Sedoreoviridae
| Reoviruses | |
|---|---|

| |
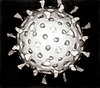
| Intact double-shelled Rotavirus particles | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Duplornaviricota |
| Class: | Resentoviricetes |
| Order: | Reovirales |
| Family: | Sedoreoviridae |
| Subfamilies and genera | |
Reoviridae is a family of viruses. They have a wide host range, including vertebrates, invertebrates, plants, protists and fungi.[1] They lack lipid envelopes and package their genomes of discrete double-stranded segments of RNA within multi-layered capsids. Lack of a lipid envelope has allowed three-dimensional structures of these large complex viruses (diameter,∼60–100 nm) to be obtained, revealing a structural and likely evolutionary relationship to the Cystovirus family of Bacteriophage.[2] There are currently 97 species in this family, divided among 15 genera in two subfamilies.[3] Reoviruses can affect the gastrointestinal system (such as Rotavirus) and respiratory tract.[4] The name "Reo-" is derived from respiratory enteric orphan viruses.[5] The term "orphan virus" refers to the fact that some of these viruses have been observed not associated with any known disease. Even though viruses in the family Reoviridae have more recently been identified with various diseases, the original name is still used.
Reovirus infection occurs often in humans, but most cases are mild or subclinical. Rotavirus, however, can cause severe diarrhea and intestinal distress in children, and lab studies in mice have implicated Orthoreovirus in the expression of coeliac disease in pre-disposed individuals.[6] The virus can be readily detected in feces, and may also be recovered from pharyngeal or nasal secretions, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, and blood. Despite the ease of finding Reovirus in clinical specimens, their role in human disease or treatment is still uncertain.
Some viruses of this family, such as Phytoreovirus and Oryzavirus, infect plants. Most of the plant-infecting reoviruses are transmitted between plants by insect vectors. The viruses replicate in both the plant and the insect, generally causing disease in the plant, but little or no harm to the infected insect.[7]
Structure

Reoviruses are non-enveloped and have an icosahedral capsid composed of an outer (T=13) and inner (T=2) protein shell.[1][5] Ultrastructural studies shows that virion capsids composed of two or tree separate layers which depend their type. The innermost layer(core) has T=1 icosahedral symmetry and composed of 60 different type of structural proteins. The core contains genom segments, each of them encode variety enzyme structure which is required for transcription. The core is covered by capsid layer T=13 icosahedral symmetry. Reovirus has unique structure which is contain glycolisated spike protein on the surface. [8]The genomes of viruses in Reoviridae contain 10–12 segments which are grouped into three categories corresponding to their size: L (large), M (medium) and S (small). Segments range from about 0.2 to 3 kbp and each segment encodes 1–3 proteins (10–14 proteins in total[1]). Proteins of viruses in the Reoviridae are denoted by the Greek character corresponding to the segment it was translated from (the L segment encodes for λ proteins, the M segment encodes for μ proteins and the S segment encodes for σ proteins).[5]
| Genus | Structure | Symmetry | Capsid | Genomic arrangement | Genomic segmentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aquareovirus | Icosahedral | T=13, T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Segmented |
| Rotavirus | Icosahedral | T=13, T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Segmented |
| Seadornavirus | Icosahedral | T=13, T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Segmented |
| Coltivirus | Icosahedral | T=13, T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Segmented |
| Fijivirus | Icosahedral | T=13, T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Segmented |
| Phytoreovirus | Icosahedral | T=13, T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Segmented |
| Mimoreovirus | Icosahedral | T=13, T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Segmented |
| Orbivirus | Icosahedral | T=13, T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Segmented |
| Cypovirus | Icosahedral | T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Segmented |
| Orthoreovirus | Icosahedral | T=13, T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Segmented |
| Idnoreovirus | Icosahedral | T=13, T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Segmented |
| Dinovernavirus | Icosahedral | T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Segmented |
| Oryzavirus | Icosahedral | T=13, T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Segmented |
| Cardoreovirus | Icosahedral | T=13, T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Segmented |
| Mycoreovirus | Icosahedral | T=13, T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Segmented |
Life cycle
Viruses in the family Reoviridae have genomes consisting of segmented, double-stranded RNA (dsRNA).[4] Because of this, replication occurs exclusively in the cytoplasm and the virus encodes several proteins which are needed for replication and conversion of the dsRNA genome into (+)-RNAs. The virus can enter the host cell via a receptor on the cell surface. The receptor is not known but is thought to include sialic acid and junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs).[9] The virus is partially uncoated by proteases in the endolysosome, where the capsid is partially digested to allow further cell entry. The core particle then enters the cytoplasm by a yet unknown process where the genome is transcribed conservatively causing an excess of (+) sense strands, which are used as mRNA templates to synthesize (−) sense strands. The genome of rotavirus is separated via 11 segmented as mentioned before. These 11 segmented genome associated with VP1 molecule which responsible for RNA synthesizes. In early events the selection process is occurred to allow the entry of 11 different RNA species in the cell. This procedure is performed by newly synthesized RNAs. This event ensures to receives one each of the 11 different RNA species. In late events transcription process is occurred again but this time are not capped unlikely early events. For virus different amounts of RNAs are required therefore in translation step there is a control machinery. There are same quantities RNAs but different quantities of proteins. The reason of this, RNAs are not translated same rate.[10]
Viral particles begin to assemble in the cytoplasm 6–7 hours after infection. Translation takes place by leaky scanning, suppression of termination, and ribosomal skipping. The virus exits the host cell by monopartite non-tubule guided viral movement, cell to cell movement, and existing in occlusion bodies after cell death and remaining infectious until finding another host.[1]
| Genus | Host details | Tissue tropism | Entry details | Release details | Replication site | Assembly site | Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aquareovirus | Aquatic vertebrates: fish; aquatic invertebrates: shellfish; aquatic invertebrates: crustaceans | None | Cell receptor endocytosis | Cell death | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
| Cardoreovirus | Crustaceans: crabs | None | Cell receptor endocytosis | Cell death | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Arthropod bite |
| Coltivirus | Humans; rodents; ticks; mosquitoes | Erythrocytes | Cell receptor endocytosis | Cell death | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Arthropod bite |
| Cypovirus | Insects | Midgut; goblet; fat | Cell receptor endocytosis | Cell death | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Polyhedra: oral-fecal; vertical: eggs |
| Dinovernavirus | Insects; Mosquitoes | None | Unknown | Cell death | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Unknown |
| Fijivirus | Plants: gramineae; plants: liliacea; planthoppers | Phloem | Viral movement; mechanical inoculation | Cell death | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Delphacid plant hoppers |
| Idnoreovirus | Hymenoptera | Gut | Cell receptor endocytosis | Cell death | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Unknown |
| Mimoreovirus | Algae | None | Cell receptor endocytosis | Cell death | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Arthropod bite |
| Mycoreovirus | Fungi | Mycelium | Cell death; cytoplasmic exchange, sporogenesis; hyphal anastomosis | Cell death; cytoplasmic exchange, sporogenesis; hyphal anastomosis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasmic exchange, sporogenesis; hyphal anastomosis |
| Orbivirus | Vertebrates; mosquitoes; midges; gnats; sandflies; ticks | None | Cell receptor endocytosis | Cell death | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Arthropod bite |
| Orthoreovirus | Vertebrates | Epithelium: intestinal; epithelium:bile duct; epithelium: lung; leukocytes; endothelium: CNS | Clathrin-mediated endocytosis | Cell death | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Aerosol; oral-fecal |
| Oryzavirus | Plants: graminae, Oryza sativa; planthoppers | None | Viral movement; mechanical | Cell death | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Delphacid planthoppers |
| Phytoreovirus | Oryza sativa; leafhoppers | Phloem | Viral movement; mechanical inoculation | Cell death | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Leafhoppers |
| Rotavirus | Humans; vertebrates | Intestinal mucosa | Clathrin-mediated endocytosis | Cell death | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Oral-fecal |
| Seadornavirus | Humans; cattle; pigs; mosquitoes | None | Cell receptor endocytosis | Cell death | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Zoonosis; arthropod bite |
Multiplicity reactivation
Multiplicity reactivation (MR) is the process by which two or more virus genomes, each containing inactivating genome damage, can interact within an infected cell to form a viable virus genome. McClain and Spendlove[11] demonstrated MR for three types of reovirus after exposure to ultraviolet irradiation. In their experiments, reovirus particles were exposed to doses of UV-light that would be lethal in single infections. However, when two or more inactivated viruses were allowed to infect individual host cells MR occurred and viable progeny were produced. As they stated, multiplicity reactivation by definition involves some type of repair. Michod et al.[12] reviewed numerous examples of MR in different viruses, and suggested that MR is a common form of sexual interaction in viruses that provides the benefit of recombinational repair of genome damages.
Taxonomy
Group: dsRNA
- Family: Reoviridae
- Sub-Family: Sedoreovirinae
- Genus: Orbivirus
- African horse sickness virus
- Bluetongue virus
- Changuinola virus
- Chenuda virus
- Chobar Gorge virus
- Corriparta virus
- Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus
- Equine encephalosis virus
- Eubenangee virus
- Great Island virus
- Ieri virus
- Lebombo virus
- Orungo virus
- Palyam virus
- Peruvian horse sickness virus
- St Croix River virus
- Umatilla virus
- Wad Medani virus
- Wallal virus
- Warrego virus
- Wongorr virus
- Yunnan orbivirus
- Sub-Family: Spinareovirinae
The Reoviridae are divided into two subfamilies[13] based on the presence of a "turret" protein on the inner capsid.[14][15] From ICTV communications: "The name Spinareovirinae will be used to identify the subfamily containing the spiked or turreted viruses and is derived from 'reovirus' and the Latin word 'spina' as a prefix, which means spike, denoting the presence of spikes or turrets on the surface of the core particles. The term 'spiked' is an alternative to 'turreted', that was used in early research to describe the structure of the particle, particularly with the cypoviruses. The name Sedoreovirinae will be used to identify the subfamily containing the non-turreted virus genera and is derived from 'reovirus' and the Latin word 'sedo', which means smooth, denoting the absence of spikes or turrets from the core particles of these viruses, which have a relatively smooth morphology."[16]

Other Reoviridae
Additionally, there is one proposed genus that has not yet been accepted by the ICTV:
Piscine reovirus is a Spinareovirinae-like virus that has not yet been classified.[18]
Therapeutic applications
Although reoviruses are mostly nonpathogenic in humans, these viruses have served as very productive experimental models for studies of viral pathogenesis.[19] Newborn mice are exquisitely sensitive to reovirus infection and have been used as the preferred experimental system for studies of reovirus pathogenesis.[20]
The reoviruses have been demonstrated to have oncolytic (cancer-killing) properties, encouraging the development of reovirus-based therapies for cancer treatment.[21][22]
Reolysin is a formulation of reovirus (reovirus serotype 3-dearing strain[23]) that is currently in clinical trials for the treatment of various cancers,[24] including studies currently developed to investigate the role of Reolysin combined with other immunotherapies.[23]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- ^ Polly Roy (Ed.). Reoviruses: Entry, Assembly and Morphogenesis. Springer (2006). pg.5
- ^ a b "Virus Taxonomy: 2019 Release". talk.ictvonline.org. International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Retrieved 11 May 2020.
- ^ a b c MicrobiologyBytes Archived 2015-05-21 at the Wayback Machine—Reoviruses
- ^ Bouziat, R; et al. (April 7, 2017). "Reovirus infection triggers inflammatory responses to dietary antigens and development of celiac disease". Science. 356 (6333): 44–50. Bibcode:2017Sci...356...44B. doi:10.1126/science.aah5298. PMC 5506690. PMID 28386004.
- ^ Carter, John, Saunders, Venetis (2007). Virology Principles and Applications. West Sussex: Jonn WILEY. p. 148. ISBN 978-0-470-02386-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Payne S (2017). "Family Reoviridae". Viruses: 219–226. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-803109-4.00026-X.
- ^ Barton, ES; Forrest, JC; Connolly, JL; Chappell, JD; Liu, Y; Schnell, FJ; Nusrat, A; Parkos, CA; Dermody, TS (February 9, 2001). "Junction adhesion molecule is a receptor for reovirus". Cell. 104 (3): 441–51. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00231-8. PMID 11239401.
- ^ Virology: Principles and Applications by John Carter and Venetica Saunders Saunders (2007)
- ^ McClain ME, Spendlove RS (November 1966). "Multiplicity reactivation of reovirus particles after exposure to ultraviolet light". J. Bacteriol. 92 (5): 1422–9. doi:10.1128/JB.92.5.1422-1429.1966. PMC 276440. PMID 5924273.
- ^ Michod, R. E.; Bernstein, H.; Nedelcu, A. M. (2008). "Adaptive value of sex in microbial pathogens". Infection, Genetics and Evolution. 8 (3): 267–285. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2008.01.002. PMID 18295550.
- ^ Carstens, E. B. (January 2010). "Ratification vote on taxonomic proposals to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2009)". Archives of Virology. 155 (1): 133–146. doi:10.1007/s00705-009-0547-x. PMC 7086975. PMID 19960211.
- ^ Hill, Claire; Booth T; et al. (1999). "The structure of a cypovirus and the functional organization of dsRNA viruses". Nature Structural Biology. 6 (6): 565–9. doi:10.1038/9347. PMID 10360362.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Knipe, David; Howley P; et al. (2006). Fields Virology. Philadelphia, Pa.: Wolters Kluwer, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 1855. ISBN 978-0-7817-6060-7.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Attoui, Houssam; Mertens, Peter. "Template for Taxonomic Proposal to the ICTV Executive Committee To create a new SubFamily in an existing Family". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. 2007.127-129V.v2.Spina-Sedoreovirinae. pp. 1–9.
- ^ Deng, X. X.; Lü, L.; Ou, Y. J.; Su, H. J.; Li, G.; Guo, Z. X.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, P. R.; Chen, Y. G.; He, J. G.; Weng, S. P. (2012). "Sequence analysis of 12 genome segments of mud crab reovirus (MCRV)". Virology. 422 (2): 185–194. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2011.09.029. PMID 22088215.
- ^ Kibenge MJ, Iwamoto T, Wang Y, Morton A, Godoy MG, Kibenge FS (2013). "Whole-genome analysis of piscine reovirus (PRV) shows PRV represents a new genus in family Reoviridae and its genome segment S1 sequences group it into two separate sub-genotypes". Virol. J. 10: 230. doi:10.1186/1743-422X-10-230. PMC 3711887. PMID 23844948.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Acheson, Nicholas H. Fundamentals of Molecular Virology. John Wiley and Sons (2011). p.234
- ^ Polly Roy (Ed.). Reoviruses: Entry, Assembly and Morphogenesis. Springer (2006). pg.18
- ^ Lal R, Harris D, Postel-Vinay S, de Bono J (October 2009). "Reovirus: Rationale and clinical trial update". Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 11 (5): 532–9. PMID 19806501.
- ^ Kelland, K. (13 June 2012). "Cold virus hitches a ride to kill cancer: study". Reuters. Retrieved 17 June 2012.
- ^ a b Babiker, H.M.; Riaz, I.B.; Husnain, M.; Borad, M.J. (February 2017). "Oncolytic virotherapy including Rigvir and standard therapies in malignant melanoma". Oncolytic Virotherapy. 6. Dovepress, New Zealand NLM: 11–18. doi:10.2147/OV.S100072. ISSN 2253-1572. PMC 5308590. PMID 28224120. 101629828.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Thirukkumaran C, Morris DG (2009). "Oncolytic viral therapy using reovirus". Methods Mol. Biol. Methods in Molecular Biology. 542: 607–34. doi:10.1007/978-1-59745-561-9_31. ISBN 978-1-934115-85-5. PMID 19565924.
External links
- Viralzone: Reoviridae
- ICTV: Reoviridae
- Description of plant viruses: Reoviridae
- ViPR: Reoviridae
- "Reoviridae". NCBI Taxonomy Browser. 10880.