Franco-Mongol alliance: Difference between revisions
Doric Loon (talk | contribs) →Cartography: linkfix |
"Ancient" implies prior to 476 AD. |
||
| Line 301: | Line 301: | ||
There is no record of any reply, and Ghazan moved ahead, the Mongols successfully taking the city of [[Aleppo]]. There, Ghazan was joined by King Hetoum, whose forces included some Templars and Hospitallers from the kingdom of Armenia, who participated in the rest of the offensive.<ref>Demurger, p.142 (French edition) "He was soon joined by King Hethum, whose forces seem to have included Hospitallers and Templars from the kingdom of Armenia, who participate to the rest of the campaign."</ref> The Mongols and their allies defeated the Mamluks in the [[Battle of Wadi al-Khazandar]], <!-- Note: Demurger says that this was the Second Battle of Homs --> on December 23 or 24, 1299.<ref>Demurger, p.142</ref> One group of Mongols then split off from Ghazan's army, and pursued the retreating Mamluk troops as far as [[Gaza]],<ref>Demurger, p.142 "The Mongols pursued the retreating troops towards the south, but stopped at the level of Gaza"</ref> pushing them back to Egypt. The bulk of Ghazan's forces then proceeded on to Damascus, which surrendered somewhere between December 30, 1299, and January 6, 1300, though its Citadel resisted.<ref>Demurger 142-143</ref><ref>Runciman, p.439</ref> A contemporary Arab writer mentions the exactions in Damas of the Armenian and Georgian Christians together with the Mongols.<ref>"Ibn Kathir attributes partially the responsibility of these massacres and destructions to the Georgian and Armenian Christians that were accompanying the Mongols", "Textes Spirituels D'Ibn Taymiyya", Chap XI</ref><!-- This is a primary source quote that I recommend removing --><!-- Not at all, this is a comment from the scholar translating Ibn Taymiyya --> Ghazan then retreated most of his forces in February, probably because their horses needed fodder. He promised to return in the winter of 1300-1301 to attack Egypt.<ref>Demurger, p.146</ref> |
There is no record of any reply, and Ghazan moved ahead, the Mongols successfully taking the city of [[Aleppo]]. There, Ghazan was joined by King Hetoum, whose forces included some Templars and Hospitallers from the kingdom of Armenia, who participated in the rest of the offensive.<ref>Demurger, p.142 (French edition) "He was soon joined by King Hethum, whose forces seem to have included Hospitallers and Templars from the kingdom of Armenia, who participate to the rest of the campaign."</ref> The Mongols and their allies defeated the Mamluks in the [[Battle of Wadi al-Khazandar]], <!-- Note: Demurger says that this was the Second Battle of Homs --> on December 23 or 24, 1299.<ref>Demurger, p.142</ref> One group of Mongols then split off from Ghazan's army, and pursued the retreating Mamluk troops as far as [[Gaza]],<ref>Demurger, p.142 "The Mongols pursued the retreating troops towards the south, but stopped at the level of Gaza"</ref> pushing them back to Egypt. The bulk of Ghazan's forces then proceeded on to Damascus, which surrendered somewhere between December 30, 1299, and January 6, 1300, though its Citadel resisted.<ref>Demurger 142-143</ref><ref>Runciman, p.439</ref> A contemporary Arab writer mentions the exactions in Damas of the Armenian and Georgian Christians together with the Mongols.<ref>"Ibn Kathir attributes partially the responsibility of these massacres and destructions to the Georgian and Armenian Christians that were accompanying the Mongols", "Textes Spirituels D'Ibn Taymiyya", Chap XI</ref><!-- This is a primary source quote that I recommend removing --><!-- Not at all, this is a comment from the scholar translating Ibn Taymiyya --> Ghazan then retreated most of his forces in February, probably because their horses needed fodder. He promised to return in the winter of 1300-1301 to attack Egypt.<ref>Demurger, p.146</ref> |
||
In the meantime the remaining forces of the Mongols, about 10,000 horsemen under the Mongol general [[Mulay]], ruled over Syria,<ref>Demurger (p.146, French edition): "After the Mamluk forces retreated south to Egypt, the main Mongol forces retreated north in February, Ghazan leaving his general Mulay to rule in Syria".</ref> and engaged in raids as far south as Jerusalem and Gaza.<ref name=schein-raid>"Meanwhile the Mongol and Armenian troops raided the country as far south as Gaza." Schein, 1979, p. 810</ref><ref>"He pursued the Sarazins as far as Gaza, and then turn to Damas, conquering and destroying the Sarazins". Original French: "Il chevaucha apres les Sarazins jusques a Guadres et puis se mist vers Domas concuillant et destruyant les Sarazins." Le Templier de Tyr, #609</ref><ref>"Arab historians however, like Moufazzal Ibn Abil Fazzail, an-Nuwairi and Makrizi, report that the Mongols raided the country as far as Jerusalem and Gaza"— Sylvia Schein, p.810</ref><ref>The Arab historian Yahia Michaud, in the 2002 book ''Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels I-XVI'', Chap XI, describes that there were some firsthand accounts at the time, of forays of the Mongols into Palestine, and quotes two |
In the meantime the remaining forces of the Mongols, about 10,000 horsemen under the Mongol general [[Mulay]], ruled over Syria,<ref>Demurger (p.146, French edition): "After the Mamluk forces retreated south to Egypt, the main Mongol forces retreated north in February, Ghazan leaving his general Mulay to rule in Syria".</ref> and engaged in raids as far south as Jerusalem and Gaza.<ref name=schein-raid>"Meanwhile the Mongol and Armenian troops raided the country as far south as Gaza." Schein, 1979, p. 810</ref><ref>"He pursued the Sarazins as far as Gaza, and then turn to Damas, conquering and destroying the Sarazins". Original French: "Il chevaucha apres les Sarazins jusques a Guadres et puis se mist vers Domas concuillant et destruyant les Sarazins." Le Templier de Tyr, #609</ref><ref>"Arab historians however, like Moufazzal Ibn Abil Fazzail, an-Nuwairi and Makrizi, report that the Mongols raided the country as far as Jerusalem and Gaza"— Sylvia Schein, p.810</ref><ref>The Arab historian Yahia Michaud, in the 2002 book ''Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels I-XVI'', Chap XI, describes that there were some firsthand accounts at the time, of forays of the Mongols into Palestine, and quotes two medieval Arab sources stating that Jerusalem was one of the cities that was invaded by the Mongols</ref> But that small force had to retreat when the Mamluks returned in May 1300. |
||
====Frankish interventions (Feb-July 1300)==== |
====Frankish interventions (Feb-July 1300)==== |
||
| Line 319: | Line 319: | ||
However, Phillips, in ''The Medieval Expansion of Europe'', states that "Jerusalem had not been taken or even besieged."<ref name=phillips-128>Phillips, p. 128. ""Disillusionment came swiftly. Jerusalem had not been taken or even besieged; Ghazan evacuated Syria within a few weeks of its conquest probably because his horses were short of fodder. He attacked it again in 1301, and planned further campaigns for the next two years, but achieved nothing. His bitterness at the failure of the European powers to provide the military assistance he had asked for expressed itself in 1303 in yet another embassy to Philip IV and Edward I, to which Edward replied tactfully that he and Philip had been at war and could not send help."</ref> In ''The Crusades'', Riley-Smith chalked up any stories of a capture of Jerusalem, to rumors.<ref name=riley-smith>"In 1300 a rumour swept the West that the Mongols had conquered Palestine and handed it over to the Christians. Pope Boniface VIII sent 'the great and joyful news' to Edward of England and probably to Philip of France as well. He encouraged the faithful to go at once to the Holy Land and he ordered the exiled Catholic bishops to return to their sees. All over Europe men hurriedly took the cross and in Genoa several ladies sold their jewelry to help pay for a crusading fleet, although in the end the project was dropped." (Riley-Smith, p. 246)</ref> Schein, in her 1979 article "Gesta Dei per Mongolos", stated "The alleged recovery of the Holy Land never happened,"<ref name=gesta-805>Schein, 1979, p. 805</ref> David Morgan in ''The Mongols'', using Schein as a reference, agrees that of the taking of Jerusalem, "this had not in fact happened."<ref>''The Mongols'' by David Morgan, p. 161. "Indeed, at one point Europe was swept with rumours that the Mongols had actually taken Jerusalem from the Mamluks and had returned it to Christian rule. Although this had not in fact happened, the stories did reflect the reality of Ghazan's remarkable successes in 1299-1300 when he drove the Mamluk forces completely out of Syria, only to withdraw again to Persia."[http://books.google.com/books?id=AZdK54YuEPsC&pg=PA161&dq=mongols+jerusalem+1299&sig=9P8Y67RNJkOEGBLcfVkDKVEZFfk Source]</ref> |
However, Phillips, in ''The Medieval Expansion of Europe'', states that "Jerusalem had not been taken or even besieged."<ref name=phillips-128>Phillips, p. 128. ""Disillusionment came swiftly. Jerusalem had not been taken or even besieged; Ghazan evacuated Syria within a few weeks of its conquest probably because his horses were short of fodder. He attacked it again in 1301, and planned further campaigns for the next two years, but achieved nothing. His bitterness at the failure of the European powers to provide the military assistance he had asked for expressed itself in 1303 in yet another embassy to Philip IV and Edward I, to which Edward replied tactfully that he and Philip had been at war and could not send help."</ref> In ''The Crusades'', Riley-Smith chalked up any stories of a capture of Jerusalem, to rumors.<ref name=riley-smith>"In 1300 a rumour swept the West that the Mongols had conquered Palestine and handed it over to the Christians. Pope Boniface VIII sent 'the great and joyful news' to Edward of England and probably to Philip of France as well. He encouraged the faithful to go at once to the Holy Land and he ordered the exiled Catholic bishops to return to their sees. All over Europe men hurriedly took the cross and in Genoa several ladies sold their jewelry to help pay for a crusading fleet, although in the end the project was dropped." (Riley-Smith, p. 246)</ref> Schein, in her 1979 article "Gesta Dei per Mongolos", stated "The alleged recovery of the Holy Land never happened,"<ref name=gesta-805>Schein, 1979, p. 805</ref> David Morgan in ''The Mongols'', using Schein as a reference, agrees that of the taking of Jerusalem, "this had not in fact happened."<ref>''The Mongols'' by David Morgan, p. 161. "Indeed, at one point Europe was swept with rumours that the Mongols had actually taken Jerusalem from the Mamluks and had returned it to Christian rule. Although this had not in fact happened, the stories did reflect the reality of Ghazan's remarkable successes in 1299-1300 when he drove the Mamluk forces completely out of Syria, only to withdraw again to Persia."[http://books.google.com/books?id=AZdK54YuEPsC&pg=PA161&dq=mongols+jerusalem+1299&sig=9P8Y67RNJkOEGBLcfVkDKVEZFfk Source]</ref> |
||
===== |
=====Medieval sources===== |
||
The Arab historian Yahia Michaud, in the 2002 book ''Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels I-XVI'', describes that there were some firsthand accounts at the time, of forays of the Mongols into Palestine, and quotes two |
The Arab historian Yahia Michaud, in the 2002 book ''Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels I-XVI'', describes that there were some firsthand accounts at the time, of forays of the Mongols into Palestine, and quotes two medieval Arab sources stating that Jerusalem was one of the cities that was invaded by the Mongols:<ref>Michaud Yahia (Oxford Centre for Islamic Studies) (2002). Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels I-XVI (in French). Chap. XI.</ref> <!-- He was not providing a history book, he was just reproducing spiritual texts. I challenge whether this is a reliable secondary source --> |
||
{{quote|"The Tatars then made a raid against Jerusalem and against the city of Khalil. They massacred the inhabitants of these two cities (...) it is impossible to describe the amount of atrocities, destructions, plundering they did, the number of prisonners, children and women, they took as slaves".|Ibn Abi L-Fada'Il, Histoire.<ref>Quoted in Michaud Yahia, p.66-67 Transl. Blochet t.XIV, p.667, quotes in Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels, Chap XI</ref>}} <!-- This is a primary source quote, and should be moved to wikisource or wikiquote --> |
{{quote|"The Tatars then made a raid against Jerusalem and against the city of Khalil. They massacred the inhabitants of these two cities (...) it is impossible to describe the amount of atrocities, destructions, plundering they did, the number of prisonners, children and women, they took as slaves".|Ibn Abi L-Fada'Il, Histoire.<ref>Quoted in Michaud Yahia, p.66-67 Transl. Blochet t.XIV, p.667, quotes in Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels, Chap XI</ref>}} <!-- This is a primary source quote, and should be moved to wikisource or wikiquote --> |
||
Revision as of 20:16, 9 January 2008
This article's factual accuracy is disputed. |
A Franco-Mongol alliance,[1][2][3][4][5][6] or attempts towards such an alliance,[7][8] was the objective of a series of diplomatic endeavours between the Franks (designating all western Europeans, but especially those associated with the Crusader States)[9] and the Mongols in the mid-1200s and the early 1300s, starting around the time of the Seventh Crusade. Historians note that in hindsight, an alliance between the Mongols and the Franks often appears a logical choice.[8][10][11] The Mongols were already very sympathetic to Christianity as many Mongols were Nestorian Christians. The Europeans were open to the idea of assistance coming from the East, due to the longrunning legend of a mythical Prester John, an Eastern king in a magical kingdom who many believed would arrive someday to help with the fight in the Holy Land. The Mongols and the Franks also shared a common enemy in the Muslims. There were numerous exchanges of letters, gifts and emissaries between the Mongols and the Europeans as well as offers for varying types of cooperation.[8] However, despite many attempts, there was never any successful military collaboration.[12] Modern historians also debate whether or not such an alliance, if it had been successful, would have been effective in shifting the balance of power in the region, and/or whether or not it would have been a wise choice on the part of the Europeans.[13] Traditionally, the Mongols tended to see outside parties as either subjects, or enemies, with little room in the middle for something such as an ally.
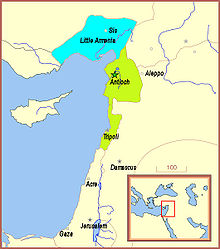
The closest thing to actual Frankish cooperation with Mongol military actions was the alliance, or overlord-subject relationship, between the Mongols and the Frankish Principality of Antioch and County of Tripoli.[14][15][16][17][18] Other Christian vassal states included Georgia, and Cilician Armenia.[19] Once these countries had submitted, they were required to provide military forces to fight under the Mongol banner, and these forces often showed great enthusiasm in attacking Muslim targets.[20]
The most successful points of both collaboration and non-collaboration between the Mongols and the Christians were in 1260, when most of Muslim Syria was briefly conquered by the joint efforts of the Mongols and the Christians of Armenia and Antioch.[21] However, that same year there were other Christians, the Franks of Acre, who entered into a passive truce with the other side, the Egyptian Mamluks. This unusual neutrality on the part of the Franks allowed the Muslim Egyptians to advance northwards through Palestine, to obtain a major and historic success against the Mongols at 1260's pivotal Battle of Ain Jalut.
The Mongols again invaded Syria several times between 1281 and 1312, sometimes in attempts at joint operations[22] with the Europeans, though there were considerable logistical difficulties involved, which usually resulted in the forces arriving months apart, and being unable to satisfactorily combine their activities. Ultimately, the attempts at alliance bore little fruit, and ended with the victory of the Egyptian Mamluks, the total eviction of both the Franks and the Mongols from Palestine by 1303, and a treaty of peace between the Mongols and the Mamluks in 1322.
Christianity among the Mongols
Overall, Mongols were highly tolerant of most religions, and typically sponsored several at the same time, though shamanism, Buddhism, and Christianity were the most popular in the early 1200s. When Temüjin, a shamanist who would later be titled Genghis Khan, declared the Baljuna Covenant with 17 of his companions, several of them were Christian.[23] Many Mongol tribes, such as the Kerait,[24] the Naiman, the Merkit, and to a large extent the Kara Khitan, were Nestorian Christian.[25] All the sons of Genghis Khan had taken Christian wives, from the tribe of the Kerait. While the men were away at battle, the empire was effectively run by the Christian women.[26][27] Genghis Khan's grandson Sartaq was Christian;[28] as was the general Kitbuqa,[29] commander of the Mongol forces of the Levant. Under Mongka, another of Genghis Khan's grandsons, the main religious influence was that of the Nestorians.[30] Marital alliances with Western powers also occurred, as in the 1265 marriage of Maria Despina Palaiologina, the Christian daughter of Emperor Michael VIII Palaeologus, with Hulagu's son, the Mongol khan Abaqa, who himself was a Buddhist.
Early contacts (1209-1244)

Among Europeans, there had long been rumors and expectations that a great Christian ally would come from "the East." These rumors circulated as early as the First Crusade, and usually surged in popularity after the loss of a battle by the Crusaders, which resulted in a natural human desire that a Christian hero would arrive from a distant land, to help save the day. This resulted in the development of a legend about a figure known as Prester John. The legend fed upon itself, and some individuals who came from the East were greeted with the expectations that they might be the long-awaited Christian heroes. For example, around 1210, news reached the West of the battles of the Mongol Kuchlug, leader of the largely Christian tribe of the Naiman, against the powerful Khwarezmian Empire, whose leader was Muhammad II of Khwarezm. Rumors circulated in Europe that Kuchlug was the mythical Prester John, and was again battling the Muslims in the East.[31]
During the Fifth Crusade, as the Christians were unsuccessfully laying siege to the Egyptian city of Damietta in 1221, the legends of Prester John again conflated with the reality of the Mongols under Genghis Khan.[32] Mongol raiding parties were beginning to invade the eastern Islamic world, in Transoxania and Persia in 1219-1221.[33] Rumors circulated among the Crusaders that a "Christian king of the Indies", a King David who was either Prester John or one of his descendants, had been attacking Muslims in the East, and was on his way to help the Christians in their Crusades.[34] In a letter dated June 20, 1221, Pope Honorius III even commented about "forces coming from the Far East to rescue the Holy Land".[35]
In 1220, the Mongols invaded Persian territory, successfully destroying the Turkish Khwarezmian Empire (some of the remains of which moved West in 1244 to ally with the Egyptian Mamluks, taking Jerusalem from the Christians along the way). But Genghis Khan then returned to Mongolia, and Persia was reconquered by Muslim forces.[36] In 1231, a much larger Mongol army arrived, under the general Chormaqan. He ruled over Persia and Azerbaijan from 1231 to 1241.[37] In 1242, Baichu further invaded the Seldjuk kingdom, ruled by Kaikhosrau, in modern Turkey. The Mongol conquest was seen by the Europeans as a positive one, since the Mongols were eliminating an enemy of Christendom.[38]
Genghis Khan died in 1227, and his Empire was split up into four sections, for each of his sons. The northern section, known as the Golden Horde began to encroach upon Europe, primarily via Hungary and Poland. The southwestern section, known as the Ilkhanid, under the leadership of Genghis Khan's son Hulagu, continued to advance towards Persia and the Holy Land. City after city fell to the Mongols, including some Christian realms in their path. Christian Georgia was repeatedly attacked starting in 1220,[39] and in 1243 Queen Rusudan formally submitted to the Mongols, turning Georgia into a vassal state which then became a regular ally in the Mongol military conquests.[40][41] This was a common practice in use by the growing Mongol empire -- as they conquered new territories, they would absorb the populace and warriors into their own Mongol army, which they would then use to further expand the empire.
Papal overtures (1245-1248)
The Mongol invasion of Europe subsided in 1242 with the death of the Great Khan Ögedei, successor of Genghis Khan. However, the relentless march westward of the Mongols had displaced the Khawarizmi Turks, who themselves moved west, and on their way to ally with the Ayyubid Muslims in Egypt, took Jerusalem from the Christians in 1244.[43] This event prompted Christian kings to prepare for a new Crusade, decided by Pope Innocent IV at the First Council of Lyons in June 1245, and revived hopes that the Mongols, who had their Nestorian Christian princesses among them and had brought so much destruction to Islam, could be converted to Christianity and become allies of Christendom.[44][45]
In 1245, Pope Innocent IV issued bulls and sent an envoy in the person of the Franciscan John of Plano Carpini to the "Emperor of the Tartars". The message initiated what was to be a regular pattern in Christian-Mongol communications:[46] Pope Innocent asked the Mongol ruler to become a Christian and to stop killing Christians. The new Mongol khan Güyük was installed at Karakorum on April 8, 1246[47] and received numerous personalities and ambassadors from foreign countries including John of Plano Carpini: the Grand Duc of Moscow Yaroslav II of Vladimir, the incumbents for the throne of Georgia, the brother of the king of Armenia Sempad, the future Seljukid Kilij Arslan IV, ambassadors of the Baghdad Califate and of the emperor of India.[48]. He replied to the Pope's letter with a demand for his submission and a visit from the rulers of the West in homage to Mongol power:[49]
"You must say with a sincere heart: "We will be your subjects; we will give you our strength". You must in person come with your kings, all together, without exception, to render us service and pay us homage. Only then will we acknowledge your submission. And if you do not follow the order of God, and go against our orders, we will know you as our enemy."

This pattern was to be repeated over and over during the coming decades. In 1245 Innocent sent another mission, through another route, led by the Dominican Ascelin of Lombardia, also bearing letters. The mission met with the Mongol commander Baichu near the Caspian Sea in 1247. Baichu, who had plans to capture Baghdad, welcomed the possibility of an alliance and had envoys, Aïbeg and Serkis, accompany the embassy back to Rome, where they stayed for about a year.[51] They met with Innocent IV in 1248, who again appealed to the Mongols to stop their killing of Christians.[52][53]
Mongol relations with Cilician Armenia
In the meantime, the Christian king Hetoum I of Cilician Armenia, seeing that the Mongols were approaching rapidly and he had to choose between submission or annihilation,[20] sent his brother Sempad to the Mongol court in Karakorum. Sempad met Kublai Khan's brother Mongke Khan, and made a formal agreement in 1247 between Cilicia and the Mongols, against their common enemy the Muslims.[54] The nature of this relationship is disputed by various historians, some of whom call it an alliance,[55] and others who say that the Armenians had submitted to Mongol overlordship, and had become a vassal state similar to any other conquered region.[41][56] Armenian and Georgian military leaders were required to serve in the Mongol army, and many of them perished in Mongol battles.[20]
Seventh Crusade: Saint Louis and the Mongols (1248-1254)

Louis IX of France, also called Saint Louis, had a series of written exchanges with the Mongol rulers of the period, and went on crusade twice, once in 1248 and once in 1270.
His contacts with the Mongols started in 1248 with the Seventh Crusade. After Louis left France and disembarked at Nicosia in Cyprus, he was met on December 20, 1248, in Nicosia by two Mongol envoys, Nestorians from Mossul named David and Marc, bearing a letter from Eljigidei, the Mongol ruler of Armenia proper and Persia.[57] They communicated a proposal to form an alliance against the Muslim Ayyubids, whose Caliphate was based in Baghdad.[58] The medieval historian Jean de Joinville said about the communiques:
"Whilst the King was tarrying in Cyprus, the great King of the Tartars sent messengers to him, greeting him courteously, and bearing word, amongst other things, that he was ready to help him conquer the Holy Land and deliver Jerusalem out of the hand of the Saracens. The King received them most graciously, and sent in reply messengers of his own, who remained away two years, before they returned to him. Moreover the King sent to the King of the Tartars by the messengers a tent made in the style of a chapel, which cost a great deal, for it was made wholly of good fine scarlet cloth. And to entice them if possible into our faith, the King caused pictures to be inlaid in the said chapel, portraying the annunciation of Our Lady, and all the other points of the Creed. These things he sent them by two Preaching Friars, who knew Arabic, in order to show and teach them what they ought to believe."
— "The Memoirs of the Lord of Joinville", Chap. V, Jean de Joinville.[59]
Eljigidei was planning an attack on the Muslims in Baghdad in 1248, and sought assistance from Louis and his forces. According to the 13th century monk and historian Guillaume de Nangis, Eljigidei suggested that King Louis should land in Egypt, while Eljigidei attacked Baghdad, in order to prevent the Saracens of Egypt and those of Syria from joining forces.[60]
Though at least one historian has criticized Louis as being "naive" in trusting the ambassadors, and Louis himself later admitted that he regretted the decision,[61] Louis sent André de Longjumeau, a Dominican priest, as an emissary to the Great Khan Güyük in Mongolia. However, Güyük died, from drink, before the emissary arrived at his court, and his widow Oghul Ghaimish simply gave the emissary a gift and a condescending letter to take back to King Louis,[62] demanding that the king pay tribute to the Mongols.[63]
Louis IX did go on to attack Egypt, starting with the rapid capture of the port of Damietta in June 1249.[64] However, Güyük's early death made Eljigidei postpone operations until after the interregnum. Louis's attack did cause some disruption in the Muslim Ayyubid empire, especially as the current sultan was on his deathbed. But the march from Damietta towards Cairo through the Nile River Delta went slowly. During this time, the Ayyubid sultan died, and a sudden power shift took place, as the sultan's slave wife Shajar al-Durr set events in motion which were to make her Queen, and eventually place the Egyptian's slave army of the Mamluks in power. Louis eventually lost his army at the Battle of al Mansurah and was captured by the Egyptians. His release was eventually negotiated, in return for a ransom (some of which was a loan from the Templars), and the surrender of the city of Damietta.[65]

In 1252, Louis attempted an alliance with the Egyptians, for the return of Jerusalem if the French assisted with the subduing of Damascus. And in 1253, Louis tried to seek allies from among both the Ismailian Assassins and the Mongols.[67] Louis received word that the Mongol leader Sartaq, son of Batu, had converted to Christianity,[68] While in Cyprus, he also saw a letter from Sempad, brother of the Armenian ruler Hetoum I, who, on an embassy to the Mongol court in Karakorum, was describing to the Western ruler a Central Asian realm of oasis with many Christians, generally of the Nestorian rite.[69]
Louis dispatched an envoy to the Mongol court in the person of the Franciscan William of Rubruck, who went to visit the Great Khan Möngke in Mongolia. William entered into a famous competition at the Mongol court, as the khan encouraged a formal debate between the Christians, Buddhists, and Muslims, to determine which faith was correct, as determined by three judges, one from each faith. The debate drew a large crowd, and as with most Mongol events, a great deal of alcohol was involved. As described by Jack Weatherford in his book Genghis Khan and the Making of the Modern World:
No side seemed to convince the other of anything. Finally, as the effects of the alcohol became stronger, the Christians gave up trying to persuade anyone with logical arguments, and resorted to singing. The Muslims, who did not sing, responded by loudly reciting the Koran in an effort to drown out the Christians, and the Buddhists retreated into silent mediation. At the end of the debate, unable to convert or kill one another, they concluded the way most Mongol celebrations concluded, with everyone simply too drunk to continue.
— Jack Weatherford, Genghis Khan and the Making of the Modern World, p. 173
But even after the competition, Möngke replied only with a letter to William in 1254, asking for the King's submission to Mongol authority.[70]
His Crusade a failure, Louis returned to France in 1254, due to the death of his mother and regent, Blanche de Castille.
In the early 1250s, the Latin emperor of Constantinople Baldwin II also sent an embassy to Mongolia in the person of the knight Baudoin de Hainaut, who, following his return, met in Constantinople with the departing William of Rubruck.[71]
Collaboration in the Middle East (1258-1260)

A certain amount of military collaboration between the Christians and the Mongols did not really take place until 1258-1260, when Bohemond VI of Antioch and Tripoli, the Christian Armenians under his father-in-law Hetoum I, and the Christian Georgians combined forces with the Mongols under Hulagu. Hetoum I had also himself visited the court of Mangu Khan at Karakorum in 1254 to renew the Cilician-Mongol alliance.[72][73]
The leader of the Ilkhanid section of the Mongol Empire, Hulagu, was generally favourable to Christianity. He was the son of a Christian woman, Sorghaghtani Beki, and one of his most important generals, Kitbuqa, was a Naiman Christian.
The years from 1258 to 1260 brought both some of the greatest Mongol victories in the region, and their first major defeat. On the one hand, the combined forces of the Mongols with their Christian allies (or vassals) successfully conquered Syria, and in Iraq they conquered the center of the most powerful Islamic dynasty in existence at that time, that of the Abbasids in Baghdad. On the other hand, because of the neutrality of the Franks in Acre, and the passive alliance which was struck between the Franks and the Egyptian Mamluks, in late 1260 the Mamluks achieved a decisive victory against the Mongols at the pivotal Battle of Ain Jalut. This action effectively stopped the Mongol expansion into the area, and set the western border for the Mongol Empire.
Bohemond VI and the Mongols

Sometime in the 1250s, Bohemond VI, Frank ruler of the Principality of Antioch and the County of Tripoli, and one of the Outremer's most important power-brokers,[74] allied (or submitted) to the Mongols.[75][76][77] The Principality of Antioch was the most ancient of the Frankish realms, and its capital Antioch was the largest Frank city in the Levant.[78] Some historians also describe that Bohemond submitted to Mongol and accepted their overlordship to become their vassal.[79] According to the historian Reuven Amitai-Preiss however, Bohemond showed "unreserved support for the Mongols".[80]
There is a possibility that Antioch had actually become a tributary of the Mongols even earlier: in 1247 the Dominicans under Carpini placed the limit of Mongol dominions 2 days' journey south of Antioch, and Matthew Paris included Bohemond V among those who in 1246 became tributary to the Mongols.[81] According to Alain Demurger and De Reuven Amitai-Preiss, Cilician Armenia as well as Antioch and Tripoli were paying tribute and supplying troops to the Mongols since 1247.[82][83]
Bohemond was certainly induced into this alliance by his father-in-law the Armenian king Hetoum I, with whom he was closely connected since a rapprochement organized by Louis IX in 1254, and concretized by Bohemond's marriage with the daughter of the Armenian ruler.[84] Hetoum's own association with the Mongols had netted him some rich rewards, since his own submission in 1247. Bohemond resided permanently in Tripoli and from 1254 left the daily management of his dominion of Antioch to the Armenians, so that Antiochian Franks were drawn into the long-standing Armeno-Mongol alliance.[85]
When the Principality of Antioch joined with the Mongols, a Mongol representative and a Mongol garrison were stationed in the capital city of Antioch, where they remained until the capture of the city by the Mamluks in 1268.[86] In return for Bohemond's submission, and Bohemond's acceptance of the restoration of a Greek patriarch, Euthymius, to the patriarchate of Antioch, Hulagu returned to Bohemond all the Antiochene territories which had been lost to the Muslims in 1243. These included Darkush, Kafar-dubbin, Laodicea, and Jabala, which Bohemond re-claimed with Templar help.[87][14]
For his relations with the Mongols, Bohemond was temporarily excommunicated by Jacques Pantaléon, the Latin Patriarch of Jerusalem.[88][89][90] At the time, the Patriarch saw the Mongols as a clear threat, and had written to the Pope to warn him about them in 1256. In 1259 and 1260, Pope Alexander IV had even been encouraging a new Crusade against the Mongols. Alexander had put Bohemond's case on the agenda of his upcoming council (as well as the cases of Hetoum I of Armenia, and Daniel of Russia).[91] However, Alexander died in 1261, just months before the Council could be convened, and before the new Crusade could be launched. For a new Pope, the choice fell to Pantaléon, the same Patriarch of Jerusalem who had earlier been warning of the Mongol threat. He took the name Pope Urban IV, and tried to raise money for a new crusade, but could not succeed, since the French clergy pointed out that there was a truce with the Muslims. In May 1263, Pope Urban, having heard Bohemond's explanation, suspended his excommunication sentence.[92]
Christian involvement in the conquest of Baghdad (1258)

On February 15, 1258, the Mongols were successful in the Siege of Baghdad, an event often considered as the single most catastrophic event in the history of Islam. The attacking army also had a large contingent of Christian forces. The Georgians and Armenians participated in the offensive.[93][94] According to Alain Demurger, Frankish troops from the Principality of Antioch also participated, and Bohemond VI was present at Baghdad in 1258.[95]
When they conquered the city, the Mongols demolished buildings, burned entire neighborhoods, and massacred nearly 80,000 men, women, and children. The Georgians had been the first to breach the walls, and were among the fiercest in their destruction.[96] At the intervention of the Mongol Hulagu's Nestorian Christian wife Dokuz Khatun, the Christian inhabitants were spared.[97][98] Hulagu offered the royal palace to the Nestorian Catholicus Mar Makikha, and ordered a cathedral to be built for him.[99]
The conquest of Baghdad marked the tragic end of the Abbasid Caliphate. The city of Baghdad, which had been the jewel of Islam and one of the largest and most powerful cities in the world for 500 years, became a minor provincial town.
Participation of the Franks to the Mongol invasion of the Levant (1260)

After Baghdad, in 1260 the Mongol forces, along with their Christian allies, conquered Muslim Syria, domain of the Ayyubid dynasty. They took the city of Aleppo with the help of the Franks of Antioch,[100] and on March 1, 1260 proceeded to capture Damascus,[101][102] under the Christian Mongol general Kitbuqa. Numerous historians, some of them quoting Le Templier de Tyr, explain that Kitbuqa entered the city of Damascus in triumph together with Hethoum and Bohemond VI, and that great Christian celebrations were made.[103][104][105][106][107] According to Peter Jackson, writing in 1980, Bohemond VI of Antioch was said to be present in some later accounts but not in contemporary sources, and it is likely a later legend.[108] In 2005 however, Peter Jackson wrote that Bohemond is recorded to have participated to the Mongol conquest of Baalbek, not far from Damascus, and that he may have ridden into Damascus with the Mongols.[109] The historian De Reuven Amitai-Preiss concludes that the accounts may be exagerated, but have some truth to them, and says of Bohemond VI that after his passage at Baalbek "it is most probable that he also passed through Damascus".[110]
According to the contemporary account of Le Templier de Tyr, mass was celebrated in the Grand Mosque of the Umayyads (the former cathedral of Saint John the Baptist),[111], and numerous mosques were profaned:
"The king of Armenia and the Prince of Antioch went to the army of the Tatars, and they all went off to take Damascus. When Damascus was taken, the Prince, to the shame of the Sarasins, established a beautiful church, which at the time of the Greeks used to belong to the Christians, and where since then the Sarasins had prayed Mahomet. The Prince had mass held for the Franks and the bells rung. In the other mosques of Mahomet, where the Sarazins were, shrubs were placed, wine was sprayed on the walls, and fresh pork grease was smeared. And if he commanded his people to do some dirt, they would do tenfold."
— Gestes des Chiprois, Le Templier de Tyr, quoted in "Histoire des Croisades III", René Grousset[112]
On the contrary the southern Franks of the Kingdom of Jerusalem were weary of the Mongols, but their policy was rather incoherent.[113] At the beginning of 1260, the Templars and knights from the Kingdom of Jerusalem launched an offensive against the Muslim cities of Tibnin and Tiberias. The offensive was a failure, and ended with many knights being imprisoned, including Guillaume de Beaujeu and Thibaud Gaudin, future Grand Masters of the Templars, so that they had to be ransommed. Afterwards however, the southern Franks made a passive alliance with the Mamluks, which facilitated the Mamluk victory over the Mongols at Ain Jalut.[114]
The Mongol invasion effectively destroyed the Ayyubid Dynasty, who had been overthrown in Egypt ten years before but had held on in Syria. The last Ayyubid king An-Nasir Yusuf died in 1260.[115] With the Islamic power centers of Baghdad and Damascus gone, the center of Islamic power transferred to the Egyptian Mamluks in Cairo.
After the victory, Hulagu gave numerous gifts to Bohemond VI, including some of the conquered cities, including Lattakieh.[116] But then because of a new internal conflict in Turkestan, Hulagu had to stop the Mongol invasion before it reached Egypt, and departed with the bulk of his forces, leaving only about 10,000 Mongol horsemen in Syria under Kitbuqa to occupy the conquered territory,[117] including Nablus and Gaza in the south, as well as the fortress of Ajlun, east of River Jordan.[118] The Mongols engaged in raids southward towards Egypt, reaching as far as Ascalon and Jerusalem, and a Mongol garrison of about 1,000 was placed in Gaza,[119][120][121] with another garrison located in Naplouse.[122] Runciman considers that Nablus and Gaza were occupied, but that Jerusalem itself was not reached by the Mongols.[29] The Mongols however claimed repeatedly that they had remitted Jerusalem to the Christians on this occasion.[123]
Sidon incident (1260)

With Mongol territory now bordering the Franks, a few incidents occurred, one of them leading to large-scale trouble in Sidon. Julian de Grenier, Lord of Sidon and Beaufort, described by his contemporaries as irresponsible and light-headed, took the opportunity to raid and plunder the area of the Bekaa in Mongol territory. When the Mongol general Kitbuqa sent his nephew with a small force to obtain redress, they were ambushed and killed by Julian. Kitbuqa responded forcefully by raiding the city of Sidon, although the Castle of the city was left unattained.[29][124] Another similar incident occurred when John II of Beirut and some Templars led a raid into Galilee.[125] These events generated a significant level of distrust between the Mongols and the Crusader forces, whose own center of power was now in the coastal city of Acre. The incidents also raised the ire of the Mamluk leader Baibars. He declared that the treaty that had been signed between the Crusaders and the Mamluks in 1240 had been invalidated when Christian forces assisted the Mongols to capture Damascus. He demanded the evacuation of Saphet and Beaufort, and when the Christians balked, Baibars used that as his excuse to violate the pre-existing truce, and start launching new attacks on such settlements as Nazareth, Mount Tabor, and Bethlehem.[126]
Battle of Ain Jalut (1260)
The Franks of the Principality of Antioch and the County of Tripoli and the Armenians aside, in 1260, the Franks of Acre maintained a position of cautious neutrality between the Mongols and the Mamluks. The powerful Venetian commercial interests in the city regarded with concern the expansion of the northern trade routes opened by the Mongols and serviced by the Genoese, and they favoured an appeasement policy with the Mamluks, that would support their traditional trade routes to the south. In May 1260 they sent a letter to Charles of Anjou, complaining about Mongol expansion and Bohemond's subservience to them, and asking for his support.[127]
They did send the Dominican David of Ashby to the court of Hulagu in 1260,[128] but also entered into a passive alliance with the Egyptian Mamluks, which allowed the Mamluk forces to move through Christian territory unhampered,[129] in exchange for an agreement to purchase captured Mongol horses at a low price in the event of a Mamluk victory (a promisse which was not honoured by the Mamluks).[130] This allowed the Mamluks to counter-attack the Mongols, at the pivotal Battle of Ain Jalut on September 3, 1260. It was the first major battle that the Mongols lost, and effectively set the western border for what had seemed an unstoppable Mongol expansion. According to the 13th century historian Kirakos, many Armenians and Georgians were also fighting in the ranks of Kitbuqa.[131] The Armenian historian Smpad writes that about 500 troops from Armenia accompanied the Mongols.[132]
Following Ain Jalut, the remainder of the Mongol army retreated to Cilician Armenia under the commander Ilka, where it was received and re-equipped by Hetoum I. Hulagu sent a counter-attack which briefly occupied Aleppo, but it was repelled by the princes of Hama and Homs, subjects to the Sultan.[133]
Papal-Mongol agreement (1263)

On April 10, 1262, the Mongol leader Hulagu sent through John the Hungarian a new letter to the French king Louis IX from the city of Maragheh, offering again an alliance.[134] The letter mentioned Hulagu's intention to capture Jerusalem for the benefit of the Pope, and asked for Louis to send a fleet against Egypt. Though Hulagu promised the restoration of Jerusalem to the Christians, he also still insisted on Mongol sovereignty, in their quest for conquering the world. King Louis transmitted the letter to Pope Urban IV, who answered by asking for Hulagu's conversion to Christianity.[135]
The Pope also issued the papal bull Exultavit cor nostrum, which congratulated Hulegu on his expression of goodwill towards the Christian faith. The historian Knobler described it as saying that the Pope tentatively agreed to Hulagu's plans, but only cautiously.[34]
The French historian Jean Richard describes this event as the turning point in the relations with the Mongols, from which the Mongols were considered as allies, rather than enemies.[136] He also claims that the exact terms of this alliance offered in 1262, can be learned from the report of the monk Richardus, which were presented in 1274 at the Council of Lyon (other historians, however, question that report as being embellished [citation needed]). Richard says that according to Richardus, that Hulagu had welcomed the Christian ambassadors to his court, and then agreed to exempt Latin Christians from taxes and charges, in exchange for their prayers for the Qaghan. Hulagu also prohibited that Frank establishments should be molested, and committed to return Jerusalem to the Franks.[137] Richard further says that the successful offensives of the Sultan Baibars at the time helped rally Westerners to the idea of an alliance,[138] and that it was in response to this coalition between the Franks, Ilkhanid Mongols and Byzantines, that the Mongols of the Golden Horde allied with the Muslim Mamluks in return.[139]
Meanwhile, the Mamluk leader Baibars began to threaten Antioch, which (as a vassal of the Armenians) had earlier supported the Mongols.[140] In the summer of 1262, the king of Armenia went to the Mongols and again obtained their intervention to deliver the city.[141][142] The city was saved through Mongol intervention.[143]
Bohemond VI was again present at the court of Hulagu in 1264, trying to obtain as much support as possible from Mongol rulers against the Mamluk progression. His presence is described by the Armenian saint Vartan:[144]
"In 1264, l'Il-Khan had me called, as well as the vartabeds Sarkis (Serge) and Krikor (Gregory), and Avak, priest of Tiflis. We arrived at the place of this powerful monarch at the beginning of the Tartar year, in July, period of the solemn assembly of the kuriltai. Here were all the Princes, Kings and Sultans submitted by the Tartars, with wonderful presents. Among them, I saw Hetoum I, king of Armenia, David, king of Georgia, the Prince of Antioch (Bohemond VI), and a quantity of Sultans from Persia.
— Vartan, trad. Dulaurier.[145]
However, in response to Hetoum I and Bohemond VI's request for help, Hulagu was only capable of attacking the frontier fort of Al-Bira (1264-1265).[146]
Death of Hulagu

Following the death of Hulagu in 1265, the Muslim leader Baibars attacked the Franks, and brought terrible devastation to the kingdom of Little Armenia.
In 1265, the new Khan Abaqa further pursued Western cooperation. He corresponded with Pope Clement IV through 1267-1268, and reportedly sent a Mongol ambassador in 1268. Abaqa proposed a joint alliance between his forces, those of the West, and the father of Abaqa's wife, the Byzantine emperor Michael VIII Palaeologos. Abaqa received responses from Rome and from Jaume I of Aragon, though it is unclear if this was what led to Jaume's unsuccessful expedition to Acre in 1269.[34]
In 1268, the Mamluk leader Baibars raided the area of Acre, taking the castle of Beaufort, and attacked Tripoli, where Bohemond VI was entrenched with his subjects. Baibars then arrived in front of Antioch, the largest of the Frankish cities, on May 14, 1268, and took the city after a siege of only 4 days.[148] After this defeat, Bohemond obtained a truce with Baibars[149] but this left Bohemond with no estates except Tripoli.[150]
Cooperation during the Eighth and Ninth Crusades
Abaqa (1234-1282) was the second Mongol emperor in Persia, controlling that quarter of the Mongol empire known as the Ilhanate. A devout Buddhist, he reigned from 1265-1282. Upon his succession, he received the hand of the Christian Maria Despina Palaiologina, the illegitimate daughter of Emperor Michael VIII Palaeologus, in marriage.[151] During his reign, he attempted to convert the Muslims and harassed them mercilessly by promoting Nestorian and Buddhist interests ahead of the Muslims, many of whom attempted to assassinate him.
Letters and embassies (1266-1268)

In the 1260s, the Mamluks were extending their conquests in Syria, putting the Syrian Franks in a difficult situation. In 1266 Pope Clement IV was considering an alliance with the Mongols, although he famously explained that, in spite of the fact that the Mongols were allies against the Sarazins, they could not benefit from the "Crusade indulgence", as they were not Christians.[152] In preparation for the Eighth Crusade (the second of Louis IX), letters about coordinated operations were again exchanged between Pope Clement IV and the Mongols. Abaqa sent an embassy in late 1266 or early 1267 to Pope Clement IV and Jaime I of Aragon, who had already taken the cross for the Eighth Crusade against Egypt. In 1267, Pope Clement IV and James I of Aragon responded by sending an ambassador to the Mongol ruler Abaqa in the person of Jayme Alaric de Perpignan.[153] In his 1267 letter from Viterbo, the Pope wrote:
"The kings of France and Navarre, taking to heart the situation in the Holy Land, and decorated with the Holy Cross, are readying themselves to attack the enemies of the Cross. You wrote to us that you wished to join your father-in-law (the Greek emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos) to assist the Latins. We abundantly praise you for this, but we cannot tell you yet, before having asked to the rulers, what road they are planning to follow. We will transmit to them your advice, so as to enlighten their deliberations, and will inform your Magnificence, through a secure message, of what will have been decided."
— 1267 letter from Pope Clement IV to Abaqa[154]
Abaqa again sent a letter and an embassy accompanied by Jayme Alaric in 1268, explaining that he would send troops under his brother Ejei to assist the Christians, possibly in response to the recent Loss of Antioch. Pope Clement welcomed Abaqa's proposal in a non-committal manner, but did inform him of an upcoming Crusade. The embassy further endeavoured to meet with Louis IX, who had just taken the cross, but while in Genoa encountered an embassy from Baibars in the city's main square, leading to a full-blown skirmish.[155]
Aragonese Crusade (1269)
The Pope's communications were also followed by a small crusade initiated by James I of Aragon, but ultimately handled by his two bastards Fernando Sanchez and Pedro Fernandez after a storm forced most of the fleet to return, which arrived in Acre in December 1269. At that time, Abaqa had to face an invasion in Khorasan by fellow Mongols from Turkestan, and could only commit a small force on the Syrian frontier from October 1269, only capable of brandishing the threat of an invasion.[156]
When Abaqa finally defeated his eastern enemies near Herat in 1270, he wrote to Louis IX offering military support as soon as the Crusaders landed in Palestine.[156]
Failed second Crusade of Louis IX
Louis IX, who had been preparing for a new Crusade since March 24, 1267, left on July 1, 1270. However, his travels in the Eighth Crusade took him to Tunis in modern Tunisia instead of Syria, apparently with the intention of first conquering Tunis, and then to move his troops along the coast to reach Alexandria. Saint-Louis seems to have coordinated his second Crusade with the Mongols.[157] According to the French historian Jean Richard, he probably postponed his attack on the Middle-East, and instead temporarily derouted his Crusades to Tunis following a message from Abaqa that he would not be able to commit his forces in 1270, asking to postpone the campaign to 1271.[158] Envoys from the Byzantine emperor, the Armenians and the Mongols of Abaqa were present at Tunis, but events put a stop to plans for a continued Crusade.[159] Louis IX did not achieve his goal, and instead died of illness in Tunis. According to legend, his last words were "Jerusalem".[160]
Cooperation during the Ninth Crusade (1269-1274)

In 1269, the English Prince Edward (the future Edward I), inspired by tales of his uncle, Richard the Lionheart, and the second crusade of the French King Louis, started on a Crusade of his own, the Ninth Crusade.[161] The number of knights and retainers that accompanied Edward on the crusade was quite small,[162] possibly around 230 knights, with a total complement of approximately 1,000 people, transported in a flotilla of 13 ships.[163][164] Many of the members of Edward's expedition were close friends and family including his wife Eleanor of Castile, his brother Edmund, and his first cousin Henry of Almain.
When Edward finally arrived in Acre on May 9, 1271, the situation in the Holy Land was particularly critical. Baibars was besieging Bohemond VI in the city of Tripoli. Baibars sent a letter to Bohemond threatening him with total annihilation and taunting him for his alliance with the Mongols:
"Our yellow flags have repelled your red flags, and the sound of the bells has been replaced by the call: "Allâh Akbar!" (...) Warn your walls and your churches that soon our siege machinery will deal with them, your knights that soon our swords will invite themselves in their homes (...) We will see then what use will be your alliance with Abagha"
— Letter from Baibars to Bohemond VI, 1271[165]
At the same time, in 1271, one of the vassals of Bohemond VI, named Barthélémy de Maraclée, lord of Khrab Marqiya, a small coastal town between Baniyas and Tortosa, is recorded as having fled from the Mamluk offensive, taking refuge in Persia at the Mongol Court of Abaqa, where he exhorted the Mongols to intervene in the Holy Land.[166][167]
As soon as Edward arrived in Acre he renewed the Mongol alliance,[168] and immediately sent an embassy to the Mongol ruler Abaqa.[169] Edward's plan was to use the help of the Mongols to attack the Muslim leader Baibars.[170] The embassy from Edward to Abaqa was led by Reginald Russel, Godefrey Welles and John Parker.[171] [172] Abaqa answered positively to Edward's request in a letter dated September 4, 1271. In mid-October 1271, the Mongol troops requested by Edward arrived in Syria and ravaged the land from Aleppo southward. Abaqa, occupied by other conflicts in Turkestan, could only send 10,000 Mongol horsemen under general Samagar from the occupation army in Seljuk Anatolia, plus auxiliary Seljukid troops,[173] but they triggered an exodus of Muslim populations (who remembered the previous campaigns of Kithuqa) as far south as Cairo.[171] The Mongols defeated the Turcoman troops that protected Aleppo, putting to flight the Mamluk garrison in that city, and continued their advance to Maarat an-Numan and Apamea.[173] The historians Runciman and Grousset quote the medieval historian William of Tyre:

"The messengers that Sir Edward and the Christians had sent to the Tartars to ask for help came back to Acre, and they did so well that they brought the Tartars with them, and raided all the land of Antioch, Aleppo, Haman and La Chamele, as far as Caesarea the Great. And they killed all the Sarazins they found."
When Baibars mounted a counter-offensive from Egypt on November 12, 1271, the Mongols had already retreated beyond the Euphrates, unable to face the full Mamluk army.
There is dispute among historians as to the effectiveness of Edward's actions. Most historians say that they accomplished little. For example, historian Geoffrey Hindley described it as saying that Edward's forces merely engaged in some fairly ineffectual raids that did not actually achieve success in gaining any new territory.[176] According to Tyerman, Edward "saw some action" in defending Acre from Baibars in December 1271, and "launched a couple of military promenades into the surrounding countryside."[177] Runciman also agrees that when Edward engaged in a raid into the Plain of Sharon, he proved unable to even take the small Mamluk fortress of Qaqun.[178] The Muslim leader Baibars later taunted Edward for not even being able to take a small fortified house.[179]
However, other historians point out that as a result of Edward's military operations, limited though they were, he was able to obtain a 10-year truce between the city of Acre and the Mamluks, signed in 1272.[178] In June 1272, Edward was wounded by an assassination attempt with a poisoned dagger, but he survived, and after recuperating returned to England in September,[176] arriving in 1274.
Promulgation of a new Crusade in liaison with the Mongols (1274)

As soon as he was elected in 1271, Pope Gregory X received a letter from the Mongol Khan Kubilai, remitted by Niccolo and Maffeo Polo following their travels to his court in Mongolia. Kubilai was asking for the dispatch of a hundred missionaries, and some oil from the lamp of the Holy Sepulcher. The two Polos (this time accompanied by the young Marco Polo) returned to Mongolia, accompanied by two Dominican monks, Niccolo de Vicence and Guillaume de Tripoli, and remitted the presents from the Pope to Kubilai in 1275.[180]
The Second Council of Lyon was convened by Pope Gregory X in 1274. The Mongol leader Abaqa sent a delegation of 16 Mongols to the Council, which created a great stir, particularly when their leader underwent a public baptism. Among the embassy were David of Ashby, and the clerk Rychaldus.[181] According to one chronicler, "The Mongols came, not because of the Faith, but to conclude an alliance with the Christians".[182]

Abaqa's Latin secretary Rychaldus delivered a report to the Council, which outlined previous European-Ilkhanid relations under Abaqa's father, Hulagu, where after welcoming the Christian ambassadors to his court, Hulagu had agreed to exempt Latin Christians from taxes and charges, in exchange for their prayers for the Qaghan. According to Richardus, Hulagu had also prohibited the molestation of Frank establishments, and had committed to return Jerusalem to the Franks.[184] Richardus told the assembly that even after Hulagu's death, Abaqa was still determined to drive the Mamluks from Syria.[185]
At the Council, Pope Gregory promulgated a Crusade, to start in 1278 in liaison with the Mongols.[186] The Pope put in place a vast program to launch the Crusade, which was written down in his “Constitutions for the zeal of the faith”. This text puts forward four main decisions to accomplish the Crusade: the imposition of a new tax during three years, the interdiction of any kind of trade with the Sarazins, the supply of ships by the Italian maritime Republics, and the alliance of the West with Byzantium and the Il-Khan Abagha.[187]

After the Council, the Mongol embassy visited Edward I of England on January 28th, 1275. A letter from Edward is known, in which he acknowledges Abagha's promise to fight together with the Crusaders.[189] David of Ashby, another member of the embassy wrote a treatise on the Mongols, entitled "Les faits des Tartares" ("The facts about the Tartars").[190]
Following these exchanges, Abagha sent another embassy, led by the Georgian Vassali brothers, to further notify Western leaders of military preparations. Gregory answered that his legates would accompany the Crusade, and that they would be in charge of coordinating military operations with the Il-Khan.[191]
These projects of a major new Crusade essentially came to a halt with the death of Gregory X on January 10, 1276. The money which had been saved to finance the expedition was distributed in Italy.[192] His successors however continued to pursue projects of cooperation with the Mongols and Byzantines for future Crusades.[193] From that time, hopes of reconquering the Holy Land rested on the Mongol alliance.[194]
Joint invasion of Syria (1280-1281)
Without support from the Crusades, some Franks of Syria, particularly the Hospitallers, and to some extent the Franks of Cyprus and Antioch, joined in combined operations with the Mongols in 1280-1281. The historian Zoe Oldenbourg in The Crusades mentions in 1280 the "Alliance of Franks and Mongols against Qalawun".[195]
Campaign of autumn 1280
Following the death of Baibars in 1277, and the ensuing disorganisation of the Muslim realm, conditions were ripe for a new action in the Holy Land.[196] The Mongols seized the opportunity and organized a new invasion of Syrian land. In September 1280, the Mongols occupied Baghras and Darbsak, and took Aleppo on October 20, where they massacred many inhabitants.
"Abagha ordered the Tartars to occupy Syria, the land and the cities, and remit them to be guarded by the Christians."
— Monk Hayton of Corycus, "Fleur des Histoires d'Orient", circa 1300[197]
On the Frank side the king of Cyprus Hugues III and Bohemond VI also mobilized their army, but they could not intervene because the Mamluks had already positionned themselves between them and the Mongols.[198] In October 1280, the Mongols sent envoys to Acre to request military support for the campaign, but the Vicar of the Patriarch invoked that the city was suffering from hunger, and that the king of Jerusalem was embroiled in another war.[199] The Mongols also requested support for a campaign the following winter, informing the Franks that they would bring 50,000 Mongol horsemen and 50,000 Mongol infantry, but the request apparently remained without a response.[200]
According to Runciman, Abagha and Leo III of Armenia urged the Franks to start a new Crusade, but only the Hospitallers and Edward I (who could not come for lack of funds) responded favourably.[201] The Hospitallers of Marquab made combined raids into the Buqaia, and won several engagements against the Sultan.[202] They raided as far as the Krak des Chevaliers in October 1280, and defeated the Mamluk army of the Krak in February 1281.[203]
The Mongols finally retreated, pledging to come back for the winter of 1281.
Campaign of Autumn 1281

In order to prevent new combined actions between the Franks and the Mongols, the new Muslim sultan Qalawun signed a new 10-year truce on May 3, 1281 (following the expiration of the old truce from 1271) with the Barons of Acre (a truce he would later breach)[204] and a second 10-year truce with Bohemond VII of Tripoli, on July 16, 1281. The truce also authorized pilgrim access to Jerusalem.[205]
The announced Mongol invasion started in September 1281. They were joined by the Armenians under Leo II, and by about 200 Hospitaliers knights of the fortress of Marqab,[206][207] who considered they were not bound by the truce with the Mamluks.[208] Some knights from Cyprus also probably accompanied them.[209]
"In the year 1281 of the incarnation of Christ, the Tatars left their realm, crossed Aygues Froides with a very great army and invaded the land of Aleppo, Haman and La Chemele and did great damage to the Sarazins and killed many, and with them were the king of Armenia and some Frank knights of Syria."
— Le Chevalier de Tyre, Chap. 407[210]
On October 30, 1281, 50,000 Mongol troops, together with 30,000 Armenians, Georgians, Greeks, and the Hospitalier Knights of Marqab fought against the Muslim leader Qalawun at the Second Battle of Homs, but they were repelled, with heavy losses on both sides.[208]
With Abaqa's death in 1282, and his replacement by the Muslim Mongol ruler Teguder, the Sultan Qalawun was free again to attacks Frankish territory.[211]
Arghun's proposals for a new crusade (1284-1291)

The new Mongol ruler Arghun, son of Abaqa, again revived the idea of an alliance with the West, and sent envoys to Europe. He promised that if Jerusalem were conquered, he would have himself baptised. But Western Europe was no longer as interested in the crusades, and the missions were ultimately fruitless,[213] except for the dispatch of a corps of 800 Genoese to the Mongol realm to establish a naval raiding force in the Indian Ocean. During his reign, the Mamluks continuously increased their power in Syria, and the Sultan Qalawun managed to capture the northern fortress of Margat in 1285, Lattakia in 1287, and completing the Fall of Tripoli in 1289 and the Fall of Acre in 1291 managed to eliminate the last major Christian bases in the Levant.[214]
First mission to the Pope
In 1285, Arghun sent an embassy and a letter to Pope Honorius IV, a Latin translation of which is preserved in the Vatican.[215][216] Arghun's letter mentioned the links that Arghun's family had to Christianity, and proposed a combined military conquest of Muslim lands:[217]
"As the land of the Muslims, that is, Syria and Egypt, is placed between us and you, we will encircle and strangle ("estrengebimus") it. We will send our messengers to ask you to send an army to Egypt, so that us on one side, and you on the other, we can, with good warriors, take it over. Let us know through secure messengers when you would like this to happen. We will chase the Saracens, with the help of the Lord, the Pope, and the Great Khan."
— Extract from the 1285 letter from Arghun to Honorius IV, Vatican[218]
Second mission, to Kings Philip and Edward

Apparently left without an answer, Arghun sent another embassy to European rulers in 1287, headed by the Nestorian Rabban Bar Sauma, with the objective of contracting a military alliance to fight the Muslims in the Middle East, and take the city of Jerusalem.[215] The responses were positive but vague. Sauma returned in 1288 with positive letters from Pope Nicholas IV, Edward I of England, and Philip IV the Fair of France.[219] According to the medieval Syriac History of the two Nestorian Chinese monks, Bar Sawma of Khan Balik and Markos of Kawshang, as translated in Sir Wallis Budge's book The Monks of Kublai Khan Emperor of China, Philip seemingly responded positively to the request of the embassy, gave him numerous presents, and sent one of his noblemen, Gobert de Helleville, to accompany Bar Sauma back to Mongol lands:
"And the King Philip said: if it be indeed so that the Mongols, though they are not Christians, are going to fight against the Arabs for the capture of Jerusalem, it is meet especially for us that we should fight [with them], and if our Lord willeth, go forth in full strength. . . And he said unto us, "I will send with you one of the great Amirs whom I have here with me to give an answer to King Arghon"; and the king gave Rabban Sawma gifts and apparel of great price."
— "The Monks of Kublai Khan Emperor of China[220]

Gobert de Helleville departed on February 2, 1288, with two clerics Robert de Senlis and Guillaume de Bruyères, as well as arbaletier Audin de Bourges. They joined Bar Sauma in Rome, and accompanied him to Persia.[221]
According to a medieval historian, King Edward was also said to have welcomed the embassy enthusiastically:
"King Edward rejoiced greatly, and he was especially glad when Rabban Sauma talked about the matter of Jerusalem. And he said "We the kings of these cities bear upon our bodies the sign of the Cross, and we have no subject of thought except this matter. And my mind is relieved on the subject about which I have been thinking, when I hear that King Arghun thinketh as I think"
— Account of the travels of Rabban Bar Sauma, Chap. VII.[222]
In one of his letters, Nicholas IV also recognized the role of many Franks in the service of the Il-Khan, among them Ugi de Sienne, ilduci in the Guard of the Il-Khan, who would also bring a message to the West.[223]
Third mission
In 1289, Arghun sent a third mission to Europe, in the person of Buscarel of Gisolfe, a Genoese who had settled in Persia. The objective of the mission was to determine at what date concerted Christian and Mongol efforts could start. Arghun committed to march his troops as soon as the Crusaders had disembarked at Saint-Jean-d'Acre. Buscarel was in Rome between July 15 and September 30, 1289, and in Paris in November-December 1289. He remitted a letter from Arghun to Philippe le Bel, answering to Philippe's own letter and promises, offering the city of Jerusalem as a potential prize, and attempting to fix the date of the offensive from the winter of 1290 to spring of 1291:[226]
"Under the power of the eternal sky, the message of the great king, Arghun, to the king of France..., said: I have accepted the word that you forwarded by the messengers under Saymer Sagura (Bar Sauma), saying that if the warriors of Il Khaan invade Egypt you would support them. We would also lend our support by going there at the end of the Tiger year’s winter [1290], worshiping the sky, and settle in Damascus in the early spring [1291].
If you send your warriors as promised and conquer Egypt, worshiping the sky, then I shall give you Jerusalem. If any of our warriors arrive later than arranged, all will be futile and no one will benefit. If you care to please give me your impressions, and I would also be very willing to accept any samples of French opulence that you care to burden your messengers with.
I send this to you by Myckeril and say: All will be known by the power of the sky and the greatness of kings. This letter was scribed on the sixth of the early summer in the year of the Ox at Ho’ndlon."
Buscarello was also bearing a memorandum explaining that the Mongol ruler would prepare all necessary supplies for the Crusaders, as well as 30,000 horses.[229] Buscarel then went to England to bring Arghun's message to King Edward I. He arrived in London January 5, 1290. Edward, whose answer has been preserved, answered enthusiastically to the project but remained evasive about its actual implementation, for which he deferred to the Pope.[230]
In a concrete example of military collaboration, a maritime raiding force consisting in two war galleys was prepared in Baghdad by a corps of Genoese, in order to curtail the maritime trade of the Mamluks. A contingent of 800 Genoese carpenters and sailors was sent in 1290 to Baghdad, as well as a force of arbaletiers, but the enterprise apparently foundered when the Genoese government ultimatey disowned the project, and an internal fight erupted at the Persian Gulf port of Basra among the Geneose (between the Guelfe and the Gibelin families).[231][232]
Fourth mission

Arghun then sent a fourth mission to European courts in 1290, led by a certain Andrew Zagan (or Chagan), who was accompanied by Buscarel of Gisolfe and a Christian named Sahadin.[233]
In 1290, the Pope sent the Franciscan John of Montecorvino to the Mongol court in Khanbaliq.[234]
As a result, with Acre in great danger, Pope Nicolas IV proclaimed a Crusade and negotiated agreements with Arghun, Hetoum II of Armenia, the Jacobites, the Ethiopians and the Georgians. On January 5, 1291, he addressed a vibrant prayer to all the Christians to save the Holy Land, and predicators started to rally Christians to follow Edward I in a Crusade.[235]
However, all these attempts to mount a combined offensive were too little and too late. Arghun himself died on March 10, 1291, and Pope Nicholas IV in March 1292, putting an end to their efforts towards combined action.[236] On May 18th 1291, Saint-Jean-d'Acre was conquered by the Mamluks in the Siege of Acre.
According to the 20th century historian Runciman, "Had the Mongol alliance been achieved and honestly implemented by the West, the existence of Outremer would almost certainly have been prolonged. The Mameluks would have been crippled if not destroyed; and the Ilkhanate of Persia would have survived as a power friendly to the Christians and the West"[225]
Alliance to recapture the Levant (1297-1303)

In 1297, the new Mongol ruler Ghazan was able to resume offensives against the Mamluks and revive the Franco-Mongol alliance.[237] Ghazan had been baptized and raised as a Christian, though he had became a Muslim upon accession to the throne.[238] He retained however a strong enmity towards the Egyptian Mamluks.
These coordinated actions between the Mongols and the Franks of Cyprus came very close to succeeding.[239] The plan was to coordinate actions between the Christian military orders, the King of Cyprus, the aristocracy of Cyprus and Little Armenia and the Mongols of the khanate of Ilkhan (Persia).[240] The Christian forces of Cyprus and Armenia were determined to reconquer the Holy Land in liaison with the Mongol offensives. However, they had little support from Europe, and Crusades to help sustain their actions.[241]
According to the French historian Alain Demurger, the Knights Templar and their leader Jacques de Molay strongly advocated, and attempted a collaboration with the Mongols under Ghazan to fight against the Mamluks.[242] In an interview, Demurger credited the Templars and De Molay with being the artisans of the alliance with the Mongols from 1299-1303.[243] Another French historian, Laurent Dailliez in Les Templiers explains that the Templars allied with the Mongols and that Jacques de Molay signed a treaty with them against their common Muslim enemy.[244] However, some other historians put less emphasis on Templar involvement in the matter, and some barely mention the hopes of Mongol involvement at all. Of the attempts of military action that were there, Jackson in "The Mongols and the West" gives the credit to King Henry II of Cyprus, and says that the actions were joint efforts of all of the Cypriots.[245] He mentions however that Jacques de Molay seems to have been particularly enthousiastic about the project.[246] In a 1300 letter to the Mamluk Sultan, Ghazan boasted that the contingents ranged under his banner now included Franks.[247]
Armenian campaigns (1298-1299)
In 1298 or 1299, the military orders—the Knights Templar and Knights Hospitaller—and their leaders, including Jacques de Molay, Otton de Grandson and the Great Master of the Hospitallers, briefly campaigned in Armenia, in order to fight off an invasion by the Mamluks.[248][249][250] However, they were not successful, and soon, the fortress of Roche-Guillaume in the Belen pass, the last Templar stronghold in Antioch, was lost to the Muslims.[251]
Campaign of winter 1299-1300


In the summer of 1299, King Hetoum II of Armenia sent a message to the Mongol khan of Persia, Ghâzân to obtain his support. In response, Ghazan marched with his forces towards Syria and sent letters to the Franks of Cyprus (the King of Cyprus, and the heads of the Knights Templar, the Hospitallers and the Teutonic Knights), inviting them to come join him in his attack on the Mamluks in Syria. Ghazan's first letter was sent on October 21, which arrived 15 days later. He sent a second letter in November.[252]
There is no record of any reply, and Ghazan moved ahead, the Mongols successfully taking the city of Aleppo. There, Ghazan was joined by King Hetoum, whose forces included some Templars and Hospitallers from the kingdom of Armenia, who participated in the rest of the offensive.[253] The Mongols and their allies defeated the Mamluks in the Battle of Wadi al-Khazandar, on December 23 or 24, 1299.[254] One group of Mongols then split off from Ghazan's army, and pursued the retreating Mamluk troops as far as Gaza,[255] pushing them back to Egypt. The bulk of Ghazan's forces then proceeded on to Damascus, which surrendered somewhere between December 30, 1299, and January 6, 1300, though its Citadel resisted.[256][257] A contemporary Arab writer mentions the exactions in Damas of the Armenian and Georgian Christians together with the Mongols.[258] Ghazan then retreated most of his forces in February, probably because their horses needed fodder. He promised to return in the winter of 1300-1301 to attack Egypt.[259]
In the meantime the remaining forces of the Mongols, about 10,000 horsemen under the Mongol general Mulay, ruled over Syria,[260] and engaged in raids as far south as Jerusalem and Gaza.[261][262][263][264] But that small force had to retreat when the Mamluks returned in May 1300.
Frankish interventions (Feb-July 1300)

Finally in early 1300, two Frank rulers, Guy d'Ibelin and Jean II de Giblet, had moved in with their troops from Cyprus in response to Ghazan's earlier call, and established a base in the castle of Nefin in Gibelet on the Syrian coast with the intention of joining him, but Ghazan was already gone.[265][266] They also started to besiege the new city of Tripoli, but in vain.[267] They soon had to reembark for Cyprus.
The Mongol leader Ghazan had sent letters in late 1299 requesting Frankish help, primarily with naval operations.[268] Naval operations were mounted in July 1300. A fleet of sixteen galleys with some smaller vessels was equipped in Cyprus,[269][268][270], commanded by King Henry II of Jerusalem, the king of Cyprus, accompanied by his brother, Amalric, Lord of Tyre and the heads of the military orders. The banner of the Mongol Il-Khan was hoisted on the boats, because Ghazan's ambassador was onboard.[271][272] The ships left Famagusta on July 20, 1300, to raid the coasts of Egypt and Syria: Rosette,[268] Alexandria, Acre, Tortosa, and Maraclea, before returning to Cyprus.[270] According to the French historian Jean Richard, the raids along the way were directed by Admiral Baudoin de Picquigny, who was accompanied onboard by the envoy of the Mongols Isol the Pisan, and when the raids took place at Alexandria, they were able to free Christian prisoners who had been captive since the Fall of Acre in 1291.[273]
The ships then returned to Cyprus, and prepared for an attack on Tortosa in late 1300. James II of Aragon also sent a congratulation letter to Ghazan for his victories.[274]
The fate of Jerusalem in early 1300

There are pervasive contemporary accounts, whether from European, Armenian or Arab sources, claiming that the Mongols occupied Jerusalem around that time. There is little evidence however that this actually happened, and modern scholars are divided on the question. After the Mamluk forces retreated south to Egypt, the main Mongol forces retreated north in February, and Ghazan left his general Mulay to rule in Syria.[275] Accordingly, there existed a period of about four months from February to May 1300, when the Mongol il-Khan was the "de facto" lord of the Holy Land.[276] But that small force had to retreat when the Mamluks returned in May 1300.[277][278] Ghazan also promised to return in the winter of 1300-1301 to attack Egypt.[279]
In Les Templiers, Alain Demurger states that "in December 1299, he (Ghazan) vanquished the Mamluks at the Second Battle of Homs and captured Damascus, and even Jerusalem",[280] and that the Mongol general Mulay occupied the city in 1299-1300.[281] In The Crusaders and the Crusader States, Andrew Jotischky used Schein's 1979 article and later 1991 book to state, "after a brief and largely symbolic occupation of Jerusalem, Ghazan withdrew to Persia"[282]. According to Peter Jackson in The Mongols and the West, the Mongols liberated the Holy City.[283] Steven Runciman in "A History of the Crusades, III" stated that Ghazan penetrated as far as Jerusalem, but not until the year 1308.[284] Claude Mutafian, in Le Royaume Arménien de Cilicie mentions the writings and the 14th century Armenian Dominican which claim that the Armenian king visited Jerusalem as it was temporarily removed from Muslim rule.[285] Demurger, in Jacques de Molay, mentions the possibility that the Mongols may have occupied Jerusalem, quoting an Armenian tradition describing that Hethoum celebrated mass in Jerusalem in January 1300.[286]
However, Phillips, in The Medieval Expansion of Europe, states that "Jerusalem had not been taken or even besieged."[287] In The Crusades, Riley-Smith chalked up any stories of a capture of Jerusalem, to rumors.[288] Schein, in her 1979 article "Gesta Dei per Mongolos", stated "The alleged recovery of the Holy Land never happened,"[289] David Morgan in The Mongols, using Schein as a reference, agrees that of the taking of Jerusalem, "this had not in fact happened."[290]
Medieval sources
The Arab historian Yahia Michaud, in the 2002 book Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels I-XVI, describes that there were some firsthand accounts at the time, of forays of the Mongols into Palestine, and quotes two medieval Arab sources stating that Jerusalem was one of the cities that was invaded by the Mongols:[291]
"The Tatars then made a raid against Jerusalem and against the city of Khalil. They massacred the inhabitants of these two cities (...) it is impossible to describe the amount of atrocities, destructions, plundering they did, the number of prisonners, children and women, they took as slaves".
— Ibn Abi L-Fada'Il, Histoire.[292]
"The Mongols first marched against Syria in 699 (1299-1300)... In Jerusalem, in Jabal al-Salihiyya, in Naplouse, in Daraya and other places, they killed a number of people, and made a number a number of captives only known to God."

In February 1300, a Francisan monk in Nicosia, Cyprus wrote a letter saying that King Hetoum had celebrated mass in Jerusalem,[295] evidently at the Holy Sepulchre on January 6, 1300. The modern French historian Demurger said, "There is a tradition that Hethoum celebrated a religious office at the Saint-Sepulcre on the day of the Epiphany (January 6).[296]
Dr. Schein's research also compiled a detailed list of any fragments of sources which might indicate that Jerusalem had in fact been either conquered by the Mongols, or at least briefly occupied. For example, she listed in both her 1979 paper and 1991 book Fidelis Crucis, the medieval Armenian source (an Armenian monk named Nerses Balients, converted to Catholicism by the Dominicans)[297] which stated that the Armenian King Hetoum II, with a small force, had reached the outskirts of Cairo and then spent some fifteen days in Jerusalem visiting the Holy Places after its capture by the Mongols:
"The king of Armenia, back from his raid against the Sultan, went to Jerusalem. He found that all the enemies had been put to flight or exterminated by the Tatars, who had arrived before him. As he entered into Jerusalem, he gathered the Christians, who had been hiding in caverns out of fright. During the 15 days he spent in Jerusalem, he held Christian ceremonies and solemn festivities in the Holy Sepulchre. He was greatly comforted by his visits to the places of the pilgrims. He was still in Jerusalem when he received a certificate from the Khan, bestowing him Jerusalem and the surrounding country. He then returned to join Ghazan in Damas, and spend the winter with him"
— Recueil des Historiens des Croisades, Historiens Armeniens I, p.660[298]

According to the historian Claude Mutafian, this may be on this occasion that Hetoum II remitted his amber scepter to the Armenian convent of Saint James of Jerusalem.[299]
Schein expanded on this slightly in her 1991 book, by mentioning in a footnote that the Mongols must have conquered Jerusalem because they had removed a gate from the Dome of the Rock, and transferred it to Damascus.[300] She also pointed out that in a 1301 letter, the Sultan al-Malik an-Nasir accused Ghazan of introducing the Christian Armenians and Georgians into Jerusalem.[301] And in her 1991 book, Schein expanded her earlier statement to say that the Armenian information about Hetoum's visit was confirmed by Arab chroniclers.[302]
However, Schein's interpretation of the sources has been challenged by Angus Donal Stewart in his 2001 book The Armenian Kingdom and the Mamluks, where he called the Armenian statement an "absurd claim" from an unreliable source, and said that the Arab chroniclers did not confirm it in any way.[303] He also had criticisms for several other errors in Schein's work. Another historian, Reuven Amitai, also did a detailed comparison of all of the available primary sources about the events around the Battle of Wadi al-Khazindar, and concluded that the Armenian account was in error, as it did not match up with other similar sources about the same events, was provably full of exaggerations and inaccuracies, and had been written as to glorify the Armenian king Hetoum. Amitai also pointed out that despite Dr. Schein's acceptance of the source as genuine, that even the original editor of the work, Edouard Dulaurier, had "unequivocally" denied the veracity of the Armenian account.[304] However, Edouard Dulaurier actually only mentions that Nerses Balients may have added a few fantastic details to exagerate Hetoum's accomplishments somewhat, specifically disputing that Hetoum went as far as Cairo when Ghazan himself sent 15,000 men only as far as Gaza, but he does not otherwise challenge the account of the Mongol's capture of Jerusalem and Hetoum's visit to the Holy City for 15 days afterwards.[305]
Other reports also mention that Christians were in Jerusalem in April to celebrate Easter.[306].
In a general comment on Jerusalem in her 2005 posthumous book Gateway to the Heavenly City: Crusader Jerusalem and the Catholic West (1099-1187), Schein said nothing about Mongol conquest, but simply noted: "After 1187 and for the rest of the Middle Ages, Earthly Jerusalem, ruled by the Moslems (except for the short period of 1229-1244), was to loom large in all types of late medieval apocalypticism."[307]
European rumors about the conquest of Jerusalem
Most scholars agree that whatever the facts involving Jerusalem, that the situation led to wild rumors in Europe, though there is disagreement as to when exactly the rumors started, when the word about the Mongol activities reached Europe, and which sources from the time were reliable, and which were embellished, misinformed, or simply false.
According to Demurger in The Last Templar, the first announcement of the Mongol success was in a letter written in Cyprus in March 1300, which mentions that Ghazan controlled both Damas and Jerusalem:[308]
"Ghazan dispatched messengers to the kings of Jerusalem and Cyprus, and to the communes and to the religious orders, asking them to come to him in Damas or Jerusalem, so that he could remit to them all the lands the Christians held at the time of Godefroy de Bouillon".
— Letter of Thomas Gras, Cyprus, March 24, 1300[309]
According to Schein, the earliest letter was dated March 19, 1300, and was probably based on accounts from Venetian merchants who had just arrived from Cyprus, which they had left on February 3, 1300.[310] The account gave a more or less accurate picture of the Mongol successes in Syria, but then expanded to say that the Mongols had "probably" taken the Holy Land by that point.

One thing that is certain, is that whatever their source, that once they had reached Europe, the rumours spread and were inflated widely, due to wishful thinking, and the urban legend environment of large crowds that had gathered in Rome for the Jubilee. The story grew to say (falsely) that the Mongols had taken Egypt, that the Mongol Ghazan had appointed his brother as the new king there, and that the Mongols were going to further conquer Barbary and Tunis. The rumors also stated that Ghazan had freed the Christians who were held captive in Damascus and in Egypt, and that some of those prisoners had already made their way to Cyprus. From Italy, the rumors spread to Austria and Germany, and then to France.[311]
By April 1300, Pope Boniface was sending a letter announcing the "great and joyful news to be celebrated with special rejoicing,"[288] that the Mongol Ghazan had conquered the Holy Land and offered to hand it over to the Christians. In Rome, as part of the Jubilee celebrations in 1300, the Pope ordered processions to "celebrate the recovery of the Holy Land," and he further encouraged everyone to depart for the newly-recovered area. Edward I was asked to encourage his subjects to depart as well, to visit the Holy Places. And Pope Boniface even referred to the recovery of the Holy Land from the Mongols, in his bull Ausculta fili.
In the summer of the Jubilee year, Pope Boniface VIII received a dozen ambassadors, dispatched from various kings and princes. One of the groups was of 100 Mongols, led by the Florentine Guiscard Bustari, the ambassador for the il-khan. The embassy, abundantly mentioned in contemporary sources, participated in the Jubilee ceremonies. Supposedly this ambassador was also the man nominated by Ghazan to supervise the re-establishment of the Franks, in the territories that Ghazan was going to return to them. There was great rejoicing for a short time, but the Pope soon learned about the true state of affairs in Syria, from which in fact Ghazan had withdrawn the bulk of his forces in February 1300, and the Mamluks had reclaimed by May.[312] But the rumors continued through at least September 1300.[313]
19th century reconstructions

The story of this alleged capture of Jerusalem was retold by historians during the following centuries, and even expanded in the 19th century to claims that Jerusalem was taken not by Mongols, but by Jacques de Molay, Grand Master of the Knights Templar.[314] In 1805, the French historian/ playwright Raynouard said, "In 1299, the Grand-Master was with his knights at the taking of Jerusalem."[315] The story was also expanded to say that Jacques de Molay had actually been placed in charge of one of the Mongol divisions. According to Demurger in The Last Templar, this may have been because the medieval history Templar of Tyre referred to a Mongol general named Mulay.[316] In the 1861 edition of the French encyclopedia, the Nouvelle Biographie Universelle, it says in the "Molay" article:
"Jacques de Molay was not inactive in this decision of the Great Khan. This is proven by the fact that Molay was in command of one of the wings of the Mongol army. With the troops under his control, he invaded Syria, participated in the first battle in which the Sultan was vanquished, pursued the routed Malik Nasir as far as the desert of Egypt: then, under the guidance of Kutluk, a Mongol general, he was able to take Jerusalem, among other cities, over the Muslims, and the Mongols entered to celebrate Easter"
— Nouvelle Biographie Universelle, "Molay" article, 1861.[317]
There is even a painting, Molay Prend Jerusalem, 1299 ("Molay Takes Jerusalem, 1299"), hanging in the French national museum in Versailles, created in 1846 by Claude Jacquand,[318] which depicts the supposed event in 1299. However, De Molay was certainly nowhere near Jerusalem at the time. His actual whereabouts were that he was recorded in Armenia in 1298-1299 for a failed military operation, and may or may not have participated in the Crusader coastal raids during the summer of 1300, attacking such cities as Alexandria and Acre. He was also surely on the island of Ruad in November 1300, attempting (unsuccessfully) to retake the coastal city of Tortosa. But there are no reliable sources that say that he was anywhere near the landlocked city of Jerusalem in 1299 or 1300.[319]
Campaign of winter 1300-1301
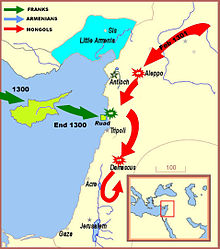
According to Demurger's account, the medieval historian the Templar of Tyre wrote that Ghazan sent ambassadors to Cyprus in 1300, led by the Italian Isol le Pisan, the Mongols' chief ambassador to Cyprus. In agreement with the Cypriotes, a joint embassy was then sent to the Pope.[320][321] In 1300 the Templars sent men of arms to Cyprus for coordinated actions with the Mongols.[322] In May 1300, the king of Aragon announced that he was sending ships and warriors, in exchange for a fifth of the Holy Land.[323]
Ruad bridgehead
In the end of 1300, another message came from Ghazan asking to coordinate operations, inviting the Cypriots to meet him in Armenia.[270] The Cypriots then prepared a land-based force of approximately 600 men: 300 under Amalric of Lusigan, son of Hugh III of Cyprus, and similar contingents from the Templars and Hospitallers.[270] The men and their horses were ferried from Cyprus to a staging area on the island of Ruad, a mile off the coast of Tortosa.[268][270] From there, they had a certain amount of success attacking Tortosa (some sources say they engaged in raids, others that they captured the city), but when the hoped-for Mongol reinforcements were delayed (sources differ on whether the delay was caused by weather or illness), the Crusaders had to retreat to Ruad.[324][325] When the Mongols still did not appear, the majority of the Christian forces returned to Cyprus, though they left a garrison on Ruad which was manned by rotating groups of different Cypriot forces.
Mongol operations by Kutlushah

A few months later, in February 1301, the Mongols did arrive with a force of 60,000, but could do little else than engage in some raids around Syria. Kutlushah (Qutlugh-Shah for the Mongols, Cotelesse in Frank sources) stationed 20,000 horsemen in the Jordan valley to protect Damas, where a Mongol governor was stationed.[326] Soon however, they had to withdraw:
"That year [1300], a message came to Cyprus from Ghazan, king of the Tatars, saying that he would come during the winter, and that he wished that the Franks join him in Armenia (...) Amalric of Lusignan, Constable of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, arrived in November (...) and brought with him 300 knights, and as many or more of the Templars and Hospitallers (...) In February a great admiral of the Tatars, named Cotlesser, came to Antioch with 60,000 horsemen, and requested the visit of the king of Armenia, who came with Guy of Ibelin, Count of Jaffa, and John, lord of Giblet. And when they arrived, Cotelesse told them that Ghazan had met great trouble of wind and cold on his way. Cotlesse raided the land from Haleppo to La Chemelle, and returned to his country without doing more".
— Le Templier de Tyre, Chap 620-622[327]
From mid-1301, the Knights Templar left a small garrison to maintain the island of Ruad, in anticipation of further operations with the Mongols.[328]
Canceled campaign of winter 1301-1302

Plans for combined operations were again made for the following winter offensive. A letter has been kept from Jacques de Molay to Edward I, and dated April 8, 1301, informing him of the troubles encountered by Ghazan (who had to fight against a relative in Khorasan, whom Molay names "Portefferi"), but announcing that Ghazan was supposed to come in Autumn 1301:
"And our convent, with all our galleys and ships, transported itself to the island of Tortosa, in order to wait for the army of Ghazan and his Tatars."
— Jacques de Molay, letter to Edward I, April 8th, 1301.[330]
And in a letter to James II of Aragon on November 8, 1301:
"The king of Armenia sent his messengers to the king of Cyprus to tell him (...) that Ghazan was now close to arriving on the lands of the Sultan with a multitude of Tatars. And we, learning this, have the intention to go on the island of Tortosa where our convent has been stationed with weapons and horses during the present year, causing great devastation on the littoral, and capturing many Sarassins. We have the intention to get there and settle there, to wait for the Tatars."
— Jacques de Molay, letter to the king of Aragon, 1301.[331]
In late 1301, Ghazan sent a letter to the Pope, asking the Pope to send troops, priests, peasants, in order to make the Holy Land a Frank state again,[332] but this time Ghazan did not appear with his troops due to a very cold winter and terrible road conditions.
Campaign of winter 1302-1303
On April 12, 1302, Ghazan sent a letter and an embassy to Pope Boniface VIII, apparently in answer to an encouraging letter by the latter suggesting Western troops would be dispatched for the 1302/1303 offensive.[333]
"We for our part, are making our preparations. You too should prepare your troops, send word to the rulers of the various nations and not fail to keep the rendezvous. Heaven willing, we shall make the great work [i.e. the war. against the Mamelukes] our sole aim."
— Letter from Ghazan to Pope Boniface VIII, 1302.[334]
Ghazan's ambassadors stayed at the court of Charles II of Anjou. When they returned to Persia after April 27, 1303, they were accompanied by Gualterius de Lavendel, as ambassador of Charles II to Ghazan.[335]
Loss of Ruad
In September 1302, a Mamluk fleet of 16 ships left Egypt and reached Tripoli to assemble a fighting force. The fleet then attacked the island of Ruad and disembarked in two points. The island had been occupied by 120 Templar knights, 500 bowmen and 400 men and women serving the garrison, all under the command of Barthélemy de Quincy, Marshall of the Order of the Knight Templars.
After some fighting, the Muslims managed to establish themselves on the island, and started the siege of the fortifications. Barthélemy de Quincy died in the ensuing combat. The Templars finally surrendered on September 26th, at the condition that they could safely escape to a Christian land of their choice. However the Mamluks did not respect the agreement. All the bowmen and Syrian Christians were executed, and the Templars were taken prisoners to Cairo, where they died of starvation after during years of ill-treatment.[336]
Defeat of Shaqhab

The remaining Templars from Cyprus continued making raids on the Syrian coast in early 1303, and ravaged the city of Damour, south of Beyrouth. As they had lost Ruad, though, they were not capable of providing important troops.[338]
In 1303, the Mongols appeared in great strength (about 80,000) together with the Armenians, but they were defeated at Homs on March 30, 1303, and at the decisive Battle of Shaqhab, south of Damas, on April 21, 1303.[338] It is considered to be the last major Mongol invasion of Syria.[339] Also in 1303, Ghazan had again sent a letter to Edward I, in the person of Buscarello de Ghizolfi, reinterating Hulagu's promise that they would give Jerusalem to the Franks in exchange for help against the Mamluks.[340] But Ghazan died on May 10, 1304, and dreams of a rapid reconquest of the Holy Land were destroyed.
New attempts at a joint Crusade (1305-1313)
Oljeitu, also named Mohammad Khodabandeh, was the great-grandson of the Ilkhanate founder Hulagu, and brother and successor of Ghazan. His Christian mother baptized him as a Christian and gave him the name Nicholas.[341] In his youth he at first converted to Buddhism and then to Sunni Islam together with his brother Ghazan. He then changed his first name to the Islamic name Muhammad.

In April 1305, Oljeitu sent letters to the French king Philip the Fair,[342] the French Pope Clement V, and Edward I of England. After his predecessor Arghun, he offered a military collaboration between the Christian nations of Europe and the Mongols against the Mamluks, re-stating the merits of concord between the Christian nations of Europe and the Mongols against the Mamluks:
"We, Sultan Oljaitu. We speak. We, who by the strength of the Sky, rose to the throne (...), we, descendant of Genghis Khan (...). In truth, there cannot be anything better than concord. If anybody was not in concord with either you or ourselves, then we would defend ourselves together. Let the Sky decide!"
— Extract from the letter of Oljeitu to Philip the Fair. French national archives.[343]
He also explained that internal conflicts between the Mongols were now over:
"Now all of us, Timur Khagan, Tchapar, Toctoga, Togba and ourselves, main descendants of Gengis-Khan, all of us, descendants and brothers, are reconciled through the inspiration and the help of God. So that, from Nangkiyan (China) in the Orient, to Lake Dala our people is united and the roads are open."
— Extract from the letter of Oljeitu to Philip the Fair. French national archives.[344]
This message reassured European nations that the Franco-Mongol alliance, or at least attempts towards such an alliance, had not ceased, even though the Khans had converted to Islam.[345]
Overtures from Clement V
Clement V ordered studies on the preparation of a new Crusade. On June 6, 1306, he invited the leaders of the Templars and Hospitallers for a consultation on this subject and that of the fusion of the Orders.[346] In 1307 Jacques de Molay remitted a memorandum for a new Crusade.[347]

The Armenian monk Hayton of Corycus also went to visit Pope Clement V in Poitiers, where he wrote his famous "Flor des Histoires d'Orient", a compilation of the events of the Holy Land describing the alliance with the Mongols, and setting recommendations for a new Crusade:
"God has also shown the Christians that the time is right because the Tartars themselves have offered to give help to the Christians against the Saracens. For this reason Gharbanda, King of the Tartars, sent his messengers offering to use all his power to undo the enemies of the Christian land. Thus, at present, the Holy Land might be recovered with the help of the Tartars and the realm of Egypt, easily conquered without peril or danger. And so Christian forces ought to leave for the Holy Land without any delay.
— Hayton, Flor des Estoires d'Orient, Book IV.[348]
Another embassy was sent to the West in 1307, led by Tommaso Ugi di Siena, an Italian described as Oljeitu's ildüchi ("Sword-bearer").[349][350] This embassy encouraged Pope Clement V to speak in 1307 of the strong possibility that the Mongols could remit the Holy Land to the Christians, and to declare that the Mongol embassy from Oljeitu "cheered him like spiritual sustenance".[351] Relations were quite warm: in 1307, the Pope named John of Montecorvino the first Archbishop of Khanbalik and Patriarch of the Orient.[352] A corps of Frank mangonel specialists is known to have accompanied the Ilkhanid army in the conquest of Herat in 1307.[353]
On April 4, 1312, a Crusade was promulgated by Pope Clement V at the Council of Vienne. Another embassy was sent by Oljeitu to the West and to Edward II in 1313.[354] That same year, the French king Philippe le Bel "took the cross", making the vow to go on a Crusade in the Levant, thus responding to Clement V's call for a Crusade. He was however warned against leaving by Enguerrand de Marigny,[355] and died soon after in a hunting accident.[356]
Oljeitu finally launched a last campaign against the Mamluks (1312-13), in which he was unsuccessful. A final settlement with the Mamluks would only be found when Oljeitu's son signed the Treaty of Aleppo with the Mamluks in 1322.
Last contacts (1322)

In 1320, the Egyptian sultan Naser Mohammed ibn Kelaoun invaded and ravaged Christian Armenian Cilicia. In a letter dated July 1, 1322, Pope John XXII sent a letter from Avignon to the Mongol ruler Abu Sa'id, reminding him of the alliance of his ancestors with Christians, asking him to intervene in Cilicia. At the same time he advocated that he abandon Islam in favor of Christianity. Mongol troops were sent to Cilicia, but only arrived after a ceasefire had been negotiated for 15 years between Constantin, patriarch of the Armenians, and the sultan of Egypt. After Abu Sa'id, relations between Christian princes and the Mongols were totally abandoned.[citation needed][357]
He died without heir and successor. The state lost its status after his death, becoming a plethora of little kingdoms run by Mongols, Turks, and Persians.
Technology exchanges
In these invasions westward, the Mongols brought with them a variety of eastern, often Chinese technologies, which may have been transmitted to the West on these occasions. The original weaknesses of the Mongols in siege warfare (they were essentially a nation of horsemen) were compensated by the introduction of Chinese engineering corps within their army,[358] who therefore had ample contacts with Western lands.
Weaponry
One theory of how gunpowder came to Europe is that it made its way along the Silk Road through the Middle East; another is that it was brought to Europe during the Mongol invasion in the first half of the 13th century.[359][360] Direct Franco-Mongol contacts occurred as in the 1259-1260 military alliance of the Franks knights of the ruler of Antioch Bohemond VI and his father-in-law Hetoum I with the Mongols under Hulagu.[102] William of Rubruck, an ambassador to the Mongols in 1254-1255, a personal friend of Roger Bacon, is also often designated as a possible intermediary in the transmission of gunpowder know-how between the East and the West.[361]
Other innovations, such as printing, may have transited through the Mongol routes during that period. John of Marignolli came back from the Mongols in 1353, with a request from the Great Khan to send more Franscicans to China. Most contacts were interrupted however when the Great Plague started to sweep Europe. The reopening of relations would not occur until the 16th century.[362]
Cartography

The Mongol Empire connected the European and western Islamic world with the Chinese sphere. It enabled the integration of a large amount of geographical knowledge.
In 1286 Jamāl al-Dīn made Khubilai Khan a proposal for merging several maps of the empire into a single world map, and it resulted in the Tianxia Dili Zongtu (天下地理總圖; now lost). Since most of the official maps are lost, relatively new manuscripts of private, supposedly less accurate maps are known today. The most famous one is the Kangnido (1402), a Korean variant preserved in Japan. Like Istakhri's and al-Idrisi's, the Kangnido depicts Africa, the Arabian Peninsula and Europe. The Kangnido also mentions a hundred European place names.[363]
Rashid al-Din, the Jewish Prime Minister of Ghazan and later Oljeitu, wrote an extensive History of the Franks (1305/1306), probably based on information from Isol the Pisan or Dominican friars, providing much details on Europe's political organization, the use of mappae mundi by Italian mariners, and regnal chronologies derived from the chronicle of Martin of Opava (d. 1278).[364]
A Mongol embassy (documented in Chinese sources but not European ones) visited Europe in 1314-1320 and brought back geographical knowledge which was incorporated in a Chinese geographical treatise of the middle of the 14th century.[365] Chinese maps produced in the 13th and 14th century do provide some information about Europe.[366]

Conversely, in Europe the landmark 1459 Fra Mauro map is also said to have been partly based on a Chinese map. Ramusio explained that Fra Mauro's map is an improved copy of the world map brought from Cathay by Marco Polo.[367]
Aftermath
Events reminiscent of the Franco-Mongol alliance occurred in the 15th century, when the Mongol ruler Tamerlane developed a friendly, if remote, relationship with Western powers. Tamerlane exchanged letters with Western rulers, inviting ambassadors and traders.[368] He also fought the Ottoman state as it was on the point of conquering Constantinople in around 1402, and defeating the Ottoman ruler Bazajet in 1402.[369] Tamerlane was long considered in a very positive light in the West due to his actions against the common Turk enemy.
Modern interpretations
There is disagreement among historians over the nature and extent of the alliance between the Franks and the Mongols. There is also dispute about the definition of the term "Frank", and whether it should refer to the Kingdom of Cilician Armenia. Most historians agree that the Armenians, when the Mongols were advancing into their territory in the mid-1200s, did ally with the Mongols for a few years.[370] The neighboring Frank Principality of Antioch and County of Tripoli, headed by Bohemond VI, was also long-time recognized allies of the Mongols.[371][372][373][374][375] But there is dispute about whether or not the Mongols ever had a formal alliance with the Franks, meaning some of the Crusader States, Western Europe and the Papacy.[citation needed] Also, some historians describe the relationship of Armenia and Antioch/Tripoli as a "vassal" relationship, not as an alliance.[376][377]
See also
- History of gunpowder
- History of printing
- Al-'Āḍid, the teenaged Muslim caliph in Egypt, who entered into an alliance with the Christians in the 1100s
Notes
- ^ Jean Richard, the leading French expert on the Crusades, has the Franco-Mongol alliance start in earnest in the 1260s: "The sustained attacks of Baibars (...) rallied the Occidentals to this alliance, to which the Mongols also convinced the Byzantines to adhere", in "Histoire des Croisades", p.453. It continued on-and-off but was strongly revived by Ghazan, to continue to have an influence until 1322 "In 1297 Ghazan resumes his projects against Egypt (...) the Franco-Mongol cooperation had thus survived, to the loss of Acre by the Franks, and to the conversion of the khan to Islam. It was to remain one of the political factors of the policy of the Crusades, until the peace treaty with the Mamluks, which was concluded in 1322 by khan Abu Said." in "Histoire des Croisades", p.468. And concludes on the many missed opportunities the alliance offered: "The Franco-Mongol alliance (...) seems to have been rich with missed opportunities" in "Histoire des Croisades", 1996, Jean Richard, p.469
- ^ Grousset, p521: "Louis IX et l'Alliance Franco-Mongole", p.653 "Seul Edward I comprit la valeur de l'Alliance Mongole", p.686 "la coalition Franco-Mongole dont les Hospitaliers donnaient l'exemple"
- ^ Demurger, p.147 "Cette expedition avait surtout l'avantage de sceller, par un acte concret l'alliance Mongole", Demurger p.145 "La strategie de l'alliance Mongole en action", "De Molay anime la lutte pour la reconquete de Jerusalem, en s'appuyant sur une alliance avec les Mongols" (Demurger, back cover)
- ^ Angus Steward says "Franco-Mongol entente" [1]
- ^ Prawer, p. 32. "The attempts of the crusaders to create an alliance with the Mongols failed."
- ^ Tyerman, p. 816. "The Mongol alliance, despite six further embassies to the west between 1276 and 1291, led nowhere."
- ^ "The possibility of an alliance between the il-khans and the Franks was explored by both parties. . . Contacts between the two were quite frequent and aimed at establishing a coordination of eastern and western forces to counterbalance the formidable Mamluk threat. . . For a number of reasons which it cannot be our task to analyze here, the alliance between the il-khans and the West failed to become operative." Sinor, Denis. "Mongols and the West" in Journal of Asian History[2]
- ^ a b c "Despite numerous envoys and the obvious logic of an alliance against mutual enemies, the papacy and the Crusaders never achieved the often-proposed alliance against Islam". Atwood, Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire, p. 583, "Western Europe and the Mongol Empire"
- ^ Between the 11th to the 15th century, the Crusaders were usually called Franks. More broadly the term applied to any persons originating in Catholic western Europe (medieval Middle Eastern history). The term led to derived usage by other cultures, such as Farangi, firang, farang and barang. "The term [Frank] was used by all the populations of the eastern Mediterranean to designate the totality of the Crusaders as well as the settlers" Atlas des Croisades,1996, Jonathan Riley-Smith, ISBN 2862605530
- ^ "In later years Christian chroniclers would bemoan a lost opportunity in which Crusaders and Mongols might have joined forces to defeat the Muslims. But they were writing from the benefit of hindsight, after the Crusader States had been destroyed by the Muslim Mamluks." Nicolle, David, The Mongol Warlords, p. 114
- ^ ""The failure of Ilkhanid-Western negotiations, and the reasons for it, are of particular importance in view of the widespread belief in the past that they might well have succeeded." Jackson, Peter Mongols and the West, p. 4
- ^ "Arghun had persisted in the quest for a Western alliance right down to his death without ever taking the field against the mutual enemy." Jackson, Mongols and the West, p. 170
- ^ See History in Dispute: The Crusades, 1095-1291 where the question that is debated is, "Would a Latin-Ilkhan Mongol alliance have strengthened and preserved the Crusader States?'"[3]
- ^ a b Tyerman, p. 806. The Frankish Antiochenes assisted in the Mongols' capture of Aleppo, thus in part achieving a very traditional Frankish target, and had received lands in reward."
- ^ "Hetoum tried to win the Latin princes over to the idea of a Christian-Mongol alliance, but could convince only Bohemond VI of Antioch." Nersessian, "The Kingdom of Cilician Armenia" in Setton's Crusades, p. 653
- ^ ""The authorities of the crusader states, with the exception of Antioch, opted for a neutrality favourable to the Mamluks." Morgan, David. "The Mongols and the Eastern Mediterranean", p. 204
- ^ "The Barons of the Holy Land refused an alliance with the Mongols, except for the king of Armenia and Bohemond VI, prince of Antioch and Count of Tripoli" Lebedel, Claude Les Croisades, Origines et consequences, p. 75
- ^ "The refusal of the Latin Christian states in the area to follow Hetoum's example and adapt to changing conditions by allying themselves with the new Mongol empire must stand as one of the saddest of the many failures of Outremer. Burger, Glenn A Lytell Chronicle, pp. xiii-xiv
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
stewart-8was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Bournotian, p. 109. "It was at this juncture that the main Mongol armies appeared [in Armenia] in 1236. The Mongols swiftly conquered the cities. Those who resisted were cruelly punished, while submitting were rewarded. News of this spread quickly and resulted in the submission of all of historic Armenia and parts of Georgia by 1245.... Armenian and Georgian military leaders had to serve in the Mongol army, where many of them perished in battle. In 1258 the Ilkhanid Mongols, under the leadership of Hulagu, sacked Baghdad, ended the Abbasis Caliphate and killed many Muslims."
- ^ "On 1 March Kitbuqa entered Damascus at the head of a Mongol army. With him were the King of Armenia and the prince of Antioch. The citizens of the ancient capital of the Caliphate saw for the first time for six centuries three Christian potentates ride in triumph through their streets", Runciman p.307
- ^ "The Mongol alliance, despite six further embassies to the west between 1276 and 1291, led nowhere. The prospect of an anti-Mamluk coalition faded as the westerners' inaction rendered them useless as allies for the Mongols, who, in turn, would only seriously be considered by western rulers as potential partners in the event of a new crusade which never happened." Tyerman, p. 816
- ^ Weatherford, p. 58
- ^ "The Keraits, who were a semi-nomadic people of Turkish origin, inhabited the country round the Orkhon river in modern Outer Mongolia. Early in the eleventh century their ruler had been converted to Nestorian Christianity, together with most of his subjects; and the conversion brought the Keraits into touch with the Uighur Turks, amongst whom were many Nestorians", Runciman, p.238
- ^ "In 1196, Gengis Khan succeeded in the unification under his authority of all the Mongol tribes, some of which had been converted to Nestorian Christianity" "Les Croisades, origines et conséquences", p.74
- ^ Weatherford, pp. 160-161
- ^ "In 1196, Gengis Khan succeeded in the unification under his authority of all the Mongol tribes, some of which had been converted to Nestorian Christianity" "Les Croisades, origines et conséquences", p.74
- ^ "Early in 1253 a report reached Acre that one of the Mongol princes, Sartaq, son of Batu, had been converted to Christianity", Runciman, p.280
- ^ a b c "Kitbuqa, as a Christian himself, made no secret of his sympathies", Runciman, p.308
- ^ Under Mongka "The chief religious influence was that of the Nestorian Christians, to whom Mongka showed especial favour in memory of his mother Sorghaqtani, who had always remained loyal to her faith" Runciman, p. 296
- ^ Foltz, p.111
- ^ Foltz, p.112
- ^ Mongol Raids, p. 236
- ^ a b c Adam Knobler (Fall 1996). "Pseudo-Conversions and Patchwork Pedigrees: The Christianization of Muslim Princes and the Diplomacy of Holy War". Journal of World History. 7 (2): 181–197.
{{cite journal}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|journal=(help) - ^ Regesta Honorii Papae III, no 1478, I, p.565. Quoted in Runciman, p.246
- ^ Runciman, p.249
- ^ Runciman, p.250
- ^ Runciman, p.253
- ^ Runciman, p.246-247
- ^ Runciman, p.250
- ^ a b Weatherford, p. 181. "To supplement his own army, Hulegu summoned the armies of the vassal states of Armenia and Georgia"
- ^ David Wilkinson, Studying the History of Intercivilizational Dialogues [4]
- ^ Runciman, p.256
- ^ Runciman, p.254
- ^ Sharan Newman, "Real History Behind the Templars" p. 174, about Grand Master Thomas Berard: "Under Genghis Khan, they [the Mongols] had already conquered much of China and were now moving into the ancient Persian Empire. Tales of their cruelty flew like crows through the towns in their path. However, since they were considered "pagans" there was hope among the leaders of the Church that they could be brought into the Christian community and would join forces to liberate Jerusalem again. Franciscan missionaries were sent east as the Mongols drew near."
- ^ Richard, p. 422 (english) "In all the conversations between the popes and the il-khans, this difference of approach remained: the il-khans spoke of military coopration, the popes of adhering to the Christian faith."
- ^ Catholic Encyclopedia, "The Crusades"
- ^ Jean-Paul Roux, L'Asie Centrale, p.312
- ^ David Wilkinson, Studying the History of Intercivilizational Dialogues [5]
- ^ Quoted in Michaud, Yahia (Oxford Centre for Islamic Studies) (2002). Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels I-XVI". Chap XI
- ^ Runciman, p.259
- ^ David Wilkinson, Studying the History of Intercivilizational Dialogues [6]
- ^ Runciman, p.259
- ^ Bournotian, p. 100. "Smbat met Kubali's brother, Mongke Khan and in 1247, made an alliance against the Muslims"
- ^ Mutafian describes it as "The Armeno-Mongol Alliance", p.56
- ^ Stewart, "Logic of Conquest", p. 8. "The Armenian king saw alliance with the Mongols -- or, more accurately, swift and peaceful subjection to them -- as the best course of action."
- ^ Peter Jackson (July 1980). "The Crisis in the Holy Land in 1260". The English Historical Review. 95 (376): 481–513.
- ^ Grousset, p.523
- ^ The Memoirs of the Lord of Joinville
- ^ "The Memoirs of the Lord of Joinville", Chap. V, Jean de Joinville.The Memoirs of the Lord of Joinville
- ^ Tyerman, p. 786
- ^ Runciman, p.260
- ^ Tyerman, p. 798. "Louis's embassy under Andrew of Longjumeau had returned in 1251 carrying a demand from the Mongol regent, Oghul Qaimush, for annual tribute, not at all what the king had anticipated.
- ^ Tyerman, p. 787
- ^ Tyerman, pp. 789-798
- ^ "Le Royaume Armenien de Cilicie", p66
- ^ Runciman, pp. 279-280
- ^ Runciman, p.380
- ^ Jean Richard, “Histoire des Croissades”, p. 376
- ^ J. Richard, 1970, p. 202., Encyclopedia Iranica, [7]
- ^ Jean Richard, p. 377
- ^ Bournotian, p. 101
- ^ Guillaume de Tyr, Chap. II. The event is mentionned and quoted in Runciman.
- ^ "Bohemond VI, briefly one of Outremer's most important power broker", Tyerman, p.806
- ^ "Bohemond of Antioch-Tripoli became their [the Mongol's] ally” John Riley-Smith, The Oxford History of the Crusades, p.136
- ^ "Hethoum's attempts to build a great Christian alliance to aid the Mongols was well received by the local Christian; and Bohemond of Antioch, who was under his father-in-law's influence, gave his adhesion. But the Franks of Asia held aloof.", Runciman, p.299
- ^ "The Armenians, in the person of king Hethoum, sided with the Mongols, as did Bohemond of Antioch". Amin Maalouf, p.261 (Les Croisades vues par les Arabes). Also: "Bohemond of Antioch and Hethoum of Armenia, principal allies of the Mongols". Amin Maalouf, p.265 (Les Croisades vues par les Arabes)
- ^ Amin Maalouf, "Les Croisades..", p267
- ^ "Customary marks of submission to which Bohemond VI ... had had to conform." (Jean Richard, p. 422).
- ^ "Bohemond VI's unreserved support for the Mongols was probably looked upon with disfavor by the leaders of Acre. The Papal legate was certainly displeased: he excommunicated Bohemond early in 1260.", in Mongols and Mamluks, p.39
- ^ Jackson, p.103
- ^ Demurger, "Jacques de Molay", p.55. "The Count of Tripoli and Prince of Antioch (the two state had the same ruler), and the king of Cilician Armenia (or Little Armenia) had made their submission to the Mongols. Since 1247 already, they had paid tribute and supplied troops. King Hetoum I went to Karakorum to make his submission in 1253, and Bohemond VI was present in Baghdad in 1258."
- ^ De Reuven Amitai-Preiss Mongols and Mamluks, p.24 "Already in 1246, it is reported that Bohemond V of Antioch, along with king Hetoum of Cilician Armenia had become tributary of the Mongols"
- ^ Bohemond entered in a relationship with the Mongols because of pressure from his father-in-law Hethoum I: "The principality of Antioch was dominated by its Armenian neighbour -- it was through the will of the Armenian king that the Antiochenes came to aid Hulegu in 1259-60." ("The Logic of Conquest" Al-Masaq, v. 14, No.1, March 2002, p. 8)
- ^ The Islamic World in Ascendency: From the Arab conquest to the Siege of Vienna by Dr. Martin Sicker (p.111): "Bohemond, however, resided exclusively in Tripoli and, as a practical matter, Hetoum, whose realm was contiguous with it, ruled Antioch. Accordingly, Antioch was drawn into the Mongolian-Armenian alliance".
- ^ "Bohemond VI, briefly one of Outremer's most important power broker, had already accepted Mongol overlordship, with a Mongol resident and battalion stationed in Antioch itself, where they stayed until the fall of the city to the Mamluks in 1268". Tyerman, p. 806
- ^ Jean Richard, p.425
- ^ Online Reference Book for Medieval studies
- ^ Runciman, p.307, "Bohemond was excommunicated by the Pope for this alliance (Urban IV, Registres, 26 May 1263
- ^ Saunders, p. 115
- ^ Jean Richard, p.423
- ^ Jean Richard, p.426
- ^ Grousset, p.574, mentionning the account of Kirakos, Kirakos, #12
- ^ "After this, [the Mongols] convened a great assembly of the old and new cavalry of the Georgians and Armenians and went against the city of Baghdad with a countless multitude." Grigor of Akner's History of the Nation of Archers, Chap 12, circa 1300
- ^ In Alain Demurger's Jacques de Molay, p.55: "The Count of Tripoli and Prince of Antioch (the two state had the same ruler), and the king of Cilician Armenia (or Little Armenia) had made their submission to the Mongols. Since 1247 already, they had paid tribute and supplied troops. King Hetoum I went to Karakorum to make his submission in 1253, and Bohemond VI was present in Baghdad in 1258." In Demurger Les Templiers (p.80-81): "The main adversary of the Mongols in the Middle-East was the Mamluk Sultanate and the Califate of Baghdad; in 1258 they take the city, sack it, massacre the population and exterminate the Abassid familly who ruled the Califate since 750; the king of Little Armenia (of Cilicia) and the troops of Antioch participated to the fight and the looting together with the Mongols." In Demurger Croisades et Croisés au Moyen-Age (p.284): "The Franks of Tripoli and Antioch, just as the Armenians of Cilicia who since the submission of Asia Minor in 1243 had to recognize Mongol overlordship and pay tribute, participated to the capture of Baghdad."
- ^ "The Georgian troops, who had been the first to break through the walls, were particularly fiercest in their destruction" Runciman, p.303
- ^ Maalouf, p. 243
- ^ "A history of the Crusades", Steven Runciman, p.306
- ^ Foltz, p.123
- ^ Tyerman, p.806 "The Frankish Antiochenes assisted the Mongols' capture of Aleppo".
- ^ Saudi Aramco World "The Battle of Ain Jalut"
- ^ a b Grousset, p. 581
- ^ Grousset, p.586: "We known from Le Templier de Tyr that the king of Armenia Hetoum I and the Prince of Antioch Bohemond VI accompanied Kitbuqa in this offensive: "The king of Armenia and the Prince of Antioch went to the army of the Tartars and went to take Damas"."
- ^ "On 1 March Kitbuqa entered Damascus at the head of a Mongol army. With him were the King of Armenia and the Prince of Antioch. The citizens of the ancient capital of the Caliphate saw for the first time for six centuries three Christian potentates ride in triumph through their streets", Runciman, p.307
- ^ Jean Richard, p.423: "Bohemond... supported Hulegu with his troops in the siege of Aleppo; he also occupied Baalbek, and entering into Damascus with the Mongols, had the satisfaction of celebrating mass in the great Mosque"
- ^ "On March 1st 1260, Damascus had to let general Kitbuqa inside its walls. He was accompanied by king Hetoum and Prince Bohemond" Jean-Paul Roux, Histoire de l'Empire Mongol, p.346
- ^ "The Mongols then attacked Muslim Syria, and they were accompanied by Hetoum and his son-in-law Bohemond when they took Aleppo and Damascus", Claude Mutafian, p.58
- ^ Peter Jackson, "Crisis in the Holy Land in 1260," English Historical Review 376 (1980) 486
- ^ Jackson, "The Mongols and the West", p.117. Jackson also references Al-Yunani as recording Bohemond in Ba'labakk (Baalbek), and later asking to receive the land from the Mongols.
- ^ "While this report cannot be taken literally, it may contain a grain of truth. Armenian troops were part of Ketbuqa's force, while some time during the Mongol occupation Bohemond visited Baalbek and even intended to ask Hulegu for possession of the town. (...) If this prince reached as far as Baalbek, it is most probable that he also passed through Damascus." De Reuven Amitai-Preiss, "Mongols and Mamluks", p.31
- ^ Jean Richard, p.423
- ^ "Le roy d'Arménie et le Prince d'Antioche alèrent en l'ost des Tatars et furent à prendre Damas...". Quoted in "Histoire des Croisades III", Rene Grousset, p586
- ^ Demurger, "Jacques de Molay", p.55-56
- ^ Demurger, "Jacques de Molay", p.55-56
- ^ Atlas des Croisades, p.108
- ^ "Subsequently, Hulegu sent presents to [sent for, oe41] the duke of Antioch [Bohemond VI] who was a relative of the King of Armenia [son-in-law of the King of Armenia, oe41], and ordered that all the districts [g50] of his kingdom which the Saracens had held be returned to him. He also bestowed many other favors on him." Fleur des Histoires d'Orient, Chap.29
- ^ Runciman, p.310
- ^ Grousset, p.586
- ^ Jean Richard, p.428
- ^ Amin Maalouf, p.264
- ^ Tyerman, p.806
- ^ Amin Maalouf, p.262
- ^ "Hulegu informed Louis IX that he had handed over the Holy City to the Franks already, during the brief Mongol occupation in 1260 (although, as we have seen, this is nowhere indicated in any of the Muslim sources, still less in the Frankish appeals for help to the West), and the claim was reiterated in 1274 by Abaqa's envoys.", Jackson, p.174
- ^ "It happened that some men from Sidon and Belfort gathered together, went to the Saracens' villages and fields, looted them, killed many Saracens and took others into captivity together with a great deal of livestock. A certain nephew of Kit-Bugha who resided there, taking along but few cavalry, pursued the Christians who had done these things to tell them on his uncle's behalf to leave the booty. But some of the Christians attacked and killed him and some other Tartars. When Kit-Bugha learned of this, he immediately took the city of the Sidon and destroyed most of the walls [and killed as many Christians as he found. But the people of Sidon fled to an island, and only a few were slain. oe43]. Thereafter the Tartars no longer trusted the Christians, nor the Christians the Tartars." Fleur des Histoires d'Orient, Chap. 30
- ^ Runciman, p.309
- ^ Richard, p. 416 (english)
- ^ Runciman, p.307
- ^ Encyclopedia Iranica article
- ^ Runciman, p.312
- ^ "They allowed the Mamluks to cross their territory, in exchange for a promesse to be able to purchase at a low price the horses captured from the Mongols", Richard, "Histoire des Croisades", p.425
- ^ "Among Ket-Bugha's warriors were many Armenians and Georgians who were killed with him" Kirikos, Chap. 62
- ^ "These, however, were not all Mongol horsemen, but included contingents from Georgia and Lesser Armenia; Smpad writes that the latter numbered 500 men." Mongols and Mamluks, p.40
- ^ Jean Richard, p.428
- ^ Richard, p. 436 (french), p. 422 (english). "What Hulegu was offering was an alliance. And, contrary to what has long been written by the best authorities, this offer was not in response to appeals from the Franks."
- ^ Encyclopedia Iranica article
- ^ "On the side of the Franks of Syria, things had taken a different orientation. The point was not anymore to lead a Crusade against the Mongols. From that time on, the point was to engage in a Crusade together with them." Jean Richard, p.427
- ^ Jean Richard, p.435
- ^ "The sustained attacks of Baibar (...) rallied the Occidentals to this alliance, to which the Mongols also convinced the Byzantines to adhere", in "Histoire des Croisades", p.453.
- ^ "In 1264, to the coalition between the Franks, Mongols and Byzantines, responded the coalition between the Golden Horde and the Mamluks.” In Jean Richard, p.436
- ^ Runciman, p.313
- ^ "Antioch was only saved (...) by the intervention of Hethoum who called the Mongols to intervene in favour of Bohemond. Les Gestes des Chiprois even seems to say that the Armenia monarch went in person to fetch the nearest Mongol troops". Grousset, p.609
- ^ Mentionned in Grousset, p.609. In 1262, the king of Armenia went to the Mongols and again obtained their intervention to deliver the city. - "In the year 1262, the sultan Bendocdar of Babiloine, who had taken the name of Melec el Vaher, put the city of Antioch under siege, but the king of Armenia went to see the Tatars and had them come, so that the Sarazins had to leave the siege and return to Babiloine.". Original French:"Et en lan de lincarnasion .mcc. et .lxii. le soudan de Babiloine Bendocdar quy se fist nomer Melec el Vaher ala aseger Antioche mais le roy dermenie si estoit ale a Tatars et les fist ehmeuer de venir et les Sarazins laiserent le siege dantioche et sen tornerent en Babiloine."Guillame de Tyr "Historia rerum in partibus transmarinis gestarum" #316
- ^ ”In the meantime, [Baibars] condicted his troops to Antioch, and started to besiege the city, which was saved by a Mongol intervention” Jean Richard, p.429
- ^ "Grousset, p565
- ^ Quoted in Grousset, p.565
- ^ Jean Richard, p.428
- ^ Mutafian, p.58
- ^ Amin Maalouf, p.267
- ^ Amin Maalouf, p.268 (French)
- ^ Runciman, 325-327
- ^ Runciman, p.320
- ^ Jean Richard, p. 435
- ^ Runciman, p330-331
- ^ Quoted in Grousset, p.644
- ^ All information in this paragraph from Jackson, p.167
- ^ a b Runciman, p.332
- ^ ”It really seems that Saint Louis’s initial project in his second Crusade was an operation coordinated with the offensive of the Mongols.” Demurger, “Croisades et Croises”, p.285
- ^ Jean Richard, p.443
- ^ Jean Richard, p.445
- ^ Grousset, p.647
- ^ Hindley, pp. 205-206
- ^ Nicolle, p. 47
- ^ Tyerman, p. 818
- ^ Grousset, p.656
- ^ Quoted in Grousset, p.650
- ^ Grousset, p.650
- ^ Runciman, p334
- ^ "Edward I renewed the precious Mongol Alliance", Grousset "L'épopée des Croisades", p.301
- ^ "When he disembarked in Acre, Edward immediately sent envoys to Abagha (…) As he (Abagha) could not commit himself to the offensive, he ordered the Mongol forces stationned in Turkey under Samaghar to attack Syria in order to relieve the Crusaders” Jean Richard, p.446
- ^ "Edward was horrified at the state of affairs in Outremer. He knew that his own army was small, but he hoped to unite the Christians of the East into a formidable body and then to use the help of the Mongols in making an effective attack on Baibars", Runciman, p.335
- ^ a b Grousset, p.653.
- ^ Runciman, p.336
- ^ a b c Runciman, p.336
- ^ "Et revindrent en Acre li message que mi sire Odouart et la Crestiente avoient envoies as Tartars por querre secors; et firent si bien la besoigne quil amenerent les Tartars et corurent toute la terre dantioche et de Halape de Haman et de La Chamele jusques a Cesaire la Grant. Et tuerent ce quil trouverent de Sarrazins", Estoire d'Eracles, Chap XIV
- ^ Quoted in Grousset, p.653
- ^ a b Hindley, pp. 207-208
- ^ Tyerman, p. 813
- ^ a b Runciman, p.337
- ^ "The Sultan said to the messengers of the king of Charles d'Anjou that, since so many men had failed to take a house, it was not likely they should conquer the kingdom of Jerusalem!" Grousset, p.655
- ^ "Le Livre des Merveilles", p.5-17
- ^ Richard, "Histoire des Croisades", p.452
- ^ Quoted in Jean Richard, p.452
- ^ "1274: Promulgation of a Crusade, in liaison with the Mongols", Jean Richard, "Histoire des Croisades", p.502
- ^ Jean Richard, p.435
- ^ Jackson, pp. 167-168
- ^ "1274: Promulgation of a Crusade, in liaison with the Mongols", Jean Richard, "Histoire des Croisades", p.502
- ^ ”Le Pape Grégoire X s’efforce alors de mettre sur pied un vaste programme d’aide à la Terre Sainte, les “Constitutions pour le zèle de la foi”, qui sont acceptées au Concile de Lyon de 1274. Ce texte prévoit la levée d’une dime pendant trois ans pour la croisade, l’interdiction de tout commerce avec les Sarasins, la fourniture de bateaux par les républiques maritimes italiennes, et une alliance de l’Occident avec Byzance et l’Il-Khan Abagha » Michel Balard, Les Latins en Orient (XIe-XVe siècle), p.210
- ^ "Le Livre des Merveilles", p.18
- ^ Richard, "Histoire des Croisades", p.452
- ^ Richard, "Histoire des Croisades", p.452
- ^ Richard, "Histoire des Croisades", p.465
- ^ Riley-Smith, "Atlas des Croisades", p.69
- ^ "They continued the cooperation projects between the Latins, the Byzantines and the Mongols for future Crusades" Jean Richard, p.453
- ^ "Success in re-capturing the Holy Land now depended on the Mongol alliance", Richard, "Histoire des Croisades", p.454
- ^ Oldenbourg, "The Crusades", p.620 "1280: Alliance of Franks and Mongols against Qalawun")
- ^ Richard, "Histoire des Croisades", p.465
- ^ Quoted in Grousset, p.689
- ^ Richard, "Histoire des Croisades", p.465
- ^ Richard, "Histoire des Croisades", p.466
- ^ Runciman, p.390
- ^ Runciman, p.387
- ^ Runciman, p.390
- ^ Richard, "Histoire des Croisades", p.466
- ^ Qalawun inadvertanly laid siege to, and captured, Marqab in the spring of 1285. Grousset, p.692
- ^ Grousset, p. 688
- ^ Grousset, p.687
- ^ "The Crusades Through Arab Eyes", p. 253: The fortress of Marqab was held by the Knights Hospitallers, called al-osbitar by the Arabs, "These monk-knights had supported the Mongols wholeheartedly, going so far as to fight alongside them during a fresh attempted invasion in 1281."
- ^ a b "Mangu Timur commanded the Mongol centre, with other Mongol princes on his left, and on his right his Georgian auxiliaries, with King Leo and the Hospitallers", Runciman, p391-392
- ^ The “Syrian knights” were probably including knights from Cyprus. in Jean Richard, p.466
- ^ Original French:"En lan de .m. et .cc. et .lxxxi. de lincarnasion de Crist les Tatars nyssirent de lor terres et passerent les Aygues Froides a mout grant host et coururent la terre de Halape et de Haman et de La Chemele et la saresterent et firent grant damage as Sarazins et en tuerent ases et fu le roy dermenie aveuc yaus et aucuns chevaliers frans de Surie." Guillame de Tyr "Historia rerum in partibus transmarinis gestarum". Nota: "Aucuns" means "several", "some" in 13th century French Online French dictionary, and is always used with this meaning in Le Chevalier de Tyre.
- ^ Tyerman, p.817
- ^ Grands Documents de l'Histoire de France, Archives Nationales de France, p.38, 2007.
- ^ Prawdin, p. 372. "Argun revived the idea of an alliance with the West, and envoys from the Ilkhans once more visited European courts. He promised the Christians the Holy Land, and declared that as soon as they had conquered Jerusalem he would have himself baptised there. The Pope sent the envoys on to Philip the Fair of France and to Edward I of England. But themission was fruitless. Western Europe was no longer interested in crusading adventures.
- ^ Tyerman, p.817
- ^ a b Runciman, p.398
- ^ "This Arghon loved the Christians very much, and several times asked to the Pope and the king of France how they could together destroy all the Sarazins" - Le Templier de Tyr - French original:"Cestu Argon ama mout les crestiens et plusors fois manda au pape et au roy de France trayter coment yaus et luy puissent de tout les Sarazins destruire" Guillame de Tyr (William of Tyre) "Historia rerum in partibus transmarinis gestarum" #591
- ^ "The Crusades Through Arab Eyes" p. 254: Arghun, grandon of Hulegu, "had resurrected the most cherished dream of his predecessors: to form an alliance with the Occidentals and thus to trap the Mamluk sultanate in a pincer movement. Regular contacts were established between Tabriz and Rome with a view to organizing a joint expedition, or at least a concerted one."
- ^ Quote in "Histoires des Croisades III", Rene Grousset, p700
- ^ Boyle, in Camb. Hist. Iran V, pp. 370-71; Budge, pp. 165-97. Source
- ^ http://www.aina.org/books/mokk/mokk.htm
- ^ "Histoires des Croisades III", Rene Grousset, quoting "La Flor des Estoires d'Orient" by Haiton
- ^ "The Monks of Kublai Khan Emperor of China", Sir E. A. Wallis Budge Source
- ^ Richard, "Histoire des Croisades", p.469
- ^ Runciman, p. 399
- ^ a b Runciman, p.402
- ^ Runciman, p.401
- ^ Alternative translation of Arghun's letter
- ^ For another translation here
- ^ Jean Richard, p.468
- ^ "Histoire des Croisades III", p.713, Rene Grousset.
- ^ "Only a contingent of 800 Genoese arrived, whom he (Arghun) employed in 1290 in building shipd at Baghdad, with a view to harassing Egyptian commerce at the southern approaches to the Red Sea", p.169, Peter Jackson, The Mongols and the West
- ^ Jean Richard, p.468
- ^ Runciman, p.402
- ^ Foltz, p.130
- ^ Dailliez, p.324-325
- ^ Runciman, p.412
- ^ ”Ghazan resumed his plans against Egypt in 1297: the Franco-Mongol cooperation had thus survived, in spite of the loss of Acre by the Franks, and the conversion of the Persian Mongols to Islam. It was to remain one of the political factors of the policy of the Crusades, until the peace treaty with the Mumluks, which was only signed in 1322 by the khan Abu Said”, Jean Richard, p.468
- ^ Foltz, p.128
- ^ ”The renewed offensives of the Mongol Khan, the Il-Khan Ghazan, in the year 1299-1302, deployed in collaboration with the Christians forces of Cyprus, were very close to succeed”. Demurger, “Croisades et croises”, p.287
- ^ "The Trial of the Templars", Malcolm Barber, 2nd edition, page 22: "The aim was to link up with Ghazan, the Mongol Il-Khan of Persia, who had invited the Cypriots to participate in joint operations against the Mamluks".
- ^ ”During these years, no Crusade was preached in the Occident. Only the Frank forces of Cyprus and Little Armenia did cooperate with the Mongols”. Demurger, “Croisades et croises”, p287
- ^ Demurger, p.139 "During four years, Jacques de Molay and his order were totally committed, with other Christian forces of Cyprus and Armenia, to an enterprise of reconquest of the Holy Land, in liaison with the offensives of Ghazan, the Mongol Khan of Persia". Also p.283: "But especially, from 1299 to 1303, he [Molay] plays the Mongol card to the utmost. With his Order, and the other Christian forces of the kingdoms of Cyprus and Little Armenia, he tries to coordinate some operations with the Ilkha Khanate."
- ^ "The order of the Templars, and its last Grand-Master Jacques de Molay, were the artisans of the alliance with the Mongols against the Mameluks in 1299-1303, in order to regain a foothold in the Holy Land" ("L’ordre du Temple et son dernier grand maître, Jacques de Molay, ont été les artisans de l’alliance avec les Mongols de Perse contre les Mamelouks en 1299-1303, afin de reprendre pied en Terre sainte.") Alain Demurger, Master of Conference at Université Paris-I, in an interview with Le Point, "La Chute du Temple", May 27th 2008. Also: Online article
- ^ "The Mongols, after taking Damascus and several important cities from the Turks, after having been routed by the Sultan of Egypt at Tiberiade in 1260, allied themselves with the Templars. Jacques de Molay, in his letter to the king of England said that he had to sign such a treaty to fight against the Muslims, "our common enemy" Dailliez, p.306-307
- ^ Jackson
- ^ "The Templar Master, Jacques de Molay, seems to have been particularly enthousiastic about the project", Jackson, p.171
- ^ Jackson, p.182
- ^ Demurger, p.142-143
- ^ Hayton of Corycus mentions "Otton de Grandson and the Masters of the Temple and of the Hospitallers as well as their convents, who were at that time [1298 or 1299] in these regions [Cilician Armenia]", quoted in Demurger, p.116
- ^ Newman, p. 231, that says that De Molay had an "ill-fated expedition to Armenia around 1299, in which the last Templar holding in that kingdom was lost."
- ^ Demurger, p.142
- ^ Demurger, p.143
- ^ Demurger, p.142 (French edition) "He was soon joined by King Hethum, whose forces seem to have included Hospitallers and Templars from the kingdom of Armenia, who participate to the rest of the campaign."
- ^ Demurger, p.142
- ^ Demurger, p.142 "The Mongols pursued the retreating troops towards the south, but stopped at the level of Gaza"
- ^ Demurger 142-143
- ^ Runciman, p.439
- ^ "Ibn Kathir attributes partially the responsibility of these massacres and destructions to the Georgian and Armenian Christians that were accompanying the Mongols", "Textes Spirituels D'Ibn Taymiyya", Chap XI
- ^ Demurger, p.146
- ^ Demurger (p.146, French edition): "After the Mamluk forces retreated south to Egypt, the main Mongol forces retreated north in February, Ghazan leaving his general Mulay to rule in Syria".
- ^ "Meanwhile the Mongol and Armenian troops raided the country as far south as Gaza." Schein, 1979, p. 810
- ^ "He pursued the Sarazins as far as Gaza, and then turn to Damas, conquering and destroying the Sarazins". Original French: "Il chevaucha apres les Sarazins jusques a Guadres et puis se mist vers Domas concuillant et destruyant les Sarazins." Le Templier de Tyr, #609
- ^ "Arab historians however, like Moufazzal Ibn Abil Fazzail, an-Nuwairi and Makrizi, report that the Mongols raided the country as far as Jerusalem and Gaza"— Sylvia Schein, p.810
- ^ The Arab historian Yahia Michaud, in the 2002 book Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels I-XVI, Chap XI, describes that there were some firsthand accounts at the time, of forays of the Mongols into Palestine, and quotes two medieval Arab sources stating that Jerusalem was one of the cities that was invaded by the Mongols
- ^ Demurger, p.144
- ^ "After Ghazan had left, some Christians from Cyprus arrived in Gibelet and Nefin, led by Guy, Count of Jaffa, and Jean d'Antioche with their knights, and from there proceeded to go to Armenia where the camp of the Tatars was. But Ghazan was gone, so they had to return."|Le Templier de Tyr, 614. - Le Templier de Tyr, 614: "Et apres que Cazan fu partis aucuns crestiens de Chipre estoient ales a Giblet et a Nefin et en seles terres de seles marines les quels vous nomeray: Guy conte de Jaffe et messire Johan dantioche et lor chevaliers; et de la cuyderent aler en Ermenie quy estoit a lost des Tatars. Cazan sen estoit retornes: il se mist a revenir"
- ^ Jean Richard, p.481
- ^ a b c d Demurger, p.147
- ^ According to the "Chronicle of Cyprus", by Florio Bustron, quoted in in "Adh-Dhababi's Record of the Destruction of Damascus by the Mongols in 1299-1301", Note 18, p.359
- ^ a b c d e Schein, 1979, p. 811
- ^ "The banner of the Mongol Il-Khan was hoisted on the boats, because he [Ghazan's ambassador] was onboard" ("La banniere de l'Ilkhan fut hissee sur les bateaux parce qu'il etait a bord"), Demurger, "Jacques de Molay", p.147
- ^ Templar of Tyre: "At Rosetta Our men returned to their galleys, and then the Saracens saw Ghazan's banner on our galleys. Ghazan's envoys, whom Ghazan had sent to the king in Cyprus, had placed it there and had raised it over our galleys. Because of Ghazan's banner, four Tartars who were with the forty mounted Saracens that I have mentioned and now had been held there by the Saracens as if in prison, spurred their horses and came galloping up to our galleys. Our men received them..."
- ^ Jean Richard, p.481
- ^ "Adh-Dhababi's Record of the Destruction of Damascus by the Mongols in 1299-1301", Note 18, p.359
- ^ Demurger, p.146
- ^ "For a brief period, some four months in all, the Mongol Il-Khan was de facto the lord of the Holy Land", Schein, p810
- ^ Schein, 1979, p. 810
- ^ Le Templier de Tyr mentions that one of the generals of Ghazan was named Molay, whom he left in Damas with 10,000 Mongols - "611. Ghazan, when he had vanquished the Sarazins returned in his country, and left in Damas one of his Admirals, who was named Molay, who had with him 10,000 Tatars and 4 general."611. Cacan quant il eut desconfit les Sarazins se retorna en son pais et laissa a Domas .i. sien amiraill en son leuc quy ot a nom Molay qui ot o luy .xm. Tatars et .iiii. amiraus.", but it is thought that this could instead designate a Mongol general "Mûlay". - Demurger, p.279
- ^ Demurger, p.146
- ^ Demurger, Les Templiers, 2007, p.84
- ^ "Mulay, a Mongol general who was effectively present in Jerusalem in 1299-1300", Demurger, Les Templiers, 2007, p.84
- ^ Jotischky, The Crusaders and the Crusader States, p. 249
- ^ "The Mongol liberation of the Holy City, of course, furnished the opportunity for Pope Boniface and Western chroniclers alike to castigate Latin princes by claiming that God had preferred a pagan ruler as His instrument", p.173, Peter Jackson, The Mongols and the West
- ^ Runciman, p.439. "Five years later, in 1308, Ghazzan again entered Syria and now penetrated as far as Jerusalem itself. It was rumoured that he would have willingly handed over the Holy City to the Christians had any Christian state offered him its alliance."
- ^ Claude Mutafian, p.73
- ^ Demurger, p.143
- ^ Phillips, p. 128. ""Disillusionment came swiftly. Jerusalem had not been taken or even besieged; Ghazan evacuated Syria within a few weeks of its conquest probably because his horses were short of fodder. He attacked it again in 1301, and planned further campaigns for the next two years, but achieved nothing. His bitterness at the failure of the European powers to provide the military assistance he had asked for expressed itself in 1303 in yet another embassy to Philip IV and Edward I, to which Edward replied tactfully that he and Philip had been at war and could not send help."
- ^ a b "In 1300 a rumour swept the West that the Mongols had conquered Palestine and handed it over to the Christians. Pope Boniface VIII sent 'the great and joyful news' to Edward of England and probably to Philip of France as well. He encouraged the faithful to go at once to the Holy Land and he ordered the exiled Catholic bishops to return to their sees. All over Europe men hurriedly took the cross and in Genoa several ladies sold their jewelry to help pay for a crusading fleet, although in the end the project was dropped." (Riley-Smith, p. 246)
- ^ Schein, 1979, p. 805
- ^ The Mongols by David Morgan, p. 161. "Indeed, at one point Europe was swept with rumours that the Mongols had actually taken Jerusalem from the Mamluks and had returned it to Christian rule. Although this had not in fact happened, the stories did reflect the reality of Ghazan's remarkable successes in 1299-1300 when he drove the Mamluk forces completely out of Syria, only to withdraw again to Persia."Source
- ^ Michaud Yahia (Oxford Centre for Islamic Studies) (2002). Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels I-XVI (in French). Chap. XI.
- ^ Quoted in Michaud Yahia, p.66-67 Transl. Blochet t.XIV, p.667, quotes in Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels, Chap XI
- ^ Quoted in Michaud Yahia, p.66-67 Transl. Blochet t.XIV, p.667, quotes in Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels, Chap XI
- ^ Also quoted in "L'Orient au Temps des Croisades", p.125
- ^ A letter from a Franciscan monk in Nicosia, dated February 4, 1300, relates that Hethoum celebrated mass in Jerusalem and informs that "Our Minister and a lot of our brothers are preparing to go to Syria, together with Knights and soldiers, and all the others of the religious orders". Quoted in Demurger, p.145
- ^ Demurger, p.143: "There is a tradition that Hethoum celebrated a religious office at the Saint-Sepulcre on the day of the Epiphany (January 6th)."
- ^ Mutafian, p.73
- ^ Historiens Armeniens, p.660
- ^ Mutafian, p.73
- ^ "The conquest of Jerusalem by the Mongols was confirmed by Niccolo of Poggibonsi who noted (Libro d'Oltramare 1346-1350, ed. P. B. Bagatti (Jerusalem 1945), 53, 92) that the Mongols removed a gate from the Dome of the Rock and had it transferred to Damascus. Schein, 1991, p. 163
- ^ "In a letter dated 3 October 1301, Ghazan was accused by the Sultan al-Malik an-Nasir of introducing the Christian Armenians and Georgians into Jerusalem 'the most holy sanctuary to Islam, second only to Mecca!". Schein, 1979, p. 810.
- ^ Schein, Fidelis Crucis, p. 163. "According to an Armenian source confirmed by Arab chroniclers, Hetoum II with a small force reached the outskirts of Cairo and then spent some fifteen days in Jerusalem visiting the Holy Places.
- ^ Stewart, p. 14. "At one point, 'Arab chroniclers' are cited as being in support of an absurd claim made by a later Armenian source, but on inspection of the citations, they do no such thing." Also Footnote #55, where Stewart further criticizes Schein's work: "The Armenian source cited is the RHC Arm. I version of the 'Chronicle of the Kingdom', but this passage was in fact inserted into the translation of the chronicle by its editor, Dulaurier, and originates in the (unreliable) work of Nerses Balienc... The "Arab chroniclers" cited are Mufaddal (actually a Copt; the edition of Blochet), al-Maqrizi (Quatremere's translation) and al-Nuwayrf. None of these sources confirm Nerses' story in any way; in fact, as is not made clear in the relevant [Schein] footnote, it is not the text of al-Nuwayrf that is cited, but D.P. Little's discussion of the writer in his Introduction to Mamluk Historiography (Montreal 1970; 24-27), and in that there is absolutely no mention made of any Armenian involvement at all in the events of the year. It is disappointing to find such a cavalier attitude to the Arabic source material."
- ^ Mongol Raids, p. 246. "A less charitable attitude can be taken towards the other Armenian source, written by the anonymous continuator of Constable Smpad's work. His account is full of exaggerations and inaccuracies, the first of which is the year given for the campaign (751 of the Armenian calendar which equals 5 Jan. 1302 - 4 Jan. 1303). This unknown writer does not even mention Mulay or the Mongols in the raid into Palestine. In their stead only King Het'um of Armenia is found: after the victory of Hims, the king rushed forward to pursue the fleeing sultan. He was joined by 4,000 of his troops. After eleven days of hard riding, Het'um arrived at a location near Cairo called Doli (which I cannot identify). Throughout the pursuit, the sultan was but 10-12 miles ahead of the king. The latter soon withdrew from Doli because he was afraid of being captured. On his return, Het'um entered Jerusalem and gathered all the Christians from the city who had hitherto hidden in caves. During the 15 days he spent in Jerusalem, Het'um performed magnificent Christian ceremonies and also received a patent from Ghazan granting him the city and its surroundings. Afterwards, Het'um left Jerusalem and rejoined Ghazan in Damascus, spending the rest of the winter with him. Even the editor of this work, Edouard Dulaurier, unequivocally denies the veracity of the account and writes that the author's purpose was to glorify King Het'um. There is little resemblance between the facts described here and the Mamluk works or even the account of the historian Het'um, who certainly cannot be accused of lacking a desire to eulogize the Armenian king. It is quite improbable that the Mamluk writers would have missed an opportunity to attack [the muslim] Ghazan for such a despicable action, i.e., abandoning Muslim territory, especially Jerusalem to Christian depredations."
- ^ Receuil des Historiens des Croisades, Historiens Armeniens I, Chronique du Royaume de Petite Armenie, p. 659-660 Page 659, note 1:
"The account of the battle of Homs, in which Ghazan routs the Egyptians, on December 23, 1299, can be compared with that of Hayton, De Tartare, cap. XLII, and the narration of M. d'Ohsson, Hist. des Mongols, liv. VI, Chap. vi, t. IV, p.233-240. It is obvious that Nerses Balients added here a few fantastic details, devised to enhance the role played by the king of Armenia Hetoum II, as an auxiliary of the Tartars. We can very certainly put in doubt the pursuing of the Egyptians by this prince, after the battle, as far as the place named Doli by the compiler, which he located near Cairo. Indeed, the Mongol general who had been dispatched with a body of 15,000 men to pursue Sultan Nacer, did not go farther than Gaza, and stopped at the desert limit between Syria and Egypt". End of the note. - ^ Chroniques de France, edited by Jules Viard: "Et a Pasques ensivant, si comme l'en dit, en Jherusalem le service de Dieu les crestiens avec exaltacion de grant joie celebrerent". Quoted in Demurger, p.280
- ^ Schein, 2005, p. 157
- ^ Demurger, p. 145
- ^ Demurger, p.145
- ^ "The earliest letter was dated 19 March 1300 and addressed to Boniface VIII. Its contents suggest that it was probably written by the Doge Pietro Gradenigo (1289-1311). - Schein, 1979, p. 814
- ^ Schein, pp. 814-815
- ^ Schein, p.815-816
- ^ Schein, p. 805
- ^ Demurger, p.278-279
- ^ "Le grand-maître s'etait trouvé avec ses chevaliers en 1299 à la reprise de Jerusalem." François Raynouard (1805). "Précis sur les Templiers".
- ^ Le Templier de Tyr mentions that one of the generals of Ghazan was named Molay, whom he left in Damas with 10,000 Mongols - "611. Ghazan, we he had vanquished the Sarazins returned in his country, and left in Damas one of his Admirals, who was named Molay, who had with him 10,000 Tatars and 4 general."611. Cacan quant il eut desconfit les Sarazins se retorna en son pais et laissa a Domas .i. sien amiraill en son leuc quy ot a nom Molay qui ot o luy .xm. Tatars et .iiii. amiraus.", but it is thought that this could instead designate a Mongol general "Mûlay". - Demurger, p.279
- ^ Demurger, p. 279
- ^ Claudius Jacquand (1846). "Jacques Molay Prend Jerusalem.1299" (painting). Hall of Crusades, Versailles. Retrieved 2007-09-09.
- ^ "He was seldom on the field: in Armenia in 1298 or 1299 maybe, at Ruad in november 1300 surely, but probably not in the naval operations of July-August 1300 in Alexandria, Acre, Tortosa. If the planned 1301 offensive of the Mongols had occurred, he would have been at the head of his troops in combat." Demurger, p. 159
- ^ Demurger, p.146
- ^ Demurger, p.136. "From the Tatars, the king of Armenia, the king of Cyprus, the Great Master of the Templars or other nobles from Outremer, are arriving embassadors on a visit to the Pope. They are already in Apulia and should reach the Pope in the next few days" - Letter by Romeu de Marimundo, counsellor of the king of Aragon, dated July 2nd, 1300, in Barcelona, quoted by Demurger
- ^ ”In 1300 , again, the Templars were able to send a few hundred combattants to Cyprus, in view of combined operations with the Mongols”. Demurger, “Croisades et croises”, p.189
- ^ Jean Richard, p.481
- ^ "The Trial of the Templars", Malcolm Barber, 2nd edition, page 22: "In November, 1300, James of Molay and the king's brother, Amaury of Lusignan, attempted to occupy the former Templar stronghold of Tortosa. A force of 600 men, of which the Templars supplied about 150, failed to establish itself in the town itself, although they were able to leave a garrison of 120 men on the island of Ruad, just off the coast.
- ^ "That year [1300], a message came to Cyprus from Ghazan, king of the Tatars, saying that he would come during the winter, and that he wished that the Franks join him in Armenia (...) Amalric of Lusignan, Constable of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, arrived in November (...) and brought with him 300 knights, and as many or more of the Templars and Hospitallers (...) In February a great admiral of the Tatars, named Cotlesser, came to Antioch with 60,000 horsemen, and requested the visit of the king of Armenia, who came with Guy of Ibelin, Count of Jaffa, and John, lord of Giblet. And when they arrived, Cotelesse told them that Ghazan had met great trouble of wind and cold on his way. Cotlesse raided the land from Haleppo to La Chemelle, and returned to his country without doing more". - Le Templier de Tyre, Chap 620-622. Quoted in Demurger, p.147. Original:Guillame de Tyr (William of Tyre), Historia rerum in partibus transmarinis gestarum #620-622
- ^ Jean Richard, p.481
- ^ Quoted in Demurger, p.147. Original:Guillame de Tyr (William of Tyre), Historia rerum in partibus transmarinis gestarum #620-622
- ^ "From 1299, Jacques de Molay and his Order fully committed, with the other Christian forces of Cyprus and Armenia, to a reconquest of the Holy Land in liaison with the offensives of Ghazan, the Mongol khan of Persia; the occupation of Ruad for two years, on the Syrian coast near Tortosa, must be understood in this perspective, and would even add, in this perspective only." Alain Demurger, p.139
- ^ Michaud, Yahia (Oxford Centre for Islamic Studies) (2002). Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels I-XVI", Chap. XI
- ^ Quoted in Demurger, p.154. Full letter from Jacques de Molay to Edward I, London, Record Office, LV No22, transcripted in Laurent Dailliez, "Jacques de Molay, dernier maitre du Temple, p.190, Note 65:
"Excellentissimo et potentissimo Domino, domino Eabardo (sic) Dei gratia serenissimo regi Anglie et domino Hibernie et duci Aquitanie et (... Jacobus de Mol)lay Dei gratia humilis magister pauperis milicie Templi salutem et separatum mandatus regis( tota)liter obediri. Quia de (...) edimus quos dominatio regia cup(it or iat) informari ideo eaque ad presens novimus regie majestati per presentes (...) Hanc est quod Casanus Tartarorum rex pungnavit cum domino Portefferi qui esse dicitur suus germanus et Casanus (...) suo exercitu (...) bellavit et extitit deinde de hostibus triumphator. Intelliximus etiam quod in mense septembris pro servicio venturo (...) et trahit in insula Turtesie. Casani et surrum tartarorum adventum attendendo; et per Dei gratiam noster conventus taliter (...)ndo dampna Saracenis et Fragendo casalia eorumdem quod per actum ipsorum casum (...) et votis precipere (...) intendere si altissimus noster (...)tetur his diebus. Nos igitur (...)nam potentiam flexis genibus (...) quod sua pietate ita dignetur dirigere et flaci approbare quod certa negotia Terre Sancte Comoda vel (...) dominationem regiam humiliter deprecamur ut nos nostroque et nostra bona sub protectione regia (...) et noster conventus parati sumus dominationis vestre mandatis totaliter obedire. Data Nomocie IX aprilis." - ^ Demurger, p.154-155
- ^ Jean Richard, p.481
- ^ "Ghazan's letter to Boniface VIII, dated 12 April, 1302, suggests that, having received an encouraging letter from the Pope, he counted on Christian participation in his expedition to Syria in 1303.
- ^ A. Mostaert and F. W. Cleaves,. "Trois documents mongols des Archives secretes vaticanes", H.J AJ. xv,. 419-506 Journal of Semitic Studies
- ^ Schein, p.813
- ^ "Nearly 40 of these men were still in prison in Cairo years later where, according to a former fellow prisoner, the Genoese Matthew Zaccaria, they died of starvation, having refused an offer of 'many riches and goods' in return for apostatising"" The Trial of the Templars, Malcolm Barber, p.22
- ^ In "Le Royaume Armenien de Cilicie", p.74-75
- ^ a b Demurger, p158
- ^ Nicolle, p. 80
- ^ Encyclopedia Iranica article
- ^ "Arghun had one of his sons baptized, Khordabandah, the future Oljaitu, and in the Pope's honour, went as far as giving him the name Nicholas", Histoire de l'Empire Mongol, Jean-Paul Roux, p.408
- ^ Mostaert and Cleaves, pp. 56-57, Encyclopedia Iranica
- ^ Quoted in Jean-Paul Roux, "Histoire de l'Empire Mongol", p.437
- ^ Les hégémonies mongoles
- ^ Jean-Paul Roux, in Histoire de l'Empire Mongol ISBN 2213031649: "The Occident was reassured that the Mongol alliance had not ceased with the conversion of the Khans to Islam. However, this alliance could not have ceased. The Mamelouks, through their repeated military actions, were becoming a strong enough danger to force Iran to maintain relations with Europe.", p.437
- ^ Demurger, p.284
- ^ Demurger, p.202
- ^ Flor des Estoires d'Orient, Book IV
- ^ Peter Jackson, p.173
- ^ Demurger, p.203
- ^ Peter Jackson, The Mongols and the West, p.171
- ^ Foltz, p.131
- ^ Peter Jackson, The Mongols and the West, p.315
- ^ Peter Jackson, p.172
- ^ Jean Richard, "Histoire des Croisades", p.485
- ^ Richard, p.485
- ^ Les hégémonies mongoles
- ^ "Atlas des Croisades", p.112
- ^ Norris 2003:11
- ^ Chase 2003:58
- ^ "The Eastern Origins of Western Civilization", John M.Hobson, p186, ISBN 0521547245
- ^ Foltz, p.133
- ^ Jackson, p.330
- ^ Jackson, p.329-330
- ^ Jackson, p.330
- ^ Jackson, p. 330
- ^ "Dichiarazione d'alcuni luoghi ne' libri di messer Marco Polo, con l'istoria del reubarbaro", preface to Marco Polo's book. Quoted in "Fra Mauro's world map" Piero Falchetta, p61
- ^ Encyclopedia Iranica
- ^ ”Istanbul”, p.16
- ^ "The fact that they [the Mongols] were anti-Muslim was good enough reason for the king [of Armenia] to place his entire army at their disposal. This unholy alliance took the field in 1259", also: "Their Christian allies joined them [the Mongols] in a triumphal entry, forcing the defeated Muslims to carry the cross before them, and later turned one of the city's mosques into a Christian church" in p.8 The Mongols, Stephen Turnbull.
- ^ "In 1258 they [the Mongols] sacked Baghdad and two years later Aleppo. Bohemond VI of Antioch-Tripoli (1252-1275) became their ally." p.136 The Oxford History of the Crusades", Joanthan Riley-Smith.
- ^ "Bohemond VI, briefly one of Outremer's most important power broker, had already accepted Mongol overlordship, with a Mongol resident and battalion stationed in Antioch itself, where they stayed until the fall of the city to the Mamluks in 1268. The Frankish Antiochenes assisted in the Mongols' capture of Aleppo, thus in part achieving a very traditional Frankish target, and had received lands in reward." (Tyerman, p.806)
- ^ Claude Lebédel, p.75
- ^ "In 1258 they [the Mongols] sacked Baghdad and two years later Aleppo. Bohemond VI of Antioch-Tripoli (1252-1275) became their ally." p.136 The Oxford History of the Crusades", Joanthan Riley-Smith.
- ^ "The fact that they [the Mongols] were anti-Muslim was good enough reason for the king [of Armenia] to place his entire army at their disposal. This unholy alliance took the field in 1259", also: "Their Christian allies joined them [the Mongols] in a triumphal entry, forcing the defeated Muslims to carry the cross before them, and later turned one of the city's mosques into a Christian church" in p.8 The Mongols, Stephen Turnbull.
- ^ Prawdin, p. 284. "Their Georgian and Armenian vassals."
- ^ "The principality of Antioch was dominated by its Armenian neighbour -- it was through the will of the Armenian king that the Antiochenes came to aid Hulegu in 1259-60." ("The Logic of Conquest" Al-Masaq, v. 14, No.1, March 2002, p. 8)
References
Medieval sources
- Adh-Dhababi, Record of the Destruction of Damascus by the Mongols in 1299-1301 Translated by Joseph Somogyi. From: Ignace Goldziher Memorial Volume, Part 1, Online (English translation).
- Jean de Joinville, The Memoirs of Lord of Joinville, translated by Ethel Wedwood Online (English translation).
- Le Templier de Tyr (circa 1300). Chronicle du Templier de Tyr, Online (Original French).
- Hayton of Corycus (1307). Flowers of the Histories of the East, Online (English translation).
- Guillaume de Tyr (circa 1300). History of Deeds Done Beyond the Sea, Online (Original French).
- Kirakos (circa 1300). History of the Armenians, Online, (English translation).
- The history and Life of Rabban Bar Sauma.
{{cite book}}:|format=requires|url=(help) (online)
Modern sources
- Amitai, Reuven (1987). "Mongol Raids into Palestine (AD 1260 and 1300)". JRAS: 236–255.
- Balard, Michel (2006). Les Latins en Orient (XIe-XVe siècle). Presses Universitaires de France, Paris. ISBN 2130518117.
- Barber, Malcolm (2001). The Trial of the Templars (2nd edition ed.). University Press, Cambridge. ISBN 978-0-521-67236-8.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - Bournoutian, George A. (2002). A Concise History of the Armenian People: From Ancient Times to the Present. Mazda Publishers. ISBN 1568591411.
- "The Monks of Kublai Khan Emperor of China", Sir E. A. Wallis Budge. Online
- Dailliez, Laurent (1972). Les Templiers (in French). Editions Perrin. ISBN 2-262-02006-X.
- Demurger, Alain (2007). Les Templiers (in French). Editions Jean-Paul Gisserot. ISBN 2877479552.
- Grousset, René (1935). Histoire des Croisades III, 1188-1291 (in French). Editions Perrin. ISBN 2-262-02569-X.
- Grousset, René (1935). L'épopée des Croisades (in French). Editions Perrin. ISBN 2262018642.
- Encyclopedia Iranica, Article on Franco-Persian relations
- Foltz, Richard (2000). "Religions of the Silk Road : overland trade and cultural exchange from antiquity to the fifteenth century". New York: St. Martin's Griffin. ISBN 0-312-23338-8.
- Demurger, Alain (2007). Jacques de Molay (in French). Editions Payot&Rivages. ISBN 2228902357.
- Eddé, Anne-Marie (2002). L'Orient au temps des croisades (in French). GF Flammarion. ISBN 2080711210.
- Hazard, Harry W. (editor) (1975). Volume III: The Fourteenth and Fifteenth Centuries. A History of the Crusades. Kenneth M. Setton, general editor. The University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 0-299-06670-3.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help) - Jackson, Peter (2005). The Mongols and the West: 1221-1410. Longman. ISBN 978-0582368965.
- Lebédel, Claude (2006). Les Croisades, origines et conséquences (in French). Editions Ouest-France. ISBN 2737341361.
- Maalouf, Amin (1984). The Crusades Through Arab Eyes. New York: Schocken Books. ISBN 0-8052-0898-4.
- Maalouf, Amin (1983). Les croisades vues par les Arabes. JC Lattes.
- Michaud, Yahia (Oxford Centre for Islamic Studies) (2002). Ibn Taymiyya, Textes Spirituels I-XVI (in French). "Le Musulman", Oxford-Le Chebec.
{{cite book}}: External link in|title= - Mutafian, Claude (1993, 2001). Le Royaume Armenien de Cilicie (in French). CNRS Editions. ISBN 2271051053.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Newman, Sharan (2006). Real History Behind the Templars. Berkley Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-425-21533-3.
- Nicolle, David (2001). The Crusades. Essential Histories. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84176-179-4.
- Oldenbourg, Zoe (2006). The Crusades. Phoenix Press. ISBN 1842122231.
- Phillips, John Roland Seymour (1998). The Medieval Expansion of Europe. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0198207409.
- Prawdin, Michael (pseudonym for Charol, Michael) (1940/1961). Mongol Empire. Collier-Macmillan Canada. ISBN 1412805198.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Prawer, Joshua (1972). The Crusaders' Kingdom: European Colonialism in the Middle Ages. Praeger. ISBN 9780297993971.
- Richard, Jean (1996). Histoire des Croisades. Fayard. ISBN 2-213-59787-1.
- Riley-Smith, Jonathan (1987, 2005). The Crusades: A History (2nd edition ed.). Yale Nota Bene. ISBN 0-300-10128-7.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - Riley-Smith, Jonathan (1996, 2005). Atlas des Croisades (in French). Autrement. ISBN 2862605530.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Riley-Smith, Jonathan (2002). The Oxford History of the Crusades. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0192803123.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Jean-Paul Roux, L'Asie Centrale, Paris, 1997, ISBN 9782213598949
- Runciman, Steven (1987 (first published in 1952-1954)). A history of the Crusades 3. Penguin Books. ISBN 9780140137057.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Saunders, J. J. (2001). The History of the Mongol Conquests. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 0812217667.
- Schein, Sylvia (October 1979). "Gesta Dei per Mongolos 1300. The Genesis of a Non-Event". The English Historical Review. 94 (373): 805–819.
- Schein, Sylvia (1991). Fideles Crucis: The Papacy, the West, and the Recovery of the Holy Land. Clarendon. ISBN 0198221657.
- Schein, Sylvia (2005). Gateway to the Heavenly City: crusader Jerusalem and the catholic West. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. ISBN 075460649X.
- Sinor, Denis (1999). "The Mongols in the West". Journal of Asian History. 33 (1).
- Stewart, Angus Donal. The Armenian Kingdom and the Mamluks: War and Diplomacy During the Reigns of Het'Um II (1289-1307). BRILL. ISBN 9004122923.
- Turnbull, Stephen (1980). The Mongols. Osprey Publishing Ltd. ISBN 9780850453720.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Tyerman, Christopher (2006). God's War: A New History of the Crusades. Harvard University Press. ISBN 0674023870.
- Weatherford, Jack (2004). Genghis Khan and the Making of the Modern World. Three Rivers Press. ISBN 0-609-80964-4.
- Wood, Frances (2002). The Silk Road. University of California Press. ISBN 0520243404.
External links
- Template:Fr icon "Alain Demurger interview, "La Chute du Temple"". Le Point. 11/08/2005. Retrieved 2007-09-25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)
