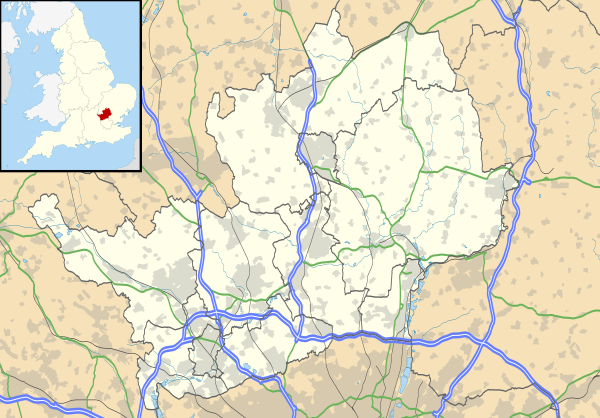
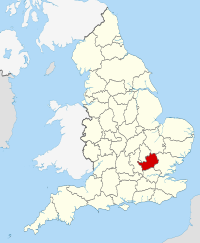
Hertfordshire
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2018) |
Hertfordshire | |
|---|---|
| Motto(s): "Trust and fear not" | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 51°54′N 0°12′W / 51.9°N 0.2°W | |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Constituent country | England |
| Region | East |
| Established | Ancient |
| Time zone | UTC+0 (GMT) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (BST) |
| UK Parliament | List of MPs |
| Police | Hertfordshire Constabulary |
| Ceremonial county | |
| Lord Lieutenant | Robert Voss |
| High Sheriff | Mrs Suzana R Harvey of Wickham Hall, Bishop's Stortford [1] (2018-19) |
| Area | 1,643 km2 (634 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 36th of 48 |
| Population (2022)[2] | 1,204,588 |
| • Rank | 13th of 48 |
| Density | 733/km2 (1,900/sq mi) |
| Non-metropolitan county | |
| County council | Hertfordshire County Council |
| Control | Conservative |
| Admin HQ | Hertford |
| Area | 1,643 km2 (634 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 21st of 21 |
| Population (2022)[3] | 1,204,588 |
| • Rank | 6th of 21 |
| Density | 733/km2 (1,900/sq mi) |
| ISO 3166-2 | GB-HRT |
| GSS code | E10000015 |
| ITL | UKH23 |
| Website | www |
| Districts | |
 Districts of Hertfordshire | |
| Districts | |
Hertfordshire (/ˈhɑːrtfərdʃɪər/ [n 1]; often abbreviated Herts) is one of the home counties in England. It is bordered by Bedfordshire to the north, Cambridgeshire to the northeast, Essex to the east, Buckinghamshire to the west and Greater London to the south. For government statistical purposes, it is placed in the East of England region.
In 2013, the county had a population of 1,140,700[4] living in an area of 634 square miles (1,640 km2).[5] Four towns have between 50,000 and 100,000 residents: Hemel Hempstead, Stevenage, Watford and St Albans. Hertford, once the main market town for the medieval agricultural county, derives its name from a hart (stag) and a ford, used as the components of the county's coat of arms and flag. Elevations are high for the region in the north and west. These reach over 800 feet (240 m) in the western projection around Tring which is in the Chilterns. The county's borders are approximately the watersheds of the Colne and Lea; both flowing to the south; each accompanied by a canal. Hertfordshire's undeveloped land is mainly agricultural and much is protected by green belt.
The county's landmarks span many centuries, ranging from the Six Hills in the new town of Stevenage built by local inhabitants during the Roman period, to Leavesden Film Studios. The volume of intact medieval and Tudor buildings surpasses London, in places in well-preserved conservation areas, especially in St Albans which includes some remains of Verulamium, the town where in the 3rd century an early recorded British martyrdom took place. Saint Alban, a Romano-British soldier, took the place of a Christian priest and was beheaded on Holywell Hill. His martyr's cross of a yellow saltire on a blue background is reflected in the flag and coat of arms of Hertfordshire.
Hertfordshire is well-served with motorways and railways, providing good access to London. The largest sector of the economy of the county is in services.
History
Hertfordshire was the area assigned to a fortress constructed at Hertford under the rule of Edward the Elder in 913. Hertford is derived from the Anglo-Saxon heort ford, meaning deer crossing (of a watercourse). The name Hertfordshire is first recorded in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle in 1011. Deer feature in many county emblems.
There is evidence of humans living in Hertfordshire from the Mesolithic period. It was first farmed during the Neolithic period and permanent habitation appeared at the beginning of the Bronze Age. This was followed by tribes settling in the area during the Iron Age.
Following the Roman conquest of Britain in AD 43, the aboriginal Catuvellauni quickly submitted and adapted to the Roman life; resulting in the development of several new towns, including Verulamium (St Albans) where in c. 293 the first recorded British martyrdom is traditionally believed to have taken place. Saint Alban, a Romano-British soldier, took the place of a Christian priest and was beheaded on Holywell Hill. His martyr's cross of a yellow saltire on a blue background is reflected in the flag and coat of arms of Hertfordshire as the yellow background to the stag or Hart representing the county. He is the Patron Saint of Hertfordshire.
With the departure of the Roman Legions in the early 5th century, the now unprotected territory was invaded and colonised by the Anglo-Saxons. By the 6th century the majority of the modern county was part of the East Saxon kingdom. This relatively short lived kingdom collapsed in the 9th century, ceding the territory of Hertfordshire to the control of the West Anglians of Mercia. The region finally became an English shire in the 10th century, on the merger of the West Saxon and Mercian kingdoms.
A century later, William of Normandy received the surrender of the surviving senior English Lords and Clergy at Berkhamsted, resulting in a new Anglicised title of William the Conqueror before embarking on an uncontested entry into London and his coronation at Westminster. Hertfordshire was used for some of the new Norman castles at Bishop's Stortford, and at King's Langley, a staging post between London and the royal residence of Berkhamsted.
The Domesday Book recorded the county as having nine hundreds. Tring and Danais became one—Dacorum—from Danis Corum or Danish rule harking back to a Viking not Saxon past. The other seven were Braughing, Broadwater, Cashio, Edwinstree, Hertford, Hitchin and Odsey.
The first shooting-down of a zeppelin over Great Britain during WW1 happened in Cuffley.[6]
As London grew, Hertfordshire became conveniently close to the English capital; much of the area was owned by the nobility and aristocracy, this patronage helped to boost the local economy. However, the greatest boost to Hertfordshire came during the Industrial Revolution, after which the population rose dramatically. In 1903, Letchworth became the world's first garden city and Stevenage became the first town to redevelop under the New Towns Act 1946.
From the 1920s until the late 1980s, the town of Borehamwood was home to one of the major British film studio complexes, including the MGM-British Studios. Many well-known films were made here including the first three Star Wars movies (IV, V, & VI). The studios generally used the name of Elstree. American director Stanley Kubrick not only used to shoot in those studios but also lived in the area until his death. Big Brother UK and Who Wants To Be A Millionaire? have been filmed there. EastEnders is filmed at Elstree. Hertfordshire has seen development at Leavesden Film Studios developed on the Leavesden Aerodrome site; the Harry Potter series was filmed here and the 1995 James Bond film GoldenEye.[7]
On 17 October 2000, the Hatfield rail crash killed four people with over 70 injured.[8] The crash exposed the shortcomings of Railtrack, which consequently saw speed restrictions and major track replacement. On 10 May 2002, the second of the Potters Bar rail accidents occurred killing seven people; the train was at high speed when it derailed and flipped into the air when one of the carriages slid along the platform where it came to rest.
In early December 2005, the 2005 Hemel Hempstead fuel depot explosions occurred at the Hertfordshire Oil Storage Terminal.[9][10][11]
In 2012, the canoe and kayak slalom events of the 2012 Summer Olympic Games took place in the town of Waltham Cross, within the borough of Broxbourne.
Geography
Hertfordshire is the county immediately north of London and is part of the East of England region, a mainly statistical unit.[12] A significant minority of the population across all districts are City of London commuters. To the east is Essex, to the west is Buckinghamshire and to the north are Bedfordshire and Cambridgeshire.
The county's boundaries were roughly fixed by the Counties (Detached Parts) Act 1844 which eliminated exclaves; amended when, in 1965 under the London Government Act 1963, East Barnet Urban District and Barnet Urban District were abolished, their area was transferred to form part of the present-day London Borough of Barnet and the Potters Bar Urban District of Middlesex was transferred to Hertfordshire.
The highest point in the county is at 245 metres (804 ft) (AOD) on the Ridgeway long distance national path, on the border of Hastoe near Tring with Drayton Beauchamp, Buckinghamshire.
As at the 2011 census of the ten Districts, East Hertfordshire had the minimal, 290 people per km2, whereas Watford had the maximal 4210 people per km2
An unofficial status, the purple star-shaped flower with yellow stamens, the Pasqueflower is among endemic county flowers.[13]
Geology
The rocks of Hertfordshire belong to the great shallow syncline known as the London Basin. The beds dip in a south-easterly direction towards the syncline's lowest point roughly under the River Thames. The most important formations are the Cretaceous Chalk, exposed as the high ground in the north and west of the county, forming the Chiltern Hills and the younger Palaeocene, Reading Beds and Eocene, London Clay which occupy the remaining southern part. The eastern half of the county was covered by glaciers during the Ice Age and has a superficial layer of glacial boulder clays.
Natural resources and environment

Much of the county is given over to agriculture. One product, now largely defunct, was water-cress, based in Hemel Hempstead and Berkhamsted supported by reliable, clean chalk rivers. [citation needed]
Some quarrying of sand and gravel occurs in the St Albans area. In the past, clay has supplied local brick-making and still does in Bovingdon, just south-west of Hemel Hempstead. The chalk that is the bedrock of much of the county provides an aquifer that feeds streams and is also exploited to provide water supplies for much of the county and beyond. Chalk has also been used as a building material and, once fired, the resultant lime was spread on agricultural land to improve fertility. The mining of chalk since the early 18th century has left unrecorded underground galleries that occasionally collapse unexpectedly and endanger buildings.[14]
Fresh water is supplied to London from Ware, using the New River built by Hugh Myddleton and opened in 1613. Local rivers, although small, supported developing industries such as paper production at Nash Mills.[15]
Hertfordshire affords habitat for a variety of flora and fauna. One bird common in the shire is the Hooded Crow, the old name of which is the eponymous name of the regional newspaper, the Royston Crow published in Royston.
Urban areas
In November 2013, the uSwitch Quality of Life Index listed Hertfordshire as the third-best place to live in the UK.[16]
Economy

This is a table of trends of regional gross value added of Hertfordshire at current basic prices with figures in millions of British Pounds Sterling.[17]
| Year | Regional Gross Value Added[n 2] | Agriculture[n 3] | Industry[n 4] | Services[n 5] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 11,742 | 96 | 3,292 | 8,354 |
| 2000 | 18,370 | 77 | 4,138 | 14,155 |
| 2003 | 20,937 | 82 | 4,348 | 16,507 |
Hertfordshire has headquarters of many large well-known UK companies. Hemel Hempstead is home to DSG International. Welwyn Garden City hosts Tesco, as well as Roche UK's headquarters (subsidiary of the Swiss pharmaceutical firm Hoffman-La Roche) and Cereal Partners production facilities, Pure the DAB radio maker is based in Kings Langley. JD Wetherspoon is in Watford. Skanska is in Rickmansworth, GlaxoSmithKline has plants in Ware and Stevenage. Hatfield used to be connected with the aircraft industry, as it was where de Havilland developed the world's first commercial jet liner, the Comet. Now the site is a business park and new campus for the University of Hertfordshire. This major new employment site is home to, among others, EE, Computacenter and Ocado. A subsidiary of BAE Systems and Finmeccanica in Stevenage, MBDA, develops missiles. In the same town Airbus (Defence & Space Division) produces satellites. The National Pharmacy Association (NPA), the trade association for all of the UK's community pharmacies, is based in St Albans. Warner Bros. also owns and runs Warner Studios in Leavesden.
Sport
Football

As of the 2018-19 season, there are three professional football teams in Hertfordshire: Arsenal W.F.C., Stevenage F.C., and Watford F.C..
Arsenal W.F.C. play at Meadow Park alongside Conference Premier side Boreham Wood, in Borehamwood, Hertfordshire.[18] The club was formed in 1987 and have played in the FA Women's Super League since its inaugural season in 2011.[19]
Stevenage F.C. have played at the Lamex Stadium since 1980.[20] Stevenage was the first club to win a competitive match at the new Wembley Stadium, beating Kidderminster Harriers 2-3 in the 2007 FA Trophy Final.[21] The club currently play in the EFL League Two and have been managed by former player Dino Maamria since March 2018.[22]
Watford F.C. play their home games at Vicarage road, where the club has played since 1922.[23] The club joined the football league in 1920 as a founding member of the third division[24] and first played in the First Division of English football in 1982.[24] Watford have played in the Premier League since their promotion from the EFL Championship following the 2014-15 season.[25][26][27]
There are several semi-professional and amateur football clubs in Hertfordshire. Most notable amongst these are Borehamwood F.C. who play in the Conference Premier, the fifth tier of English football, and Hemel Hempstead Town F.C. and St. Albans F.C. who both play in the National League South, part of the sixth tier of English football.
Rugby
Rugby league
Hemel Stags are a rugby league team based in Hemel Hempstead.[28] Hemel Stags have played at Pennine Way Stadium since the club's founding in 1981.[29][30] The club plays in league 1, the third tier of the British rugby league system.[31]
Rugby union
The Hertfordshire Rugby Football Union is the governing body for rugby union in Hertfordshire, the governing body is responsible for any interested parties involved in rugby.[32]
Tring Rugby are rugby union team based in Tring, who play matches at Cow Lane, Tring.[33] The first XV currently play in the London & South East Premier,[34] a level 4 league.
Landmarks





Below is a list of notable visitor attractions in Hertfordshire:
- Aldenham Country Park
- Ashridge. The estate surrounding the neo-Gothic house by James Wyatt (not open to the public) is National Trust land
- Bridgewater Monument built in 1832 in memory of Francis Egerton, 3rd Duke of Bridgewater. 108 feet (33 m) tall and open to the public to ascend to the top
- Berkhamsted Castle
- Butterfly World, Chiswell Green
- Cedars Park, Broxbourne – a historic public park on the site of a Tudor palace
- de Havilland Aircraft Heritage Centre, between London Colney and South Mimms
- Gardens of the Rose, Chiswell Green, near St Albans. Home of the Royal National Rose Society
- Hatfield
- Hatfield House – Jacobean house, gardens and park
- Mill Green Watermill in Hatfield
- Henry Moore Foundation, Much Hadham – sculpture park on the work of Henry Moore
- Knebworth House, 250 acres (1.0 km2) of country park, venue of regular rock and pop festivals
- Leavesden Film Studios, home of the Warner Bros. Making of Harry Potter studio tour
- Letchworth Garden City World's first Garden City. Home of the first planned Green Belt, the UK's first roundabout, and a number of experiments in early town planning and house and factory design
- Magic Roundabout (Hemel Hempstead) a complex road junction
- Royston Cave – in Royston town centre
- Rye House Gatehouse in Hoddesdon (part of the Rye House Plot to assassinate King Charles II)
- St Albans
- Beech Bottom Dyke – large scale iron age defensive or boundary ditch
- Sopwell Nunnery
- St Albans Cathedral
- Verulamium – Roman town remains, including museum of Roman life and the remains of a Roman amphitheatre
- Scott's Grotto, Ware in its protected rural buffer area
- Shaw's Corner, Ayot St Lawrence – home of George Bernard Shaw
- Stevenage – the first UK New Town
- Therfield Heath – a local nature reserve in the north of the county
- University of Hertfordshire – a public research university based in Hatfield
- Welwyn Viaduct to the north of Welwyn Garden City
- Walter Rothschild Zoological Museum, Tring a museum-annotated collection of dead mammals, birds, reptiles and insects.
- Watford Museum, fine art and local artefacts
Main national footpaths
Intra-county notable footpaths
Transport



Hertfordshire lies across major road and rail routes connecting London to the Midlands, Northern England and Scotland. As one of the home counties, many towns in the county form part of the London commuter belt.
The county has some of the principal roads in England: A1, A1(M), A5, A6, A41, M1, M11, and M25.
Four principal national railway lines pass through the county:
- the West Coast Main Line from Euston. West Midlands Trains provides local commuter and regional services in the far west of the county. Virgin Trains also operates high speed inter-city services via Watford Junction to the Midlands, North Wales, the North West England and Scotland
- the East Coast Main Line from London King's Cross. Local commuter and regional services are provided by Great Northern. London North Eastern Railway runs high speed inter-city services via Stevenage to Yorkshire, North East England and Scotland
- the Midland Main Line which forms part of the Thameslink route between Bedford and Brighton via Central London with services are provided by Thameslink. East Midlands Trains also provide inter-city services along the line from London St Pancras to the East Midlands and Yorkshire
- the West Anglia Main Line from London Liverpool Street. Local commuter and regional services are provided by Greater Anglia mainly in the east of the county
A number of other local rail routes also cross Hertfordshire:
- the London to Aylesbury Line from London Marylebone runs via Rickmansworth and Chorleywood
- the Abbey Line, a local line from Watford to St Albans Abbey
- the Cambridge Line, a branch of the East Coast line which runs via Royston and Letchworth to Cambridge
Three commuter lines operated by Transport for London enter the county:
- the Lea Valley Lines, a suburban metro line from Liverpool Street to Cheshunt via Seven Sisters
- the Watford DC Line, a suburban metro line from Euston to Watford Junction
- five stations on the London Underground Metropolitan line— Chorleywood, Croxley, Moor Park, Rickmansworth and Watford — are in Hertfordshire.
Stansted and Luton are within 10 miles (16 km) of the county's borders. A commercial airfield is at Elstree for light aircraft.
The Grand Union Canal passes through much of the far west of Hertfordshire: Rickmansworth, Watford, Hemel Hempstead, Berkhamsted and Tring.
Local bus services are run by a number of private operators. Intalink is an organisation run by the county council that manages transport and funds bus services in rural areas.
Education

Hertfordshire has 26 independent schools and 73 state secondary schools. The state secondary schools are entirely comprehensive, although 7 schools in the south and southwest of the county are partially selective (see Education in Watford). All state schools have sixth forms, and there are no sixth form colleges. The tertiary colleges, each with multiple campuses, are Hertford Regional College, North Hertfordshire College, Oaklands College and West Herts College. The University of Hertfordshire is a modern university based largely in Hatfield. It has more than 23,000 students.
Literature
Hertfordshire is the location of Jack Worthing's country house in Oscar Wilde's play The Importance of Being Earnest.
Jane Austen's novel Pride and Prejudice is primarily set in Hertfordshire.[35]
The location of Mr Jarndyce's Bleak House in Charles Dickens's Bleak House is near St Albans.[36]
The eponymous residence in E. M. Forster's novel Howards End was based on Rooks Nest House just outside Stevenage.[37]
George Orwell based Animal Farm on Wallington, Hertfordshire where he lived between 1936 and 1940. Manor Farm and The Great Barn both feature in the novel.[38][39][40]
See also
- Lord Lieutenant of Hertfordshire
- High Sheriff of Hertfordshire
- Custos Rotulorum of Hertfordshire – Keeper of the Rolls
- Hertfordshire (UK Parliament constituency) – Historical list of MPs for Hertfordshire constituency
- List of Jewish communities in Hertfordshire
- Hertfordshire GAA
Notes
References
- ^ "No. 62229". The London Gazette. 15 March 2018. pp. 4814–4814.
- ^ "Mid-2022 population estimates by Lieutenancy areas (as at 1997) for England and Wales". Office for National Statistics. 24 June 2024. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ^ "Mid-Year Population Estimates, UK, June 2022". Office for National Statistics. 26 March 2024. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ^ "Resident Population". Hertfordshire Local Information System. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- ^ "Area Measurements". Hertfordshire Local Information System. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- ^ "Zeppelin Raids - Herts at War". www.hertsatwar.co.uk. Retrieved 23 January 2017.
- ^ [1] Archived 7 August 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Hatfield train crash remembered". BBC News. 17 October 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ Lewis, Katy (11 December 2015). "'I thought a plane had landed on us'". BBC News. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ Staff and agencies (11 December 2005). "Fuel depot blaze 'will last for days'". the Guardian. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ "Buncefield blast companies sentenced to pay £9m". The Independent. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ "The East of England". East of England Local Government Association. Retrieved 23 January 2012.
- ^ "Wild Plants: Pasqueflower" Plantlife. Retrieved 26 February 2015
- ^ "About the chalk mines". Dacorum Borough Council. 2008. Retrieved 7 February 2009.
- ^ "Sir Hugh Myddleton New River". Intriguing History. 25 April 2015. Retrieved 17 June 2018.
- ^ Hassan, Jafar. "UK Quality of Life Index". uSwitch. Retrieved 14 November 2013.
- ^ Regional Gross Value Added Archived 1 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine, Office for National Statistics, pp. 240–253.
- ^ DigitalFC. "Meadow Park, home to Boreham Wood, Arsenal Ladies, Arsenal Development - Football Ground Map". www.footballgroundmap.com. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ Conn, David (7 April 2011). "Women's Super League aims to step out of men's shadow | David Conn". the Guardian. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ "The Lamex Stadium - Stevenage Football Club". www.stevenagefc.com. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ "Kidderminster 2-3 Stevenage". 12 May 2007. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ "Dino Maamria: Stevenage appoint Nuneaton Town boss as manager". BBC Sport. 20 March 2018. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ "Vicarage Road - Watford - The Stadium Guide". www.stadiumguide.com. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ a b "Watford Football Club archive 1881-2017". www.watfordfcarchive.com. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ Smith, Alex (25 April 2015). "Watford promoted to Premier League". ISSN 0307-1235. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ Whaling, James (25 April 2015). "Promotions and relegations in the Football League". mirror. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ "Watford look set for their fifth manager inside a year after making an approach for Quique Flores". The Independent. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ "Rugby League Clubs Hertfordshire | Rugby League Club | Welwyn Garden City, Watford, Ware, Waltham Cross, Stevenage, Royston, Rickmansworth, Tring, Letchworth, Hoddesdon, Hitchin, Hertford, Hemel Hempstead, Hatfield, Borehamwood, Bishops Stortford, Baldock". www.rugbyclubs.info. Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- ^ "Find Us - Hemel Stags - Rugby League Team". Hemel Stags. Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- ^ "World famous Bradford Bulls are on their way to Pennine Way this Sunday". Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- ^ "National League Division One Table - Rugby Union". BBC Sport. Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- ^ "Hertfordshire Rugby Football Union - News - Fullerians RFC". www.fullerians.co.uk. Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- ^ Caminsky, Spencer. "Area Guide: Scenery, culture and a manageable commute, Tring has it all". Herts Advertiser. Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- ^ "London & SE Division". RFU. Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- ^ "Pride and Prejudice - the Hertford connection". Our Hertford and Ware. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ "Charles Dickens". Herts Memories. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ Forster, E. M. (Edward Morgan) (1 November 2001). "Howards End" – via Project Gutenberg.
- ^ "At the gates of Animal Farm". Telegraph. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ "Over the road from Animal Farm". The Independent. Retrieved 2 August 2018.
- ^ "All villages are equal". the Guardian. 24 May 1999. Retrieved 2 August 2018.