List of Japanese inventions and discoveries: Difference between revisions
→See also: template added |
Yoganate79 (talk | contribs) →Technology: Added tag to uncited entry in list |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Citations missing|date=December 2009}} |
|||
{{Accuracy|date=December 2009}} |
|||
This is a '''list of [[Japan]]ese [[invention]]s'''. |
This is a '''list of [[Japan]]ese [[invention]]s'''. |
||
| Line 6: | Line 8: | ||
[[File:Karaoke subtitle.jpg|225px|right|thumb|Japanese karaoke display]] |
[[File:Karaoke subtitle.jpg|225px|right|thumb|Japanese karaoke display]] |
||
;[[Karaoke]] |
;[[Karaoke]] |
||
: Karaoke is a form of entertainment in which amateur singers sing along with recorded music or video using a microphone and public address system. The first karaoke machine was invented in 1971 by Japanese musician [[Daisuke Inoue]] in Kobe, Japan. After becoming popular in Japan, karaoke spread to East and Southeast Asia during the 1980s and subsequently to other parts of the world. |
: Karaoke is a form of entertainment in which amateur singers sing along with recorded music or video using a microphone and public address system. The first karaoke machine was invented in 1971 by Japanese musician [[Daisuke Inoue]] in Kobe, Japan. After becoming popular in Japan, karaoke spread to East and Southeast Asia during the 1980s and subsequently to other parts of the world. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
===Film and animation=== |
===Film and animation=== |
||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
;[[Bullet Time]] |
;[[Bullet Time]] |
||
: Long before the emergence of a technology permitting a live-action application, bullet-time as a concept was frequently developed in [[Traditional animation|cel animation]]. The earliest example is the shot at the end of the title sequence for the late-sixties Japanese [[anime]] series ''[[Speed Racer]]'': as Speed leaps from the [[Mach Five]], he freezes in mid-jump, and then the camera does an arc shot from front to sideways. The show was later an inspiration for ''[[The Matrix]]'' (1999). |
: Long before the emergence of a technology permitting a live-action application, bullet-time as a concept was frequently developed in [[Traditional animation|cel animation]]. The earliest example is the shot at the end of the title sequence for the late-sixties Japanese [[anime]] series ''[[Speed Racer]]'': as Speed leaps from the [[Mach Five]], he freezes in mid-jump, and then the camera does an arc shot from front to sideways. The show was later an inspiration for ''[[The Matrix]]'' (1999). {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
[[File:Toon-shader.jpg|thumb|312px|Object with a basic cel-shader (also known as a ''toon shader'') and border detection.]] |
[[File:Toon-shader.jpg|thumb|312px|Object with a basic cel-shader (also known as a ''toon shader'') and border detection.]] |
||
;[[Cel-shaded animation]] |
;[[Cel-shaded animation]] |
||
: True cel-shaded animation was introduced by [[Sega]]'s [[3D computer graphics|3D]] [[video game]], ''[[Jet Set Radio]]'' (2000), for the [[Dreamcast]]. |
: True cel-shaded animation was introduced by [[Sega]]'s [[3D computer graphics|3D]] [[video game]], ''[[Jet Set Radio]]'' (2000), for the [[Dreamcast]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Space habitat|Fictional space habitats]] |
;[[Space habitat|Fictional space habitats]] |
||
: The earliest fictional depiction of space habitats resembling cities were the [[Space colony (Gundam)|space colonies]] in [[Yoshiyuki Tomino]]'s 1979 [[anime]] series ''[[Mobile Suit Gundam]]'' (1979). |
: The earliest fictional depiction of space habitats resembling cities were the [[Space colony (Gundam)|space colonies]] in [[Yoshiyuki Tomino]]'s 1979 [[anime]] series ''[[Mobile Suit Gundam]]'' (1979). {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Man with No Name]] |
;[[Man with No Name]] |
||
| Line 35: | Line 37: | ||
;[[Psychological horror]] |
;[[Psychological horror]] |
||
: [[Hideo Nakata]]'s ''[[Ring (film)|Ring]]'' (1998), the first of the [[J-Horror]] [[Ring Trilogy]], is considered the earliest psychological [[horror film]]. |
: [[Hideo Nakata]]'s ''[[Ring (film)|Ring]]'' (1998), the first of the [[J-Horror]] [[Ring Trilogy]], is considered the earliest psychological [[horror film]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Real Robot]] |
;[[Real Robot]] |
||
: The Real Robot [[mecha]] genre began with [[Yoshiyuki Tomino]]'s [[anime]] series ''[[Mobile Suit Gundam]]'' in 1979. It was followed by many more [[Gundam]] series as well as other Real Robot anime series such as ''[[Macross]]''. |
: The Real Robot [[mecha]] genre began with [[Yoshiyuki Tomino]]'s [[anime]] series ''[[Mobile Suit Gundam]]'' in 1979. It was followed by many more [[Gundam]] series as well as other Real Robot anime series such as ''[[Macross]]''. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Samurai cinema]] |
;[[Samurai cinema]] |
||
: The earliest [[samurai]] films were [[Senkichi Taniguchi]]'s ''Jakoman and Tetsu'' (1949) and [[Akira Kurosawa]]'s ''[[Rashomon (film)|Rashomon]]'' (1950). |
: The earliest [[samurai]] films were [[Senkichi Taniguchi]]'s ''Jakoman and Tetsu'' (1949) and [[Akira Kurosawa]]'s ''[[Rashomon (film)|Rashomon]]'' (1950). {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Steadicam]] [[tracking shot]] |
;[[Steadicam]] [[tracking shot]] |
||
| Line 53: | Line 55: | ||
;[[Super Robot]] |
;[[Super Robot]] |
||
: The Super Robot [[mecha]] genre began with [[Go Nagai]]'s [[manga]] and [[anime]] series ''[[Mazinger Z]]'' in 1972. |
: The Super Robot [[mecha]] genre began with [[Go Nagai]]'s [[manga]] and [[anime]] series ''[[Mazinger Z]]'' in 1972. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Yakuza film]] |
;[[Yakuza film]] |
||
: The first [[Yakuza]] film was [[Akira Kurosawa]]'s ''[[Drunken Angel]]'' (1948), starring [[Toshiro Mifune]]. |
: The first [[Yakuza]] film was [[Akira Kurosawa]]'s ''[[Drunken Angel]]'' (1948), starring [[Toshiro Mifune]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
===Literature=== |
===Literature=== |
||
| Line 65: | Line 67: | ||
;[[Gesaku]] |
;[[Gesaku]] |
||
: A pre-modern genre of [[Japanese literature]]. |
: A pre-modern genre of [[Japanese literature]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
[[File:Genji emaki 01003 002.jpg|thumb|Written text from the earliest illustrated handscroll (12th century) of ''The Tale of Genji'']] |
[[File:Genji emaki 01003 002.jpg|thumb|Written text from the earliest illustrated handscroll (12th century) of ''The Tale of Genji'']] |
||
| Line 85: | Line 87: | ||
;[[Aikido]] |
;[[Aikido]] |
||
: A Japanese martial art developed by Morihei Ueshiba as a synthesis of his martial studies, philosophy, and religious beliefs. |
: A Japanese martial art developed by Morihei Ueshiba as a synthesis of his martial studies, philosophy, and religious beliefs. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
[[File:石井と鈴木.jpg|225px|right|thumb|[[All-Japan Judo Championships]], 2007 men's final.]] |
[[File:石井と鈴木.jpg|225px|right|thumb|[[All-Japan Judo Championships]], 2007 men's final.]] |
||
;[[Judo]] |
;[[Judo]] |
||
: Judo is a modern Japanese martial art and combat sport, that originated in Japan in the late nineteenth century. Its most prominent feature is its competitive element, where the object is to either throw one's opponent to the ground, immobilize or otherwise subdue one's opponent with a grappling manoeuvre, or force an opponent to submit by joint locking the elbow or by executing a choke. The early history of judo is inseparable from its founder, Japanese polymath and educator [[Jigoro Kano]]. |
: Judo is a modern Japanese martial art and combat sport, that originated in Japan in the late nineteenth century. Its most prominent feature is its competitive element, where the object is to either throw one's opponent to the ground, immobilize or otherwise subdue one's opponent with a grappling manoeuvre, or force an opponent to submit by joint locking the elbow or by executing a choke. The early history of judo is inseparable from its founder, Japanese polymath and educator [[Jigoro Kano]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Karate]] |
;[[Karate]] |
||
| Line 103: | Line 105: | ||
===Video games=== |
===Video games=== |
||
;[[Action role-playing game]] |
;[[Action role-playing game]] |
||
: Japanese developers, with their recent interest in the [[Role-playing game (video games)|role-playing game]] (RPG) genre, tweaked the formula a bit to create a new brand of action RPG. The company at the forefront of this was [[Nihon Falcom]]. ''[[Dragon Slayer]]'', released in [[1984 in video gaming|1984]], was a simple real-time treasure grab game. However, its sequel, ''[[Dragon Slayer II: Xanadu|Xanadu]]'', released in [[1985 in video gaming|1985]], was a full-fledged RPG, with character stats and a large quest. What set ''Xanadu'' apart from other RPGs was its action-based combat. The next two years would see the release of two games that would further define the action/RPG genre in Japan: Nintendo's ''[[The Legend of Zelda (video game)|The Legend of Zelda]]'' in [[1986 in video gaming|1986]] and Falcom's ''[[Ys (series)|Ys]]'' in [[1987 in video gaming|1987]]. While not strictly an action/RPG since it lacks RPG elements such as experience points, ''The Legend of Zelda'' influenced later games in the action-RPG genre.<ref name=zeldainfluence>{{cite web | title =GameSpy's 30 Most Influential People in Gaming | publisher =[[GameSpy]] | url =http://archive.gamespy.com/articles/march02/top30/61/index3.shtm | accessdate = 2007-04-01}}</ref> ''[[Zelda II: The Adventure of Link|Zelda II]]'' also implemented an RPG-esque system with action elements, making it closer to an action-RPG than other ''Zeldas''. ''Ys'', on the other hand, used true RPG principles. |
: Japanese developers, with their recent interest in the [[Role-playing game (video games)|role-playing game]] (RPG) genre, tweaked the formula a bit to create a new brand of action RPG. The company at the forefront of this was [[Nihon Falcom]]. ''[[Dragon Slayer]]'', released in [[1984 in video gaming|1984]], was a simple real-time treasure grab game. However, its sequel, ''[[Dragon Slayer II: Xanadu|Xanadu]]'', released in [[1985 in video gaming|1985]], was a full-fledged RPG, with character stats and a large quest. What set ''Xanadu'' apart from other RPGs was its action-based combat. The next two years would see the release of two games that would further define the action/RPG genre in Japan: Nintendo's ''[[The Legend of Zelda (video game)|The Legend of Zelda]]'' in [[1986 in video gaming|1986]] and Falcom's ''[[Ys (series)|Ys]]'' in [[1987 in video gaming|1987]]. While not strictly an action/RPG since it lacks RPG elements such as experience points, ''The Legend of Zelda'' influenced later games in the action-RPG genre.<ref name=zeldainfluence>{{cite web | title =GameSpy's 30 Most Influential People in Gaming | publisher =[[GameSpy]] | url =http://archive.gamespy.com/articles/march02/top30/61/index3.shtm | accessdate = 2007-04-01}}</ref> ''[[Zelda II: The Adventure of Link|Zelda II]]'' also implemented an RPG-esque system with action elements, making it closer to an action-RPG than other ''Zeldas''. ''Ys'', on the other hand, used true RPG principles. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Active Time Battle]] |
;[[Active Time Battle]] |
||
: [[Hiroyuki Itō]] introduced the "Active Time Battle" system in ''[[Final Fantasy IV]]'' (1991),<ref name="GT-FFRetrospectiveXIII">{{cite web| url = http://www.gametrailers.com/player/27455.html| title = Final Fantasy Retrospective Part XIII| publisher = [[GameTrailers]]| date = 2007-11-02| accessdate = 2009-03-30}}</ref> where the [[Time-keeping systems in games|time-keeping system]] does not stop.<ref name="gsff4"/> [[Square Co.]], Ltd. filed a United States [[patent application]] for the ATB system on March 16, 1992, under the title "Video game apparatus, method and device for controlling same" and was awarded the patent on February 21, 1995. On the battle screen, each character has an ATB meter that gradually fills, and the player is allowed to issue a command to that character once the meter is full.<ref>{{US patent reference| number = 5390937| y = 1995| m = 02| d = 21| inventor = Hironobu Sakaguchi and Hiroyuki Itou| title = Video game apparatus, method and device for controlling same}}</ref> The fact that enemies can attack or be attacked at any time is credited with injecting urgency and excitement into the combat system.<ref name="gsff4">{{cite web | url = http://www.gamespot.com/features/vgs/universal/finalfantasy_hs/sec1_4_2.html | title = The History of Final Fantasy - Final Fantasy IV | author = Andrew Vestal | publisher = GameSpot | date = 1998-11-02 | accessdate = 2008-12-31 }}</ref> The ATB system was fully developed in ''[[Final Fantasy V]]'' (1992) and continued to be used in later ''[[Final Fantasy]]'' games until ''[[Final Fantasy X-2]]'' (2003) as well as other Square games such as ''[[Chrono Trigger]]'' (1995). |
: [[Hiroyuki Itō]] introduced the "Active Time Battle" system in ''[[Final Fantasy IV]]'' (1991),<ref name="GT-FFRetrospectiveXIII">{{cite web| url = http://www.gametrailers.com/player/27455.html| title = Final Fantasy Retrospective Part XIII| publisher = [[GameTrailers]]| date = 2007-11-02| accessdate = 2009-03-30}}</ref> where the [[Time-keeping systems in games|time-keeping system]] does not stop.<ref name="gsff4"/> [[Square Co.]], Ltd. filed a United States [[patent application]] for the ATB system on March 16, 1992, under the title "Video game apparatus, method and device for controlling same" and was awarded the patent on February 21, 1995. On the battle screen, each character has an ATB meter that gradually fills, and the player is allowed to issue a command to that character once the meter is full.<ref>{{US patent reference| number = 5390937| y = 1995| m = 02| d = 21| inventor = Hironobu Sakaguchi and Hiroyuki Itou| title = Video game apparatus, method and device for controlling same}}</ref> The fact that enemies can attack or be attacked at any time is credited with injecting urgency and excitement into the combat system.<ref name="gsff4">{{cite web | url = http://www.gamespot.com/features/vgs/universal/finalfantasy_hs/sec1_4_2.html | title = The History of Final Fantasy - Final Fantasy IV | author = Andrew Vestal | publisher = GameSpot | date = 1998-11-02 | accessdate = 2008-12-31 }}</ref> The ATB system was fully developed in ''[[Final Fantasy V]]'' (1992) and continued to be used in later ''[[Final Fantasy]]'' games until ''[[Final Fantasy X-2]]'' (2003) as well as other Square games such as ''[[Chrono Trigger]]'' (1995). {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Beat 'em up]] |
;[[Beat 'em up]] |
||
| Line 112: | Line 114: | ||
;[[Dating sim]] |
;[[Dating sim]] |
||
: A [[Game (simulation)|simulation game]] subgenre originating in Japan. |
: A [[Game (simulation)|simulation game]] subgenre originating in Japan. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Fighting game]] |
;[[Fighting game]] |
||
| Line 125: | Line 127: | ||
: ''[[Space Panic]]'', a 1980 arcade release, is sometimes credited as the first platform game.<ref> |
: ''[[Space Panic]]'', a 1980 arcade release, is sometimes credited as the first platform game.<ref> |
||
{{cite book|title=[[Chris Crawford on Game Design]]|isbn=0-88134-117-7|last=Crawford|first=Chris |
{{cite book|title=[[Chris Crawford on Game Design]]|isbn=0-88134-117-7|last=Crawford|first=Chris |
||
|authorlink=Chris Crawford|year=2003|publisher=New Riders}}</ref> It was clearly an influence on the genre, with gameplay centered on climbing ladders between different floors, a common element in many early platform games. ''[[Donkey Kong (video game)|Donkey Kong]]'', an [[arcade game]] created by [[Nintendo]], released in July 1981, was the first game that allowed players to jump over obstacles and across gaps, making it the first true platformer.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.arcade-history.com/index.php?page=detail&id=666 | title=Donkey Kong| publisher=Arcade History|date=2006-11-21|accessdate=2006-11-21}}</ref> This game also introduced [[Mario]], an icon of the genre. ''[[Mario Bros]]'', a platform game that offered two-player simultaneous cooperative play, laid the groundwork for other popular two-player cooperative platformers, like ''[[Fairyland Story]]'' and ''[[Bubble Bobble]]'', which in turn influenced [[Platform game#Comical Action Game|many of the single-screen platformers]] that would follow. |
|authorlink=Chris Crawford|year=2003|publisher=New Riders}}</ref> It was clearly an influence on the genre, with gameplay centered on climbing ladders between different floors, a common element in many early platform games. ''[[Donkey Kong (video game)|Donkey Kong]]'', an [[arcade game]] created by [[Nintendo]], released in July 1981, was the first game that allowed players to jump over obstacles and across gaps, making it the first true platformer.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.arcade-history.com/index.php?page=detail&id=666 | title=Donkey Kong| publisher=Arcade History|date=2006-11-21|accessdate=2006-11-21}}</ref> This game also introduced [[Mario]], an icon of the genre. ''[[Mario Bros]]'', a platform game that offered two-player simultaneous cooperative play, laid the groundwork for other popular two-player cooperative platformers, like ''[[Fairyland Story]]'' and ''[[Bubble Bobble]]'', which in turn influenced [[Platform game#Comical Action Game|many of the single-screen platformers]] that would follow. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Postmodernism|Postmodern]] [[videogame]] |
;[[Postmodernism|Postmodern]] [[videogame]] |
||
| Line 134: | Line 136: | ||
;[[Racing game]] |
;[[Racing game]] |
||
: The first true racing game was the [[Namco]] game ''[[Pole Position]]'' in 1982. The player had AI cars to race against, and time limit to keep pushing the players to go faster. ''Pole Position'' is also the first game to be based on a real racing circuit. Pole Position introduced color graphics at a much higher resolution than earlier titles. |
: The first true racing game was the [[Namco]] game ''[[Pole Position]]'' in 1982. The player had AI cars to race against, and time limit to keep pushing the players to go faster. ''Pole Position'' is also the first game to be based on a real racing circuit. Pole Position introduced color graphics at a much higher resolution than earlier titles. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Rhythm game]] |
;[[Rhythm game]] |
||
: ''[[Dance Aerobics]]'' was released in 1987, and allowed players to create music by stepping on Nintendo's [[Power Pad]] peripheral. It has been called the first rhythm-action game in retrospect,<ref name="block">Block, Gerry, [http://uk.gear.ign.com/articles/886/886870p1.html NES Power Pad Rocking Rhythm-Action Play], ''IGN'', July 7, 2008, Accessed Apr 10, 2009</ref> although the 1996 title ''[[PaRappa the Rapper]]'' has also been deemed the first rhythm game, whose basic template forms the core of subsequent games in the genre. In 1997, [[Konami]]'s ''[[Beatmania]]'' sparked an emergent market for rhythm games in Japan. The company's music division, [[Bemani]], released a number of music games over the next several years. The most successful of these was dance mat game ''[[Dance Dance Revolution (1998 video game)|Dance Dance Revolution]]'', which was also the only one to achieve large-scale success out with Japan. |
: ''[[Dance Aerobics]]'' was released in 1987, and allowed players to create music by stepping on Nintendo's [[Power Pad]] peripheral. It has been called the first rhythm-action game in retrospect,<ref name="block">Block, Gerry, [http://uk.gear.ign.com/articles/886/886870p1.html NES Power Pad Rocking Rhythm-Action Play], ''IGN'', July 7, 2008, Accessed Apr 10, 2009</ref> although the 1996 title ''[[PaRappa the Rapper]]'' has also been deemed the first rhythm game, whose basic template forms the core of subsequent games in the genre. In 1997, [[Konami]]'s ''[[Beatmania]]'' sparked an emergent market for rhythm games in Japan. The company's music division, [[Bemani]], released a number of music games over the next several years. The most successful of these was dance mat game ''[[Dance Dance Revolution (1998 video game)|Dance Dance Revolution]]'', which was also the only one to achieve large-scale success out with Japan. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Platform game#Scrolling era|Scrolling platformer]] |
;[[Platform game#Scrolling era|Scrolling platformer]] |
||
| Line 146: | Line 148: | ||
;[[Stealth game]] |
;[[Stealth game]] |
||
: The first stealth-based [[videogame]] was [[Sega]]'s ''[[005]]'' (1981).<ref name=Popularplay>{{cite web|title=005 from Sega|publisher=Popularplay|url=http://www.popularplay.com/a/61/005-from-Sega-.php|accessdate=2009-08-20}}</ref><ref>{{KLOV game|id=6759}}</ref><ref>[http://www.arcade-history.com/?n=005&page=detail&id=3 005], Arcade History</ref> The first commercially successful stealth game was [[Hideo Kojima]]'s ''[[Metal Gear]]'' (1987), the first in the [[Metal Gear (series)|''Metal Gear'' series]]. It was followed by ''[[Metal Gear 2: Solid Snake]]'' (1990) which significantly expanded the genre, and then ''[[Metal Gear Solid]]'' (1998) which was a mainstream success and established stealth games as a genre. |
: The first stealth-based [[videogame]] was [[Sega]]'s ''[[005]]'' (1981).<ref name=Popularplay>{{cite web|title=005 from Sega|publisher=Popularplay|url=http://www.popularplay.com/a/61/005-from-Sega-.php|accessdate=2009-08-20}}</ref><ref>{{KLOV game|id=6759}}</ref><ref>[http://www.arcade-history.com/?n=005&page=detail&id=3 005], Arcade History</ref> The first commercially successful stealth game was [[Hideo Kojima]]'s ''[[Metal Gear]]'' (1987), the first in the [[Metal Gear (series)|''Metal Gear'' series]]. It was followed by ''[[Metal Gear 2: Solid Snake]]'' (1990) which significantly expanded the genre, and then ''[[Metal Gear Solid]]'' (1998) which was a mainstream success and established stealth games as a genre. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Steampunk#Fantasy-world|Steampunk fantasy]] |
;[[Steampunk#Fantasy-world|Steampunk fantasy]] |
||
| Line 155: | Line 157: | ||
;[[Tactical role-playing game]] |
;[[Tactical role-playing game]] |
||
: It is generally accepted that [[Nintendo]] released and published the first tactical RPG, ''[[Fire Emblem: Ankoku Ryū to Hikari no Tsurugi]]'' for the [[Nintendo Entertainment System]] (NES), created and developed by [[Intelligent Systems]]. Released in Japan in 1990, ''[[Fire Emblem]]'' was an archetype for the whole genre, establishing gameplay elements that are still used in tactical CRPGs today. Combining the basic console RPG concepts from games like ''[[Dragon Quest]]'' and simple turn-based strategy elements, Nintendo created a hit, which spawned many sequels and imitators. |
: It is generally accepted that [[Nintendo]] released and published the first tactical RPG, ''[[Fire Emblem: Ankoku Ryū to Hikari no Tsurugi]]'' for the [[Nintendo Entertainment System]] (NES), created and developed by [[Intelligent Systems]]. Released in Japan in 1990, ''[[Fire Emblem]]'' was an archetype for the whole genre, establishing gameplay elements that are still used in tactical CRPGs today. Combining the basic console RPG concepts from games like ''[[Dragon Quest]]'' and simple turn-based strategy elements, Nintendo created a hit, which spawned many sequels and imitators. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Visual novel]] |
;[[Visual novel]] |
||
: An [[interactive fiction]] genre featuring mostly static graphics, usually with [[anime]]-style art, originating in Japan. |
: An [[interactive fiction]] genre featuring mostly static graphics, usually with [[anime]]-style art, originating in Japan. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
==Philosophy== |
==Philosophy== |
||
| Line 164: | Line 166: | ||
;[[5 Whys]] |
;[[5 Whys]] |
||
: [[Sakichi Toyoda]] developed the concept of [[5 Whys]]: When a problem occurs, ask 'why' five times to try to find the source of the problem, then put into place something to prevent the problem from recurring. This concept is used today as part of applying [[Lean manufacturing|lean methodologies]] to solve problems, improve quality, and reduce costs. |
: [[Sakichi Toyoda]] developed the concept of [[5 Whys]]: When a problem occurs, ask 'why' five times to try to find the source of the problem, then put into place something to prevent the problem from recurring. This concept is used today as part of applying [[Lean manufacturing|lean methodologies]] to solve problems, improve quality, and reduce costs. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Lean manufacturing]] |
;[[Lean manufacturing]] |
||
: A generic process management philosophy derived mostly from the [[Toyota Production System]] (TPS) (hence the term Toyotism is also prevalent) and identified as "Lean" only in the 1990s.<ref name="womack">{{cite book |last=Womack |first=James P. |coauthors=Daniel T. Jones, and Daniel Roos |title=The Machine That Changed the World |year=1990}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Holweg |first=Matthias |title=The genealogy of lean production |journal=Journal of Operations Management |volume=25 |issue=2 |pages=420–437 |year=2007}}</ref> It is renowned for its focus on reduction of the original Toyota ''[[Muda (Japanese term)|seven wastes]]'' in order to improve overall customer value, but there are varying perspectives on how this is best achieved. |
: A generic process management philosophy derived mostly from the [[Toyota Production System]] (TPS) (hence the term Toyotism is also prevalent) and identified as "Lean" only in the 1990s.<ref name="womack">{{cite book |last=Womack |first=James P. |coauthors=Daniel T. Jones, and Daniel Roos |title=The Machine That Changed the World |year=1990}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Holweg |first=Matthias |title=The genealogy of lean production |journal=Journal of Operations Management |volume=25 |issue=2 |pages=420–437 |year=2007}}</ref> It is renowned for its focus on reduction of the original Toyota ''[[Muda (Japanese term)|seven wastes]]'' in order to improve overall customer value, but there are varying perspectives on how this is best achieved. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
==Science== |
==Science== |
||
| Line 173: | Line 175: | ||
;[[Rashomon effect]] |
;[[Rashomon effect]] |
||
: The [[Psychology|psychological]] effect of the [[subjectivity]] of [[perception]] on recollection, by which observers of an event are able to produce substantially different but equally plausible accounts of it. The concept was inspired by [[Akira Kurosawa]]'s 1950 film ''[[Rashomon (film)|Rashomon]]'', in which a crime witnessed by four individuals is described in four mutually contradictory ways. The film was based on two short stories by [[Ryūnosuke Akutagawa]], "Rashōmon" (for the setting) and "In a Grove" (for the story line). |
: The [[Psychology|psychological]] effect of the [[subjectivity]] of [[perception]] on recollection, by which observers of an event are able to produce substantially different but equally plausible accounts of it. The concept was inspired by [[Akira Kurosawa]]'s 1950 film ''[[Rashomon (film)|Rashomon]]'', in which a crime witnessed by four individuals is described in four mutually contradictory ways. The film was based on two short stories by [[Ryūnosuke Akutagawa]], "Rashōmon" (for the setting) and "In a Grove" (for the story line). {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
===Biomedical science=== |
===Biomedical science=== |
||
;[[Aberic acid]] |
;[[Aberic acid]] |
||
: Discovered by [[Umetaro Suzuki]] in 1910. |
: Discovered by [[Umetaro Suzuki]] in 1910. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Aspergillus|Aspergillus genomes]] |
;[[Aspergillus|Aspergillus genomes]] |
||
| Line 221: | Line 223: | ||
;[[B vitamins|B vitamin]] |
;[[B vitamins|B vitamin]] |
||
: The first B vitamin to be discovered was [[thiamine]] (vitamin B<sub>1</sub>), by [[Umetaro Suzuki]] in 1910. |
: The first B vitamin to be discovered was [[thiamine]] (vitamin B<sub>1</sub>), by [[Umetaro Suzuki]] in 1910. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Epinephrine|Epinephrine (Adrenaline)]] |
;[[Epinephrine|Epinephrine (Adrenaline)]] |
||
| Line 228: | Line 230: | ||
;[[Methamphetamine]] |
;[[Methamphetamine]] |
||
: Methamphetamine was first synthesized from [[ephedrine]] in Japan in [[1894]] by chemist [[Nagayoshi Nagai]].<ref>{{cite journal|author =Nagai N.|title = Kanyaku maou seibun kenkyuu seiseki (zoku)|journal= Yakugaku |
: Methamphetamine was first synthesized from [[ephedrine]] in Japan in [[1894]] by chemist [[Nagayoshi Nagai]].<ref>{{cite journal|author =Nagai N.|title = Kanyaku maou seibun kenkyuu seiseki (zoku)|journal= Yakugaku |
||
Zashi |year=1893|volume= 13|pages= 901}}</ref> In [[1919]], crystallized methamphetamine was synthesized by [[Akira Ogata]] via [[redox|reduction]] of [[ephedrine]] using red [[phosphorus]] and [[iodine]]. |
Zashi |year=1893|volume= 13|pages= 901}}</ref> In [[1919]], crystallized methamphetamine was synthesized by [[Akira Ogata]] via [[redox|reduction]] of [[ephedrine]] using red [[phosphorus]] and [[iodine]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Nuclear medicine]] |
;[[Nuclear medicine]] |
||
: [[Taro Takemi]] was the first to study the application of [[nuclear physics]] to [[medicine]]. |
: [[Taro Takemi]] was the first to study the application of [[nuclear physics]] to [[medicine]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Electrocardiography|Portable electrocardiograph]] |
;[[Electrocardiography|Portable electrocardiograph]] |
||
: [[Taro Takemi]] built the first portable electrocardiograph in 1937. |
: [[Taro Takemi]] built the first portable electrocardiograph in 1937. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Takadiastase]] |
;[[Takadiastase]] |
||
: A form of [[diastase]] which results from the growth, development and nutrition of a distinct microscopic fungus known as ''[[Aspergillus oryzae]]''. [[Jokichi Takamine]] developed the method first used for its extraction in the late 19th century. |
: A form of [[diastase]] which results from the growth, development and nutrition of a distinct microscopic fungus known as ''[[Aspergillus oryzae]]''. [[Jokichi Takamine]] developed the method first used for its extraction in the late 19th century. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Thiamine|Thiamine (Vitamin B<sub>1</sub>)]] |
;[[Thiamine|Thiamine (Vitamin B<sub>1</sub>)]] |
||
| Line 243: | Line 245: | ||
;[[Vectorcardiography]] |
;[[Vectorcardiography]] |
||
: [[Taro Takemi]] is known for his invention of the vectorcardiograph in 1939. |
: [[Taro Takemi]] is known for his invention of the vectorcardiograph in 1939. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Vitamin]] |
;[[Vitamin]] |
||
: The first vitamin to be discovered was the [[B vitamins|B vitamin]], [[thiamine]] (vitamin B<sub>1</sub>), by [[Umetaro Suzuki]] in 1910. |
: The first vitamin to be discovered was the [[B vitamins|B vitamin]], [[thiamine]] (vitamin B<sub>1</sub>), by [[Umetaro Suzuki]] in 1910. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
===Food science=== |
===Food science=== |
||
;[[Cup noodles]] |
;[[Cup noodles]] |
||
: Invented in 1970 by [[Nissin Foods]]. |
: Invented in 1970 by [[Nissin Foods]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
[[File:Instantnoodles.jpg|225px|right|thumb|Instant noodles]] |
[[File:Instantnoodles.jpg|225px|right|thumb|Instant noodles]] |
||
;[[Instant noodles]] |
;[[Instant noodles]] |
||
: Instant noodles are dried or precooked noodles fused with oil, and often sold with a packet of flavoring. Dried noodles are usually eaten after being cooked or soaked in boiling water for 3 to 5 minutes, while precooked noodles can be reheated, or eaten straight from the packet. [[Momofuku Ando]] was the Taiwanese Japanese founder and chairman of Nissin Food Products Co., Ltd., and the inventor of world's first instant noodles in 1971. |
: Instant noodles are dried or precooked noodles fused with oil, and often sold with a packet of flavoring. Dried noodles are usually eaten after being cooked or soaked in boiling water for 3 to 5 minutes, while precooked noodles can be reheated, or eaten straight from the packet. [[Momofuku Ando]] was the Taiwanese Japanese founder and chairman of Nissin Food Products Co., Ltd., and the inventor of world's first instant noodles in 1971. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Monosodium glutamate]] |
;[[Monosodium glutamate]] |
||
| Line 260: | Line 262: | ||
;[[Umami]] |
;[[Umami]] |
||
: Umami as a separate [[taste]] was first identified in 1908 by [[Kikunae Ikeda]] of the Tokyo Imperial University while researching the strong flavor in seaweed broth.<ref name=ikeda02>{{cite journal |author=Ikeda K |title=New seasonings |journal=[[Chem. Senses]] |volume=27 |issue=9 |pages=847–9 |year=2002 |month=November |pmid=12438213 |doi= 10.1093/chemse/27.9.847|url=http://chemse.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12438213}} (partial translation of {{cite journal | last=Ikeda | first=Kikunae | title=New Seasonings[japan.] | journal=Journal of the Chemical Society of Tokyo | year= 1909 | volume=30 | pages= 820–836}})</ref> He isolated [[monosodium glutamate]] as the chemical responsible and, with the help of the [[Ajinomoto]] company, began commercial distribution of MSG products. |
: Umami as a separate [[taste]] was first identified in 1908 by [[Kikunae Ikeda]] of the Tokyo Imperial University while researching the strong flavor in seaweed broth.<ref name=ikeda02>{{cite journal |author=Ikeda K |title=New seasonings |journal=[[Chem. Senses]] |volume=27 |issue=9 |pages=847–9 |year=2002 |month=November |pmid=12438213 |doi= 10.1093/chemse/27.9.847|url=http://chemse.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12438213}} (partial translation of {{cite journal | last=Ikeda | first=Kikunae | title=New Seasonings[japan.] | journal=Journal of the Chemical Society of Tokyo | year= 1909 | volume=30 | pages= 820–836}})</ref> He isolated [[monosodium glutamate]] as the chemical responsible and, with the help of the [[Ajinomoto]] company, began commercial distribution of MSG products. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
===Mathematics=== |
===Mathematics=== |
||
| Line 266: | Line 268: | ||
;[[Aitken's delta-squared process]] |
;[[Aitken's delta-squared process]] |
||
: It was first known to [[Seki Kōwa]] at the end of the 17th century and was found for the rectification of the circle, i.e. the calculation of [[Pi|π]]. It is most useful for accelerating the convergence of a sequence that is converging linearly. He used it to obtain a value for π that was correct to the 10th decimal place. |
: It was first known to [[Seki Kōwa]] at the end of the 17th century and was found for the rectification of the circle, i.e. the calculation of [[Pi|π]]. It is most useful for accelerating the convergence of a sequence that is converging linearly. He used it to obtain a value for π that was correct to the 10th decimal place. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
[[File:Seki Kowa Katsuyo Sampo Bernoulli numbers.png|thumb|right|180px|A page from Seki Kōwa's ''Katsuyo Sampo'' (1712), tabulating binomial coefficients and Bernoulli numbers]] |
[[File:Seki Kowa Katsuyo Sampo Bernoulli numbers.png|thumb|right|180px|A page from Seki Kōwa's ''Katsuyo Sampo'' (1712), tabulating binomial coefficients and Bernoulli numbers]] |
||
| Line 280: | Line 282: | ||
;[[Ford circle]] |
;[[Ford circle]] |
||
: A typical problem, which is presented on an 1824 tablet in the [[Gunma Prefecture]], covers the relationship of three touching circles with a common [[tangent]]. It describes the [[Ford circle]] over a century before [[L. R. Ford]] did in 1938. |
: A typical problem, which is presented on an 1824 tablet in the [[Gunma Prefecture]], covers the relationship of three touching circles with a common [[tangent]]. It describes the [[Ford circle]] over a century before [[L. R. Ford]] did in 1938. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Laplace expansion]] |
;[[Laplace expansion]] |
||
: After the first work by [[Seki Kōwa]] in 1683, Laplace's formula was given by two independent groups of scholars: Uima Tanaka and Tomonori Iseki (''Sampo-Hakki'', published in 1690), and Seki Kōwa, Kaaki Takebe and Katahiro Takebe (''Taisei-Sankei'', written at least before 1710). |
: After the first work by [[Seki Kōwa]] in 1683, Laplace's formula was given by two independent groups of scholars: Uima Tanaka and Tomonori Iseki (''Sampo-Hakki'', published in 1690), and Seki Kōwa, Kaaki Takebe and Katahiro Takebe (''Taisei-Sankei'', written at least before 1710). {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Newton's method|Newton-Raphson method]] |
;[[Newton's method|Newton-Raphson method]] |
||
: [[Horner scheme|Horner's method]], though earlier completed by [[Chinese mathematics|Chinese mathematicians]], was not transmitted to Japan in its final form. So [[Seki Kōwa]] had to work it out by himself independently. In 1683, he suggested an improvement to Horner's method: to omit higher order terms after some iterations. This happens to be the same as the [[Newton's method|Newton-Raphson method]], predating [[Joseph Raphson]]'s work in 1690. |
: [[Horner scheme|Horner's method]], though earlier completed by [[Chinese mathematics|Chinese mathematicians]], was not transmitted to Japan in its final form. So [[Seki Kōwa]] had to work it out by himself independently. In 1683, he suggested an improvement to Horner's method: to omit higher order terms after some iterations. This happens to be the same as the [[Newton's method|Newton-Raphson method]], predating [[Joseph Raphson]]'s work in 1690. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Resultant]] |
;[[Resultant]] |
||
| Line 296: | Line 298: | ||
===Physics=== |
===Physics=== |
||
;[[Meson]] |
;[[Meson]] |
||
: In 1949, [[Hideki Yukawa]] was awarded the [[Nobel Prize in Physics]] for predicting the existence of the meson. He called the particle the meson (from ''mesos'', Greek for ''intermediate'') because its mass was between that of the [[electron]] and [[proton]]. |
: In 1949, [[Hideki Yukawa]] was awarded the [[Nobel Prize in Physics]] for predicting the existence of the meson. He called the particle the meson (from ''mesos'', Greek for ''intermediate'') because its mass was between that of the [[electron]] and [[proton]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Pion]] |
;[[Pion]] |
||
: In 1949, [[Hideki Yukawa]] also received the [[Nobel Prize in Physics]] for his prediction of the [[pion]] in 1947. |
: In 1949, [[Hideki Yukawa]] also received the [[Nobel Prize in Physics]] for his prediction of the [[pion]] in 1947. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Strong force]] |
;[[Strong force]] |
||
:In 1935, [[Hideki Yukawa]] proposed the first significant theory of the strong force to explain how the nucleus holds together. |
:In 1935, [[Hideki Yukawa]] proposed the first significant theory of the strong force to explain how the nucleus holds together. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Yukawa interaction]] |
;[[Yukawa interaction]] |
||
: Developed by [[Hideki Yukawa]], it can be used to describe the [[strong nuclear force]] between [[nucleon]]s (which are [[fermion]]s), mediated by [[pion]]s (which are pseudoscalar [[meson]]s). The Yukawa interaction is also used in the [[Standard Model]] to describe the coupling between the [[Higgs field]] and massless [[quark]] and [[electron]] fields. |
: Developed by [[Hideki Yukawa]], it can be used to describe the [[strong nuclear force]] between [[nucleon]]s (which are [[fermion]]s), mediated by [[pion]]s (which are pseudoscalar [[meson]]s). The Yukawa interaction is also used in the [[Standard Model]] to describe the coupling between the [[Higgs field]] and massless [[quark]] and [[electron]] fields. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Yukawa potential]] |
;[[Yukawa potential]] |
||
: [[Hideki Yukawa]] showed in the 1930s that such a potential arises from the exchange of a massive [[scalar field (quantum field theory)|scalar field]] such as the field of the [[pion]] whose mass is <math>m</math>. |
: [[Hideki Yukawa]] showed in the 1930s that such a potential arises from the exchange of a massive [[scalar field (quantum field theory)|scalar field]] such as the field of the [[pion]] whose mass is <math>m</math>. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
==Technology== |
==Technology== |
||
| Line 317: | Line 319: | ||
;[[Autonomation]] ([[autonomous automation]]) |
;[[Autonomation]] ([[autonomous automation]]) |
||
: [[Sakichi Toyoda]]'s most famous invention was the automatic [[power loom]] in which he implemented the principle of ''Jidoka'' (autonomation or autonomous automation). The principle of ''Jidoka'', which means that the machine stops itself when a problem occurs, became later a part of the [[Toyota Production System]]. |
: [[Sakichi Toyoda]]'s most famous invention was the automatic [[power loom]] in which he implemented the principle of ''Jidoka'' (autonomation or autonomous automation). The principle of ''Jidoka'', which means that the machine stops itself when a problem occurs, became later a part of the [[Toyota Production System]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Chi Machine]] |
;[[Chi Machine]] |
||
: A device created by Japanese scientist Dr. [[Shizuo Inoue]]. It holds US FDA approval as a Class 1 Medical Device Regulation #890.5660.<ref>http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfRL/Listing.cfm?ID=71537</ref> It apparently [[oxygenate]]s the body via "passive aerobic exercise", which the manufacturer claims stimulates the [[lymphatic system]] and supposedly enables detoxification. |
: A device created by Japanese scientist Dr. [[Shizuo Inoue]]. It holds US FDA approval as a Class 1 Medical Device Regulation #890.5660.<ref>http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfRL/Listing.cfm?ID=71537</ref> It apparently [[oxygenate]]s the body via "passive aerobic exercise", which the manufacturer claims stimulates the [[lymphatic system]] and supposedly enables detoxification. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Cold fusion|Cold fusion methods]] |
;[[Cold fusion|Cold fusion methods]] |
||
| Line 326: | Line 328: | ||
;[[Cultured pearl]] |
;[[Cultured pearl]] |
||
: Primarily the result of discoveries made in the late 19th and early 20th centuries by the Japanese researchers Tokishi Nishikawa and Tatsuhei Mise. What they discovered was a specific technique for inducing the creation of a round [[pearl]] within the gonad of an oyster. This technique was patented by [[Kokichi Mikimoto]] shortly thereafter, and the first harvest of rounds was produced in 1916. This discovery revolutionized the pearl industry, because it allowed pearl farmers to reliably cultivate large numbers of high-quality pearls. |
: Primarily the result of discoveries made in the late 19th and early 20th centuries by the Japanese researchers Tokishi Nishikawa and Tatsuhei Mise. What they discovered was a specific technique for inducing the creation of a round [[pearl]] within the gonad of an oyster. This technique was patented by [[Kokichi Mikimoto]] shortly thereafter, and the first harvest of rounds was produced in 1916. This discovery revolutionized the pearl industry, because it allowed pearl farmers to reliably cultivate large numbers of high-quality pearls. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Japanese typewriter]] |
;[[Japanese typewriter]] |
||
| Line 332: | Line 334: | ||
;[[TohoScope]] |
;[[TohoScope]] |
||
: Toho Scope is an [[anamorphic]] [[lens (optics)|lens]] system developed in the late 1950s by [[Toho|Toho Studios]]. |
: Toho Scope is an [[anamorphic]] [[lens (optics)|lens]] system developed in the late 1950s by [[Toho|Toho Studios]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
===Audio technology=== |
===Audio technology=== |
||
;[[Analog modeling synthesizer]] |
;[[Analog modeling synthesizer]] |
||
: A [[synthesizer]] that emulates the sounds of traditional [[analog synthesizer]]s using [[digital signal processing]] components. The earliest was [[Korg]]'s [[Korg Prophecy|Prophecy]] in the mid-1990s. |
: A [[synthesizer]] that emulates the sounds of traditional [[analog synthesizer]]s using [[digital signal processing]] components. The earliest was [[Korg]]'s [[Korg Prophecy|Prophecy]] in the mid-1990s. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Compact Disc player]] |
;[[Compact Disc player]] |
||
| Line 348: | Line 350: | ||
;[[Digital audio]] |
;[[Digital audio]] |
||
: Digital recording of classical and jazz music began in the early 1970s, pioneered by Japanese companies such as [[Denon]], and was soon adopted by British companies such as the [[BBC]] and record label [[Decca Records|Decca]]. |
: Digital recording of classical and jazz music began in the early 1970s, pioneered by Japanese companies such as [[Denon]], and was soon adopted by British companies such as the [[BBC]] and record label [[Decca Records|Decca]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Digital synthesizer]] |
;[[Digital synthesizer]] |
||
| Line 354: | Line 356: | ||
;[[Digital waveguide synthesis]] |
;[[Digital waveguide synthesis]] |
||
: Developed in 1989 by [[Yamaha]] alongside [[Stanford University]]. |
: Developed in 1989 by [[Yamaha]] alongside [[Stanford University]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[PCM adaptor]] |
;[[PCM adaptor]] |
||
: The [[Sony]] PCM-1600 was the first video-based 16-bit PCM recorder (using a special [[U-matic]] VCR for a transport), and continues in its 1610 and 1630 incarnations. The 1600 was one of the first systems used for mastering audio [[compact disc]]s in the early 1980s by many major record labels. |
: The [[Sony]] PCM-1600 was the first video-based 16-bit PCM recorder (using a special [[U-matic]] VCR for a transport), and continues in its 1610 and 1630 incarnations. The 1600 was one of the first systems used for mastering audio [[compact disc]]s in the early 1980s by many major record labels. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Phase distortion synthesis]] |
;[[Phase distortion synthesis]] |
||
: A [[Sound synthesis|synthesis]] method introduced in 1984 by [[Casio]] in its [[Casio CZ synthesizers|CZ range of synths]]. |
: A [[Sound synthesis|synthesis]] method introduced in 1984 by [[Casio]] in its [[Casio CZ synthesizers|CZ range of synths]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Physical modelling synthesis]] |
;[[Physical modelling synthesis]] |
||
| Line 366: | Line 368: | ||
;[[Polyphony (instrument)|Polyphony]] |
;[[Polyphony (instrument)|Polyphony]] |
||
: In 1976, the first true music [[synthesizer]]s to offer polyphony had begun to appear, in the form of the [[Yamaha GX1]], CS-50, CS-60 and [[Yamaha CS-80|CS-80]]. |
: In 1976, the first true music [[synthesizer]]s to offer polyphony had begun to appear, in the form of the [[Yamaha GX1]], CS-50, CS-60 and [[Yamaha CS-80|CS-80]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Portable CD player]] |
;[[Portable CD player]] |
||
| Line 375: | Line 377: | ||
;[[Walkman]] |
;[[Walkman]] |
||
: In 1979, the Walkman was introduced by [[Sony]], in the form of the world's first portable music player. Though it was originally invented by [[Andreas Pavel]] in 1972. Sony refused to acknowledge that he was the inventor of the device, but after numerous trials the court ruled in favour of Pavel and forced Sony to pay royalties. |
: In 1979, the Walkman was introduced by [[Sony]], in the form of the world's first portable music player. Though it was originally invented by [[Andreas Pavel]] in 1972. Sony refused to acknowledge that he was the inventor of the device, but after numerous trials the court ruled in favour of Pavel and forced Sony to pay royalties. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
===Aviation=== |
===Aviation=== |
||
| Line 382: | Line 384: | ||
;[[Undercarriage|Landing gear]] |
;[[Undercarriage|Landing gear]] |
||
: [[Chūhachi Ninomiya]]'s "Karasu-gata mokei hikouki" ("[[Crow]]-type model aircraft") in 1891 had three wheels as landing gear. |
: [[Chūhachi Ninomiya]]'s "Karasu-gata mokei hikouki" ("[[Crow]]-type model aircraft") in 1891 had three wheels as landing gear. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Pusher configuration|Pusher propeller]] |
;[[Pusher configuration|Pusher propeller]] |
||
: Invented by [[Chūhachi Ninomiya]] in 1891 as part of his "Karasu-gata mokei hikouki" ("Crow-type model aircraft"). The four-blade pusher [[propeller]], inspired from a [[bamboo-copter]], was driven by a rubber band. His "Tamamushi-gata hikouki"("Jewel beetle type flyer") in 1893 was also equipped with a four-blade pusher propeller. |
: Invented by [[Chūhachi Ninomiya]] in 1891 as part of his "Karasu-gata mokei hikouki" ("Crow-type model aircraft"). The four-blade pusher [[propeller]], inspired from a [[bamboo-copter]], was driven by a rubber band. His "Tamamushi-gata hikouki"("Jewel beetle type flyer") in 1893 was also equipped with a four-blade pusher propeller. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Stabilizer (aircraft)|Stabilizer]] |
;[[Stabilizer (aircraft)|Stabilizer]] |
||
: [[Chūhachi Ninomiya]]'s "Karasu-gata mokei hikouki" ("Crow-type model aircraft") in 1891 was the earliest to be equipped with a [[horizontal stabilizer]] at its tail and a [[vertical stabilizer]] at its nose. |
: [[Chūhachi Ninomiya]]'s "Karasu-gata mokei hikouki" ("Crow-type model aircraft") in 1891 was the earliest to be equipped with a [[horizontal stabilizer]] at its tail and a [[vertical stabilizer]] at its nose. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Tailless aircraft]] |
;[[Tailless aircraft]] |
||
| Line 395: | Line 397: | ||
===Calculators=== |
===Calculators=== |
||
;[[Calculator#Technical improvements|Credit-card-sized calculator]] |
;[[Calculator#Technical improvements|Credit-card-sized calculator]] |
||
: The first credit-card-sized calculator was the [[Casio]] ''Mini Card LC-78'', of 1978, which could run for months of normal use on button cells. |
: The first credit-card-sized calculator was the [[Casio]] ''Mini Card LC-78'', of 1978, which could run for months of normal use on button cells. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Calculator#The development of electronic calculators|Electric compact calculator]] |
;[[Calculator#The development of electronic calculators|Electric compact calculator]] |
||
: The [[Casio|Casio Computer Co.]], in Japan, released the Model ''14-A'' calculator in 1957, which was the world's first all-electric compact calculator. |
: The [[Casio|Casio Computer Co.]], in Japan, released the Model ''14-A'' calculator in 1957, which was the world's first all-electric compact calculator. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Graphing calculator]] |
;[[Graphing calculator]] |
||
: The first graphing calculator was the [[Casio fx-7000G]], released in 1985. Many more [[Casio graphic calculators]] have been released since then. |
: The first graphing calculator was the [[Casio fx-7000G]], released in 1985. Many more [[Casio graphic calculators]] have been released since then. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Pocket calculator]] |
;[[Pocket calculator]] |
||
: The first portable calculators appeared in Japan in 1970, and were soon marketed around the world. These included the [[Sanyo]] ICC-0081 "Mini Calculator", the [[Canon (company)|Canon]] Pocketronic, and the [[Sharp Corporation|Sharp]] QT-8B "micro Compet". Sharp put in great efforts in size and power reduction and introduced in January 1971 the [[Sharp EL-8]], also marketed as the Facit 1111, which was close to being a pocket calculator. It weighed about one pound, had a vacuum fluorescent display, and rechargeable [[NiCad]] batteries. The first truly pocket-sized electronic calculator was the [[Busicom]] LE-120A "HANDY", which was marketed early in 1971.<ref>"The one-chip calculator is here, and it's only the beginning", Electronic Design, February 18, 1971, p34.</ref> Made in Japan, this was the first calculator to use an [[LED]] display, the first hand-held calculator to use a single integrated circuit (then proclaimed as a "calculator on a chip"), and the first electronic calculator to run off replaceable batteries. Using four AA-size cells, the LE-120A measures 4.9x2.8x0.9 in (124x72x24 mm). |
: The first portable calculators appeared in Japan in 1970, and were soon marketed around the world. These included the [[Sanyo]] ICC-0081 "Mini Calculator", the [[Canon (company)|Canon]] Pocketronic, and the [[Sharp Corporation|Sharp]] QT-8B "micro Compet". Sharp put in great efforts in size and power reduction and introduced in January 1971 the [[Sharp EL-8]], also marketed as the Facit 1111, which was close to being a pocket calculator. It weighed about one pound, had a vacuum fluorescent display, and rechargeable [[NiCad]] batteries. The first truly pocket-sized electronic calculator was the [[Busicom]] LE-120A "HANDY", which was marketed early in 1971.<ref>"The one-chip calculator is here, and it's only the beginning", Electronic Design, February 18, 1971, p34.</ref> Made in Japan, this was the first calculator to use an [[LED]] display, the first hand-held calculator to use a single integrated circuit (then proclaimed as a "calculator on a chip"), and the first electronic calculator to run off replaceable batteries. Using four AA-size cells, the LE-120A measures 4.9x2.8x0.9 in (124x72x24 mm). {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Calculator#Technical improvements|Solar-powered calculator]] |
;[[Calculator#Technical improvements|Solar-powered calculator]] |
||
: With low power consumption came the possibility of using [[solar cells]] as the power source, realised around 1978 by the [[Sharp Corporation|Sharp]] ''EL-8026''. |
: With low power consumption came the possibility of using [[solar cells]] as the power source, realised around 1978 by the [[Sharp Corporation|Sharp]] ''EL-8026''. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
===Cameras=== |
===Cameras=== |
||
;[[Camcorder]] |
;[[Camcorder]] |
||
: In 1982, [[Sony]] released the first professional camcorder, named the [[Betacam]]. |
: In 1982, [[Sony]] released the first professional camcorder, named the [[Betacam]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Digital camera]] |
;[[Digital camera]] |
||
: The first true digital camera that recorded images as a computerized file was the [[Fujifilm|Fuji]] DS-1P, in 1988. It recorded to a 16 MB internal memory card that used a battery to keep the data in memory. |
: The first true digital camera that recorded images as a computerized file was the [[Fujifilm|Fuji]] DS-1P, in 1988. It recorded to a 16 MB internal memory card that used a battery to keep the data in memory. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Digital single-lens reflex camera]] |
;[[Digital single-lens reflex camera]] |
||
: On August 25, 1981 Sony unveiled a prototype of the first still video camera, the [[Sony Mavica]]. This camera was an analog electronic camera that featured interchangeable lenses and a [[Single-lens reflex camera|SLR]] viewfinder. At [[Photokina]] in 1986, [[Nikon]] revealed a prototype analog electronic still SLR camera, the [[Nikon SVC]], the first digital SLR. The prototype body shared many features with the N8008.<ref name="Jarleton">[http://apphotnum.free.fr/N2BE2.html Nikon SLR-type digital cameras], Pierre Jarleton</ref> In 1999, Nikon announced the [[Nikon D1]], the first DSLR to truly compete with, and begin to replace, film cameras in the professional photojournalism and sports photography fields. This camera was able to use current autofocus Nikkor lenses available at that time for the Nikon film series cameras, and was also able to utilize the older Nikon and similar, independent mount lenses designed for those cameras. A combination of price, speed, and image quality was the beginning of the end of [[35 mm film]] for these markets. |
: On August 25, 1981 Sony unveiled a prototype of the first still video camera, the [[Sony Mavica]]. This camera was an analog electronic camera that featured interchangeable lenses and a [[Single-lens reflex camera|SLR]] viewfinder. At [[Photokina]] in 1986, [[Nikon]] revealed a prototype analog electronic still SLR camera, the [[Nikon SVC]], the first digital SLR. The prototype body shared many features with the N8008.<ref name="Jarleton">[http://apphotnum.free.fr/N2BE2.html Nikon SLR-type digital cameras], Pierre Jarleton</ref> In 1999, Nikon announced the [[Nikon D1]], the first DSLR to truly compete with, and begin to replace, film cameras in the professional photojournalism and sports photography fields. This camera was able to use current autofocus Nikkor lenses available at that time for the Nikon film series cameras, and was also able to utilize the older Nikon and similar, independent mount lenses designed for those cameras. A combination of price, speed, and image quality was the beginning of the end of [[35 mm film]] for these markets. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Digital camera#Analog electronic cameras|Handheld electronic camera]] |
;[[Digital camera#Analog electronic cameras|Handheld electronic camera]] |
||
: Handheld electronic [[camera]]s, in the sense of a device meant to be carried and used like a handheld film camera, appeared in 1981 with the demonstration of the [[Sony Mavica]] (Magnetic Video Camera). This was an analog camera, in that it recorded pixel signals continuously, as videotape machines did, without converting them to discrete levels; it recorded television-like signals to a 2 × 2 inch [[Video Floppy]]. Analog electronic cameras do not appear to have reached the market until 1986 with the Canon RC-701. Canon demonstrated a prototype of this model at the [[1984 Summer Olympics]], printing the images in the ''[[Yomiuri Shimbun]]'', a Japanese newspaper. |
: Handheld electronic [[camera]]s, in the sense of a device meant to be carried and used like a handheld film camera, appeared in 1981 with the demonstration of the [[Sony Mavica]] (Magnetic Video Camera). This was an analog camera, in that it recorded pixel signals continuously, as videotape machines did, without converting them to discrete levels; it recorded television-like signals to a 2 × 2 inch [[Video Floppy]]. Analog electronic cameras do not appear to have reached the market until 1986 with the Canon RC-701. Canon demonstrated a prototype of this model at the [[1984 Summer Olympics]], printing the images in the ''[[Yomiuri Shimbun]]'', a Japanese newspaper. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
===Chindogu=== |
===Chindogu=== |
||
| Line 427: | Line 429: | ||
Chindogu is the Japanese art of inventing ingenious everyday [[gadget]]s that, on the face of it, seem like an ideal solution to a particular problem. However, Chindogu has a distinctive feature: anyone actually attempting to use one of these inventions would find that it causes so many new problems, or such significant social [[embarrassment]], that effectively it has no [[utility]] whatsoever. Thus, Chindōgu are sometimes described as "unuseless" – that is, they cannot be regarded as 'useless' in an absolute sense, since they do actually solve a problem; however, in practical terms, they cannot positively be called "useful." The term "Chindogu" was coined by [[Kenji Kawakami]]. Examples of Chindogu include: |
Chindogu is the Japanese art of inventing ingenious everyday [[gadget]]s that, on the face of it, seem like an ideal solution to a particular problem. However, Chindogu has a distinctive feature: anyone actually attempting to use one of these inventions would find that it causes so many new problems, or such significant social [[embarrassment]], that effectively it has no [[utility]] whatsoever. Thus, Chindōgu are sometimes described as "unuseless" – that is, they cannot be regarded as 'useless' in an absolute sense, since they do actually solve a problem; however, in practical terms, they cannot positively be called "useful." The term "Chindogu" was coined by [[Kenji Kawakami]]. Examples of Chindogu include: |
||
* a combined [[Feather duster|household duster]] and [[Cocktail shaker|cocktail-shaker]], for the housewife who wants to reward herself as she's going along; |
* a combined [[Feather duster|household duster]] and [[Cocktail shaker|cocktail-shaker]], for the housewife who wants to reward herself as she's going along; {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
* the all-day tissue dispenser, which is basically a [[Tissue paper|toilet roll]] fixed on top of a hat, for [[hay fever]] sufferers; |
* the all-day tissue dispenser, which is basically a [[Tissue paper|toilet roll]] fixed on top of a hat, for [[hay fever]] sufferers; {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
* duster [[slipper]]s for cats, so they can help out with the housework; |
* duster [[slipper]]s for cats, so they can help out with the housework; {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
* the all-over plastic [[Swimsuit|bathing costume]], to enable people who suffer from [[aquaphobia]] to swim without coming into contact with water. |
* the all-over plastic [[Swimsuit|bathing costume]], to enable people who suffer from [[aquaphobia]] to swim without coming into contact with water. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
===Domestic appliances=== |
===Domestic appliances=== |
||
| Line 441: | Line 443: | ||
===Electronics=== |
===Electronics=== |
||
;[[Blue laser]] |
;[[Blue laser]] |
||
: Following the research of Professor [[Isamu Akasaki]]'s group, the first commercially viable blue laser was invented by [[Shuji Nakamura]] while working at [[Nichia Corporation]]. |
: Following the research of Professor [[Isamu Akasaki]]'s group, the first commercially viable blue laser was invented by [[Shuji Nakamura]] while working at [[Nichia Corporation]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Integrated circuit|Glass integrated circuit]] |
;[[Integrated circuit|Glass integrated circuit]] |
||
| Line 447: | Line 449: | ||
;[[Indium gallium nitride]] |
;[[Indium gallium nitride]] |
||
: Indium gallium nitride (InGaN) is a [[semiconductor]] invented by [[Shuji Nakamura]]. |
: Indium gallium nitride (InGaN) is a [[semiconductor]] invented by [[Shuji Nakamura]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Microprocessor]] |
;[[Microprocessor]] |
||
: The world's first microprocessor, the [[Intel 4004]], was designed by [[Masatoshi Shima]] of [[Busicom]] alongside [[Marcian Hoff]] and [[Federico Faggin]]. |
: The world's first microprocessor, the [[Intel 4004]], was designed by [[Masatoshi Shima]] of [[Busicom]] alongside [[Marcian Hoff]] and [[Federico Faggin]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Personal digital assistant]] |
;[[Personal digital assistant]] |
||
: The first PDA is considered to be the [[Casio]] PF-3000 released in May 1983. |
: The first PDA is considered to be the [[Casio]] PF-3000 released in May 1983. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Central processing unit|Plastic central processing unit]] |
;[[Central processing unit|Plastic central processing unit]] |
||
| Line 463: | Line 465: | ||
===Game controllers=== |
===Game controllers=== |
||
;[[Analog stick]] |
;[[Analog stick]] |
||
: In 1996, [[Nintendo]] introduced the first analog thumbstick on the [[Nintendo 64 controller]]. Since then, all major [[video game console]] [[game controllers|controllers]] have included analog sticks. |
: In 1996, [[Nintendo]] introduced the first analog thumbstick on the [[Nintendo 64 controller]]. Since then, all major [[video game console]] [[game controllers|controllers]] have included analog sticks. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[D-pad]] |
;[[D-pad]] |
||
: In 1982, [[Nintendo]]'s [[Gunpei Yokoi]] elaborated on the idea of a circular pad, shrinking it and altering the points into the familiar modern "cross" design for control of on-screen characters in their ''[[Donkey Kong (video game)|Donkey Kong]]'' handheld game. It came to be known as the "D-pad".<ref name="IGN">{{cite web| last = Buchanan| first = Levi| title = From Janitor to Superstar Gunpei Yokoi, inventor of the Game Boy, would have been 67 this week.| publisher = [[IGN]]| date = 2008-09-08| url = http://retro.ign.com/articles/908/908569p1.html| accessdate = 2008-12-28}}</ref> The design proved to be popular for subsequent ''[[Game & Watch]]'' titles. This particular design was patented. In 1984, the Japanese company Epoch created a handheld game system called the [[Epoch Game Pocket Computer]]. It featured a D-pad, but it was not popular for its time and soon faded. Initially intended to be a compact controller for the ''Game & Watch'' handheld games alongside the prior non-connected style pad, Nintendo realized that Gunpei's design would also be appropriate for regular consoles, and Nintendo made the D-pad the standard directional control for the hugely successful [[Nintendo Entertainment System]] under the name "+Control Pad". All major video game consoles since have had a D-pad of some shape on their controllers. |
: In 1982, [[Nintendo]]'s [[Gunpei Yokoi]] elaborated on the idea of a circular pad, shrinking it and altering the points into the familiar modern "cross" design for control of on-screen characters in their ''[[Donkey Kong (video game)|Donkey Kong]]'' handheld game. It came to be known as the "D-pad".<ref name="IGN">{{cite web| last = Buchanan| first = Levi| title = From Janitor to Superstar Gunpei Yokoi, inventor of the Game Boy, would have been 67 this week.| publisher = [[IGN]]| date = 2008-09-08| url = http://retro.ign.com/articles/908/908569p1.html| accessdate = 2008-12-28}}</ref> The design proved to be popular for subsequent ''[[Game & Watch]]'' titles. This particular design was patented. In 1984, the Japanese company Epoch created a handheld game system called the [[Epoch Game Pocket Computer]]. It featured a D-pad, but it was not popular for its time and soon faded. Initially intended to be a compact controller for the ''Game & Watch'' handheld games alongside the prior non-connected style pad, Nintendo realized that Gunpei's design would also be appropriate for regular consoles, and Nintendo made the D-pad the standard directional control for the hugely successful [[Nintendo Entertainment System]] under the name "+Control Pad". All major video game consoles since have had a D-pad of some shape on their controllers. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Dance pad]] |
;[[Dance pad]] |
||
: The first dance pad was the [[Power Pad]], a floor mat game controller for the [[Nintendo Entertainment System]]. It is a gray mat with twelve pressure-sensors embedded between two layers of flexible plastic. It was originally developed by [[Bandai]]. |
: The first dance pad was the [[Power Pad]], a floor mat game controller for the [[Nintendo Entertainment System]]. It is a gray mat with twelve pressure-sensors embedded between two layers of flexible plastic. It was originally developed by [[Bandai]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Haptic technology|Force feedback]] |
;[[Haptic technology|Force feedback]] |
||
: Introduced for [[game controller]]s by [[Nintendo]]'s [[Rumble Pak]], for the [[Nintendo 64 controller]]. |
: Introduced for [[game controller]]s by [[Nintendo]]'s [[Rumble Pak]], for the [[Nintendo 64 controller]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Wii Remote|Motion-sensing controller]] |
;[[Wii Remote|Motion-sensing controller]] |
||
| Line 479: | Line 481: | ||
===Metallurgy=== |
===Metallurgy=== |
||
;[[Alnico]] |
;[[Alnico]] |
||
: Alnico [[magnet]]s were developed from the [[MKM steel]] invented by [[Tokuhichi Mishima]]. |
: Alnico [[magnet]]s were developed from the [[MKM steel]] invented by [[Tokuhichi Mishima]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;KS steel |
;KS steel |
||
: [[Kotaro Honda]] invented the KS steel (initials from Kichiei Sumitomo), which is a type of [[magnet]]ic resistant [[steel]] that is three times more resistant than [[tungsten]] steel. |
: [[Kotaro Honda]] invented the KS steel (initials from Kichiei Sumitomo), which is a type of [[magnet]]ic resistant [[steel]] that is three times more resistant than [[tungsten]] steel. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Magnet]]ic [[steel]] |
;[[Magnet]]ic [[steel]] |
||
: [[Kotaro Honda]] invented the KS steel, a type of magnetic resistant steel that is three times more resistant than [[tungsten]] steel. In 1931, [[Tokuhichi Mishima]] discovered that a strongly magnetic steel could be created by adding aluminum to non-magnetic nickel steel. |
: [[Kotaro Honda]] invented the KS steel, a type of magnetic resistant steel that is three times more resistant than [[tungsten]] steel. In 1931, [[Tokuhichi Mishima]] discovered that a strongly magnetic steel could be created by adding aluminum to non-magnetic nickel steel. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[MKM steel]] |
;[[MKM steel]] |
||
: An [[alloy]] containing [[nickel]] and [[aluminum]], it was invented in 1931 by the Japanese metallurgist [[Tokuhichi Mishima]]. While conducting research into the properties of nickel, Mishima discovered that a strongly [[magnet]]ic [[steel]] could be created by adding aluminum to non-magnetic nickel steel. |
: An [[alloy]] containing [[nickel]] and [[aluminum]], it was invented in 1931 by the Japanese metallurgist [[Tokuhichi Mishima]]. While conducting research into the properties of nickel, Mishima discovered that a strongly [[magnet]]ic [[steel]] could be created by adding aluminum to non-magnetic nickel steel. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
===Robotics=== |
===Robotics=== |
||
| Line 511: | Line 513: | ||
;[[Digital Audio Tape]] |
;[[Digital Audio Tape]] |
||
: A signal recording and playback medium developed by [[Sony]] in the mid 1980s. |
: A signal recording and playback medium developed by [[Sony]] in the mid 1980s. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[DVD]] |
;[[DVD]] |
||
: The DVD [[optical disc]] format was developed by [[Sony]] alongside [[Philips]]. |
: The DVD [[optical disc]] format was developed by [[Sony]] alongside [[Philips]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Flash memory]] |
;[[Flash memory]] |
||
: Flash memory (both [[Flash memory#NOR flash|NOR]] and [[Flash memory#NAND flash|NAND]] types) was invented by Dr. [[Fujio Masuoka]] while working for [[Toshiba]] ''circa'' 1980.<ref>{{cite web|last=Fulford|first=Benjamin|title=Unsung hero|publisher=Forbes|date=24 June 2002|accessdate=2008-03-18|url=http://www.forbes.com/global/2002/0624/030.html}}</ref><ref>{{patent|US|4531203|Fujio Masuoka}}</ref> According to Toshiba, the name "flash" was suggested by Dr. Masuoka's colleague, Mr. Shoji Ariizumi, because the erasure process of the memory contents reminded him of a [[flash (photography)|flash]] of a camera. Dr. Masuoka presented the invention at the [[IEEE]] 1984 International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) held in [[San Francisco, California|San Francisco]], [[California]]. |
: Flash memory (both [[Flash memory#NOR flash|NOR]] and [[Flash memory#NAND flash|NAND]] types) was invented by Dr. [[Fujio Masuoka]] while working for [[Toshiba]] ''circa'' 1980.<ref>{{cite web|last=Fulford|first=Benjamin|title=Unsung hero|publisher=Forbes|date=24 June 2002|accessdate=2008-03-18|url=http://www.forbes.com/global/2002/0624/030.html}}</ref><ref>{{patent|US|4531203|Fujio Masuoka}}</ref> According to Toshiba, the name "flash" was suggested by Dr. Masuoka's colleague, Mr. Shoji Ariizumi, because the erasure process of the memory contents reminded him of a [[flash (photography)|flash]] of a camera. Dr. Masuoka presented the invention at the [[IEEE]] 1984 International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) held in [[San Francisco, California|San Francisco]], [[California]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Floppy disk]] |
;[[Floppy disk]] |
||
: A Japanese inventor, [[Yoshiro Nakamatsu]], invented the core floppy disk technology and, in 1952, registered a Japanese patent for his [http://www.iht.com/articles/1995/04/10/matscon.ttt.php|invention]. He later [http://www.pingmag.jp/2006/10/20/twilight-zone-dr-nakamats-inventions licensed] 16 patents to IBM for the creation of the floppy disk. |
: A Japanese inventor, [[Yoshiro Nakamatsu]], invented the core floppy disk technology and, in 1952, registered a Japanese patent for his [http://www.iht.com/articles/1995/04/10/matscon.ttt.php|invention]. He later [http://www.pingmag.jp/2006/10/20/twilight-zone-dr-nakamats-inventions licensed] 16 patents to IBM for the creation of the floppy disk. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Heat-assisted magnetic recording]] |
;[[Heat-assisted magnetic recording]] |
||
| Line 526: | Line 528: | ||
;[[Memory card]] |
;[[Memory card]] |
||
: The first [[flash memory]] card to be released was the [[JEIDA memory card]] by the [[Japan Electronic Industries Development Association]]. |
: The first [[flash memory]] card to be released was the [[JEIDA memory card]] by the [[Japan Electronic Industries Development Association]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Perpendicular recording]] |
;[[Perpendicular recording]] |
||
: A technology for data recording on [[hard disk]]s. It was first proven advantageous in 1976 by Shun-ichi Iwasaki, then professor of [[Tohoku University]] in Japan, and first commercially implemented in 2005. |
: A technology for data recording on [[hard disk]]s. It was first proven advantageous in 1976 by Shun-ichi Iwasaki, then professor of [[Tohoku University]] in Japan, and first commercially implemented in 2005. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Video cassette]] |
;[[Video cassette]] |
||
: In 1969, [[Sony]] introduced a prototype for the first video cassette, the 3/4" (1.905 cm) [[composite video|composite]] [[U-matic]] system, which Sony introduced commercially in September 1971 after working out industry standards with other manufacturers. Sony later refined it to ''Broadcast Video U-matic'' or BVU. |
: In 1969, [[Sony]] introduced a prototype for the first video cassette, the 3/4" (1.905 cm) [[composite video|composite]] [[U-matic]] system, which Sony introduced commercially in September 1971 after working out industry standards with other manufacturers. Sony later refined it to ''Broadcast Video U-matic'' or BVU. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Video Floppy]] |
;[[Video Floppy]] |
||
: A [[video]] storage medium in the form of a 2" magnetic [[floppy disk]] used to store still frames of analog [[composite video]]. Video floppies were first developed by [[Sony]] in 1981 for their [[Mavica]] and later used by [[Panasonic]] and [[Canon (company)|Canon]] for their still video cameras introduced in the late 1980s, such as the Canon Xapshot from 1988. |
: A [[video]] storage medium in the form of a 2" magnetic [[floppy disk]] used to store still frames of analog [[composite video]]. Video floppies were first developed by [[Sony]] in 1981 for their [[Mavica]] and later used by [[Panasonic]] and [[Canon (company)|Canon]] for their still video cameras introduced in the late 1980s, such as the Canon Xapshot from 1988. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
===Timekeeping=== |
===Timekeeping=== |
||
| Line 541: | Line 543: | ||
;[[Quartz clock|Quartz]] [[Watch|wristwatch]] |
;[[Quartz clock|Quartz]] [[Watch|wristwatch]] |
||
: The world's first quartz [[Watch|wristwatch]] was revealed in 1967: the prototype of the [[Astron (wristwatch)|Astron]] revealed by [[Seiko]] in Japan, where it was in development since 1958. It was eventually released to the public in 1969.<ref name=IEEE>{{cite web | publisher = IEEE History Center | title = Electronic Quartz Wristwatch, 1969 | url=http://www.ieee.org/web/aboutus/history_center/seiko.html | accessdate = 2007-08-31 }}</ref> The inherent accuracy and low cost of production has resulted in the proliferation of quartz clocks and watches since that time. By the 1980s quartz technology had taken over applications such as kitchen [[timer]]s, [[alarm clock]]s, bank vault [[time lock]]s, and time [[fuze]]s on munitions, from earlier mechanical [[balance wheel]] movements. |
: The world's first quartz [[Watch|wristwatch]] was revealed in 1967: the prototype of the [[Astron (wristwatch)|Astron]] revealed by [[Seiko]] in Japan, where it was in development since 1958. It was eventually released to the public in 1969.<ref name=IEEE>{{cite web | publisher = IEEE History Center | title = Electronic Quartz Wristwatch, 1969 | url=http://www.ieee.org/web/aboutus/history_center/seiko.html | accessdate = 2007-08-31 }}</ref> The inherent accuracy and low cost of production has resulted in the proliferation of quartz clocks and watches since that time. By the 1980s quartz technology had taken over applications such as kitchen [[timer]]s, [[alarm clock]]s, bank vault [[time lock]]s, and time [[fuze]]s on munitions, from earlier mechanical [[balance wheel]] movements. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Quartz clock|Quartz]] [[chronograph]] |
;[[Quartz clock|Quartz]] [[chronograph]] |
||
: Invented by [[Seiko]] in the 1970s. |
: Invented by [[Seiko]] in the 1970s. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
===Transport=== |
===Transport=== |
||
| Line 551: | Line 553: | ||
;[[High-speed rail|Dedicated high-speed rail lines]] |
;[[High-speed rail|Dedicated high-speed rail lines]] |
||
: Japan was the first country to build dedicated railway lines for high speed travel. Because of the mountainous terrain, the existing network consisted of {{RailGauge|42}} [[Narrow gauge railways|narrow gauge]] lines, which generally took indirect routes and could not be adapted to higher speeds. Consequently, Japan had a greater need for new high speed lines than countries where the existing [[standard gauge]] or [[broad gauge]] rail system had more upgrade potential. |
: Japan was the first country to build dedicated railway lines for high speed travel. Because of the mountainous terrain, the existing network consisted of {{RailGauge|42}} [[Narrow gauge railways|narrow gauge]] lines, which generally took indirect routes and could not be adapted to higher speeds. Consequently, Japan had a greater need for new high speed lines than countries where the existing [[standard gauge]] or [[broad gauge]] rail system had more upgrade potential. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Continuously variable transmission|Electronically-controlled continuously variable transmission]] |
;[[Continuously variable transmission|Electronically-controlled continuously variable transmission]] |
||
| Line 565: | Line 567: | ||
;[[Kei car]] |
;[[Kei car]] |
||
: A category of small [[automobiles]], including [[Automobile|passenger car]]s, [[Microvan|vans]], and [[Kei truck|pickup trucks]]. They are designed to exploit local [[tax]] and [[insurance]] relaxations, and in more rural areas are exempted from the requirement to certify that adequate [[parking]] is available for the vehicle.<ref name="nunn">[http://www.jama-english.jp/europe/news/2005/jan-feb/peternunn.html "Minicars: Cheap and Cheerful"], Peter Nunn, [[Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association|JAMA]], January-February 2005</ref><ref name="sendai">[http://www.sendaiedu.com/owningacar.html "Owning a Car in Japan"], ALTs in Sendai</ref> These standards originated in the times following the end of the [[Second World War]], when most Japanese could not afford a full-sized car yet had enough to buy a [[motorcycle]]. To promote the growth of the car industry, as well as to offer an alternative delivery method to small business and shop owners, kei car standards were created. |
: A category of small [[automobiles]], including [[Automobile|passenger car]]s, [[Microvan|vans]], and [[Kei truck|pickup trucks]]. They are designed to exploit local [[tax]] and [[insurance]] relaxations, and in more rural areas are exempted from the requirement to certify that adequate [[parking]] is available for the vehicle.<ref name="nunn">[http://www.jama-english.jp/europe/news/2005/jan-feb/peternunn.html "Minicars: Cheap and Cheerful"], Peter Nunn, [[Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association|JAMA]], January-February 2005</ref><ref name="sendai">[http://www.sendaiedu.com/owningacar.html "Owning a Car in Japan"], ALTs in Sendai</ref> These standards originated in the times following the end of the [[Second World War]], when most Japanese could not afford a full-sized car yet had enough to buy a [[motorcycle]]. To promote the growth of the car industry, as well as to offer an alternative delivery method to small business and shop owners, kei car standards were created. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
===Visual display units=== |
===Visual display units=== |
||
;[[Aperture grille]] |
;[[Aperture grille]] |
||
: The first [[patent]]ed aperture grille [[television]]s were manufactured by [[Sony]] in the late 1960s under the [[Trinitron]] brand name, which the company carried over to its line of [[Cathode ray tube|CRT]] [[computer monitor]]s. Subsequent designs, either licensed from Sony or manufactured after the patent's expiration, tend to use the -tron suffix, such as [[Mitsubishi]]'s DiamondTron and [[ViewSonic]]'s SonicTron. Today, Trinitron displays are still produced for markets such as [[Bangladesh]], [[China]], [[India]] and [[Pakistan]]. |
: The first [[patent]]ed aperture grille [[television]]s were manufactured by [[Sony]] in the late 1960s under the [[Trinitron]] brand name, which the company carried over to its line of [[Cathode ray tube|CRT]] [[computer monitor]]s. Subsequent designs, either licensed from Sony or manufactured after the patent's expiration, tend to use the -tron suffix, such as [[Mitsubishi]]'s DiamondTron and [[ViewSonic]]'s SonicTron. Today, Trinitron displays are still produced for markets such as [[Bangladesh]], [[China]], [[India]] and [[Pakistan]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Flat panel display]] |
;[[Flat panel display]] |
||
: The first flat-panel displays were the flat [[Cathode ray tube|CRTs]]<ref>http://www.taschenfernseher.de/bilder/sony-flat.jpg</ref><ref>http://www.ebeaminc.com/images/cap02.jpg</ref> used by [[Sony]] in their [[Sony Watchman|Watchman]] series (the [http://www.guenthoer.de/bilder-neu/fd-210-gr.jpg FD-210] was introduced in 1982). One of the last flat-CRT models was the [http://www.guenthoer.de/bilder-neu/fd-10-gr.jpg FD-120A]. The CRT in these units was flat with the [[electron gun]] located roughly at right angles below the display surface thus requiring sophisticated electronics to create an undistorted picture free from effects such as [[keystoning]]. |
: The first flat-panel displays were the flat [[Cathode ray tube|CRTs]]<ref>http://www.taschenfernseher.de/bilder/sony-flat.jpg</ref><ref>http://www.ebeaminc.com/images/cap02.jpg</ref> used by [[Sony]] in their [[Sony Watchman|Watchman]] series (the [http://www.guenthoer.de/bilder-neu/fd-210-gr.jpg FD-210] was introduced in 1982). One of the last flat-CRT models was the [http://www.guenthoer.de/bilder-neu/fd-10-gr.jpg FD-120A]. The CRT in these units was flat with the [[electron gun]] located roughly at right angles below the display surface thus requiring sophisticated electronics to create an undistorted picture free from effects such as [[keystoning]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Handheld television|Handheld colour television]] |
;[[Handheld television|Handheld colour television]] |
||
: In 1990, a color model of the [[Sony Watchman]] with an [[active-matrix liquid crystal display|active-matrix LCD]] was released. |
: In 1990, a color model of the [[Sony Watchman]] with an [[active-matrix liquid crystal display|active-matrix LCD]] was released. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Handheld television|Handheld]] [[liquid crystal display television]] |
;[[Handheld television|Handheld]] [[liquid crystal display television]] |
||
: In 1990, a color model of the [[Sony Watchman]] with an [[active-matrix liquid crystal display|active-matrix LCD]] was released. |
: In 1990, a color model of the [[Sony Watchman]] with an [[active-matrix liquid crystal display|active-matrix LCD]] was released. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Liquid crystal display television]] |
;[[Liquid crystal display television]] |
||
: In 1988, [[Sharp Corporation]] introduced the first commercial [[liquid crystal display|LCD]] television, a 14" model. |
: In 1988, [[Sharp Corporation]] introduced the first commercial [[liquid crystal display|LCD]] television, a 14" model. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Mechanical television]] |
;[[Mechanical television]] |
||
: In the 1920s, the Japanese electrical scientist [[Yasujiro Niwa]] invented a simple device for phototelegraphic transmission through [[cable]] and later via [[radio]], a precursor to mechanical television. |
: In the 1920s, the Japanese electrical scientist [[Yasujiro Niwa]] invented a simple device for phototelegraphic transmission through [[cable]] and later via [[radio]], a precursor to mechanical television. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Plasma display|Plasma colour display]] |
;[[Plasma display|Plasma colour display]] |
||
: In 1992, [[Fujitsu]] introduced the world's first full-color plasma display. It was a hybrid, based upon the plasma display created at the [[University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign]] and [[NHK]] [[STRL]], achieving superior brightness. |
: In 1992, [[Fujitsu]] introduced the world's first full-color plasma display. It was a hybrid, based upon the plasma display created at the [[University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign]] and [[NHK]] [[STRL]], achieving superior brightness. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Plasma display|Plasma television]] |
;[[Plasma display|Plasma television]] |
||
: In 1997, [[Pioneer Corporation|Pioneer]] released the first plasma [[television]]. |
: In 1997, [[Pioneer Corporation|Pioneer]] released the first plasma [[television]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Handheld television|Pocket television]] |
;[[Handheld television|Pocket television]] |
||
: In 1982, [[Sony]] released the first television that could fit in a pocket: the [[Sony Watchman|Watchman]]; a [[pun]] on [[Walkman]]. |
: In 1982, [[Sony]] released the first television that could fit in a pocket: the [[Sony Watchman|Watchman]]; a [[pun]] on [[Walkman]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
===Weapons=== |
===Weapons=== |
||
;[[Fire balloon]] |
;[[Fire balloon]] |
||
: A fire balloon, or balloon bomb, was an experimental weapon launched by [[Japan]] from 1944 to 1945, during [[World War II]]. |
: A fire balloon, or balloon bomb, was an experimental weapon launched by [[Japan]] from 1944 to 1945, during [[World War II]]. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Katana]] |
;[[Katana]] |
||
| Line 603: | Line 605: | ||
;[[Shuriken]] |
;[[Shuriken]] |
||
: The earliest known mention of a school teaching ''shuriken-jutsu'' is Ganritsu Ryu, prevalent during the 1600s. There are also earlier mentions in written records, such as the ''Osaka Gunki'' (''The Military Records of Osaka''), of the standard knife and short sword being thrown in battle, and [[Miyamoto Musashi]] is said to have won a duel by throwing his short sword at his opponent, killing him. |
: The earliest known mention of a school teaching ''shuriken-jutsu'' is Ganritsu Ryu, prevalent during the 1600s. There are also earlier mentions in written records, such as the ''Osaka Gunki'' (''The Military Records of Osaka''), of the standard knife and short sword being thrown in battle, and [[Miyamoto Musashi]] is said to have won a duel by throwing his short sword at his opponent, killing him. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
===Wireless transmission=== |
===Wireless transmission=== |
||
;[[Directional antenna]] |
;[[Directional antenna]] |
||
: The first directional or beam antenna was the [[Yagi antenna]], invented by [[Hidetsugu Yagi]] and [[Shintaro Uda]] in 1926. |
: The first directional or beam antenna was the [[Yagi antenna]], invented by [[Hidetsugu Yagi]] and [[Shintaro Uda]] in 1926. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[High-gain antenna]] |
;[[High-gain antenna]] |
||
: The first high-gain antenna was also the [[Yagi antenna]] in 1926. |
: The first high-gain antenna was also the [[Yagi antenna]] in 1926. {{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
;[[Yagi antenna]] |
;[[Yagi antenna]] |
||
: The Yagi-Uda antenna was invented in 1926 by [[Shintaro Uda]] of [[Tohoku University|Tohoku Imperial University]], [[Sendai, Miyagi|Sendai]], [[Japan]], with the collaboration of [[Hidetsugu Yagi]], also of Tohoku Imperial University. Yagi published the first English-language reference on the antenna in a 1928 survey article on short wave research in Japan and it came to be associated with his name. However, Yagi always acknowledged Uda's principal contribution to the design, and the proper name for the antenna is, as above, the Yagi-Uda antenna (or array). |
: The Yagi-Uda antenna was invented in 1926 by [[Shintaro Uda]] of [[Tohoku University|Tohoku Imperial University]], [[Sendai, Miyagi|Sendai]], [[Japan]], with the collaboration of [[Hidetsugu Yagi]], also of Tohoku Imperial University. Yagi published the first English-language reference on the antenna in a 1928 survey article on short wave research in Japan and it came to be associated with his name. However, Yagi always acknowledged Uda's principal contribution to the design, and the proper name for the antenna is, as above, the Yagi-Uda antenna (or array).{{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 21:02, 23 December 2009
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2009) |
This article's factual accuracy is disputed. (December 2009) |
This is a list of Japanese inventions.
Arts
- Karaoke
- Karaoke is a form of entertainment in which amateur singers sing along with recorded music or video using a microphone and public address system. The first karaoke machine was invented in 1971 by Japanese musician Daisuke Inoue in Kobe, Japan. After becoming popular in Japan, karaoke spread to East and Southeast Asia during the 1980s and subsequently to other parts of the world. [citation needed]
Film and animation
- Bullet Time
- Long before the emergence of a technology permitting a live-action application, bullet-time as a concept was frequently developed in cel animation. The earliest example is the shot at the end of the title sequence for the late-sixties Japanese anime series Speed Racer: as Speed leaps from the Mach Five, he freezes in mid-jump, and then the camera does an arc shot from front to sideways. The show was later an inspiration for The Matrix (1999). [citation needed]
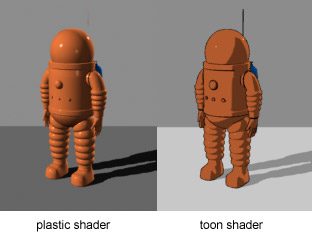
- Cel-shaded animation
- True cel-shaded animation was introduced by Sega's 3D video game, Jet Set Radio (2000), for the Dreamcast. [citation needed]
- Fictional space habitats
- The earliest fictional depiction of space habitats resembling cities were the space colonies in Yoshiyuki Tomino's 1979 anime series Mobile Suit Gundam (1979). [citation needed]
- Man with No Name
- A stock character that originated with Akira Kurosawa's Yojimbo (1961), where the archetype was first portrayed by Toshiro Mifune. The archetype was adapted by Sergio Leone for his Spaghetti Western Dollars Trilogy (1964-1966), with Clint Eastwood playing the role of the "Man with No Name". It is now a common archetype in Samurai films and Western films as well as other genres.[1]
- Mecha
- The mecha genre of science fiction was founded in Japan. The first depiction of mecha Super Robots being piloted by a user from within a cockpit was introduced in the manga and anime series Mazinger Z by Go Nagai in 1972.[2]
- Post-apocalyptic steampunk
- The earliest examples are Hayao Miyazaki's anime works Future Boy Conan (1978)[3] and Nausicaä of the Valley of the Wind (1984).[4]
- Postcyberpunk animation/film
- The first postcyberpunk media work in an animated/film format was Ghost in the Shell: Stand Alone Complex in 2002. It has been called "the most interesting, sustained postcyberpunk media work in existence."[5]
- Psychological horror
- Hideo Nakata's Ring (1998), the first of the J-Horror Ring Trilogy, is considered the earliest psychological horror film. [citation needed]
- Real Robot
- The Real Robot mecha genre began with Yoshiyuki Tomino's anime series Mobile Suit Gundam in 1979. It was followed by many more Gundam series as well as other Real Robot anime series such as Macross. [citation needed]
- Samurai cinema
- The earliest samurai films were Senkichi Taniguchi's Jakoman and Tetsu (1949) and Akira Kurosawa's Rashomon (1950). [citation needed]
- Steadicam tracking shot
- Though the film was produced 35 years before the invention of the Steadicam, Akira Kurosawa's Rashomon (1950) featured a complex tracking shot that would appear to have been made by a Steadicam to modern viewers. The shot is credited to the cinematographer Kazuo Miyagawa.[6]
- Steampunk animation
- The earliest examples of steampunk animation are Hayao Miyazaki's anime works Future Boy Conan (1978),[3] Nausicaä of the Valley of the Wind (1984)[4] and Castle in the Sky (1986).[7][8]
- Superflat
- A postmodern art form, founded by the artist Takashi Murakami, which is influenced by manga and anime.[9]
- Super Robot
- The Super Robot mecha genre began with Go Nagai's manga and anime series Mazinger Z in 1972. [citation needed]
- Yakuza film
- The first Yakuza film was Akira Kurosawa's Drunken Angel (1948), starring Toshiro Mifune. [citation needed]
Literature
- Flying saucer
- A manuscript illustration of the 10th-century Japanese narrative, The Tale of the Bamboo Cutter, depicts a round flying machine similar to a flying saucer.[10]
- Gesaku
- A pre-modern genre of Japanese literature. [citation needed]

- Historical novel
- The Tale of Genji, written by Lady Murasaki Shikibu in 11th-century Japan, is regarded as the first historical novel.[11]
- Novel
- The Tale of Genji is also regarded as the first novel in general.[12]
- Psychological novel
- The Tale of Genji is also regarded as the first psychological novel.[13]
- Time travel
- The 8th-century tale of Urashima Tarō has been identified as the earliest example of a story involving time travel.[14]
Martial arts
- Aikido
- A Japanese martial art developed by Morihei Ueshiba as a synthesis of his martial studies, philosophy, and religious beliefs. [citation needed]

- Judo
- Judo is a modern Japanese martial art and combat sport, that originated in Japan in the late nineteenth century. Its most prominent feature is its competitive element, where the object is to either throw one's opponent to the ground, immobilize or otherwise subdue one's opponent with a grappling manoeuvre, or force an opponent to submit by joint locking the elbow or by executing a choke. The early history of judo is inseparable from its founder, Japanese polymath and educator Jigoro Kano. [citation needed]
- Karate
- It began as a common fighting system known as "ti" (or "te") among the pechin class of the Ryukyuans. There were few formal styles of ti, but rather many practitioners with their own methods. One surviving example is the Motobu-ryū school passed down from the Motobu family by Seikichi Uehara.[15] Early styles of karate are often generalized as Shuri-te, Naha-te, and Tomari-te, named after the three cities from which they emerged.[16]
- Ninjutsu
- Developed by groups of people mainly from the Iga Province and Kōka, Shiga of Japan. Throughout history, many different schools (ryū) have taught their unique versions of ninjutsu. An example of these is the Togakure-ryū. This ryū was developed after a defeated samurai warrior called Daisuke Togakure escaped to the region of Iga. Later he came in contact with the warrior-monk Kain Doshi who taught him a new way of viewing life and the means of survival (ninjutsu).[17]
- Okinawan martial arts
- In the 14th century, when the three kingdoms on Okinawa (Chūzan, Hokuzan, and Nanzan) entered into a tributary relationship with the Ming Dynasty of China, Chinese Imperial envoys and other Chinese arrived, some of whom taught Chinese Chuan Fa (Kempo) to the Okinawans. The Okinawans combined Chinese Chuan Fa with the existing martial art of Te to form Tō-de (唐手, Okinawan: Tū-dī, Tang hand), sometimes called Okinawa-te (沖縄手).[18] By the 18th century, different types of Te had developed in three different villages - Naha, Shuri, and Tomari. The styles were named Naha-te, Shuri-te, and Tomari-te, respectively. Practitioners from these three villages went on to develop modern karate.[19]
Video games
- Action role-playing game
- Japanese developers, with their recent interest in the role-playing game (RPG) genre, tweaked the formula a bit to create a new brand of action RPG. The company at the forefront of this was Nihon Falcom. Dragon Slayer, released in 1984, was a simple real-time treasure grab game. However, its sequel, Xanadu, released in 1985, was a full-fledged RPG, with character stats and a large quest. What set Xanadu apart from other RPGs was its action-based combat. The next two years would see the release of two games that would further define the action/RPG genre in Japan: Nintendo's The Legend of Zelda in 1986 and Falcom's Ys in 1987. While not strictly an action/RPG since it lacks RPG elements such as experience points, The Legend of Zelda influenced later games in the action-RPG genre.[20] Zelda II also implemented an RPG-esque system with action elements, making it closer to an action-RPG than other Zeldas. Ys, on the other hand, used true RPG principles. [citation needed]
- Active Time Battle
- Hiroyuki Itō introduced the "Active Time Battle" system in Final Fantasy IV (1991),[21] where the time-keeping system does not stop.[22] Square Co., Ltd. filed a United States patent application for the ATB system on March 16, 1992, under the title "Video game apparatus, method and device for controlling same" and was awarded the patent on February 21, 1995. On the battle screen, each character has an ATB meter that gradually fills, and the player is allowed to issue a command to that character once the meter is full.[23] The fact that enemies can attack or be attacked at any time is credited with injecting urgency and excitement into the combat system.[22] The ATB system was fully developed in Final Fantasy V (1992) and continued to be used in later Final Fantasy games until Final Fantasy X-2 (2003) as well as other Square games such as Chrono Trigger (1995). [citation needed]
- Beat 'em up
- The first game to feature fist fighting was Sega's boxing game Heavyweight Champ (1976), but it was Data East's fighting game Karate Champ (1984) which popularized martial arts themed games.[24] The same year, Hong Kong cinema-inspired Kung-Fu Master laid the foundations for scrolling beat 'em ups with its simple gameplay and multiple enemies.[24][25] Nekketsu Kōha Kunio-kun, released in 1986 in Japan, deviated from the martial arts themes of earlier games and introduced street brawling to the genre. Renegade (released the same year) added an underworld revenge plot that proved more popular with gamers than the principled combat sport of other games.[26] Renegade set the standard for future beat 'em up games as it introduced the ability to move both horizontally and vertically.[27]
- Dating sim
- A simulation game subgenre originating in Japan. [citation needed]
- Fighting game
- Sega's black and white boxing game Heavyweight Champ was released in 1976 as the first video game to feature fist fighting.[28] However, Data East's Karate Champ from 1984 is credited with establishing and popularizing the one-on-one fighting game genre, and went on to influence Konami's Yie Ar Kung-Fu from 1985.[29] Yie Ar Kung Fu expanded on Karate Champ by pitting the player against a variety of opponents, each with a unique appearance and fighting style.[29][30] Capcom's Street Fighter (1987) introduced the use of special moves that could only be discovered by experimenting with the game controls. Street Fighter II (1991) established the conventions of the fighting game genre and, whereas previous games allowed players to combat computer-controlled fighters, Street Fighter II allowed players to play against each other.[31]
- Parallax scrolling
- A special scrolling technique in computer graphics, seen first in the 1982 arcade game, Moon Patrol.[32] Pac-Land (1984) later introduced multi-layered parallax scrolling.[33][34]

- Platform game
- Space Panic, a 1980 arcade release, is sometimes credited as the first platform game.[35] It was clearly an influence on the genre, with gameplay centered on climbing ladders between different floors, a common element in many early platform games. Donkey Kong, an arcade game created by Nintendo, released in July 1981, was the first game that allowed players to jump over obstacles and across gaps, making it the first true platformer.[36] This game also introduced Mario, an icon of the genre. Mario Bros, a platform game that offered two-player simultaneous cooperative play, laid the groundwork for other popular two-player cooperative platformers, like Fairyland Story and Bubble Bobble, which in turn influenced many of the single-screen platformers that would follow. [citation needed]
- Postmodern videogame
- Hideo Kojima's Metal Gear Solid 2: Sons of Liberty (2001) is regarded as the first example of a postmodern video game.[37][38]
- Psychological horror game
- Silent Hill (1999) was praised for moving away survival horror games from B movie horror elements to the psychological style seen in art house or Japanese horror films,[39] due to the game's emphasis on a disturbing atmosphere rather than visceral horror.[40] The original Silent Hill is considered one of the scariest games of all time,[41] and the strong narrative from Silent Hill 2 in 2001 has made the series one of the most influential in the genre.[42] Fatal Frame from 2001 was a unique entry into the genre, as the player explores a mansion and takes photographs of ghosts in order to defeat them.[43][44]
- Racing game
- The first true racing game was the Namco game Pole Position in 1982. The player had AI cars to race against, and time limit to keep pushing the players to go faster. Pole Position is also the first game to be based on a real racing circuit. Pole Position introduced color graphics at a much higher resolution than earlier titles. [citation needed]
- Rhythm game
- Dance Aerobics was released in 1987, and allowed players to create music by stepping on Nintendo's Power Pad peripheral. It has been called the first rhythm-action game in retrospect,[45] although the 1996 title PaRappa the Rapper has also been deemed the first rhythm game, whose basic template forms the core of subsequent games in the genre. In 1997, Konami's Beatmania sparked an emergent market for rhythm games in Japan. The company's music division, Bemani, released a number of music games over the next several years. The most successful of these was dance mat game Dance Dance Revolution, which was also the only one to achieve large-scale success out with Japan. [citation needed]
- Scrolling platformer
- The first platform game to use scrolling graphics was Jump Bug (1981), a simple platform-shooter developed by Alpha Denshi.[46] In August 1982, Taito released Jungle King,[47] which featured scrolling jump and run sequences that had players hopping over obstacles. Namco took the scrolling platformer a step further with the 1984 release Pac-Land. Pac-Land came after the genre had a few years to develop, and was an evolution of earlier platform games, aspiring to be more than a simple game of hurdle jumping, like some of its predecessors.[48] It closely resembled later scrolling platformers like Wonder Boy and Super Mario Bros and was probably a direct influence on them. It also had multi-layered parallax scrolling.[33][34]
- Shoot 'em up
- Space Invaders is frequently cited as the "first" or "original" in the genre.[49][50] Space Invaders pitted the player against multiple enemies descending from the top of the screen at a constantly increasing rate of speed.[50] As with subsequent shoot 'em ups of the time, the game was set in space as the available technology only permitted a black background. The game also introduced the idea of giving the player a number of "lives". Space Invaders was a massive commercial success, causing a coin shortage in Japan.[51][52] The following year, Namco's Galaxian took the genre further with more complex enemy patterns and richer graphics.[49][53]
- Stealth game
- The first stealth-based videogame was Sega's 005 (1981).[54][55][56] The first commercially successful stealth game was Hideo Kojima's Metal Gear (1987), the first in the Metal Gear series. It was followed by Metal Gear 2: Solid Snake (1990) which significantly expanded the genre, and then Metal Gear Solid (1998) which was a mainstream success and established stealth games as a genre. [citation needed]
- Steampunk fantasy
- The earliest steampunk work set entirely in a fantasy world was Square's console role-playing game, Final Fantasy VI (1994), though aspects of steampunk can also be found in earlier Final Fantasy games.[57]
- Survival horror
- The survival horror video game genre began with Capcom's Resident Evil (1996), which coined the term "survival horror" and defined the genre.[58][59] The game was inspired by Capcom's earlier horror game Sweet Home (1989).[60]
- Tactical role-playing game
- It is generally accepted that Nintendo released and published the first tactical RPG, Fire Emblem: Ankoku Ryū to Hikari no Tsurugi for the Nintendo Entertainment System (NES), created and developed by Intelligent Systems. Released in Japan in 1990, Fire Emblem was an archetype for the whole genre, establishing gameplay elements that are still used in tactical CRPGs today. Combining the basic console RPG concepts from games like Dragon Quest and simple turn-based strategy elements, Nintendo created a hit, which spawned many sequels and imitators. [citation needed]
- Visual novel
- An interactive fiction genre featuring mostly static graphics, usually with anime-style art, originating in Japan. [citation needed]
Philosophy
- 5 Whys
- Sakichi Toyoda developed the concept of 5 Whys: When a problem occurs, ask 'why' five times to try to find the source of the problem, then put into place something to prevent the problem from recurring. This concept is used today as part of applying lean methodologies to solve problems, improve quality, and reduce costs. [citation needed]
- Lean manufacturing
- A generic process management philosophy derived mostly from the Toyota Production System (TPS) (hence the term Toyotism is also prevalent) and identified as "Lean" only in the 1990s.[61][62] It is renowned for its focus on reduction of the original Toyota seven wastes in order to improve overall customer value, but there are varying perspectives on how this is best achieved. [citation needed]
Science
- Rashomon effect
- The psychological effect of the subjectivity of perception on recollection, by which observers of an event are able to produce substantially different but equally plausible accounts of it. The concept was inspired by Akira Kurosawa's 1950 film Rashomon, in which a crime witnessed by four individuals is described in four mutually contradictory ways. The film was based on two short stories by Ryūnosuke Akutagawa, "Rashōmon" (for the setting) and "In a Grove" (for the story line). [citation needed]
Biomedical science
- Aberic acid
- Discovered by Umetaro Suzuki in 1910. [citation needed]
- Aspergillus genomes
- Initially kept secret, the genome for Aspergillus oryzae, Aspergillus nidulans and Aspergillus fumigatus was released by a consortium of Japanese biotechnology companies,[63] in late 2005.[64]
- B vitamin
- The first B vitamin to be discovered was thiamine (vitamin B1), by Umetaro Suzuki in 1910. [citation needed]
- Epinephrine (Adrenaline)
- Japanese chemist Jokichi Takamine and his assistant Keizo Uenaka first discovered epinephrine in 1900.[65][66] In 1901 Takamine successfully isolated and purified the hormone from the adrenal glands of sheep and oxen.[67]
- Methamphetamine
- Methamphetamine was first synthesized from ephedrine in Japan in 1894 by chemist Nagayoshi Nagai.[68] In 1919, crystallized methamphetamine was synthesized by Akira Ogata via reduction of ephedrine using red phosphorus and iodine. [citation needed]
- Nuclear medicine
- Taro Takemi was the first to study the application of nuclear physics to medicine. [citation needed]
- Portable electrocardiograph
- Taro Takemi built the first portable electrocardiograph in 1937. [citation needed]
- Takadiastase
- A form of diastase which results from the growth, development and nutrition of a distinct microscopic fungus known as Aspergillus oryzae. Jokichi Takamine developed the method first used for its extraction in the late 19th century. [citation needed]
- Thiamine (Vitamin B1)
- Thiamine was the first of the water-soluble vitamins to be described,[69] leading to the discovery of more such trace compounds essential for survival and to the notion of vitamin. It was not until 1884 that Kanehiro Takaki (1849-1920) attributed beriberi to insufficient nitrogen intake (protein deficiency). In 1910, Japanese scientist Umetaro Suzuki succeeded in extracting a water-soluble complex of micronutrients from rice bran and named it aberic acid. He published this discovery in a Japanese scientific journal.[70] The Polish biochemist Kazimierz Funk later proposed the complex be named "Vitamine" (a portmanteau of "vital amine") in 1912.[71]
- Vectorcardiography
- Taro Takemi is known for his invention of the vectorcardiograph in 1939. [citation needed]
- Vitamin
- The first vitamin to be discovered was the B vitamin, thiamine (vitamin B1), by Umetaro Suzuki in 1910. [citation needed]
Food science
- Cup noodles
- Invented in 1970 by Nissin Foods. [citation needed]

- Instant noodles
- Instant noodles are dried or precooked noodles fused with oil, and often sold with a packet of flavoring. Dried noodles are usually eaten after being cooked or soaked in boiling water for 3 to 5 minutes, while precooked noodles can be reheated, or eaten straight from the packet. Momofuku Ando was the Taiwanese Japanese founder and chairman of Nissin Food Products Co., Ltd., and the inventor of world's first instant noodles in 1971. [citation needed]
- Monosodium glutamate
- Invented and patented by Kikunae Ikeda.[72]
- Umami
- Umami as a separate taste was first identified in 1908 by Kikunae Ikeda of the Tokyo Imperial University while researching the strong flavor in seaweed broth.[73] He isolated monosodium glutamate as the chemical responsible and, with the help of the Ajinomoto company, began commercial distribution of MSG products. [citation needed]
Mathematics
- Aitken's delta-squared process
- It was first known to Seki Kōwa at the end of the 17th century and was found for the rectification of the circle, i.e. the calculation of π. It is most useful for accelerating the convergence of a sequence that is converging linearly. He used it to obtain a value for π that was correct to the 10th decimal place. [citation needed]

- Bernoulli number
- Studied by Seki Kōwa and published by him in 1712, slightly anticipating their publication in Europe by Jacob Bernoulli.[74][75][76]
- Determinant
- In Japan, determinants were introduced to study elimination of variables in systems of higher-order algebraic equations. They used it to give short-hand representation for the resultant. The determinant as an independent function was first studied by Seki Kōwa in 1683.[76][77]
- Elimination theory
- In 1683 (Kai-Fukudai-no-Hō), Seki Kōwa came up with elimination theory, based on resultant.[77] To express resultant, he developed the notion of determinant.[77]
- Ford circle
- A typical problem, which is presented on an 1824 tablet in the Gunma Prefecture, covers the relationship of three touching circles with a common tangent. It describes the Ford circle over a century before L. R. Ford did in 1938. [citation needed]
- Laplace expansion
- After the first work by Seki Kōwa in 1683, Laplace's formula was given by two independent groups of scholars: Uima Tanaka and Tomonori Iseki (Sampo-Hakki, published in 1690), and Seki Kōwa, Kaaki Takebe and Katahiro Takebe (Taisei-Sankei, written at least before 1710). [citation needed]
- Newton-Raphson method
- Horner's method, though earlier completed by Chinese mathematicians, was not transmitted to Japan in its final form. So Seki Kōwa had to work it out by himself independently. In 1683, he suggested an improvement to Horner's method: to omit higher order terms after some iterations. This happens to be the same as the Newton-Raphson method, predating Joseph Raphson's work in 1690. [citation needed]
- Resultant
- In 1683 (Kai-Fukudai-no-Hō), Seki Kōwa came up with elimination theory, based on resultant. To express resultant, he developed the notion of determinant.[77]
- Sangaku
- Japanese geometrical puzzles in Euclidean geometry on wooden tablets created during the Edo period (1603–1867) by members of all social classes. The Dutch Japanologist Isaac Titsingh first introduced sangaku to the West when he returned to Europe in the late 1790s after more than twenty years in the Far East.[78]
Physics
- Meson
- In 1949, Hideki Yukawa was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for predicting the existence of the meson. He called the particle the meson (from mesos, Greek for intermediate) because its mass was between that of the electron and proton. [citation needed]
- Pion
- In 1949, Hideki Yukawa also received the Nobel Prize in Physics for his prediction of the pion in 1947. [citation needed]
- Strong force
- In 1935, Hideki Yukawa proposed the first significant theory of the strong force to explain how the nucleus holds together. [citation needed]
- Yukawa interaction
- Developed by Hideki Yukawa, it can be used to describe the strong nuclear force between nucleons (which are fermions), mediated by pions (which are pseudoscalar mesons). The Yukawa interaction is also used in the Standard Model to describe the coupling between the Higgs field and massless quark and electron fields. [citation needed]
- Yukawa potential
- Hideki Yukawa showed in the 1930s that such a potential arises from the exchange of a massive scalar field such as the field of the pion whose mass is . [citation needed]
Technology
- Automatic power loom
- Sakichi Toyoda invented numerous weaving devices. His most famous invention was the automatic power loom in which he implemented the principle of Jidoka (autonomation or autonomous automation). It was the 1924 Toyoda Automatic Loom, Type G, a completely automatic high-speed loom featuring the ability to change shuttles without stopping and dozens of other innovations. At the time it was the world's most advanced loom, delivering a dramatic improvement in quality and a twenty-fold increase in productivity.[79]
- Autonomation (autonomous automation)
- Sakichi Toyoda's most famous invention was the automatic power loom in which he implemented the principle of Jidoka (autonomation or autonomous automation). The principle of Jidoka, which means that the machine stops itself when a problem occurs, became later a part of the Toyota Production System. [citation needed]
- Chi Machine
- A device created by Japanese scientist Dr. Shizuo Inoue. It holds US FDA approval as a Class 1 Medical Device Regulation #890.5660.[80] It apparently oxygenates the body via "passive aerobic exercise", which the manufacturer claims stimulates the lymphatic system and supposedly enables detoxification. [citation needed]
- Cold fusion methods
- Shunpei Yamazaki was granted patents for several cold nuclear fusion methods, including the "Electrochemical Method for Creating Nuclear Fusion", the "Plasma Method for Creating Nuclear Fusion", and an "Electrode for Use in Nuclear Fusion".[81]
- Cultured pearl
- Primarily the result of discoveries made in the late 19th and early 20th centuries by the Japanese researchers Tokishi Nishikawa and Tatsuhei Mise. What they discovered was a specific technique for inducing the creation of a round pearl within the gonad of an oyster. This technique was patented by Kokichi Mikimoto shortly thereafter, and the first harvest of rounds was produced in 1916. This discovery revolutionized the pearl industry, because it allowed pearl farmers to reliably cultivate large numbers of high-quality pearls. [citation needed]
- Japanese typewriter
- The first typewriter to be based on the Japanese writing system was invented by Kyota Sugimoto in 1929.[82]
- TohoScope
- Toho Scope is an anamorphic lens system developed in the late 1950s by Toho Studios. [citation needed]
Audio technology
- Analog modeling synthesizer
- A synthesizer that emulates the sounds of traditional analog synthesizers using digital signal processing components. The earliest was Korg's Prophecy in the mid-1990s. [citation needed]
- Compact Disc player
- Sony released the world's first CD Player, called the CDP-101,[83] in 1982, utilising a slide-out tray design for the Compact Disc.
- Digital audio
- Digital recording of classical and jazz music began in the early 1970s, pioneered by Japanese companies such as Denon, and was soon adopted by British companies such as the BBC and record label Decca. [citation needed]
- Digital synthesizer
- The Yamaha DX7 in 1983 was the first stand-alone all-digital synthesizer.[84] It became indispensable to many music artists of the 1980s.[85]
- Digital waveguide synthesis
- Developed in 1989 by Yamaha alongside Stanford University. [citation needed]
- PCM adaptor
- The Sony PCM-1600 was the first video-based 16-bit PCM recorder (using a special U-matic VCR for a transport), and continues in its 1610 and 1630 incarnations. The 1600 was one of the first systems used for mastering audio compact discs in the early 1980s by many major record labels. [citation needed]
- Phase distortion synthesis
- A synthesis method introduced in 1984 by Casio in its CZ range of synths. [citation needed]
- Physical modelling synthesis
- The first commercially available physical modelling synthesizer was Yamaha's VL-1 in 1994.[86]
- Polyphony
- In 1976, the first true music synthesizers to offer polyphony had begun to appear, in the form of the Yamaha GX1, CS-50, CS-60 and CS-80. [citation needed]
- Portable CD player
- Sony's Discman, released in 1984, was the first portable CD player.[87]
- Vowel-Consonant synthesis
- A type of hybrid Digital-analogue synthesis first employed by the early Casiotone keyboards in the early 1980s.
- Walkman
- In 1979, the Walkman was introduced by Sony, in the form of the world's first portable music player. Though it was originally invented by Andreas Pavel in 1972. Sony refused to acknowledge that he was the inventor of the device, but after numerous trials the court ruled in favour of Pavel and forced Sony to pay royalties. [citation needed]
Aviation
- Biplane
- Chūhachi Ninomiya's "Tamamushi-gata hikouki"("Jewel beetle type flyer") in 1893 is the earliest known biplane.[88]
- Landing gear
- Chūhachi Ninomiya's "Karasu-gata mokei hikouki" ("Crow-type model aircraft") in 1891 had three wheels as landing gear. [citation needed]
- Pusher propeller
- Invented by Chūhachi Ninomiya in 1891 as part of his "Karasu-gata mokei hikouki" ("Crow-type model aircraft"). The four-blade pusher propeller, inspired from a bamboo-copter, was driven by a rubber band. His "Tamamushi-gata hikouki"("Jewel beetle type flyer") in 1893 was also equipped with a four-blade pusher propeller. [citation needed]
- Stabilizer
- Chūhachi Ninomiya's "Karasu-gata mokei hikouki" ("Crow-type model aircraft") in 1891 was the earliest to be equipped with a horizontal stabilizer at its tail and a vertical stabilizer at its nose. [citation needed]
- Tailless aircraft
- Chūhachi Ninomiya's "Tamamushi-gata hikouki"("Jewel beetle type flyer") in 1893 is the earliest known tailless aircraft.[88]
Calculators
- Credit-card-sized calculator
- The first credit-card-sized calculator was the Casio Mini Card LC-78, of 1978, which could run for months of normal use on button cells. [citation needed]
- Electric compact calculator
- The Casio Computer Co., in Japan, released the Model 14-A calculator in 1957, which was the world's first all-electric compact calculator. [citation needed]
- Graphing calculator
- The first graphing calculator was the Casio fx-7000G, released in 1985. Many more Casio graphic calculators have been released since then. [citation needed]
- Pocket calculator
- The first portable calculators appeared in Japan in 1970, and were soon marketed around the world. These included the Sanyo ICC-0081 "Mini Calculator", the Canon Pocketronic, and the Sharp QT-8B "micro Compet". Sharp put in great efforts in size and power reduction and introduced in January 1971 the Sharp EL-8, also marketed as the Facit 1111, which was close to being a pocket calculator. It weighed about one pound, had a vacuum fluorescent display, and rechargeable NiCad batteries. The first truly pocket-sized electronic calculator was the Busicom LE-120A "HANDY", which was marketed early in 1971.[89] Made in Japan, this was the first calculator to use an LED display, the first hand-held calculator to use a single integrated circuit (then proclaimed as a "calculator on a chip"), and the first electronic calculator to run off replaceable batteries. Using four AA-size cells, the LE-120A measures 4.9x2.8x0.9 in (124x72x24 mm). [citation needed]
- Solar-powered calculator
- With low power consumption came the possibility of using solar cells as the power source, realised around 1978 by the Sharp EL-8026. [citation needed]
Cameras
- Camcorder
- In 1982, Sony released the first professional camcorder, named the Betacam. [citation needed]
- Digital camera
- The first true digital camera that recorded images as a computerized file was the Fuji DS-1P, in 1988. It recorded to a 16 MB internal memory card that used a battery to keep the data in memory. [citation needed]
- Digital single-lens reflex camera
- On August 25, 1981 Sony unveiled a prototype of the first still video camera, the Sony Mavica. This camera was an analog electronic camera that featured interchangeable lenses and a SLR viewfinder. At Photokina in 1986, Nikon revealed a prototype analog electronic still SLR camera, the Nikon SVC, the first digital SLR. The prototype body shared many features with the N8008.[90] In 1999, Nikon announced the Nikon D1, the first DSLR to truly compete with, and begin to replace, film cameras in the professional photojournalism and sports photography fields. This camera was able to use current autofocus Nikkor lenses available at that time for the Nikon film series cameras, and was also able to utilize the older Nikon and similar, independent mount lenses designed for those cameras. A combination of price, speed, and image quality was the beginning of the end of 35 mm film for these markets. [citation needed]
- Handheld electronic camera
- Handheld electronic cameras, in the sense of a device meant to be carried and used like a handheld film camera, appeared in 1981 with the demonstration of the Sony Mavica (Magnetic Video Camera). This was an analog camera, in that it recorded pixel signals continuously, as videotape machines did, without converting them to discrete levels; it recorded television-like signals to a 2 × 2 inch Video Floppy. Analog electronic cameras do not appear to have reached the market until 1986 with the Canon RC-701. Canon demonstrated a prototype of this model at the 1984 Summer Olympics, printing the images in the Yomiuri Shimbun, a Japanese newspaper. [citation needed]
Chindogu
Chindogu is the Japanese art of inventing ingenious everyday gadgets that, on the face of it, seem like an ideal solution to a particular problem. However, Chindogu has a distinctive feature: anyone actually attempting to use one of these inventions would find that it causes so many new problems, or such significant social embarrassment, that effectively it has no utility whatsoever. Thus, Chindōgu are sometimes described as "unuseless" – that is, they cannot be regarded as 'useless' in an absolute sense, since they do actually solve a problem; however, in practical terms, they cannot positively be called "useful." The term "Chindogu" was coined by Kenji Kawakami. Examples of Chindogu include:
- a combined household duster and cocktail-shaker, for the housewife who wants to reward herself as she's going along; [citation needed]
- the all-day tissue dispenser, which is basically a toilet roll fixed on top of a hat, for hay fever sufferers; [citation needed]
- duster slippers for cats, so they can help out with the housework; [citation needed]
- the all-over plastic bathing costume, to enable people who suffer from aquaphobia to swim without coming into contact with water. [citation needed]
Domestic appliances
- Electric rice cooker
- Invented by designers at the Mitsubishi Electric Corporation in the late 1940s.[91]
- RFIQin
- An automatic cooking device, invented by Mamoru Imura and patented in 2007.[92][93]
Electronics
- Blue laser
- Following the research of Professor Isamu Akasaki's group, the first commercially viable blue laser was invented by Shuji Nakamura while working at Nichia Corporation. [citation needed]
- Glass integrated circuit
- Shunpei Yamazaki invented an integrated circuit made entirely from glass and with an 8-bit central processing unit.[81]
- Indium gallium nitride
- Indium gallium nitride (InGaN) is a semiconductor invented by Shuji Nakamura. [citation needed]
- Microprocessor
- The world's first microprocessor, the Intel 4004, was designed by Masatoshi Shima of Busicom alongside Marcian Hoff and Federico Faggin. [citation needed]
- Personal digital assistant
- The first PDA is considered to be the Casio PF-3000 released in May 1983. [citation needed]
- Plastic central processing unit
- Shunpei Yamazaki invented a central processing unit made entirely from plastic.[81]
- Videocassette recorder
- The first machines (the VP-1100 videocassette player and the VO-1700 videocassette recorder) to use the first videocassette format, U-matic, was introduced by Sony in 1971.[94]
Game controllers
- Analog stick
- In 1996, Nintendo introduced the first analog thumbstick on the Nintendo 64 controller. Since then, all major video game console controllers have included analog sticks. [citation needed]
- D-pad
- In 1982, Nintendo's Gunpei Yokoi elaborated on the idea of a circular pad, shrinking it and altering the points into the familiar modern "cross" design for control of on-screen characters in their Donkey Kong handheld game. It came to be known as the "D-pad".[95] The design proved to be popular for subsequent Game & Watch titles. This particular design was patented. In 1984, the Japanese company Epoch created a handheld game system called the Epoch Game Pocket Computer. It featured a D-pad, but it was not popular for its time and soon faded. Initially intended to be a compact controller for the Game & Watch handheld games alongside the prior non-connected style pad, Nintendo realized that Gunpei's design would also be appropriate for regular consoles, and Nintendo made the D-pad the standard directional control for the hugely successful Nintendo Entertainment System under the name "+Control Pad". All major video game consoles since have had a D-pad of some shape on their controllers. [citation needed]
- Dance pad
- The first dance pad was the Power Pad, a floor mat game controller for the Nintendo Entertainment System. It is a gray mat with twelve pressure-sensors embedded between two layers of flexible plastic. It was originally developed by Bandai. [citation needed]
- Force feedback
- Introduced for game controllers by Nintendo's Rumble Pak, for the Nintendo 64 controller. [citation needed]
- Motion-sensing controller
- Invented by Nintendo for the Wii, the Wii Remote is the first controller with motion-sensing capability. It was a candidate for Time's Best Invention of 2006.[96]
Metallurgy
- Alnico
- Alnico magnets were developed from the MKM steel invented by Tokuhichi Mishima. [citation needed]
- KS steel
- Kotaro Honda invented the KS steel (initials from Kichiei Sumitomo), which is a type of magnetic resistant steel that is three times more resistant than tungsten steel. [citation needed]
- Magnetic steel
- Kotaro Honda invented the KS steel, a type of magnetic resistant steel that is three times more resistant than tungsten steel. In 1931, Tokuhichi Mishima discovered that a strongly magnetic steel could be created by adding aluminum to non-magnetic nickel steel. [citation needed]
- MKM steel
- An alloy containing nickel and aluminum, it was invented in 1931 by the Japanese metallurgist Tokuhichi Mishima. While conducting research into the properties of nickel, Mishima discovered that a strongly magnetic steel could be created by adding aluminum to non-magnetic nickel steel. [citation needed]
Robotics
- Android
- The world's first android, DER 01, was developed by a Japanese research group, The Intelligent Robotics Lab, directed by Hiroshi Ishiguro at Osaka University, and Kokoro Co., Ltd. The Actroid is a humanoid robot with strong visual human-likeness developed by Osaka University and manufactured by Kokoro Company Ltd. (the animatronics division of Sanrio). It was first unveiled at the 2003 International Robot Exposition in Tokyo, Japan. The Actroid woman is a pioneer example of a real machine similar to imagined machines called by the science fiction terms android or gynoid, so far used only for fictional robots. It can mimic such lifelike functions as blinking, speaking, and breathing. The "Repliee" models are interactive robots with the ability to recognise and process speech and respond in kind.[97][98][99]
- Hybrid assistive limb
- The HAL 5 is the first hybrid assistive limb, a powered exoskeleton suit currently in development by Tsukuba University of Japan.[100]
- Landmine-clearing robot
- Shigeo Hirose is involved in work with the United Nations to develop a remotely controlled robot capable of clearing landmines.[101]
- Ninja robot
- Invented by Shigeo Hirose, it is capable of climbing buildings and a seven-ton robot capable of climbing mountainous slopes with the aim of installing bolts in the ground so as to prevent landslides.[102]
Storage technology
- Blu-ray Disc
- After Shuji Nakamura's invention of practical blue laser diodes,[103] Sony started two projects applying the new diodes: UDO (Ultra Density Optical) and DVR Blue (together with Pioneer), a format of rewritable discs which would eventually become the Blu-ray Disc.[104]
- Compact Disc
- Sony first publicly demonstrated an optical digital audio disc in September 1976. In September 1978, they demonstrated an optical digital audio disc with a 150 minute playing time, and with specifications of 44,056 Hz sampling rate, 16-bit linear resolution, cross-interleaved error correction code, that were similar to those of the Compact Disc they introduced in 1982.[105]
- Digital Audio Tape
- A signal recording and playback medium developed by Sony in the mid 1980s. [citation needed]
- DVD
- The DVD optical disc format was developed by Sony alongside Philips. [citation needed]
- Flash memory
- Flash memory (both NOR and NAND types) was invented by Dr. Fujio Masuoka while working for Toshiba circa 1980.[106][107] According to Toshiba, the name "flash" was suggested by Dr. Masuoka's colleague, Mr. Shoji Ariizumi, because the erasure process of the memory contents reminded him of a flash of a camera. Dr. Masuoka presented the invention at the IEEE 1984 International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) held in San Francisco, California. [citation needed]
- Floppy disk
- A Japanese inventor, Yoshiro Nakamatsu, invented the core floppy disk technology and, in 1952, registered a Japanese patent for his [1]. He later licensed 16 patents to IBM for the creation of the floppy disk. [citation needed]
- Heat-assisted magnetic recording
- HAMR was developed by Fujitsu in 2006 so that it could achieve one terabit per square inch densities.[108]
- Memory card
- The first flash memory card to be released was the JEIDA memory card by the Japan Electronic Industries Development Association. [citation needed]
- Perpendicular recording
- A technology for data recording on hard disks. It was first proven advantageous in 1976 by Shun-ichi Iwasaki, then professor of Tohoku University in Japan, and first commercially implemented in 2005. [citation needed]
- Video cassette
- In 1969, Sony introduced a prototype for the first video cassette, the 3/4" (1.905 cm) composite U-matic system, which Sony introduced commercially in September 1971 after working out industry standards with other manufacturers. Sony later refined it to Broadcast Video U-matic or BVU. [citation needed]
- Video Floppy
- A video storage medium in the form of a 2" magnetic floppy disk used to store still frames of analog composite video. Video floppies were first developed by Sony in 1981 for their Mavica and later used by Panasonic and Canon for their still video cameras introduced in the late 1980s, such as the Canon Xapshot from 1988. [citation needed]
Timekeeping

- Quartz wristwatch
- The world's first quartz wristwatch was revealed in 1967: the prototype of the Astron revealed by Seiko in Japan, where it was in development since 1958. It was eventually released to the public in 1969.[109] The inherent accuracy and low cost of production has resulted in the proliferation of quartz clocks and watches since that time. By the 1980s quartz technology had taken over applications such as kitchen timers, alarm clocks, bank vault time locks, and time fuzes on munitions, from earlier mechanical balance wheel movements. [citation needed]
- Quartz chronograph
- Invented by Seiko in the 1970s. [citation needed]
Transport
- Bullet train
- The world's first high volume capable (initially 12 car maximum) "high-speed train" was Japan's Tōkaidō Shinkansen, that officially opened in October 1964, with construction commencing in April 1959.[110] The 0 Series Shinkansen, built by Kawasaki Heavy Industries, achieved maximum passenger service speeds of 210 km/h (130 mph) on the Tokyo–Nagoya–Kyoto–Osaka route, with earlier test runs hitting top speeds in 1963 at 256 km/h.[110]
- Dedicated high-speed rail lines
- Japan was the first country to build dedicated railway lines for high speed travel. Because of the mountainous terrain, the existing network consisted of 42 narrow gauge lines, which generally took indirect routes and could not be adapted to higher speeds. Consequently, Japan had a greater need for new high speed lines than countries where the existing standard gauge or broad gauge rail system had more upgrade potential. [citation needed]
- Electronically-controlled continuously variable transmission
- In early 1987, Subaru launched the Justy in Tokyo with an electronically-controlled continuously variable transmission (ECVT) developed by Fuji Heavy Industries, which owns Subaru.[111]
- Kei car
- A category of small automobiles, including passenger cars, vans, and pickup trucks. They are designed to exploit local tax and insurance relaxations, and in more rural areas are exempted from the requirement to certify that adequate parking is available for the vehicle.[112][113] These standards originated in the times following the end of the Second World War, when most Japanese could not afford a full-sized car yet had enough to buy a motorcycle. To promote the growth of the car industry, as well as to offer an alternative delivery method to small business and shop owners, kei car standards were created. [citation needed]
Visual display units
- Aperture grille
- The first patented aperture grille televisions were manufactured by Sony in the late 1960s under the Trinitron brand name, which the company carried over to its line of CRT computer monitors. Subsequent designs, either licensed from Sony or manufactured after the patent's expiration, tend to use the -tron suffix, such as Mitsubishi's DiamondTron and ViewSonic's SonicTron. Today, Trinitron displays are still produced for markets such as Bangladesh, China, India and Pakistan. [citation needed]
- Flat panel display
- The first flat-panel displays were the flat CRTs[114][115] used by Sony in their Watchman series (the FD-210 was introduced in 1982). One of the last flat-CRT models was the FD-120A. The CRT in these units was flat with the electron gun located roughly at right angles below the display surface thus requiring sophisticated electronics to create an undistorted picture free from effects such as keystoning. [citation needed]
- Handheld colour television
- In 1990, a color model of the Sony Watchman with an active-matrix LCD was released. [citation needed]
- Handheld liquid crystal display television
- In 1990, a color model of the Sony Watchman with an active-matrix LCD was released. [citation needed]
- Liquid crystal display television
- In 1988, Sharp Corporation introduced the first commercial LCD television, a 14" model. [citation needed]
- Mechanical television
- In the 1920s, the Japanese electrical scientist Yasujiro Niwa invented a simple device for phototelegraphic transmission through cable and later via radio, a precursor to mechanical television. [citation needed]
- Plasma colour display
- In 1992, Fujitsu introduced the world's first full-color plasma display. It was a hybrid, based upon the plasma display created at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and NHK STRL, achieving superior brightness. [citation needed]
- Plasma television
- In 1997, Pioneer released the first plasma television. [citation needed]
- Pocket television
- In 1982, Sony released the first television that could fit in a pocket: the Watchman; a pun on Walkman. [citation needed]
Weapons
- Fire balloon
- A fire balloon, or balloon bomb, was an experimental weapon launched by Japan from 1944 to 1945, during World War II. [citation needed]
- Katana
- The katana originated in the Muromachi period (1392–1573) as a result of changing battle conditions requiring faster response times. The katana facilitated this by being worn with the blade facing up, which allowed the samurai to draw and cut their enemy in a single motion. Previously, the curved sword of the samurai was worn with the blade facing down. The ability to draw and cut in one motion also became increasingly useful in the daily life of the samurai.[116]
- Shuriken
- The earliest known mention of a school teaching shuriken-jutsu is Ganritsu Ryu, prevalent during the 1600s. There are also earlier mentions in written records, such as the Osaka Gunki (The Military Records of Osaka), of the standard knife and short sword being thrown in battle, and Miyamoto Musashi is said to have won a duel by throwing his short sword at his opponent, killing him. [citation needed]
Wireless transmission
- Directional antenna
- The first directional or beam antenna was the Yagi antenna, invented by Hidetsugu Yagi and Shintaro Uda in 1926. [citation needed]
- High-gain antenna
- The first high-gain antenna was also the Yagi antenna in 1926. [citation needed]
- Yagi antenna
- The Yagi-Uda antenna was invented in 1926 by Shintaro Uda of Tohoku Imperial University, Sendai, Japan, with the collaboration of Hidetsugu Yagi, also of Tohoku Imperial University. Yagi published the first English-language reference on the antenna in a 1928 survey article on short wave research in Japan and it came to be associated with his name. However, Yagi always acknowledged Uda's principal contribution to the design, and the proper name for the antenna is, as above, the Yagi-Uda antenna (or array).[citation needed]
References
- ^ Moving Image program notes for Yojimbo
- ^ Mark Gilson, "A Brief History of Japanese Robophilia", Leonardo 31 (5), p. 367–369 [368].
- ^ a b "Unprecedented level of game service operation' from Steampunk MMORPG Neo Steam". June 29, 2008. Retrieved 2009-06-13.
- ^ a b Anthony Nield (2005-09-26). "Nausicaä of the Valley of the Wind". DVD Times. Retrieved 2009-06-13.
- ^ Person, Lawrence (2006-01-15). "Ghost in the Shell: Stand Alone Complex". Locus Online. Retrieved 2008-02-07.
- ^ James Kendrick. "Rashomon". Q Network. Retrieved 2009-06-15.
- ^ "the news and media magazine of the British Science Fiction Association". Matrix Online. 2008-06-30. Retrieved 2009-02-13.
- ^ Cynthia Ward (20 August 2003). "Hayao Miyazaki: The Greatest Fantasy Director You Never Heard Of?". Retrieved 2009-06-13.
- ^ Natalie Avella, Graphic Japan: From Woodblock and Zen to Manga and Kawaii, Rotovision, 2004, p111. ISBN 2880467713
- ^ Richardson, Matthew (2001), The Halstead Treasury of Ancient Science Fiction, Rushcutters Bay, New South Wales: Halstead Press, ISBN 1875684646 (cf. "Once Upon a Time", Emerald City (85), September 2002, retrieved 2008-09-17)
- ^ Tyler, Royall (2003), The Tale of Genji, Penguin Classics, p. xxvi, ISBN 014243714X
- ^ Tyler, Royall (2003), The Tale of Genji, Penguin Classics, pp. i-ii & xii, ISBN 014243714X
- ^ Jorge Luis Borges, The Total Library:
[The Tale of Genji, as translated by Arthur Waley,] is written with an almost miraculous naturalness, and what interests us is not the exoticism — the horrible word — but rather the human passions of the novel. Such interest is just: Murasaki's work is what one would quite precisely call a psychological novel. ... I dare to recommend this book to those who read me. The English translation that has inspired this brief insufficient note is called The Tale of Genji.
- ^ Yorke, Christopher (February 2006), "Malchronia: Cryonics and Bionics as Primitive Weapons in the War on Time", Journal of Evolution and Technology, 15 (1): 73–85, retrieved 2009-08-29
- ^ Bishop, Mark (1989). Okinawan Karate. p. 154. ISBN 0-7136-5666-2. Motobu-ryū & Seikichi Uehara
- ^ Higaonna, Morio (1985). Traditional Karatedo Vol. 1 Fundamental Techniques. p. 19. ISBN 0-87040-595-0.
- ^ Hayes, Stephen. “The Ninja and Their Secret Fighting Art.” ISBN 0804816565, Tuttle Publishing, 1990: 18-21
- ^ msisshinryu.com | Okinawan Masters
- ^ msisshinryu.com | History of Karate
- ^ "GameSpy's 30 Most Influential People in Gaming". GameSpy. Retrieved 2007-04-01.
- ^ "Final Fantasy Retrospective Part XIII". GameTrailers. 2007-11-02. Retrieved 2009-03-30.
- ^ a b Andrew Vestal (1998-11-02). "The History of Final Fantasy - Final Fantasy IV". GameSpot. Retrieved 2008-12-31.
- ^ US patent 5390937, Hironobu Sakaguchi and Hiroyuki Itou, "Video game apparatus, method and device for controlling same", issued 1995-02-21
- ^ a b Spencer, Spanner, The Tao of Beat-'em-ups, Eurogamer, Feb 6, 2008, Accessed Mar 18, 2009
- ^ Kunkel, Bill; Worley, Joyce; Katz, Arnie, "The Furious Fists of Sega!", Computer Gaming World, Oct 1988, pp. 48-49
- ^ Spencer, Spanner, The Tao of Beat-'em-ups (part 2), EuroGamer, Feb 12, 2008, Accessed Mar 18, 2009
- ^ Evolution of a Genre: Beat 'Em Ups, ABC Television, Nov 6, 2007, Accessed March 24, 2009
- ^ Ashcraft, p. 94.
- ^ a b Ryan Geddes & Daemon Hatfield (2007-12-10). "IGN's Top 10 Most Influential Games". IGN. Retrieved 2009-04-14.
- ^ Hjul, Alison (1986-03). "Yie Ar Kung Fu" (3). Your Sinclair: 19.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "The History of Street Fighter". GameSpot. Retrieved 2008-10-11.
- ^ Stahl, Ted (July 26, 2006). "Chronology of the History of Video Games: Golden Age". Retrieved 2009-07-06.
- ^ a b Wheatley, Sean (2003-05-15). "Namco". TNL. Retrieved 2006-11-23.
- ^ a b "Namco History Vol 4". Anime Densetsu. Retrieved 2006-11-24.
{{cite web}}:|first=missing|last=(help) - ^ Crawford, Chris (2003). Chris Crawford on Game Design. New Riders. ISBN 0-88134-117-7.
- ^ "Donkey Kong". Arcade History. 2006-11-21. Retrieved 2006-11-21.
- ^ Chris Zimbaldi, Dr. Konkle (April 30, 2004). "Metal Gear Solid 2: Sons of Liberty as a Post-Modern Tragedy". metalgearsolid.org. Archived from the original on 2008-09-20. Retrieved 2007-02-21.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|year=/|date=mismatch (help); Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ Rogers, Tim (2004). "Dreaming in an Empty Room: A Defense of Metal Gear Solid 2". insert credit. Retrieved 30 January 2007.
{{cite web}}: External link in|work=|dateformat=ignored (help) - ^ Richard J. Hand (2004). "Proliferating Horrors: Survival Horror and the Resident Evil Franchise". In Steffen Hantke (ed.). Horror Film. Univ. Press of Mississippi.
{{cite book}}: Text "page 117-134" ignored (help) - ^ Baldric (1999-03-01). "Game Revolution Review Page - Game Revolution". Game Revolution. Retrieved 2009-04-17.
- ^ "Gametrailers.com - GT Countdown - Top Ten Scariest Games". GameTrailers. 2007-10-27. Retrieved 2009-04-17.
- ^ Jim Sterling (2008-06-09). "Fear 101: A Beginner's Guide to Survival Horror". IGN. Retrieved 2009-04-17.
- ^ Clara Barraza (2008-09-01). "The Evolution of the Survival Horror Genre". IGN. Retrieved 2009-04-17.
- ^ "Best Survival Horror Games - Fatal Frame". UGO Networks. Retrieved 2009-04-17.
- ^ Block, Gerry, NES Power Pad Rocking Rhythm-Action Play, IGN, July 7, 2008, Accessed Apr 10, 2009
- ^ "ジャンプバグ レトロゲームしま専科". Retrieved 2008-06-18.
- ^ "KLOV: Jungle King". KLOV. Retrieved 2007-02-08.
- ^ "Pac-Land". Arcade History. Retrieved 2006-11-21.
- ^ a b Game Genres: Shmups, Professor Jim Whitehead, January 29, 2007, Accessed June 17, 2008
- ^ a b Buchanan, Levi, Space Invaders, IGN, March 31, 2003, Accessed June 14, 2008
- ^ Ashcraft pp. 72–73
- ^ Design your own Space Invaders, Science.ie, 4 March 2008, Accessed 17 June 2008
- ^ Buchanan, Levi, Galaxian Mini, IGN, April 21, 2003, Accessed June 17, 2008
- ^ "005 from Sega". Popularplay. Retrieved 2009-08-20.
- ^ List of Japanese inventions and discoveries at the Killer List of Videogames
- ^ 005, Arcade History
- ^ Steampunk genre in video games including Thief: The Dark Project
- ^ Justin Speer and Cliff O'Neill. ""The History of Resident Evil"". GameSpot. Retrieved 2009-04-17.
- ^ "Enter The Survival Horror... A Resident Evil Retrospective," Game Informer 174 (October 2007): 132-133.
- ^ "Top 11 Survival Horror Games: Sweet Home". UGO Networks. 2008-05-21. Retrieved 2009-04-17.
- ^ Womack, James P. (1990). The Machine That Changed the World.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Holweg, Matthias (2007). "The genealogy of lean production". Journal of Operations Management. 25 (2): 420–437.
- ^ Goffeau, André (2005). "Multiple moulds". Nature. 438 (7071): 1092–1093. doi:10.1038/4381092b. PMID 16371993.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|quotes=and|coauthors=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Machida, Masayuki; et al. (2005). "Genome sequencing and analysis of Aspergillus oryzae". Nature. 438: 1157–1161. doi:10.1038/nature04300. PMID 16372010.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|quotes=and|coauthors=(help); Explicit use of et al. in:|first=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Yamashima T (2003). "Jokichi Takamine (1854–1922), the samurai chemist, and his work on adrenalin". J Med Biogr. 11 (2): 95–102. PMID 12717538.
- ^ Bennett M (1999). "One hundred years of adrenaline: the discovery of autoreceptors". Clin Auton Res. 9 (3): 145–59. doi:10.1007/BF02281628. PMID 10454061.
- ^ Takamine J (1901). The isolation of the active principle of the suprarenal gland. Great Britain: Cambridge University Press. pp. xxix–xxx.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ Nagai N. (1893). "Kanyaku maou seibun kenkyuu seiseki (zoku)". Yakugaku Zashi. 13: 901.
{{cite journal}}: line feed character in|journal=at position 9 (help) - ^ Mahan LK, Escott-Stump S, editors. Krause's food, nutrition, & diet therapy. 10th ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company; 2000
- ^ Tokyo Kagaku Kaishi (1911)
- ^ Funk, C. and H. E. Dubin. The Vitamines. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins Company, 1922.
- ^ History of Property Rights - Ikeda, Kikunae
- ^ Ikeda K (2002). "New seasonings". Chem. Senses. 27 (9): 847–9. doi:10.1093/chemse/27.9.847. PMID 12438213.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) (partial translation of Ikeda, Kikunae (1909). "New Seasonings[japan.]". Journal of the Chemical Society of Tokyo. 30: 820–836.) - ^ Selin, Helaine. (1997), An Introduction to the History of Mathematics. Saunders College Publishing. p. 891, ISBN 0030295580
- ^ Poole, David. (2005), Linear algebra: a modern introductio. p. 279, ISBN 0534998453 .
- ^ a b Styan, George P. H.; Trenkler, Götz. (2007), . Journal of Applied Mathematics and Decision Sciences, 2007, Hindawi Publishing Corporation, pp. 2
- ^ a b c d Howard Eves: "An Introduction to the History of Mathematics", page 405, Saunders College Publishing, 1990. (ISBN 0030295580)
- ^ Association of American Geographers (1911). Annals of the Association of American Geographers, Vol. I, p. 35
- ^ "Non-Stop Shuttle Change Toyoda Automatic Loom, Type G" (in Japanese). The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
- ^ http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfRL/Listing.cfm?ID=71537
- ^ a b c "Top US Patent Holder is Legendary Japanese Inventor Shunpei Yamazaki". Impact Lab. February 26, 2006. Retrieved 2009-06-13.
- ^ Japan Patent Office , Kyota Sugimoto (Japanese Typewriter), 28th January 2009.
- ^ "CDP-101 The first Compact Disc Audio CD Player from 1982". 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-05.
- ^ Le Heron, Richard B.; Harrington, James W. (2005), New Economic Spaces: New Economic Geographies, Ashgate Publishing, p. 41, ISBN 0754644502
- ^ Three Yamaha products that reshaped the industry mark 20th anniversary, Music Trades, February 2004, pp. 70–74
- ^ Aikin, Jim (2003), Software Synthesizers: The Definitive Guide to Virtual Musical Instruments, Backbeat Books, p. 4, ISBN 0879307528
- ^ "Sony Celebrates Walkman 20th Anniversary". Sony Press Release. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ^ a b 根本智『パイオニア飛行機物語』(オーム社、1996年、ISBN 4-274-0231401)、p66
- ^ "The one-chip calculator is here, and it's only the beginning", Electronic Design, February 18, 1971, p34.
- ^ Nikon SLR-type digital cameras, Pierre Jarleton
- ^ Toshiba Firsts of Their Kind: Automatic Electric Rice Cooker
- ^ "Mamoru Imura Patent Inventor Overland Park, KS". FreshPatents.com. Retrieved 2006-12-24.
{{cite web}}: External link in|publisher= - ^ "United States Patent 7157675". United States Patent and Trademark Office. Retrieved 2007-01-03.
- ^ Sony sold 15,000 U-matic machines in the U.S. in its first year. "Television on a Disk," Time, Sep. 18, 1972.
- ^ Buchanan, Levi (2008-09-08). "From Janitor to Superstar Gunpei Yokoi, inventor of the Game Boy, would have been 67 this week". IGN. Retrieved 2008-12-28.
- ^ Lev Grossman (2006). "Best Inventions". Time. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ MacDorman, Karl F. (2006). "The uncanny advantage of using androids in social and cognitive science research" (pdf). Interaction Studies. 7 (3): 297–337. ISSN 1572–0373. Retrieved 2008-05-25.
{{cite journal}}: Check|issn=value (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Christensen, Bill (2005-06-28). "New robot looks strikingly human". LiveScience. Retrieved 2008-05-25.
- ^ Whitehouse, David (2005-07-12). "Japanese develop 'female' android". BBC News. Retrieved 2008-05-25.
- ^ Faster, Better, Stronger: HAL Robot Exoskeletons Available for Rent", Elain Chow, Gizmodo, 7 October 2008. Retrieved 7 October 2008
- ^ Technology for the front lines: robotic scientists and engineers come up with novel ways to slow the spread of landmines, Upfront, Japan Inc., BNET.com
- ^ Robot menagerie, Landslide danger, BBC News
- ^ Martyn Williams (2002-08-12). "Opening the Door for New Storage Options". pcworld.com. Retrieved 2007-10-18.
- ^ S.B. Luitjens (2001-06-15). "Blue laser bolsters DTV storage, features". planetanalog.com. Retrieved 2007-10-19.
- ^ "A Long Play Digital Audio Disc System". AES. Retrieved 2009-02-14.
- ^ Fulford, Benjamin (24 June 2002). "Unsung hero". Forbes. Retrieved 2008-03-18.
- ^ US 4531203 Fujio Masuoka
- ^ http://www.tgdaily.com/content/view/30024/135/
- ^ "Electronic Quartz Wristwatch, 1969". IEEE History Center. Retrieved 2007-08-31.
- ^ a b Shinkansen Chronology, byun byun Shinkansen.
- ^ Poulton, M.L. (1997). Fuel Efficient Car Technology. Computational Mechanics Publications. p. 69. ISBN 1853124478.
- ^ "Minicars: Cheap and Cheerful", Peter Nunn, JAMA, January-February 2005
- ^ "Owning a Car in Japan", ALTs in Sendai
- ^ http://www.taschenfernseher.de/bilder/sony-flat.jpg
- ^ http://www.ebeaminc.com/images/cap02.jpg
- ^ Nagayama, Kokan (1997). The Connoisseur's Book of Japanese Swords. Tokyo, Japan: Kodansha International Ltd. p. 28. ISBN 4-7700-2071-6.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)

