Coluracetam: Difference between revisions
m Dating maintenance tags: {{Medcn}} {{Full}} {{When}} |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Drugbox |
{{Drugbox |
||
| IUPAC_name = N-(2,3- |
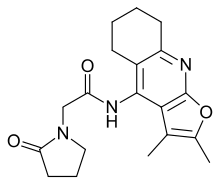
| IUPAC_name = ''N''-(2,3-Dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofuro[2,3-''b'']quinolin-4-yl)-2-(2-oxo-1-pyrrolidinyl)acetamide |
||
| image = Coluracetam.svg |
| image = Coluracetam.svg |
||
| image2 = Coluracetam3d.png |
| image2 = Coluracetam3d.png |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Coluracetam''' ([[International Nonproprietary Name|INN]]) (code name '''BCI-540'''; formerly '''MKC-231''') is a [[nootropic]] [[drug|agent]] of the [[racetam]] family.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Bessho | first1 = T | last2 = Takashina | first2 = K | last3 = Tabata | first3 = R | last4 = Ohshima | first4 = C | last5 = Chaki | first5 = H | last6 = Yamabe | first6 = H | last7 = Egawa | first7 = M | last8 = Tobe | first8 = A | last9 = Saito | first9 = K | title = Effect of the novel high affinity choline uptake enhancer 2-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)-N-(2,3-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofuro2,3-b quinolin-4-yl)acetoamide on deficits of water maze learning in rats | journal = Arzneimittel-Forschung | volume = 46 | issue = 4 | pages = 369–73 | year = 1996 | pmid = 8740080}}</ref> It was initially developed and tested by the [[Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation]] for [[Alzheimer's disease]]. After the drug failed to reach endpoints in its clinical trials it was in-licensed by [[BrainCells Inc]] for investigations into [[major depressive disorder]] (MDD), which was preceded by being awarded a "Qualifying Therapeutic Discovery Program Grant" by the state of California.<ref name="CAgrants">[http://www.irs.gov/businesses/small/article/0,,id=228970,00.html Qualifying Therapeutic Discovery Project Grants for the State of California], IRS.gov.</ref> Findings from [[Phases of clinical research#Phase II|phase IIa]] [[clinical trial]]s have suggested that it would be |
'''Coluracetam''' ([[International Nonproprietary Name|INN]]) (code name '''BCI-540'''; formerly '''MKC-231''') is a [[nootropic]] [[drug|agent]] of the [[racetam]] family.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Bessho | first1 = T | last2 = Takashina | first2 = K | last3 = Tabata | first3 = R | last4 = Ohshima | first4 = C | last5 = Chaki | first5 = H | last6 = Yamabe | first6 = H | last7 = Egawa | first7 = M | last8 = Tobe | first8 = A | last9 = Saito | first9 = K | title = Effect of the novel high affinity choline uptake enhancer 2-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)-N-(2,3-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofuro2,3-b quinolin-4-yl)acetoamide on deficits of water maze learning in rats | journal = Arzneimittel-Forschung | volume = 46 | issue = 4 | pages = 369–73 | year = 1996 | pmid = 8740080}}</ref> It was initially developed and tested by the [[Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation]] for [[Alzheimer's disease]]. After the drug failed to reach endpoints in its clinical trials it was in-licensed by [[BrainCells Inc]] for investigations into [[major depressive disorder]] (MDD), which was preceded by being awarded a "Qualifying Therapeutic Discovery Program Grant" by the state of California.<ref name="CAgrants">[http://www.irs.gov/businesses/small/article/0,,id=228970,00.html Qualifying Therapeutic Discovery Project Grants for the State of California], IRS.gov.</ref> Findings from [[Phases of clinical research#Phase II|phase IIa]] [[clinical trial]]s have suggested that it would be a potential medication for [[comorbidity|comorbid]] MDD with [[generalized anxiety disorder]] (GAD).<ref name="PR-06142010">[http://www.braincellsinc.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/06/BCI-PR-06142010.pdf BrainCells Inc. Announces Results From Exploratory Phase 2a Trial of BCI-540]</ref>{{dead link}} BrainCells Inc is currently{{when|date=January 2015}} out-licensing the drug for this purpose.<ref name="BCI-540">[Pipeline,BCI-540], BCI-540 (coluracetam).</ref>{{full|date=January 2015}} It may also have potential use in prevention and treatment of [[ischemia|ischemic]] [[retinopathy]] and [[retina]]l and [[optic nerve]] injury.{{medcn|date=January 2015}} |
||
Coluracetam has been shown to reverse the loss of [[choline acetyltransferase]] production in the [[medial septal nucleus]] of rats exposed to [[PCP_(drug)|phencyclidine]] (PCP), and is considered a potential therapeutic drug for [[schizophrenia]].<ref>{{cite pmid|17467960}}</ref> |
Coluracetam has been shown to reverse the loss of [[choline acetyltransferase]] production in the [[medial septal nucleus]] of rats exposed to [[PCP_(drug)|phencyclidine]] (PCP), and is considered a potential therapeutic drug for [[schizophrenia]].<ref>{{cite pmid|17467960}}</ref> |
||
==Mechanism of action== |
==Mechanism of action== |
||
Coluracetam enhances high-affinity [[choline]] [[reuptake|uptake]], which is the rate-limiting step of acetylcholine (ACh) [[biosynthesis|synthesis]]. Studies have shown coluracetam to improve [[learning impairment]] on a single oral dose given to rats which have been exposed to cholinergic [[neurotoxin]]s. Subsequent studies have shown that it may induce long-lasting [[nootropic|procognitive]] effects in [[cholinergic]] neurotoxin-treated |
Coluracetam enhances high-affinity [[choline]] [[reuptake|uptake]], which is the rate-limiting step of acetylcholine (ACh) [[biosynthesis|synthesis]]. Studies have shown coluracetam to improve [[learning impairment]] on a single oral dose given to rats which have been exposed to cholinergic [[neurotoxin]]s. Subsequent studies have shown that it may induce long-lasting [[nootropic|procognitive]] effects in [[cholinergic]] neurotoxin-treated rats by changing the [[choline transporter]] regulation system.<ref name="PMID18461272">{{Cite journal | pmid = 18461272 | title = MKC-231, a choline-uptake enhancer: long-lasting cognitive improvement after repeated administration in AF64A-treated rats}}</ref> |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 16:33, 23 January 2015
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H23N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 341.404 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Coluracetam (INN) (code name BCI-540; formerly MKC-231) is a nootropic agent of the racetam family.[1] It was initially developed and tested by the Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation for Alzheimer's disease. After the drug failed to reach endpoints in its clinical trials it was in-licensed by BrainCells Inc for investigations into major depressive disorder (MDD), which was preceded by being awarded a "Qualifying Therapeutic Discovery Program Grant" by the state of California.[2] Findings from phase IIa clinical trials have suggested that it would be a potential medication for comorbid MDD with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).[3][dead link] BrainCells Inc is currently[when?] out-licensing the drug for this purpose.[4][full citation needed] It may also have potential use in prevention and treatment of ischemic retinopathy and retinal and optic nerve injury.[medical citation needed]
Coluracetam has been shown to reverse the loss of choline acetyltransferase production in the medial septal nucleus of rats exposed to phencyclidine (PCP), and is considered a potential therapeutic drug for schizophrenia.[5]
Mechanism of action
Coluracetam enhances high-affinity choline uptake, which is the rate-limiting step of acetylcholine (ACh) synthesis. Studies have shown coluracetam to improve learning impairment on a single oral dose given to rats which have been exposed to cholinergic neurotoxins. Subsequent studies have shown that it may induce long-lasting procognitive effects in cholinergic neurotoxin-treated rats by changing the choline transporter regulation system.[6]
See also
References
- ^ Bessho, T; Takashina, K; Tabata, R; Ohshima, C; Chaki, H; Yamabe, H; Egawa, M; Tobe, A; Saito, K (1996). "Effect of the novel high affinity choline uptake enhancer 2-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)-N-(2,3-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofuro2,3-b quinolin-4-yl)acetoamide on deficits of water maze learning in rats". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 46 (4): 369–73. PMID 8740080.
- ^ Qualifying Therapeutic Discovery Project Grants for the State of California, IRS.gov.
- ^ BrainCells Inc. Announces Results From Exploratory Phase 2a Trial of BCI-540
- ^ [Pipeline,BCI-540], BCI-540 (coluracetam).
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 17467960, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=17467960instead. - ^ "MKC-231, a choline-uptake enhancer: long-lasting cognitive improvement after repeated administration in AF64A-treated rats". PMID 18461272.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
