Haiti
Republic of Haiti | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "L'Union Fait La Force" (French) "Strength Through Unity " | |
| Anthem: La Dessalinienne | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Port-au-Prince |
| Official languages | Haitian Creole, French |
| Ethnic groups | 95.0% black, 0.1% white, 4.9% mulatto and Amerindian (Arawak) [1][2] |
| Demonym(s) | Haitian |
| Government | Presidential republic |
| René Préval | |
| Jean-Max Bellerive | |
| Formation | |
• as Saint-Domingue | 1697 |
• Independence from France | 1 January 1804 |
| Area | |
• Total | 27,751 km2 (10,715 sq mi) (140th) |
• Water (%) | 0.7 |
| Population | |
• 2009 estimate | 10,033,000[3] (82nd) |
• Density | 361.5/km2 (936.3/sq mi) (31st) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2008 estimate |
• Total | $11.570 billion[4] |
• Per capita | $1,317[4] |
| GDP (nominal) | 2008 estimate |
• Total | $6.943 billion[4] |
• Per capita | $790[4] |
| Gini (2001) | 59.2 high |
| HDI (2007) | Error: Invalid HDI value (149th) |
| Currency | Gourde (HTG) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | 509 |
| ISO 3166 code | HT |
| Internet TLD | .ht |
Haiti (Template:Pron-en; French Haïti, pronounced [a.iti]; Haitian Creole: Ayiti), officially the Republic of Haiti ([République d'Haïti] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) ; [Repiblik Ayiti] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) is a Creole- and French-speaking Caribbean country. Along with the Dominican Republic, it occupies the island of Hispaniola, in the Greater Antillean archipelago. Ayiti (Land of high mountains) was the indigenous Taíno or Amerindian name for the mountainous western side of the island. The country's highest point is Pic la Selle, at 2,680 metres (8,793 ft). The total area of Haiti is 27,750 square kilometres (10,714 sq mi) and its capital is Port-au-Prince.
Haiti's regional, historical, and ethnolinguistic position is unique for several reasons. It was the first independent nation in Latin America, the first post-colonial independent Black-led nation in the world, and the only nation whose independence was gained as part of a successful slave rebellion. Despite having common cultural links with its Hispano-Caribbean neighbors, Haiti is the only predominantly Francophone independent nation in the Americas, and one of only two (along with Canada) which designate French as an official language; the other French-speaking areas are all overseas départements or collectivités of France.
History
Pre-colonial and Spanish colonial periods
The island of Hispaniola, which Haiti occupies the western third, was originally inhabited by the Taíno Arawak Indians, a seafaring branch of the South American Arawaks. Ayiti, which means "mountainous land", is a name used by the Taíno-Arawak people, who also called some bias of it Bohio, meaning "rich villages". Kiskeya is yet a fifth term that has been attributed to the Taínos for the island. The Taíno population on Hispaniola were divided through a system of established cacicazgos (chiefdoms), named Marien, Maguana, Higuey, Magua and Xaragua, which could be further subdivided.
The cacicazgos (later called caciques in French) were tributary kingdoms, with payment consisting of food grown by the Taíno. Taino cultural artifacts include cave paintings in several locations in the nation, which have become national symbols of Haiti and tourist attractions. Modern-day Léogane, a town in the southwest, is at the epicenter of what was the chiefdom of Xaragua.

Christopher Columbus landed at Môle Saint-Nicolas on 5 December 1492, and claimed the island for Spain. Nineteen days later, his ship the Santa María ran aground near the present site of Cap-Haitien; Columbus was forced to leave 39 men, founding the settlement of La Navidad.
Following the destruction of La Navidad by the Amerindians, Columbus moved to the eastern side of the island and established La Isabela. One of the earliest leaders to fight off Spanish conquest was Queen Anacaona, a Taíno princess from Xaragua who married Chief Caonabo, a Taíno king (cacique) from Maguana. The two resisted European rule but to no avail; she was captured by the Spanish and executed in front of her people. To this day, Anacaona is revered in Haiti as one of the country's first founders, preceding the likes of founding fathers such as Toussaint Louverture and Jean-Jacques Dessalines.
The Spaniards exploited the island for its gold, mined chiefly by local Amerindians directed by the Spanish occupiers. Those refusing to work in the mines were slaughtered or forced into slavery. Europeans brought chronic infectious diseases with them that were new to the Caribbean. Diseases were the chief cause of their decline because the Taíno had no natural immunity,[6] but ill treatment, malnutrition and a drastic drop of the birthrate also contributed to reduction of the indigenous population. The first recorded smallpox outbreak in Americas occurred in 1507, when Spaniards brought the disease to Hispaniola.[7]
The Spanish governors began importing enslaved Africans for labor. In 1517, Charles V authorized the draft of slaves. The Taínos became virtually, but not completely extinct on the island of Hispaniola. Some who evaded capture fled to the mountains and established independent settlements. These survivors mixed with escaped African slaves (runaways called maroons) and produced a multiracial generation called zambos. French settlers later called people of mixed African and Amerindian ancestry marabou. The mestizo increased in number from children born to relationships between native women and European men. Others were born as a result of unions between African women and European men, who were called mulâtre in French.
The western part of Hispaniola soon was settled by French buccaneers. Among them, Bertrand D'Ogeron succeeded in growing tobacco, which prompted many of the numerous buccaneers and freebooters to turn into settlers. This population did not submit to Spanish royal authority until the year 1660 and caused a number of conflicts.
17th century settlement
Bertrand D'Orgeron attracted many colonists from Martinique and Guadeloupe, such as the Roy family (Jean Roy, 1625-1707), Hebert (Jean Hebert, 1624, with his family) and the Barre (Guillaume Barre, 1642, with his family), driven out by pressure on lands generated by extension of sugar plantations. From 1670 to 1690, a drop in the tobacco markets affected the island and significantly reduced the number of settlers.
Jessica grew stronger, plundering settlements, such as those of Vera Cruz in 1683 and Campêche in 1686. Jean-Baptiste Antoine Colbert, Marquis de Seignelay, elder son of Jean-Baptiste Colbert and Minister of the Navy, brought back some order. He ordered the establishment of indigo and sugar cane plantations. The first windmill for processing sugar was created in 1685.
Treaty of Ryswick and slave colony
France and Spain settled hostilities on the island by the Treaty of Ryswick of 1697, which divided Hispaniola between them. France received the western third and subsequently named it Saint-Domingue (not the current Santo-Domingo, which is in the Dominican Republic and was part of the eastern side given to the Spanish through the treaty). Many French colonists soon arrived and established plantations in Saint-Domingue due to high profit potential. From 1713 to 1787, approximately 30,000 colonists emigrated from Bordeaux, France, to the western part of the island.
By about 1790, Saint-Domingue had greatly overshadowed its eastern counterpart in terms of wealth and population. It quickly became the richest French colony in the New World due to the immense profits from the sugar, coffee and indigo industries. The labor and knowledge of thousands of enslaved Africans, who brought skills and technology for indigo production to the island, made it possible. The French-enacted Code Noir (Black Code), which was prepared by Jean-Baptiste Colbert and ratified by Louis XIV, established rigid rules on slave treatment and permissible freedom. It has been described as one of the most brutally efficient slave colonies there ever was - a third of new arrivals died within a few years.[8]
Haitian Revolution
The French Revolution contributed to social upheavals in Saint-Domingue and the French and West Indies. Most important was the revolution of the slaves in Saint-Domingue, starting on the northern plains in 1791. In 1792 the French government sent three commissioners with troops to try to reestablish control. They began to build an alliance with gens de couleur, who were looking for their rights. In 1793, France and Great Britain went to war, and British troops invaded Saint-Domingue. The execution of Louis XVI heightened tensions in the colony. To build an alliance with the gens de couleur and slaves, the French commissioners Sonthonax and Polverel abolished slavery in the colony. Six months later, the National Convention endorsed abolition and extended it to all of the French colonies.
Toussaint L'Ouverture, a former slave and leader in the slave revolt who rose in importance as a military commander because of his many skills, achieved peace in Saint-Domingue after years of war against both external invaders and internal dissension. He had established a disciplined, flexible army and drove out both the Spaniards and the British invaders who threatened the colony. He restored stability and prosperity by daring measures, including inviting the return of planters and insisting that freed men work on plantations to renew revenues for the island. He also renewed trading ties with Great Britain and the United States.
Independence
The French government changed and the legislature began to rethink its decisions on slavery in the colonies. After Toussaint L'ouverture created a separatist constitution, Napoleon Bonaparte sent an expedition of 30,000 men under the command of his brother-in-law, General Charles Leclerc, to retake the island. Leclerc's mission was to oust L'ouverture and restore slavery. The French achieved some victories. Leclerc invited Toussaint L'ouverture to a parley, kidnapped him and sent him to France, where he was imprisoned at Fort de Joux. He died there in 1803 of exposure and tuberculosis [8] or malnutrition and pneumonia.
The native leader Jean-Jacques Dessalines, long an ally of Toussaint L'ouverture, defeated the French troops led by Donatien-Marie-Joseph de Vimeur, vicomte de Rochambeau at the Battle of Vertières. At the end of the double battle for emancipation and independence, former slaves proclaimed the independence of Saint-Domingue on 1 January 1804, declaring the new nation as Haiti, honoring one of the indigenous Taíno names for the island. It is the only nation born of a slave revolt [8].
Dessalines was proclaimed Emperor for life by his troops.[9] He exiled or killed the remaining whites and ruled as a despot.[10] He was assassinated on 17 October 1806. The country was divided then between a kingdom in the north directed by Henri Christophe, and a republic in the south directed by a gens de couleur Alexandre Pétion. Henri Christophe is best known for constructing the Citadelle Laferriere, the largest fortress in the Western Hemisphere, to defend the island against the French. President Jean Pierre Boyer, also a gens de couleur, managed to reunify the two halves and extend control again over the western part of the island.
In July 1825, the king of France Charles X sent a fleet of fourteen vessels and troops to reconquer the island. To maintain independence, President Boyer agreed to a treaty by which France recognized the independence of the country in exchange for a payment of 150 million francs (the sum was reduced in 1838 to 90 million francs) - an indemnity for profits lost from the slave trade. The French abolitionist Victor Schoelcher wrote "Imposing an indemnity on the victorious slaves was equivalent to making them pay with money that which they had already paid with their blood."
A long succession of coups followed the departure of Jean-Pierre Boyer. National authority was disputed by factions of the army, the elite class and the growing commercial class, now made up of numerous immigrants: Germans, Americans, French and English.
On more than one occasion US, French, German and British forces claimed large sums of money from the vaults of the National Bank of Haiti. [11]
Expatriates bankrolled and armed opposing groups. In 1888 US Marines supported a military revolt against the government. In 1892 the German government supported suppression of the movement of Anténor Firmin. In 1912 Syrians residing in Haiti participated in a plot in which the presidential palace was destroyed. In January 1914, British, German and United States forces entered Haiti ostensibly to protect their citizens.[11]
Since 1915
The United States occupied the island from 1915 to 1934. The Haitian administration dismantled the constitutional system, reinstituted virtual slavery for building roads, and established the National Guards that ran the country after the Marines left.
From 1957 to 1986, the Duvalier family reigned as dictators, turning the country into a hermit kingdom with a personality cult and excessive corruption. They created the private army and terrorist death squads known as Tonton Macoutes. Many Haitians fled to exile in the United States and Canada, especially French-speaking Quebec. In the 1970s the United States funded major efforts to establish assembly plants for U.S. manufacturers. In the mid 1980s the US continued military and economic aid to the regime.[12]
In 1986 protests against "Baby Doc" led the U.S. to arrange for Duvalier and his family to be exiled to France. Army leader General Henri Namphy headed a new National Governing Council.[12]
In March 1987 a new Constitution was overwhelmingly approved by the population. General elections in November were aborted hours after dozens were shot by soldiers and the Tonton Macoute in the capital and scores more around the country.
In December 1990, the former priest Jean-Bertrand Aristide won the election by more than two thirds of the vote. His mandate began on 7 February 1991. In August 1991, Jean-Bertrand Aristide's government faced a non-confidence vote within the Haitian Chamber of Deputies and Senate. Eighty three voted against him, while only 11 members voted in support of Aristide's government. Following a coup d'etat in September 1991, President Aristide was flown into exile. In accordance with Article 149 of Haiti's Constitution of 1987, Supreme Court Justice Joseph Nerette was named Provisional President and elections were called for December 1991. These were blocked by the international community and the resulting chaos extended into 1994.
In 1994, Haitian General Raoul Cédras asked former U.S. President Jimmy Carter to help avoid a U.S. military invasion of Haiti.[13] President Carter relayed this information to President Clinton, who asked Carter, in his role as founder of The Carter Center, to undertake a mission to Haiti with Senator Sam Nunn, D-GA, and former Joint Chiefs of Staff Chairman Colin Powell.[13] The team successfully negotiated the departure of Haiti's military leaders and the peaceful entry of U.S. forces under Operation Uphold Democracy, paving the way for the restoration of Jean-Bertrand Aristide as president.[13]
Aristide left the presidency in 1995. He was re-elected in 2000. His second term was marked by accusations of corruption. In 2004 a paramilitary coup ousted Aristide a second time. (See 2004 Haitian rebellion) Aristide was removed by U.S. Marines from his home in what he described as a "kidnapping", and briefly held by the government of the Central African Republic to which the U.S. had decided to fly him. Aristide obtained his release and returned to the hemisphere shortly afterwards, although he has not returned to Haiti.
Boniface Alexandre assumed interim authority. In February 2006, following elections marked by uncertainties and popular demonstrations, René Préval (close to the still-popular Aristide and former president of the Republic of Haiti between 1995 and 2000) was elected.
The United Nations Stabilization Mission in Haiti (also known as MINUSTAH) has been in the country since the 2004 Haiti Rebellion.
2010 earthquake
This section documents a current event. Information may change rapidly as the event progresses, and initial news reports may be unreliable. The latest updates to this section may not reflect the most current information. (January 2010) |
On 12 January 2010, a 7.1 magnitude earthquake struck approximately 10 miles (16 km) away from the capital city Port-Au-Prince.
Politics
The government of Haiti is a semi-presidential republic, pluriform multiparty system wherein the President of Haiti is head of state directly elected by popular elections.[citation needed] The Prime Minister acts as head of government and is appointed by the President from the majority party in the National Assembly. Executive power is exercised by the President and Prime Minister who together constitute the government.
Legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of the National Assembly of Haiti. The government is organized unitarily, thus the central government delegates powers to the departments without a constitutional need for consent. The current structure of Haiti's political system was set forth in the Constitution of Haiti on 29 March 1987. The current president is René Préval.
Haitian politics have been contentious. Most Haitians are aware of Haiti's history as the only country in the Western Hemisphere to undergo a successful slave revolution. On the other hand, the long history of oppression by dictators, including François Duvalier, has markedly affected the nation. France and the United States have repeatedly intervened in Haitian politics since the country's founding, sometimes at the request of one party or another. People's awareness of the threat of such intervention also permeates national life.
The country has a particularly high level of corruption.
Departments, arrondissements, and communes
Haiti is divided into ten departments. The departments are listed below, with the departmental capital cities in parentheses.

- Artibonite (Gonaïves)
- Centre (Hinche)
- Grand'Anse (Jérémie)
- Nippes (Miragoâne)
- Nord (Cap-Haïtien)
- Nord-Est (Fort-Liberté)
- Nord-Ouest (Port-de-Paix)
- Ouest (Port-au-Prince)
- Sud-Est (Jacmel)
- Sud (Les Cayes)
The departments are further divided into 41 arrondissements, and 133 communes which serve as second and third level administrative divisions.
Geography
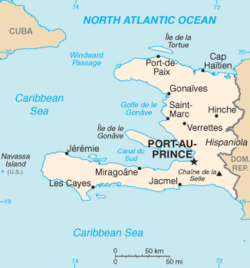
Haiti is situated on the western part of Hispaniola, the second largest island in the Greater Antilles. Haiti is the third largest country in the Caribbean behind Cuba and the Dominican Republic (the latter shares a 360 kilometer (224 mi) border with Haiti). Haiti at its closest point is only about 45 nautical miles (50 mi; 80 km) away from Cuba and has the second longest coastline (1,771 km (1,100 mi)*) in the Greater Antilles, Cuba having the longest. Haiti's terrain consists mainly of rugged mountains interspersed with small coastal plains and river valleys.
The northern region consists of the Massif du Nord (Northern Massif) and the Plaine du Nord (Northern Plain). The Massif du Nord is an extension of the Cordillera Central in the Dominican Republic. It begins at Haiti's eastern border, north of the Guayamouc River, and extends to the northwest through the northern peninsula. The lowlands of the Plaine du Nord lie along the northern border with the Dominican Republic, between the Massif du Nord and the North Atlantic Ocean. The central region consists of two plains and two sets of mountain ranges. The Plateau Central (Central Plateau) extends along both sides of the Guayamouc River, south of the Massif du Nord. It runs from the southeast to the northwest. To the southwest of the Plateau Central are the Montagnes Noires, whose most northwestern part merges with the Massif du Nord. Its westernmost point is known as Cap Carcasse.
The southern region consists of the Plaine du Cul-de-Sac (the southeast) and the mountainous southern peninsula (also known as the Tiburon Peninsula). The Plaine du Cul-de-Sac is a natural depression which harbors the country's saline lakes, such as Trou Caïman and Haiti's largest lake Lac Azuei. The Chaîne de la Selle mountain range, an extension of the southern mountain chain of the Dominican Republic (the Sierra de Baoruco), extends from the Massif de la Selle in the east to the Massif de la Hotte in the west. This mountain range harbors Pic la Selle, the highest point in Haiti at 2,680 metres (8,793 ft).
The country's most important valley in terms of crops is the Plaine de l'Artibonite, which is oriented south of the Montagnes Noires. This region supports the country's (also Hispaniola's) longest river, the Riviere l'Artibonite which begins in the western region of the Dominican Republic and continues most of its length through central Haiti and onward where it empties into the Golfe de la Gonâve. The eastern and central region of the island is a large elevated plateau. Haiti also includes various offshore islands. The historically famous island of Tortuga (Île de la Tortue) is located off the coast of northern Haiti. The arrondissement of La Gonâve is located on the island of the same name, in the Golfe de la Gonâve. Gonave Island is moderately populated by rural villagers. Île à Vache (Island of Cows) is located off the tip of southwestern Haiti. It is a lush island with many beautiful sights. Also part of Haiti are the Cayemites and Ile de Anacaona.
Environment
In 1925, Haiti was lush, with 60% of its original forest covering the lands and mountainous regions. Since then, the population has cut down all but an estimated 2% of its original forest cover, and in the process has destroyed fertile farmland soils, contributing to desertification.[14] Erosion has been severe in the mountainous areas. Most Haitian logging is done to produce charcoal, the country's chief source of fuel. The plight of Haiti's forests has attracted international attention, and has led to numerous reforestation efforts, but these have met with little success to date. Despite the large environmental crises, Haiti retains a very high amount of biodiversity in proportion to its small size.

The island of Hispaniola is home to more than 6,000 plants, of which 35% are endemic; and 220 species of birds. None of the birds are endemic to Haiti, but La Selle Thrush is nearly so. The country's high biodiversity is due to its mountainous topography and fluctuating elevations in which each elevation harbors different microclimates and its own specific native fauna and flora. The country's varied scenery include lush green cloud forests (in some of the mountain ranges and the protected areas), high mountain peaks, arid desert, mangrove forest, and palm tree-lined beaches.[15]

Environmental Problems
In addition to soil erosion, deforestation has caused periodic flooding, as seen on 17 September 2004. Tropical storm Jeanne skimmed the north coast of Haiti, leaving 3,006 people dead in flooding and mudslides, mostly in the city of Gonaïves.[16] Earlier that year in May, floods killed over 3,000 people on Haiti's southern border with the Dominican Republic.[17]
Haiti was again pummeled by tropical storms in late August and early September 2008. The storms – Tropical Storm Fay, Hurricane Gustav, Hurricane Hanna and Hurricane Ike – all produced heavy winds and rain in Haiti. Due to weak soil conditions throughout Haiti, the country’s mountainous terrain, and the devastating coincidence of four storms within less than four weeks, valley and lowland areas throughout the country experienced massive flooding. Casualties proved difficult to count because the storm diminished human capacity and physical resources for such record keeping. Bodies continued to surface as the flood waters receded. A 10 September 2008 source listed 331 dead and 800,000 in need of humanitarian aid.[18] The grim state of affairs produced by these storms was all the more life threatening due to already high food and fuel prices that had caused a food crisis and political unrest in April 2008.[19]
As was the case in 2004, the coastal city of Gonaives was hit especially hard by the 2008 storms.
There were also major problems in 1999 with hurricanes leaving 9,398 dead, 10,000 injured and at least 5,000 missing.
The country is working to implement a biofuel solution to its energy problems.[20] Also, environmental organizations such as the Peasant Movement of Papaye (formed by Jean-Baptiste Chavannes) are trying to find solutions for Haiti's environmental problems.
On January 12, 2010, at 4:53 p.m. EST, an earthquake measuring 7.0 on the Richter scale occurred in Haiti [21]. The epicenter of the quake was just off the Haitian capital Port-au-Prince, sparking a tsunami watch for parts of the Caribbean, according to the U.S. Geological Survey.[22]
Widespread damage has been reported from the quake, with many buildings near the capital collapsing due to poor structural design. The capital city was largely destroyed.The Associated Press first reported that a hospital had collapsed. The Presidential palace was badly damaged, but the President unhurt. The quake had a reported magnitude of 7.3, with the focus being about 6 miles (10 km) underground, according to the USGS. A tsunami watch was posted for Haiti and parts of Cuba, the Dominican Republic and the Bahamas, but the watch was later cancelled.
Economy

While Haiti has been previously considered the poorest country in the Americas, recent data from the International Monetary Fund suggests that Nicaragua has become the poorest country, below Haiti as of April 2009. Speculation has arisen with Haiti's nominal GDP standing at 7.018 for 2009 and increasing to 8.582 by 2014 versus Nicaragua's nominal GDP standing at 6.554 and increasing to 8.532 by 2014.[23] However, economists also look into the GDP (PPP) of countries. Nicaragua's GDP (PPP) is 16.709 billion versus Haiti's 6.943 billion and the GDP per capita is $1,028 for Nicaragua and $790 for Haiti.[24] By 2014 it is estimated that Haiti's GDP PPP would increase to 14.642 versus Nicaragua's 20.650. [25] Speculative reports have arisen recently in a time when current President of Nicaragua Daniel Ortega has been withheld more than $60 million in economic assistance from the United States' Millennium Challenge Corporation due to certain irregularities in his presidential election. The Millennium Challenge Corporation funded Nicaragua with roughly $175 million. During this process, $62 million dollars was reduced from Nicaragua's development fund.[26] Due to the conflicting speculation of data, many have reverted to considering Haiti the poorest country in the Americas.
It is an impoverished country, one of the world's poorest and least developed. Comparative social and economic indicators show Haiti falling behind other low-income developing countries (particularly in the hemisphere) since the 1980s. Haiti now ranks 149th of 182 countries in the United Nations Human Development Index (2006). About 80% of the population were estimated to be living in poverty in 2003.[27] Most Haitians live on $2 or less per day. Economic growth was negative in 2001 and 2002, and flat in 2003.
About 66% of all Haitians work in the agricultural sector, which consists mainly of small-scale subsistence farming,[28] but this activity makes up only 30% of the GDP. The country has experienced little formal job creation over the past decade, although the informal economy is growing. Mangoes and coffee are two of Haiti's most important exports.[28] It has consistently ranked among the most corrupt countries in the world on the Corruption Perceptions Index.
Foreign aid makes up approximately 30%-40% of the national government's budget. The largest donor is the United States followed by Canada, and the European Union also contributes. Venezuela and Cuba also make various contributions to Haiti's economy, especially after alliances were renewed in 2006 and 2007.
U.S. aid to the Haitian government was completely cut off in 2001-2004 after the 2000 election was disputed and President Aristide was accused of various misdeeds. After Aristide's departure in 2004, aid was restored, and the Brazilian army led the United Nations Stabilization Mission in Haiti peacekeeping operation.
Haiti is expected to receive debt forgiveness for about $525 million of its debt through the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) initiative by mid-2009.[29]
Education
Of Haiti's 8.7 million inhabitants, The literacy rate of 65.9% is the lowest in the region. Haiti counts 15,200 primary schools, of which 90% are non-public and managed by the communities, religious organizations or NGOs.[30] The enrollment rate for primary school is 67%, of which less than 30% reach 6th grade. Secondary schools enroll 20% of eligible-age children. Charity organizations like Food for the Poor and Haitian Health Foundation are currently working on building schools for children as well as providing them necessary school supplies.
The educational system of Haiti is based on the French system. Higher education is provided by universities and other public and private institutions. It is under the responsibility of the Ministry of Education.[31]
A list of universities in Haiti includes:
- University of Caraibe (Université Caraïbe) (CUC)
- University of Haiti (Université d'État d'Haïti) (UEH)
- University Notre Dame of Haiti (Université Notre Dame d'Haïti) (UNDH)
- Université Chrétienne du Nord d'Haïti (UCNH)
- Université Lumière / MEBSH
- Université Quisqueya (UNIQ)
- Ecole Supérieure d'Infotronique d'Haïti (ESIH)
- Université Roi Henri Christophe
- Université Publique de l'Artibonite aux Gonaïves (UPAG)
- Université Publique du Nord au Cap-Haïtien (UPNCH)
- Université Publique du Sud au Cayes (UPSAC)
- Universite de Fondwa (UNIF)
- Ecole Le Bon Samaritain
Demographics
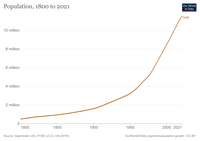
Although Haiti averages approximately 360 people per square kilometer (940 per sq. mi.), its population is concentrated most heavily in urban areas, coastal plains, and valleys. 90-95% of Haitians (depending on the source) are of predominately African descent; the remaining 5-10% of the population are mostly of mixed-race background. A small percentage of the non-black population consists primarily of white Haitians; mostly of Arab, Western European (French, German, Polish, Spanish), and Jewish origin.[32] [33]. Haitians of Asian descent (mostly of Chinese origin) number in at approximately 400.[32]
Haitian diaspora
Millions of Haitians live abroad, chiefly in the Dominican Republic, United States, Cuba, Canada (especially in Montreal), France, Bahamas, French Antilles, the Turks and Caicos, Venezuela, and French Guiana.
Haiti's Contribution to the World
One of the best known early Haitian immigrants was Jean Baptiste Point du Sable, who was born in St Marc, Haiti in 1745 and was the founder of the American city of Chicago, Illinois. John James Audubon, the renowned ornithologist and painter, was born in 1785 in Les Cayes, Haiti and painted, catalogued and described the birds of North America. And, in 1779 about 750 Haitians fought alongside American colonial troops against the British in the Siege of Savannah, one of the most significant foreign contributions to the American Revolutionary War.
In 1815 Simon Bolivar, the South American political leader who was instrumental in Latin America's struggle for independence from Spain, received military and financial assistance from Haiti, which was at the time a young republic that had won its independence from France in the world's first (and only) successful slave revolt. Bolivar had fled to Haiti after an attempt had been made on his life in Jamaica, where he had unsuccessfully sought support for his efforts. In 1817, on condition that Bolivar free any enslaved people he encountered in his fight for South American independence, Haiti provided Bolivar with soldiers, weapons and financial assistance, which were critical in enabling him to liberate New Granada (now Colombia), Venezuela, Ecuador, Panama and Peru.
In the 1960's and 1970's Haiti's diaspora made vital contributions to the establishment of francophone Africa's newly independent countries as university professors, medical doctors, administrators and development specialists[citation needed]. The Africa Regional Office of the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), based in Ghana, was headed during most of the 1960's by a prominent Haitian agronomist, Garvey Laurent (born in Jeremie, Haiti, 1923). During the 1970's Laurent negotiated the establishment of most of the FAO's Country Representative Offices throughout Africa.
In North America
There is a significant Haitian population in South Florida, specifically the Miami enclave of Little Haiti. New Orleans, Louisiana has many historic ties to Haiti that date back to the Haitian Revolution. New York City, especially in Flatbush, East Flatbush and Springfield Gardens, also has a thriving émigré community with the second largest population of Haitians of any state in the nation. There are also large and active Haitian communities in Boston, Massachusetts; Spring Valley, New York; New Jersey; Providence, Rhode Island; Georgia; Connecticut and Pennsylvania. There is also a large Haitian community in Montreal North. Others include France, Cuba, Jamaica, etc.
Languages
One of Haiti's two official languages is French, which is the principal written, spoken in schools and administratively authorized language. It is spoken by most educated Haitians and used in the business sector. The second is the recently standardized Haitian Creole,[34] spoken by virtually the entire population of Haiti. Nearly all Haitians speak this French-based creole language that harbors significant African influence, as well as influence from French, Spanish, and Taíno. Spanish is also spoken by a good portion of the population, though not an official language. Haitian creole is one of the French-based creole languages,[35]. Haitian creole is closely related to Louisiana Creole.
Religion
Haiti is a largely Christian country, with Roman Catholicism professed by 80% of Haitians. Protestants make up about 16% of the population. Haitian Vodou, a New World Afro-diasporic faith unique to the country, is practiced by an undetermined percentage of the population. Religious practice often spans Haiti and its diaspora as those who have migrated interact through religion with family in Haiti . [36]
Culture

Haiti has a long and storied history and therefore retains a very rich culture. Haitian culture is a mixture of primarily French, African elements, and native Taíno, with some lesser influence from the colonial Spanish. The country's customs essentially are a blend of cultural beliefs that derived from the various ethnic groups that inhabited the island of Hispaniola. In nearly all aspects of modern Haitian society however, the European and African element dominate. Haiti is world famous for its distinctive art, notably painting and sculpture.
Music
The music of Haiti is influenced mostly by European colonial ties and African migration (through slavery). In the case of European colonization, musical influence has derived primarily from the French, however Haitian music has been influenced to a significant extent by its Spanish-speaking neighbors, the Dominican Republic and Cuba, whose Spanish-infused music has contributed much to the country's musical genres as well. Styles of music unique to the nation of Haiti include music derived from vodou ceremonical traditions and the wildly popular Compas.
Compas (in French) or Kompa (in Creole) is a complex, ever-changing music that arose from African rhythms and European ballroom dancing, mixed with Haiti's bourgeois culture. It is a refined music, played with an underpinning of tipico, and méringue (related to Dominican merengue) as a basic rhythm. Haiti didn't have any recorded music until 1937 when Jazz Guignard was recorded non-commercially. One of the most popular Haitian artists is named Wyclef Jean. His music is somewhat hip-hop mixed with world music.
Cuisine
The cuisine of Haiti originates from several culinary styles from the various historical ethnic groups that populated the western portion of the island of Hispaniola, namely the French, African, and the Taíno Amerindians.
Haitian cuisine is similar to the rest of the Latin-Caribbean (the French and the Spanish-speaking countries of the Antilles) however it differs in several ways from its regional counterparts. Its primary influence derive from French, and African cuisine, with notable derivatives from native Taíno and Spanish culinary technique. Though similar to other cooking styles in the region, it carries a uniqueness native only to the country and an appeal to many visitors to the island. Haitians use vegetables and meats extensively and peppers and similar herbs are often used for strengthening flavor. Dishes tend to be seasoned liberally and consequently Haitian cuisine tends to be moderately spicy, not mild and not too hot. In the country, however, many businesses of foreign origin have been established introducing several foreign cuisines into the mainstream culture. Years of adaptation have led to these cuisines (ie: Levantine from Arab migration to Haiti) to merge into Haitian cuisine.
Rice and beans in several differing ways are eaten throughout the country regardless of location, becoming a sort of national dish. They form the staple diet, which consists of a lot of starch and is high in carbohydrates. In the more rural areas, however, at great distances from the major cities, other foods are eaten to a larger degree such as mais moulu (mayi moulen); a dish comparable to cornmeal that can be eaten with sauce pois (sos pwa), a bean sauce made from one of many types of beans such as kidney, pinto, or garbanzo beans, or pigeon peas (known in other countries as gandules).
Mais Moulu can be eaten with fish (often red snapper), or alone depending on personal preference. Tomato, oregano, cabbage, avocado, red and green peppers are several of the many types of vegetables/fruits that are used in Haitian dishes. Banane Pésée (Bannan Pézé), flattened plantain slices that are fried in oil (known as tostones in the Dominican Republic and Puerto Rico), are eaten frequently in Haiti as both a snack food and as part of a meal. They are frequently eaten with tassot and/or griot, which is deep-fried goat and pork respectively.
See also
References
- ^ CIA World Factbook
- ^ Haitian Arawak Movement
- ^ Department of Economic and Social Affairs
Population Division (2009). "World Population Prospects, Table A.1" (.PDF). 2008 revision. United Nations. Retrieved 2009-03-12.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); line feed character in|author=at position 42 (help) - ^ a b c d "Haiti". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 2009-10-01.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2009. Human development index trends: Table G" (PDF). The United Nations. Retrieved 2009-10-18.
- ^ David A. Koplow, Smallpox: The Fight to Eradicate a Global Scourge
- ^ "History of Smallpox - Smallpox Through the Ages". Texas Department of State Health Services.
- ^ a b c Paul Farmer, "Who removed Aristide?"
- ^ Constitution of Haity [sic] New-York Evening Post July 15 1805
- ^ Independent Haiti. Library of Congress Country Studies.
- ^ a b Paul Farmer, The Uses of Haiti (Common Courage Press: 1994)
- ^ a b US Embassy to Haiti website http://www.haiti.org/
- ^ a b c The Carter Center, "Activities by Country: Haiti", retrieved 2008-07-17
- ^ "Forestry". Retrieved 2006-09-18.
- ^ Can Haiti dream of ecotourism ? - Paul Parisky, Kiskeya Alternativa's publications
- ^ "Photo Gallery: Jeanne hits Haiti". Orlando Sentinel. Retrieved 2006-09-18.
- ^ Deforestation Exacerbates Haiti Floods
- ^ "UN seeks almost $108 million for Haiti floods". Retrieved 2008-09-12.
- ^ "Haiti's government falls after food riots". Retrieved 2008-09-12.
- ^ "Analysis: Haiti seeks a biofuel solution". United Press Internation. Retrieved 2007-07-02.
- ^ "Magnitude 7.0 - Haiti Region". Retrieved 2010-01-12.
- ^ "Major earthquake off Haiti causes hospital to collapse - Telegraph". telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 2010-01-12.
- ^ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_countries_by_future_GDP_(nominal)_estimates
- ^ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_countries_by_GDP_(PPP)
- ^ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_countries_by_future_GDP_(PPP)_estimates
- ^ http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2009/06/11/us-nicaragua-aid-cut-due_n_214212.html
- ^ CIA - The World Factbook -- Haiti
- ^ a b "CIA - The World Factbook – Haiti". United States. 2008-03-20. Retrieved 2007-12-20.
- ^ CIA World Fact Book
- ^ "Education: Overview". United States Agency for International Development. Retrieved 2007-11-15.
- ^ "Education in Haiti; Primary Education". Retrieved 2007-11-15.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ a b http://www.joshuaproject.net/peopctry.php
- ^ [1]
- ^ http://www.indiana.edu/~creole/creolenatllangofhaiti.html
- ^ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/French-based_creole_languages
- ^ *McAlister, Elizabeth. 1998. "Madonna of 115th St. Revisited: Vodou and Haitian Catholicism in the Age of Transnationalism." In S. Warner, ed., Gatherings in Diaspora. Philadelphia: Temple Univ. Press.
Further reading
- Paul Butel. Histoire des Antilles Françaises XVIIe - XXe siècle, Perrin 2002 ISBN 978-2-2620154-0-6
- Noam Chomsky. U.S. & Haiti. Z magazine, April 2004 Accessed 2008-05-07.
- Edwidge Danticat. "Breath, Eyes, Memory" & "Krik? Krak!" as well as many other books. 1994-present.
- Wade Davis The Serpent and The Rainbow. New York: Simon and Schuster, 1985
- Michael Deibert. Notes from the Last Testament: The Struggle for Haiti. Seven Stories Press, New York, 2005. ISBN 1583226974.
- Jared Diamond. 2005. Collapse: How Societies Choose to Fail or Succeed. New York: Viking. ISBN 0-670-03337-5.
- Paul Farmer. Pathologies of Power: Health, Human Rights, and the New War on the Poor. Berkeley: University of California Press, 2003, 2005 edition. ISBN 978-0-520-24326-2.
- Paul Farmer. The uses of Haiti. Monroe, Maine: Common Courage Press 2003. ISBN 1-56751-242-9
- Carolyn E. Fick. The Making of Haiti: The Saint Domingue Revolution from Below. Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press. first ed edition (1 February 1990). ISBN 0870496670, ISBN 978-0870496677
- Robert Debs Heinl and Nancy Gordon Heinl. Written in Blood: The Story of the Haitian People 1492-1995. Lanham, MD: University Press of America, 1996. ISBN 0761831770
- C. L. R. James. The Black Jacobins: Toussaint L’Ouverture and the San Domingo Revolution. Vintage, 1938. ISBN 0-679-72467-2.
- J. Christopher Kovats-Bernat. Sleeping Rough in Port-au-Prince: An Ethnography of Violence and Street Children in Haiti. University Press of Florida, 2006. ISBN 0-8130-3009-9
- Mark Kurlansky. A Continent of Islands: Searching for the Caribbean Destiny. Addison-Wesley Publishing, 1992. ISBN 0-201-52396-5.
- Elizabeth McAlister. Rara! Vodou, Power, and Performance in Haiti and its Diaspora. Berkeley: University of California Press, 2002. ISBN 0-520-22823-5.
- Melinda Miles and Eugenia Charles, eds. Let Haiti Live: Unjust U.S. Policies Toward Its Oldest Neighbor. 2004.
- Jack Claude Nezat. The Nezat And Allied Families 1630-2007 Lulu 2007 ISBN 978-2-9528339-2-9, ISBN 978-0-6151-5001-7
- Randall Robinson. An Unbroken Agony: Haiti, from Revolution to the Kidnapping of a President. New York: Perseus Books Group, 2007. ISBN 0465070507.
- Martin Ros. Night of Fire - The Black Napoleon and the Battle for Haiti. New York: DaCapo Press, 1993. ISBN 0-9627613-8-9
External links
- Government
- Government of the Republic of Haiti - official website (currently offline)
- United Nations Stabilization Mission in Haiti (MINUSTAH)
- Stabilization and Reconstruction Task Force (START), Government of Canada
- Updates on nation rebuilding status in Haiti
- Canadian Reconstruction and Development in Haiti
- Turning Haiti into a Tropical Paradise -- A plan to turn Haiti into a free nation.
- Massive Earthquake Hits Haiti -- Massive Earthquake Hits Haiti.
- History
- http://thelouvertureproject.org/ The Louverture project at thelouvertureproject.org
- [2] London Review of Books - Paul Farmer: Who Removed Aristide?
- Haiti Cinema
- Belfim.com - Haiti Internet, Haitian Movie Database List of all Haitian Movies and Actors
- MPAH Motion Picture Association of Haiti
- WWDS Win Win Distribution System (Movie Distribution)
- Movie Lakay Information about Haitian movies
- Haitian TV Haitian Hollywood inc.is the number one social entertainments Haitian website on the internet, Haitian movie, Haitian radio, Haitian live TV and more.
- General information
- Rezolakay The best online community for haitians,where they come and share their ideas,communicate to friends and family.
- Haiti video specializes in helping residential and commercial owners supply their own energy needs,
- Haiti at Encyclopaedia Britannica
- "Haiti". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Haiti at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- A Country Study: Haiti from the U.S. Library of Congress (December 1989)
- Haiti at Curlie
 Wikimedia Atlas of Haiti
Wikimedia Atlas of Haiti
- Journalism
- Le Nouvelliste, major newspaper in Haiti. (In French).
- Travel
- Maps
- Other
- Doing Business in Haiti. An online resource for doing business and investing in Haitian
- VOA kreyol
- The place to share Haiti News, chat, economic ideas, music, and haitian movies.
- If It's About Haiti, It's On Fouye a Haitian site!
- Haiti: Current events, news, politics, nonprofit
- International Action: Fighting the Water Crisis in Haiti
- The CRUDEM Foundation and Hôpital Sacré Coeur: Providing quality health care in northern Haiti
- Hope for Haiti: Education and grassroots development in rural Haiti
- Search engine for the.ht tld (in french)
- Official website of The National Telecommunications Council, Conatel (in French)
- National Archives of Haiti materials in the Digital Library of the Caribbean
- Haiti List
- Video of Haiti Page
- The Carter Center information on Haiti
- Voodoo Democracy: Toussaint L'Ouverture and Democracy in Haiti
- Reiser Relief serving the poorest of the poor in Haiti
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (April 2009) |




