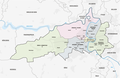
Bern
Bern Berne | |
|---|---|
 Aerial view of the Old City | |
| Country | Switzerland |
| Canton | Bern |
| District | Bern-Mittelland administrative district |
| Government | |
| • Executive | Gemeinderat with 5 members |
| • Mayor | Stadtpräsident (list) Alexander Tschäppät SPS/PSS (as of 2014) |
| • Parliament | Stadtrat with 80 members |
| Area | |
| • Total | 51.62 km2 (19.93 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 542 m (1,778 ft) |
| Highest elevation (Gurten) | 864 m (2,835 ft) |
| Lowest elevation (Aare) | 480 m (1,570 ft) |
| Population (31 December 2018)[2] | |
| • Total | 133,883 |
| • Density | 2,600/km2 (6,700/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Bernese (Berner) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (Central European Time) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (Central European Summer Time) |
| Postal code(s) | 3000–3030 |
| SFOS number | 0351 |
| ISO 3166 code | CH-BE |
| Surrounded by | Bremgarten bei Bern, Frauenkappelen, Ittigen, Kirchlindach, Köniz, Mühleberg, Muri bei Bern, Neuenegg, Ostermundigen, Wohlen bei Bern, Zollikofen |
| Website | www SFSO statistics |
The city of Bern or Berne (German: Bern, pronounced [bɛrn] ; French: Berne [bɛʁn]; Italian: Berna [ˈbɛrna]; Template:Lang-rm [ˈbɛrnə]; Berndeutsch/Bärndütsch (Bernese German): Bärn [b̥æːrn]) is the Bundesstadt (federal city, de facto[3] capital) of Switzerland, and, with a population of 137,980 (end of 2013), is the fourth most populous city in Switzerland.[4] The Bern agglomeration, which includes 36 municipalities, has a population of 328,616 in 2000.[5] The metropolitan area had a population of 660,000 in 2000.[6] Bern is also the capital of the Canton of Bern, the second most populous of Switzerland's cantons.
The official language of Bern is (the Swiss variety of Standard) German, but the main spoken language is the Alemannic Swiss German dialect called Bernese German.
In 1983 the historic old town in the centre of Bern became a UNESCO World Heritage Site and Bern is ranked among the world’s top ten cities for the best quality of life (2010).[7]
Name
The etymology of the name Bern is uncertain. According to the local legend, based on folk etymology, Berchtold V, Duke of Zähringen, the founder of the city of Bern, vowed to name the city after the first animal he met on the hunt, and this turned out to be a bear. It has long been considered likely that the city was named after the Italian city of Verona, which at the time was known as Bern in Middle High German. As a result of the find of the Bern zinc tablet in the 1980s, it is now more common to assume that the city was named after a pre-existing toponym of Celtic origin, possibly *berna "cleft".[8] The bear was the heraldic animal of the seal and coat of arms of Bern from at least the 1220s. The earliest reference to the keeping of live bears in the Bärengraben dates to the 1440s.
History
Early history

No archaeological evidence that indicates a settlement on the site of today′s city centre prior to the 12th century has been found so far. In antiquity, a Celtic oppidum stood on the "Engehalbinsel" north of Bern, fortified since the 2nd century BC (late La Tène period), thought to be one of the twelve oppida of the Helvetii mentioned by Caesar. During the Roman era, there was a Gallo-Roman vicus on the same site. The Bern zinc tablet has the name Brenodor "dwelling of Breno". In the Early Middle Ages, there was a settlement in Bümpliz, now a city district of Bern, some 4 km (2 mi) from the medieval city.
The medieval city is a foundation of the Zähringer ruling family, which rose to power in Upper Burgundy in the 12th century. According to 14th century historiography (Cronica de Berno, 1309), Bern was founded in 1191 by Berthold V, Duke of Zähringen.
In 1218, after Berthold died without an heir, Bern was made a free imperial city by the Goldene Handfeste of Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II.
Old Swiss Confederacy
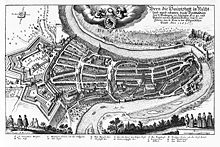
In 1353 Bern joined the Swiss Confederacy, becoming one of the "eight cantons" of the formative period of 1353 to 1481. Bern invaded and conquered Aargau in 1415 and Vaud in 1536, as well as other smaller territories, there by becoming the largest city-state north of the Alps, by the 18th century comprising most of what is today the canton of Bern and the canton of Vaud.
The city grew out towards the west of the boundaries of the peninsula formed by the River Aare. Initially, the Zytglogge tower marked the western boundary of the city from 1191 until 1256, when the Käfigturm took over this role until 1345, which, in turn, was then succeeded by the Christoffelturm (located close to today's railway station) until 1622. During the time of the Thirty Years' War two new fortifications, the so-called big and small Schanze (entrenchment), were built to protect the whole area of the peninsula.
After a major blaze in 1405, the original wooden buildings were gradually replaced by half-timbered houses and later the sandstone buildings that came to be characteristic for the Old Town. Despite the waves of pestilence that hit Europe in the 14th century, the city continued to grow mainly due to immigration from the surrounding countryside.[9]
Modern history
Bern was occupied by French troops in 1798 during the French Revolutionary Wars, when it was stripped of parts of its territories. It regained the Bernese Oberland in 1802, and following the Congress of Vienna of 1814 newly acquired the Bernese Jura, once again becoming the largest canton of the confederacy as it stood during the Restoration, and further until the secession of the canton of Jura in 1979. In 1848 Bern was made the Federal City (seat of the Federal Assembly) of the new Swiss federal state.
A number of congresses of the socialist First and Second Internationals were held in Bern, particularly during World War I when Switzerland was neutral; see Bern International.
The city's population rose from about 5,000 in the 15th century to about 12,000 by 1800 and to above 60,000 by 1900, passing the 100,000 mark during the 1920s. Population peaked during the 1960s at 165,000, and has since decreased slightly, to below 130,000 by 2000. As of 31 December 2009, the resident population was at 130,289 of which 101,627 were Swiss citizens and 28,662 (22%) resident foreigners. Another estimated 350,000 people live in the immediate urban agglomeration.[10]
Geography


Bern lies on the Swiss plateau in the Canton of Bern, slightly west of the centre of Switzerland and 20 km (12 mi) north of the Bernese Alps. The countryside around Bern was formed by glaciers during the most recent Ice Age. The two mountains closest to Bern are Gurten with a height of 864 m (2,835 ft) and Bantiger with a height of 947 m (3,107 ft). The site of the old observatory in Bern is the point of origin of the CH1903 coordinate system at 46°57′08.66″N 7°26′22.50″E / 46.9524056°N 7.4395833°E.
The city was originally built on a hilly peninsula surrounded by the River Aare, but outgrew the natural boundaries by the 19th century. A number of bridges have been built to allow the city to expand beyond the Aare.
Bern is built on very uneven ground. There is an elevation difference of several metres between the inner city districts on the Aare (Matte, Marzili) and the higher ones (Kirchenfeld, Länggasse).
Bern has an area, as of 2009[update], of 51.62 square kilometers (19.93 sq mi). Of this area, 9.79 square kilometers (3.78 sq mi) or 19.0% is used for agricultural purposes, while 17.33 square kilometers (6.69 sq mi) or 33.6% is forested. Of the rest of the land, 23.25 square kilometers (8.98 sq mi) or 45.0% is settled (buildings or roads), 1.06 square kilometers (0.41 sq mi) or 2.1% is either rivers or lakes and 0.16 square kilometers (0.062 sq mi) or 0.3% is unproductive land.[11]
Of the developed, 3.6% consists of industrial buildings, 21.7% housing and other buildings, and 12.6% is devoted to transport infrastructure. Power and water infrastructure as well as other special developed areas made up 1.1% of the city, while another 6.0% consists of parks, green belts and sports fields. 32.8% of the total land area is heavily forested. Of the agricultural land, 14.3% is used for growing crops and 4.0% is designated to be used as pastures. The rivers and streams provide all the water in the municipality.[11]
Climate
| Climate data for Bern (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 2.8 (37.0) |
4.7 (40.5) |
9.5 (49.1) |
13.4 (56.1) |
18.2 (64.8) |
21.6 (70.9) |
24.3 (75.7) |
23.7 (74.7) |
19.1 (66.4) |
13.8 (56.8) |
7.3 (45.1) |
3.5 (38.3) |
13.5 (56.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −0.4 (31.3) |
0.7 (33.3) |
4.7 (40.5) |
8.1 (46.6) |
12.7 (54.9) |
16.0 (60.8) |
18.3 (64.9) |
17.7 (63.9) |
13.7 (56.7) |
9.3 (48.7) |
3.7 (38.7) |
0.6 (33.1) |
8.8 (47.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −3.6 (25.5) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
0.2 (32.4) |
3.0 (37.4) |
7.4 (45.3) |
10.5 (50.9) |
12.5 (54.5) |
12.3 (54.1) |
8.9 (48.0) |
5.4 (41.7) |
0.4 (32.7) |
−2.3 (27.9) |
4.3 (39.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 60 (2.4) |
55 (2.2) |
73 (2.9) |
82 (3.2) |
119 (4.7) |
111 (4.4) |
106 (4.2) |
116 (4.6) |
99 (3.9) |
88 (3.5) |
76 (3.0) |
74 (2.9) |
1,059 (41.7) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 12.8 (5.0) |
13.1 (5.2) |
7.0 (2.8) |
0.8 (0.3) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.1 (0.0) |
5.5 (2.2) |
13.3 (5.2) |
52.6 (20.7) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 9.6 | 9.0 | 10.6 | 10.4 | 12.6 | 11.1 | 10.8 | 10.7 | 8.9 | 10.4 | 10.2 | 9.9 | 124.2 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 1.0 cm) | 4.1 | 3.5 | 2.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 3.1 | 14.1 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 84 | 79 | 73 | 71 | 73 | 71 | 71 | 73 | 79 | 84 | 85 | 85 | 77 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 64 | 87 | 137 | 159 | 182 | 205 | 236 | 217 | 165 | 113 | 68 | 49 | 1,682 |
| Source: MeteoSwiss[12] | |||||||||||||
Subdivisions
The municipality is administratively subdivided into six districts (Stadtteile), each of which consists of several quarters (Quartiere).
Demographics
| Largest groups of foreign residents 2012 | ||
| Nationality | Amount | % total (foreigners) |
|---|---|---|
| 5,957 | 4.7 (20.0) | |
| 4,113 | 3.2 (13.5) | |
| 1,977 | 1.6 (6.5) | |
| 1,433 | 1.1 (4.7) | |
| 1,161 | 0.9 (3.8) | |
| 1,120 | 0.9 (3.7) | |
| 1,085 | 0.9 (3.6) | |
| 898 | 0.7 (3.0) | |
| 898 | 0.7 (3.0) | |
| 668 | 0.5 (2.2) | |
| 629 | 0.5 (2.1) | |
Bern has a population (as of December 2020[update]) of 134,794.[13] As of 2010[update], 23.2% of the population are resident foreign nationals. Over the last 10 years (2000–2010) the population has changed at a rate of 0.6%. Migration accounted for 1.3%, while births and deaths accounted for −2.1%.[14]
Most of the population (as of 2000[update]) speaks German (104,465 or 81.2%) as their first language, Italian is the second most common (5,062 or 3.9%) and French is the third (4,671 or 3.6%). There are 171 people who speak Romansh.[15]
As of 2008[update], the population was 47.5% male and 52.5% female. The population was made up of 44,032 Swiss men (35.4% of the population) and 15,092 (12.1%) non-Swiss men. There were 51,531 Swiss women (41.4%) and 13,726 (11.0%) non-Swiss women.[16] Of the population in the municipality, 39,008 or about 30.3% were born in Bern and lived there in 2000. There were 27,573 or 21.4% who were born in the same canton, while 25,818 or 20.1% were born somewhere else in Switzerland, and 27,812 or 21.6% were born outside of Switzerland.[15]

As of 2000[update], children and teenagers (0–19 years old) make up 15.1% of the population, while adults (20–64 years old) make up 65% and seniors (over 64 years old) make up 19.9%.[14]
As of 2000[update], there were 59,948 people who were single and never married in the municipality. There were 49,873 married individuals, 9,345 widows or widowers and 9,468 individuals who are divorced.[15]

As of 2000[update], there were 67,115 private households in the municipality, and an average of 1.8 persons per household.[14] There were 34,981 households that consist of only one person and 1,592 households with five or more people. In 2000[update], a total of 65,538 apartments (90.6% of the total) were permanently occupied, while 5,352 apartments (7.4%) were seasonally occupied and 1,444 apartments (2.0%) were empty.[17] As of 2009[update], the construction rate of new housing units was 1.2 new units per 1000 residents.[14]
As of 2003[update] the average price to rent an average apartment in Bern was 1108.92 Swiss francs (CHF) per month (US$890, £500, €710 approx. exchange rate from 2003). The average rate for a one room apartment was 619.82 CHF (US$500, £280, €400), a two-room apartment was about 879.36 CHF (US$700, £400, €560), a three-room apartment was about 1040.54 CHF (US$830, £470, €670) and a six or more room apartment cost an average of 2094.80 CHF (US$1680, £940, €1340). The average apartment price in Bern was 99.4% of the national average of 1116 CHF.[18] The vacancy rate for the municipality, in 2010[update], was 0.45%.[14]
Historic population
The historical population is given in the following chart:[19]

| Historic Population Data[19] | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Total Population | German Speaking | French Speaking | Protestant | Catholic | Jewish | Christian Catholic | Other or no religion given | No religion given | Swiss | Non-Swiss |
| 1700 | 14,219 | ||||||||||
| 1730 | 15,932 | ||||||||||
| 1764 | 14,515 | ||||||||||
| 1798 | 12,186 | ||||||||||
| 1818 | 18,997 | ||||||||||
| 1837 | 24,362 | ||||||||||
| 1850 | 29,670 | 27,986 | 1,478 | 206 | 28,009 | 1,661 | |||||
| 1880 | 44,087 | 41,784 | 1,875 | 39,948 | 3,456 | 387 | 296 | 40,463 | 3,624 | ||
| 1910 | 90,937 | 83,144 | 4,566 | 78,234 | 9,650 | 1,056 | 1,997 | 81,335 | 9,602 | ||
| 1930 | 111,783 | 102,444 | 6,378 | 95,600 | 13,280 | 854 | 2,049 | 104,864 | 6,919 | ||
| 1950 | 146,499 | 129,781 | 10,262 | 118,823 | 23,295 | 1,089 | 792 | 2,500 | 139,367 | 7,132 | |
| 1970 | 162,405 | 133,737 | 8,041 | 115,779 | 41,374 | 635 | 561 | 4,056 | 139,873 | 22,532 | |
| 1990 | 136,338 | 110,279 | 5,236 | 79,889 | 36,723 | 335 | 334 | 19,057 | 10,006 | 112,599 | 23,739 |
Politics


Bern is governed by the Gemeinderat, an executive council with five members, one of them the elected mayor (Stadtpräsident). The parliament has 80 members and is called Stadtrat. Both the legislative and the executive are elected in general elections for a term of four years. The last elections were held in November 2008 with a 43.48% participation.
The executive council has a left-green majority with two representatives, including the mayor Alexander Tschäppät, of the Social Democratic Party of Switzerland (SPS) and one representative of the leftist Green party Grünes Bündnis (GB). It also has a majority of three women against two men.
The seat of the Gemeinderat is the Erlacherhof.
The 80 members of the legislative council belong to 18 different political parties, the strongest being the Social Democratic Party with 20 representatives, followed by the conservative Free Democratic Party of Switzerland (FDP) with 10 and the moderate Green party Grüne Freien Liste (GFL) with 9 seats. Both the far right Swiss People's Party (SVP) and the leftist Green party Grünes Bündnis have 8 seats each.
The Stadtrat meets on Thursday evenings at the Rathaus (town hall).
The representatives of the Social Democratic Party and of the Green Parties, collectively referred to as "Red-Green-Center" (Rot-Grüne-Mitte), hold a majority in both councils and mostly determine city policy, although no formal coalition agreement exists and, under the system of direct democracy that prevails in Switzerland, most important issues are settled by general vote.
In the 2007 federal election the most popular party was the SPS which received 29.12% of the vote. The next three most popular parties were the Green Party (24.88%), the SVP (16.73%) and the FDP (15.7%). In the federal election, a total of 43,783 votes were cast, and the voter turnout was 51.5%.[20]
Main sights


The structure of Bern's city centre is largely medieval and has been recognised by UNESCO as a Cultural World Heritage Site. Perhaps its most famous sight is the Zytglogge (Bernese German for "Time Bell"), an elaborate medieval clock tower with moving puppets. It also has an impressive 15th century Gothic cathedral, the Münster, and a 15th-century town hall. Thanks to 6 kilometres (4 miles) of arcades, the old town boasts one of the longest covered shopping promenades in Europe.
Since the 16th century, the city has had a bear pit, the Bärengraben, at the far end of the Nydeggbrücke to house its heraldic animals. The currently four bears are now kept in an open-air enclosure nearby, and two other young bears, a present by the Russian president, are kept in Dählhölzli zoo.[21]
The Federal Palace (Bundeshaus), built from 1857 to 1902, which houses the national parliament, government and part of the federal administration, can also be visited.
Albert Einstein lived in a flat at the Kramgasse 49, the site of the Einsteinhaus, from 1903 to 1905, the year in which the Annus Mirabilis Papers were published.
The Rose Garden (Rosengarten), from which a scenic panoramic view of the medieval town centre can be enjoyed, is a well-kept Rosarium on a hill, converted into a park from a former cemetery in 1913.
There are eleven Renaissance allegorical statues on public fountains in the Old Town. Nearly all the 16th century fountains, except the Zähringer fountain which was created by Hans Hiltbrand, are the work of the Fribourg master Hans Gieng. One of the more interesting fountains is the Kindlifresserbrunnen (Bernese German: Child Eater Fountain but often translated Ogre Fountain) which is claimed to represent a Jew,[22] the Greek god Chronos or a Fastnacht figure that scares disobedient children.[23]
Bern's most recent sight is the set of fountains in front of the Federal Palace. It was inaugurated on 1 August 2004.
The Universal Postal Union is situated in Bern.

Heritage sites of national significance
Bern is home to 114 Swiss heritage sites of national significance.[24]
It includes the entire Old Town, which is also a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and many sites within and around it. Some of the most notable in the Old Town include the Cathedral which was started in 1421 and is the tallest cathedral in Switzerland, the Zytglogge and Käfigturm towers, which mark two successive expansions of the Old Town, and the Holy Ghost Church, which is one of the largest Swiss Reformed churches in Switzerland. Within the Old Town, there are eleven 16th century fountains, most attributed to Hans Gieng, that are on the list.
Outside the Old Town the heritage sites include the Bärengraben, the Gewerbeschule Bern (1937), the Eidgenössisches Archiv für Denkmalpflege, the Kirchenfeld mansion district (after 1881), the Thunplatzbrunnen, the Federal Mint building, the Federal Archives, the Swiss National Library, the Historical Museum (1894), Alpine Museum, Museum of Communication and Natural History Museum.
Culture



Theatres
- Bern Theatre[25]
- Narrenpack Theatre Bern[26]
- Schlachthaus Theatre[27]
- Tojo Theater
- The Theatre on the Effinger-Street[28]
- Theatre am Käfigturm[29]
Cinemas
Bern has several dozen cinemas. As is customary in Switzerland, films are generally shown in their original language (e.g., English) with German and French subtitles. Only a small number of screenings are dubbed in German.
Film festivals
- Shnit international shortfilmfestival shnit International Shortfilmfestival, held annually in early October.
- Queersicht – gay and lesbian film festival, held annually in the second week of November.
Festivals
- BeJazz Summer and Winter Festival
- Buskers' festival
- Gurtenfestival
- Internationales Jazzfestival Bern
- SHNIT International Short Film Festival
- Taktlos-Festival
Fairs
- Zibelemärit – The Zibelemärit (onion market) is an annual fair held on the fourth Monday in November.
- Bernese Fassnacht (Carnival)
Sport

Bern was the site of the 1954 Football (Soccer) World Cup Final, a huge upset for the Hungarian Golden Team, who were beaten 3–2 by West Germany.
The football team BSC Young Boys is based in Bern at the Stade de Suisse Wankdorf, which also was one of the venues for the European football championship 2008.
The Stade de Suisse hosted three matches during the 2008 UEFA Euro Cup tournament.
SC Bern is the major ice hockey team of Bern who plays at the PostFinance Arena.
The PostFinance Arena was the main host of the 2009 IIHF Ice Hockey World Championship, including the opening game and the final of the tournament.
The PostFinance Arena was also the host of the 2011 European Figure Skate Championships.
Bern Cardinals is the baseball and softball team of Bern, which plays at the Allmend
Bern Grizzlies is the American football club in Bern and plays at Athletics Arena Wankdorf.
Bern was a candidate to host the 2010 Winter Olympics, but withdrew its bid in September 2002 after a referendum was passed that showed that the bid was not supported by locals. Those games were eventually awarded to Vancouver, Canada.
RC Bern is the local rugby club (since 1972) and plays at the Allmend. The ladies team was founded in 1995.
Economy
As of 2010[update], Bern had an unemployment rate of 3.3%. As of 2008[update], there were 259 people employed in the primary economic sector and about 59 businesses involved in this sector. 16,413 people were employed in the secondary sector and there were 950 businesses in this sector. 135,973 people were employed in the tertiary sector, with 7,654 businesses in this sector.[14]
In 2008[update] the total number of full-time equivalent jobs was 125,037. The number of jobs in the primary sector was 203, of which 184 were in agriculture and 19 were in forestry or lumber production. The number of jobs in the secondary sector was 15,476 of which 7,650 or (49.4%) were in manufacturing, 51 or (0.3%) were in mining and 6,389 (41.3%) were in construction. The number of jobs in the tertiary sector was 109,358. In the tertiary sector; 11,396 or 10.4% were in wholesale or retail sales or the repair of motor vehicles, 10,293 or 9.4% were in the movement and storage of goods, 5,090 or 4.7% were in a hotel or restaurant, 7,302 or 6.7% were in the information industry, 8,437 or 7.7% were the insurance or financial industry, 10,660 or 9.7% were technical professionals or scientists, 5,338 or 4.9% were in education and 17,903 or 16.4% were in health care.[30]
In 2000[update], there were 94,367 workers who commuted into the municipality and 16,424 workers who commuted away. The municipality is a net importer of workers, with about 5.7 workers entering the municipality for every one leaving.[31] Of the working population, 50.6% used public transport to get to work, and 20.6% used a private car.[14]
Religion
From the 2000 census[update], 60,455 or 47.0% belonged to the Swiss Reformed Church, while 31,510 or 24.5% were Roman Catholic. Of the rest of the population, there were 1,874 members of an Orthodox church (or about 1.46% of the population), there were 229 persons (or about 0.18% of the population) who belonged to the Christian Catholic Church, and there were 5,531 persons (or about 4.30% of the population) who belonged to another Christian church. There were 324 persons (or about 0.25% of the population) who were Jewish, and 4,907 (or about 3.81% of the population) who were Muslim. There were 629 persons who were Buddhist, 1,430 persons who were Hindu and 177 persons who belonged to another church. 16,363 (or about 12.72% of the population) belonged to no church, are agnostic or atheist, and 7,855 persons (or about 6.11% of the population) did not answer the question.[15]
Education

The University of Bern, whose buildings are mainly located in the Länggasse quarter, is located in Bern, as well as the University of Applied Sciences (Fachhochschule) and several vocations schools.
In Bern, about 50,418 or (39.2%) of the population have completed non-mandatory upper secondary education, and 24,311 or (18.9%) have completed additional higher education (either university or a Fachhochschule). Of the 24,311 who completed tertiary schooling, 51.6% were Swiss men, 33.0% were Swiss women, 8.9% were non-Swiss men and 6.5% were non-Swiss women.[15]
The Canton of Bern school system provides one year of non-obligatory kindergarten, followed by six years of primary school. This is followed by three years of obligatory lower secondary school where the pupils are separated according to ability and aptitude. Following the lower secondary pupils may attend additional schooling or they may enter an apprenticeship.[32]
During the 2009–10 school year, there were a total of 10,979 pupils attending classes in Bern. There were 89 kindergarten classes with a total of 1,641 pupils in the municipality. Of the kindergarten pupils, 32.4% were permanent or temporary residents of Switzerland (not citizens) and 40.2% have a different mother language than the classroom language. The municipality had 266 primary classes and 5,040 pupils. Of the primary pupils, 30.1% were permanent or temporary residents of Switzerland (not citizens) and 35.7% have a different mother language than the classroom language. During the same year, there were 151 lower secondary classes with a total of 2,581 pupils. There were 28.7% who were permanent or temporary residents of Switzerland (not citizens) and 32.7% have a different mother language than the classroom language.[33]
Bern is home to 8 libraries. These libraries include; the Schweiz. Nationalbibliothek/ Bibliothèque nationale suisse, the Universitätsbibliothek Bern, the Kornhausbibliotheken Bern, the BFH Wirtschaft und Verwaltung Bern, the BFH Gesundheit, the BFH Soziale Arbeit, the Hochschule der Künste Bern, Gestaltung und Kunst and the Hochschule der Künste Bern, Musikbibliothek. There was a combined total (as of 2008[update]) of 10,308,336 books or other media in the libraries, and in the same year a total of 2,627,973 items were loaned out.[34]
As of 2000[update], there were 9,045 pupils in Bern who came from another municipality, while 1,185 residents attended schools outside the municipality.[31]
Transport

Public transport works well in Bern, with the Bern S-Bahn, Bern tramway network, Bern trolleybus system and a bus network forming an integrated all-four style scheme connecting the different parts of the city.
A funicular railway leads from the Marzili district to the Bundeshaus. The Marzilibahn funicular is, with a length of 106 m (348 ft), the second shortest public railway in Europe after the Zagreb funicular.
Several Aare bridges connect the old parts of the city with the newer districts outside of the peninsula.
Bern is well connected to other cities by several motorways (A1, A12, A6).
Bern railway station connects the city to the national and international railways network.
Bern is also served by Bern Airport, located outside the city near the town of Belp. The regional airport, colloquially called Bern-Belp or Belpmoos, is connected to several European cities. Additionally Zürich Airport, Geneva Airport and EuroAirport Basel-Mulhouse-Freiburg also serve as international gateways, all reachable within two hours by car or train from Bern.
Notable people

- Mikhail Bakunin died in Bern on 1 July 1876
- Vladimir Lenin resided in Bern from 1914 until 1917
- Albert Einstein worked out his theory of relativity while living in Bern, employed as a clerk at the patent office
- Albrecht von Haller
- Louise Elisabeth de Meuron, a famed eccentric and noble lady
- Paul Emmert, painter
- Ferdinand Hodler, painter
- Michael Kauter, fencer
- Mark Streit, ice hockey player
- Christoph von Graffenried, founder of New Bern in the US state of North Carolina
- Peter Bieri, philosophy professor and novelist
- Adolf Wölfli, visual artist
- Roman Josi, ice hockey player
- Mani Matter, songwriter
- Léon Savary, Swiss writer and journalist
- Hans Urwyler, Christian minister
- Aimé Félix Tschiffely, Famous Longrider
- Algirdas Paleckis, diplomat and politician, was born in Bern
- Emil Theodor Kocher, recipient of 1909 Nobel Prize.
Twin Cities
The city council of the city of Bern decided against having twinned cities except for a temporary (during the UEFA Euro 2008) cooperation with the austrian city Salzburg[35][36]
Notes and references
- ^ a b "Arealstatistik Standard - Gemeinden nach 4 Hauptbereichen". Federal Statistical Office. Retrieved 13 January 2019.
- ^ . Federal Statistical Office https://www.pxweb.bfs.admin.ch/pxweb/de/. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Holenstein, André (2012). "Die Hauptstadt existiert nicht" (PDF). http://www.kommunikation.unibe.ch (scientific article). UniPress (in German) (UniPress 152: Die Hauptstatdtregion). Berne: University of Berne: 16–19. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
Als 1848 ein politisch-administratives Zentrum für den neuen Bundesstaat zu bestimmen war, verzichteten die Verfassungsväter darauf, eine Hauptstadt der Schweiz zu bezeichnen und formulierten stattdessen in Artikel 108: «Alles, was sich auf den Sitz der Bundesbehörden bezieht, ist Gegenstand der Bundesgesetzgebung.» Die Bundesstadt ist also nicht mehr und nicht weniger als der Sitz der Bundesbehörden.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|website= - ^ "Stadt Bern – Aktuelles". Bern.ch (in German). City of Berne. Retrieved 15 April 2014.
- ^ "Eidgenössische Volkszählung: Bevölkerungsentwicklung in Stadt und erweiterter Agglomeration Bern" (PDF). www.bern.ch (press information) (in German). City of Berne. 17 January 2003. Retrieved 15 April 2014.
- ^ "Office fédéral du développement territorial ARE – B3: Les aires métropolitaines" (PDF). www.are.admin.ch (in French, German, and or Italian). Federal Office for Spatial Development ARE. 7 June 2006. p. 4. Retrieved 17 April 2014.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "''Quality of Living global city rankings – Mercer survey''". Mercer.com. Retrieved 26 October 2012.
- ^ Andres Kristol (ed.): Lexikon der schweizerischen Gemeindenamen. Huber, Frauenfeld 2005, ISBN 3-7193-1308-5, p. 143.
- ^ Bern: Development of the settlement and the population in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.Error in template * invalid parameter (Template:HDS): "1"
- ^ municipal statistics,[1] includes 6,816 weekend commuters not included in the federal statistics of 123,466.[2]
- ^ a b Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics 2009 data Template:De icon accessed 25 March 2010
- ^ "Climate Normals Bern/Zollikofen 1981–2010" (PDF). Climate diagrams and normals from Swiss measuring stations. Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology (MeteoSwiss). Retrieved 21 January 2013.
- ^ "Ständige und nichtständige Wohnbevölkerung nach institutionellen Gliederungen, Geburtsort und Staatsangehörigkeit". bfs.admin.ch (in German). Swiss Federal Statistical Office - STAT-TAB. 31 December 2020. Retrieved 21 September 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g Swiss Federal Statistical Office accessed 23-January-2012
- ^ a b c d e STAT-TAB Datenwürfel für Thema 40.3 – 2000 Template:De icon accessed 2 February 2011
- ^ Statistical office of the Canton of Bern Template:De icon accessed 4 January 2012
- ^ Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB – Datenwürfel für Thema 09.2 – Gebäude und Wohnungen Template:De icon accessed 28 January 2011
- ^ Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Rental prices 2003 data Template:De icon accessed 26 May 2010
- ^ a b Bern in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- ^ Swiss Federal Statistical Office, Nationalratswahlen 2007: Stärke der Parteien und Wahlbeteiligung, nach Gemeinden/Bezirk/Canton Template:De icon accessed 28 May 2010
- ^ "City of bears receives Russian bruins". swissinfo.ch. 16 September 2009.
- ^ City Council of Bern minutes of the 14 May 1998 5:00PM session accessed 23 November 2008Template:De icon
- ^ Hofer, 281
- ^ "Kantonsliste A-Objekte". KGS Inventar (in German). Federal Office of Civil Protection. 2009. Retrieved 25 April 2011.
{{cite web}}: External link in|work= - ^ "Stadttheater Bern". Retrieved 12 April 2009.
- ^ "Narrenpack Theatre Bern". Retrieved 12 April 2009.
- ^ "Schlachthaus Theatre Bern". Retrieved 12 April 2009.
- ^ "Das Theatre an der Effingerstrasse". Retrieved 12 April 2009.
- ^ "Theater am Käfigturm". Retrieved 12 April 2009.
- ^ Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB Betriebszählung: Arbeitsstätten nach Gemeinde und NOGA 2008 (Abschnitte), Sektoren 1–3 Template:De icon accessed 28 January 2011
- ^ a b Swiss Federal Statistical Office – Statweb Template:De icon accessed 24 June 2010
- ^ EDK/CDIP/IDES (2010). Kantonale Schulstrukturen in der Schweiz und im Fürstentum Liechtenstein / Structures Scolaires Cantonales en Suisse et Dans la Principauté du Liechtenstein (PDF) (Report). Retrieved 24 June 2010.
- ^ Schuljahr 2009/10 pdf documentTemplate:De icon accessed 4 January 2012
- ^ Swiss Federal Statistical Office, list of libraries Template:De icon accessed 14 May 2010
- ^ "EURO 2008 – Partnerschaft von Stadt und Kanton Bern sowie mit Stadt und Land Salzburg". www.bern.ch (in German). Abteilung Kommunikation und Amt für Information, City of Berne. 30 May 2006. Retrieved 6 April 2014.
…in einer gemeinsamen Erklärung die Absicht bekundet, mittels einer zeitlich befristeten Partnerschaft zwischen den Städten und Ländern…
- ^ "Interpellation Fraktion SP/JUSO Andreas Flückiger/Markus Lüthi, SP): Das orange Wunder von Bern: Diese Freundschaft muss gepflegt werden! Was können wir tun?". www.bern.ch (in German). Der Gemeinderat (city council). 22 October 2008. Archived from the original on 30 November 2012. Retrieved 14 October 2014.
Bisher hat die Stadt Bern bewusst auf eine Städtepartnerschaft verzichtet
External links
- City of Bern
- Bern (Gemeinde) in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Archived 2007-10-23 at the Wayback Machine
- Bern Public Transportation Website (BernMobil)
 Bern travel guide from Wikivoyage
Bern travel guide from Wikivoyage- CityHunter Bern
- Gurtenfestival
- Municipalities of the canton of Bern
- Bern
- 1191 establishments in Switzerland
- Canton of Bern
- Cantonal capitals of Switzerland
- Capitals in Europe
- Cities in Switzerland
- Cultural property of national significance in the canton of Bern
- Populated places on the Aare
- World Heritage Sites in Switzerland
- University towns