Solar eclipse of November 25, 2011
| Solar eclipse of November 25, 2011 | |
|---|---|
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | −1.0536 |
| Magnitude | 0.9047 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 68°36′S 82°24′W / 68.6°S 82.4°W |
| Times (UTC) | |
| (P1) Partial begin | 4:23:14 |
| Greatest eclipse | 6:21:24 |
| (P4) Partial end | 8:17:16 |
| References | |
| Saros | 123 (53 of 70) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9534 |
A partial solar eclipse occurred on Friday 25 November, 2011. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. This eclipse was visible across Antarctica in its summer 24-hour day sunlight, and New Zealand near sunset with less than 20% of the Sun obscured. Parts of the western Antarctic Peninsula experienced nearly 90% obscuration of the Sun. The eclipse belonged to Saros 123 and was number 53 of 70 eclipses in the series.
This was the last of four partial solar eclipses in 2011, with the others occurring on January 4, 2011, June 1, 2011, and July 1, 2011.
Images
Related eclipses
Eclipses of 2011
- A partial solar eclipse on January 4.
- A partial solar eclipse on June 1.
- A total lunar eclipse on June 15.
- A partial solar eclipse on July 1.
- A partial solar eclipse on November 25.
- A total lunar eclipse on December 10.
It proceeded the total lunar eclipse which occurred on December 10, 2011.
Solar eclipses 2011–2014
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
The partial solar eclipses on January 4, 2011 and July 1, 2011 occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2011 to 2014 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
118 Partial in Tromsø, Norway |
June 1, 2011 Partial |
1.21300 | 123 Hinode XRT footage |
November 25, 2011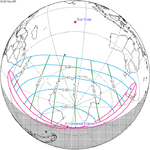 Partial |
−1.05359 | |
128 Annularity in Red Bluff, CA, USA |
May 20, 2012 Annular |
0.48279 | 133 Totality in Mount Carbine, Queensland, Australia |
November 13, 2012 Total |
−0.37189 | |
138 Annularity in Churchills Head, Australia |
May 10, 2013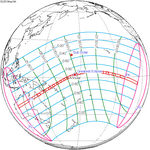 Annular |
−0.26937 | 143 Partial in Libreville, Gabon |
November 3, 2013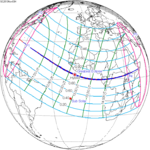 Hybrid |
0.32715 | |
148 Partial in Adelaide, Australia |
April 29, 2014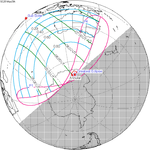 Annular (non-central) |
−0.99996 | 153 Partial in Minneapolis, MN, USA |
October 23, 2014 Partial |
1.09078 | |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| 21 eclipse events between July 1, 2000 and July 1, 2076 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 1–2 | April 19–20 | February 5–7 | November 24–25 | September 12–13 |
| 117 | 119 | 121 | 123 | 125 |
 July 1, 2000 |
 April 19, 2004 |
 February 7, 2008 |
 November 25, 2011 |
 September 13, 2015 |
| 127 | 129 | 131 | 133 | 135 |
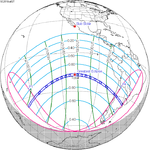 July 2, 2019 |
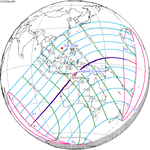 April 20, 2023 |
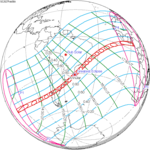 February 6, 2027 |
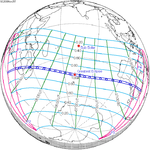 November 25, 2030 |
 September 12, 2034 |
| 137 | 139 | 141 | 143 | 145 |
 July 2, 2038 |
 April 20, 2042 |
 February 5, 2046 |
 November 25, 2049 |
 September 12, 2053 |
| 147 | 149 | 151 | 153 | 155 |
 July 1, 2057 |
 April 20, 2061 |
 February 5, 2065 |
 November 24, 2068 |
 September 12, 2072 |
| 157 | ||||
 July 1, 2076 | ||||
Notes
References
- APOD December 2, 2011 [1]
- http://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/SEplot/SEplot2001/SE2011Nov25P.GIF
- www.space.com: Solar Eclipse Wows Lucky Skywatchers in New Zealand
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.





