Abanoquil
Appearance
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is an old revision of this page, as edited by DMacks (talk | contribs) at 05:44, 17 June 2020 (Remove malformatted |molecular_weight= when infobox can autocalculate it, per Wikipedia talk:WikiProject Pharmacology#Molecular weights in drugboxes (via WP:JWB)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 05:44, 17 June 2020 by DMacks (talk | contribs) (Remove malformatted |molecular_weight= when infobox can autocalculate it, per Wikipedia talk:WikiProject Pharmacology#Molecular weights in drugboxes (via WP:JWB))
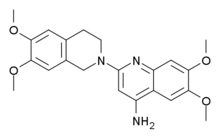 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H25N3O4 |
| Molar mass | 395.459 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Abanoquil (INN) is an α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist.[1]
See also
References
- ^ Tham TC, Guy S, Shanks RG, Harron DW (April 1992). "Dose-dependent alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist activity of the anti-arrhythmic drug, abanoquil (UK-52,046), without reduction in blood pressure in man". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 33 (4): 405–9. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1992.tb04059.x. PMC 1381330. PMID 1349492.
| Sympatholytics (antagonize α-adrenergic vasoconstriction) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Other antagonists |
| ||||
| |||||
Urologicals, including antispasmodics (G04B) | |
|---|---|
| Acidifiers | |
| Urinary antispasmodics (primarily antimuscarinics) | |
| Other urologicals | |
| α1 |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α2 |
| ||||
| β |
| ||||
This antihypertensive-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
This drug article relating to the genito-urinary system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
Retrieved from "https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Abanoquil&oldid=962995868"
