |||
| Szekszárd ( |
Nemesnádudvar | 31 | 21 | 68% | 0 |  | ||||
| Levél ( |
Rajka |
15 | 15 | 100% | N/A |  | ||||
| Győr East ( |
Győr North | 9 | 9 | 100% | N/A |  | ||||
| Kál East ( |
Eger | 18 | 18 | 100% | N/A |  | ||||
| Emőd ( |
Miskolc | Tornyosnémeti |
86 | 86 | 100% | N/A |  | |||
| Nagytarcsa ( |
Gödöllő ( |
12 | 12 | 100% | N/A |  | ||||
| Görbeháza ( |
Debrecen | Berettyóújfalu ( |
69 | 69 | 100% | N/A |  | |||
| Szeged ( |
Makó | Csanádpalota |
58 | 58 | 100% | N/A |  | |||
| Nagykőrös ( |
Szarvas | Békéscsaba | 111 | 80 | 72% | 14 |  | |||
| Budapest ( |
(section of the former route of |
Budapest ( |
4 | 4 | 100% | N/A |  | |||
| Bóly ( |
Pécs – Szigetvár ( |
Barcs |
97 | 32 | 33% | 0 |  | |||
| Letenye ( |
Tornyiszentmiklós |
21 | 21 | 100% | N/A |  | ||||
| Hollád ( |
Keszthely – Zalaegerszeg | Körmend ( |
83 | 9 | 11% | 0 |  | |||
| Körmend ( |
Rábafüzes |
28 | 27 | 96% | 1 |  | ||||
| Győr ( |
Pápa | 36 | 0 | 0% | 36 |  | ||||
| Győr ( |
Csorna ( |
Sopron |
95 | 89 | 94% | 6 |  | |||
| Körmend ( |
Szombathely ( |
Levél ( |
122 | 64 | 53% | 0 |  | |||
| Szombathely ( |
Kőszeg |
22 | 1 | 5% | 0 |  | ||||
Major motorways
- M1

The M1 starts from the western part of Budapest, it connects the Hungarian capital with Győr and northwestern part of Hungary, towards Vienna. The motorway is part of the Pan-European Corridor IV, and European route E60, E65 and E75. Average daily traffic is 75,510 near Budapest and 56,421 vehicles/day near Győr.[3] The construction of the motorway began 1964, it took more than thirty years to reach Hegyeshalom and the Austrian border. Its significance has increased since the change of regime in 1990, and today it is the most important western connection in Hungary.
Main junctions:
 M1-M85 Győr-west, towards to Sopron and Szombathely (M86)*
M1-M85 Győr-west, towards to Sopron and Szombathely (M86)* M1-M15 Mosonmagyaróvár-west, toward to Bratislava
M1-M15 Mosonmagyaróvár-west, toward to Bratislava
- M3

The M3 starts from north-eastern part of Budapest, it connects the Hungarian capital with Nyíregyháza and northeast part of Hungary, towards Mukachevo. The motorway is part of the Venice-Trieste-Ljubljana-Budapest-Lviv-Kyiv line Central-East Europe Corridor V, and European route E71, E79, E573 and E579. This is one of the most important route of the Hungarian motorway and road network, the southwest-north-eastern diagonal main line of traffic forming part of Budapest. Through Ukraine, Eastern Europe, and through Slovakia, creates a highway connection to the countries of north-eastern Europe.
Main junctions:
- M5

The M5 starts from Budapest, it connects the Hungarian capital with Szeged and southeast part of Hungary, towards Belgrade. It was the third motorway in Hungary that reached the border. The motorway is part of the Pan-European Corridor X, and European route E75. The motorway was built in the 1980s and reached the Serbian border in March 2006.
Main junctions:
- M6

The M6 starts from Budapest (M0-M6 Interchange), it connects the Hungarian capital with Mohács, on the right bank of the Danube in the south, towards Osijek and Sarajevo. The motorway is part of the European route E73. The final section reaching the border is currently under construction with a planned opening date in 2024. The connecting Croatian section is scheduled to be delivered a year earlier.
Main junctions:
 M6-M8 Dunaújváros-south, toward to Veszprém and Kecskemét
M6-M8 Dunaújváros-south, toward to Veszprém and Kecskemét M6-M60 Bóly, toward to Pécs
M6-M60 Bóly, toward to Pécs
- M7

The M7 starts from western part of Budapest, it connects the Hungarian capital with Lake Balaton and southwestern part of Hungary, towards Zagreb. The motorway is part of the Pan-European Corridor V, and European route E71. Average daily traffic is 62,779 near Budapest and 49,273 vehicles/day near Székesfehérvár.[3] The motorway was built in the 1960s and reached the Croatian border in October 2008.
Main junctions:
Gallery
-
Pentele Bridge in M8
-
M15 near Rajka
-
Sajó Bridge in M30
-
M35 near Derecske
-
M43 near Szeged-Sándorfalva
-
M60 near Kozármisleny
-
Eastern section of M0
-
M2 near Vác
-
The end of M9 near Dusnok
-
Korongi Bridge in M70
-
M85-M86 near Csorna
-
M86 near Szombathely
Planned Highways
List of planned highways (motorways and expressways)
| Sign | E-roads | Class | Route | Planned total length (km) |
Planning status |
Map | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| From | Via | To | ||||||
| Budapest ( |
Pilisvörösvár – Kesztölc ( |
Esztergom |
34 km | under planning |
 | |||
| Abony ( |
Kál ( |
63 km | under planning |
 | ||||
| Vásárosnamény ( |
Záhony |
39 km | under planning |
 | ||||
| Őr ( |
Mátészalka | Csenger |
45 km | under planning |
 | |||
| Sárbogárd ( |
Kisigmánd ( |
Komárom |
114 km | under planning |
 | |||
| Hollád ( |
Kaposvár – Szigetvár ( |
Szeged ( |
90 + 131 km | under planning |
 | |||
| Bicske ( |
Kesztölc ( |
32 km | under planning |
 | ||||
Rapid Roads
A third tier of highways, called 'Rapid Road' (in Hungarian: Gyorsút), was introduced in a 2015 Government Decree.[4] Rapid roads were defined as dual carriageways with lower standards than that of an expressway, and the level intersection (e.g., traffic light node, roundabout) is permissible. Similarly to expressways, the speed limit was defined as 110 km/h or 70 mph. The concept was abandoned in 2018, with some Rapid Roads upgraded as expressways, and others becoming 2x2 lane main roads.
This is a list of previously planned Rapid Roads:
| Number | Route | Length | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| R8 | Székesfehérvár - Herend | 58 km | name changed back to main road |
| ? km | replaced with expressways | ||
| Hatvan |
? km | name changed back to main road | |
| 46 km | renamed to main road | ||
| Győr ( |
36 km | upgraded to expressway |


Main roads with 2x2 traffic lanes
- Road
 between M3 and Gyöngyös (7 km)
between M3 and Gyöngyös (7 km) - Several parts of Road
 between Budapest and Püspökladány (40 km) (The way between Budapest and Püspökladány is about 165 km/103miles)
between Budapest and Püspökladány (40 km) (The way between Budapest and Püspökladány is about 165 km/103miles) - Road
 between M5 and Kecskemét (8 km)
between M5 and Kecskemét (8 km) - Road
 between Szekszárd and Tolna (4 km)
between Szekszárd and Tolna (4 km) - Several parts of Road
 between Veszprém and Székesfehérvár
between Veszprém and Székesfehérvár
- In the future this sections will be part of M8.
- Road
 between Budapest and Szentendre (4 km and 9 km within the city limit of Budapest)
between Budapest and Szentendre (4 km and 9 km within the city limit of Budapest) - Several parts of Road
 between Hatvan and Salgótarján
between Hatvan and Salgótarján
- In the future this sections will be part of R21.
- Road
 between Miskolc and Sajóbábony (10 km)
between Miskolc and Sajóbábony (10 km) - Road
 between Békéscsaba and Gyula (11 km)
between Békéscsaba and Gyula (11 km) - Road
 between Szeged and Hódmezővásárhely (24 km)
between Szeged and Hódmezővásárhely (24 km) - Road
 between Pécs and Pécs-Pogány International Airport (10 km)
between Pécs and Pécs-Pogány International Airport (10 km) - Road
 between Sopron and the border with Austria (4 km)
between Sopron and the border with Austria (4 km)
Toll requirements

The e-vignette user charge system applies to motorcycles, passenger cars and their trailers, as well as cargo vehicles with a maximum permissible gross weight of 3.5 tonnes, campers and buses, and their trailers. These vehicles are authorized to use the Hungarian toll speedway network's roads exclusively with pre-purchased –purchased prior to entering a toll speedway section– road use authorization, i.e. e-vignettes. The amount of toll charges depends on the category of the vehicle and the type of the e-vignette. The category of the motor vehicles must be determined according to the official entry that appears in the vehicle registration certificate, based on the maximum permissible gross weight of the motor vehicle and the number of persons it is allowed to transport.[5]
Hungarian system has 2 main type in terms of salary.
1, time-based fee vignettes (E-matrica) with a validity of either 10 days (2975 HUF), 1 month (4780 HUF) or 1 year (42980 HUF). The following motorway sections are toll-free for cars up to 3.5 t:[6]
- the following sections of the M0 expressway: - 63 km
- the section between Main Road 1 (exit -1) and the M5 motorway (exit 32),
- the section between M4 expressway (exit 41) and M3 motorway (exit 68),
- Megyeri Bridge (the section between Main Road 11 and Main Road 2), (exit 74-77).
- the M31 motorway - 12 km
- the section of M4 expressway (sign of Main Road 4) between the road leading from Vecsés to Budapest Liszt Ferenc International Airport (section between km section 19+550 and km section 20+518)
- the M8 motorway
- the Pécs south-west loop section of the M60 motorway between roads no. 58 (exit 30) and 5826 (exit 32) - 2 km
- 2, regional vignettes
History
Development of the overall length (at the end of):
| Year | 1964 | 1970 | 1975 | 1980 | 1985 | 1990 | 1996 | 2002 | 2006 | 2010 | 2014 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Length in km | 7 | 85 | 136 | 213 | 302 | 361 | 440 | 638 | 967 | 1,290 | 1,382 | 1,481 | 1,489 | 1,524 | 1,600 | 1,740 |
| Year | Length (km) | Year | Length (km) | Year | Length (km) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1964 | 7 | 2003 | 667 | 2013 | 1,361 | ||
| 1970 | 85 | 2004 | 717 | 2014 | 1,370 | ||
| 1975 | 136 | 2005 | 803 | 2015 | 1,447 | ||
| 1980 | 213 | 2006 | 967 | 2016 | 1,481 | ||
| 1985 | 302 | 2007 | 1,037 | 2017 | 1,490 | ||
| 1990 | 361 | 2008 | 1,113 | 2018 | 1,524 | ||
| 1996 | 440 | 2009 | 1,118 | 2019 | 1,600 | ||
| 2001 | 571 | 2010 | 1,290 | 2020 | 1,740 | ||
| 2002 | 638 | 2011 | 1,321 | 2021 | 1,851 | ||
| IEA-PVPS,[7] | |||||||
Hungarian highways network since 1964
Gallery
-
Traffic sign for an autópálya (motorway)
-
Traffic sign for an autóút (expressway)
Italic text'Italic text== Opening of new highway sections == Construction of new motorways in recent years has been hampered due to corruption scandals and austerity measures as well as owing to new European rules under which old EIA assessments lapsed. In the coming years, the highway network expansion focuses on connecting all major cities into the highway network, and on the completion of highways in the border region of Hungary. Construction of non-radial roads continues to be slow.
| Sign | From | To | Length | Construction started | Planned opening | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Győr | Tét | 17.6 km | 10/2020 | Q4/2023[9] | connects the city of Pápa into the highway system | |
| Tét | Pápa | 18.4 km | 10/2020 | Q4/2023[10] | connects the city of Pápa into the highway system | |
| Bóly | Ivándárda | 20 km | 07/2021 | Q1/2024[11] | extends the motorway to the border with Croatia | |
| Lakitelek | Szentkirály | 4.6 km | 02/2020 | Q1/2024[12] | ||
| Sopron North (Fertőrákos) | Sopron North-West | 4.0 km | 12/2019 | Q3/2024[13] | includes a 780 m long tunnel | |
| Kecskemét (M5) | Szentkirály | 32.3 km | 03/2022 | Q1/2025[14] | completes M44 and connects the city of Békéscsaba into the highway system |
See also
- Transport in Hungary
- Roads in Hungary
- List of controlled-access highway systems
- Evolution of motorway construction in European nations
References
- ^ Állami Autópályakezelő Zrt. (ÁAK) (2013). "Az ÁAK által kezelt úthálózat részletes adatai (2013)". Nemzetiutdij.hu. Archived from the original on 2015-03-23. Retrieved 2015-05-14.
- ^ a b "Podnikateľský plán 2019" [Business plan 2019] (PDF). ndsas.sk (in Slovak). Národná diaľničná spoločnosť, a.s. 2018-11-06. p. 42. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-04-28.
- ^ a b "Az autópálya-hálózat forgalmi menedzsment tervének elõkészítõ vizsgálatai – forgalmi elemzések" (PDF) (in Hungarian). ktenet.hu.
- ^ 1784/2015. (X. 30.) Korm. határozat
- ^ "National Toll Payment Services PLC". toll-charge.hu.
- ^ "National Toll Payment Services PLC". toll-charge.hu.
- ^ http://www.irena.org/DocumentDownloads/Publications/IRENA_RE_Capacity_Statistics_2017.pdf [bare URL PDF]
- ^ This list contains the limited-access roads (expressways) in Hungary with (at least) four traffic lanes and median.
- ^ "Indul az építkezés: 36 kilométernyi négysávos úttal gazdagodik Észak-Dunántúl". Nif.hu. Retrieved 2022-06-29.
- ^ "Indul az építkezés: 36 kilométernyi négysávos úttal gazdagodik Észak-Dunántúl". Nif.hu. Retrieved 2022-06-29.
- ^ "Letették az M6 autópálya befejező szakaszának szakasz alapkövét". Nif.hu. Retrieved 2022-06-29.
- ^ "Békéscsaba megközelítése - M44 Szentkiraly-Lakitelek". Nif.hu. Retrieved 2022-06-29.
- ^ "Sopron megközelítése, M85 autóút Fertőrákos csomópont – Sopron oh. szakasz a 8647. jelű Sopron ÉNy-i elkerülő úttal alapkövét". Nif.hu. Retrieved 2022-06-29.
- ^ "Megkezdődnek a munkák az M44 gyorsforgalmi út M5 autópálya és Szentkirály közötti szakaszán". Nif.hu. Retrieved 2022-06-29.
- General
- Magyarország autóatlasz (Road atlas of Hungary), Dimap-Szarvas, Budapest, 2004
- Magyarország autóatlasz (Road atlas of Hungary), Dimap-Szarvas, Budapest, 2013
External links
- National Toll Payment Services Plc (in Hungarian, some information also in English)
- Home page of the National Toll Payment Services Plc.
- Detailed map of the Hungarian motorway system (2021)