Chengdu J-10
| J-10 Vigorous Dragon F-10 Vanguard | |
|---|---|
| File:J-10a zhas.png | |
| J-10A seen at Zhuhai airshow. | |
| Role | Multirole combat aircraft |
| National origin | China |
| Manufacturer | Chengdu Aircraft Industry Corporation |
| Designer | Chengdu Aircraft Design Institute |
| First flight | 23 March 1998[1] |
| Introduction | 2005[2] |
| Status | In service |
| Primary user | People's Liberation Army Air Force |
| Produced | 2002 – present[3] |
| Number built | ~400 As of August 2014[update][4] |
| Developed from | Chengdu J-9[5] |
The Chengdu J-10 (simplified Chinese: 歼-10; traditional Chinese: 殲-10, Known in the West as the "Vigorous Dragon",[6]) is a multirole fighter aircraft designed and produced by the People's Republic of China's Chengdu Aircraft Corporation (CAC) for the People's Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF). the J-10 is a multirole combat aircraft capable of all-weather operation.
Currently, the Pakistan Air Force is the only export contractor for the J-10.[7][8]
Development
The program was authorized by Deng Xiaoping who allocated ¥ 0.5 billion to develop an indigenous aircraft. Work on Project #10[1] started several years later in January 1988,[9] as a response to the Mikoyan MiG-29 and Sukhoi Su-27 then being introduced by the USSR. Development was delegated to the 611 Institute, also known as the Chengdu Aircraft Design Institute and Song Wencong was nominated as the chief designer, as he had previously been the chief designer of the J-7III. The aircraft was initially designed as a specialized fighter, but later became a multirole aircraft capable of both air to air combat and ground attack missions.
The J-10 bears some resemblance to the IAI Lavi[10] and some news and technical articles have claimed that some of the Lavi's technology had been sold to China by the Israelis, these claims have been denied by both China and Israel.[11][12] The general designer Song Wencong said that J-10 was a development of the indigenous J-9 which preceded the Lavi.[13][14] This was echoed by a PLAAF's major Zhang Weigang in a 2012 interview.[15]
In 2006, the Russian Siberian Aeronautical Research Institute (SibNIA) confirmed its participation in the J-10 program; SibNIA claimed to have only observed and instructed as "scientific guides", while its engineers also believed the J-10 was "more or less a version" of the Lavi design, incorporating "a melting pot of foreign technology and acquired design methods".[16]
The J-10 was officially unveiled by the Chinese government in January 2007, when photographs were published by Xinhua News Agency. The aircraft's existence was known long before the announcement, although concrete details remained scarce due to secrecy. A J-10 prototype was speculated to have crashed during flight testing.[17] Xinhua News Agency and the PLA Daily denied such rumors, and listed this as one of the test pilots' accomplishments.[18]
The prototype "J-10 01" was rolled out in November 1997 and first flown on 23 March 1998[1][19] in a twenty-minute flight.
AVIC plans to market an upgraded J-10 for export, most likely the J-10B, once development is complete. Several countries have shown interest.[20]
Operational history
China

The first aircraft were delivered to the 13th Test Regiment on 23 February 2003. The aircraft was declared 'operational' in December of the same year, after 18 years in development.[1][10] The first operational regiment was the 131st Regiment of the 44th Division.
Pakistan
In February 2006, the then President of Pakistan, Pervez Musharraf, toured the J-10 and JF-17 production facilities on a trip to China during which the Pakistan Air Force (PAF) was offered the J-10,[21][22] and the purchase of 36 FC-20s, a Pakistan-specific J-10B variant, was approved in April 2006.[22] In November 2009, Pakistan signed a deal with China to buy 36 J-10B fighters in a deal worth around $1.4 billion.[23][24] Deliveries to Pakistan were expected to begin from 2014–15 and the aircraft was to be designated as FC-20 in Pakistan.[23]
In July 2011, Daily Jang reported that China will give a squadron of the advanced J-10B fighter aircraft to Pakistan. According to the report,"the offer was made by senior Chinese military leaders to visiting Pakistan Army's Chief of General Staff, Lt Gen Waheed Arshad".[25][26] In March 2012, talks were held between the two countries to discuss the delivery of latest J-10B fighter jets to Pakistan.[27]
Design
This section needs additional citations for verification. (March 2010) |
J-10 was designed by the Chengdu Aircraft Design Institute (CADI), a subsidiary of Chengdu Aircraft Corporation.
Airframe
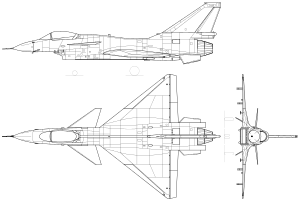
The airframe is constructed from metal alloys and composite materials for high strength and low weight, the airframe's aerodynamic layout adopts a "tail-less canard delta" wing configuration. A large delta wing is mid-mounted towards the rear of the fuselage, while a pair of canards (or foreplanes) are mounted higher up and towards the front of the fuselage, behind and below the cockpit. This configuration provides very high agility, especially at low speeds, and also reduces stall speed, allowing for a lower airspeed during instrument approaches. A large vertical tail is present on top of the fuselage and small ventral fins underneath the fuselage provide further stability.[citation needed]
A rectangular air intake is located underneath the fuselage, providing the air supply to the engine. Also under the fuselage and wings are 11 hardpoints, used for carrying various types of weaponry and drop-tanks containing extra fuel.[citation needed]
The retractable undercarriage comprises a steerable pair of nose-wheels underneath the air intake and two main gear wheels towards the rear of the fuselage.[citation needed]

The cockpit is covered by a two-piece bubble canopy providing 360 degrees of visual coverage for the pilot. The canopy lifts upwards to permit cockpit entry and exit. The Controls take the form of a conventional centre stick and a throttle stick located to the left of the pilot. These also incorporate "hands on throttle and stick" (HOTAS) controls.[citation needed] A zero-zero ejection seat is provided for the pilot, permitting safe ejection in an emergency even at zero altitude and zero speed.[citation needed]
Due to the J-10's aerodynamically unstable design, a digital quadruplex-redundant fly-by-wire (FBW) flight control system (FCS) aids the pilot in flying the aircraft. The FCS typically monitors pilot control inputs, (similar in purpose to a high performance vehicle equipped with electronic stability control) preventing the pilot from accidentally exiting the flight envelope from applying too much control input during high performance flight situations.[citation needed] This is critical in canard wing aircraft, as they are capable of turning in a much tighter radius than conventional aircraft. The massive control surfaces are capable of moving so far that they can completely destroy the aircraft in flight at high airspeeds if not kept in check by the FCS.[citation needed]
Avionics
The cockpit had three liquid crystal (LCD) Multi-function displays (MFD) along with a Chinese developed holographic head-up display (HUD), all of which are fully compatible with a domestic Chinese advanced helmet mounted sight (HMS), claimed by Chinese to be superior than the HMS on Sukhoi Su-27 sold to China.[28][29]
Radar
According to Chengdu Aircraft Industry Corporation officials the J-10 uses a multi-mode fire-control radar designed in China. The radar has a mechanically scanned planar array antenna and is capable of tracking 10 targets. Of the 10 targets tracked, 2 can be engaged simultaneously with semi-active radar homing missiles or 4 can be engaged with active radar homing missiles.[30]
The radar is believed to be designated the Type 1473. The radar is possibly based on the Israeli EL/M-2035 and is seen on the prototype. The production units use the newer, upgraded Type 1473G.[31]
For J-10B, the nose cone is modified to accommodate an active phased array airborne radar (AESA) radar.[32][33] The general designer of AESA for J-10B is Mr. Zhang Kunhui (张昆辉, 1963 -), the head of 607 Research Institute in Neijiang, Sichuan. Mr. Zhang Kunhui became the deputy head of 607th Research Institute in 1997, and four years later in 2001, he became the head of the institute, when the AESA program for J-10B started. The primary contractor of this AESA is the Radar and Electronic Equipment Research Academy of Aviation Industry Corporation of China located in Sichuan, formed in March 2004 by combining the 607th Research Institute and 171st Factory together with Mr. Zhang Kunhui was named as the head of the research academy. According to Chinese governmental media, the AESA for J-10B took 8 years to develop, finally completed in 2008, and Chinese fighter radars hence achieved a quantum leap in that it went from mechanically scanned planar slotted array directly into AESA, skipping the passive phased array PESA radar.[34] Many suspected the radar is a PESA, but during its brief debuts in the 7th China International Defense Electronics Exhibition (CIDEX) in May 2010 and the 6th International Conference on Radar held in Beijing in Sept 2011, Chinese official sources have claimed it is an AESA.[35]
Propulsion

The J-10A is powered by a single Russian Lyulka-Saturn AL-31FN turbofan engine giving a maximum static power output of 12,500 kgf.[36] The AL-31FN is based on the AL-31F which was designed for a twin engine aircraft such as the Su-27, to fit the smaller J-10 the engine parts have been moved and re-designed to fit the smaller engine bay in the J-10.
The J-10 was intended to be powered by the Chinese WS-10 Taihang turbofan, but development difficulties forced the J-10A to use a Russian engine instead.[37] Future J-10 will likely be equipped with an improved WS-10 type engine designed specifically for it, as the chinese aeroengine industry matures and political / military pressure to indigenize increases.[38]
China have entered into contract to purchase the upgraded AL-31FN Series 3 that provides 13,700 kgf thrust and a 2,250-hour service life for future deliveries.[39]
Weaponry and external loads
The aircraft's internal armament consists of a Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-23 twin-barrel cannon, located underneath the port side of the intake. Other weaponry and equipment is mounted externally on 11 hardpoints, to which 6,000 kg (13,228 lb)[40] of either missiles and bombs, drop-tanks containing fuel, or other equipment such as avionics pods can be attached.
Air-to-air missiles deployed may include short range air-to-air missiles such as the PL-8 and PL-9, medium-range radar-guided air-to-air missiles such as the PL-11 and PL-12, unguided and precision guided munitions such as laser-guided bombs, anti-ship missiles such as the YJ-9K and anti-radiation missiles such as the PJ-9.[citation needed]
Variants

- J-10A: Single seat multi-role variant. The export designation is F-10A.[41]
- J-10AY: Unarmed single seater for the August 1st aerobatic team[citation needed]
- J-10SY: Unarmed twin seater for the August 1st aerobatic team[citation needed]
- J-10SH: twin seater for the Navy
- J-10S: Twin-seat fighter-trainer variant of the J-10A. The forward fuselage of the aircraft is stretched to accommodate an additional pilot seat, two pilots sit in tandem with a single large bubble canopy. Also incorporates an enlarged dorsal spine which may accommodate additional avionics equipment or fuel. As well as serving as training aircraft, the J-10S may also be used for the ground attack role where the rear seat pilot would act as the weapon systems operator.[42]
- J-10AH: Naval version of the J-10A.[43]
- J-10B: An upgraded variant of the J-10 with new technologies.[44] Numerous images of a new J-10 variant have surfaced, showing a prototype J-10 modified with increased radar absorbent material, next generation of integrated EW suite, increased use of composites which have reduced the weight by one ton, new generation avionics, MAW, a diverterless supersonic inlet (DSI), an infra-red search and track (IRST) sensor, modified vertical stabiliser and wings, ventral fins, housings fitted under the wings, an upgraded Series 3 Al-31FN engine, next generation of solid-state integrated electronics, and a modified nose with an AESA radar.[45][46] It had its first flight in December 2008. Full Production of J-10B had started with first J-10B appearing on production line on July 2013 [47]
- FC-20: An export variant of the J-10B designed for the Pakistan Air Force.[48] First flight stated to take place in 2009.[49]
Operators
- People's Liberation Army Air Force: 256 As of August 2012[update][4]
- People's Liberation Army Naval Air Force: 24 As of August 2012[update][4]
Accidents and incidents
The first crash is speculated to have been a prototype during testing in 1998 & 2014 with the most likely cause cited as failure of the fly-by-wire flight control system,[17][failed verification] however, China has officially denied such an occurrence.[18]
On 15 November 2014, a J-10B crashed in Pi county (Pi Xian) near Chengdu city in Sichuan province with the pilot ejected safely. Coming down in an artificial lake near a newly built residential compound, the accident injured at least seven on the ground. The aircraft was painted yellow, indicating it was either a new aircraft or a prototype.[50]
Specifications (J-10A)

General characteristics
- Crew: 1[10]
Performance
- Thrust/weight: 1.024 (with AL-31); 1.085 (with WS-10A)
- Maximum g-load: +9/–3 g[6]
Armament
- Guns: 1× Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-23
- Hardpoints: 11 in total (6× under-wing, 5× under-fuselage) with a capacity of 6,600 kg (13,228 lb) external fuel and ordnance[51][40]
- Rockets: 90 mm unguided rocket pods
- Missiles:
- Bombs:
laser-guided bombs: (LT-2)
glide bombs: (LS-6, GB3, GB2A, GB3A)
satellite-guided bombs: (FT-1)
unguided bombs: 250 kg, 500 kg - Others:
- Up to 3 external fuel drop-tanks (1× under-fuselage, 2× under-wing) for extended range and loitering time
Avionics
- Type 1473G pulse-doppler fire control radar
- Externally mounted avionics pods:
See also
Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
Related lists
References
- ^ a b c d Wang Jieqing. "J-10 Fighter Test Flight Process Secret Revealed". Southern Weekend.
- ^ "China's J10C Ground Attack Aircraft". Strategypage.com. 15 October 2006. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^ "Chengdu J-10 (Jian-10, Fighter aircraft-10 / F-10)". globalsecurity.org.
- ^ a b c "The AMR Regional Air Force Directory 2012". Asian Military Review. August 2014. Retrieved 7 January 2013.
- ^ "Chinese J-10 'benefited from the Lavi project' – Jane's Defence Systems News". Janes.com. 19 May 2008. Retrieved 21 March 2010.
- ^ a b c "J-10 (Jian 10) – Vigorous Dragon Multi-Role Tactical Fighter, China". SPG Media Limited. 10 February 2008. Retrieved 12 October 2008.
- ^ "China Eyes J-10A Sale To Iran". Spacewar.com. 14 December 2007. Retrieved 11 July 2013.
- ^ "China Takes An Expensive Hit". Strategy Page. 21 October 2011. Retrieved 11 July 2013.
- ^ John Pike (28 June 2002). "Chinese Aircraft – J-10". Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^ a b c d "Sinodefence.com: J-10 Multirole Fighter Aircraft". Retrieved 9 April 2007.[dead link]
- ^ David Isenberg (4 December 2002). "Israel's role in China's new warplane".
- ^ "Chinese J-10 'benefited from the Lavi project' – Jane's Defence News". Janes.com. 19 May 2008. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^ "J-9 Head Engineer Talks About J-10". Aerospace Files. 2007.
- ^ "Exclusive Interview with J-10 General Designer Song Wencong". 2007.
- ^ "少将驳斥"战机抄袭论":歼-10源自于歼-9". 2012.
- ^ "SibNIA remains center of Russian innovation". 2007.
- ^ a b "China tries to hide J-10 fighter crashes". Defense. Professionals.
- ^ a b "首席试飞员揭歼10"试飞史":创"零坠毁"奇迹" news.xinhuanet.com, 10 January 2013
- ^ Zhang Baoxin (1 January 2007). "CAC J-10 External Design Did Not Receive Foreign Assistance". Aerospace World magazine.
- ^ Siva Govindasamy, "China's AVIC steps up sales push for FC-1, J-10 fighters", Flight International, Retrieved: 2 October 2009
- ^ "Pakistan will stand by China against US 'siege', says Rashid". Daily Times (Pakistan). 23 February 2006. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
- ^ a b Ansari, Usman (3 August 2011). "China Officially Offers Pakistan J-10 Variant". Defense News. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
- ^ a b "Pakistan signs deal for Chinese J-10 fighters". Flight International. 13 November 2009. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
- ^ Bokhari, Farhan (10 November 2009). "Pakistan in Chinese fighter jet deal". Financial Times. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
- ^ "China to give squadron of J10-B fighters to Pakistan". Hindustan Times. 30 July 2011. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
- ^ "China to give squadron of J10-B fighters to Pakistan". Greater Kashmir. 31 July 2011. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
- ^ "J-10B fighter planes, 6 marines for Pakistan as Cino-Pak talks underway". The News Tribe. 22 March 2012. Retrieved 10 September 2013.
- ^ J-10 HMS
- ^ Chengdu J-10 HMS
- ^ "Jian-10 (J-10, F-10) Multirole Fighter Aircraft". SinoDefence.com. Retrieved 21 March 2010.[dead link]
- ^ http://chinese-military-aviation.blogspot.in/p/fighters-ii.html
- ^ J-10B radar
- ^ J-10B AESA
- ^ "创新超越促发展--记中航工业雷电院长张昆辉" cannews.com.cn 14 January 2013
- ^ J10B Active phased array radar
- ^ "AL-31FN" (in Russian). Salyut. Retrieved 12 January 2013.
- ^ "Liming WS10A Taihang Engine". globalsecurity.org. 11 July 2011. Retrieved 12 January 2013.
- ^ Richard, Fisher, Jr. (15 October 2011). "China's Maturing Fighter Force". International Strategy and Assessment Center. Retrieved 12 January 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Al-31FN Series 3" Salut, 24 December 2013.
- ^ a b New generation of fighter jets on horizon, Global Times, 10 November 2009, p. 2, retrieved 10 November 2009
- ^ "Pakistan approves purchase of Lockheed Martin F-16s and Chengdu J-10 fighters-13 April 2006-Washington DC-Flight International". Flightglobal.com. 13 April 2006. Retrieved 21 March 2010.
- ^ SinoDefence (14 April 2006). "J-10B Fighter-Trainer". SinoDefense.
- ^ Hui Tong. "Chinese Military Aviation | China Air Force". Cnair.top81.cn. Retrieved 17 September 2011.[self-published source?]
- ^ Ivanov, Henry (9 January 2006), China working on "Super-10" advanced fighter, Janes Defence World, archived from the original on 11 January 2006
- ^ "New J-10 Variant sighted". Janes Defence News. 23 March 2009. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^ "Jian-10B (J-10B) Multirole Fighter Aircraft". SinoDefence.com. 28 March 2009. Retrieved 21 March 2010.[dead link]
- ^ http://www.janes.com/article/31880/china-marks-aviation-milestones-with-j-10b-production-second-y-20-prototype-flight
- ^ "PAF to start serial production of JF-17 fighter aircraft soon". Associated Press Of Pakistan. Retrieved 21 March 2010.
- ^ 23-Nov-2009 07:02 EST (23 November 2009). "Pakistan's JF-17 Fighter Program". Defenseindustrydaily.com. Retrieved 21 March 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Weening, Cornelius. http://www.janes.com/ http://www.janes.com/article/45809/j-10b-crashes-near-chengdu. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
{{cite web}}: External link in|website=|title=(help) - ^ http://chinese-military-aviation.blogspot.in/p/fighters-ii.html
- ^ a b c d e "J-10 (Jian 10) – Vigorous Dragon Multi-Role Tactical Fighter – Air Force Technology". Airforce-technology.com. Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ "Chinese Chengdu J-10 Emerges". Aviation Week. 14 January 2010. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^ "J-10A / F-10, J-10B, Jian-10, Vigorous Dragon". Deagel.com. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- ^ http://chinese-military-aviation.blogspot.in/p/fighters-ii.html
- ^ http://chinese-military-aviation.blogspot.in/p/fighters-ii.html
- ^ http://chinese-military-aviation.blogspot.in/p/fighters-ii.html
see also International AirPower Revue, Vol. 22, Focus Aircraft: Chengdu J-10, p. 40-59, ISSN 1473-9917, AIRtime Publishing, 2007.
External links
- AirForce-Technology.com J-10 factsheet
- AirForceWorld.com J-10 article
- J-10B fighter jet article
- GlobalSecurity.org article on the J-10
- SinoDefence.com J-10 factsheet and pictures
- Chinese Military Aviation at Stormpages.com
- Milavia.com J-10 article and pictures (includes J-10 specifications from Air Forces Monthly magazine)
- SinoDefence.com article on J-10B
- Jane's Defence article on J-10B
