Buyid dynasty
Buyid Dynasty آل بویه al-e Buye | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 934–1062[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||
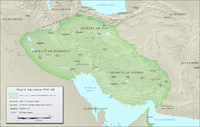
 The Buyid dynasty in 970 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Shiraz (Buyids of Fars, 934–1062) Ray (Buyids of Jibal, 943–1029) Baghdad (Buyids of Iraq, 945–1055) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Shia Islam[4] (also Sunni, Mu'tazila Islam, Christianity, Zoroastrianism, Judaism) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Hereditary monarchy | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Emir/Shahanshah | |||||||||||||||||||||||
• 934–949 | Imad al-Dawla | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1048–1062 | Abu Mansur Fulad Sutun | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• Established | 934 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• Imad al-Dawla proclaimed himself "Emir" | 934 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• Adud al-Dawla becomes the supreme ruler of the Buyid dynasty | 979 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
• Disestablished | 1062[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 980 est.[5][6] | 1,600,000 km2 (620,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| History of Iran |
|---|
 |
|
Timeline |
The Buyid dynasty, or the Buyids (Persian: آل بویه Âl-e Buye; also known as Buwaihids, Bowayhids, Buyahids, or Buyyids), was a Shia Iranian dynasty[7] of Daylamite origin.[8] Coupled with the rise of other Iranian dynasties in the region, the approximate century of Buyid rule represents the period in Iranian history sometimes called the 'Iranian Intermezzo' since, after the Muslim conquest of Persia, it was an interlude between the rule of the Abbasid Caliphate and the Seljuk Empire.[9]
The Buyid dynasty was founded by 'Ali ibn Buya, who in 934 conquered Fars and made Shiraz his capital. His younger brother Hasan ibn Buya conquered parts of Jibal in the late 930s, and by 943 managed to capture Ray, which he made his capital. In 945, the youngest brother, Ahmad ibn Buya, conquered Iraq and made Baghdad his capital. He received the laqab or honorific title of Mu'izz al-Dawla ("Fortifier of the State"). The eldest, 'Ali, was given the title of 'Imad al-Dawla ("Support of the State"), and Hasan was given the title of Rukn al-Dawla ("Pillar of the State").
As Daylamite Iranians, the Buyids consciously revived symbols and practices of Iran's Sasanian Empire.[10] Beginning with 'Adud al-Dawla, they used the ancient Sasanian title Shahanshah (شاهنشاه), literally "king of kings".[11][12]
At its greatest extent, the Buyid dynasty encompassed territory of most of today's Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, and Syria, along with parts of Oman, the UAE, Turkey, Afghanistan and Pakistan. During the 10th and 11th centuries, just prior to the invasion of the Seljuq Turks, the Buyids were the most influential dynasty in the Middle East.[13] Under king 'Adud al-Dawla, it became briefly the most powerful dynasty in the Middle East.[14]
Origins
The word Būya (Arabic Buwayh) is a Middle Persian name ending in the diminutive ـویه (Middle Persian -ōē, modern Persian -ūyeh, Arabic -uwayh). The Buyids were descendants of Panah-Khusrow, a Zoroastrian from Daylam. He had a son named Buya, who was a fisherman from Lahijan,[15] and later left Zoroastrianism and converted to Islam.[16]: 274 Buya later had three sons, named Ahmad, 'Ali, and Hasan, who would later carve the Buyid kingdom together. Most historians agree that the Buyids were Daylamites.[16]: 251–52 [17][18][19][20][21][22][23] The Buyids claimed royal lineage from Bahram V, 15th king of the Sasanian Empire.[24]
History
Rise (934-945)
The founder of the dynasty, 'Ali ibn Buya, was originally a soldier in the service of the Daylamite warlord Makan ibn Kaki,[25] but later changed his adherence to the Iranian ruler Mardavij, who had established the Ziyarid dynasty, and was himself related to the ruling dynasty of Gilan,[26] a region bordering Dailam. 'Ali was later joined by his two younger brothers, Hasan ibn Buya and Ahmad ibn Buya. In 932, 'Ali was given Karaj as his fief, and thus was able to enlist other Daylamites into his own army. However, 'Ali's independent actions made Mardavij plan to have him killed, 'Ali was informed of Mardavij's plan by the latter's own vizier. The Buyids brother, with 400 of their Daylamite supporters, then fled to Fars,[27] where they managed to take control of Arrajan.[28] However, the Buyids and the Abbasid general Yaqut shortly came into a struggle for the control of Fars, from which the Buyids eventually emerged victorious.[25] This victory opened the way for the conquest of the capital of Fars, Shiraz.[29]
'Ali also made an alliance with the landowners of Fars, which included the Fasanjas family, which would later produce many prominent statesmen for the Buyids. Furthermore, 'Ali also to enlist more soldiers, which included the Turks, who were made part of the cavalry. 'Ali then sent his brother Ahmad on an expedition to Kerman, but was forced to withdraw from them after opposition from the Baloch people and the Qafs.[30] However, Mardavij, who sought to depose the Abbasid caliph of Baghdad and recreate a Zoroastrian Iranian Empire, shortly wrested Khuzestan from the Abbasids and forced 'Ali to recognize him as his suzerain.[31]
Luckily for the Buyids, Mardavij was shortly assassinated in 935, which caused chaos in the Ziyarid territories, a perfect situation for the Buyid brothers; Ali and Ahmad conquered Khuzistan, while Hasan captured the Ziyarid capital of Isfahan, and in 943 captured Rey, which became his capital, thus conquering all of Jibal. In 945, Ahmad entered Iraq and made the Abbasid Caliph his vassal, at the same receiving the laqab Mu'izz ad-Dawla ("Fortifier of the State"), while 'Ali was given the laqab Imād al-Dawla ("Support of the State"), and Hasan was given the laqab Rukn al-Dawla ("Pillar of the State").
Height of power and Golden age (945-983)
In addition to the other territories the Buyids had conquered, Kerman was conquered in 967, Oman (967), the Jazira (979), Tabaristan (980), and Gorgan (981). After this, however, the Buyids went into a slow decline, with pieces of the confederation gradually breaking off and local dynasties under their rule becoming de facto independent.
Decline and fall (983–1062)
The death of Adud al-Dawla is considered the starting point of the decline of the Buyid dynasty;[32] his son Abu Kalijar Marzuban, who was in Baghdad at the time of his death, first kept his death secret in order to ensure his succession and avoid civil war. When he made the death of his father public, he was given the title of "Samsam al-Dawla". However, Adud's other son, Shirdil Abu'l-Fawaris, challenged the authority of Samsam al-Dawla, resulting in a civil war.[33] Meanwhile, a Marwanid chieftain named Badh, seized Diyabakr and forced Samsam al-Dawla to recognize him as the vassal ruler of the region.[33] Furthermore, Mu'ayyad al-Dawla also died during this period, and he was succeeded by Fakhr al-Dawla, who with the aid of Mu'ayyad al-Dawla's vizier Sahib ibn 'Abbad became the ruler of Mu'ayyad al-Dawla's possessions.[34] Another son of Adud al-Dawla, Abu Tahir Firuzshah, established himself as the ruler of Basra and took the title of "Diya' al-Dawla", while another son, Abu'l-Husain Ahmad, established himself as the ruler of Khuzistan, taking the title of "Taj al-Dawla".
Shirdil Abu'l-Fawaris (known by his title of "Sharaf al-Dawla") quickly seized Oman from Samsam al-Dawla, and in 983, the Turkic troops of Samsam al-Dawla mutinied against him, and left Iraq for Fars, but most of them were persuaded by his relative Ziyar ibn Shahrakawayh to stay in Iraq. However, Iraq was in grim affairs, and several rebellions occurred, which he however, managed to suppress, the most dangerous rebellion being under Asfar ibn Kurdawayh, who tried to make Abu Nasr Firuz Kharshadh (known by his title of "Baha' al-Dawla") the ruler of Iraq. During the same period, Samsam al-Dawla also managed to seize Basra and Khuzistan, forcing his two brothers to flee to Fakhr al-Dawla's territory.
During the mid-11th century, the Buyid amirates gradually fell to the Ghaznavid and Seljuq Turks. In 1029, Majd al-Dawla, who was facing an uprising by his Dailami troops in Ray, requested assistance from Mahmud of Ghazna.[35] When Sultan Mahmud arrived, he deposed Majd al-Dawla, replaced him with a Ghaznavid governor and ended the Buyid dynasty in Ray.[36][37]
In 1055, Tughrul conquered Baghdad, the seat of the caliphate, and ousted the last of the Buyid rulers.[38] Like the Buyids, the Seljuqs kept the Abbasid caliphate as the titular ruler.[39]
Government
The Buyids established a confederation in Iraq and western Iran. This confederation formed three principalities - one in Fars, with Shiraz as its capital - the second one in Jibal, with Ray as its capital - and the last one in Iraq, with Baghdad as its capital. However, during their late period, more principalities formed in the Buyid confederation. Succession of power was hereditary, with fathers dividing their land among their sons.
The title used by the Buyid rulers was amir, meaning "governor" or "prince". Generally, one of the amirs would be recognized as having seniority over the others; this individual would use the title of amir al-umara,[12] or senior amir. Although the senior amīr was the formal head of the Būyids, he did not usually have any significant control outside of his own personal amirate; each amir enjoyed a high degree of autonomy within his own territories. As mentioned above, some of the stronger amirs used the Sassanid title of Shahanshah. Furthermore, several other titles such as malik ("king"), and malik al-muluk ("king of kings"), were also used by the Buyids. On a smaller scale, the Buyid territory was also be ruled by princes from other families, such as the Hasanwayhids.
Military

During the beginning of the Buyid dynasty, their army consisted mainly of their fellow Daylamites, a warlike and brave people of mostly peasant origin, who served as foot soldiers. The Daylamites had a long history of military activity dating back to the Sasanian period, and had been mercenaries in various places in Iran and Iraq, and even as far as Egypt. The Daylamites, during a battle, normally bore a sword, a shield, and three spears. Furthermore, they were also known for their formidable shield formation, which was hard to break through.[40]
But when the Buyid territories increased, they began recruiting Turks into their cavalry,[29] who had played a prominent role in the Abbasid military.[41] The Buyid army also consisted of Kurds, who, along with the Turks, were Sunnis, while the Daylamites were Shi'i Muslims.[42] However, the army of the Buyids of Jibal mainly composed of Daylamites.[43]
The Daylamites and Turks often quarrelled with each other in an attempt to be the dominant force within the army.[44] To compensate their soldiers the Buyid amīrs often distributed iqtāʾs, or the rights to a percentage of tax revenues from a province (tax farming), although the practice of payment in kind was also frequently used.[45] While the Turks were favoured in Buyid Iraq, the Daylamites were favoured in Buyid Iran.[46]
Religion
Like most Daylamites at the time, the Buyids were Shia and have been called Twelvers. However, it is more likely that they began as Zaydis.[47][48] As the reason of this turning from Zaydism to Twelverism, Moojen Momen suggests that since the Buyids were not descendants of Ali, the first Shi'i Imam, Zaydism would have urged them to install an Imam from Ali's family. For that reason Buyids tended toward Twelverism, which has an occulted Imam, which was more politically attractive to them.[47]
The Buyids rarely attempted to enforce a particular religious view upon their subjects except when in matters where it would be politically expedient. The Sunni Abbasids retained the caliphate but were deprived of all secular power.[49] In addition, in order to prevent tensions between the Shia and the Sunnis from spreading to government agencies, the Buyid amirs occasionally appointed Christians to high offices instead of Muslims from either sect.[50]
Buyid rulers
Major rulers
Generally, the three most powerful Buyid amirs at any given time were those in control of Fars, Jibal and Iraq. Sometimes a ruler would come to rule more than one region, but no Buyid rulers ever exercised direct control of all three regions.
Buyids in Fars
- Imad al-Dawla (934–949)
- 'Adud al-Dawla (949–983)
- Sharaf al-Dawla (983–989)
- Samsam al-Dawla (989–998)
- Baha' al-Dawla (998–1012)
- Sultan al-Dawla (1012–1024)
- Abu Kalijar (1024–1048)
- Abu Mansur Fulad Sutun (1048–1051)
- Abu Sa'd Khusrau Shah (1051–1054)
- Abu Mansur Fulad Sutun (1051–1062)

Buyids in Ray
- Rukn al-Dawla (935–976)
- Fakhr al-Dawla (976–980)
- Mu'ayyad al-Dawla (980–983)
- Fakhr al-Dawla (restored) (984–997)
- Majd al-Dawla (997–1029)
Buyids in Iraq
- Mu'izz al-Dawla (945–967)
- 'Izz al-Dawla (966–978)
- 'Adud al-Dawla (978–983)
- Samsam al-Dawla (983–987)
- Sharaf al-Dawla (987–989)
- Baha' al-Dawla (989–1012)
- Sultan al-Dawla (1012–1021)
- Musharrif al-Dawla (1021–1025)
- Jalal al-Dawla (1025–1044)
- Abu Kalijar (1044–1048)
- Al-Malik al-Rahim (1048–1055)
Minor rulers
It was not uncommon for younger sons to found collateral lines, or for individual Buyid members to take control of a province and begin ruling there. The following list is incomplete.
Buyids in Basra
- Diya' al-Dawla (980s)
Buyids in Hamadan
- Mu'ayyad al-Dawla (976–983)
- Shams al-Dawla (997–1021)
- Sama' al-Dawla (1021–1024)
Buyids in Kerman
- Qawam al-Dawla (1012–1028)
Buyids of Khuzistan
- Taj al-Dawla (980s)
Family tree
| Buya | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Imad al-Dawla 934–949 | Rukn al-Dawla 935–976 | Mu'izz al-Dawla 945–967 | Kama | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abu Ishaq Ibrahim | Izz al-Dawla 967–978 | Sanad al-Dawla | Marzuban | Zubayda | Abu Tahir | Ali ibn Kama | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marzuban ibn Bakhtiyar | Salar | Unnamed princess | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fakhr al-Dawla 976–997 | 'Adud al-Dawla 949–983 | Mu'ayyad al-Dawla 980–983 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shams al-Dawla 997–1021 | Majd al-Dawla 997–1029 | Sharaf al-Dawla 983–989 | Samsam al-Dawla 983–998 | Baha' al-Dawla 998–1012 | Shahnaz | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sama' al-Dawla 1021–1024 | Qawam al-Dawla 1012–1028 | Sultan al-Dawla 1012–1024 | Musharrif al-Dawla 1021–1025 | Jalal al-Dawla 1027–1044 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fana-Khusrau | Abu Dulaf | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abu Kalijar 1024–1048 | Al-Malik al-Aziz | Abu Mansur Ali | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abu Ali Fana-Khusrau | Abu Mansur Fulad Sutun 1048–1062 | Al-Malik al-Rahim 1048–1055 | Kamrava | Abu'l-Muzaffar Bahram | Abu Sa'd Khusrau Shah | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abu'l-Ghana'im al-Marzuban | Surkhab | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
References
- ^ C.E. Bosworth, The New Islamic Dynasties, (Columbia University Press, 1996), 154.
- ^ a b Fereshteh Davaran, Continuity in Iranian Identity: Resilience of a Cultural Heritage, (Routledge, 2010), 156.
- ^ Davaran, Fereshteh (2010-02-26). Continuity in Iranian Identity: Resilience of a Cultural Heritage. Routledge. p. 156. ISBN 9781134018314.
Middle Persian was now replaced by new Persian as the popular language; and thus, the writings of historians , scientists and theologians of the Buyid court, which were in either Middle Persian or Arabic, were accessible to the vast majority of the Iranians only after translation"
- ^ Abbasids, B.Lewis, The Encyclopaedia of Islam, Vol. I, Ed. H.A.R.Gibb, J.H.Kramers, E. Levi-Provencal and J. Schacht, (Brill, 1986), 19.
- ^ Turchin, Peter; Adams, Jonathan M.; Hall, Thomas D (December 2006). "East-West Orientation of Historical Empires". Journal of World-systems Research. 12 (2): 222. ISSN 1076-156X. Retrieved 12 September 2016.
- ^ Rein Taagepera (September 1997). "Expansion and Contraction Patterns of Large Polities: Context for Russia". International Studies Quarterly. 41 (3): 475–504. doi:10.1111/0020-8833.00053. JSTOR 2600793.
- ^ Grousset, René (2002). The Empire of the Steppes: A History of Central Asia. trans. Naomi Walford. New Brunswick: Rutgers University Press. ISBN 978-0813506272.
- ^ Felix, Wolfgang; Madelung, Wilferd. "Deylamites". Encyclopaedia Iranica, VII/4. pp. 342–347. Retrieved 28 November 2016.The most successful actors in the Deylamite expansion were the Buyids. The ancestor of the house, Abū Šojāʿ Būya, was a fisherman from Līāhej, the later region of Lāhījān.
- ^ Blair, Sheila (1992). The Monumental Inscriptions From Early Islamic Iran and Transoxiana. Leiden: E.J. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-09367-6.
- ^ Goldschmidt, Arthur (2002). A Concise History of the Middle East (7 ed.). Boulder, CO: Westview Press. p. 87. ISBN 978-0813338859.
- ^ Clawson, Patrick; Rubin, Michael (2005), Eternal Iran: Continuity and Chaos, Middle East in Focus (1st ed.), New York: Palgrave Macmillan, p. 19, ISBN 978-1-4039-6276-8
- ^ a b Kabir, Mafizullah (1964). The Buwayhid Dynasty of Baghdad, 334/946–447/1055. Calcutta: Iran Society.
- ^ Wink, André (2002). Al-Hind: The Making of the Indo-Islamic World, Vol. 2, Slave Kings and the Islamic Conquest 11th–13th Centuries. Boston: Brill Academic Publishers. hdl:2027/heb.03189.0001.001. ISBN 978-0391041745. – via Questia (subscription required)
- ^ Ch. Bürgel & R. Mottahedeh 1988, pp. 265–269.
- ^ Felix, Wolfgang; Madelung, Wilferd. "Deylamites". Encyclopaedia Iranica, VII/4. pp. 342–347. Retrieved 28 November 2016.
- ^ a b Busse, Heribert (1975). "Iran Under the Buyids". In Frye, Richard N. (ed.). The Cambridge History of Iran, Vol. 4: From the Arab Invasion to the Saljuqs. London: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521200936.
- ^ "ʿAżod-Al-Dawla, Abū Šojāʾ Fannā Ḵosrow (936-83)" at Encyclopædia Iranica
- ^ "Buyids" at Encyclopædia Iranica
- ^ Bosworth, Clifford Edmund (1996). The New Islamic Dynasties: A Chronological and Genealogical Manual. New York: Columbia University Press. pp. 154–155. ISBN 978-0231107143.
- ^ Rypka, Jan (2013). History of Iranian Literature. Springer. ISBN 978-94-010-3479-1.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help), page 146 - ^ Kennedy, Hugh (2015). The Prophet and the Age of the Caliphates: The Islamic Near East from the 6th to the 11th Century. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-317-37638-5.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help), page 211 - ^ Houtsma, Martijn Theodoor, ed. (1993). E.J. Brill's First Encyclopaedia of Islam, 1913–1936 (Reprint ed.). Leiden: E.J. Brill. ISBN 978-9004097964.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Karsh, Efraim (2007). Islamic Imperialism: A History. New Haven: Yale University. ISBN 978-0-300-12263-3.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Alram, Michael. "The Cultural Impact of Sasanian Persia along the Silk Road – Aspects of Continuity". E-Sasanika. 14: 10. The article uses Wahram Gūr for the king's name.
- ^ a b Nagel 1990, p. 578–586.
- ^ Kennedy 2004, p. 211.
- ^ Kennedy 2004, p. 212.
- ^ Bosworth 1975, p. 255.
- ^ a b Kennedy 2004, p. 213.
- ^ Bosworth 1975, p. 257.
- ^ Bosworth 1975, p. 256.
- ^ Kennedy 2004, p. 234.
- ^ a b Bosworth 1975, p. 289.
- ^ Bosworth 1975, p. 290.
- ^ C.E. Bosworth, The Ghaznavids 994-1040, (Edinburgh University Press, 1963), 53,59,234.
- ^ C.E. Bosworth, The Ghaznavids 994-1040, 53,59,234.
- ^ The Political and Dynastic History of the Iranian World (A.D. 1000-1217), C.E. Bosworth, Cambridge History of Iran, Vol. V, ed. J. A. Boyle, (Cambridge University Press, 1968), 37.
- ^ André Wink, Al-Hind: The Making of the Indo-Islamic World, Vol. 2, (Brill, 2002), 9. – via Questia (subscription required)
- ^ Bernard Lewis, The Middle East: A Brief History of the Last 2,000 Years, (New York: Scribner, 1995) p. 89.
- ^ Bosworth 1975, p. 251.
- ^ Sohar and the Daylamī interlude (356–443/967–1051), Valeria Fiorani Piacentini, Proceedings of the Seminar for Arabian Studies, Vol. 35, Papers from the thirty-eighth meeting of the Seminar for Arabian Studies held in London, 22–24 July 2004 (2005), 196.
- ^ Bosworth 1975, p. 287.
- ^ Kennedy 2004, p. 244.
- ^ Busse, Heribert (1975), "Iran Under the Buyids", in Frye, R. N. (ed.), The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 4: From the Arab Invasion to the Saljuqs, Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, pp. 265, 298, ISBN 978-0-521-20093-6
- ^ Sourdel-Thomine, J. "Buwayhids." The Encyclopedia of Islam, Volume I. New Ed. Leiden: E. J. Brill, 1960. p. 1353.
- ^ Bosworth 1975, p. 252.
- ^ a b Momen, Moojan (1985), An Introduction to Shi'i Islam, Yale University Press, pp. 75–76, ISBN 978-0-300-03531-5
- ^ Berkey, Jonathan (2003). The Formation of Islam: Religion and Society in the Near East, 600-1800. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-58813-3.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help), p. 135 - ^ Abbasids, Bernard Lewis, The Encyclopaedia of Islam, Vol. I, ed. H. A. R. Gibb, J. H. Kramers, E. Levi-Provencal, J. Schacht, (E.J. Brill, 1986), 19.
- ^ Heribert, pp. 287-8
Sources
- Bosworth, C. E. (1975). "Iran under the Buyids". In Frye, Richard N. (ed.). The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 4: From the Arab Invasion to the Saljuqs. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 250–305. ISBN 0-521-20093-8.*Donohue, John J. (2003). The Buwayhid Dynasty in Iraq 334 H./945 to 403 H./1012: Shaping Institutions for the Future. Leiden and Boston: Brill. ISBN 90-04-12860-3.
- Edward Granville Browne, Islamic Medicine, 2002, ISBN 81-87570-19-9
- Bürgel, Ch.; Mottahedeh, R. (1988). "ʿAŻOD-AL-DAWLA, ABŪ ŠOJĀʾ FANNĀ ḴOSROW". Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. III, Fasc. 3. London u.a.: Routledge & Kegan Paul. pp. 265–269.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Clawson, Patrick; Rubin, Michael (2005). Eternal Iran: Continuity and Chaos. ISBN 978-1-4039-6276-8. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Hill, Donald Routledge, Islamic Science And Engineering, Edinburgh University Press (1993), ISBN 0-7486-0455-3
- Ibn Isfandiyar (1905). An Abridged Translation of the History of Tabaristan. University of Michigan: BRILL. pp. 1–356. ISBN 9789004093676.
'.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kabir, Mafizullah (1964). The Buwayhid Dynasty of Baghdad, 334/946-447/1055. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kennedy, Hugh (2004). The Prophet and the Age of the Caliphates: The Islamic Near East from the 6th to the 11th Century (Second ed.). Harlow: Longman. ISBN 978-0-582-40525-7.
- Kraemer, Joel L. (1992). Humanism in the Renaissance of Islam: The Cultural Revival During the Buyid Age. BRILL. ISBN 9789004097360.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Madelung, W. (1975). "The Minor Dynasties of Northern Iran". In Frye, Richard N. (ed.). The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 4: From the Arab Invasion to the Saljuqs. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 198–249. ISBN 0-521-20093-8.
- Madelung, Wilferd; Felix, Wolfgang (1995). "DEYLAMITES". Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. BII, Fasc. 4. pp. 342–347.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Nagel, Tilman (1990). "BUYIDS". Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. IV, Fasc. 6. London u.a.: Routledge & Kegan Paul. pp. 578–586.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Turner, John P. (2006). "'Adud al-Dawla". Medieval Islamic Civilization: A-K, index. Taylor & Francis. p. 16.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
External links
- "Buyids" Tilman Nagel
- Encyclopedia Iranica: DEYLAMITES
- [1] The Buyid Domination as the Historical Background for the Flourishing of Muslim Scholarship During the 4th/10th Century by Dr. M. Ismail Marcinkowski
- The Buwaihids in Iran and Iraq