Solar eclipse of April 8, 2024
| Solar eclipse of April 8, 2024 | |
|---|---|
 The solar eclipse during totality, seen from Dallas, Texas | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 0.3431 |
| Magnitude | 1.0566 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 268 s (4 min 28 s) |
| Location | Nazas, Durango, Mexico |
| Coordinates | 25°18′N 104°06′W / 25.3°N 104.1°W |
| Max. width of band | 198 km (123 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| (P1) Partial begin | 15:42:07 |
| (U1) Total begin | 16:38:44 |
| Greatest eclipse | 18:18:29 |
| (U4) Total end | 19:55:29 |
| (P4) Partial end | 20:52:14 |
| References | |
| Saros | 139 (30 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9561 |
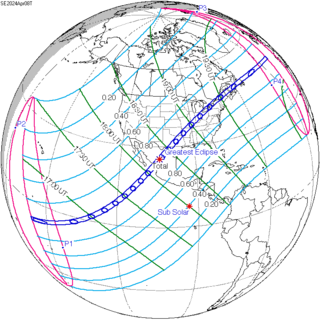
A total solar eclipse will take place on April 8, 2024, visible across North America and Central America. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. With a magnitude of 1.0566, its longest duration of totality will be of four minutes and 28 seconds near the town of Nazas, Durango, Mexico, and the nearby city of Torreón, Coahuila.
Visibility

Totality will be visible in a narrow strip of land in North America, beginning at the Pacific coast, then crossing northern Mexico through the states of Sinaloa, Durango and Coahuila, in the United States, through the states of Texas, Arkansas, Missouri, Illinois, Kentucky, Indiana, Ohio, New York, and Vermont, and finally the southern parts of the provinces Ontario, Quebec and New Brunswick, western Prince Edward Island, and the island of Newfoundland in eastern Canada. Then, it will vanish at the eastern Atlantic Coast of Newfoundland. It will be the 2nd total eclipse visible from the central United States in just 7 years, coming after the August 21, 2017 eclipse.[1]
In Canada, the path of totality will pass over parts of southern Ontario (including Hamilton, Niagara Falls, Kingston, and Cornwall), parts of southern Québec (including Montréal and Sherbrooke), central New Brunswick (including Fredericton), western Prince Edward Island (including Tignish and Summerside) and central Newfoundland Island (including Gander and Grand Falls-Windsor). Note that some of these cities listed lie on an edge of the path of totality, such as Hamilton and Montréal. Toronto and Moncton, New Brunswick, lie just north and south of the path of totality, respectively.
Related eclipses
This eclipse will be the first total solar eclipse to be visible in Mexico since the solar eclipse of July 11, 1991.[2]
The path of this eclipse crosses the path of the prior total solar eclipse of August 21, 2017, with the intersection of the two paths being in southern Illinois in Makanda just south of Carbondale. A small land area, including the cities of Carbondale, Cape Girardeau, Missouri, and Paducah, Kentucky, will thus experience two total solar eclipses within a span of fewer than seven years.
Solar eclipses 2022-2025
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[3]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2022 to 2025 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
119 Partial in CTIO, Chile |
April 30, 2022 Partial |
−1.19008 | 124 Partial from Saratov, Russia |
October 25, 2022 Partial |
1.07014 | |
129 Partial in Magetan, Indonesia |
April 20, 2023 Hybrid |
−0.39515 | 134 Annularity in Hobbs, NM, USA |
October 14, 2023 Annular |
0.37534 | |
139 Totality in Dallas, TX, USA |
April 8, 2024 Total |
0.34314 | 144 Annularity in Santa Cruz Province, Argentina |
October 2, 2024 Annular |
−0.35087 | |
| 149 | March 29, 2025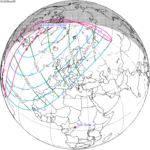 Partial |
1.04053 | 154 | September 21, 2025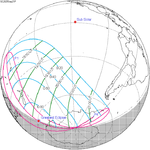 Partial |
−1.06509 | |
Saros 139
This eclipse is a part of Saros series 139, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 71 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on May 17, 1501. It contains hybrid eclipses from August 11, 1627 through December 9, 1825 and total eclipses from December 21, 1843 through March 26, 2601. There are no annular eclipses in this set. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on July 3, 2763. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of totality will be produced by member 61 at 7 minutes, 29.22 seconds on July 16, 2186. This date is the longest solar eclipse computed between 4000 BC and AD 6000.[4] All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit.[5]
| Series members 18–39 occur between 1801 and 2200: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 18 | 19 | 20 |
 November 29, 1807 |
 December 9, 1825 |
 December 21, 1843 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 |
 December 31, 1861 |
 January 11, 1880 |
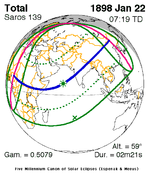 January 22, 1898 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 |
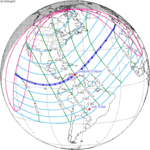 February 3, 1916 |
 February 14, 1934 |
 February 25, 1952 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 |
 March 7, 1970 |
 March 18, 1988 |
 March 29, 2006 |
| 30 | 31 | 32 |
 April 8, 2024 |
 April 20, 2042 |
 April 30, 2060 |
| 33 | 34 | 35 |
 May 11, 2078 |
 May 22, 2096 |
 June 3, 2114 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 |
 June 13, 2132 |
 June 25, 2150 |
 July 5, 2168 |
| 39 | ||
 July 16, 2186 | ||
Tritos series
This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1801 and 2200 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
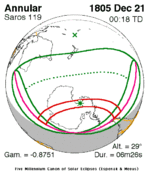 December 21, 1805 (Saros 119) |
 November 19, 1816 (Saros 120) |
 October 20, 1827 (Saros 121) |
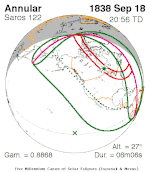 September 18, 1838 (Saros 122) |
 August 18, 1849 (Saros 123) |
 July 18, 1860 (Saros 124) |
 June 18, 1871 (Saros 125) |
 May 17, 1882 (Saros 126) |
 April 16, 1893 (Saros 127) |
 March 17, 1904 (Saros 128) |
 February 14, 1915 (Saros 129) |
 January 14, 1926 (Saros 130) |
 December 13, 1936 (Saros 131) |
 November 12, 1947 (Saros 132) |
 October 12, 1958 (Saros 133) |
 September 11, 1969 (Saros 134) |
 August 10, 1980 (Saros 135) |
 July 11, 1991 (Saros 136) |
 June 10, 2002 (Saros 137) |
 May 10, 2013 (Saros 138) |
 April 8, 2024 (Saros 139) |
 March 9, 2035 (Saros 140) |
 February 5, 2046 (Saros 141) |
 January 5, 2057 (Saros 142) |
 December 6, 2067 (Saros 143) |
 November 4, 2078 (Saros 144) |
 October 4, 2089 (Saros 145) |
 September 4, 2100 (Saros 146) |
 August 4, 2111 (Saros 147) |
 July 4, 2122 (Saros 148) |
 June 3, 2133 (Saros 149) |
 May 3, 2144 (Saros 150) |
 April 2, 2155 (Saros 151) |
 March 2, 2166 (Saros 152) |
 January 29, 2177 (Saros 153) |
 December 29, 2187 (Saros 154) |
 November 28, 2198 (Saros 155) | |||
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| 21 eclipse events between June 21, 1982 and June 21, 2058 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| June 21 | April 8–9 | January 26 | November 13–14 | September 1–2 |
| 117 | 119 | 121 | 123 | 125 |
 June 21, 1982 |
 April 9, 1986 |
 January 26, 1990 |
 November 13, 1993 |
 September 2, 1997 |
| 127 | 129 | 131 | 133 | 135 |
 June 21, 2001 |
 April 8, 2005 |
 January 26, 2009 |
 November 13, 2012 |
 September 1, 2016 |
| 137 | 139 | 141 | 143 | 145 |
 June 21, 2020 |
 April 8, 2024 |
 January 26, 2028 |
 November 14, 2031 |
 September 2, 2035 |
| 147 | 149 | 151 | 153 | 155 |
 June 21, 2039 |
 April 9, 2043 |
 January 26, 2047 |
 November 14, 2050 |
 September 2, 2054 |
| 157 | ||||
 June 21, 2058 | ||||
References
- ^ http://xjubier.free.fr/en/site_pages/solar_eclipses/TSE_2024_GoogleMapFull.html
- ^ Total Solar Eclipse in Mexico, 1991 (in Spanish). National Autonomous University of Mexico. Retrieved 2009-04-02.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ Ten Millennium Catalog of Long Solar Eclipses, −3999 to +6000 (4000 BCE to 6000 CE) Fred Espenak.
- ^ "NASA - Catalog of Solar Eclipses of Saros 139". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.