Dioxaphetyl butyrate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Amidalgon, Spasmoxal |
| Routes of administration | Oral, Other ROA Unknown |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.731 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
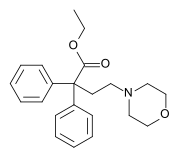
| Formula | C22H27NO3 |
| Molar mass | 353.45 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Dioxaphetyl butyrate (INN; trade names Amidalgon, Spasmoxal) is an opioid analgesic which is a diphenylacetic acid derivative, related to other open-chain opioid drugs such as dextropropoxyphene, levacetylmethadol (LAAM), lefetamine and dimenoxadol.[1][2]
It produces similar effects to other opioids, including dependence, euphoria, analgesia, sedation, constipation, dizziness and nausea.[3]
In the United States it is a Schedule I Narcotic controlled substance with an ACSCN of 9621 and a 2013 annual aggregate manufacturing quota of zero.[4]
References
- ^ PubChem. "Dioxaphetyl butyrate". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2019-06-03.
- ^ "Dioxaphetyl butyrate | C22H27NO3 | ChemSpider". www.chemspider.com. Retrieved 2019-06-03.
- ^ "dioxaphetyl butyrate". drugcentral.org. Retrieved 2019-06-03.
- ^ "Misuse of Drugs Act : Legislative history · Part I Class A · Section 1(a): Explicitly named Class A substances". isomerdesign.com. Retrieved 2019-06-03.
