Trump peace plan: Difference between revisions
Selfstudier (talk | contribs) Removing images, this is NOT vandalism, please see talk pages and discuss. |
BlueMadrigal (talk | contribs) m This is vandalism and an extreme position. Removal of the pictures, which they depict the facts of the relevant events, facts that they depict are in already included in the text. If I'm not wrong you personally copy edited. |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
In November 2019, the US abandoned its four-decades-old position that Jewish settlements in the West Bank were inconsistent with international law.<ref name="BBC280120" /> |
In November 2019, the US abandoned its four-decades-old position that Jewish settlements in the West Bank were inconsistent with international law.<ref name="BBC280120" /> |
||
{{multiple image|perrow = 4|total_width=400 |
|||
<!-- Layout parameters --> |
|||
| align = center |
|||
| background color = <!-- box background as a 'hex triplet' web color (include the initial #) --> |
|||
| caption_align = center |
|||
<!-- Header --> |
|||
| header_background = <!-- header background as a 'hex triplet' web color (include the initial #) --> |
|||
| header_align = center |
|||
| header = 'Paradigm-Busting'<ref name="Kinninmont" /> |
|||
<!--image 1--> |
|||
| image1 = President Trump Gives a Statement on Jerusalem, December 2017.webm |
|||
| width1 = <!-- displayed width of image; overridden by "width" above --> |
|||
| caption1 = [[United States recognition of Jerusalem as capital of Israel|Jerusalem]] |
|||
<!--image 2--> |
|||
| image2 = President Trump Welcome the Prime Minister of Israel to the White House, 25 March 2019.jpg |
|||
| width2 = <!-- displayed width of image; overridden by "width" above --> |
|||
| caption2 = [[United States recognition of the Golan Heights as part of Israel|Golan Heights]] |
|||
<!--image 3--> |
|||
| image3 = West Bank Access Restrictions.pdf |
|||
| width3 = <!-- displayed width of image; overridden by "width" above --> |
|||
| caption3 = Settlements are lawful |
|||
<!-- Footer --> |
|||
| footer_background = <!-- footer background as a 'hex triplet' web color (include the initial #) --> |
|||
| footer_align = <!-- left (default), center, right --> |
|||
| footer = Redefinition of the parameters for U.S. approach}} |
|||
The Trump plan was presented as the best option regarding possible future developments by Kushner who stated "The Palestinian leadership have to ask themselves a question: Do they want to have a state? Do they want to have a better life? If they do, we have created a framework for them to have it, and we're going to treat them in a very respectful manner. If they don't, then they're going to screw up another opportunity like they've screwed up every other opportunity that they've ever had in their existence."<ref>{{cite news |last1=Winer |first1=Stuart |title=Kushner slams Palestinian leadership, urges giving up 'fairy tales' for peace |url=https://www.timesofisrael.com/kushner-slams-palestinian-leadership-urges-giving-up-fairytales-for-peace/ |work=The Times of Israel |access-date=January 30, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200130141639/https://www.timesofisrael.com/kushner-slams-palestinian-leadership-urges-giving-up-fairytales-for-peace/ |archive-date=January 30, 2020 |url-status=live}}</ref> Kushner said that the peace proposal will not include the phrase "[[two-state solution]]", saying "If you say 'two-state', it means one thing to the Israelis, it means one thing to the Palestinians. We said, 'You know, let's just not say it. Let's just say, let's work on the details of what this means.'"<ref>{{cite news |url=https://nypost.com/2019/05/03/jared-kushner-says-mideast-peace-plan-wont-say-two-states/ |title=Jared Kushner says Mideast peace plan won't say 'two states' |last1=Steinbuch |first1=Yaron |date=May 3, 2019 |work=New York Post |accessdate=June 23, 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190624193602/https://nypost.com/2019/05/03/jared-kushner-says-mideast-peace-plan-wont-say-two-states/ |archive-date=June 24, 2019 |url-status=live}}</ref> A top-ranking Saudi diplomat stated that the plan includes a "clear path leading to complete Palestinian independence".<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.jpost.com/Israel-News/Saudi-official-says-Deal-of-Century-leads-to-full-Palestinian-statehood-593306 |title=Saudi official says 'Deal of Century' leads to full Palestinian statehood |work=The Jerusalem Post |accessdate=June 23, 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190622173150/https://www.jpost.com/Israel-News/Saudi-official-says-Deal-of-Century-leads-to-full-Palestinian-statehood-593306 |archive-date=June 22, 2019 |url-status=live}}</ref> [[Robert Malley]], director of the [[International Crisis Group]] and a leading Middle East expert in former US administrations stated: "Strip away the domestic and Israeli political considerations that determined the timing of the plan's release, and the message to the Palestinians, boiled down to its essence, is: You've lost, get over it." |
The Trump plan was presented as the best option regarding possible future developments by Kushner who stated "The Palestinian leadership have to ask themselves a question: Do they want to have a state? Do they want to have a better life? If they do, we have created a framework for them to have it, and we're going to treat them in a very respectful manner. If they don't, then they're going to screw up another opportunity like they've screwed up every other opportunity that they've ever had in their existence."<ref>{{cite news |last1=Winer |first1=Stuart |title=Kushner slams Palestinian leadership, urges giving up 'fairy tales' for peace |url=https://www.timesofisrael.com/kushner-slams-palestinian-leadership-urges-giving-up-fairytales-for-peace/ |work=The Times of Israel |access-date=January 30, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200130141639/https://www.timesofisrael.com/kushner-slams-palestinian-leadership-urges-giving-up-fairytales-for-peace/ |archive-date=January 30, 2020 |url-status=live}}</ref> Kushner said that the peace proposal will not include the phrase "[[two-state solution]]", saying "If you say 'two-state', it means one thing to the Israelis, it means one thing to the Palestinians. We said, 'You know, let's just not say it. Let's just say, let's work on the details of what this means.'"<ref>{{cite news |url=https://nypost.com/2019/05/03/jared-kushner-says-mideast-peace-plan-wont-say-two-states/ |title=Jared Kushner says Mideast peace plan won't say 'two states' |last1=Steinbuch |first1=Yaron |date=May 3, 2019 |work=New York Post |accessdate=June 23, 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190624193602/https://nypost.com/2019/05/03/jared-kushner-says-mideast-peace-plan-wont-say-two-states/ |archive-date=June 24, 2019 |url-status=live}}</ref> A top-ranking Saudi diplomat stated that the plan includes a "clear path leading to complete Palestinian independence".<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.jpost.com/Israel-News/Saudi-official-says-Deal-of-Century-leads-to-full-Palestinian-statehood-593306 |title=Saudi official says 'Deal of Century' leads to full Palestinian statehood |work=The Jerusalem Post |accessdate=June 23, 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190622173150/https://www.jpost.com/Israel-News/Saudi-official-says-Deal-of-Century-leads-to-full-Palestinian-statehood-593306 |archive-date=June 22, 2019 |url-status=live}}</ref> [[Robert Malley]], director of the [[International Crisis Group]] and a leading Middle East expert in former US administrations stated: "Strip away the domestic and Israeli political considerations that determined the timing of the plan's release, and the message to the Palestinians, boiled down to its essence, is: You've lost, get over it." |
||
| Line 55: | Line 81: | ||
The political portion of the plan was rolled out on January 28, 2020. The timing of roll-out showed a contrast with the Trump impeachment trial and Netanyahu faces an election in five weeks.<ref name="Roll">{{cite news |title=Timing of Mideast peace plan rollout appears designed to contrast with impeachment trial: Analysis |url=https://abcnews.go.com/Politics/timing-mideast-peace-plan-rollout-appears-designed-contrast/story?id=68560569 |publisher=ABC News |language=en |access-date=January 30, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200130042809/https://abcnews.go.com/Politics/timing-mideast-peace-plan-rollout-appears-designed-contrast/story?id=68560569 |archive-date=January 30, 2020 |url-status=live}}</ref> Government insist that revealing the plan now was not designed to distract from impeachment, but was rather a reaction to political realities in Israel.<ref name="Roll" /> Running to [[2020 Israeli legislative election]] Israel had [[April 2019 Israeli legislative election]], which Netanyahu part in what is known as forming the [[Union of the Right-Wing Parties]] by uniting the [[The Jewish Home|Jewish Home]] party with the [[far-right]] [[Otzma Yehudit]] party.<ref>{{cite news |author=Michal Wilner |newspaper=Jerusalem Post |url=https://www.jpost.com/Israel-Elections/Netanyahu-says-he-will-accept-Kahanists-in-government-Who-are-they-581247 |title=Who are the Kahanists of Otzma Netanyahu opened Knesset door to? - Israel Elections |access-date=January 30, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191218093404/https://www.jpost.com/Israel-Elections/Netanyahu-says-he-will-accept-Kahanists-in-government-Who-are-they-581247 |archive-date=December 18, 2019 |url-status=live}}</ref> Otzma widely characterized as racist and traces its origins to the extremist [[Kahanism|Kahanist]] movement.<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2019/02/24/world/middleeast/benjamin-netanyahu-otzma-yehudit-jewish-power.html |title=Netanyahu Sparks Outrage Over Pact With Racist Party |first=David M. |last=Halbfinger |date=February 24, 2019 |newspaper=The New York Times |access-date=January 30, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191009104820/https://www.nytimes.com/2019/02/24/world/middleeast/benjamin-netanyahu-otzma-yehudit-jewish-power.html |archive-date=October 9, 2019 |url-status=live}}</ref> On September 10, 2019, Netanyahu pledged to annex part of the occupied [[West Bank]] on the border with [[Jordan]] and promised to apply "Israeli sovereignty over the [[Jordan Valley]] and northern [[Dead Sea]]" if re-elected.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-49655226 |title=Netanyahu pledges to annex occupied Jordan Valley |date=September 10, 2019 |access-date=January 30, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191205061822/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-49655226 |archive-date=December 5, 2019 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
The political portion of the plan was rolled out on January 28, 2020. The timing of roll-out showed a contrast with the Trump impeachment trial and Netanyahu faces an election in five weeks.<ref name="Roll">{{cite news |title=Timing of Mideast peace plan rollout appears designed to contrast with impeachment trial: Analysis |url=https://abcnews.go.com/Politics/timing-mideast-peace-plan-rollout-appears-designed-contrast/story?id=68560569 |publisher=ABC News |language=en |access-date=January 30, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200130042809/https://abcnews.go.com/Politics/timing-mideast-peace-plan-rollout-appears-designed-contrast/story?id=68560569 |archive-date=January 30, 2020 |url-status=live}}</ref> Government insist that revealing the plan now was not designed to distract from impeachment, but was rather a reaction to political realities in Israel.<ref name="Roll" /> Running to [[2020 Israeli legislative election]] Israel had [[April 2019 Israeli legislative election]], which Netanyahu part in what is known as forming the [[Union of the Right-Wing Parties]] by uniting the [[The Jewish Home|Jewish Home]] party with the [[far-right]] [[Otzma Yehudit]] party.<ref>{{cite news |author=Michal Wilner |newspaper=Jerusalem Post |url=https://www.jpost.com/Israel-Elections/Netanyahu-says-he-will-accept-Kahanists-in-government-Who-are-they-581247 |title=Who are the Kahanists of Otzma Netanyahu opened Knesset door to? - Israel Elections |access-date=January 30, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191218093404/https://www.jpost.com/Israel-Elections/Netanyahu-says-he-will-accept-Kahanists-in-government-Who-are-they-581247 |archive-date=December 18, 2019 |url-status=live}}</ref> Otzma widely characterized as racist and traces its origins to the extremist [[Kahanism|Kahanist]] movement.<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2019/02/24/world/middleeast/benjamin-netanyahu-otzma-yehudit-jewish-power.html |title=Netanyahu Sparks Outrage Over Pact With Racist Party |first=David M. |last=Halbfinger |date=February 24, 2019 |newspaper=The New York Times |access-date=January 30, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191009104820/https://www.nytimes.com/2019/02/24/world/middleeast/benjamin-netanyahu-otzma-yehudit-jewish-power.html |archive-date=October 9, 2019 |url-status=live}}</ref> On September 10, 2019, Netanyahu pledged to annex part of the occupied [[West Bank]] on the border with [[Jordan]] and promised to apply "Israeli sovereignty over the [[Jordan Valley]] and northern [[Dead Sea]]" if re-elected.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-49655226 |title=Netanyahu pledges to annex occupied Jordan Valley |date=September 10, 2019 |access-date=January 30, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191205061822/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-49655226 |archive-date=December 5, 2019 |url-status=live}}</ref> |
||
{{multiple image|perrow = 4|total_width=400 |
|||
<!-- Layout parameters --> |
|||
| align = center |
|||
| background color = <!-- box background as a 'hex triplet' web color (include the initial #) --> |
|||
| caption_align = center |
|||
<!-- Header --> |
|||
| header_background = <!-- header background as a 'hex triplet' web color (include the initial #) --> |
|||
| header_align = center |
|||
| header = Trump Peace Plan Negotiations with Israel |
|||
<!--image 1--> |
|||
| image1 = Embassy_Dedication_Ceremony_(28279991058).jpg |
|||
| width1 = <!-- displayed width of image; overridden by "width" above --> |
|||
| caption1 = Special Envoy [[Jared Kushner]] |
|||
<!--image 2--> |
|||
| image2 = President Trump's Special Representative for International Negotiations Jason Greenblatt (36824108840).jpg |
|||
| width2 = <!-- displayed width of image; overridden by "width" above --> |
|||
| caption2 = Chief negotiator [[Jason Greenblatt]] (2017–2019) Lawyer |
|||
<!--image 3--> |
|||
| image3 = Dedication ceremony of the Embassy of the United States in Jerusalem 2647 (41431886714).jpg |
|||
| width3 = <!-- displayed width of image; overridden by "width" above --> |
|||
| caption3 = Chief negotiator [[Avi Berkowitz]] (2019-) Lawyer (left) |
|||
<!--image 4--> |
|||
| image4 = President_Donald_Trump_receives_a_briefing_on_a_military_strike.jpg |
|||
| width4 = <!-- displayed width of image; overridden by "width" above --> |
|||
| caption4 = Liaison [[Dina Powell]], (2017-December 8, 2017) [[Deputy National Security Advisor (United States)|D.N.S.A]] (only female) |
|||
<!--image 5--> |
|||
| image5 = Donald_Trump_with_Reuven_Rivlin_in_Israel_2017_(7).jpg |
|||
| width5 = <!-- displayed width of image; overridden by "width" above --> |
|||
| caption5 = Liaison [[David M. Friedman|David Friedman]], Ambassador (front row fourth from right) |
|||
<!--image 6--> |
|||
| image6 = President_Trump_visit_to_Israel,_May_2017_DSC_3545ODS_(34789024376).jpg |
|||
| width6 = <!-- displayed width of image; overridden by "width" above --> |
|||
| caption6 = President [[Donald Trump|Trump]] (far right) Liaison [[Ivanka Trump]], (from center to right) |
|||
<!-- Footer --> |
|||
| footer_background = <!-- footer background as a 'hex triplet' web color (include the initial #) --> |
|||
| footer_align = <!-- left (default), center, right --> |
|||
| footer = During their official works |
|||
}} |
|||
==Stated aims of the plan== |
==Stated aims of the plan== |
||
Revision as of 11:56, 5 February 2020
Peace to Prosperity: A Vision to Improve the Lives of the Palestinian and Israeli People, commonly known as the Trump peace plan, is a proposal by the Trump administration bearing the stated intention of resolving the Israeli–Palestinian conflict. Donald Trump formally unveiled the plan in a White House press conference alongside Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu on January 28, 2020; Palestinian representatives were not invited.[1]
The plan was authored by a team led by Trump's son-in-law, Senior Advisor to the President of the United States Jared Kushner.[2] Both the West Bank settlers' Yesha Council[3] and the Palestinian leadership rejected the plan: the former because it envisaged a Palestinian state,[3] the latter arguing it is too biased in favor of Israel.[1] The plan is divided into two parts, an economic portion and a political portion. On June 22, 2019, the Trump administration released the economic portion of the plan, titled "Peace to Prosperity". The political portion was released in late January 2020.[1]
During the press conference announcing the plan, Netanyahu announced that the Israeli government would immediately annex the Jordan Valley and West Bank settlements while committing not to create new settlements in areas left to the Palestinians for at least four years. US Ambassador to Israel David M. Friedman claimed that the Trump administration had given permission for an immediate annexation, stating that "Israel does not have to wait at all" and "we will recognize it". The Likud spokesman tweeted that Israeli sovereignty over settlements would be declared on the following Sunday. The Trump administration clarified that no such green light had been given. No decision would take place before new elections and a new government had been formed.[4]
Opponents of the Trump Peace Plan – including all the leading Democratic presidential candidates[5] – have denounced it as a "smokescreen" for this annexation.[6][7]
Proposed benefits to the Palestinians from the plan are contingent on a list of conditions that have been denounced by opponents of the plan as "impossible" or "fantastic".[8][9] An editorial of the Los Angeles Times stated that the plan had arrived 'dead in the water'.[10] The New York Times's regional correspondents state that the plan deprives Palestinians of almost everything they have fought for.[11]
Background
The British government during the dissolution of the Ottoman Empire endorsed a Zionist proposal to open up Palestine to Jewish immigration in order to establish a national home for Jews with the Balfour Declaration and subsequent Mandate for Palestine endorsed by the League of nations as part of partitioning of the Ottoman lands. In 1917, Jews constituted less than 8% of the population. By 1947, over two-thirds of the population consisted of Palestinians while Jews owned less than 7% of the land. In that year, Arab countries rejected the United Nations Partition Plan, which allotted the majority of the land to the Jewish 30% of the population, and in the ensuing war, Israel conquered half of the portion assigned in the plan to Arabs, assuming control over 78% of historic Palestine, with 80% of the Palestinians who had fled no longer permitted to return to their homes in Israel. The remaining 22% was conquered in the Six Day War in 1967, and Israel thereafter began to colonize that new land with settlements in violation of international law. In the Oslo Accords of 1993, the Palestinians gained a restricted autonomy in a scattered mosaic of small areas in the West Bank. [12]
The State of Palestine is recognized by 138 UN members and since 2012 has a status of a non-member observer state in the United Nations – which implies recognition of statehood. Israel and the U.S do not recognize Palestine as a state.[13][14][15] The terms "Palestine", "State of Palestine", "occupied Palestinian territory" (oPt or OPT) may be used interchangeably depending on context. Specifically the term "occupied Palestinian territory" refers as a whole to the geographical area of the Palestinian territory occupied by Israel since 1967. References to land or territory refer to land claimed by the State of Palestine.[16]
The first American attempt to settle the contentions began with Bill Clinton's parameters, set forth in 2000 in the Camp David Summit, which foresaw Israeli annexation of its settlements, while allowing a degree of autonomy to a demilitarized Palestinian state. Though, according to the IDF[12][17] Palestinians constitute the majority of the population in the area Israel now controls (Israel, the Gaza Strip, and the West Bank), both Clinton's and the subsequent Trump plan confine that majority to an area less than a quarter of the land.[12]
Development of the plan
Development of the plan began in November 2017, led by Kushner, chief negotiator Jason Greenblatt, deputy national security adviser Dina Powell, and ambassador David Friedman.[18] Kushner, a property developer married to Trump's daughter Ivanka, had no prior experience of diplomacy,[19] asked the parties not to talk about history, and never really discussed his plan with the Palestinians.[20] Friedman, a lawyer who became was chosen as ambassador to Israel after representing Trump's bankrupted casinos[21], had close ties to the Israeli settlers in the occupied West Bank, compared Jewish American critics of Israel to collaborators with Nazism and was skeptical about the idea that Palestinians should have a state.[20]
In December 2017, Trump recognized Jerusalem as Israel's capital. A key member of Trump's team, the Arabist Dina Powell, left the team "on good terms" two days after the announcement.[22] The move was condemned by Arab countries, and Palestinians broke off contacts with the Trump administration.[2] Regardless of PA's boycott over the Jerusalem decision the intelligence cooperation with the CIA continued.[23] Trump reacted by ending both bilateral aid for Palestinians and contributions for UNRWA,[2][24] citing the PA's refusal to take part in the administration's peace initiative.[25] The United States also shut down the Palestinian diplomatic office in Washington.[26]
Only 7 months before Greenblatt's resignation, in September 2019, Jared Kushner and Jason Greenblatt finalized the "political plan", access to which was restricted to only Kushner, Greenblatt, Friedman and Kushner's former employee and aide Avi Berkowitz.[27] In February 2019, Kushner and his personal adviser Berkowitz flew to Oman, Bahrain, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, Turkey and Saudi Arabia in order to unveil closely-guarded plan.[28] When asked Qatari Foreign Ministry Spokeswoman Lolwah Al Khater gave no indication that meeting provided much in the way of details on the political plan.[28] Following the Kushners trip to Arab states and Turkey, Jason Greenblatt played an important role in Trump's March 25 2019 acceptance of United States recognition of the Golan Heights as part of Israel, was thereafter shunned by the Palestinian authority. In their view, he acted as Israel's spokesman, a country he would never criticize, while, in the two years of the position, he would frequently lambast the Palestinian side on his Twitter account.[29]
In April 2019, Greenblatt said that plan does not call for a confederation model[30] or for a transfer of land from Egypt's Sinai Peninsula to the Palestinians.[31] When asked in June 2019, Greenblatt said that the Trump plan "will include a resolution to all of the core issues, including the refugee issue, and will also focus on Israel's security concerns". Greenblatt resigned, realizing according to Martin Indyk, that the plan had no future,[32] and was replaced by Berkowitz, a young lawyer who worked for Kushner's companies and whom like Kushner, was raised as an orthodox Jew with deep ties to Israel.[33]
In late June 2019, the "economic plan" was unveiled at a U.S.-led "Peace to Prosperity" conference in Manama, Bahrain. The Palestinian leadership boycotted the entire event.[34] According to Bess Levin, writing for Vanity Fair, the whole conference was 'panned by experts', citing one who described it as "the Monty Python sketch of Israeli-Palestinian peace initiatives".[34]Kushner has likened the plan to the Marshall Plan to rebuild Western European economies after World War II.[35] The Economic Vision's empowerment by "doing tourism" was perceived as challenged by the Israel and Egypt's 12-year blockade of the Hamas-controlled territory, and 52-year-long occupation of the West Bank.[36]
The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) accused the US of trying to sell a "mirage of economic prosperity" that would in reality "only perpetuate the Palestinians' captivity". Hamas leader Ismail Haniyeh criticized the Arab leaders attending the conference, saying "The (Palestinian) people, who have been fighting for one hundred years, did not commission anyone to concede or to bargain. Jerusalem is ours, the land is ours, and everything is ours."[37] Regarding the controversy over cultural heritage of Palestinian people; Kushner said that critics of the Trump peace plan must "divorce [themselves] from all of the history[36]
In November 2019, the US abandoned its four-decades-old position that Jewish settlements in the West Bank were inconsistent with international law.[2]
The Trump plan was presented as the best option regarding possible future developments by Kushner who stated "The Palestinian leadership have to ask themselves a question: Do they want to have a state? Do they want to have a better life? If they do, we have created a framework for them to have it, and we're going to treat them in a very respectful manner. If they don't, then they're going to screw up another opportunity like they've screwed up every other opportunity that they've ever had in their existence."[39] Kushner said that the peace proposal will not include the phrase "two-state solution", saying "If you say 'two-state', it means one thing to the Israelis, it means one thing to the Palestinians. We said, 'You know, let's just not say it. Let's just say, let's work on the details of what this means.'"[40] A top-ranking Saudi diplomat stated that the plan includes a "clear path leading to complete Palestinian independence".[41] Robert Malley, director of the International Crisis Group and a leading Middle East expert in former US administrations stated: "Strip away the domestic and Israeli political considerations that determined the timing of the plan's release, and the message to the Palestinians, boiled down to its essence, is: You've lost, get over it." [42]
The political portion of the plan was rolled out on January 28, 2020. The timing of roll-out showed a contrast with the Trump impeachment trial and Netanyahu faces an election in five weeks.[43] Government insist that revealing the plan now was not designed to distract from impeachment, but was rather a reaction to political realities in Israel.[43] Running to 2020 Israeli legislative election Israel had April 2019 Israeli legislative election, which Netanyahu part in what is known as forming the Union of the Right-Wing Parties by uniting the Jewish Home party with the far-right Otzma Yehudit party.[44] Otzma widely characterized as racist and traces its origins to the extremist Kahanist movement.[45] On September 10, 2019, Netanyahu pledged to annex part of the occupied West Bank on the border with Jordan and promised to apply "Israeli sovereignty over the Jordan Valley and northern Dead Sea" if re-elected.[46]
Stated aims of the plan
The stated purpose of the Trump peace plan is to outline the terms of an agreement, to be signed by both parties, to end the conflict between Israelis and Palestinians and clear all claims made by both parties to the conflict. Section 21 of the plan stipulates that this will be proposed in a new UN Security Council resolution and a new United Nations General Assembly resolution[47] The authors of the proposal envisage that the achievement of such a solution would endow Palestinians with the right of self-governance while denying them any powers that might constitute a threat to Israel.[48] The successful solution will direct flights between the State of Israel and its neighbors.[49]The Trump administration stated that it would break with the worn paradigms of past approaches to the Israeli–Palestinian peace process, removing two core issues[38] by implementing two measures in 2017 and 2019, that suggested the United States' redefinition of the parameters for definitively resolving the conflict in large part espoused Israeli positions.[50]These were (1) recognizing Jerusalem as Israel's capital on December 6, 2017 and (2) on November 18, 2019 stating that Jewish settlements in the West Bank were consistent with international law.[2][51] As a visible signal of its break with the past, the United States opened its embassy in the building of the U.S. consulate's compound in Jerusalem's southern neighborhood of Arnona at the 70th anniversary of the establishment of the State of Israel.
Israel
The plan itself places no conditions on Israel with regard to proposals to "annex parts of the West Bank".[9]
Palestinians
The plan envisages that the PLO and the Palestinian Authority must, during the course of projected negotiations:[52]
- Refrain from any attempt to join any international organization without the consent of the State of Israel;[52]
- Take no action, and shall dismiss all pending actions, against the State of Israel, the United States and any of their citizens before the International Criminal Court, the International Court of Justice, and all other tribunals;[52]
- Take no action against any Israeli or United States citizen before Interpol or any non-Israeli or United States (as applicable) legal system;[52]
- Take all necessary actions to immediately terminate the paying of "prisoner & martyr payments" (defined as salaries to the families of terrorists serving sentences in Israeli prisons, as well as to the families of deceased terrorists; in his review of the plan, writer Jonathon Cook says that the plan requires the Palestinian Authority to strip "welfare payments" for "the families of political prisoners and martyrs killed by the Israeli army"[53]) and to develop humanitarian and welfare programs to provide essential services and support to Palestinians in need that are not based upon the commission of terrorist acts. The stated goal is have the Palestinian Authority pass laws regarding militants who have been convicted by Israeli courts of a charge of 'terrorism' in a way that will make those laws consistent with the laws of the United States.[52]
After every step of the Trump plan successfully achieved (economic, development, etc.), plan reaches to its final stage. The final step is the recognition of the State of Palestine. Israel and the United States stated that the following conditions (see: § Recognition Criteria) "must be determined to have occurred by the State of Israel and the United States, jointly".[54]
Key concepts and final status issues
| Part of a series on the Israeli–Palestinian conflict |
| Israeli–Palestinian peace process |
|---|
 |
The economic portion of the plan, consisting of two pamphlets of 40 and 96 pages each that are filled with financial tables and economic projections, was published by the Trump administration on June 22, 2019. It was presented by Kushner during the workshop in Manama, Bahrain on June 25–26.[35] The political portion of the plan was rolled out on January 28, 2020.[55]
Economy
The plan proposes a $50 billion investment fund for 179 infrastructure and business projects,[56] to be administered by a "multilateral development bank", with investments protected by "accountability, transparency, anti-corruption, and conditionality safeguards[35] The administration envisions the plan being funded mostly by Arab states and wealthy private investors.[57] Spending is divided into $26 billion in loans, $13.5 billion in grants, and $11 billion in private investment.[57]
The majority of the $50 billion would be spent in the West Bank and Gaza, with $9 billion to be spent in Egypt, $7 billion in Jordan, and $6.3 billion in Lebanon.[58] The proposal includes a number of specific projects, including construction of a travel corridor that would cross Israel to link the West Bank and Gaza with a highway and possibly a rail line,[35] vast expansion of border crossings,[58] power plant upgrades, infrastructure improvements to boost tourism, career counseling and job placement service, re-building and modernizing Palestinian hospitals and health clinics,[57] upgrading cargo terminals and building special access roads to reduce the time and costs of cross-border trade and travel,[59] creating of a modern database to register land ownership,[59] improving the potable water supply and waste water treatment,[59] and establishing a new Palestinian university in the global top 150.[60]
The plan advocates a free market including greater protection of property rights and a "pro-growth tax structure".[59]
The plan's stated goals include creating more than a million jobs, more than doubling the Palestinian GDP, and cutting the poverty rate by 50%.[60] It also aims to bring down the unemployment from 31% down to single digits, and to increase Palestinian exports as a percentage of GDP from 17% to 40%.[57] The plan also aims to increase female labor force participation rate from 20% to 35%, reduce infant mortality from 18 to 9 per 1000 births, and increase average life expectancy from 74 to 80 years.[60]
Status of State of Palestine
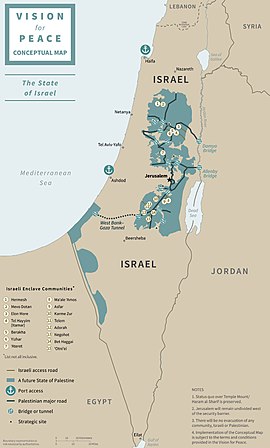
The Trump plan proposes a State of Palestine with a capital on the outskirts of East Jerusalem.[61] Trump plan is offering the Palestinians a state, a future State of Palestine, which will be not established up to four years into the execution of the plan.[62]
The plan would be conditional on Palestinians taking steps to become self-governing.[63] However, the sovereignty the State of Palestine would possess is disputed. Many argue the Trump plan creates a Palestinian state with only limited sovereignty,[26][64][65] while others argue the state would not have sovereignty.[66][67] Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu said the proposal gives Palestinians a chance to achieve "conditional, limited sovereignty".[68] The Jerusalem Post argues sovereignty of Palestine would be limited as Israel would retain full security control.[69] Israel would also control Palestine's borders and airspace.[70]
Recognition criteria
The Trump plan sets forth a criteria that Palestinians must meet before a Palestinian state is allowed to form. Whether Palestinians have met this criteria will be determined by Israel and the United States. If at anytime Israel decides the Palestinians are not meeting the criteria, the Trump plan gives Israel the right to retake military control.[71] According to US diplomat Ilan Goldenburg, this would allow Israel to determine when to end the occupation.[72]
The criteria are:
- The Palestinians shall have implemented a governing system with a constitution or another system for establishing the rule of law that provides for freedom of press, free and fair elections, respect for human rights for its citizens, protections for religious freedom and for religious minorities to observe their faith, uniform and fair enforcement of law and contractual rights, due process under law, and an independent judiciary with appropriate legal consequences and punishment established for violations of the law.
- The Palestinians shall have established transparent, independent, and credit-worthy financial institutions capable of engaging in international market transactions in the same manner as financial institutions of western democracies with appropriate governance to prevent corruption and ensure the proper use of such funds, and a legal system to protect investments and to address market-based commercial expectations. The State of Palestine should meet the independent objective criteria to join the International Monetary Fund.
- The Palestinians shall have ended all programs, including school curricula and textbooks, that serve to incite or promote hatred or antagonism towards its neighbors, or which compensate or incentivize criminal or violent activity.
- The Palestinians shall have achieved civilian and law enforcement control over all of its territory and demilitarized its population.
- The Palestinians shall have complied with all the other terms and conditions of this Vision.
Anti-Terrorism Apparatus
The State of Palestine's security criteria has to be acceptable to the State of Israel; not (less) stringent than the metrics used by either Jordan or Egypt (whichever is stricter) with respect shall be obeyed.[73] The State of Palestine's counterterrorism system must encompass all elements of counterterrorism.[73]
Defense and Border Regime
The State of Palestine shall be fully demilitarized and remain as so.[74]
The State of Israel will be responsible for security at all international crossings into the State of Palestine.[75] The State of Israel will continue to maintain control over the airspace and the electromagnetic spectrum, the Israeli Navy will have the right to block prohibited weapons and weapon-making materials from entering the State of Palestine.
The State of Palestine will not have the right to forge intelligence or security agreements with any state or organization that adversely affect the State of Israel's security, as determined by the State of Israel.[75]
Natural Resources
According to Saree Makdisi, the plan would not allow Palestine to control its water resources.[76]
Status of Jerusalem, Palestinian Capital, and Holy sites
The plan affirms Israel has a right to the entirety of "undivided Jerusalem", recognizing it as Israel's capital.[77]
The plan does accept a Palestinian capital for a future State of Palestine to be located outside, and east and north of, the Separation Barrier, in that part of East Jerusalem encompassing Kafr 'Aqab, and the eastern refugee camp of Shuafat and Abu Dis. [26][78] Martin Indyk described the Palestinian portion as "only a sliver of East Jerusalem".[72] It would bear whatever name Palestinians decide to call it, perhaps al Quds.[79]According to Dubuisson, designating such a site as Jerusalem involves a 'semantic game',[80] a fragmented entity across several neighborhoods that are miles apart from each other, separated by Israeli communities and major roads, and share little in common.[81][82] Abu Dis is variously described as a 'decrepit, lawless enclave'[81]a gang-ridden slum [82]or a grim neighbourhood, [19] with 'a single main street and higgledy-piggledy alleys shooting off at strange angles'[81] abutting a hulking concrete separation barrier, on the other side of which lies Jerusalem and its distant Holy Sites.[19]
The plan puts the Temple Mount, including Al-Aqsa mosque,[72] under Israeli sovereignty. It calls for the status quo to be maintained.[26] The plan rejects Palestinian claims to Haram al-Sharif, instead keeping it under Jordanian custodianship.[83] The plans gives Israel the task of safeguarding the Holy Sites and guaranteeing freedom of worship.[84]
Status of borders and territory
The plan recognizes Palestinian rights to roughly 70% of the West Bank.[62] The plan called for land swaps, but dismissed the idea of "1-to-1 land swaps", arguing Palestinians would not receive 100 percent of pre-1967 territory, but provided for territory that would be "reasonably comparable" to pre-1967 territory.[85] In exchange for Israel annexing parts of the West Bank, the Palestinians would annex parts of the Negev Desert;[78] these parts in the Negev would be disconnected from much of the Palestinian state.[72] The Trump plan gives Palestinians less territory than previous proposals.[86]
The plan recognizes an Israeli right to the entire Jordan Valley.[78] Israel regards the valley as militarily strategic. Palestinians regard the valley as important for agriculture.[87] The valley also allows Palestinians access to the River Jordan, which irrigates 80,000 hectares of agricultural land in the West Bank; giving Israel the valley would allow it to divert that water for its own use.[88]
Within the West Bank, approximately 97% of Palestinians would be incorporated into contiguous Palestinian territory and 97% of Israelis into contiguous Israeli territory.[85]
The implementation of the plan is conditional, being subject to the "Gaza Criteria" and would only proceed if the governance of the Gaza Strip, at present administered by Hamas, were transferred back either to the Palestinian Authority or another Palestinian entity Israel approves of.[89][90]The technical feasibility of such a transformation of Gaza governance is not clear.[91] According to these conditions, Hamas, the PIJ, and all other militias and organizations in Gaza Israel classifies as "terrorist" would have to be disarmed.[92] Gaza would be fully demilitarized.[92] Hamas itself would be required to commit itself to making peace with the State of Israel by adopting the Quartet Principles, which include unambiguously and explicitly recognizing the State of Israel, committing to nonviolence, and accepting previous agreements and obligations between the parties.[92][91]
Status of refugees
Under the Trump plan, there would be no right of return for Palestinian refugees from the wars of 1948 and 1967 into Israel,[93][94] The return of any Palestinian refugees would be subject to Israel's giving its approval.[95]
Were the deal signed, the assistance of UNRWA to the Palestinian population would be terminated.[93]
Status of prisoners
Israel would undertake to release Palestinian prisoners and detainees held under administrative detention in Israeli prisons. The proposal states that all released prisoners would assume citizenship in a future State of Palestine.[96] At the same time, Israel states that it would not release prisoners falling in any one of the following categories:[96]
- Those convicted of murder or attempted murder in Israeli courts.
- Those convicted of conspiracy to commit murder ("terrorists"), according to Israeli courts.
- Anyone classified under 1 and 2, who may happen to hold Israeli citizenship.
Palestinian and Israeli reactions
- On January 29, the US ambassador to Israel did state that before any annexation of the West Bank or the Jordan Valley took place the Trump administration "wants to form a joint committee with Israel to discuss the issue". and that "it is impossible to know how long this process will take…we need to ensure the annexation matches the map in our plan."[97]
- On January 29, 2020, Palestinian President Mahmoud Abbas said Jerusalem was "not for sale; All our rights are not for sale and are not for bargain".[98] Hamas rejected the deal on the grounds that it aspired to "liquidate the Palestinian national project".[99]
- On January 29, 2020, thousands of Palestinian protesters held a "day of rage" in the Gaza Strip.[98]
- On January 29, 2020, President Netanyahu said planning to move with annexing 30% of the West Bank at the vote due on Sunday (on February 1, 2020).[98] The meeting was never scheduled as the US message shifted on their position on annexation.[100]
- On January 30, Kushner said Washington wants Israel to wait until after its March 2 election before making any moves towards settlement annexation in the West Bank.[101]
- On February 1, 2020, Reuters (Cairo) reported that President Trump requested to speak to Abbas by phone but Abbas said no, and that President Trump wanted to send him a letter...but Abbas refused it.[23]
- On February 1, 2020, The Palestinian Authority declare cutting all ties with the United States and Israel including security relations.[23]
- On February 2,2020, Netanyahu's cabinet canceled a meeting to vote on the annexation of 30% of the West Bank after receiving mixed signals from the US.[102]
- On February 3, 2020, Saeb Erekat "What is left to negotiate? When I said these issues must be negotiated between us and Israel directly, Kushner responded by calling me a failed negotiator, unable to negotiate. He negotiated on my behalf because he knows better than I do what is best for me. This is the art of dictation, arrogance, and blackmail." [103]
- On February 3 , 2020, Trump plan raised the possibility that 11 Arab border towns, part of Israel’s 21% Arab minority, become relocated [moved to] a future Palestinian state. Residents fear losing their ties to the land. When asked David Friedman denied that Arab residents in Israel would lose citizenship.[104]
- On February 4, 2020, Israeli settler leader David Elhayani, the chairman of the Yesha Council, said 'Kushner took a knife and put it in Netanyahu's back.' The settler leader said a senior U.S. official told them that if the Palestinians didn’t agree to the plan within 48 hours, Israel would be permitted to annex more than 30 percent of the West Bank.[105]
International reactions
 United Nations reaffirmed its commitment to a two-state solution based on the boundaries pre-existing the 1967 Six Day War, before Israel seized the Palestinian territories.[99]
United Nations reaffirmed its commitment to a two-state solution based on the boundaries pre-existing the 1967 Six Day War, before Israel seized the Palestinian territories.[99] Arab League On February 1, the Arab League issued a unanimous rejection of the plan. In a joint communique, officials from the 22 member states said the deal would not lead to a just peace between both sides, and the league would not cooperate with the US to implement it.[106][107] According to Haaretz, an Arab diplomat explained that the United States did not disclose the full details of its Mideast peace plan to Arab states before its release, which is why representatives of three Arab countries attended the event unveiling it and "when they got into the minute details of the plan, we understood that there is no Palestinian state in practice and there is no capital in East Jerusalem, and more importantly, that there is an attempt to divide al-Aqsa Mosque" and "... so ultimately all the foreign ministers fell in line with the position opposing the Trump plan, and reiterated their commitment to the Arab Peace Initiative."[108]
Arab League On February 1, the Arab League issued a unanimous rejection of the plan. In a joint communique, officials from the 22 member states said the deal would not lead to a just peace between both sides, and the league would not cooperate with the US to implement it.[106][107] According to Haaretz, an Arab diplomat explained that the United States did not disclose the full details of its Mideast peace plan to Arab states before its release, which is why representatives of three Arab countries attended the event unveiling it and "when they got into the minute details of the plan, we understood that there is no Palestinian state in practice and there is no capital in East Jerusalem, and more importantly, that there is an attempt to divide al-Aqsa Mosque" and "... so ultimately all the foreign ministers fell in line with the position opposing the Trump plan, and reiterated their commitment to the Arab Peace Initiative."[108] EU On February 4, 2020, Josep Borrell, High Representative for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy and Vice-President of the European Commission in a toughening of its initial response, said that the plan broke with “internationally agreed parameters” and "Steps towards annexation, if implemented, could not pass unchallenged."[109]
EU On February 4, 2020, Josep Borrell, High Representative for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy and Vice-President of the European Commission in a toughening of its initial response, said that the plan broke with “internationally agreed parameters” and "Steps towards annexation, if implemented, could not pass unchallenged."[109]
 Bahrain's foreign ministry said in a statement "Bahrain supports all efforts toward achieving a just and comprehensive solution on the Palestinian issue," and thanked the United States for its work.[110]
Bahrain's foreign ministry said in a statement "Bahrain supports all efforts toward achieving a just and comprehensive solution on the Palestinian issue," and thanked the United States for its work.[110]
 China's Foreign ministry said that United Nations resolutions, the two-state solution, the principle of land for peace and other internationally backed measures form the basis for resolving the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.[111]
China's Foreign ministry said that United Nations resolutions, the two-state solution, the principle of land for peace and other internationally backed measures form the basis for resolving the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.[111] Egypt's Foreign Ministry issued a statement that Egypt recognizes the importance of considering the U.S. administration's initiative from the perspective of the importance of achieving the resolution of the Palestinian issue, thus restoring to the Palestinian people their full legitimate rights through the establishment of a sovereign independent state in the Palestinian occupied territories in accordance with international legitimacy and resolutions[112][113] and that "Egypt calls on the two relevant parties to undertake a careful and thorough consideration of the U.S. vision to achieve peace and open channels of dialogue, under U.S. auspices, for the resumption of negotiations."[114]
Egypt's Foreign Ministry issued a statement that Egypt recognizes the importance of considering the U.S. administration's initiative from the perspective of the importance of achieving the resolution of the Palestinian issue, thus restoring to the Palestinian people their full legitimate rights through the establishment of a sovereign independent state in the Palestinian occupied territories in accordance with international legitimacy and resolutions[112][113] and that "Egypt calls on the two relevant parties to undertake a careful and thorough consideration of the U.S. vision to achieve peace and open channels of dialogue, under U.S. auspices, for the resumption of negotiations."[114] France's Foreign Ministry initially said in a statement "France welcomes President Trump's efforts and will study closely the peace programme he has presented."[115] On January 30, President Macron said "I believe in two sovereignties" when asked by Le Figaro newspaper whether he believed in two states and suggested the plan could struggle to get off the ground; he said "You need to be two to make peace. You can't get there with just one side."[116]
France's Foreign Ministry initially said in a statement "France welcomes President Trump's efforts and will study closely the peace programme he has presented."[115] On January 30, President Macron said "I believe in two sovereignties" when asked by Le Figaro newspaper whether he believed in two states and suggested the plan could struggle to get off the ground; he said "You need to be two to make peace. You can't get there with just one side."[116] Iran's Foreign Minister Javad Zarif said that the "so-called 'Vision for Peace' is simply the dream project of a bankruptcy-ridden real estate developer", and referred to it as a "nightmare for the region and the world".[117]
Iran's Foreign Minister Javad Zarif said that the "so-called 'Vision for Peace' is simply the dream project of a bankruptcy-ridden real estate developer", and referred to it as a "nightmare for the region and the world".[117] Jordan expressed open opposition to the plan:[118] its Foreign Ministry said that the only path to a comprehensive and lasting Middle East peace was the establishment of an independent Palestinian state based on land captured by Israel in a 1967 war, and with East Jerusalem as its capital.[119]
Jordan expressed open opposition to the plan:[118] its Foreign Ministry said that the only path to a comprehensive and lasting Middle East peace was the establishment of an independent Palestinian state based on land captured by Israel in a 1967 war, and with East Jerusalem as its capital.[119] Kuwait's parliament had decided to boycott the Bahrain conference, the only Gulf state to do so. In response, Kuwait's Foreign Minister stated that "... we accept what our Palestinian brothers accept."[120] The Kuwaiti government appointed its first ambassador to Palestine shortly after[121] After the announcement of the complete plan, foreign ministry showed appreciation towards US efforts for peace, but added that a complete and fair solution is only possible if it follows international community terms and decisions, mainly "... an independent and sovereign state on the June 4, 1967 border with its capital in East Jerusalem."[122]
Kuwait's parliament had decided to boycott the Bahrain conference, the only Gulf state to do so. In response, Kuwait's Foreign Minister stated that "... we accept what our Palestinian brothers accept."[120] The Kuwaiti government appointed its first ambassador to Palestine shortly after[121] After the announcement of the complete plan, foreign ministry showed appreciation towards US efforts for peace, but added that a complete and fair solution is only possible if it follows international community terms and decisions, mainly "... an independent and sovereign state on the June 4, 1967 border with its capital in East Jerusalem."[122] Morocco's Foreign Ministry stated that Morocco "appreciates" the US plan, adding that acceptance by the parties is "fundamental to the implementation and sustainability of the plan".[123]
Morocco's Foreign Ministry stated that Morocco "appreciates" the US plan, adding that acceptance by the parties is "fundamental to the implementation and sustainability of the plan".[123] Qatar's Foreign Ministry stated that 'Qatar affirms its readiness to provide the required support for any endeavors within these foundations to resolve the Palestinian issue... peace cannot be sustainable unless the rights of the Palestinian people to establish an independent and sovereign state on the 1967 borders, including East Jerusalem, and to return to their lands are safeguarded.' [124]
Qatar's Foreign Ministry stated that 'Qatar affirms its readiness to provide the required support for any endeavors within these foundations to resolve the Palestinian issue... peace cannot be sustainable unless the rights of the Palestinian people to establish an independent and sovereign state on the 1967 borders, including East Jerusalem, and to return to their lands are safeguarded.' [124] Russia In an initial official response, presidential spokesman Dmitry Peskov raised doubts about the plan noting "It's plain enough that some of this plan's provisions do not fully correspond to the relevant resolutions by the UN Security Council" and noting the opposition of the Palestinians and Arab states.[125]
Russia In an initial official response, presidential spokesman Dmitry Peskov raised doubts about the plan noting "It's plain enough that some of this plan's provisions do not fully correspond to the relevant resolutions by the UN Security Council" and noting the opposition of the Palestinians and Arab states.[125]
 Saudi Arabia's Foreign Ministry said in a statement, "The Kingdom appreciate the efforts of President Trump's Administration to develop a comprehensive peace plan between the Palestinian and Israeli sides; and encourages the start of direct peace negotiation between the Palestinian and Israeli sides, under the auspices of the United States."[117], King Salman has repeatedly stated Saudi Arabia will not support any settlement that fails to create an independent Palestinian state with East Jerusalem as its capital.[32]
Saudi Arabia's Foreign Ministry said in a statement, "The Kingdom appreciate the efforts of President Trump's Administration to develop a comprehensive peace plan between the Palestinian and Israeli sides; and encourages the start of direct peace negotiation between the Palestinian and Israeli sides, under the auspices of the United States."[117], King Salman has repeatedly stated Saudi Arabia will not support any settlement that fails to create an independent Palestinian state with East Jerusalem as its capital.[32] Turkey's Foreign Ministry criticized the plan and said it was aimed at "stealing Palestinian lands".[126]
Turkey's Foreign Ministry criticized the plan and said it was aimed at "stealing Palestinian lands".[126] United Arab Emirates ambassador issued a statement that the plan offers an important starting point for a return to negotiations within a US-led international framework.[127]
United Arab Emirates ambassador issued a statement that the plan offers an important starting point for a return to negotiations within a US-led international framework.[127]
 United Kingdom Foreign Secretary Dominic Raab initially issued a statement cautiously welcoming the release of US proposals for peace between Israelis and Palestinians.[128] Subsequently, on January 31, Raab, in response to talk of annexation, warned against any unilateral moves.[129]
United Kingdom Foreign Secretary Dominic Raab initially issued a statement cautiously welcoming the release of US proposals for peace between Israelis and Palestinians.[128] Subsequently, on January 31, Raab, in response to talk of annexation, warned against any unilateral moves.[129]
Other reactions
On 3 February, 2020, the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, rejected the plan and "calls on all member states not to engage with this plan or to cooperate with the U.S. administration in implementing it in any form.[130]
According to Christianity Today, the reaction in the Christian world was mixed. The plan was criticised by many Middle Eastern Christians, including by Christians at Nazareth Evangelical College, Gaza Baptist Church, Presbyterian Church of Aleppo and the Arab Baptist Theological Seminary in Beirut. The plan was praised by Christians at Christians United for Israel and Beeson Divinity School in Alabama.[131]
The reaction among American Jewish groups was mixed: J Street criticised the plan while AIPAC praised it.[132] A number of conditions (see: § Recognition Criteria) these have been denounced as unachievable.[8][9]
Bibliography
- White House Staff (2020). Peace to Prosperity (PDF) (Report). The White House. The content of the website is in the public domain or licensed under Creative Commons Attribution license.[133]
References
- ^ a b c "Trump reveals Israeli-Palestinian peace plan". Deutsche Welle. January 28, 2020. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e "Trump releases long-awaited Middle-East peace plan". BBC News. January 28, 2020. Archived from the original on January 28, 2020. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ^ a b Magid, Jacob (January 28, 2020). "Settler leaders call on PM to oppose Trump plan, even at the cost of annexation". The Times of Israel. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ Yossi Verter, "How Trump's "Deal of the Century' Became the Joke of the Century" Archived February 1, 2020, at the Wayback Machine Haaretz January 31, 2020
- ^ "Democratic candidates censure Trump peace plan, warn against annexation". The Times of Israel. January 28, 2020. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
Biden: "This is a political stunt that could spark unilateral moves to annex territory; Warren: "Trump's 'peace plan' is a rubber stamp for annexation"; Buttigieg: "Peace requires both parties at the table. Not a political green light to the leader of one for unilateral annexation.
- ^ "Opinion: Trump's Israel-Palestine 'deal' has always been a fraud". Financial Times. January 28, 2020. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
It always looked like a smokescreen to mask the burial of the two-state solution — an independent Palestinian state on the occupied West Bank, and Gaza with Arab East Jerusalem as its capital living in peace alongside Israel — and greenlight the Israeli annexation of most of the West Bank.
- ^ J Street, "It's Not a Peace Plan, It's an Annexation Smokescreen", "If there was ever any doubt that the Trump-Netanyahu 'peace plan' was anything other than a smokescreen for annexation, it was disabused just moments after the plan's glitzy White House announcement."
- ^ a b Lee, Matthew; Heller, Aron (January 29, 2020). "Trump peace plan delights Israelis, enrages Palestinians". Associated Press. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
It sides with Israel on key contentious issues that have bedeviled past peace efforts, including borders and the status of Jerusalem and Jewish settlements, and attaches nearly impossible conditions for granting the Palestinians their hoped-for state
- ^ a b c "What Trump and Netanyahu just unveiled was a PR campaign, not a peace plan" Archived January 29, 2020, at the Wayback Machine: "But while the promise of Palestinian statehood is contingent on fantastic conditions, the plan sets no conditions for allowing Israel to annex the Jordan Valley and all Israeli settlements in the West Bank."
- ^ "Editorial: Trump's long-awaited Middle East peace plan is finally here. And it's dead in the water". Los Angeles Times. January 28, 2020. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ David M. Halbfinger, Isabel Kershner, "Trump's Mideast Plan Leaves Palestinians With Few Options", Archived January 30, 2020, at the Wayback Machine The New York Times January 29, 2020:'President Trump's Middle East plan deprives the Palestinians of nearly everything they had been fighting for: East Jerusalem as their national capital, the removal of Jewish settlements on the West Bank, and territorial contiguity and control over their own borders and security that a sovereign state normally enjoys.'
- ^ a b c Nathan Thrall, "Trump's Middle East Peace Plan Exposes the Ugly Truth", The New York Times January 29, 2020.
- ^ "Israel defies UN after vote on Palestine with plans for 3,000 new homes in the West Bank". The Independent. 1 December 2012. Archived from the original on 18 October 2017. Retrieved 15 September 2017.
- ^ Charbonneau, Louis (November 29, 2012). "Palestinians win implicit U.N. recognition of sovereign state". Reuters. Thomson Reuters. Archived from the original on June 5, 2014. Retrieved June 8, 2014.
- ^ Lederer, Edith M (30 November 2012). "Live Stream: Palestine asks United Nations for a 'birth certificate' ahead of vote". www.3news.com. New Zealand: MediaWorks TV. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 8 June 2014.
- ^ "United Nations Country Team Occupied Palestinian Territory" (2016), p.9
- ^ Yotam Berger, [https://www.haaretz.com/israel-news/army-presents-figures-showing-arab-majority-in-israel-territories-1.5940676 "Figures Presented by Army Show More Arabs than Jews Live in Israel, the West Bank and Gaza", Haaretz 26 May 2018
- ^ Baker, Peter (November 11, 2017). "Trump Team Begins Drafting Middle East Peace Plan". The New York Times. Archived from the original on June 24, 2019. Retrieved June 23, 2019.
- ^ a b c "Deal of the century/Steal of the century: Donald Trump gives Israel the green light to annex occupied lands" The Economist January 28, 2020,
- ^ a b McGreal, Chris (January 28, 2020). "'Don't talk about history': how Jared Kushner crafted his Middle East 'peace' plan". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on January 28, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ Peter Beinart 'What’s In It For Trump,' Jewish Currents 29 January 2020
- ^ Amir Tibon,"Amid Jerusalem Crisis, Top Middle East Advisor Dina Powell Quits White House", Archived January 29, 2020, at the Wayback Machine Haaretz December 9, 2017
- ^ a b c Staff (February 1, 2020). "Palestinian Authority cuts ties with Israel and U.S." Reuters.
- ^ "U.S. ends aid to United Nations agency supporting Palestinian refugees". The Washington Post. August 31, 2018. Archived from the original on September 2, 2018. Retrieved September 2, 2018.
- ^ "At UN, Abbas threatens to nix agreements with Israel if West Bank land annexed". The Times of Israel. September 26, 2019. Archived from the original on October 2, 2019. Retrieved October 6, 2019.
- ^ a b c d Michael Crowley, David M. Halbfinger, "Trump Releases Mideast Peace Plan That Strongly Favors Israel", The New York Times January 29, 2020.
- ^ "In leaky White House, Trump team keeps Middle East peace plan secret". Reuters. April 11, 2019. Archived from the original on November 19, 2019. Retrieved January 31, 2020.
- ^ a b "Jared Kushner Is Preparing for Another Face-to-Face Meeting with M.B.S." Vanity Fair. Archived from the original on December 25, 2019. Retrieved January 31, 2020.
- ^ Raphael Ahren, "Trump peace plan architect Jason Greenblatt to quit administration" Archived December 6, 2019, at the Wayback Machine The Times of Israel December 5, 2019
- ^ Ahren, Raphael. "Greenblatt tells ToI: US won't propose Israel-Jordan-Palestinian confederation". The Times of Israel. Archived from the original on June 24, 2019. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- ^ "U.S. Mideast plan will not include land transfer from Egypt's Sinai: envoy". Reuters. April 19, 2019. Archived from the original on June 24, 2019. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- ^ a b Martin Indyk [https://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/middle-east/2019-10-15/disaster-desert "Disaster in the Desert: Why Trump's Middle East Plan Can't Work"]. Foreign Policy November–December 2019
- ^ Relman, Eliza (April 5, 2017). "Jared Kushner's 28-year-old protégé is his right-hand man in the White House". Business Insider. Archived from the original on December 12, 2019. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ a b Bess Levin, "Jared Kushner: Palestinians Have Never Done Anything Right in Their Sad, Pathetic Lives", Archived January 30, 2020, at the Wayback Machine Vanity Fair January 29, 2020
- ^ a b c d "Exclusive: White House's Kushner unveils economic portion of Middle..." Reuters. June 23, 2019. Archived from the original on June 22, 2019. Retrieved June 23, 2019.
- ^ a b Levin, Bess. "Kushner: Palestinians Have Never Done Anything Right in Their Sad, Pathetic Lives". Vanity Fair. Archived from the original on January 30, 2020. Retrieved January 30, 2020.
- ^ "US opens debate on Mideast economic plan shunned by Palestinians". Reuters. June 26, 2019. Archived from the original on January 28, 2020. Retrieved October 6, 2019.
- ^ a b Jane Kinninmont, "Jared Kushner's 'Paradigm-busting' Mideast Peace Deal Just Won't Work", Archived December 14, 2019, at the Wayback Machine Haaretz 16 June 2019
- ^ Winer, Stuart. "Kushner slams Palestinian leadership, urges giving up 'fairy tales' for peace". The Times of Israel. Archived from the original on January 30, 2020. Retrieved January 30, 2020.
- ^ Steinbuch, Yaron (May 3, 2019). "Jared Kushner says Mideast peace plan won't say 'two states'". New York Post. Archived from the original on June 24, 2019. Retrieved June 23, 2019.
- ^ "Saudi official says 'Deal of Century' leads to full Palestinian statehood". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on June 22, 2019. Retrieved June 23, 2019.
- ^ David E. Sanger, "A Deal That Has Two Elections, Rather Than Mideast Peace, as Its Focus", Archived January 30, 2020, at the Wayback Machine The New York Times January 28, 2020
- ^ a b "Timing of Mideast peace plan rollout appears designed to contrast with impeachment trial: Analysis". ABC News. Archived from the original on January 30, 2020. Retrieved January 30, 2020.
- ^ Michal Wilner. "Who are the Kahanists of Otzma Netanyahu opened Knesset door to? - Israel Elections". Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on December 18, 2019. Retrieved January 30, 2020.
- ^ Halbfinger, David M. (February 24, 2019). "Netanyahu Sparks Outrage Over Pact With Racist Party". The New York Times. Archived from the original on October 9, 2019. Retrieved January 30, 2020.
- ^ "Netanyahu pledges to annex occupied Jordan Valley". September 10, 2019. Archived from the original on December 5, 2019. Retrieved January 30, 2020.
- ^ WhiteHouse 2020, p. 42
- ^ WhiteHouse 2020, p. 7
- ^ WhiteHouse 2020, p. 8
- ^ François Dubuisson, "Trump 'Plan' would create a fictitious Palestinian state devoid of rights under international law", Mondoweiss January 31, 2020
- ^ "Jewish settlements no longer illegal - US". BBC News. November 18, 2019. Archived from the original on December 8, 2019. Retrieved January 30, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e WhiteHouse 2020, p. 43
- ^ "The Trump plan is just a cover for Israel's final land grab". Middle East Eye. February 4, 2020. Retrieved February 4, 2020.
- ^ Peace plan, page 34
- ^ "Trump releases long-awaited Mid-East peace plan". BBC News. January 28, 2020. Archived from the original on January 28, 2020. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ^ "Jared Kushner Unveils Economic Portion Of Middle East Peace Plan". HuffPost. June 22, 2019. Archived from the original on June 23, 2019. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- ^ a b c d Cortellessa, Eric. "White House finally unveils 'Peace to Prosperity' economic plan for Palestinians". The Times of Israel. Archived from the original on June 23, 2019. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- ^ a b "White House unveils economic portion of Middle East peace plan". Jewish Telegraphic Agency. June 22, 2019. Archived from the original on June 23, 2019. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- ^ a b c d "A look at some of the details of the economic aspect of the Trump peace plan". The Times of Israel. AFP. Archived from the original on June 23, 2019. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- ^ a b c Nahmias, Omri (June 23, 2019). "White House releases detailed economic plan for Palestinian people". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on June 23, 2019. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- ^ "Trump proposes Palestinian state with capital in East Jerusalem". Reuters. January 28, 2020. Archived from the original on January 28, 2020. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ^ a b "How Trump's Peace Plan Will Change the Middle East". Time. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ^ "Trump proposes Palestinian state with capital in East Jerusalem". Reuters. January 28, 2020. Archived from the original on January 28, 2020. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ^ "Trump Says His Mideast Peace Plan Provides A 'Realistic Two-State Solution'".
However, the plan limits the sovereignty of a future Palestinian state.
- ^ Kevin Bohn; Caroline Kelly. "Former President Jimmy Carter criticizes Trump's Middle East plan".
- ^ "African nations respond to U.S. Mideast Peace Plan".
- ^ Mohammed Daraghmeh; Joseph Krauss. "'Nothing will change': Palestinians face dilemma in rejecting Trump's peace plan".
It gives enough of a veneer of statehood that it looks like statehood hasn't been completely removed from the table, when in reality of course it has, because it's been emptied of all notions of sovereignty.
- ^ "Netanyahu says Israel is offering Palestinians 'conditional' & 'limited' sovereignty, new capital will be at Abu Dis".
- ^ "Trump peace plan: Israeli control over settlements, Palestinian state".
- ^ "Savaging Trump plan, Abbas says Palestinians cutting all ties with Israel, US".
- ^ "Trump's Israel-Palestine "peace plan" is a con". Vox media.
- ^ a b c d Robin Wright, "Trump Unveils the 'Giveaway of the Century' on Middle East Peace The New Yorker January 29, 2020
- ^ a b WhiteHouse 2020, p. 51
- ^ WhiteHouse 2020, p. 22
- ^ a b WhiteHouse 2020, p. 53
- ^ "What's New About Trump's Mideast 'Peace' Plan? Only the Blunt Crudity of Its Racism".
- ^ "Trump peace plan: Palestinian state, Israeli control of settlements". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on January 28, 2020. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ^ a b c "Trump's Israel-Palestine peace plan, explained". Vox. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ "Peace for Prosperity", The White House, 2020 section 5.
- ^ François Dubuisson, "Trump 'Plan' would create a fictitious Palestinian state devoid of rights under international law", Mondoweiss January 31, 2020
- ^ a b c Isabel Kershner, David M. Halbfinger, "Capital in Trump Mideast Plan Makes 'a Joke' of Palestinian Aspirations", The New York Times January 31, 2020
- ^ a b Dalia Hatuqa "Trump's Peace Plan Is Palestinians' Worst Nightmare", Foreign Policy January 31, 2020
- ^ "How Trump's Peace Plan Will Change the Middle East". Time. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ^ "President Donald J. Trump's Vision for Peace, Prosperity, and a Brighter Future for Israel and the Palestinian People". The White House. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ a b Magid, Jacob. "Borders, security, Jerusalem, settlements, refugees: Key elements of Trump plan". The Times of Israel. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ "Trump Called His Middle East Peace Plan a 'Win Win.' Palestinians Disagree". Time. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ Bateman, Tom (January 28, 2020). "Smiles and sorrow for Trump's 'realistic' peace plan". BBC News. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ "What will Palestinians lose if Israel annexes Jordan Valley?". Al Jazeera. January 28, 2020. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ Joseph Krauss, 'Key points in Trump’s Mideast peace plan,' Associated Press/America 28 January 2020.
- ^ WhiteHouse 2020, p. 25
- ^ a b Jonah Shepp, 'Trump’s Mideast Peace Plan: Intimidate the Palestinians Into Surrender,' Intelligencer 26 January 2018:'How exactly the Palestinian Authority is supposed to regain security control of Gaza and drive Hamas entirely out of the Palestinian political arena is not clear. Eldar strongly suspects that the impossibility of these tasks is a feature, not a bug, calling them “preventive measures to scuttle any U.S. initiative” toward peace.'
- ^ a b c WhiteHouse 2020, p. 26
- ^ a b "What does Trump's plan propose for Palestinian territories?". Al Jazeera.
- ^ Robin Wright, Trump Unveils the “Giveaway of the Century” on Middle East Peace New Yorker 29 January 2020:'According to Ilan Goldenberg, . .(r)efugees who fled the wars in 1948 and 1967 would be granted some form of compensation, “wrapped in very condescending language,” but not even a symbolic number would be allowed to return.'
- ^ Rashid Khalidi, "President Trump's Peace Plan Is the Latest in a Century of Outrageous Deals for the Palestinians", Time, January 31, 2020. 'The "Deal of the Century" as Trump described it, is in fact a typical colonial concoction: put together by those who believe that they know better than the benighted natives do what is best for them, and elevating the rights and interests of one group over those of another. This pattern, set by Great Britain and the early Zionist movement, has been followed by the U.S. and Israel ever since then.... While far more extreme and one-sided than anything that preceded it, this new plan also constitutes a continuation of a much older pattern. The Palestinians, the overwhelming majority of the population of Palestine at the time, were not even mentioned in the Balfour Declaration, whose terms governed their lives for three decades. Nor were they mentioned in UNSC 242, the supposed basis for "peace-making" in the Middle East, which not surprisingly has signally failed to bring peace to Palestine/Israel in over half a century.
- ^ a b WhiteHouse 2020, p. 30
- ^ "US Ambassador to Israel: Before Israel annex, a committee is in order". The Jerusalem Post. January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ a b c "Palestinians reject Trump's Middle East peace plan". BBC News. January 29, 2020. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ a b "Trump Middle East plan: Palestinians reject 'conspiracy'" Archived January 29, 2020, at the Wayback Machine BBC News January 29, 2020
- ^ Ravid, Barak (January 20, 2020). "Netanyahu slows annexation push as White House message shifts". Axios.
- ^ "Kushner says he hopes Israel waits on sovereignty steps in West Bank". Reuters. January 30, 2020. Archived from the original on January 30, 2020. Retrieved January 30, 2020.
- ^ Kershner, Isabel (February 2, 2020). "Israel Puts Brakes on West Bank Annexation Plan". New York Times.
- ^ CNN, Nicole Gaouette. "Kushner defends conditions for Palestinians to get a state and 'take control of themselves'". CNN.
{{cite news}}:|last1=has generic name (help) - ^ "Arabs in Israeli border towns fear Trump plan will transfer them to West Bank". Reuters. February 3, 2020.
- ^ Coleman, Justine (February 4, 2020). "Israeli settler leader: 'Kushner took a knife and put it in Netanyahu's back'". TheHill.
- ^ "Arab League rejects Trump's 'deal of the century' at Cairo summit with Abbas". RT. February 1, 2020. Retrieved February 1, 2020.
- ^ "Arab League rejects Trump's Middle East plan: communique". Reuters. February 1, 2020. Retrieved February 1, 2020.
- ^ "Arab Envoys at Trump's Peace Plan Unveiling Were Misled, Diplomat Says". Haaretz. February 1, 2020. Retrieved February 1, 2020.
- ^ "EU's top diplomat warns against Trump Middle East peace plan, annexation". Reuters. February 4, 2020. Retrieved February 4, 2020.
- ^ "Bahrain, Kuwait says supports all efforts towards solution for Palestine issue". Arab News. January 29, 2020.
- ^ "China: UN resolutions are basis for resolving Palestine-Israel conflict". MEMO. January 30, 2020. Archived from the original on January 30, 2020. Retrieved January 30, 2020.
- ^ "Press statement". Egyptian Ministry of Foreign Affairs. January 28, 2020. Archived from the original on January 30, 2020. Retrieved January 30, 2020.
- ^ "Trump's Plan for Middle East Peace Hinges on Support From Arab Leaders. That's Looking Unlikely". Time. January 29, 2020. Archived from the original on January 30, 2020. Retrieved January 30, 2020.
- ^ "Egypt calls for dialogue over U.S. Mideast peace plan". Reuters. January 28, 2020. Archived from the original on January 28, 2020. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ^ "France says will study Trump's Mideast peace plan closely". Reuters. January 29, 2020. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ "Macron says believes in 'two sovereignties' between Israelis-Palestinians: Le Figaro". Reuters. January 30, 2020. Retrieved January 30, 2020.
- ^ a b "Iran, Turkey slam Trump peace plan as UAE, Saudi Arabia urge negotiations". The Times of Israel. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ Zvi Bar'el, "Trump's 'al-Aqua Mosque' Plan Leaves Palestinians With Nothing More to Lose", Archived January 30, 2020, at the Wayback Machine Haaretz January 30, 2020
- ^ "Jordan says two-state solution only path to Mideast peace". Reuters. January 28, 2020. Archived from the original on January 30, 2020. Retrieved January 30, 2020.
- ^ "Kuwait to boycott Bahrain conference". Middle East Monitor. June 25, 2019. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ "Kuwait appoints its first ambassador to Palestine". Middle East Monitor. October 30, 2019. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ "Kuwait sees abidance by int'l resolutions as fair solution to Palestine case". Kuwait News Agency (KUNA). January 29, 2020.
- ^ "Morocco 'appreciates' Mideast peace plan, says needs acceptance by parties". Reuters. January 29, 2020. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 30, 2020.
- ^ "Factbox: U.S. Middle East peace plan prompts some praise, much Arab anger", Archived January 29, 2020, at the Wayback Machine Reuters January 28, 2020
- ^ "Trump's 'deal of the century' contradicts UN resolutions - Kremlin". RT. February 2, 2020. Retrieved February 2, 2020.
- ^ "Trump's Middle East plan would steal Palestinian land: Turkey". Reuters. January 28, 2020. Archived from the original on January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ "Ambassador Yousef Al Otaiba Statement on Peace Plan". UAE Embassy in Washington, DC. Archived from the original on January 28, 2020. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ^ "Foreign Secretary statement on release of US proposals for Middle East peace". GOV.UK.
- ^ "Britain cautions Israel against advancing West Bank annexation". The Times of Israel. January 31, 2020. Retrieved February 2, 2020.
- ^ "Organization of Islamic Cooperation rejects Trump peace plan: statement". Reuters. February 3, 2020. Retrieved February 3, 2020.
- ^ "13 Christian Takes on Trump's Peace Plan for Israel and Palestine". Christianity Today.
- ^ "AIPAC, J Street offer predictably contrasting views on Trump peace plan".
- ^ "Copyright Policy". whitehouse.gov. January 16, 2017. Archived from the original on January 24, 2017. Retrieved January 24, 2017.
External links
- "Peace to Prosperity" full text
- Peace to Prosperity short overview Whitehouse.gov
- Transcript of Trump Peace Plan Speech