Gloria Macapagal Arroyo
Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo | |
|---|---|
 | |
| 14th President of the Philippines | |
| Assumed office January 20, 2001 | |
| Vice President | Teofisto Guingona Noli de Castro |
| Preceded by | Joseph Estrada |
| Member of the House of Representatives from Pampanga's 2nd district | |
| Assuming office June 30, 2010 | |
| Succeeding | Mikey Arroyo |
| 12th Vice President of the Philippines | |
| In office June 30, 1998 – January 20, 2001 | |
| President | Joseph Estrada |
| Preceded by | Joseph Estrada |
| Succeeded by | Teofisto Guingona |
| Personal details | |
| Born | April 5, 1947[1] San Juan City, Philippines |
| Political party | Lakas-Kampi-CMD (2009–present) |
| Other political affiliations | LDP (Before 1998) KAMPI (1997–2009) Lakas-CMD (1998–2009) |
| Spouse | Jose Miguel Arroyo |
| Alma mater | Edmund A. Walsh School of Foreign Service Assumption College Ateneo de Manila University University of the Philippines School of Economics |
| Profession | Economist |
| Signature | |
| Website | Official website |
Maria Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo (born April 5, 1947)[1] is the fourteenth and current president of the Philippines. Arroyo is the country's second female (after Corazon Aquino) and second longest serving (after Ferdinand Marcos) president, she is also the daughter of late former Philippine President Diosdado Macapagal and is a descendant of Don Juan Macapagal who was a great-grandson of Lakandula the last reigning Rajah (King) of Saludung.[2]
A professor of economics, Arroyo entered government in 1987, serving as assistant secretary and undersecretary of the Department of Trade and Industry upon the invitation of President Corazon Aquino. After serving as a senator from 1992 to 1998, she was elected to the vice presidency under President Joseph Estrada, despite having run on an opposing ticket. After Estrada was accused of corruption, she resigned her cabinet position as Secretary of Social Welfare and Development and joined the growing opposition to the president, who faced impeachment. Estrada was soon forced from office by what its advocates would ascribe to peaceful street demonstrations of the EDSA Revolution of 2001, but which critics credit to a conspiracy among political and business elites, military top brass and Catholic Church cardinal Jaime Sin.[3] Arroyo was sworn into the presidency by then-Chief Justice Hilario Davide, Jr. at around noon on January 20, 2001 amidst the EDSA II crowd, hours before Estrada left Malacañang. She was elected to a full six-year presidential term in the controversial May 2004 Philippine elections, and was sworn in on June 30, 2004. Arroyo is nearing her 10th year in power and is currently serving the second longest presidential term in Philippine history, next to Ferdinand Marcos.
In the 2009 rankings of Most Powerful Women by Forbes, she was ranked as the 44th most powerful woman in the world.[4]
Early life
She was born as María Gloria Macaraeg Macapagal to politician Diosdado Macapagal and his wife, Evangelina Macaraeg-Macapagal. She is the sister of Dr. Diosdado "Boboy" Macapagal, Jr. & Cielo Macapagal-Salgado. She spent the first years of her life in Lubao, Pampanga with her two older siblings from her father's first marriage.[1] At the age of four, she chose to live with her maternal grandmother in Iligan City.[5] She stayed there for three years, then split her time between Mindanao and Manila until the age of 11.[5] She is fluent in English, Tagalog, Spanish and several other Philippine languages, most importantly, Kapampangan, Ilokano, and Cebuano.
In 1961, when Arroyo was just 14 years old, her father was elected as president. She moved with her family into Malacañang Palace in Manila. A municipality was named in her honor, Gloria, Oriental Mindoro. She attended Assumption Convent for her elementary and high school education, graduating valedictorian in 1964. Arroyo then studied for two years at Georgetown University's Walsh School of Foreign Service in Washington, D.C. where she was a classmate of future United States President Bill Clinton and achieved consistent Dean's list status.[6] She then earned her Bachelor of Arts degree in Economics from Assumption College, graduating magna cum laude in 1968.
In 1968, Arroyo married lawyer and businessman José Miguel Arroyo of Binalbagan, Negros Occidental, whom she had met while still a teenager.[1] They had three children, Juan Miguel (born 1969), Evangelina Lourdes (born 1971) and Diosdado Ignacio José María (born in 1974). She pursued a Master's Degree in Economics at the Ateneo de Manila University (1978) and a Doctorate Degree in Economics from the University of the Philippines (1985).[7] From 1977 to 1987, she held teaching positions in several schools, notably the University of the Philippines and the Ateneo de Manila University. She became chairperson of the Economics Department at Assumption College.
In 1987 she was invited by President Corazon Aquino to join the government as Assistant Secretary of the Department of Trade and Industry. She was promoted to Undersecretary two years later. In her concurrent position as Executive Director of the Garments and Textile Export Board, Arroyo oversaw the rapid growth of the garment industry in the late 1980s.
Senator
Arroyo entered politics in the 1992 election, running for senator. At the first general election under the 1987 Constitution, the top twelve vote-getting senatorial candidates would win a six-year term, and the next twelve candidates would win a three-year term.[8] Arroyo ranked 13th in the elections, earning a three-year term. She was re-elected in 1995, topping the senatorial elections with nearly 16 million votes.
As a legislator, Arroyo filed over 400 bills and authored or sponsored 55 laws during her tenure as senator, including the Anti-Sexual Harassment Law, the Indigenous People's Rights Law, and the Export Development Act.[1]
The 1995 Mining Act, which allows 100% foreign ownership of Philippine mines, has come under fire from left-wing political groups.
Vice Presidency
Arroyo considered a run for the presidency in the 1998 election, but was persuaded by President Fidel V. Ramos and leaders of the administration party Lakas-Christian Muslim Democrats to instead seek the vice-presidency as the running mate of its presidential candidate, House Speaker José de Venecia, Jr.[9] Though the latter lost to popular former actor Joseph Ejército Estrada, Arroyo won the vice presidency by a large margin, garnering more than twice the votes of her closest opponent, Estrada's running mate Senator Edgardo Angara.[10]
Arroyo began her term as Vice President on June 30, 1998. Historically, she was the first and only to date female Vice President of the Philippines. She was appointed by Estrada to a concurrent position in the cabinet as Secretary of Social Welfare and Development.[9]
Arroyo resigned from the cabinet in October 2000, distancing herself from President Estrada, who was accused of corruption by a former political supporter, Chavit Singson, Governor from Ilocos Sur.[11] She had initially resisted pressure from allies to speak out against Estrada,[12] but eventually joined calls for Estrada's resignation.[11]
Presidency
| Presidential styles of Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo | |
|---|---|
| File:PhilippinePresidentialSeal.png | |
| Reference style | Her Illustrious Excellency, The Right Honourable President of the Republic of the Philippines Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo |
| Spoken style | President Arroyo, President Macapagal-Arroyo |
| Alternative style | Madame President |
First Term (2001-2004)
Succession

The last quarter of 2000 up to the first week of January 2001 was a period of political and economic uncertainty for the Philippines. On January 16, 2001, the impeachment trial has also taken a new direction. Private prosecutors walked out of the trial when pro-Estrada senators prevented the opening of an evidence (a brown envelope) containing bank records allegedly owned by President Estrada. With the walk out, the impeachment trial was not completed and the Filipinos eventually took to the street to continue the clamor for President Estrada's resignation.
From January 17 to 20, 2001, hundreds of thousands of Filipinos gathered at Epifanio de los Santos Avenue (EDSA), the site of the original People Power Revolution. The clamor for a change in the presidency gained momentum as various sectors of Philippine society – professionals, students, artists, politicians, leftist and rightist groups – joined what became known as EDSA II. Officials of the administration, the Armed Forces of the Philippines (AFP), and the Philippine National Police (PNP) also withdrew their support for President Estrada.
Days after leaving Malacañang Palace, President Estrada's lawyers questioned the legitimacy of Arroyo's presidency before the Supreme Court. He reiterated that he did not resign as president and that at most, Arroyo was just serving in an acting capacity. The high court, however, voted unanimously in upholding the legitimacy of Arroyo's succession. As a consequence, Estrada no longer enjoys immunity from charges being filed against him.
In the last week of April 2001, the Sandiganbayan ordered the arrest of Estrada and his son, Senator Jinggoy Estrada, for plunder charges. A few days later, Estrada supporters protested his arrest, gathered at the EDSA Shrine, and staged what they called, EDSA III – comparing their actions to the People Power revolution of 1986 and January 2001.
Thousands of protesters demanded the release of Estrada. Eventually, they also called for the ouster of Arroyo and the reinstatement of the former. On May 1, 2001, they marched towards Malacañang to force Arroyo to give in to their demands. Violence erupted when the protesters attempted to storm the presidential palace and the military and police were forced to use their arms to drive them back. Arroyo declared a state of rebellion because of the violence and prominent political personalities affiliated with Estrada were charged and arrested. The so-called EDSA III was the first serious political challenge to the Arroyo presidency.
Oakwood Mutiny
The Oakwood mutiny occurred in the Philippines on July 27, 2003. A group of 321 armed soldiers who called themselves "Bagong Katipuneros"[13] led by Army Capt. Gerardo Gambala and Lt. Antonio Trillanes IV of the Philippine Navy took over the Oakwood Premier Ayala Center (now Ascott Makati) serviced apartment tower in Makati City to show the Filipino people the alleged corruption of the Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo administration. They also stated that they saw signs suggesting that the President was going to declare martial law.
2004 Presidential Election
Article VII Section 4 of the 1987 Constitution explicitly states that the president of the Philippines can only serve for one term. However, the same provision also implicitly states that a president's successor who has not served for more than four years can still seek a full term for the presidency. Although Arroyo falls under this category, she initially announced on December 30, 2002 that she will no longer seek the presidency. She emphasized that she will devote her remaining months in office to serving the people and improving the economy of the Philippines.
In October 2003, Arroyo changed her mind and announced that she will run for the May 2004 presidential elections and seek a direct mandate from the people. She explained that, "there is a higher cause to change society...in a way that nourishes our future". With her decision, the initial criticisms hurled against Arroyo centered on her lack of word of honor.
As predicted by SWS exit polls, Arroyo won the election by a margin of over one million votes against Poe. However, the congressional canvassing was quite contentious as opposition lawmakers in the National Board of Canvassers argued that there were many discrepancies in the election returns and that insinuations of cheating were raised. On June 23, 2004, Congress proclaimed Arroyo and Noli de Castro as president and vice president, respectively.
Second Term (2004-present)
2004 Presidential Election rigging allegations

On June 30, 2004, in a break with tradition, Arroyo first delivered her inaugural speech at the Quirino Grandstand in Manila. She then departed for Cebu City for her oath taking, the first time that a Philippine president took the oath of office outside of Luzon.
Allegations of cheating against Arroyo gained momentum one year after the May 2004 elections. In a press conference held on June 10, 2005, Samuel Ong, former deputy director of the National Bureau of Investigation (NBI) claimed to have audio recordings of wiretapped conversations between Arroyo and an official of the Commission on Elections (COMELEC). Virgilio Garcillano, a former COMELEC commissioner, would later be identified as the official talking to Arroyo. According to Ong, the recordings allegedly proved that Arroyo ordered the rigging of the national elections for her to win by around one million votes against Poe.
The recordings of Ong became known as the Hello Garci controversy and triggered massive protests against Arroyo. Key members of her cabinet resigned from their respective posts and urged Arroyo to do the same. On June 27, 2005, Arroyo admitted to inappropriately speaking to a COMELEC official, claiming it was a "lapse in judgement". She, however, denied influencing the outcome of the elections and declared that she won the elections fairly. Arroyo did not resign despite the pressures coming from various sectors of society.
The Hello Garci controversy became the basis of the impeachment case filed against Arroyo in 2005. Attempts to impeach Arroyo failed later that year. Another impeachment case was filed against Arroyo in 2006 but was also defeated at the House of representatives.
In October 2007, lawyer Alan Paguia filed an impeachment complaint against Arroyo in connection with the issue of bribery. Paguia's complaint was based on the revelation of Pampanga Gov. Ed Panlilio that various governors received half a million pesos from Malacañang. The impeachment case, as of the middle of October 2007, has already been referred to the House of Representatives Committee on Justice.
State of Emergency
On February 24, 2006, a plot to take over the government was uncovered by authorities, allegedly headed by Gen. Danny Lim and other rightist military adventurists. General Lim and some of his men were arrested. To face the threat posed by enemies of the state, Arroyo issued Presidential Proclamation 1017 (PP 1017) and used it as basis in declaring a state of emergency throughout the Philippines. According to Arroyo, this declaration was done to quell the military rebellion, stop lawless violence, and promote peace and stability. PP 1017 also empowered the government to enforce warrantless arrests and take over strategic private utilities companies.
On February 25, 2006, the police raided the office of the Daily Tribune, a newspaper known as a critic of the Arroyo administration. The government then issued a journalism guidelines to address the threat posed by critics in the media. Presidential Management Staff chief Michael Defensor said that the guidelines were necessary in order to cope with the emergency situation.
The state of emergency existed for about one week with the purpose of curbing further violence, illegal rallies, and public disturbance throughout the Philippines. The police and the military dispersed demonstrators and protesters, especially those along Epifanio de los Santos Avenue (EDSA). Aside from General Lim, prominent personalities were also arrested in connection with their alleged participation in the attempt to overthrow the government. Among those arrested were:
- Col. Ariel Querubín - leader of a group of Philippine Marines who engaged the government in a political stand-off at Fort Bonifacio on February 25, 2005
- Randy David - led a protest rally without securing the necessary permit
- Crispín Beltrán - party-list representative of Anakpawis charged with inciting to sedition and rebellion
- Batasan Five - party-list representatives charged with rebellion and were placed under the custody of the House of Representatives; Bayan Muna's Teodoro Casiño, Satur Ocampo, and Joel Virador; Gabriela's Liza Maza, and Anakpawis' Rafael Mariano
PP 1017 was lifted on March 3, 2006 but members of the opposition, private lawyers, and concerned citizens challenged its constitutionality before the Supreme Court. On May 4, the high court declared the proclamation constitutional. However, it also said that it was illegal for the government to implement warrantless arrests and seize private institutions and companies.
Charter Change
Arroyo currently spearheads a controversial plan for an overhaul of the constitution to transform the present unitary and presidential republic with a bicameral legislature into a federal parliamentary government with a unicameral legislature.[14]
Congressional bid in Pampanga
On November 30, 2009, after much speculation, President Arroyo announced on the Philippine Broadcasting Service her congressional bid for the second district of Pampanga.[15] On December 1, 2009, she filed her candidacy under the Lakas-Kampi-CMD.[16] Lakas Kampi CMD leaders had said that they will field the president as Speaker of the Philippine House of Representatives; the ruling party has more than 100 incumbents running in the 2010 House elections, and a several running unopposed or by token opposition, Lakas-Kampi predicts an overwhelming number of their candidates will win their respective races, and that the president will have an easy time of being elected as speaker.[17] On May 12, 2010, she was proclaimed as representative of the second district by a landslide victory.[18]
Economy
Domestic Policies
Foreign Policies
Public perception
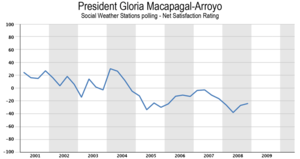
The Social Weather Stations public opinion group has conducted quarterly surveys tracking the net satisfaction rating ("satisfied" rating minus "dissatisfied" rating") of President Arroyo. She began her presidency in the first quarter of 2001 with a net satisfaction rating of +24. Her rating first dipped into the negative in the first quarter of 2003, making Arroyo the only president to achieve a negative net satisfaction rating in SWS opinion polling. Her rating rebounded well into the positive in 2004, in time for the presidential election where she won election to a new six-year term. However, net satisfaction sunk back into negative territory in the fourth quarter of 2004, and has remained negative since, dipping as low as -38 in the second quarter of 2008. Her net satisfaction rating in the first quarter of 2009 was -32.[19]
Scouting
Arroyo is both Chief Scout of the Boy Scouts of the Philippines and Chief Girl Scout of the Girl Scouts of the Philippines.[20][21]
Health
On July 3, 2009, it was announced that Arroyo had undergone a biopsy to examine lumps discovered in her breast and groin.[22][23] Press Secretary Cerge Remonde stated that the results of the biopsy were negative.[22][23] Remonde also denied reports published in July 3, 2009 editions of the Manila Bulletin and the Philippine Star that Arroyo had undergone surgery for the removal or repair of breast silicone implants.[22][23][24]
References
- ^ a b c d e "Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo". Current Biography International Yearbook 2004. The H. W. Wilson Company. Retrieved June 4, 2007.
- ^ "The Houses of Lakandula, Matanda, and Soliman (1571-1898): Genealogy and Group Identity". Philippine Quarterly of Culture and Society 18. 1990.
- ^ Bowring, Philip. "Filipino Democracy Needs Stronger Institutions". International Herald Tribune . January 22, 2001. Retrieved January 27, 2009.
- ^ http://www.forbes.com/lists/2009/11/power-women-09_Gloria-Arroyo_1YDI.html
- ^ a b Spaeth, Anthony (January 29, 2001). "Glory, Gloria!". Time Magazine. Retrieved June 4, 2007.
- ^ "Gloria Arroyo, The Most Powerful Women". Forbes. November 1, 2005. Retrieved June 4, 2007.
- ^ "President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo Biography". Office of the President. Archived from the original on May 24, 2007. Retrieved June 4, 2007.
- ^ "Article 18: Transitory Provisions". The 1987 Constitution of the Republic of the Philippines. The Official Website of the Republic of the Philippines. Archived from the original on May 27, 2007. Retrieved June 5, 2007.
- ^ a b Malaya, J. Eduardo (2004). ...So Help Us God: The Presidents of the Philippines and Their Inaugural Addresses. Pasig City: Anvil Publishing. pp. 301–303. ISBN 971-27-1487-X.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Results of the Past Presidential & Vice-Presidential Elections". The Philippine Presidency Project. Retrieved June 4, 2007.
- ^ a b Estrada v. Arroyo, G.R. No. 146710-15. (2001)
- ^ Mydans, Seth (October 13, 2000). "Philippine Vice President Quits Cabinet, Citing Scandal". The New York Times. Retrieved May 3, 2010.
- ^ Laurel, Herman T (February 22, 2006). "Small setback..." The Daily Tribune. Archived from the original on September 28, 2007. Retrieved August 10, 2007.
- ^ Dalangin-Fernandez, Lira (July 27, 2006). "People's support for Charter change 'nowhere to go but up'". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Retrieved July 27, 2006.
- ^ "Arroyo to run for Congress". Philippine Daily Inquirer. November 30, 2009. Retrieved December 31, 2009.
- ^ "Arroyo now an official bet for Congress". Philippine Daily Inquirer. December 1, 2009. Retrieved December 31, 2009.
- ^ Diaz, Jess (February 15, 2010). "Lakas to field GMA as bet for Speaker". Philippine Star.
- ^ Sisante, Johanna (May 12, 2010). "Arroyo proclaimed as Pampanga congresswoman". GMA News.
- ^ Social Weather Stations
- ^ "National Leadership (2005-2006)". Boy Scouts of the Philippines. Retrieved June 4, 2007.
- ^ "Central Board". Girl Scouts of the Philippines. Retrieved June 4, 2007.
- ^ a b c Charissa M. Luci (July 3, 2009). "Palace confirms biopsy". Manila Bulletin. Retrieved July 3, 2009.
- ^ a b c TJ Burgonio (July 3, 2009). "Biopsy, not breast job for Arroyo -- Palace". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Retrieved July 3, 2009.
- ^ Jarius Bondoc (July 3, 2009). "Thanked By Arroyo, Trumped By Customs". Philippine Star. Retrieved July 3, 2009.
External links
- Office of the President of the Philippines
- President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo official website
- Reporter's Notebook: Ang Palasyo Reporter's Notebook Special, December 4, 2007
|- |- style="text-align:center;"
|style="width:30%;" rowspan="1"|Preceded by
| style="width: 40%; text-align: center;" rowspan="1"| Chair of Lakas-Kampi-CMD
2009
| style="width: 30%; text-align: center;" rowspan="1"| Succeeded by
|- |}
- 1947 births
- Ateneo de Manila University alumni
- Ateneo de Manila University faculty
- Current national leaders
- Female heads of government
- Female heads of state
- Filipino economists
- Filipino Roman Catholics
- Filipino women in politics
- Leaders who took power by coup
- Living people
- Macapagal family
- People from Pampanga
- People of Kapampangan descent
- Philippine presidential candidates
- Presidents of the Philippines
- Recipients of the Star of Romania Order
- Scouting in the Philippines
- Senators of the Philippines
- Vice Presidents of the Philippines
- University of the Philippines alumni



