Solar eclipse of June 10, 2021
| Solar eclipse of June 10, 2021 | |
|---|---|
 Partial from Halifax, Canada | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Annular |
| Gamma | 0.9152 |
| Magnitude | 0.9435 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 231 s (3 min 51 s) |
| Coordinates | 80°48′N 66°48′W / 80.8°N 66.8°W |
| Max. width of band | 527 km (327 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 10:43:07 |
| References | |
| Saros | 147 (23 of 80) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9555 |
An annular solar eclipse will occur on June 10, 2021. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. This eclipse will be unusual as the path of the total eclipse will move to the north east, then north, north west, west, south west, south, and finally south east across the Arctic, while most eclipse paths move west to east. This reversal is only possible in polar regions.This eclipse is also notable for the fact that the path of annularity passes over the North Pole.
While the eclipse is visible primarily in the relatively unpopulated area near the Arctic Circle, in the northeastern United States and Canada, the sun will be partially eclipsed at sunrise.
Images
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses of 2018-2021
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
The partial solar eclipses on February 15, 2018 and August 11, 2018 occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2018 to 2021 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
117 Partial in Melbourne, Australia |
July 13, 2018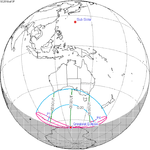 Partial |
−1.35423 | 122 Partial in Nakhodka, Russia |
January 6, 2019 Partial |
1.14174 | |
127 Totality in La Serena, Chile |
July 2, 2019 Total |
−0.64656 | 132 Annularity in Jaffna, Sri Lanka |
December 26, 2019 Annular |
0.41351 | |
137 Annularity in Beigang, Yunlin, Taiwan |
June 21, 2020 Annular |
0.12090 | 142 Totality in Gorbea, Chile |
December 14, 2020 Total |
−0.29394 | |
147 Partial in Halifax, Canada |
June 10, 2021 Annular |
0.91516 | 152 From HMS Protector off South Georgia |
December 4, 2021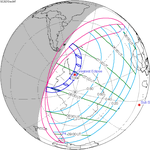 Total |
−0.95261 | |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| 20 eclipse events between June 10, 1964 and August 21, 2036 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| June 10–11 | March 28–29 | January 14–16 | November 3 | August 21–22 |
| 117 | 119 | 121 | 123 | 125 |
 June 10, 1964 |
 March 28, 1968 |
 January 16, 1972 |
 November 3, 1975 |
 August 22, 1979 |
| 127 | 129 | 131 | 133 | 135 |
 June 11, 1983 |
 March 29, 1987 |
 January 15, 1991 |
 November 3, 1994 |
 August 22, 1998 |
| 137 | 139 | 141 | 143 | 145 |
 June 10, 2002 |
 March 29, 2006 |
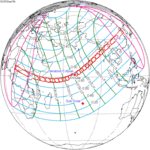 January 15, 2010 |
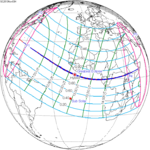 November 3, 2013 |
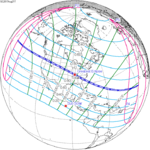 August 21, 2017 |
| 147 | 149 | 151 | 153 | 155 |
 June 10, 2021 |
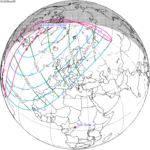 March 29, 2025 |
 January 14, 2029 |
 November 3, 2032 |
 August 21, 2036 |
Notes
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC





