Γ-Hydroxyvaleric acid
This is an old revision of this page, as edited by DMacks (talk | contribs) at 04:24, 22 June 2020 (Remove malformatted |molecular_weight= when infobox can autocalculate it, per Wikipedia talk:WikiProject Pharmacology#Molecular weights in drugboxes (via WP:JWB)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | γ-Hydroxyvaleric acid GVB |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.516 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
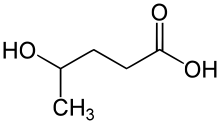
| Formula | C5H10O3 |
| Molar mass | 118.132 g·mol−1 |
γ-Hydroxyvaleric acid (GHV), also known as 4-methyl-GHB, is a designer drug related to γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB). It is sometimes seen on the grey market as a legal alternative to GHB, but with lower potency and higher toxicity,[1] properties which have tended to limit its recreational use.[2]
γ-Valerolactone (GVL) acts as a prodrug to GHV, analogously to how γ-butyrolactone (GBL) is a prodrug to GHB.[3]
See also
References
- ^ Carter LP; Chen W; Wu H; Mehta AK; Hernandez RJ; Ticku MK; Coop A; Koek W; France CP (April 2005). "Comparison of the behavioral effects of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) and its 4-methyl-substituted analog, gamma-hydroxyvaleric acid (GHV)". Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 78 (1): 91–9. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2004.10.002. PMID 15769562.
- ^ Fred Smith (31 December 2004). Handbook of Forensic Drug Analysis. Academic Press. pp. 462–. ISBN 978-0-08-047289-8.
- ^ Andresen-Streichert H, Jungen H, Gehl A, Müller A, Iwersen-Bergmann S (2013). "Uptake of gamma-valerolactone--detection of gamma-hydroxyvaleric acid in human urine samples". J Anal Toxicol. 37 (4): 250–4. doi:10.1093/jat/bkt013. PMID 23486087.
| Ionotropic |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabotropic |
| ||||
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transporter (blockers) |
| ||||||||||
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||
This drug article relating to the nervous system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- Pages with disallowed DISPLAYTITLE modifications
- Articles with short description
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Infobox drug articles with non-default infobox title
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- All stub articles
