Mobile operating system: Difference between revisions
Ryanking16 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Ryanking16 (talk | contribs) →Discontinued software platforms: Arranged |
||
| Line 394: | Line 394: | ||
* BlackBerry 10.3 – major UI revamp |
* BlackBerry 10.3 – major UI revamp |
||
* BlackBerry 10.3.3 |
* BlackBerry 10.3.3 |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | [[Firefox OS]]<ref>{{cite web |url=https://wiki.mozilla.org/B2G |title=B2G – MozillaWiki |publisher=mozilla.org |date=2011-08-24 |accessdate=2011-09-07}}</ref> is from [[Mozilla]]. It was an open source mobile operating system released under the [[Mozilla Public License]] built on the Android Linux kernel and used Android drivers, but did not use any Java-like code of Android. |
||
| ⚫ | According to [[Ars Technica]], "Mozilla says that B2G is motivated by a desire to demonstrate that the standards-based open Web has the potential to be a competitive alternative to the existing single-vendor application development stacks offered by the dominant mobile operating systems."<ref>{{cite web |last=Paul |first=Ryan |url= http://arstechnica.com/open-source/news/2011/07/mozilla-eyes-mobile-os-landscape-with-new-boot-to-gecko-project.ars |title=Mozilla eyes mobile OS landscape with new Boot to Gecko project |publisher=Arstechnica.com |date=2011-07-25 |accessdate=2011-09-07}}</ref> In September 2016, Mozilla announced that work on Firefox OS has ceased, and all B2G-related code would be removed from mozilla-central.<ref>{{Cite web |title= B2G OS and Gecko Annoucement from Ari Jaaksi & David Bryant |url= https://groups.google.com/forum/#!msg/mozilla.dev.fxos/FoAwifahNPY/Lppm0VHVBAAJ |accessdate= September 27, 2016 |date= September 27, 2016}}</ref> |
||
===BlackBerry OS=== |
|||
{{main article|BlackBerry OS}} |
|||
In 1999, [[Research In Motion|RIM]] released its first BlackBerry devices, providing secure real-time push-email communications on wireless devices. Services such as BlackBerry Messenger provide the integration of all communications into a single inbox. In September 2012, RIM announced that the 200 millionth BlackBerry smartphone was shipped. As of September 2014, there were around 46 million active BlackBerry service subscribers.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Arthur |first1=Charles |title=Ten things to know about BlackBerry -- and how much trouble it is (or isn't) in |url=https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2014/sep/29/ten-things-to-know-blackberry-john-chen |website=TheGuardian.com |publisher=The Guardian|date=September 29, 2014 |accessdate=April 19, 2015}}</ref> In early 2010s, RIM has undergone a platform transition, changing its company name to [[BlackBerry Limited]] and making new devices on a new platform named "[[BlackBerry 10]]".<ref name="Kevin McLaughlin"/> |
|||
===Windows Mobile=== |
===Windows Mobile=== |
||
| Line 401: | Line 410: | ||
Windows Mobile's market share sharply declined to only 5% in Q2 of 2010.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.appleinsider.com/articles/10/09/16/iphone_drops_to_23_8_smartphone_market_share_android_jumps_to_17.html |title=iPhone drops to 24% smartphone share, Android jumps to 17% |publisher=AppleInsider |date=2010-09-16 |accessdate=2011-09-07}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://en.yeeply.com/professionals/windows-phone |title=Windows Phone developers |website=Yeeply Windows Phone}}</ref> Microsoft phased out the Windows Mobile OS to focus on Windows Phone. |
Windows Mobile's market share sharply declined to only 5% in Q2 of 2010.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.appleinsider.com/articles/10/09/16/iphone_drops_to_23_8_smartphone_market_share_android_jumps_to_17.html |title=iPhone drops to 24% smartphone share, Android jumps to 17% |publisher=AppleInsider |date=2010-09-16 |accessdate=2011-09-07}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://en.yeeply.com/professionals/windows-phone |title=Windows Phone developers |website=Yeeply Windows Phone}}</ref> Microsoft phased out the Windows Mobile OS to focus on Windows Phone. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | [[Firefox OS]]<ref>{{cite web |url=https://wiki.mozilla.org/B2G |title=B2G – MozillaWiki |publisher=mozilla.org |date=2011-08-24 |accessdate=2011-09-07}}</ref> is from [[Mozilla]]. It was an open source mobile operating system released under the [[Mozilla Public License]] built on the Android Linux kernel and used Android drivers, but did not use any Java-like code of Android. |
||
| ⚫ | According to [[Ars Technica]], "Mozilla says that B2G is motivated by a desire to demonstrate that the standards-based open Web has the potential to be a competitive alternative to the existing single-vendor application development stacks offered by the dominant mobile operating systems."<ref>{{cite web |last=Paul |first=Ryan |url= http://arstechnica.com/open-source/news/2011/07/mozilla-eyes-mobile-os-landscape-with-new-boot-to-gecko-project.ars |title=Mozilla eyes mobile OS landscape with new Boot to Gecko project |publisher=Arstechnica.com |date=2011-07-25 |accessdate=2011-09-07}}</ref> In September 2016, Mozilla announced that work on Firefox OS has ceased, and all B2G-related code would be removed from mozilla-central.<ref>{{Cite web |title= B2G OS and Gecko Annoucement from Ari Jaaksi & David Bryant |url= https://groups.google.com/forum/#!msg/mozilla.dev.fxos/FoAwifahNPY/Lppm0VHVBAAJ |accessdate= September 27, 2016 |date= September 27, 2016}}</ref> |
||
===Symbian=== |
===Symbian=== |
||
| Line 414: | Line 418: | ||
On 25 February 2013, Samsung announced that it will stop developing Bada, moving development to [[Tizen]] instead.Bug reporting was finally terminated in April 2014.<ref>[http://www.fiercemobilecontent.com/story/samsung-scraps-bada-os-folds-it-tizen/2013-02-25 Samsung scraps Bada OS, folds it into Tizen - FierceMobileIT]. Fiercemobilecontent.com (2013-02-25). Retrieved on 2013-12-09.</ref> |
On 25 February 2013, Samsung announced that it will stop developing Bada, moving development to [[Tizen]] instead.Bug reporting was finally terminated in April 2014.<ref>[http://www.fiercemobilecontent.com/story/samsung-scraps-bada-os-folds-it-tizen/2013-02-25 Samsung scraps Bada OS, folds it into Tizen - FierceMobileIT]. Fiercemobilecontent.com (2013-02-25). Retrieved on 2013-12-09.</ref> |
||
=== |
===webOS=== |
||
| ⚫ | [[webOS]] was developed by [[Palm, Inc.|Palm]], although some parts are open source. webOS is a proprietary mobile operating system running on the Linux kernel, initially developed by Palm, which launched with the [[Palm Pre]]. After being acquired by HP, two phones (the [[HP Veer|Veer]] and the [[HP Pre 3|Pre 3]]) and a tablet (the [[HP TouchPad|TouchPad]]) running webOS were introduced in 2011. On August 18, 2011, HP announced that webOS hardware would be discontinued,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.hp.com/hpinfo/newsroom/press/2011/110818b.html?mtxs=rss-corp-news |title=HP Confirms Discussions with Autonomy Corporation plc Regarding Possible Business Combination; Makes Other Announcements |publisher=HP |date=2010-08-18 |accessdate=2011-09-13}}</ref> but would continue to support and update webOS software and develop the webOS ecosystem.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://developer.palm.com/blog/2011/08/the-next-chapter-for-webos/ |title=The next chapter for webOS |publisher=HP webOS Developer Blog |date=2010-08-19 |accessdate=2011-09-13}}</ref> HP released webOS as open source under the name Open webOS, and plans to update it with additional features.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.openwebosproject.org/discover/roadmap/#.UIgNYMXA-So |title=Open webOS::Roadmap |publisher=Open webOS Project |date=September 2012 |accessdate=2012-10-24}}</ref> On February 25, 2013 HP announced the sale of WebOS to [[LG Electronics]], who used the operating system for its "smart" or Internet-connected TVs. However, HP retained patents underlying WebOS and cloud-based services such as the App Catalog. |
||
The Nokia X platform was developed by [[Nokia]] Corporation and later on maintained by [[Microsoft Mobile]]. It was a project which is based on the open source [[Android (operating system)|Android]] Open Source Project (AOSP), but replaced all the Google Services and Apps with Nokia and Microsoft apps. Its overall UI mimics the Windows Phone UI. |
|||
===Palm OS=== |
===Palm OS=== |
||
[[Palm OS]]/Garnet OS was from [[Access Co.]] It is closed source and proprietary. [[webOS]] was introduced by Palm in January 2009 as the successor to Palm OS with Web 2.0 technologies, open architecture and multitasking abilities. |
[[Palm OS]]/Garnet OS was from [[Access Co.]] It is closed source and proprietary. [[webOS]] was introduced by Palm in January 2009 as the successor to Palm OS with Web 2.0 technologies, open architecture and multitasking abilities. |
||
=== |
===MeeGo/Maemo/Moblin === |
||
{{main article|MeeGo|Maemo|Moblin}} |
|||
| ⚫ | [[webOS]] was developed by [[Palm, Inc.|Palm]], although some parts are open source. webOS is a proprietary mobile operating system running on the Linux kernel, initially developed by Palm, which launched with the [[Palm Pre]]. After being acquired by HP, two phones (the [[HP Veer|Veer]] and the [[HP Pre 3|Pre 3]]) and a tablet (the [[HP TouchPad|TouchPad]]) running webOS were introduced in 2011. On August 18, 2011, HP announced that webOS hardware would be discontinued,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.hp.com/hpinfo/newsroom/press/2011/110818b.html?mtxs=rss-corp-news |title=HP Confirms Discussions with Autonomy Corporation plc Regarding Possible Business Combination; Makes Other Announcements |publisher=HP |date=2010-08-18 |accessdate=2011-09-13}}</ref> but would continue to support and update webOS software and develop the webOS ecosystem.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://developer.palm.com/blog/2011/08/the-next-chapter-for-webos/ |title=The next chapter for webOS |publisher=HP webOS Developer Blog |date=2010-08-19 |accessdate=2011-09-13}}</ref> HP released webOS as open source under the name Open webOS, and plans to update it with additional features.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.openwebosproject.org/discover/roadmap/#.UIgNYMXA-So |title=Open webOS::Roadmap |publisher=Open webOS Project |date=September 2012 |accessdate=2012-10-24}}</ref> On February 25, 2013 HP announced the sale of WebOS to [[LG Electronics]], who used the operating system for its "smart" or Internet-connected TVs. However, HP retained patents underlying WebOS and cloud-based services such as the App Catalog. |
||
===Maemo=== |
|||
[[Maemo]] was a platform developed by Nokia for [[smartphone]]s and [[Internet tablet]]s. It is open source and GPL, based on [[Debian GNU/Linux]] and draws much of its [[graphical user interface]] (GUI), [[Software framework|frameworks]], and [[Library (computing)|libraries]] from the GNOME project. It uses the [[Matchbox (window manager)|Matchbox]] window manager and the [[GTK]]-based [[Hildon]] as its GUI and [[application framework]]. |
|||
| ⚫ | [[MeeGo (operating system)|MeeGo]] was from non-profit organization [[The Linux Foundation]]. It is open source and GPL. At the 2010 [[Mobile World Congress]] in Barcelona, [[Nokia]] and [[Intel]] both unveiled ''MeeGo'', a mobile operating system that combined [[Moblin]] and Maemo to create an open-sourced experience for users across all devices. In 2011 Nokia announced that it would no longer pursue MeeGo in favor of Windows Phone. Nokia announced the [[Nokia N9]] on June 21, 2011 at the Nokia Connection event<ref>{{cite web|url=http://conversations.nokia.com/2011/06/21/introducing-the-nokia-n9-all-it-takes-is-a-swipe/ |title=Introducing the Nokia N9: all it takes is a swipe! | Nokia Conversations – The official Nokia Blog |publisher=Nokia |date=2011-06-21 |accessdate=2011-09-07}}</ref> in Singapore. LG announced its support for the platform.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://gigaom.com/mobile/meego-not-dead-yet-as-lg-continues-the-charge/ |title=MeeGo Not Dead Yet as LG Continues the Charge — Mobile Technology News |publisher=Gigaom.com |date=2011-04-29 |accessdate=2011-09-07}}</ref> [[Maemo]] was a platform developed by Nokia for [[smartphone]]s and [[Internet tablet]]s. It is open source and GPL, based on [[Debian GNU/Linux]] and draws much of its [[graphical user interface]] (GUI), [[Software framework|frameworks]], and [[Library (computing)|libraries]] from the GNOME project. It uses the [[Matchbox (window manager)|Matchbox]] window manager and the [[GTK]]-based [[Hildon]] as its GUI and [[application framework]]. |
||
===MeeGo=== |
|||
| ⚫ | [[MeeGo (operating system)|MeeGo]] was from non-profit organization [[The Linux Foundation]]. It is open source and GPL. At the 2010 [[Mobile World Congress]] in Barcelona, [[Nokia]] and [[Intel]] both unveiled ''MeeGo'', a mobile operating system that combined [[Moblin]] and Maemo to create an open-sourced experience for users across all devices. In 2011 Nokia announced that it would no longer pursue MeeGo in favor of Windows Phone. Nokia announced the [[Nokia N9]] on June 21, 2011 at the Nokia Connection event<ref>{{cite web|url=http://conversations.nokia.com/2011/06/21/introducing-the-nokia-n9-all-it-takes-is-a-swipe/ |title=Introducing the Nokia N9: all it takes is a swipe! | Nokia Conversations – The official Nokia Blog |publisher=Nokia |date=2011-06-21 |accessdate=2011-09-07}}</ref> in Singapore. LG announced its support for the platform.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://gigaom.com/mobile/meego-not-dead-yet-as-lg-continues-the-charge/ |title=MeeGo Not Dead Yet as LG Continues the Charge — Mobile Technology News |publisher=Gigaom.com |date=2011-04-29 |accessdate=2011-09-07}}</ref> |
||
===LiMo=== |
===LiMo=== |
||
Revision as of 07:50, 10 January 2017
A mobile operating system (or mobile OS) is an operating system for smartphones, tablets, personal digital assistants (PDAs), or other mobile devices. While computers such as typical laptops are mobile, the operating systems usually used on them are not considered mobile ones, as they were originally designed for desktop computers that historically did not have or need specific mobile features. This distinction is becoming blurred in some newer operating systems that are hybrids made for both uses. So-called mobile operating systems, or even only smartphones running them, now represent most (web) use (on weekends and averaged for whole weeks). Mobile operating systems, are now, as of late 2016, the most used kind, with traditional desktop OS, now a minority use kind; see crossover to mobile more popular. However, variations occur in popularity by regions, while desktop-minority also applies on some days in e.g., the US and UK.
Mobile operating systems combine features of a personal computer operating system with other features useful for mobile or handheld use; usually including, and most of the following considered essential in modern mobile systems; a touchscreen, cellular, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Global Positioning System (GPS) mobile navigation, camera, video camera, speech recognition, voice recorder, music player, near field communication, and infrared blaster.
Mobile devices with mobile communications abilities (e.g., smartphones) contain two mobile operating systems – the main user-facing software platform is supplemented by a second low-level proprietary real-time operating system which operates the radio and other hardware. Research has shown that these low-level systems may contain a range of security vulnerabilities permitting malicious base stations to gain high levels of control over the mobile device.[1]
Timeline
Mobile operating system milestones mirror the development of mobile phones and smartphones:
Pre-1993
- 1973–1993 – Mobile phones use embedded systems to control operation.
1993–1999
- 1994 – The first smartphone, the IBM Simon, has a touchscreen, email, and PDA features.
- 1996
- Palm Pilot 1000 personal digital assistant is introduced with the Palm OS mobile operating system.
- First Windows CE Handheld PC devices are introduced.
- 1999 – Nokia S40 Platform is introduced officially along with the Nokia 7110.
2000s
- 2000 – Symbian becomes the first modern mobile OS on a smartphone with the launch of the Ericsson R380.
- 2001 – The Kyocera 6035 is the first smartphone with Palm OS.
- 2002
- Microsoft's first Windows CE (Pocket PC) smartphones are introduced.
- BlackBerry releases its first smartphone.
- 2005 – Nokia introduces Maemo OS on the first Internet tablet N770.
- 2007
- 2008 – OHA releases Android (based on Linux kernel) 1.0 with the HTC Dream (T-Mobile G1) as the first Android phone.
- 2009 –
2010s
2010
- November – Windows Phone OS phones are released but are not compatible with the prior Windows Mobile OS.
2011
- July – MeeGo, a mobile Linux distribution, combining Maemo and Moblin, is introduced with the Nokia N9, a collaboration of Nokia, Intel, and Linux Foundation.
- September – Samsung, Intel, and the Linux Foundation announced that their efforts will shift from Bada, MeeGo to Tizen during 2011 and 2012.
- October – The Mer project was announced, based on an ultra-portable core for building products, composed of Linux, HTML5, QML, and JavaScript, which was derived from the MeeGo codebase.
2012
- July – Mozilla announced that the project formerly named Boot to Gecko (which was built atop an Android Linux kernel using Android drivers and services; however it used no Java-like code of Android) was now Firefox OS and had several handset OEMs on board.
- September – Apple releases iOS 6.
2013
- January – BlackBerry releases their new operating system for smartphones, BlackBerry 10.
- September – Apple releases iOS 7.
- October
- Canonical announced Ubuntu Touch, a version of the Linux distribution expressly designed for smartphones. The OS is built on the Android Linux kernel, using Android drivers and services, but does not use any of the Java-like code of Android.[4]
- Google releases Android KitKat 4.4.
2014
- February – Microsoft releases Windows Phone 8.1
- September
- Apple releases iOS 8
- BlackBerry release BlackBerry 10.3 with integration with the Amazon Appstore
- November – Google releases Android 5.0 "Lollipop"
2015
- February – Google releases Android 5.1 Lollipop.
- September
- Apple releases iOS 9.
- Google releases Android 6.0 Marshmallow.
- November – Microsoft releases Windows 10 Mobile.
2016
- June – Apple announced iOS 10.
- August – Google released Android 7.0 "Nougat".[5]
- September – Apple releases iOS 10.
- November - Tizen releases Tizen 3.0.
Current software platforms
These operating systems often run atop baseband or other real time operating systems that handle hardware aspects of the phone.
Android
Android (based on the Linux kernel) is an mobile operating system developed by Google Inc.[6] Besides having the largest installed base worldwide on smartphones, it is also the most popular operating system for general purpose computers (a category that includes desktop computers and mobile devices), even though Android is not a popular operating system for regular (desktop) personal computers (PCs). Although the Android operating system is free and open-source software,[7] in devices sold, much of the software bundled with it (including Google apps and vendor-installed software) is proprietary software and closed source.[8]
Android's releases before 2.0 (1.0, 1.5, 1.6) were used exclusively on mobile phones. Android 2.x releases were mostly used for mobile phones but also some tablets. Android 3.0 was a tablet-oriented release and does not officially run on mobile phones. While both phone and tablet compatibility was merged to Android 4.0. The current Android version is 7.1 Nougat.
Android's releases are named after sweets or dessert items, except for the first and second releases:
- 1.0 – (API Level 1)
- 1.1 – Alpha: (API Level 2)
- 1.2 – Beta
- 1.5 – Cupcake: (API Level 3)
- 1.6 – Donut: (API Level 4)
- 2.0 – Eclair: (API Level 5)
- 2.0.1 – Eclair: (API Level 6)
- 2.1 – Eclair: (API Level 7)
- 2.2.x – Frozen Yogurt ("Froyo"): (API Level 8)
- 2.3 – Gingerbread (minor UI tweak): (API Level 9)
- 2.3.3 – Gingerbread: (API Level 10)
- 3.0 – Honeycomb (major UI revamp): (API Level 11)
- 3.1 – Honeycomb: (API Level 12)
- 3.2 – Honeycomb: (API Level 13)
- 4.0 – Ice Cream Sandwich (minor UI tweak): (API Level 14)
- 4.0.3 – Ice Cream Sandwich: (API Level 15)
- 4.1 – Jelly Bean: (API Level 16)
- 4.2 – Jelly Bean: (API Level 17)
- 4.3 – Jelly Bean: (API Level 18)
- 4.4.4 – KitKat: (API Level 19)
- 5.0, 5.0.1, 5.0.2 – Lollipop (major UI revamp): (API Level 21)
- 5.1, 5.1.1 – Lollipop: (API Level 22)
- 6.0 & 6.0.1 – Marshmallow: (API Level 23)
- 7.0 – Nougat (API Level 24)[9]
AOKP
Android Open Kang Project (AOKP) is a custom ROM based on the Android Open Source Project (AOSP). Similar to CyanogenMod, AOKP allows Android users who can no longer obtain update support from their manufacturer to continue updating their Android version to the latest one based on official release from Google AOSP and heavy theme customization together with customizable system functions.
Current AOKP version list
- AOKP – based on Android Ice Cream Sandwich 4.0.x
- AOKP – based on Android Jelly Bean 4.1.x – 4.3.x
- AOKP – based on Android KitKat 4.4.x
ColorOS
ColorOS is a custom front-end touch interface, based on the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) and is developed by OPPO Electronics Corp. As of 2016[update], OPPO officially releases ColorOS with every OPPO device, and released an official ROM for the OnePlus One.
Current ColorOS version list
- ColorOS 1.0 (based on Android "Jelly Bean" 4.1.x – 4.3.x) (initial release)
- ColorOS 2.0 (based on Android "KitKat" 4.4.x) (minor UI upgrade)
- ColorOS 2.1 (based on Android "Lollipop" 5.0.x – 5.1.x) (minor UI upgrade)
- ColorOS 3.0 (based on Android "Marshmallow") (major UI revamp)
CyanogenMod
CyanogenMod is a custom mobile operating system based on the Android Open Source Project (AOSP). It is a custom ROM that was codeveloped by the CyanogenMod community. The OS does not include any proprietary apps unless the user installs them. Due to its open source nature, CyanogenMod allows Android users who can no longer obtain update support from their manufacturer to continue updating their OS version to the latest one based on official release from Google AOSP and heavy theme customization. The current version of the OS is CyanogenMod 13 which is based on Android Marshmallow.
Current CyanogenMod version list
- CyanogenMod 3 (based on Android "Cupcake" 1.5.x, initial release)
- CyanogenMod 4 (based on Android "Cupcake" and "Donut" 1.5.x and 1.6.x)
- CyanogenMod 5 (based on Android "Eclair" 2.0/2.1)
- CyanogenMod 6 (based on Android "Froyo" 2.2.x)
- CyanogenMod 7 (based on Android "Gingerbread" 2.3.x)
- CyanogenMod 9 (based on Android "Ice Cream Sandwich" 4.0.x, major UI revamp)
- CyanogenMod 10 (based on Android "Jelly Bean" 4.1.x – 4.3.x)
- CyanogenMod 11 (based on Android "KitKat" 4.4.x)
- CyanogenMod 12 (based on Android "Lollipop" 5.0.x – 5.1.x, major UI revamp)
- CyanogenMod 13 (based on Android "Marshmallow" 6.0.x)
- CyanogenMod 14 (based on Android "Nougat" 7.x.x, discontinued)[10]
Cyanogen OS
Cyanogen OS is based on CyanogenMod and maintained by Cyanogen Inc, however it includes proprietary apps and it is only available for commercial uses.
Current Cyanogen OS version list
- Cyanogen OS 11s (based on Android "KitKat" 4.4.x, initial release)
- Cyanogen OS 12 (based on Android "Lollipop" 5.0.x, major UI revamp)
- Cyanogen OS 12.1 (based on android "Lollipop" 5.1.x)
- Cyanogen OS 13 (based on Android "Marshmallow" 6.0.x)[11]
EMUI
Emotion User Interface (EMUI) is a front-end touch interface developed by Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd. and is based on Google's Android Open Source Project (AOSP). EMUI is preinstalled on most Huawei and Honor devices.
Current EMUI version list
- EMUI 1.x (based on Android 4.0.x "Ice Cream Sandwich" and "Jelly Bean" 4.1.x-4.3.x) (initial release)
- EMUI 2.x (based on Android "Ice Cream Sandwich" 4.0.x, "Jelly Bean" 4.1.x-4.3.x and "KitKat" 4.4.x) (minor UI tweak)
- EMUI 3.x (based on Android "KitKat" 4.4.x and "Lollipop" 5.x) (minor UI tweak)
- EMUI 4.x (based on Android "Marshmallow" 6.x)
- EMUI 5.x (based on Android "Nougat" 7.x)
Flyme OS
Flyme OS is an operating system developed by Meizu Technology Co., Ltd., an open source OS based on Google Android Open Source Project (AOSP). Flyme OS is mainly installed on Meizu Smartphones such as the MX's series, however it also has official ROM support for a few Android devices.
Current Flyme OS version list
- Flyme OS 1.x.x (based on Android "Ice Cream Sandwich" 4.0.3, initial release)
- Flyme OS 2.x.x (based on Android "Jelly Bean" 4.1.x – 4.2.x)
- Flyme OS 3.x.x (based on Android "Jelly Bean" 4.3.x)
- Flyme OS 4.x.x (based on Android "KitKat" 4.4.x)
- Flyme OS 5.x.x (based on Android "Lollipop" 5.0.x – 5.1.x)
HTC Sense
HTC Sense is a software suite developed by HTC, used primarily on the company's Android-based devices. Serving as a successor to HTC's TouchFLO 3D software for Windows Mobile, Sense modifies many aspects of the Android user experience, incorporating added features (such as an altered home screen and keyboard), widgets, HTC-developed applications, and redesigned applications. The first device with Sense, the HTC Hero, was released in 2009.
- HTC Sense 1.x (based on Android "Eclair" 2.0/2.1, initial release)
- HTC Sense 2.x (based on Android "Eclair", "Froyo" and "Gingerbread" 2.0/2.1, 2.2.x and 2.3.x, redesigned UI)
- HTC Sense 3.x (based on Android "Gingerbread" 2.3.x, redesigned UI)
- HTC Sense 4.x (based on Android "Ice Cream Sandwich" and "Jelly Bean" 4.0.x and 4.1.x, redesigned UI)
- HTC Sense 5.x (based on Android "Jelly Bean" 4.1.x – 4.3.x, redesigned UI)
- HTC Sense 6.x (based on Android "KitKat" 4.4.x, redesigned UI)
- HTC Sense 7.x (based on Android "Lollipop" 5.0.x, redesigned UI)
- HTC Sense 8.x (based on Android "Marshmallow" 6.0.x, redesigned UI)
LineageOS
Lineage Android Distribution is a custom mobile operating system based on the Android Open Source Project (AOSP). It serves as the successor to the highly popular custom ROM, CyanogenMod, from which it was forked in December 2016 when Cyanogen Inc. announced it was discontinuing development and shut down the infrastructure behind the project. Since Cyanogen Inc. retained the rights to the Cyanogen name, the project rebranded its fork as LineageOS.
Similar to CyanogenMod, it does not include any proprietary apps unless the user installs them. It allows Android users who can no longer obtain update support from their manufacturer to continue updating their OS version to the latest one based on official release from Google AOSP and heavy theme customization.
Current LineageOS version list
Due to LineageOS being recently forked, the project is currently engaged in setting up its infrastructure and has not yet released any new code.
MIUI
Mi User Interface (MIUI), developed by the Chinese electronic company Xiaomi Inc., is a mobile operating system based on the Android Open Source Project (AOSP). MIUI is mostly found in Xiaomi smartphones such as the Mi and Redmi Series, however it also has official ROM support for few Android devices. Although MIUI is based on AOSP, which is open source, it consists of closed source and proprietary software of its own.
Current MIUI version list
- MIUI V1 – based on Android Froyo 2.2.x, initial release
- MIUI V2 – based on Android Froyo 2.2.x, redesigned UI
- MIUI V3 – based on Android Gingerbread 2.3.x, redesigned UI
- MIUI V4 – based on Android Ice Cream Sandwich 4.0.x and Jelly Bean 4.1.x, redesigned UI
- MIUI V5 – based on Android Jelly Bean 4.1-4.3 and "KitKat" 4.4, redesigned UI
- MIUI V6 – based on Android KitKat 4.4 and Lollipop 5.0.x, redesigned UI
- MIUI 7 – based on Android KitKat 4.4, Lollipop 5.x and Marshmallow 6.x.
- MIUI 8 – based on Android KitKat 4.4, Lollipop 5.x and Marshmallow 6.x.
LG UX
LG UX (formerly named Optimus UI) is a front-end touch interface developed by LG Electronics with partners, featuring a full touch user interface. It is sometimes incorrectly identified as an operating system. LG UX is used internally by LG for sophisticated feature phones and tablet computers, and is not available for licensing by external parties.
Optimus UI 2 which based on Android 4.1.2 has been released on the Optimus K II and the Optimus Neo 3. It features a more refined user interface compared to the prior version based on Android 4.1.1, would include together which new functionality such as voice shutter and quick memo.
Current LG UX version list
- Optimus UI 1.x – based on Android Gingerbread 2.3.x, initial release
- Optimus UI 2.x – based on Android Ice Cream Sandwich and Jelly Bean 4.0.x and 4.1.x – 4.3.x, redesigned UI
- LG UX 3.x – based on Android KitKat and Lollipop 4.4.x and 5.0.x, redesigned UI
- LG UX 4.x – based on Android Lollipop 5.1.x and Marshmallow 5.1.x and 6.0.x, redesigned UI
OxygenOS
OxygenOS is based on the open source Android Open Source Project (AOSP) and is developed by OnePlus to replace Cyanogen OS on OnePlus devices such as the OnePlus One, and it is preinstalled on the OnePlus 2, OnePlus 3, and OnePlus X.[12] As stated by Oneplus, OxygenOS is focused on stabilizing and maintaining of stock like those found on Nexus devices. It consists of mainly Google apps and minor UI customization to maintain the sleekness of pure Android.
Current OxygenOS version list
- Oxygen OS 1.0.X (based on Android 5.0.x "Lollipop") (initial release)
- Oxygen OS 2.0.X (based on Android 5.1.x "Lollipop") (overall maintenance update)
- Oxygen OS 3.0.X (based on Android 6.0 "Marshmallow") (major Android update)
- Oxygen OS 3.1.X (based on Android 6.0.1 "Marshmallow") (minor maintenance update)
- Oxygen OS 3.2.x (based on Android 7.x "Nougat") (major Android update)
TouchWiz
TouchWiz is a front-end touch interface developed by Samsung Electronics with partners, featuring a full touch user interface. It is sometimes incorrectly identified as an independent operating system. TouchWiz is used internally by Samsung for smartphones, feature phones and tablet computers, and is not available for licensing by external parties. The Android version of TouchWiz also comes with Samsung-made apps preloaded (except starting with the Galaxy S6 which have removed all Samsung pre-loaded apps installed, leaving one with Galaxy Apps, to save storage space and initially due to the removal of MicroSD).
Current TouchWiz version list:
- TouchWiz 3.0 & 3.0 Lite – based on Android Eclair and Froyo 2.0/2.1 and 2.2.x, initial release
- TouchWiz 4.0 – based on Android Gingerbread and Ice Cream Sandwich 2.3.x and 4.0.x, redesigned UI
- TouchWiz Nature UX "1.0" and Lite – based on Android Ice Cream Sandwich and Jelly Bean 4.0.x and 4.1.x, redesigned UI
- TouchWiz Nature UX 2.x – based on Android Jelly Bean and KitKat 4.2.x – 4.3.x and 4.4.x, redesigned UI
- TouchWiz Nature UX 3.x – based on Android KitKat and Lollipop 4.4.x and 5.0.x, redesigned UI
- TouchWiz Nature UX 5.x – based on Android Lollipop 5.0.x – 5.1.x, redesigned UI
- TouchWiz Grace UX - based on Android "Marshmallow" 6.x, redesigned UI
ZenUI
ZenUI is a front-end touch interface developed by ASUS with partners, featuring a full touch user interface. ZenUI is used by Asus for its Android phones and tablet computers, and is not available for licensing by external parties. ZenUI also comes preloaded with Asus-made apps like ZenLink (PC Link, Share Link, Party Link & Remote Link).
iOS
iOS (formerly named iPhone OS) is from Apple Inc. It has the second largest installed base worldwide on smartphones, but the largest profits, due to aggressive price competition between Android-based manufacturers.[13] It is closed source and proprietary and built on open source Darwin core OS. The Apple iPhone, iPod Touch, iPad and second-generation Apple TV all use iOS, which is derived from macOS.
Native third party applications were not officially supported until the release of iPhone OS 2.0 on July 11, 2008. Before this, "jailbreaking" allowed third party applications to be installed, and this method is still available.
Currently all iOS devices are developed by Apple and manufactured by Foxconn or another of Apple's partners.
Current iOS version list:
- iPhone OS 1.x
- iPhone OS 2.x
- iPhone OS 3.x
- iOS 4.x
- iOS 5.x
- iOS 6.x
- iOS 7.x (major UI revamp)
- iOS 8.x
- iOS 9.x
- iOS 10.x
Windows 10 Mobile
Windows 10 Mobile (formerly called Windows Phone) is from Microsoft. It is closed source and proprietary. It has the third largest installed base on smartphones behind Android and iOS.
Unveiled on February 15, 2010, Windows Phone includes a user interface inspired by Microsoft's Metro Design Language. It is integrated with Microsoft services such as OneDrive and Office, Xbox Music, Xbox Video, Xbox Live games and Bing, but also integrates with many other non-Microsoft services such as Facebook and Google accounts. Windows Phone devices are made primarily by Microsoft Mobile/Nokia, and also by HTC and Samsung.
On 21 January 2015, Microsoft announced that the Windows Phone brand will be phased out and replaced with Windows 10 Mobile, bringing tighter integration and unification with its PC counterpart Windows 10, and provide a platform for smartphones and tablets with screen sizes under 8 inches.
As of 2016, Windows 10 Mobile global market share dropped below 0.6%.[14]
Current Windows Phone version list:
- Windows Phone 7
- Windows Phone 7.5
- Windows Phone 7.8 – minor UI tweak
- Windows Phone 8 – GDR1, GDR2 & GDR3, & minor UI tweak
- Windows Phone 8.1 – GDR1 & GDR2, & minor UI tweak
- Windows 10 Mobile
Sailfish OS
Sailfish OS is from Jolla. It is partly open source and adopts GNU General Public License (GPL) for core and middleware. However, the user interface is proprietary software (closed source).
After Nokia abandoned in 2011 the MeeGo project, most of the MeeGo team left Nokia, and established Jolla as a company to use MeeGo and Mer business opportunities. The MER standard allows it to be launched on any hardware with kernel compatible with MER. In 2012, Linux Sailfish OS based on MeeGo and using middleware of MER core stack distribution was launched for public use. The first device, the Jolla smartphone, was unveiled on 20 May 2013. In 2015, Jolla Tablet was launched and the BRICS countries declared it an officially supported OS there. Jolla started licensing Sailfish OS 2.0 for 3rd parties. Some devices sold are updateable to Sailfish 2.0 with no limits.
Each Sailfish OS version release is named after a Finnish lake:
| Version | Update | Lake name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0.0.5 | – | Kaajanlampi | |
| 1.0.1.1x | 1 | Laadunjärvi | |
| 1.0.2.5 | 2 | Maadajävri | |
| 1.0.3.8 | 3 | Naamankajärvi | |
| 1.0.4.20 | 4 | Ohijärvi | |
| 1.0.5.1x | 5 | Paarlamp | |
| 1.0.7.16 | 7 | Saapunki | |
| 1.0.8.19 | 8 | Tahkalampi | |
| 1.1.0.3x | 9 | Uitukka | |
| 1.1.1.2x | 10 | Vaarainjärvi | |
| 1.1.2.1x | 11 | Yliaavanlampi | |
| 1.1.4.28 | 13 | Äijänpäivänjärvi | |
| 1.1.6.27 | 15 | Aaslakkajärvi | |
| 1.1.7.24 | 16 | Björnträsket | |
| 1.1.9.28 | 17 | Eineheminlampi | Pretransition to version 2.0; major UI revamp |
| 2.0.0.10 | 18 | Saimaa | Full transition to version 2.0; minor UI and function improvements |
Tizen
Tizen is hosted by the Linux Foundation and support from the Tizen Association, guided by a Technical Steering Group composed of Intel and Samsung.
Tizen is an operating system for devices including smartphones, tablets, in-vehicle infotainment (IVI) devices, and smart TVs. It is an open source system (however the SDK was closed source and proprietary) that aims to offer a consistent user experience across devices. Tizen's main components are the Linux kernel and the WebKit runtime. According to Intel, Tizen "combines the best of LiMo and MeeGo." HTML5 apps are emphasized, with MeeGo encouraging its members to transition to Tizen, stating that the "future belongs to HTML5-based applications, outside of a relatively small percentage of apps, and we are firmly convinced that our investment needs to shift toward HTML5." Tizen will be targeted at a variety of platforms such as handsets, touch pc, smart TVs and in-vehicle entertainment.[15][16] On May 17, 2013, Tizen released version 2.1, code-named Nectarine.[17]
Currently, Tizen is the fourth largest Mobile OS in terms of market share. Tizen has the second-largest market share in the budget segment of smartphones in India as of Q4 2015.
Current Tizen version list:
- 1.0 (Larkspur)
- 2.0 (Magnolia)
- 2.1 (Nectarine)
- 2.2.x
- 2.3.x
- 2.4.x (minor UI tweaks)
- 3.0 (under development)
Ubuntu Touch OS
Ubuntu Touch OS is from Canonical Ltd.. It is open source and uses the GPL license.[17] The OS is built on the Android Linux kernel, using Android drivers and services via an LXC container, but does not use any of the Java-like code of Android.[18]
Current Ubuntu Touch version list:
- Preview Version (initial release)
- OTA 2.x
- OTA 3.x
- OTA 4.x
- OTA 5.x
- OTA 6.x
- OTA 7.x
- OTA 8.x
- OTA 9.x
- OTA 10.x
- OTA 11.x
- OTA 12.x
- OTA 13.x
H5OS
H5OS is from Acadine Technologies. The OS is based on Firefox OS.
Current H5OS version list:
- v1.0 (initial release)
Discontinued software platforms
BlackBerry 10
BlackBerry 10 (based on the QNX OS) was from BlackBerry. As a smart phone OS, it was closed source and proprietary, and only ran on phones and tablets manufactured by Blackberry.
One of the dominant platforms in the world in late 2000's, its global market share was reduced significantly by 2016. Also in late 2016, Blackberry announced that it will no longer release BlackBerry 10 devices, but will only support them.[19][20]
Current BlackBerry 10 version list:
- BlackBerry 10.0
- BlackBerry 10.1
- BlackBerry 10.2
- BlackBerry 10.3 – major UI revamp
- BlackBerry 10.3.3
Firefox OS
Firefox OS[21] is from Mozilla. It was an open source mobile operating system released under the Mozilla Public License built on the Android Linux kernel and used Android drivers, but did not use any Java-like code of Android.
According to Ars Technica, "Mozilla says that B2G is motivated by a desire to demonstrate that the standards-based open Web has the potential to be a competitive alternative to the existing single-vendor application development stacks offered by the dominant mobile operating systems."[22] In September 2016, Mozilla announced that work on Firefox OS has ceased, and all B2G-related code would be removed from mozilla-central.[23]
BlackBerry OS
In 1999, RIM released its first BlackBerry devices, providing secure real-time push-email communications on wireless devices. Services such as BlackBerry Messenger provide the integration of all communications into a single inbox. In September 2012, RIM announced that the 200 millionth BlackBerry smartphone was shipped. As of September 2014, there were around 46 million active BlackBerry service subscribers.[24] In early 2010s, RIM has undergone a platform transition, changing its company name to BlackBerry Limited and making new devices on a new platform named "BlackBerry 10".[25]
Windows Mobile
Windows Mobile is a discontinued operating system from Microsoft that it replaced with Windows Phone.[6][26] It is closed source and proprietary.
The Windows CE operating system and Windows Mobile middleware was widely spread in Asia (which mostly uses Android now). The two improved variants of this operating system, Windows Mobile 6 Professional (for touch screen devices) and Windows Mobile 6 Standard, were unveiled in February 2007. It was criticized for having a user interface which is not optimized for touch input by fingers; instead, it is more usable with a stylus. Like iOS, and most other Mobile OS, it supports both touch screen, physical and Bluetooth keyboard configurations.
Windows Mobile's market share sharply declined to only 5% in Q2 of 2010.[27][28] Microsoft phased out the Windows Mobile OS to focus on Windows Phone.
Symbian
The Symbian platform was developed by Nokia for some models of smartphones. It is proprietary software. The operating system was discontinued in 2012, although a slimmed-down version for basic phones was still developed until July 2014. Microsoft officially shelved the platform in favor of Windows Phone after its acquisition of Nokia.[29]
Bada
Bada platform (stylized as bada; Korean: 바다) was an operating system for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers. It was developed by Samsung Electronics. Its name is derived from "바다 (bada)", meaning "ocean" or "sea" in Korean. It ranges from mid- to high-end smartphones. To foster adoption of Bada OS, since 2011 Samsung reportedly has considered releasing the source code under an open-source license, and expanding device support to include Smart TVs. Samsung announced in June 2012 intentions to merge Bada into the Tizen project, but would meanwhile use its own Bada operating system, in parallel with Google Android OS and Microsoft Windows Phone, for its smartphones. All Bada-powered devices are branded under the Wave name, but not all of Samsung's Android-powered devices are branded under the name Galaxy. On 25 February 2013, Samsung announced that it will stop developing Bada, moving development to Tizen instead.Bug reporting was finally terminated in April 2014.[30]
webOS
webOS was developed by Palm, although some parts are open source. webOS is a proprietary mobile operating system running on the Linux kernel, initially developed by Palm, which launched with the Palm Pre. After being acquired by HP, two phones (the Veer and the Pre 3) and a tablet (the TouchPad) running webOS were introduced in 2011. On August 18, 2011, HP announced that webOS hardware would be discontinued,[31] but would continue to support and update webOS software and develop the webOS ecosystem.[32] HP released webOS as open source under the name Open webOS, and plans to update it with additional features.[33] On February 25, 2013 HP announced the sale of WebOS to LG Electronics, who used the operating system for its "smart" or Internet-connected TVs. However, HP retained patents underlying WebOS and cloud-based services such as the App Catalog.
Palm OS
Palm OS/Garnet OS was from Access Co. It is closed source and proprietary. webOS was introduced by Palm in January 2009 as the successor to Palm OS with Web 2.0 technologies, open architecture and multitasking abilities.
MeeGo/Maemo/Moblin
MeeGo was from non-profit organization The Linux Foundation. It is open source and GPL. At the 2010 Mobile World Congress in Barcelona, Nokia and Intel both unveiled MeeGo, a mobile operating system that combined Moblin and Maemo to create an open-sourced experience for users across all devices. In 2011 Nokia announced that it would no longer pursue MeeGo in favor of Windows Phone. Nokia announced the Nokia N9 on June 21, 2011 at the Nokia Connection event[34] in Singapore. LG announced its support for the platform.[35] Maemo was a platform developed by Nokia for smartphones and Internet tablets. It is open source and GPL, based on Debian GNU/Linux and draws much of its graphical user interface (GUI), frameworks, and libraries from the GNOME project. It uses the Matchbox window manager and the GTK-based Hildon as its GUI and application framework.
LiMo
LiMo was from the LiMo Foundation. They launched LiMo 4 on February 14, 2011. It delivers middleware and application functionality, including a flexible user interface, extended widget libraries, 3D window effects, advanced multimedia, social networking, and location-based service frameworks, sensor frameworks, multi-tasking and multitouch abilities. Also, support for scalable screen resolution and consistent APIs means that the platform can deliver a consistent user experience across multiple device types and form factors.[36]
Market share
In 2006, Android, iOS, and Windows Phone did not exist and only 64 million smartphones were sold.[37] In 2016 Q3, 363.2 million smartphones were sold and global market share was 86.8% for Android, 12.5% for iOS, 0.3% for Windows 10 Mobile and 0.4% for all other platforms.[38]
Crossover to mobile more popular
According to StatCounter web use statistics (a proxy for all use), in the week from 7–13 November 2016, "mobile" (meaning smartphones) alone (without tablets) overtook desktop, for the first time.[39] Mobile-majority applies to countries such as Paraguay in South America, Poland in Europe and Turkey; and most of Asia and Africa. The rest of the world is still desktop-majority, with it e.g. in the United States at 54.89% (but no not on all days).[40] On 22 October 2016 (and subsequent weekends), mobile has shown majority,[41] Since 27 October, the desktop hasn't shown majority, not even on weekdays.
Formerly, according to StatCounter press release, the world has turned desktop-minority;[42] as of October 2016[update], at about 49% desktop use for that month, but mobile wasn't ranked higher, tablet share had to be added to it to exceed desktop share.
World-wide share or shipments
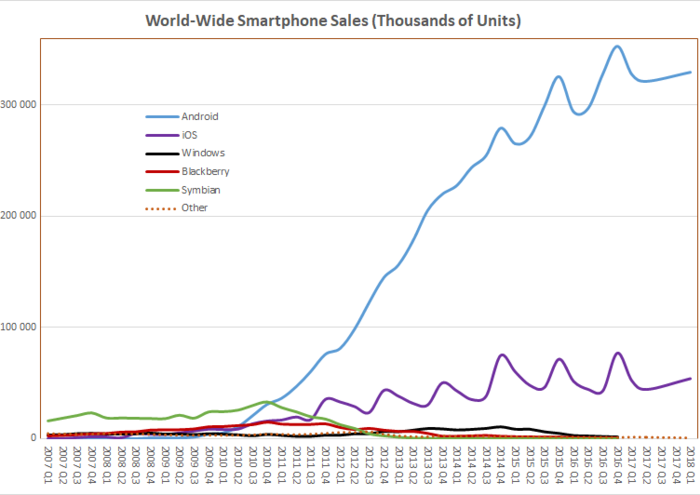
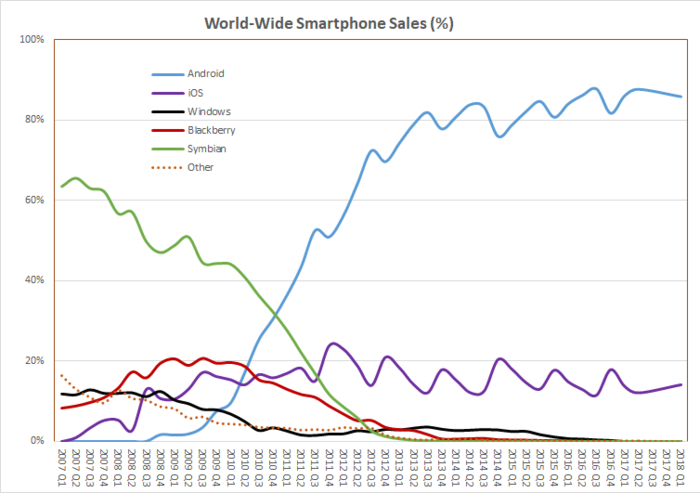
| Quarter | Windows Mobile[43] | BlackBerry OS | Symbian[44] | iOS | Android[45] | Bada | Windows Phone[46] | Other | Total smartphones | Total phones |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 Q3[47] | - | 378 | - | 43,000 | 327,674 | - | 1,484 | 755.5 | 373,292 | n/a |
| 2016 Q2[48] | - | 400 | - | 44,395 | 296,912 | - | 1,971 | 680.6 | 344,359 | n/a |
| 2016 Q1[49] | - | 660 | - | 51,630 | 293,771 | - | 2,400 | 791 | 349,251 | n/a |
| 2015 Q4[50] | - | 906.9 | - | 71,526 | 325,394 | - | 4,395 | 887.3 | 403,109 | n/a |
| 2015 Q3[51] | - | 977 | - | 46,062 | 298,797 | - | 5,874 | 1,133 | 352,844 | 477,898 |
| 2015 Q2[52] | - | 1,153 | - | 48,086 | 271,010 | - | 8,198 | 1,229 | 329,676 | 445,758 |
| 2015 Q1[53] | - | 1,325 | - | 60,177 | 265,012 | - | 8,271 | 1,268 | 336,054 | 460,261 |
| 2014 Q4[54] | - | 1,734 | - | 74,832 | 279,058 | - | 10,425 | 1,286 | 367,334 | n/a |
| 2014 Q3[55] | - | 2,420 | - | 38,187 | 254,354 | - | 9,033 | 1,310 | 305,384 | 461,064 |
| 2014 Q2[56] | - | 2,044 | - | 35,345 | 243,484 | - | 8,095 | 2,044 | 290,384 | 444,190 |
| 2014 Q1[53] | - | 1,714 | - | 43,062 | 227,549 | - | 7,580 | 1,371 | 281,637 | 448,966 |
| 2013 Q4[57] | - | 1,807 | - | 50,224 | 219,613 | - | 8,534 | 1,994 | 282,171 | 490,342 |
| 2013 Q3[58] | - | 4,401 | 458 | 30,330 | 205,023 | 633 | 8,912 | 475 | 250,232 | 455,642 |
| 2013 Q2[59] | - | 6,180 | 631 | 31,900 | 177,898 | 838 | 7,408 | 472 | 225,326 | 435,158 |
| 2013 Q1[60] | - | 6,219 | 1,349 | 38,332 | 156,186 | 1,371 | 5,989 | 600 | 210,046 | 425,822 |
| 2012 Q4[61] | - | 7,333 | 2,569 | 43,457 | 144,720 | 2,684 | 6,186 | 713 | 207,662 | 472,076 |
| 2012 Q3[62] | - | 8,947 | 4,405 | 23,550 | 122,480 | 5,055 | 4,058 | 684 | 169,179 | 427,730 |
| 2012 Q2[63] | - | 7,991 | 9,072 | 28,935 | 98,529 | 4,209 | 4,087 | 863 | 153,686 | 419,008 |
| 2012 Q1[64] | - | 9,939 | 12,467 | 33,121 | 81,067 | 3,842 | 2,713 | 1,243 | 144,392 | 419,108 |
| 2011 Q4[65] | - | 13,185 | 17,458 | 35,456 | 75,906 | 3,111 | 2,759 | 1,167 | 149,042 | 476,555 |
| 2011 Q3[66] | - | 12,701 | 19,500 | 17,295 | 60,490 | 2,479 | 1,702 | 1,018 | 115,185 | 440,502 |
| 2011 Q2[67] | - | 12,652 | 23,853 | 19,629 | 46,776 | 2,056 | 1,724 | 1,051 | 107,740 | 428,661 |
| 2011 Q1[64][68] | 982 | 13,004 | 27,599 | 16,883 | 36,350 | 1,862 | 1,600 | 1,495 | 99,775 | 427,846 |
| 2010 Q4[65] | 3,419 | 14,762 | 32,642 | 16,011 | 30,801 | 2,027 | 0 | 1,488 | 101,150 | 452,037 |
| 2010 Q3[66] | 2,204 | 12,508 | 29,480 | 13,484 | 20,544 | 921 | - | 1,991 | 81,133 | 417,086 |
| 2010 Q2[67] | 3,059 | 11,629 | 25,387 | 8,743 | 10,653 | 577 | - | 2,011 | 62,058 | 367,987 |
| 2010 Q1[68] | 3,696 | 10,753 | 24,068 | 8,360 | 5,227 | - | - | 2,403 | 54,506 | 359,605 |
| 2009 Q4[69] | 4,203 | 10,508 | 23,857 | 8,676 | 4,043 | - | - | 2,517 | 53,804 | 347,103 |
| 2009 Q3[70] | 3,260 | 8,523 | 18,315 | 7,040 | 1,425 | - | - | 2,531 | 41,093 | 308,895 |
| 2009 Q2[71] | 3,830 | 7,782 | 20,881 | 5,325 | 756 | - | - | 2,398 | 40,972 | 286,122 |
| 2009 Q1[72] | 3,739 | 7,534 | 17,825 | 3,848 | 575 | - | - | 2,986 | 36,507 | 269,120 |
| 2008 Q4[73] | 4,714 | 7,443 | 17,949 | 4,079 | 639 | - | - | 3,319 | 38,143 | 314,708 |
| 2008 Q3[74] | 4,053 | 5,800 | 18,179 | 4,720 | 0 | - | - | 3,763 | 36,515 | 308,532 |
| 2008 Q2[75] | 3,874 | 5,594 | 18,405 | 893 | - | - | - | 3,456 | 32,221 | 304,722 |
| 2008 Q1[73] | 3,858 | 4,312 | 18,400 | 1,726 | - | - | - | 4,113 | 32,408 | 294,283 |
| 2007 Q4[73] | 4,374 | 4,025 | 22,903 | 1,928 | - | - | - | 3,536 | 36,766 | 330,055 |
| 2007 Q3[74] | 4,180 | 3,192 | 20,664 | 1,104 | - | - | - | 3,612 | 32,752 | 291,142 |
| 2007 Q2[75] | 3,212 | 2,471 | 18,273 | 270 | - | - | - | 3,628 | 27,855 | 272,604 |
| 2007 Q1[73] | 2,931 | 2,080 | 15,844 | - | - | - | - | 4,087 | 24,943 | 259,039 |
| Year | Windows Mobile | RIM | Symbian | iOS | Android | Bada | Windows Phone | Other smartphones | Total smartphones |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | - | 0.37%, 0.27% | - | 16.26%, 11.95% | 80.52%, 59.16% | - | 2.47%, 1.82% | 0.38%, 0.28% | 100.0%, 73.48% |
| 2014[76] | - | 0.6%, 0.4% | - | 15.4%, 10.2% | 80.7%, 53.4% | - | 2.8%, 1.9% | 0.5%, 0.3% | 100.0%, 66.2% |
| 2013[77] | - | 1.9%, 1.0% | - | 15.6%, 8.3% | 78.4%, 42.0% | - | 3.2%, 1.7% | 0.9%, 0.5% | 100.0%, 57.6% |
| 2012[77] | - | 5.0%, 2.0% | - | 19.1%, 7.4% | 66.4%, 25.9% | - | 2.5%, 1.0% | 6.9%, 2.7% | 100.0%, 38.9% |
| 2011 | — | ||||||||
| 2010[78] | - | 16.0%, 3.0% | 37.6%, 7.0% | 15.7%, 2.9% | 22.7%, 4.2% | - | 4.2%, 0.8% | 3.8%, 0.7% | 100.0%, 18.6% |
| 2009[78] | 8.7%, 1.2% | 19.9%, 2.8% | 46.9%, 6.7% | 14.4%, 2.1% | 3.9%, 0.6% | - | - | 6.1%, 0.9% | 100.0%, 14.2% |
| 2008[79] | 11.8%, 1.3% | 16.6%, 1.9% | 52.4%, 6.0% | 8.2%, 0.9% | 0.5%, 0.1% | - | - | 10.5%, 1.2% | 100.0%, 11.4% |
| 2007[80] | 12.0%, 1.3% | 9.6%, 1.0% | 63.5%, 6.7% | 2.7%, 0.3% | - | - | - | 12.1%, 1.3% | 100.0%, 10.6% |

| Quarter | Android | iOS | Windows 10/Phone | BlackBerry OS | Other | Total smartphones | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 Q1[81] | 293.771 | 84.11% | 51.630 | 14.78% | 2.400 | 0.69% | 0.660 | 0.19% | 0.791 | 0.23% | 349.251 |
| 2015 Q4[50] | 325.394 | 80.72% | 71.526 | 17.74% | 4.395 | 1.09% | 0.907 | 0.22% | 0.887 | 0.22% | 403.109 |
| 2015 Q3[51] | 298.797 | 84.68% | 46.062 | 13.05% | 5.874 | 1.66% | 0.977 | 0.28% | 1.134 | 0.32% | 352.844 |
| 2015 Q2[52] | 271.010 | 82.20% | 48.086 | 14.59% | 8.198 | 2.49% | 1.153 | 0.35% | 1.229 | 0.37% | 329.676 |
| 2015 Q1[53] | 265.012 | 78.86% | 60.177 | 17.91% | 8.271 | 2.46% | 1.325 | 0.39% | 1.268 | 0.38% | 336.054 |
| 2014 Q4[54] | 279.058 | 75.97% | 74.832 | 20.37% | 10.425 | 2.84% | 1.734 | 0.47% | 1.287 | 0.35% | 367.334 |
| 2014 Q3[55] | 254.354 | 83.29% | 38.187 | 12.50% | 9.033 | 2.96% | 2.420 | 0.79% | 1.310 | 0.43% | 305.384 |
| 2014 Q2[56] | 243.484 | 83.85% | 35.345 | 12.17% | 8.095 | 2.79% | 2.044 | 0.70% | 2.044 | 0.70% | 290.384 |
| 2014 Q1[53] | 227.549 | 80.80% | 43.062 | 15.29% | 7.580 | 2.69% | 1.714 | 0.61% | 1.371 | 0.49% | 281.637 |
| Quarter | Android | iOS | Windows 10/Phone | BlackBerry OS | Other | Total smartphones | |||||

| Quarter | Android[45] | Android | iOS | iOS | Symbian[44] | Symbian | BlackBerry OS | BlackBerry | Linux[82] | Linux | Windows Phone | Windows Phone | Other | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 Q2[83] | 282.76 | 82.80% | 47.3 | 13.9% | - | 0.00% | 1.02 | 0.30% | - | 0.00% | 8.8 | 2.60% | 1.37 | 0.40% | 341.5 |
| 2015 Q1[84] | 260.8 | 78.00% | 61.2 | 18.30% | - | 0.00% | 1.00 | 0.30% | - | 0.00% | 9.03 | 2.70% | 2.34 | 0.70% | 334.4 |
| 2014 Q4[85] | 289.1 | 76.58% | 74.5 | 19.74% | - | 0.00% | 1.40 | 0.37% | - | 0.00% | 10.70 | 2.83% | 1.80 | 0.48% | 377.5 |
| 2014 Q3[86] | 283.0 | 84.48% | 39.2 | 11.70% | - | 0.00% | 1.68 | 0.50% | - | 0.00% | 9.72 | 2.90% | 2.00 | 0.60% | 335.0 |
| 2014 Q2[87] | 255.3 | 84.73% | 35.2 | 11.68% | - | 0.00% | 1.5 | 0.50% | - | 0.00% | 7.4 | 2.46% | 1.9 | 0.63% | 301.3 |
| 2014 Q1[88] | 234.1 | 81.20% | 43.8 | 15.20% | - | 0.00% | 1.4 | 0.50% | - | 0.00% | 7.2 | 2.50% | 2.0 | 0.70% | 288.3 |
| 2013 Q4[89] | 226.1 | 78.07% | 51.0 | 17.61% | - | 0.00% | 1.7 | 0.59% | - | 0.00% | 8.8 | 3.04% | 2.0 | 0.69% | 289.6 |
| 2013 Q3[90] | 211.6 | 81.04% | 33.8 | 12.95% | - | 0.00% | 4.5 | 1.72% | - | 0.00% | 9.5 | 3.64% | 1.7 | 0.65% | 261.1 |
| 2013 Q2[91] | 187.4 | 79.27% | 31.2 | 13.20% | 0.5 | 0.21% | 6.8 | 2.88% | 1.8 | 0.76% | 8.7 | 3.68% | 0.0 | 0.00% | 236.4 |
| 2013 Q1[92] | 162.1 | 74.98% | 37.4 | 17.30% | 1.2 | 0.56% | 6.3 | 2.91% | 2.1 | 0.97% | 7.0 | 3.24% | 0.1 | 0.05% | 216.2 |
| 2012 Q4[93] | 159.8 | 70.15% | 47.8 | 20.98% | 2.7 | 1.19% | 7.4 | 3.25% | 3.8 | 1.67% | 6.0 | 2.63% | 0.3 | 0.13% | 227.8 |
| 2012 Q3[94] | 136.0 | 75.10% | 26.9 | 14.85% | 4.1 | 2.26% | 7.7 | 4.25% | 2.8 | 1.55% | 3.6 | 1.99% | 0.0 | 0.00% | 181.1 |
| 2012 Q2[95] | 104.8 | 68.05% | 26.0 | 16.88% | 6.8 | 4.42% | 7.4 | 4.81% | 3.5 | 2.27% | 5.4 | 3.51% | 0.1 | 0.06% | 154.0 |
| 2012 Q1[96] | 89.9 | 59.03% | 35.1 | 23.05% | 10.4 | 6.83% | 9.7 | 6.37% | 3.5 | 2.30% | 3.3 | 2.17% | 0.4 | 0.26% | 152.3 |
| 2011 Q4[93] | 83.4 | 52.85% | 36.3 | 23.00% | 18.3 | 11.60% | 12.8 | 8.11% | 3.8 | 2.41% | 2.4 | 1.52% | 0.8 | 0.51% | 157.8 |
| 2011 Q3[94] | 67.7 | 57.32% | 16.3 | 13.80% | 17.3 | 14.65% | 11.3 | 9.57% | 3.9 | 3.30% | 1.4 | 1.19% | 0.1 | 0.08% | 118.1 |
| 2011 Q2[95] | 50.8 | 46.86% | 20.4 | 18.82% | 18.3 | 16.88% | 12.5 | 11.53% | 3.3 | 3.04% | 2.5 | 2.31% | 0.6 | 0.55% | 108.4 |
| 2011 Q1[96] | 36.7 | 36.12% | 18.6 | 18.31% | 26.4 | 25.98% | 13.8 | 13.58% | 3.2 | 3.15% | 2.6 | 2.56% | 0.3 | 0.30% | 101.6 |
Market share by country or region
| Region | USA | EU5[97] | China | Australia | Russia | Brazil | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quarter | iOS | Android | Windows | iOS | Android | Windows | iOS | Android | Windows | iOS | Android | Windows | iOS | Android | Windows | iOS | Android | Windows |
| 2015 Q3[98] | 29.2% | 65.9% | 3.9% | 14.4% | 74.0% | 10.6% | 19.1% | 77.4% | 3.0% | 36.8% | 54.5% | 7.4% | 10.5% | 75.9% | 11.5% | 4.0% | 91.4% | 4.7% |
| 2015 Q2[98] | 30.5% | 66.1% | 3.0% | 17.5% | 71.3% | 10.0% | 20.1% | 79.0% | 0.5% | 34.6% | 57.6% | 6.4% | 11.4% | 75.8% | 10.9% | 3.8% | 89.0% | 5.5% |
| 2015 Q1[98] | 36.5% | 58.1% | 4.3% | 20.3% | 68.4% | 9.9% | 26.1% | 72.0% | 1.2% | 38.4% | 52.3% | 7.3% | 13.4% | 73.2% | 11.2% | 3.3% | 89.6% | 6.3% |
| 2014 Q4[99] | 47.7% | 47.6% | 3.8% | 24.1% | 66.1% | 8.9% | 21.5% | 77.0% | 0.7% | 45.1% | 43.7% | 9.2% | 14.8% | 71.2% | 10.6% | 5.5% | 89.0% | 4.0% |
| 2014 Q3[100] | 32.6% | 61.8% | 4.3% | 15.4% | 73.9% | 9.2% | 15.2% | 83.4% | 0.4% | 34.7% | 58.1% | 6.2% | - | - | - | 6.1% | 88.2% | 3.6% |
| 2014 Q2[101] | 31.5% | 62.0% | 3.8% | 15.3% | 74.0% | 8.8% | 12.8% | 84.3% | 0.9% | 25.5% | 68.0% | 5.3% | - | - | - | 3.9% | 89.0% | 4.5% |
| 2014 Q1[102] | 35.9% | 57.6% | 5.3% | 19.2% | 70.7% | 8.1% | 17.9% | 80.0% | 1.0% | 33.1% | 57.3% | 6.9% | - | - | - | 3.0% | 87.6% | 5.5% |
| 2013 Q4[103] | 43.9% | 50.6% | 4.3% | 18.5% | 68.6% | 10.3% | 19.0% | 78.6% | 1.1% | 35.2% | 57.2% | 5.2% | - | - | - | 4.2% | 86.7% | 4.0% |
| 2013 Q3[104] | 35.9% | 57.3% | 4.6% | 14.6% | 71.9% | 9.8% | 13.8% | 81.1% | 2.5% | 32.9% | 55.3% | 9.3% | - | - | - | 4.3% | 83.8% | 3.4% |
| 2013 Q2[105] | 42.5% | 51.5% | 4% | 18.5% | 69.8% | 6.9% | 24.7% | 67.8% | 4.9% | 27.6% | 64.6% | 5.3% | - | - | - | 3.5% | 79.8% | 6.2% |
| 2013 Q1[106] | 43.7% | 49.3% | 5.6% | 19.4% | 68.8% | 6.5% | 24.6% | 69.4% | 2% | 31% | 61.7% | 4.1% | - | - | - | 5.8% | 76.7% | 4.7% |
| 2012 Q4[107] | 51.2% | 44.2% | 2.6% | 25.6% | 61.1% | 5.4% | 21.9% | 72.5% | 0.9% | 38.4% | 55.8% | 2.8% | - | - | - | 4.2% | 68.2% | 8.0% |
| 2012 Q4[108] | 35.7% | 57.5% | 2.9% | 16.5% | 67.1% | 4.9% | 18.6% | 65.2% | 5.7% | 23.2% | 67.1% | 4.9% | - | - | - | 5.4% | 58.1% | 8.0% |
| 2012 Q2[105] | 39.2% | 52.6% | 2.9% | 16.2% | 64.5% | 4.7% | 26.7% | 60.7% | 6.2% | 27.5% | 60.8% | 5.2% | - | - | - | 2.9% | 49.0% | 5.4% |
| 2012 Q1[106] | 44.6% | 47.9% | 3.7% | 20.4% | 58.1% | 4.1% | - | - | - | 33.8% | 52.9% | 3.3% | - | - | - | 5.3% | 48.3% | 3.8% |
Future
Microsoft’s has introduced universal apps—apps that will run on PCs, hybrids, laptops,smartphones and even the Xbox console. Artificial intelligence (AI) is a big step forward for mobile operating systems, particularly Android and iOS. At WWDC 2016 (Worldwide Developers’ Conference), Apple announced that the QuickType foundation for text typing on an iOS device will now use deep learning to enable more intelligent predictive typing, using expanded context.
Wearables, such as smart watches, have so far been positioned as the second screen for smartphones for checking mails, messages, handling calls and even using certain apps without having to take out the device. But both Google and Apple are now pushing towards making the upcoming Android Wear and WatchOS platforms less reliant on a paired smartphone; certain apps will be able to run on the smart watches, without needing a phone for data.
See also
- Comparison of mobile operating systems
- List of GPS software for mobile phones
- Smartphone
- Tablet computer
- Personal digital assistant
- Smart TV
- Information appliance
- Mobile device
- Real-time operating system
References
- ^ Thom Holwerda, OSNews, 12 November 2013, The second operating system hiding in every mobile phone
- ^ Jobs, Steve (2007-01-19). Macworld San Francisco 2007 Keynote Address. San Francisco: Apple, Inc.
- ^ Helft, Miguel (2007-11-05). "Google Enters the Wireless World". New York Times. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Ubuntu phone OS announced, first devices shipping in early 2014".
- ^ The Associated Press (2016-08-22). "Google Rolling Out Latest Android System to Nexus Phones". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2016-08-29.
- ^ a b "Gartner Says Worldwide Mobile Phone Sales Grew 35 Percent in Third Quarter 2010; Smartphone Sales Increased 96 Percent". Gartner, Inc. 2010-11-10. Table 2. Retrieved 2011-02-21.
- ^ "ICS is coming to AOSP".
- ^ Balky carriers and slow OEMs step aside: Google is defragging Android. Ars Technica. Retrieved 2013-12-24.
- ^ "Android 7.0 for Developers | Android Developers". developer.android.com. Retrieved 2016-09-09.
- ^ CM14 is discontinued, along with the CM project being shut down. Development moved to LineageOS.
- ^ "MOD ready Cyanogen OS 13.1 is now available for the OnePlus One". Android Authority. Retrieved 2016-09-09.
- ^ "OnePlus 3". oneplus.net. Retrieved 2016-09-09.
- ^ http://techcrunch.com/2015/02/26/apple-eating-all-the-profits/
- ^ "Gartner Says Five of Top 10 Worldwide Mobile Phone Vendors Increased Sales in Second Quarter of 2016". www.gartner.com. Retrieved 2016-08-19.
- ^ Welcome to Tizen!. Tizen.org (2011-09-27). Retrieved on 2012-07-03.
- ^ Ricker, Thomas. (2011-09-28)MeeGo is dead: Meet Tizen, another new open source OS based on Linux. Thisismynext.com. Retrieved on 2012-07-03.
- ^ a b "Tizen 2.1 SDK and Source Code Release". Tizen.org.
- ^ "ContainerArchitecture". Retrieved October 30, 2016.
- ^ BlackBerry has no plans to release new BB10 devices
- ^ "Android and iOS Squeeze the Competition, Swelling to 96.3% of the Smartphone Operating System Market for Both 4Q14 and CY14, According to IDC". IDC.com. 2015-02-24.
- ^ "B2G – MozillaWiki". mozilla.org. 2011-08-24. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ Paul, Ryan (2011-07-25). "Mozilla eyes mobile OS landscape with new Boot to Gecko project". Arstechnica.com. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "B2G OS and Gecko Annoucement from Ari Jaaksi & David Bryant". September 27, 2016. Retrieved September 27, 2016.
- ^ Arthur, Charles (September 29, 2014). "Ten things to know about BlackBerry -- and how much trouble it is (or isn't) in". TheGuardian.com. The Guardian. Retrieved April 19, 2015.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Kevin McLaughlinwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "CEO Ballmer Reportedly Says Microsoft 'Screwed Up' with Windows Mobile". eWeek. 28 September 2009.
- ^ "iPhone drops to 24% smartphone share, Android jumps to 17%". AppleInsider. 2010-09-16. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Windows Phone developers". Yeeply Windows Phone.
- ^ http://www.theverge.com/2014/7/17/5912289/microsoft-kills-feature-phones-in-favor-of-windows-phone
- ^ Samsung scraps Bada OS, folds it into Tizen - FierceMobileIT. Fiercemobilecontent.com (2013-02-25). Retrieved on 2013-12-09.
- ^ "HP Confirms Discussions with Autonomy Corporation plc Regarding Possible Business Combination; Makes Other Announcements". HP. 2010-08-18. Retrieved 2011-09-13.
- ^ "The next chapter for webOS". HP webOS Developer Blog. 2010-08-19. Retrieved 2011-09-13.
- ^ "Open webOS::Roadmap". Open webOS Project. September 2012. Retrieved 2012-10-24.
- ^ "Introducing the Nokia N9: all it takes is a swipe! | Nokia Conversations – The official Nokia Blog". Nokia. 2011-06-21. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "MeeGo Not Dead Yet as LG Continues the Charge — Mobile Technology News". Gigaom.com. 2011-04-29. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ^ "Limo 4 OS Launched – Devices Expected Soon". Gadgetizor.com.
- ^ "64 million smart phones shipped worldwide in 2006". Canalys, Inc. Retrieved 2012-01-13.
- ^ "Smartphone OS Market Share". www.idc.com. IDC. Retrieved 27 December 2016.
- ^ "Comparison from W34 to W45 2015". StatCounter Global Stats.
- ^ http://gs.statcounter.com/#all-comparison-ww-weekly-201645-201645-map
- ^ http://gs.statcounter.com/#all-comparison-ww-daily-20160628-20161114
- ^ "Mobile and tablet Internet usage exceeds desktop for first time worldwide". StatCounter (Press release).
- ^ 2010 Q4 contains insignificant part of Windows Phone devices
- ^ a b not including low cost devices
- ^ a b including low cost devices
- ^ 2011 Q2 and the more contains insignificant part of Windows Mobile devices
- ^ "Gartner Says Chinese Smartphone Vendors Were Only Vendors in the Global Top Five to Increase Sales in the Third Quarter of 2016". www.gartner.com. Retrieved 2016-12-09.
- ^ "Gartner Says Five of Top 10 Worldwide Mobile Phone Vendors Increased Sales in Second Quarter of 2016". www.gartner.com. Retrieved 2016-08-19.
- ^ "Gartner Says Worldwide Smartphone Sales Grew 3.9 Percent in First Quarter of 2016". www.gartner.com. Retrieved 2016-05-26.
- ^ a b "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2015 Q4". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2015-11-19.
- ^ a b "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2015 Q3". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2015-11-19.
- ^ a b "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2015 Q2". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2015-08-21.
- ^ a b c d "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2015 Q1". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2015-06-09.
- ^ a b "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2014 Q4". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2014-12-15.
- ^ a b "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2014 Q3". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2014-12-15.
- ^ a b "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2015 Q2". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2015-08-21.
- ^ "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2013 Q4". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2014-01-13.
- ^ "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2013 Q3". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2013-11-14.
- ^ "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2013 Q2". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2013-08-14.
- ^ "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2013 Q1". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2013-05-14.
- ^ "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2012 Q4". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2013-02-13.
- ^ "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2012 Q3". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2012-11-14.
- ^ "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2012 Q2". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2012-08-14.
- ^ a b "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2012 Q1". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
- ^ a b "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2011 Q4". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
- ^ a b "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2011 Q3". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
- ^ a b "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2011 Q2". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
- ^ a b "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2011 Q1". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
- ^ "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2010 Q4". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
- ^ "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2010 Q3". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
- ^ "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2010 Q2". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
- ^ "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2010 Q1". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
- ^ a b c d "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2008 Q4". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
- ^ a b "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2008 Q3". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
- ^ a b "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2008 Q2". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
- ^ "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2014". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2015-03-26.
- ^ a b "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2013". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2015-06-12.
- ^ a b "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2010". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2015-06-12.
- ^ "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2009". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2015-06-12.
- ^ "Gartner Smart Phone Marketshare 2008". Gartner, Inc. Retrieved 2015-06-12.
- ^ "Gartner Says Worldwide Smartphone Sales". www.gartner.com. Retrieved 2016-05-26.
- ^ including Bada OS
- ^ including Germany, United Kingdom, France, Italy and Spain
- ^ a b c "Kantar Worldpanel ComTech's Smartphone OS market share data". Kantar. Retrieved 2015-11-01.
- ^ "Kantar Worldpanel ComTech's Smartphone OS market share data Q4 2014". Kantar. Retrieved 2015-02-04.
- ^ "Kantar Worldpanel ComTech's Smartphone OS market share data Q3 2014". Kantar. Retrieved 2014-10-29.
- ^ "Kantar Worldpanel ComTech's Smartphone OS market share data Q2 2014". Kantar. Retrieved 2014-07-31.
- ^ "Kantar Worldpanel ComTech's Smartphone OS market share data Q1 2014". Kantar. Retrieved 2014-05-01.
- ^ "Kantar Worldpanel ComTech's Smartphone OS market share data Q4 2013". Kantar. Retrieved 2014-01-27.
- ^ "Kantar Worldpanel ComTech's Smartphone OS market share data Q3 2013". Kantar. Retrieved 2013-11-17.
- ^ a b "Kantar Worldpanel ComTech's Smartphone OS market share data Q2 2013". Kantar. Retrieved 2013-11-17.
- ^ a b "Kantar Worldpanel ComTech's Smartphone OS market share data Q1 2013". Kantar. Retrieved 2013-11-17.
- ^ "Kantar Worldpanel ComTech's Smartphone OS market share data Q4 2012". Kantar. Retrieved 2013-11-17.
- ^ "Kantar Worldpanel ComTech's Smartphone OS market share data Q3 2012". Kantar. Retrieved 2013-11-17.
