Solar eclipse of May 29, 1919
| Solar eclipse of May 29, 1919 | |
|---|---|
 From the report of Sir Arthur Eddington on the expedition to the island of Principe (off the west coast of Africa). | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | −0.2955 |
| Magnitude | 1.0719 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 411 s (6 min 51 s) |
| Coordinates | 4°24′N 16°42′W / 4.4°N 16.7°W |
| Max. width of band | 244 km (152 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 13:08:55 |
| References | |
| Saros | 136 (32 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9326 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on May 29, 1919. With a maximum duration of totality of 6 minutes 51 seconds, it was one of the longest solar eclipses of the 20th century. It was visible throughout most of South America and Africa as a partial eclipse. Totality occurred through a narrow path across central Brazil after sunrise, across the Atlantic ocean and into south central Africa ending near sunset in eastern Africa.
Observations
This eclipse was photographed from the expedition of Sir Arthur Eddington to the island of Principe (off the west coast of Africa). Positions of star images within the field near the Sun were used to test Albert Einstein's prediction of the bending of light around the Sun from his general theory of relativity. The stars which Eddington's expedition observed were in the constellation Taurus.[1]
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 1916–1920
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[2]
The solar eclipses on February 3, 1916 (total), July 30, 1916 (annular), January 23, 1917 (partial), and July 19, 1917 (partial) occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1916 to 1920 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 111 | December 24, 1916 Partial |
−1.5321 | 116 | June 19, 1917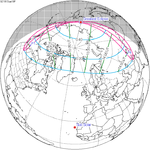 Partial |
1.2857 | |
| 121 | December 14, 1917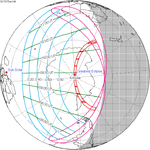 Annular |
−0.9157 | 126 | June 8, 1918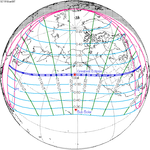 Total |
0.4658 | |
| 131 | December 3, 1918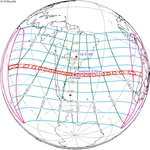 Annular |
−0.2387 | 136 Totality in Príncipe |
May 29, 1919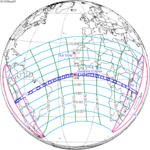 Total |
−0.2955 | |
| 141 | November 22, 1919 Annular |
0.4549 | 146 | May 18, 1920 Partial |
−1.0239 | |
| 151 | November 10, 1920 Partial |
1.1287 | ||||
Saros 136
This eclipse is a part of Saros series 136, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 71 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on June 14, 1360. It contains annular eclipses from September 8, 1504 through November 12, 1594; hybrid eclipses from November 22, 1612 through January 17, 1703; and total eclipses from January 27, 1721 through May 13, 2496. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on July 30, 2622. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of annularity was produced by member 9 at 32 seconds on September 8, 1504, and the longest duration of totality was produced by member 34 at 7 minutes, 7.74 seconds on June 20, 1955. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s descending node of orbit.[3]
| Series members 26–47 occur between 1801 and 2200: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 26 | 27 | 28 |
 March 24, 1811 |
 April 3, 1829 |
 April 15, 1847 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
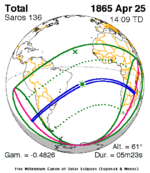 April 25, 1865 |
 May 6, 1883 |
 May 18, 1901 |
| 32 | 33 | 34 |
 May 29, 1919 |
 June 8, 1937 |
 June 20, 1955 |
| 35 | 36 | 37 |
 June 30, 1973 |
 July 11, 1991 |
 July 22, 2009 |
| 38 | 39 | 40 |
 August 2, 2027 |
 August 12, 2045 |
 August 24, 2063 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 |
 September 3, 2081 |
 September 14, 2099 |
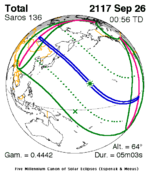 September 26, 2117 |
| 44 | 45 | 46 |
 October 7, 2135 |
 October 17, 2153 |
 October 29, 2171 |
| 47 | ||
 November 8, 2189 | ||
Notes
- ^ "A Determination of the Deflection of Light by the Sun's Gravitational Field, from Observations Made at the Total Eclipse of May 29, 1919" (PDF). Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. CCXX-A 579: 291–333. 1920. doi:10.1098/rsta.1920.0009.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ "NASA - Catalog of Solar Eclipses of Saros 136". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.
References
- NASA chart and statistics
- Fotos of Solar Corona May 29, 1919
- Wired.com: May 29, 1919: A Major Eclipse, Relatively Speaking
- Famous Eclipse of 1919




