Nanda Devi National Park
| Nanda Devi National Park | |
|---|---|
| Location | Chamoli district, Uttarakhand, India |
| Coordinates | 30°25′7″N 79°50′59″E / 30.41861°N 79.84972°E |
| Area | 630.33 km2 |
| Established | 1982 |
| Website | https://uttarakhandtourism.gov.in/destination/nanda-devi-national-park |
| Part of | Nanda Devi and Valley of Flowers National Parks |
| Criteria | Natural: (vii), (x) |
| Reference | 335-001 |
| Inscription | 1988 (12th Session) |
| Area | 62,460 ha (241.2 sq mi) |
The Nanda Devi National Park or Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve, established in 1982 is a national park situated around the peak of Nanda Devi (7816 m) in Chamoli Garhwal district of Uttarakhand, in northern India. The entire park lies at an elevation of more than 3,500 m (11,500 ft) above mean sea level.
The National Park was inscribed a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1988.[1] It was later expanded and renamed as Nanda Devi and Valley of Flowers National Parks in 2005.
Within the National Park lies the Nanda Devi Sanctuary, a glacial basin surrounded by a ring of peaks between 6,000 metres (19,700 ft) and 7,500 m (24,600 ft) high, and drained by the Rishi Ganga through the Rishi Ganga Gorge, a steep almost impassable defile.
The National Park is embedded in the 2,236.74 km2 (863.61 sq mi) sized Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve, which, in turn, is encompassed in the 5,148.57 km2 (1,987.87 sq mi)[2][3] buffer zone around the Nanda Devi and Valley of Flowers National Parks UNESCO site.
The best time to visit Nanda Devi National Park is from May to October.[4]
History
The first recorded attempt to explore the sanctuary was in 1883 by W. W. Graham, who could proceed only up to Rishi Ganga.[1] Other attempts by explorers in 1870, (T. G. Longstaff) 1926, 1927 and 1932 (Hugh Ruttledge) did not fetch fruitful results. Eric Shipton and H. W. Tilman entered the inner sanctuary through Rishi Ganga in 1934, thus opening the extensive exploration in the sanctuary. In 1939, the area was declared as a game sanctuary.[1]
2021 Glacial Outburst Flood
At approximately 10:45 a.m. IST on 7 February 2021,[5] a flooding disaster occurred all along the Rishiganga river and its valley following a landslide, avalanche or glacial lake outburst flood of the Nanda Devi glacier.
Layout of the Nanda Devi Sanctuary
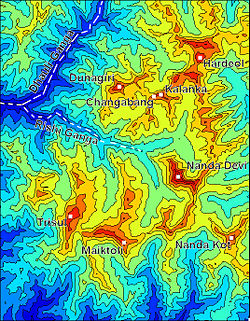
The Nanda Devi Sanctuary within the National Park can be divided into two parts, Inner and Outer. Together, they are surrounded by the main sanctuary wall, which forms a roughly square outline, with high, continuous ridges on the north, east and south sides. On the west side, less high but still imposing ridges drop from the north and south toward the Rishi Ganga Gorge, which drains the sanctuary towards the west.[6]
The Inner Sanctuary occupies roughly the eastern two-thirds of the total area, and contains Nanda Devi itself and the two major glaciers flanking the peak, the UttariRishi Glacier and the Dakshini Rishi Glacier. These are fed by the smaller Uttari Nanda Devi and Dakshini Nanda Devi Glaciers respectively.[6] The first recorded entry of the British into the Inner Sanctuary was by Eric Shipton and H. W. Tilman in 1934, via the Rishi Gorge.[7]
The Outer Sanctuary occupies the western third of the total sanctuary, and is separated from the Inner Sanctuary by high ridges, through which flows the Rishi Ganga. It is split in two by the Rishi Ganga; on the north side lies the Ramani Glacier, flowing down from the slopes of Dunagiri and Changabang, and on the south lies the Trisul Glacier, flowing from the peak of the same name. This portion of the sanctuary is accessible to the outside (though requiring the crossing of a 4,000 m (13,000 ft) pass). The first serious climbing expedition to pass through the Outer Sanctuary was that of T. G. Longstaff, who climbed Trisul I in 1907 via the eponymous glacier.[7]
Fauna
Common larger mammals are Himalayan musk deer, mainland serow and Himalayan tahr. Himalayan goral are not found within, but in the vicinity of the park. Carnivores are represented by snow leopard, Himalayan black bear and perhaps also Himalayan brown bear. Langurs are found within the park, whereas rhesus macaque are known to occur in the neighboring areas of the park. In a scientific expedition in 1993, a total of 114 bird species was recognized.[1]
Flora
Nanda Devi National Park is home to a wide variety of flora. Some 312 floral species that include 17 rare species have been found here. Fir, birch, rhododendron and juniper are the main flora.
Vegetation is scarce In the inner sanctuary due to the dryness of the conditions. One will not find vegetation near Nanda Devi Glacier. Ramani, alpine, prone mosses and lichens are other notable floral species found in Nanda Devi National Park.
Named peaks of the park and environs
Within the sanctuary

Apart from Nanda Devi, the following peaks lie on
- Nanda Devi: 7,816 m (25,643 ft)
- Devistan I, II: 6,678 metres (21,909 ft), 6,529 m (21,421 ft)
- Rishi Kot: 6,236 m (20,459 ft)
On the sanctuary wall
These peaks are listed in clockwise order, starting from just north of the Rishi Gorge. Some of them are relatively minor summits and have small topographic prominence, while others are independent peaks.

- Hanuman: 6,075 m (19,931 ft)
- Dunagiri: 7,066 m (23,182 ft)
- Changabang: 6,864 m (22,520 ft)
- Kalanka: 6,931 m (22,740 ft)
- Rishi Pahar: 6,992 m (22,940 ft)
- Mangraon: 6,568 m (21,549 ft)
- Deo Damla: 6,620 m (21,719 ft)
- Bamchu: 6,303 m (20,679 ft)
- Sakram: 6,254 m (20,518 ft)
- Latu Dhura: 6,392 m (20,971 ft)
- Sunanda Devi: 7,434 m (24,390 ft)
- Nanda Khat: 6,611 m (21,690 ft)
- Panwali Doar (or "Panwali Dwar"): 6,663 m (21,860 ft)
- Maiktoli: 6,803 m (22,320 ft)
- Devtoli: 6,788 m (22,270 ft)
- Mrigthuni: 6,855 m (22,490 ft)
- Trisul I, II, III: 7,120 metres (23,360 ft), 6,690 metres (21,949 ft), 6,008 m (19,711 ft)
- Nanda Ghunti: 6309 m (20,699 ft)
- Bethartoli Himal: 6,352 m (20,840 ft)

Few peaks of Nanda Devi Sanctuary
Just outside the wall
The following are the most notable peaks which are adjacent to the wall; they are all connected to the wall by high passes. They lie just outside the boundaries of the park.
- Hardeol: 7,151 m (23,461 ft) (northeast corner)
- Trishuli: 7,074 m (23,209 ft) (just beyond Hardeol)
- Nanda Kot: 6,861 m (22,510 ft) (southeast corner)
- Nanda Ghunti: 6,309 m (20,699 ft) (southwest corner)
Nuclear-powered spying device on Nanda Devi
During the cold war era when Chinese carried out their first nuclear test in 1964 and followed it up with missile testing, the US and India actively collaborated to spy on China's nuclear capabilities. Before the advent of spy satellites much of the clandestine intelligence gathering relied on ground based sensors. The Chinese missile testing facility was north of the Himalayan range, which was a big hurdle in detecting missile telemetry signals. CIA was looking for a Himalayan peak high enough to secure a direct line of sight to the Chinese missile testing zone. Together with the Intelligence Bureau of India, they planned a secret mission to install a nuclear powered listening device on top of the peak of Nanda Devi. A joint team of CIA hired US mountaineers together with Indian contingent from the defense forces were detailed to carry out the secret mission.[8][9] By that time the mountaineering season was concluding and the mission met with adverse climatic conditions. They left behind the plutonium fueled device with the intention of renewing their attempt during the next year's climbing season. The follow-up Indian expedition during the next season found the device missing from where it was anchored. It probably fell down due to rock fall and slid towards the glaciers carrying its plutonium with it. All the follow-up secret expeditions launched to retrieve the device met with failure. In 2018 it was reported that the Tourism Minister of Uttarakhand State Mr. Satpal Maharaj met the Prime Minister of India to express his apprehensions that the atomic device that had gone missing over 50 years ago might be polluting waters of the Ganges.[10]
See also
- List of national parks of India
- List of World Heritage Sites in India
- National Geological Monuments of India
- Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education
References
- ^ a b c d Centre, UNESCO World Heritage. "Nanda Devi and Valley of Flowers National Parks". UNESCO World Heritage Centre.
- ^ World Conservation Monitoring Centre Archived 10 July 1997 at archive.today
- ^ Kala, Chandra Prakash 2005. The Valley of Flowers: A Newly Declared World Heritage Site. Current Science, 89 (6): 919-920.
- ^ "Nanda Devi National Park". Vaibhav Laxmi Tourism. Retrieved 19 March 2022.
- ^ "Uttarakhand flood wreaks death, damage". The Indian Express. 8 February 2021. Retrieved 9 February 2021.
- ^ a b Garhwal-Himalaya-Ost, 1:150,000 scale topographic map, prepared in 1992 by Ernst Huber for the Swiss Foundation for Alpine Research, based on maps of the Survey of India. It is in the extreme northern part if India on the countries border with China. it takes up a great deal of mountain space in Uttarakhand.
- ^ a b H. W. Tilman, The Ascent of Nanda Devi, Cambridge University Press, 1937. Reprinted in The Seven Mountain-Travel Books, The Mountaineers, Seattle, 2003, ISBN 0-89886-960-9.
- ^ Beckhusen, Robert. "Inside the CIA Mission to Haul Plutonium up the Himalayas". Wired.
- ^ Takeda, Pete (January 2007). "The Secrets of Nanda Devi". Retrieved 23 December 2018.
- ^ "James Bond in the Himalayas: The buried secret of Nanda Devi". The Economic Times.


