History of Palestine
This article's lead section may be too long. (August 2014) |
| History of Palestine |
|---|
 |
|
|
The history of Palestine is the study of the past in the region of Palestine, generally defined as a geographic region in Western Asia between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River (where Israel and West Bank/ Palestine is today), and various adjoining lands. Situated at a strategic point between Europe, Asia, and Africa, and the birthplace of Judaism and Christianity,[1] the region has a long and tumultuous history as a crossroads for religion, culture, commerce, and politics. The Palestine region or parts of it have been controlled by numerous different peoples, including the Paleo-Canaanites, Amorites,[2] Ancient Egyptians, Israelites, Moabites, Ammonites, Tjeker, Philistines, Assyrians, Babylonians, Persians, Ancient Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, (Umayads, Abbasids, Seljuqs, Fatimids), French Crusaders, (Ayyubids, Mameluks, Ottoman Turks), the British, Jordianians (1948–1967, on the "West Bank") and Egyptians (in Gaza), and modern Israelis and Palestinians. Other terms for the same area include Canaan, Zion, the Land of Israel, Southern Syria, Jund Filastin, Outremer, the Holy Land and the Southern Levant.
The region was among the earliest in the world to see human habitation, agricultural communities and civilization. During the Bronze Age, independent Canaanite city-states were established, and were influenced by the surrounding civilizations of ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, Phoenicia, Minoan Crete, and Syria. During 1550–1400 BCE, the Canaanite cities became vassals to the Egyptian New Kingdom who held power until the 1178 BCE Battle of Djahy (Canaan) during the wider Bronze Age collapse. Modern archaeologists dispute parts of the Biblical tradition, the latest thinking being that the Israelites emerged from a dramatic social transformation that took place in the people of the central hill country of Canaan around 1200 BCE, with no signs of violent invasion or even of peaceful infiltration of a clearly defined ethnic group from elsewhere.[3] The Philistines, part of Sea Peoples of Southern Europe, arrived and mingled with the local population, and according to Biblical tradition, the United Kingdom of Israel was established in 1020 BCE and split within a century to form the northern Kingdom of Israel, and the southern Kingdom of Judah. The region became part of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from c. 740 BCE, which was itself replaced by the Neo-Babylonian Empire in c. 627 BCE. A war with Egypt culminated in 586 BCE when Jerusalem was destroyed by the Babylonian king Nebuchadnezzar II and the local leaders were deported to Babylonia, only to be allowed to return under the Achaemenid Empire.
In the 330s BCE, Alexander the Great conquered the area now called Palestine, and the region changed hands numerous times during the wars of the Diadochi, ultimately joining the Seleucid Empire between 219 and 200 BCE. In 116 BCE, a Seleucid civil war resulted in the independence of certain regions including the minor Hasmonean principality in the Judean Mountains. From 110 BCE, the Hasmoneans extended their authority over much of the area, creating a Judean–Samaritan–Idumaean–Ituraean–Galilean alliance.[4] The Judean (Jewish, see Ioudaioi) control over the wider region resulted in it also becoming known as Judaea, a term that had previously only referred to the smaller region of the Judean Mountains. During 73–63 BCE, the Roman Republic extended its influence into the region in the Third Mithridatic War, conquering Judea in 63 BCE, and splitting the former Hasmonean Kingdom into five districts. In 70 CE, Titus sacked Jerusalem, resulting in the dispersal of the city's Jews and Christians to Yavne and Pella. In 132 CE, Hadrian joined the province of Judaea with Galilee to form a new province and renamed it Syria Palaestina, and Jerusalem was renamed "Aelia Capitolina". During 259–272, the region fell under the rule of Odaenathus as King of the Palmyrene Empire. Following the victory of Christian emperor Constantine in the Civil Wars of the Tetrarchy (306–324), the Christianization of the Roman Empire began, and in 326, Constantine's mother Saint Helena visited Jerusalem and began the construction of churches and shrines. Palestine became a center of Christianity, attracting numerous monks and religious scholars. The Samaritan Revolts during this period caused their near extinction.
Palestine was conquered by the Islamic Empire following the 636 CE Battle of Yarmouk during the Muslim conquest of Syria. In 661 CE, with the assassination of Ali, Muawiyah I became the uncontested Caliph of the Islamic World after being crowned in Jerusalem. In 691, the Dome of the Rock became the world's first great work of Islamic architecture. The Umayyad were replaced by the Abbasids in 750. From 878 Palestine was ruled from Egypt by semi-autonomous rulers for almost a century, beginning with Ahmad ibn Tulun, and ending with the Ikhshidid rulers who were both buried in Jerusalem. The Fatimids conquered the region in 969. In 1073 Palestine was captured by the Great Seljuq Empire, only to be recaptured by the Fatimids in 1098, who then lost the region to the Crusaders in 1099. Their control of Jerusalem and most of Palestine lasted almost a century until defeat by Saladin's forces in 1187, after which most of Palestine was controlled by the Ayyubids. A rump Crusader state in the northern coastal cities survived for another century, but, despite seven further Crusades, the Crusaders were no longer a significant power in the region. The Mamluk Sultanate was indirectly created in Egypt as a result of the Seventh Crusade. The Mongol Empire reached Palestine for the first time in 1260, beginning with the Mongol raids into Palestine under Nestorian Christian general Kitbuqa and reaching an apex at the pivotal Battle of Ain Jalut. In 1486, hostilities broke out between the Mamluks and the Ottoman Turks and the Ottomans captured Palestine in 1516.
In 1832, the region was conquered by Muhammad Ali's Egypt, but, in 1840, Britain intervened and returned control of the Levant to the Ottomans in return for further capitulations.[citation needed] The turbulent period of Egyptian rule experienced two major revolts (the 1834 Arab Peasants revolt and 1838 Druze revolt) and a significant demographic change in coastal areas, populated by Egyptian Arab peasants and former soldiers of Ali. The end of the 19th century saw the beginning of Zionist immigration and the revival of the Hebrew language. Increasing Jewish immigration in the late 19th and early 20th centuries added considerably to the Jewish communities in Jerusalem, Safed, Tiberias and Jaffa.[5]
During World War I the British government issued the pro-Zionist Balfour Declaration of 1917. The British captured Jerusalem a month later. The League of Nations formally awarded Britain a mandate over Palestine in 1922. The land west of the Jordan River was under direct British administration until 1948, while the land east of the Jordan was a semi-autonomous region known as Transjordan, under the rule of the Hashemite family from the Hijaz, and gained independence in 1946. The 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine was a nationalist uprising by Palestinian Arabs against British colonial rule and mass Jewish immigration.
After the Nazi Holocaust, pressure grew for the international recognition of a Jewish state in Palestine. In 1947, the British Government announced its intention to terminate the Mandate. The United Nations General Assembly voted to partition Palestine into independent Arab and Jewish states, with a special international regime for Jerusalem. The Arabs rejected the partition of Palestine, but the Jews declared the independence of the State of Israel in May 1948. During the 1948 Palestine War, Israel overran far more territory than was proposed by the Partition Plan; Jordan captured the region today known as the West Bank, while in the Gaza Strip the All-Palestine Government was announced in September 1948. In what is known as the Nakba, or "Catastrophe", hundreds of Palestinian villages and over 70,000 Palestinian homes were ruined and destroyed .[6] 700,000 Palestinians fled or were driven from their native land by the Israelis. The Palestinian refugees were unable to return following the Lausanne Conference, 1949.[citation needed] During and after the 1948 war, a wave of Jewish refugees from Arab countries arrived in Palestine, further exacerbating the situation for Palestinian Arabs. The question of the right to return of the refugeees and their descendants remains a source of dispute.[7] The All-Palestinian Government was later moved from Gaza to Cairo and eventually dissolved in 1959 by Egyptian President Nasser. Gaza was taken into Egyptian military administration.
The Palestinian national movement gradually regrouped in the West Bank and Gaza, and in refugee camps in neighbouring Arab states. The Palestine Liberation Organisation (PLO) emerged as its leading umbrella group. During the Six Day War in June 1967, Israel seized East Jerusalem and the West Bank from Jordan and Gaza from Egypt, as well as the Golan Heights from Syria. Despite international objections and UN resolutions, Israel began a policy of establishing illegal Israeli settlements in the Israeli-occupied territories.[8] The PLO under Yasser Arafat gradually won international recognition as the representative of the Palestinian people. From 1987 to 1993, the First Palestinian Intifada against Israel took place, ending with the 1993 Oslo Peace Accords. These accords established a Palestinian National Authority (PNA - also referred to as the Palestinian Authority, or PA) as an interim body to run parts of Gaza and the West Bank (but not East Jerusalem) pending an agreed solution to the conflict.
During the Second Intifada (2000-2005), Israel withdrew from the Gaza Strip and began building the West Bank barrier. In 2006, Hamas won the Palestinian legislative elections and took control of the Gaza Strip in 2007, triggering the Israeli and Egyptian Blockade of the Gaza Strip (2007-the present). In 2008-09 and again in 2014, Israel bombed millitants in Gaza in response to rocket fire. These operations were however criticized for causing civilian deaths.[9][10]
In October 2011, UNESCO admitted the "State of Palestine" as a member in October. In November 2012, the State of Palestine was upgraded in the UN to non-member observer state status, a move that allows it to take part in General Assembly debates and improves its chances of joining other UN agencies.

The earliest human remains in Palestine were found in Ubeidiya, some 3 km south of the Sea of Galilee (Lake Tiberias), in the Jordan Rift Valley. The remains are dated to the Pleistocene, c. 1.5 million years ago. These are traces of the earliest migration of Homo erectus out of Africa. The site yielded hand axes of the Acheulean type.[11]
Wadi El Amud between Safed and the Sea of Galilee was the site of the first prehistoric dig in Palestine, in 1925. The discovery of Palestine Man in the Zuttiyeh Cave in Wadi Al-Amud near Safed in 1925 provided some clues to human development in the area.[12][13] Qafzeh is a paleoanthropological site south of Nazareth where eleven significant fossilised Homo sapiens skeletons have been found at the main rock shelter. These anatomically modern humans, both adult and infant, are now dated to about 90–100,000 years old, and many of the bones are stained with red ochre, which is conjectured to have been used in the burial process, a significant indicator of ritual behavior and thereby symbolic thought and intelligence. 71 pieces of unused red ochre also littered the site. Mount Carmel has yielded several important findings, among them Kebara Cave that was inhabited between 60,000–48,000 BP and where the most complete Neanderthal skeleton found to date. The Tabun cave was occupied intermittently during the Lower and Middle Paleolithic ages (500,000 to around 40,000 years ago). Excavations suggest that it features one of the longest sequences of human occupation in the Levant. In the nearby Es Skhul cave excavations revealed the first evidence of the late Epipalaeolithic Natufian culture, characterized by the presence of abundant microliths, human burials and ground stone tools. This also represents one area where Neanderthals—present in the region from 200,000 to 45,000 years ago—lived alongside modern humans dating to 100,000 years ago.[14] In the caves of Shuqba in Ramallah and Wadi Khareitun in Bethlehem, stone, wood and animal bone tools were found and attributed to the Natufian culture (c. 12,800–10,300 BCE). Other remains from this era have been found at Tel Abu Hureura, Ein Mallaha, Beidha and Jericho.[15]
Between 10,000 and 5000 BCE, agricultural communities were established. Evidence of such settlements were found at Tel es-Sultan in Jericho and consisted of a number of walls, a religious shrine, and a 23-foot (7.0 m) tower with an internal staircase[16][17] Jericho is believed to be one of the oldest continuously-inhabited cities in the world, with evidence of settlement dating back to 9000 BCE, providing important information about early human habitation in the Near East.[18] Along the Jericho–Dead Sea–Bir es-Saba–Gaza–Sinai route, a culture originating in Syria, marked by the use of copper and stone tools, brought new migrant groups to the region contributing to an increasingly urban fabric.[19][20][21]
By the early Bronze Age (3000–2200 BCE), independent Canaanite city-states situated in plains and coastal regions and surrounded by mud-brick defensive walls were established and most of these cities relied on nearby agricultural hamlets for their food needs.[19][22] Archaeological finds from the early Canaanite era have been found at Tel Megiddo, Jericho, Tel al-Far'a (Gaza), Bisan, and Ai (Deir Dibwan/Ramallah District), Tel an Nasbe (al-Bireh) and Jib (Jerusalem). The Canaanite city-states held trade and diplomatic relations with Egypt and Syria. Parts of the Canaanite urban civilization were destroyed around 2300 BCE, though there is no consensus as to why. Incursions by nomads from the east of the Jordan River who settled in the hills followed soon thereafter.[19][23]
In the Middle Bronze Age (2200–1500 BCE), Canaan was influenced by the surrounding civilizations of ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, Phoenicia, Minoan Crete, and Syria. Diverse commercial ties and an agriculturally based economy led to the development of new pottery forms, the cultivation of grapes, and the extensive use of bronze.[19][24] Burial customs from this time seemed to be influenced by a belief in the afterlife.[19][25] The Middle Kingdom Egyptian Execration Texts attest to Canaanite trade with Egypt during this period.[26][27] The Minoan influence is apparent at Tel Kabri.[28]
New Kingdom Egyptian period
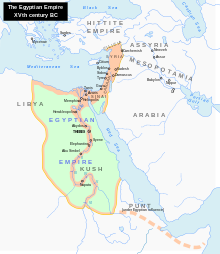

During 1550–1400 BCE, the Canaanite cities became vassals to Egypt as the Egyptian New Kingdom reunited Egypt and expanded into the Levant under Ahmose I and Thutmose I. Political, commercial and military events towards the end of this period (1450–1350 BCE) were recorded by ambassadors and Canaanite proxy rulers for Egypt in 379 cuneiform tablets known as the Amarna Letters.[29] These refer to several local proxy rulers for Egypt such as Biridiya of Megiddo, Lib'ayu of Shechem and Abdi-Heba in Jerusalem. In the first year of his reign pharaoh Seti I (ca.1294-1290 BCE) waged a campaign to resubordinate Canaan to Egyptian rule, thrusting north as far as Beit Shean, and installing local vassals to administer the area in his name. A burial site yielding a scarab bearing his name, found within a Canaanite coffin excavated in the Jezreel Valley, attests to Egypt's presence in the area.[30] Excavations have established that the late 13th, the 12th and the early 11th centuries BCE witnessed the foundation of perhaps hundreds of insignificant, unprotected village settlements, many in the mountains of Palestine.[31] From around the 11th century BCE, there was a reduction in the number of villages, though this was counterbalanced by the rise of certain settlements to the status of fortified townships.[31]
In 1178 BCE, the Battle of Djahy (Canaan) between Ramesses III and the Sea Peoples marked the beginning of the decline in power of the New Kingdom in the Levant during the wider Bronze Age collapse.[citation needed]
Independent Israelite, Philistine and Canaanite period
During the beginning of the Iron Age (c. 1175 BCE), the Philistines occupied the southern coast of Canaan, and mingled with the local population, losing their separate identity over several generations.[32][33] Pottery remains found in As, Gath (city), Ekron and Gaza decorated with stylized birds provided the first archaeological evidence for Philistine settlement in the region. The Philistines are credited with introducing iron weapons and chariots to the local population.[34]
Modern archaeologists dispute parts of the Biblical tradition.[35] In The Bible Unearthed Finkelstein and Silberman describe how, up until 1967, the Israelite heartland in the highlands of western Palestine was virtually an archaeological 'terra incognita'. Since then the traditional territories of the tribes of Judah, Benjamin, Ephraim, and Manasseh have been covered by intensive surveys. These surveys have revealed the sudden emergence of a new culture contrasting with the Philistine and Canaanite societies existing in Palestine during Iron Age I.[3] This new culture is characterised by the lack of pork remains (whereas pork formed 20% of the Philistine diet in places), an abandonment of the Philistines/Canaanite custom of having highly decorated pottery, and the practice of circumcision. According to Prof. Faust Avraham of Bar-Ilan University, the Israelite ethnic identity had been created, not from the Exodus and a subsequent conquest, but from a transformation of the existing Canaanite-Philistine cultures.[36]
Finkelstein and Silberman write: "These surveys revolutionized the study of early Israel. The discovery of the remains of a dense network of highland villages — all apparently established within the span of few generations — indicated that a dramatic social transformation had taken place in the central hill country of Canaan around 1200 BCE. There was no sign of violent invasion or even the infiltration of a clearly defined ethnic group. Instead, it seemed to be a revolution in lifestyle. In the formerly sparsely populated highlands from the Judean hills in the south to the hills of Samaria in the north, far from the Canaanite cities that were in the process of collapse and disintegration, about two-hundred fifty hilltop communities suddenly sprang up. Here were the first Israelites."[37]
From then on, over a period of hundreds of years until after the return of the exiles from Babylon, the Canaanites were gradually absorbed by the Israelites until after the period of Ezra (~450 BCE) when there is no more biblical record of them.[38] Hebrew, a dialect of Canaanite became the language of the hill country and later the valleys and plains.[39]
The first use of grapheme-based writing originated in the area, probably among Canaanite peoples resident in Egypt. All modern alphabets are descended from this writing. Written evidence of the use of Classical Hebrew exists from about 1000 BCE. It was written using the Paleo-Hebrew alphabet.
According to the Hebrew Bible, the United Kingdom of Israel was established by the Israelite tribes with Saul as its first king in 1020 BCE.[40] In 1000 BCE, Jerusalem was made the capital of King David's kingdom and it is believed that the First Temple was constructed in this period by King Solomon.[40] By 930 BCE, the united kingdom split to form the northern Kingdom of Israel, and the southern Kingdom of Judah.[40] These kingdoms coexisted with several more kingdoms in the greater Palestine area, including Philistine town states on the Southwestern Mediterranean coast, Edom, to the South of Judah, and Moab and Ammon to the East of the river Jordan.[41] The socio-political system during this period was characterized by local patrons fighting other local patrons, lasting until around the mid-9th century BCE when some local chieftains were able to create large political structures that exceeded the boundaries of those present in the Late Bronze Age Levant.[31]
Archaeological evidence from this era is believed to corroborate some Biblical events. In 925 BCE, Pharaoh Sheshonk I of the Third Intermediate Period is recorded to have invaded Canaan following the Battle of Bitter Lakes, and is thought to be the same as Shishak, the first Pharaoh mentioned in the Bible who captured and pillaged Jerusalem. There was an at least partial Egyptian withdrawal from Palestine in this period, though it is likely that Bet Shean was an Egyptian garrison as late as the beginning of the 10th century BCE.[31] The Kurkh Monolith, dated c. 835 BCE, describes King Shalmaneser III of Assyria's Battle of Qarqar, where he fought alongside the contingents of several kings, among them King Ahab and King Gindibu. The Mesha Stele, from c. 850 BCE, recounts the conquering of Moab, located East of the Dead Sea, by king Omri, and the successful revolt of Moabian king Mesha against Omri's son, presumably King Ahab (and French scholar André Lemaire reported that line 31 of the Stele bears the phrase "the house of David" (in Biblical Archaeology Review [May/June 1994], pp. 30–37).[42]). Inscriptions at Tel Dan and Tell es-Safi record parts of the conquest of the region by Hazael of Aram Damascus in the 830s BCE.[citation needed]

Developments in Palestine during this period have been the focus of debate between those who accept the version in the Hebrew Bible of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes, and those who reject it.[43] Niels Peter Lemche, of the Copenhagen School of Biblical Studies, submits that the biblical picture of ancient Israel "is contrary to any image of ancient Palestinian society that can be established on the basis of ancient sources from Palestine or referring to Palestine and that there is no way this image in the Bible can be reconciled with the historical past of the region".[31] For example, according to Jon Schiller and Hermann Austel, among others, while in the past, the Bible story was seen as historical truth, "a growing number of archaeological scholars, particularly those of the minimalist school, are now insisting that Kings David and Solomon are 'no more real than King Arthur,' citing the lack of archaeological evidence attesting to the existence of the United Kingdom of Israel, and the unreliability of biblical texts, due to their being composed in a much later period."[44][45]
Sites and artifacts, including the Large Stone Structure, Mount Ebal, the Merneptah, and Mesha stelae, among others, are subject to widely varying historical interpretations: the "conservative camp" reconstructs the history of Israel according to the biblical text and views archaeological evidence in that context, while scholars in the minimalist or deconstructionist school hold that there is no archaeological evidence supporting the idea of a United Monarchy (or Israelite nation) and the biblical account is a religious mythology created by Judean scribes in the Persian and Hellenistic periods; a third camp of centrist scholars acknowledges the value of some isolated elements of the Pentateuch and of Deuteronomonistic accounts as potentially valid history of monarchic times that can be in accord with the archaeological evidence, but argue that nevertheless the biblical narrative should be understood as highly ideological and adapted to the needs of the community at the time of its compilation.[46][47][48][49][50][51]
Neo-Assyrian and Neo-Babylonian Empires period
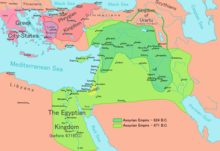
Assyrian inscriptions from c. 740 BCE record the military victories of Tiglath Pileser III in the region, during which period the Neo-Assyrian Empire conquered most of the Levant. The Bible records the Israelite cities becoming vassals to the Neo-Assyrian Empire during this period. At around this time, the Siege of Gezer (c. 733 BCE), 20 miles (32 km) west of Jerusalem, is recorded on a stone relief at the Assyrian royal palace in Nimrud. Further military expeditions into the region are recorded in the annals of Sargon and Sennacherib, as well as in the bible. According to the bible, between 722 and 720 BCE the northern Kingdom of Israel was destroyed by the Assyrian Empire and the Israelite tribes—thereafter known as the Lost Tribes—were exiled.[40] The most important finding from the southern Kingdom of Judah is the Siloam Inscription, dated c. 700 BCE, which celebrates the successful encounter of diggers, digging from both sides of the Jerusalem wall to create the Hezekiah water tunnel and water pool, mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, in 2Kings 20:20.[52][53][54][55]
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was replaced with the Neo-Babylonian Empire in c. 627 BCE, following the death of Ashurbanipal and the successful revolt of Nabopolassar.[citation needed]
The region was controlled briefly by Pharaoh Necho II of the Twenty-sixth dynasty of Egypt between the Battle of Megiddo (609 BCE) and the Battle of Carchemish four years later, and further conflict between the Babylonians and the 26th dynasty of Egypt is recorded during 601–586 BCE. According to the bible, this culminated in 586 BCE when Jerusalem and the First Temple were destroyed by the Babylonian king Nebuchadnezzar II.[40] Most of the surviving Israelite leaders, and much of the other local population, were deported to Babylonia.[32][56]
Persian (Achaemenid) Empire period
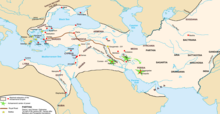
Following King Cyrus the Great's defeat of the Neo-Babylonian Empire at the Battle of Opis, the region became part of the Eber-Nari satrapy or District number V (corresponding the regions of (Syria, Phoenicia, Palestine and Cyprus) according to Herodotus and Arrian, which included three administrative areas: Phoenicia, Judah and Samaria, and the Arabian tribes. The Phoenician cities of Tyre, Sidon, Byblos, and Aradus were vassal states ruled by hereditary local kings who struck their own silver coins and whose power was limited by the Persian satrap and local popular assemblies. The economies of these cities were mainly based on maritime trade. During military operations, the Phoenicians were obliged to put their fleet at the disposal of the Persian kings. Judah and Samaria enjoyed considerable internal autonomy. Bullae and seal impressions of the end of the 6th and beginning of the 5th centuries mention the province of Judah. Its governors included Sheshbazzar and Zerubbabel under Cyrus and Darius I; Nehemiah ; Bagohi, who succeeded Nehemiah and whose ethnicity is difficult to determine; and "Yehizkiyah the governor" and "Yohanan the priest", known from coins struck in Judah in the 4th century BCE. From the second half of the 5th century the province of Samaria was governed by Sanballat and his descendants.[57][58][59][60]
According to the bible and implications from the Cyrus Cylinder, Jews were allowed to return to what their holy books had termed the Land of Israel, and having been granted some autonomy by the Persian administration, it was during this period that the Second Temple in Jerusalem was built.[32][61] Sebastia, near Nablus, was the northernmost province of the Persian administration in Palestine, and its southern borders were drawn at Hebron.[32][62] Some of the local population served as soldiers and lay people in the Persian administration, while others continued to agriculture. In 400 BCE, the Nabataeans made inroads into southern Palestine and built a separate civilization in the Negev that lasted until 160 BCE.[32][63] The end of the Persian period was marked by a number of revolts in the region, including a significant uprising against Artaxerxes III in 350 BCE, which resulted in the destruction of Jerusalem.[citation needed]
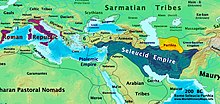

In the late 330s BCE, Alexander the Great conquered the region, during his six-year Macedonian conquest of the empire of Darius III of Persia. Alexander's armies took Palestine without complication while traveling to Egypt after the Siege of Tyre, beginning an important period of Hellenistic influence in the land.[64][65]
During 323–301 BCE, the region changed hands numerous times during the wars of the Diadochi, with rulers including Laomedon of Mytilene, Ptolemy I Soter and Antigonus I Monophthalmus. In 312 BCE Ptolemy I Soter defeated Antigonus' son Demetrius I at the Battle of Gaza, but withdrew from the region shortly thereafter. It is probable that Seleucus I Nicator, then an Admiral under Ptolemy's command, took part in the battle, as following the battle he was given 800 infantry and 200 cavalry and immediately travelled to Babylon where he founded the Seleucid Empire. The region was finally re-captured by Ptolemy I Soter after Antigonus I Monophthalmus was killed at the Battle of Ipsus. Ptolemy had not taken part in the battle, and the victors Seleucus I Nicator and Lysimachus had carved up the Antigonid Empire between them, with Southern Syria intended to become part of the Seleucid Empire. Although Seleucus did not attempt to conquer the area he was due, Ptolemy's pre-emptive move led to the Syrian Wars, which began in 274 BCE between the successors of the two leaders. The northern portion of Palestine ultimately fell into the hands of the Seleucid Empire in 219 through the betrayal of Governor Theodotus of Aetolia, who had held the province on behalf of Ptolemy IV Philopator. The Seleucids advanced on Egypt, but were defeated at the Battle of Raphia (Rafah) in 217. However, in 200 BCE Southern Palestine also fell under the control of the Seleucid Empire following the Battle of Panium (part of the Fifth Syrian War) in which Antiochus III the Great defeated the Ptolemies.[66]
The landscape during this period was markedly changed by extensive growth and development that included urban planning and the establishment of well-built fortified cities.[62][64] Hellenistic pottery was produced that absorbed Philistine traditions. Trade and commerce flourished, particularly in the most Hellenized areas, such as Ashkelon, Jaffa,[67] Jerusalem,[68] Gaza,[69] and ancient Nablus (Tell Balatah).[64][70]
The Persians had not interfered with the internal affairs of the various subject-peoples of the region, but the Greeks followed a policy of deliberate Hellenisation, encouraging, although not normally enforcing, Greek culture. Hellenisation took root first in the densely settled coastal and lowland areas, and only really began to impinge on more backward areas such as Judea in the early 2nd century. According to Josephus and the Books of the Maccabees, the continued Hellenization of Palestine by the Seleucids resulted in an uprising in the Judean Mountains, known as the Maccabean Revolt. Although the revolt was quelled in 160 BCE at the Battle of Elasa, the Seleucid Empire entered a period of rapid decline in 145–144 BCE, beginning with the overthrowing of King Alexander Balas at the Battle of Antioch (145 BCE) (the capital of the empire) by Demetrius II Nicator in alliance with Ptolemy VI Philometor of Egypt, as well as the capturing of Seleucia (the previous capital of the empire) by Mithradates I of Parthia. By 116 BCE, a civil war between Seleucid half-brothers Antiochus VIII Grypus and Antiochus IX Cyzicenus resulted in a breakup of the kingdom and the independence of certain principalities, including Judea.[71][72] This allowed Judean leader John Hyrcanus to carry out the first military conquests of the independent Hasmonean kingdom in 110 BCE, raising a mercenary army to capture Madaba and Schechem, significantly increasing the regional influence of Jerusalem[73][74] The Hasmoneans gradually extended their authority over much of the region, forcibly converting the populations of neighbouring regions, and creating a Judean-Samaritan-Idumaean-Ituraean-Galilean alliance in the process.[4] The Judean (Jewish, see Ioudaioi) control over the wider region resulted in it also becoming known as Judaea, a term that had previously only referred to the smaller region of the Judean Mountains.[75][76]
During 73–63 BCE, the Roman Republic extended its influence into the region in the Third Mithridatic War. During the war, Armenian King Tigranes the Great took control of Syria and prepared to invade Judea but retreated following an invasion of Armenia by Lucullus.[77][78] According to Armenian historian Movses Khorenatsi writing in c. 482 CE, Tigranes captured Jerusalem and deported Hyrcanus to Armenia, however most scholars deem this account to be incorrect.[79][80]
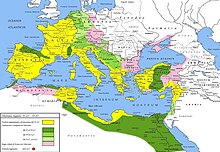
Following the Roman conquest of Judea led by Pompey in 63 BCE, Aulus Gabinius, proconsul of Syria, split the former Hasmonean Kingdom into five districts of legal and religious councils known as sanhedrin based at Jerusalem, Sepphoris (Galilee), Jericho, Amathus (Perea) and Gadara.[81][82] Roman rule was solidified when Herod, whose dynasty was of Idumean ancestry, was appointed as king.[64][83] Following a brief intervention by Pacorus I of Parthia, from 37 Iudaea under Herod I was a client kingdom of the Roman Empire.
Urban planning under the Romans was characterized by cities designed around the Forum—the central intersection of two main streets—the Cardo, running north-south and the Decumanus running east-west.[84] Cities were connected by an extensive road network developed for economic and military purposes. Among the most notable archaeological remnants from this era are Herodium (Tel al-Fureidis) to the south of Bethlehem,[85] Masada and Caesarea Maritima.[64][86] Herod arranged a renovation of the Second Temple in Jerusalem, with a massive expansion of the Temple Mount platform and major expansion of the Jewish Temple around 19 BCE. The Temple Mount's natural plateau was extended by enclosing the area with four massive retaining walls and filling the voids. This artificial expansion resulted in a large flat expanse, which today forms the eastern section of the Old City of Jerusalem.[citation needed]
Around the time associated with the birth of Jesus, Roman Palestine was in a state of disarray and direct Roman rule was re-established.[64][87] In 6 CE, the Herodian governorate ended with the deposition of Herod Archelaus as the ethnarch of the Tetrarchy of Judea. The Herodian Dynasty was then replaced by Roman prefects and after 44 CE by procurators, beginning with Coponius. Herodians continued to rule elsewhere in Palestine. Senator Quirinius was appointed Legate of the Roman province of Syria (to which Judea had been "added" according to Josephus[88] though Ben-Sasson claims it was a "satellite of Syria" and not "legally part of Syria"[89]) and carried out the tax census of both Syria and Judea known as the Census of Quirinius. Caesarea Palaestina replaced Jerusalem as the administrative capital of the region.[90]
Most scholars agree that Jesus was a Galilean Jew, born around the beginning of the first century,[91][92] and hold that Jesus lived in Galilee and Judea and did not preach or study elsewhere.[93][94][95] Using the gospel accounts with historical data, most scholars arrive at a date of birth between 6 and 4 CE for Jesus,[96][97] but some propose estimates that lie in a wider range.[[#cite_note-FOOTNOTEFor_example,_John_P._Meier_states_that_Jesus'_birth_year_is_''c.''_7/6_BC,'"`UNIQ--ref-00000086-QINU`"'_while_Finegan_favors_''c.''_3/2_BC.'"`UNIQ--ref-00000087-QINU`"'-100|[100]]] The general scholarly consensus is that Jesus was a contemporary of John the Baptist and was crucified by Roman governor Pontius Pilate.[101] Most scholars agree that his crucifixion was between 30 and 33 CE.[102][103]
As a result of the First Jewish-Roman War (66–73), Titus sacked Jerusalem (in 70 CE) destroying the Second Temple, leaving only supporting walls, including the Western Wall. According to Josephus, the estimated death toll was 250,000–1,100,000. Pharisee rabbi Yokhanan ben Zakai, a student of Hillel, fled during the siege of Jerusalem to negotiate with the Roman General Titus. Yokhanan obtained permission to reestablish a Sanhedrin in the coastal city of Iamnia (modern Yavne) (see also Council of Jamnia). He founded a school of Torah there that would eventually evolve, through the Mishna in around 200 CE, into Rabbinic Judaism. The region's leading Christians (Jewish Christians) relocated to Pella. Other Jewish groups such as Sadducees and Essenes are no longer recorded as groups in history.[citation needed]
In 106 CE, the Nabatean territory was incorporated into the Roman province of Arabia.[104]
Roman Syria Palaestina period

In 132 CE, the Emperor Hadrian joined the province of Iudaea (comprising Samaria, Judea proper, and Idumea) with Galilee to form new province of Syria Palaestina. Hadrian probably chose a name that revived the ancient name of Philistia (Palestine), combining it with that of the neighboring province of Syria, in an attempt to suppress Jewish connection to the land.[105][106][107] However Cassius Dio, the Roman historian from whom we have the bulk of our understanding of the revolt, does not mention the change of name nor the reason behind it in his "Roman History".[108] Jerusalem was renamed "Aelia Capitolina" and temples were built there to honor Roman gods, particularly Jupiter. In 135 CE, the victory in Bar Kokhba's revolt by Hadrian resulted in 580,000 Jews killed (according to Cassius Dio) and destabilization of the region's Jewish population.[109]
Jerusalem was re-established as the Roman military colony of Aelia Capitolina; a largely unsuccessful attempt was made to prevent Jews and Christians from living there. Many Jews and Christians left Palestine altogether for the Diaspora communities, and large numbers of prisoners of war were sold as slaves throughout the Empire. Christianity in particular was practiced in secret and the Hellenization of Palestine continued under Septimius Severus (193–211 CE).[64] New pagan cities were founded in Judea at Eleutheropolis (Bayt Jibrin), Diopolis (Lydd), and Nicopolis (Emmaus).[62][64] Some two hundred Jewish communities remained, as gradually certain religious freedoms were restored, such as exemption from the imperial cult and internal self-administration. The Romans made no such concession to the Samaritans, to whom religious liberties were denied, while their sanctuary on Mt.Gerizim was defiled by a pagan temple, as part of measures were taken to suppress the resurgence of Samaritan nationalism.[109]
A number of events with far-reaching consequences took place during this period, including further religious schisms between Christianity and Rabbinic Judaism such as a council held by the bishops of Palestine in Caesarea in 195 that decreed that Easter was to be always kept on a Sunday, and not with the Jewish Passover. The Romans destroyed the community of the Mother Church in Jerusalem, which had existed since the time of Jesus[110] The line of Jewish bishops in Jerusalem, which is claimed to have started with Jesus's brother James the Righteous as its first bishop, ceased to exist, within the Empire. Hans Kung suggests that the Jewish Christians sought refuge in Arabia and he quotes with approval a view that this created a paradox of truly world-historical significance that while Jewish Christianity was swallowed up in the Christian church, it preserved itself in Islam.[111]
During 259–272, the region fell under the rule of Odaenathus as King of the Palmyrene Empire after the capture of Emperor Valerian by Shapur I at the Battle of Edessa caused the Roman Empire to splinter until Aurelian defeated the Palmyrenes at the Battle of Emesa (Homs).[citation needed]
Late Antiquity period
Late Roman Empire period

Following the victory of Christian emperor Constantine in the Civil Wars of the Tetrarchy (306–324), the total Christianization of the Roman Empire began.[112][113] Within a few months, the First Council of Nicaea (first worldwide Christian council) confirmed the status of Aelia (Jerusalem) as a patriarchate,[114] at which point the city is generally taken to have been renamed Jerusalem. Theodosius I declared Christianity the state religion of the empire in 380, and Palestine became part of the Eastern Roman Empire ("Byzantium") after the division of the Roman Empire into east and west (a fitful process that was not finalized until 395 CE).[citation needed]

The Byzantines redrew the borders of the Land of Palestine. The various Roman provinces (Syria Palaestina, Samaria, Galilee, and Peraea) were reorganized into three diocese of Palaestina, reverting to the name first used by Greek historian Herodotus in the mid-5th century BCE: Palaestina Prima, Secunda, and Tertia or Salutaris (First, Second, and Third Palestine), part of the Diocese of the East.[112][115] Palaestina Prima consisted of Judea, Samaria, the Paralia, and Peraea with the governor residing in Caesarea. Palaestina Secunda consisted of the Galilee, the lower Jezreel Valley, the regions east of Galilee, and the western part of the former Decapolis with the seat of government at Scythopolis. Palaestina Tertia included the Negev, southern Jordan—once part of Arabia—and most of Sinai with Petra as the usual residence of the governor. Palestina Tertia was also known as Palaestina Salutaris.[112][116] According to historian H.H. Ben-Sasson,[117] this reorganisation took place under Diocletian (284–305), although other scholars suggest this change occurred later in 390.[citation needed]
This was the period of Palestine's greatest prosperity in antiquity.[citation needed] Urbanization increased, large new areas were put under cultivation, monasteries proliferated and synagogues were restored. The cities of Palestine, such as Caesarea Maritima, Jerusalem, Scythopolis, Neapolis, and Gaza reached their peak population, and the population West of the Jordan may have reached as many as one million.[109] Bede in his Historia Ecclesiastica, drew on Orosius' information gathered from the local Jews to describe Palestine as one of the provinces of "Syria, which is called Aran by the Hebrews. The place is between the River Euphrates and the Great Sea, and extends towards Egypt; its largest provinces are Commagene, Phoenicia, and Palestine, as well as the countries of the Saraceni and the Nabathaei. It has twelve gentes."54[118]
In 326, Constantine's mother Saint Helena visited Jerusalem and ordered the destruction of Hadrian's temple to Venus, which had been built on Calvary.[112] Accompanied by Macarius of Jerusalem, the excavation reportedly discovered the True Cross, the Holy Tunic and the Holy Nails. The first Church of the Holy Sepulcher in Jerusalem, the first Church of the Nativity in Bethlehem and the first Church of the Ascension on the Mount of Olives were all built during Constantine's reign.[112]
The earliest monasteries in Christianity outside of Egypt were built in Palestine during this period,[62][112] notably those of Hilarion near Gaza, Saint Epiphanius at Ad near the city of Eleutheropolis (Bayt Jibrin, the head of the largest bishopric in Palestine at this time), Tyrannius Rufinus and Melania the Elder on the Mount of Olives, Euthymius the Great at Pharan, Sabbas the Sanctified in the Kidron Valley as well as St. George's Monastery in Wadi al-Qelt, the Monastery of the Temptation and Deir Hajla near Jericho, and Deir Mar Saba and Deir Theodosius east of Bethlehem.[112] The sack of Rome in 410 caused a significant episode of migration to Palestine as a group of aristocratic ladies responded to the holy man Jerome's invitation to settle in Aelia Capitolina and Bethlehem.[109] In 451, the Council of Chalcedon confirmed Jerusalem's status as a Patriarchate as one of the Pentarchy, and Juvenal of Jerusalem became the first Patriarch of Jerusalem[119]
Notable works by Christian scholars were produced in Palestine in the disciplines of rhetoric, historiography, Eusebian ecclesiastical history, classicizing history and hagiography.[120] Saint Cyril of Jerusalem delivered his Mystagogical Catecheses, instructions on the principal topics of Christian faith and practise, and Saint Jerome moved to Jerusalem in order to commence work on the Vulgate, commissioned by Pope Damasus I and instrumental in the fixation of the Biblical canon in the West.[citation needed] Procopius, from Caesarea Palaestina, became the Byzantine Empire's principal historian of the 6th century, writing the Wars of Justinian, the Buildings of Justinian and the celebrated Secret History.

Under Byzantine rule, the two dioceses of Palaestina proper became a center of Christianity, while retaining significant Jewish and Samaritan communities. Some areas, like Gaza, were well known as pagan holdouts, and remained attached to the worship of Dagon and other deities as their ancestors had been for thousands of years.[121] Ghassanid Arab migration in the 4th and 5th centuries established an Arab Christian domain with a capital on the Golan, forming a buffer of Christian Byzantium against the wild tribes of Arabia. The "Life of Barsauma of Samosata", a 6th-century Christian polemic about the Monophysite monk of the early 5th century, stated that Jews, Samaritans and pagans formed a large part of the population and persecuted Christians during this period.[122][123] In 351–352, a Jewish revolt against Byzantine rule in Tiberias and other parts of the Galilee was brutally suppressed. In 361, Neoplatonist Julian the Apostate becomes Roman Emperor and attempted to reverse the growing influence of Christianity by encouraging other religions. As a result, Alypius of Antioch was commissioned to rebuild the Temple in Jerusalem and Jews were formally allowed to return to the city[124] However, two years later the Galilee earthquake of 363 together with the re-establishment of Christianity's dominance following the death of Julian the Apostate at the Battle of Samarra ended the attempts to rebuild the Temple. In 438 CE, the Empress Eudocia allowed Jews to return to Jerusalem to live.[citation needed]
The Samaritan self-rule had shortly gained a level of independence under the leadership of Baba Rabba in late 4th century. However, they were again subdued by Byzantine forces. Samaritan attempts to gain independence from Byzantines peaked during the 5th and 6th centuries in a series of Samaritan Revolts, some of which had messianic aspirations. The outcome of Samaritan strife with Christian Byzantines, supported by Ghassanid Arabs, turned disastrous. After the Third Samaritan revolt in 529–531, led by Julianus ben Sabar, and the Fourth Revolt in 555. With Samaritan casualties went well beyond 100,000, cities and worship places destroyed, many enslaved and expelled, the Samaritan community dwindled.[citation needed]
On 1 July 536 CE, Justinian I promoted Stephanus (Stephen) the governor at Caesarea to proconsul (anthypatos), giving him authority over the two remaining consulars. Justinian believed that the elevation of the governor was appropriate because he was responsible for "the province in which our Lord Jesus Christ... appeared on earth".[120][125] Justinian I undertook a number of building works in Jerusalem, including the once magnificent Nea Ekklesia of the Theotokos ("the Nea") and the extension of the Cardo thoroughfare.[126]

Byzantine administration of Palestine was temporarily suspended during the Persian occupation of 614–28. In 613 CE, the Persian Sassanian Empire under Khosrau II had invaded the Levant led by General Shahrbaraz, taking Antioch and later Caesaria. Jews under Benjamin of Tiberias assisted the conquering Persians, revolting against the Byzantine Empire under Heraclius and hoping of controlling Jerusalem autonomously. In 614 CE, Persian-Jewish forces conquered Jerusalem, destroying most of the churches, taking Patriarch Zacharias prisoner, taking the True Cross and other relics to Ctesiphon, and massacring much of the Christian population.[127][128] The Jews of Jerusalem gained autonomy to some degree, but frustrated with its limitations and anticipating its loss offered to assist the Byzantines in return for amnesty for the revolt. In 617 CE, the Jewish governor Nehemiah ben Hushiel was killed by a mob of Christian citizens, three years after his appointment. The Sassanids quelled the uprising and appointed a Christian governor to replace him. At that time the Persians betrayed the agreements with the Jews and expelled the Jewish population from Jerusalem, forbidding them to live within 3 miles (4.8 km) of it.[citation needed] In 625 CE (or 628 CE), the Byzantinian army returned to the area, promising amnesty to Jews who had joined the Persians, and was greeted by Benjamin of Tiberias. In 629 CE, the Byzantine Emperor Heraclius marched into Jerusalem at the head of his army, following the decisive defeat of the Sassanid Empire at the Battle of Nineveh (627). Heraclius personally returned the True Cross to the city.[129]
The Nabateans roamed the Negev by the Roman Period, and by the Byzantine Period dominated the swath of sparsely populated deserts, from the Sinai to the Negev to the northwest coast of Arabia, the outlands that the Byzantines called the diocese of Palaestina Salutoris (meaning something like "near Palestine"). Its capital Petra was formally the capital of the Roman province of Arabia Petraea. The Nabateans also inhabited the outland of Jordan and southern Syria, improperly called the diocese of Arabia because its capital Bostra was within the northern extremity of the Roman province of Arabia Petrae. The origin of the Nabateans remains obscure, but they were Aramaic speakers, and the term "Nabatean" was the Arabic name for an Aramean of Syria and Iraq. By the 3rd century during the Late Roman Period, the Nabateans stopped writing in Aramaic and began writing in Greek, and by the Byzantine Period they converted to Christianity.[130]
Trading relations existed between the cities of Palestine and the Arab tribes of the Hejaz, particularly with the southern cities of Petra and Gaza. Muhammed, his father (Abd Allah) and his great-grandfather (Hashim, who died in Gaza) all travelled on trading routes through the region in the 6th century,[131] and in 583 Muhammed is said to have met with Nestorian monk Bahira at Bosra.[citation needed]
From the beginning of Islam in 610,[132] Jerusalem became the Qibla (focal point for Muslim prayers) for fourteen years until it was replaced by Mecca in 624, 18 months after the Hijra (Muhammad's migration to Medina). According to Sahih al-Bukhari, Muhammad then ordained the Al-Aqsa Mosque as one of the three holy mosques of Islam[133] A decade later, Byzantium lost control of the region during the Muslim conquest of Syria, during which the empire's forces were decisively defeated at the Battle of Yarmouk in 636. Jerusalem capitulated in 638 and Caesarea between 640 and 642.[120] The subsequent Rashidun and Umayyad Caliphates saw a century of rapid expansion of Arab power well beyond the Arabian peninsula in the form of a vast Muslim Arab Empire.[citation needed]
Rashidun, Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates period

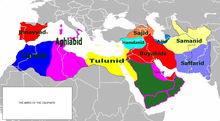
In 638, following the Siege of Jerusalem, the Caliph Omar Ibn al-Khattab and Safforonius, the Patriarch of Jerusalem, signed Al-Uhda al-'Omariyya (The Umariyya Covenant), an agreement that stipulated the rights and obligations of all non-Muslims in Palestine.[112] Christians and Jews were considered People of the Book, enjoyed some protection (dhimmi) but had to pay a special poll tax called jizyah ("tribute") in return for this protection. According to Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari, the covenant guaranteed Christians freedom of religion but prohibited Jews from living in Jerusalem. However, during the early years of Muslim control of the city, a small permanent Jewish population returned to Jerusalem after a 500-year absence.[134]
Umar, the second of the initial four Rashidun Caliphs, was the first conqueror of Jerusalem to enter the city on foot, and when visiting the site that now houses the Haram al-Sharif, he declared it a sacred place of prayer.[135][136] Cities that accepted the new rulers, as recorded in registrars from the time, were: Jerusalem, Nablus, Jenin, Acre, Tiberias, Bisan, Caesarea, Lajjun, Lydd, Jaffa, Imwas, Beit Jibrin, Gaza, Rafah, Hebron, Yubna, Haifa, Safed and Ashkelon.[137]
In Arabic, the area approximating the Byzantine Diocese of Palaestina I in the south (roughly Judea, Philistia, and southern Jordan) was called Jund Filastin (meaning "the military district of Palestine", as a tax administrative area),[138] and the Diocese of Palaestina II in the north (roughly Samaria, Galilee, Golan, and northern Jordan) Jund al-Urdunn.[citation needed]
In 661, with the assassination of Ali, the last of the Rashidun Caliphs, Muawiyah I became the uncontested Caliph of the Islamic World. Muawiyah I was ordained as Caliph in Jerusalem, ending the First Fitna and marking the beginning of the Umayyad Empire.[citation needed]
Under Umayyad rule, the Byzantine province of Palaestina Prima became the administrative and military sub-province (jund) of Filastin—the Arabic name for Palestine from that point forward.[139] It formed one of five subdivisions of the larger province of ash-Sham (Arabic for Greater Syria).[140] Jund Filastin (Arabic جند فلسطين, literally "the army of Palestine") was a region extending from the Sinai to the plain of Acre. Major towns included Rafah, Caesarea, Gaza, Jaffa, Nablus and Jericho.[141] Lod served as the headquarters of the province of Filastin and the capital later moved to Ramla. Jund al-Urdunn (literally "the army of Jordan") was a region to the north and east of Filastin, which included the cities of Acre, Bisan and Tiberias.[141]

In 687–691, during the Second Fitna, the Dome of the Rock was built under Caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan, becoming the world's first great work of Islamic architecture.[26] The Temple Mount (known as Haram Ash-Sharif in the Islamic world and the site where the Islamic prophet Muhammad is believed by Muslims to have begun his nocturnal journey to heaven), had remained unbuilt for c. 600 years since Titus's destruction of Herod's Temple in 70.[citation needed]
About a decade afterward, Caliph Al-Walid I had the Al-Aqsa Mosque built.[142]
It was under Umayyad rule that Christians and Jews were granted the official title of "Peoples of the Book" to underline the common monotheistic roots they shared with Islam.[137][143] Christian pilgrims visited and made generous donations to Christian holy places in Jerusalem and Bethlehem,[144] and the establishment of the Pilgrims' Inn in Jerusalem during this period was seen as a fulfillment of Umar's pledge to Bishop Sophronious to allow freedom of religion and access to Jerusalem for Christian pilgrims.[145] The Christian monasteries throughout the region continued to operate, and between 730-749 John of Damascus, previously chief adviser to Caliph Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik, moved to the monastery Mar Saba outside Jerusalem and became the major opponent of the First Iconoclasm through his theological writings.[citation needed]
Trading relations between Palestine and Europe were strong, and a trade fair took place in Jerusalem every year on September 15 where merchants from Pisa, Genoa, Venice and Marseilles converged to acquire spices, soaps, silks, olive oil, sugar and glassware in exchange for European products.[144]
In 744 riots broke out in the major cities of Palestine and Syria during the reign of Marwan II, and were quelled in 745–6. These rebellions were followed by further revolts in the East of the empire, which culminated in the defeat of the Umayyad army in 750 at the Battle of the Zab. The Abbasids took control of the entire empire including Palestine, forcing Marwan II to flee via Gaza to Egypt where he was assassinated.[citation needed]
The Baghdad-based Abbasid Caliphs renovated and visited the holy shrines and sanctuaries in Jerusalem, with Al-Mansur arranging in 758 the renovation of the Dome of the Rock that had collapsed in an earthquake[146] and Al-Ma'mun arranging further renovations following a visit to Jerusalem in 813.[147] The Abbasids continued to build up Ramle, which had become the capital of Jund Filastin.[137][148] Coastal areas were fortified and developed and port cities like Acre, Haifa, Caesarea, Arsuf, Jaffa and Ashkelon received monies from the state treasury.[144] However, the Abbasid caliphs visited the region less frequently than the Umayyads since their capital in Baghdad was a further 500 miles (800 km) east.[citation needed]
The Abbasid period marked the beginning of the Islamic Golden Age, in which a number of scholars from Palestine, such as the Gazan-born jurist and founder of the Shafi'i school of fiqh Muhammad ibn Idris ash-Shafi`i and the Jerusalemite geographer Al-Muqaddasi, played an integral part.[citation needed]
The influence of the Arabian tribes declined during the Abbasid period and the only context where they are reported is in uprising against the central authority.[149] However, a dispute between the Mudhar and Yamani tribes broke out in Jund al-Urdunn towards the end of the 8th century leading to Civil War in Palestine (793–796). Harun al-Rashid viewed this as a rebellion and sent a large army under Ja'far ibn Yahya al-Barmaki to quell the revolt. According to historian Moshe Gil, "he put down the rebels with an iron hand and much blood was spilled."[149] The cities of Gaza, Bayt Jibrin, Ascalon in Jund Filastin and the town Sariphaea in Jund al-Urdunn were completely destroyed in the conflict by Bedouin tribes.[149] Several towns and villages in western Palestine were also sacked.[150] The monasteries of St. Chariton, St. Cyriacus, St. Sabas, St. Theodosius, and St. Euthymius were also attacked.[151] The combined casualties of the tribal federations totalled roughly 1,200.[152]
During Harun al-Rashid's (786–809) reign the first formal contacts with the Frankish Kingdom of Charlemagne occurred, as part of the attempted Abbasid–Carolingian alliance[153] In 797, Harun al-Rashid is reported to have offered the custody of the Christian holy places in Jerusalem to Charlemagne, in return for Charlemagne sending money for construction and improvements.[154] As a result, the Church of the Holy Sepulchre was restored and the Latin hospital was enlarged and placed under the control of the Benedictines.[155] Two years later Charlemagne sent another mission to Patriarch George of Jerusalem.[156]
Towards the end of the 9th century, the Baghdad-based Abbasids began to lose control of their western provinces. From 878 Palestine was ruled from Egypt by semi-autonomous rulers for almost a century, beginning with Ahmad ibn Tulun, ruler of Egypt and founder of the Tulunid dynasty, who conquered Palestine and most of Syria four years after declaring Egypt's independence from the Abbasid court in Baghdad. The Abbasids regained direct control of Palestine in 904, after their invasion forced the army of Tulunid Emir Harun to retreat to Egypt where the Tulunids were defeated the following year.[citation needed]
Direct control from Baghdad was maintained until 939 when Muhammad bin Tughj Al-Ikhshid, governor of Abbasid Egypt and Palestine, was granted independent control over his domain and the title Al-Ikhshid (Prince) by Abbasid Caliph Ar-Radi. Like the Tulunids, the relative proximity of the Ikhshidid capital to Palestine resulted in a greater focus on the region, such that both Ikhshidid rulers, Muhammad bin Tughj Al-Ikhshid and Abu al-Misk Kafur, were buried in Jerusalem.[citation needed]
The death of Abu al-Misk Kafur in 968 resulted in a fatal division of the Ikhshidid government as they prepared for the expected invasion by the Fatimids.[citation needed]
Fatimid Caliphate period

From their base in Tunisia, General Gawhar Al-Siqilli of the Ismaili Shi'ite Fatimids, who claimed to be descendants of Muhammad through his daughter Fatimah, conquered the Ikhshidid domains of Palestine and Egypt in 969, following a treaty guaranteeing the local Sunnis freedom of religion.[157] They moved their capital to the new city of Cairo, just north of the Ikhshidid capital of Fustat.[citation needed]
The Fatimids continued their expansion to the borders of the Byzantine Empire, and a failed attack on Antioch in 971 was followed up by a Byzantine defeat outside of Amida.[158] However, the Byzantines fought back and in 975 Emperor John I Tzimiskes's second campaign took Syria and much of northern Palestine, including Tiberias, Nazareth and Caesarea Palaestina, but was defeated en route to Jerusalem. The emperor became ill and died suddenly in 976 on his return from the campaign, and the Byzantines withdrew shortly thereafter to face the Bulgar threat in the north of their empire.[159]
Jerusalem, Nablus, and Askalan were expanded and renovated under Fatimid rule.[144] However, in 1009, Fatimid Caliph Al-Hakim ordered the destruction of all churches and synagogues in the empire, including the Church of the Holy Sepulchre. However, this was reversed twenty years later by the Al-Hakim' successor as Caliph, Ali az-Zahir, who authorized the rebuilding of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre and other Christian churches in a treaty with Byzantine Emperor Romanos III Argyros. Romanos' successor Constantine IX Monomachos paid for the restoration, and a number of other Christian buildings, including the Muristan hospital, church and monastery were built during this period. Az-Zahir also undertook a major renovation of the Dome of the Rock during his reign. After the 10th century, the division of Palestine into Junds began to break down.[144]
During the early 11th century, Seljuk Turks invaded large portions of West Asia and both the Fatimids and the Byzantines suffered setbacks from the fighting. Warfare between the Fatimids and Seljuks caused great disruption for the local population and for western pilgrims. In 1073 Palestine was captured by Malik-Shah I's Isfahan-based Great Seljuq Empire[160] under Emir Atsiz ibn Uvaq, who was advancing south into the weakening Fatimid Empire following the decisive defeat over the Byzantine army at the Battle of Manzikert two years previously and a devastating six-year famine in Egypt between 1067 and 1072.[161] The Seljuk rule was unpopular, and in 1077 Jerusalem revolted against their rule while Emir Atsiz ibd Uvaq was fighting the Fatimid Empire in Egypt. On his return to Jerusalem, Atsiz re-took the city and massacred the local population.[162] As a result, Atsiz was executed by the governor of Syria Tutush I, the brother of Seljuk leader Malik-Shah I. Tutush I appointed Artuq bin Ekseb, later founder of the Artuqid dynasty, as governor. Artuq bin Ekseb died in 1091, and was succeeded as governor by his sons Ilghazi and Sokmen, known as the Artuqid dynasty. Malik Shah died in 1092, and the Great Seljuk Empire split into smaller warring states. Control of Palestine was disputed between Duqaq and Radwan after the death of their father Tutush I in 1095. The ongoing rivalry weakens Syria, and Fatimid Regent Al-Afdal Shahanshah recaptured the region in 1098 from the Artuqids, just before the arrival of the crusaders.[163]
In 1054, the Great Schism formally divided the Christian church into east and west, resulting in the holy sites of Palestine falling under the jurisdiction of the Eastern Orthodox Church. However, in 1090, Byzantine Emperor Alexios I Komnenos began taking reconciliatory measures towards the Papacy,[164] with the intention of seeking western support against the Seljuqs. In 1095 his ambassadors appeared before Pope Urban II at the Council of Piacenza,[165] to request mercenary forces, and later that year at the Council of Clermont Pope Urban II called for the First Crusade.[citation needed]
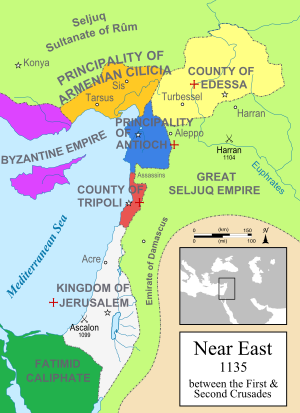

The Kingdom of Jerusalem was a Christian kingdom established in the Levant in 1099 as a result of the First Crusade. Its control of Jerusalem and most of Palestine lasted almost a century until defeat by Saladin's forces in 1187, after which most of Palestine was controlled by the Ayyubids.[citation needed]
Shortly after Crusader rule was established in Palestine, Godfrey of Bouillon promised to turn over the rule of the region to the Papacy once the crusaders had captured Egypt. However, the invasion of Egypt did not occur as Godfrey died shortly thereafter and Baldwin was proclaimed the first King of Jerusalem after politically outmanoeuvering Dagobert of Pisa who had previously been appointed as the Latin Patriarch.[166]
At first the Crusader kingdom was little more than a loose collection of towns and cities captured during the first crusade. At its height, the kingdom roughly encompassed the territory of modern-day Israel and the State of Palestine. It extended from modern Lebanon in the north to the Sinai Desert in the south, and into modern Jordan and Syria in the east. There were also attempts to expand the kingdom into Fatimid Egypt. Its kings held a certain amount of authority over the other crusader states to the north: the County of Tripoli, the Principality of Antioch, and the County of Edessa.[citation needed]
Many customs and institutions were imported from the territories of Western Europe from which the crusaders came, and there were close familial and political connections with the West throughout the kingdom's existence. It was, however, a relatively minor kingdom in comparison and often lacked financial and military support from Europe. Locally based military orders were founded in the kingdom to fill this vacuum. The foundation of the Knights Hospitaller by Gerard Thom at the Muristan Christian hospice in Jerusalem was confirmed by a Papal Bull from Pope Paschal II in 1113, and the founding by Hugues de Payens and Godfrey de Saint-Omer of the Knights Templar took place in 1119 in the Al Aqsa Mosque.[citation needed]
The kingdom grew closer to the neighbouring Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia and the Byzantine Empire, from which it inherited "oriental" qualities, and the kingdom was also influenced by pre-existing Muslim institutions. However, when Arnulf of Chocques was appointed Latin Patriarch of Jerusalem for the second time in 1112, he prohibited non-Catholic worship at the Church of the Holy Sepulchre. Socially, the "Latin" inhabitants from Western Europe had almost no contact with the Muslims and Eastern Christians whom they ruled.[citation needed]
The Royal Palace of the Kingdom was based in the Al-Aqsa Mosque, and the Dome of the Rock was converted into a church. Under the Crusader rule, fortifications, castles, towers and fortified villages were built, rebuilt and renovated across Palestine largely in rural areas.[144][167] A notable urban remnant of the Crusader architecture of this era is found in Acre's old city[144][168] and on the island of Arwad.[citation needed]
Numerous Muslim families emigrated Palestine during this period, including those of notable Islamic scholars Ibn Qudamah and Diya al-Din al-Maqdisi.[citation needed]
During the period of Crusader control, it has been estimated that Palestine had only 1,000 poor Jewish families.[169] Jews fought alongside the Muslims against the Crusaders in Jerusalem in 1099 and Haifa in 1100. Some Jews from Europe visited the country, like Benjamin of Tudela who wrote about it.[170] Maimonides visited Palestine after escaping from the Almohads in 1165 and visited Acre, Jerusalem and Hebron, finally choosing to settle in Fostat in Egypt.[171]
In July 1187, the Cairo-based Kurdish General Saladin commanded his troops to victory in the Battle of Hattin,[172][173] shortly followed by the Siege of Jerusalem (1187) in which Saladin captured Jerusalem.[citation needed]



Following the crusader defeat by Saladin's forces in 1187, most of Palestine was controlled by the Ayyubids. However a rump crusader state in the northern coastal cities known as the Kingdom of Acre survived in the region for another hundred years until 1291, throughout the Ayyubid Period and well into the Mamluk Period. However, despite seven further crusades from Europe, the Crusader state was no longer a significant power in the region after the fall of Jerusalem in 1187.[citation needed]
The Ayyubids allowed Jewish and Orthodox Christian settlement in the region, and the Dome of the Rock was converted back into an Islamic center of worship. The Mosque of Omar was built under Saladin outside the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, commemorating Umar the Great's decision to pray outside the church so as not to set a precedent and thereby endanger the Church's status as a Christian site. About eighty years after Saladin's conquest, the Catalan Rabbi Nahmanides left Europe following the disputation of Barcelona,[174] and spent the last three years of his life in Palestine, primarily in Acre. He established the Ramban Synagogue in the Old City of Jerusalem and thus, having found only two Jewish people living in the city at the time, re-established Jewish communal life in Jerusalem.[citation needed]
The defeat of the Europeans provoked further crusades from Europe, varying in size and success. In 1192, after preventing the Third Crusade under Richard the Lionheart from recapturing Jerusalem, Saladin entered into the Treaty of Ramla in which he agreed that Western Christian pilgrims could worship freely in Jerusalem. The threat remained, however, and Ayyubid Emir Al-Mu'azzam destroyed Jerusalem's city walls in 1219 to prevent the Crusaders from capturing a fortified city. To end the Sixth Crusade, a 10-year treaty was signed between Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor and Ayyubid Sultan Al-Kamil, allowing Christians freedom to live in the unfortified Jerusalem, as well as Nazareth and Bethlehem, although the Ayyubids retained control of the Muslim holy places.[172]
These areas were returned to Ayyubid control after the peace treaty expired in 1239 and An-Nasir Dawud, Ayyubid Emir of Kerak, occupied the cities. For the four following years, control of the cities was contested between An-Nasir Dawud and his cousin As-Salih Ayyub who had allied with the Crusaders, aided by the diplomatic efforts of Thibaut IV of Champagne. In order to permanently retake the city from the rival breakaway rulers who had allied with the Crusaders, As-Salih Ayyub summoned a huge mercenary army of Khwarezmians, who were available for hire following the defeat of the Khwarazm Shah dynasty by the Mongols ten years earlier.[175] The Khwarezmians could not be controlled by As-Salih Ayyub, and destroyed Jerusalem. A few months later, the two sides met again at the decisive Battle of La Forbie, marking the end of the Crusader influence in southern and central Palestine. Two years later the Ayyubids regained control of Jerusalem after the Khwarezmians were defeated by Al-Mansur Ibrahim at Lake Homs.[citation needed]
The Mamluk Sultanate was indirectly created in Egypt as a result of the Seventh Crusade, which had been launched in reaction to the 1244 destruction of Jerusalem. The crusade failed after Louis IX of France was defeated and captured by Ayyubid Sultan Turanshah at the Battle of Fariskur in 1250. Turanshah was killed by his Mamluk soldiers a month after the battle and his step-mother Shajar al-Durr became Sultana of Egypt with the Mamluk Aybak as Atabeg. The Ayyubids relocated to Damascus, where they continued to control Palestine for a further 10 years.[citation needed]
In the late 13th century, Palestine and Syria became the primary front against the fast-expanding Mongol Empire. The Army of the Mongol Empire reached Palestine for the first time in 1260, beginning with the Mongol raids into Palestine under Nestorian Christian general Kitbuqa. Mongol leader Hulagu Khan sent a message to Louis IX of France that Jerusalem had been remitted to the Christians under the Franco-Mongol Alliance, however shortly thereafter he had to return to Mongolia following the death of Mongke, leaving Kitbuqa and a reduced army. Kitbuqa then engaged with the Mamluks under Baibars in the pivotal Battle of Ain Jalut in the Jezreel Valley. The Mamluks' decisive victory in Palestine is seen as one of world history's most significant battles, establishing a high-water mark for the Mongol conquests. The Mongols were, however, able to engage into some further brief Mongol raids into Palestine in 1300 under Ghazan and Mulay, reaching as far as Gaza. Jerusalem was held by the Mongols for four months (see Ninth Crusade).[citation needed]
In 1270, Sultan Baibars expelled the remaining Crusaders from most of the country, and the last major Crusader stronghold, Acre fell in 1291, at the Siege of Acre.[172] Thereafter, any remaining Europeans either went home or merged with the local population.[173]
The Mamluks, continuing the policy of the Ayyubids, made the strategic decision to destroy the coastal area and to bring desolation to many of its cities, from Tyre in the north to Gaza in the south. Ports were destroyed and various materials were dumped to make them inoperable. The goal was to prevent attacks from the sea, given the fear of the return of the crusaders. This had a long term affect on those areas, that remained sparsely populated for centuries. The activity in that time concentrated more inland.[176]
Palestine formed a part of the Damascus Wilayah (district) under the rule of the Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt and was divided into three smaller Sanjaks (subdivisions) with capitals in Jerusalem, Gaza, and Safed.[173] Due in part to the many conflicts, earthquakes and the Black Death that hit the region during this era, the population is estimated to have dwindled to around 200,000. The Mamluks constructed a "postal road" from Cairo to Damascus, that included lodgings for travelers (khans) and bridges, some of which survive to this day (Jisr Jindas, near Lod). The period also saw the construction of many schools and the renovation of mosques neglected or destroyed during the Crusader period.[177]
In 1377 the major cities of Palestine and Syria revolted, following the death of Al-Ashraf Sha'ban. The revolt was quelled and a coup d'etat was staged by Barquq in Cairo in 1382, founding the Mamluk Burji dynasty.[citation needed]
Palestine was celebrated by Arab and Muslim writers of the time as the "blessed land of the prophets and Islam's revered leaders",[173] Muslim sanctuaries were "rediscovered" and received many pilgrims.[177] In 1496, Mujir al-Din al-'Ulaymi wrote his history of Palestine known as The Glorious History of Jerusalem and Hebron".[citation needed]
In 1486, hostilities broke out between the Mamluks and the Ottoman Turks in a battle for control over western Asia. The Mamluk armies were eventually defeated by the forces of the Ottoman Sultan, Selim I, and lost control of Palestine after the 1516 battle of Marj Dabiq.[173][178]
Ottoman period
Early Ottoman period

In 1516, when the Ottoman Turks occupied Palestine,[179] the land became part of the Ottoman Empire, and Istanbul appointed local governors. After the Ottoman conquest, the name "Palestine" was no longer used as the official name of an administrative unit, as the Turks often called their (sub)provinces after the capital. The majority of historical Palestine became part of the Eyalet of Damascus until 1660, and later became part of the Eyalet of Sidon. Nonetheless, the old name remained in popular and semi-official use,[180] with many examples of its usage in the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries surviving.[181][182][183] For example, Thomas Salmon's 18th-century book, Modern history or, the present state of all nations, states that "Jerusalem is still reckoned the capital city of Palestine."[184]
In 1624, following the Battle of Anjar, Druze prince Fakhr-al-Din II was appointed the "Emir of Arabistan" by the Ottomans to govern the region from Aleppo to Jerusalem. He toured his new provinces in the same year.[185] He was deposed and hanged a decade later by the wali of Damascus

The region saw an influx of tribal immigrants from the south (Arabian Peninsula) and east (the Mesopotamian valleys) during the 17th and 18th centuries.[186] An area around Tiberias was given to Don Joseph Nasi for a Jewish enclave. Following the expulsions from Spain, the Jewish population of Palestine rose to around 25%[citation needed] (includes non-Ottoman citizens, excludes Bedouin) and regained its former stronghold of Eastern Galilee. That ended in 1660 when they were massacred at Safed and Jerusalem. During the reign of Daher el-Omar, Pasha of the Galilee, Jews from Ukraine began to resettle Tiberias.[citation needed]
Napoleon of France briefly waged war against the Ottoman Empire (allied then with Great Britain), and held territory in Palestine during the 7 March 1799—July 1799 French occupation of Jaffa, Haifa, and Caesarea. At the Siege of Acre in 1799, Napoleon requested that the Jews of Asia and Africa help the French to capture Jerusalem. This was mostly to curry favour with Haim Farkhi the Jewish finance minister and adviser to the Pasha of Syria/Palestine.[187] He was later assassinated and his brothers formed an army with Ottoman permission to conquer the Galilee.[188]

On 10 May 1832, the area of Ottoman Syria, which include modern Syria, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon, and Israel were conquered and annexed by Muhammad Ali's expansionist Egypt (nominally still Ottoman) in the 1831 Egyptian-Ottoman War. Britain sent the navy to shell Beirut and an Anglo-Ottoman expeditionary force landed, causing local uprisings against the Egyptian occupiers. A British naval squadron anchored off Alexandria. The Egyptian army retreated to Egypt. Muhammad Ali signed the Treaty of 1841. Britain returned control of the Levant to the Ottomans, and as a result was able to increase the extraterritorial rights that various European nations had enjoyed throughout previous centuries under the terms of the Capitulations of the Ottoman Empire. One American diplomat wrote that "Extraordinary privileges and immunities had become so embodied in successive treaties between the great Christian Powers and the Sublime Porte that for most intents and purposes many nationalities in the Ottoman empire formed a state within the state."[189]
In 1834, there was a peasants revolt against conscription into the Egyptian army. Local pre-Zionist Jews of the Old Yishuv, complacent with the Egyptian rule, were targeted by the general Arab Muslim and Druze discontent during the Safed Plunder.
In common usage from 1840 onwards, "Palestine" was used either to describe the Consular jurisdictions of the Western Powers[190] or for a region that extended in the north-south direction typically from Rafah (south-east of Gaza) to the Litani River (now in Lebanon). The western boundary was the sea, and the eastern boundary was the poorly defined place where the Syrian desert began. In various European sources, the eastern boundary was placed anywhere from the Jordan River to slightly east of Amman. The Negev Desert was not included.[191] The Consuls were originally magistrates who tried cases involving their own citizens in foreign territories. While the jurisdictions in the secular states of Europe had become territorial, the Ottomans perpetuated the legal system they inherited from the Byzantine Empire. The law in many matters was personal, not territorial, and the individual citizen carried his nation's law with him wherever he went.[192] Capitulatory law applied to foreigners in Palestine. Only Consular Courts of the State of the foreigners concerned were competent to try them. That was true, not only in cases involving personal status, but also in criminal and commercial matters.[193] According to American Ambassador Morgenthau, Turkey had never been an independent sovereignty.[194] The Western Powers had their own courts, marshals, colonies, schools, postal systems, religious institutions, and prisons. The Consuls also extended protections to large communities of Jewish protégés who had settled in Palestine.[195]
The Muslim, Christian, and Jewish communities of Palestine were allowed to exercise jurisdiction over their own members according to charters granted to them. For centuries the Jews and Christians had enjoyed a large degree of communal autonomy in matters of worship, jurisdiction over personal status, taxes, and in managing their schools and charitable institutions. In the 19th century those rights were formally recognized as part of the Tanzimat reforms and when the communities were placed under the protection of European public law.[196][197]
In the 1860s, the Ottoman military was able to restore order east of Jordan by halting tribal conflicts and Bedouin raids. This invited migration to the east, notably the Salt area, from various populations in Lebanon, Syria and Palestine to take advantage of new lands. This influx amounted to some 12,000 over the period from 1880 to just before the First World War, while the Bedouin population east of Jordan increased to 56,000.[198] However, with the creation of the Transjordanian emirate in 1921–22, the hamlet of Amman, which had been recently resettled by Circassians, attracted most of the new immigrants from Palestine, and many of those that had previously moved to Salt.[199]
In the reorganisation of 1873, which established the administrative boundaries that remained in place until 1914, Palestine was split between three major administrative units. The northern part, above a line connecting Jaffa to north Jericho and the Jordan, was assigned to the vilayet of Beirut, subdivided into the sanjaks (districts) of Acre, Beirut and Nablus.[200] The southern part, from Jaffa downwards, was part of the Mutasarrifate of Jerusalem, a special district under the direct authority of Istanbul.[201] Its southern boundaries were unclear but petered out in the eastern Sinai Peninsula and northern Negev Desert. Most of the central and southern Negev was assigned to the vilayet of Hejaz, which also included the Sinai Peninsula and the western part of Arabia.[200]
The Ottomans regarded "Filistin" as an abstract term referring to the "Holy Land", and not one consistently applied to a clearly defined area.[202] Among the educated Arab public, Filastin was a common concept, referring either to the whole of Palestine or to the Jerusalem sanjak alone[203] or just to the area around Ramle.[204] The publication of the daily paper Falastin (Palestine) from 1911 was one example of the increasing currency of this concept.[205]
The rise of Zionism, the national movement of the Jewish people started in Europe in the 19th century seeking to recreate a Jewish state in Palestine, and return the original homeland of the Jewish people. The end of the 19th century saw the beginning of Zionist immigration.[citation needed] The "First Aliyah" was the first modern widespread wave of Zionist aliyah. Jews who migrated to Palestine in this wave came mostly from Eastern Europe and from Yemen. This wave of aliyah began in 1881–82 and lasted until 1903.[206] An estimated 25,000[207]–35,000[208] First Aliyah laid the cornerstone for Jewish settlement in Israel and created several settlements such as Rishon LeZion, Rosh Pina, Zikhron Ya'akov and Gedera.[citation needed]
In 1891, a group of Jerusalem notables sent a petition to the central Ottoman government in Istanbul calling for the cessation of Jewish immigration, and land sales to Jews.[209][210]

The "Second Aliyah" took place between 1904 and 1914, during which approximately 40,000 Jews immigrated, mostly from Russia and Poland,[211] and some from Yemen. The Second Aliyah immigrants were primarily idealists, inspired by the revolutionary ideals then sweeping the Russian Empire who sought to create a communal agricultural settlement system in Palestine. They thus founded the kibbutz movement. The first kibbutz, Degania, was founded in 1909. Tel Aviv was founded at that time, though its founders were not necessarily from the new immigrants.[citation needed]
The Second Aliyah is largely credited with the revival of the Hebrew language and establishing it as the standard language for Jews in Israel. Eliezer Ben-Yehuda contributed to the creation of the first modern Hebrew dictionary. Although he was an immigrant of the First Aliyah, his work mostly bore fruit during the second.[citation needed]
Ottoman rule over the eastern Mediterranean lasted until World War I when the Ottomans sided with the German Empire and the Central Powers. During World War I, the Ottomans were driven from much of the region by the British Empire during the dissolution of the Ottoman Empire.[citation needed]
British Mandate period



In World War I, the Ottoman Empire sided with Germany. As a result, it was embroiled in a conflict with Great Britain. Under the secret Sykes–Picot Agreement of 1916, it was envisioned that most of Palestine, when freed from Ottoman control, would become an international zone not under direct French or British colonial control. Shortly thereafter, British foreign minister Arthur Balfour issued the Balfour Declaration of 1917, which promised to establish a "Jewish national home" in Palestine[212] but appeared to contradict the 1915–16 Hussein-McMahon Correspondence, which contained an undertaking to form an Arab state in exchange for the Great Arab Revolt. McMahon's promises could have been seen by Arab nationalists as a pledge of immediate Arab independence, an undertaking violated by the region's subsequent partition into British and French League of Nations mandates under the secret Sykes-Picot Agreement of May 1916, which became the real cornerstone of the geopolitics structuring the entire region. The Balfour Declaration, likewise, was seen by Jewish nationalists as the cornerstone of a future Jewish homeland.
The British-led Egyptian Expeditionary Force, commanded by Edmund Allenby, captured Jerusalem on 9 December 1917 and occupied the whole of the Levant following the defeat of Turkish forces in Palestine at the Battle of Megiddo in September 1918 and the capitulation of Turkey on 31 October.[213][214] Allenby famously dismounted from his horse when he entered Jerusalem as a mark of respect for the Holy City and was greeted by the Christian, Jewish, and Islamic leaders of the city.[citation needed]
Following the First World War and the occupation of the region by the British, the principal Allied and associated powers drafted the mandate, which was formally approved by the League of Nations in 1922. Great Britain administered Palestine on behalf of the League of Nations between 1920 and 1948, a period referred to as the "British Mandate". The preamble of the mandate declared:
"Whereas the Principal Allied Powers have also agreed that the Mandatory should be responsible for putting into effect the declaration originally made on November 2nd, 1917, by the Government of His Britannic Majesty, and adopted by the said Powers, in favor of the establishment in Palestine of a national home for the Jewish people, it being clearly understood that nothing should be done which might prejudice the civil and religious rights of existing non-Jewish communities in Palestine, or the rights and political status enjoyed by Jews in any other country."[215]
Not all were satisfied with the mandate. The purported objective of the League of Nations mandate system was to administer parts of the defunct Ottoman Empire, which had been in control of the Middle East since the 16th century, "until such time as they are able to stand alone".[216] Some of the Arabs felt that Britain was violating the McMahon-Hussein Correspondence and the understanding of the Arab Revolt. Some wanted a unification with Syria: in February 1919, several Muslim and Christian groups from Jaffa and Jerusalem met and adopted a platform endorsing unity with Syria and opposition to Zionism (this is sometimes called the First Palestinian National Congress). A letter was sent to Damascus authorizing Faisal to represent the Arabs of Palestine at the Paris Peace Conference. In May 1919 a Syrian National Congress was held in Damascus, and a Palestinian delegation attended its sessions.[217]
The 1922 census of Palestine recorded the population of Palestine as 757,000, of which 78% were Muslims, 11% were Jews, 10% were Christians and 1% were Druze.[218] In the early years of the Mandate, Jewish immigration to Palestine was quite substantial. In April 1920, violent Arab disturbances against the Jews in Jerusalem occurred, which came to be known as the 1920 Palestine riots. The riots followed rising tensions in Arab-Jewish relations over the implications of Zionist immigration. The British military administration's erratic response failed to contain the rioting, which continued for four days. As a result of the events, trust among the British, Jews, and Arabs eroded. One consequence was that the Jewish community increased moves towards an autonomous infrastructure and security apparatus parallel to that of the British administration.[citation needed]
In April 1920, the Allied Supreme Council (the United States, Great Britain, France, Italy and Japan) met at Sanremo and formal decisions were taken on the allocation of mandate territories. The United Kingdom obtained a mandate for Palestine and France obtained a mandate for Syria. The boundaries of the mandates and the conditions under which they were to be held were not decided. The Zionist Organization's representative at Sanremo, Chaim Weizmann, subsequently reported to his colleagues in London:
There are still important details outstanding, such as the actual terms of the mandate and the question of the boundaries in Palestine. There is the delimitation of the boundary between French Syria and Palestine, which will constitute the northern frontier and the eastern line of demarcation, adjoining Arab Syria. The latter is not likely to be fixed until the Emir Feisal attends the Peace Conference, probably in Paris.[219]

In July 1920, the French drove Faisal bin Husayn from Damascus, ending his already negligible control over the region of Transjordan, where local chiefs traditionally resisted any central authority. The sheikhs, who had earlier pledged their loyalty to the Sharif of Mecca, asked the British to undertake the region's administration. Herbert Samuel asked for the extension of the Palestine government's authority to Transjordan, but at meetings in Cairo and Jerusalem between Winston Churchill and Emir Abdullah in March 1921 it was agreed that Abdullah would administer the territory (initially for six months only) on behalf of the Palestine administration. In the summer of 1921 Transjordan was included within the Mandate, but excluded from the provisions for a Jewish National Home.[220] On 24 July 1922, the League of Nations approved the terms of the British Mandate over Palestine and Transjordan. On 16 September the League formally approved a memorandum from Lord Balfour confirming the exemption of Transjordan from the clauses of the mandate concerning the creation of a Jewish national home and Jewish settlement.[221] With Transjordan coming under the administration of the British Mandate, the mandate's collective territory became constituted of 23% Palestine and 77% Transjordan. The mandate for Palestine, while specifying actions in support of Jewish immigration and political status, stated, in Article 25, that in the territory to the east of the Jordan River, Britain could 'postpone or withhold' those articles of the Mandate concerning a Jewish National Home. Transjordan was a very sparsely populated region (especially in comparison with Palestine proper) due to its relatively limited resources and largely desert environment.[222][223]
In 1923, an agreement between the United Kingdom and France confirmed the border between the British Mandate of Palestine and the French Mandate of Syria. The British handed over the southern Golan Heights to the French in return for the northern Jordan Valley. The border was re-drawn so that both sides of the Jordan River and the whole of the Sea of Galilee, including a 10-metre-wide strip along the northeastern shore, were made a part of Palestine,[224] with the provisions that Syria have fishing and navigation rights in the lake.[225]
The Palestine Exploration Fund published surveys and maps of Western Palestine (aka Cisjordan) starting in the mid-19th century. Even before the Mandate came into legal effect in 1923 (text), British terminology sometimes used '"Palestine" for the part west of the Jordan River and "Trans-Jordan" (or Transjordania) for the part east of the Jordan River.[226][227]

The first reference to the Palestinians, without qualifying them as Arabs, is to be found in a document of the Permanent Executive Committee, composed of Muslims and Christians, presenting a series of formal complaints to the British authorities on 26 July 1928.[228]
Infrastructure and development
Between 1922 and 1947, the annual growth rate of the Jewish sector of the economy was 13.2%, mainly due to immigration and foreign capital, while that of the Arab was 6.5%. Per capita, these figures were 4.8% and 3.6% respectively. By 1936, the Jewish sector had eclipsed the Arab one, and Jewish individuals earned 2.6 times as much as Arabs. In terms of human capital, there was a huge difference. For instance, the literacy rates in 1932 were 86% for the Jews against 22% for the Arabs, but Arab literacy was steadily increasing.[229]
In 1933, Adolf Hitler came to power in Germany, Haavara agreement is in place between the Zionist Federation and the German government of the Third Reich to facilitate the emigration of German Jews.
The office of "Mufti of Jerusalem", traditionally limited in authority and geographical scope, was refashioned by the British into that of "Grand Mufti of Palestine". Furthermore, a Supreme Muslim Council (SMC) was established and given various duties, such as the administration of religious endowments and the appointment of religious judges and local muftis. During the revolt (see below) the Arab Higher Committee was established as the central political organ of the Arab community of Palestine.[citation needed]
During the Mandate period, many factories were established and roads and railroads were built throughout the country. The Jordan River was harnessed for production of electric power and the Dead Sea was tapped for minerals—potash and bromine.[citation needed]
1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine
Sparked off by the death of Shaykh Izz ad-Din al-Qassam at the hands of the British police near Jenin in November 1935, in the years 1936–1939 the Arabs participated in the Great Uprising to protest against British rule and against mass Jewish immigration. The revolt manifested in a strike and armed insurrection started sporadically, becoming more organized with time. Attacks were mainly directed at British strategic installations such as the Trans Arabian Pipeline (TAP) and railways, and to a lesser extent against Jewish settlements, secluded Jewish neighbourhoods in the mixed cities, and Jews, both individually and in groups.[citation needed]
Violence abated for about a year while the Peel Commission deliberated and eventually recommended partition of Palestine. With the Arab rejection of this proposal, the revolt resumed during the autumn of 1937. Violence continued throughout 1938 and eventually petered out in 1939.[citation needed]
The British responded to the violence by greatly expanding their military forces and clamping down on Arab dissent. "Administrative detention" (imprisonment without charges or trial), curfews, and house demolitions were among British practices during this period. More than 120 Arabs were sentenced to death and about 40 hanged. The main Arab leaders were arrested or expelled.[citation needed]
The Haganah (Hebrew for "defense"), a Jewish paramilitary organization, actively supported British efforts to quell the insurgency, which reached 10,000 Arab fighters at their peak during the summer and fall of 1938. Although the British administration did not officially recognize the Haganah, the British security forces cooperated with it by forming the Jewish Settlement Police and Special Night Squads.[230] A terrorist splinter group of the Haganah, called the Irgun (or Etzel)[231] adopted a policy of violent retaliation against Arabs for attacks on Jews.[232] At a meeting in Alexandria in July 1937 between Jabotinsky and Irgun commander Col. Robert Bitker and chief-of-staff Moshe Rosenberg, the need for indiscriminate retaliation due to the difficulty of limiting operations to only the "guilty" was explained. The Irgun launched attacks against public gathering places such as markets and cafes.[233]

The revolt did not achieve its goals, although it is "credited with signifying the birth of the Arab Palestinian identity".[234] It is generally credited with forcing the issuance of the White Paper of 1939, which renounced Britain's intent of creating a Jewish National Home in Palestine, as proclaimed in the 1917 Balfour Declaration.[citation needed]
Another outcome of the hostilities was the partial disengagement of the Jewish and Arab economies in Palestine, which were more or less intertwined until that time. For example, whereas the Jewish city of Tel Aviv previously relied on the nearby Arab seaport of Jaffa, hostilities dictated the construction of a separate Jewish-run seaport for Tel Aviv.[citation needed]
World War II and Palestine
When the Second World War broke out, the Jewish population sided with Britain. David Ben-Gurion, head of the Jewish Agency, defined the policy with what became a famous motto: "We will fight the war as if there were no White Paper, and we will fight the White Paper as if there were no war." While this represented the Jewish population as a whole, there were exceptions (see below).[citation needed]
As in most of the Arab world, there was no unanimity among the Palestinian Arabs as to their position regarding the combatants in World War II. A number of leaders and public figures saw an Axis victory as the likely outcome and a way of securing Palestine back from the Zionists and the British. Mohammad Amin al-Husayni, Grand Mufti of Jerusalem, spent the rest of the war in Nazi Germany and the occupied areas. About 6,000 Palestinian Arabs and 30,000 Palestinian Jews joined the British forces.[citation needed]
On 10 June 1940, Italy declared war on the British Commonwealth and sided with Germany. Within a month, the Italians attacked Palestine from the air, bombing Tel Aviv and Haifa.[235]
In 1942, there was a period of anxiety for the Yishuv, when the forces of German General Erwin Rommel advanced east in North Africa towards the Suez Canal and there was fear that they would conquer Palestine. This period was referred to as the two hundred days of anxiety. This event was the direct cause for the founding, with British support, of the Palmach[236]—a highly trained regular unit belonging to Haganah (which was mostly made up of reserve troops).

On 3 July 1944, the British government consented to the establishment of a Jewish Brigade with hand-picked Jewish and also non-Jewish senior officers. The brigade fought in Europe, most notably against the Germans in Italy from March 1945 until the end of the war in May 1945. Members of the Brigade played a key role in the Berihah's efforts to help Jews escape Europe for Palestine. Later, veterans of the Jewish Brigade became key participants of the new State of Israel's Israel Defense Forces.[citation needed]
Starting in 1939 and throughout the war and the Holocaust, the British reduced the number of Jewish immigrants allowed into Palestine, following the publication of the MacDonald White Paper. Once the 15,000 annual quota was exceeded, Jews fleeing Nazi persecution were placed in detention camps or deported to places such as Mauritius.[237]
In 1944 Menachem Begin assumed the Irgun's leadership, determined to force the British government to remove its troops entirely from Palestine. Citing that the British had reneged on their original promise of the Balfour Declaration, and that the White Paper of 1939 restricting Jewish immigration was an escalation of their pro-Arab policy, he decided to break with the Haganah. Soon after he assumed command, a formal 'Declaration of Revolt' was publicized, and armed attacks against British forces were initiated. Lehi, another splinter group, opposed cessation of operations against the British authorities all along. The Jewish Agency, which opposed those actions and the challenge to its role as government in preparation responded with "The Hunting Season"—severe actions against supporters of the Irgun and Lehi, including turning them over to the British.[citation needed]
The country developed economically during the war, with increased industrial and agricultural outputs and the period was considered an `economic Boom'. In terms of Arab-Jewish relations, these were relatively quiet times.[238]
End of the British Mandate 1945–1948


In the years following World War II, Britain's control over Palestine became increasingly tenuous. This was caused by a combination of factors, including:
- World public opinion turned against Britain as a result of the British policy of preventing Holocaust survivors from reaching Palestine, sending them instead to Cyprus internment camps, or even back to Germany, as in the case of Exodus 1947.
- The costs of maintaining an army of over 100,000 men in Palestine weighed heavily on a British economy suffering from post-war depression, and was another cause for British public opinion to demand an end to the Mandate.[240]
- Rapid deterioration due to the actions of the Jewish paramilitary organizations (Hagana, Irgun and Lehi), involving attacks on strategic installations (by all three) as well as on British forces and officials (by the Irgun and Lehi). This caused severe damage to British morale and prestige, as well as increasing opposition to the mandate in Britain itself, public opinion demanding to "bring the boys home".[citation needed]
- The U.S. Congress was delaying a loan necessary to prevent British bankruptcy. The delays were in response to the British refusal to fulfill a promise given to Truman that 100,000 Holocaust survivors would be allowed to emigrate to Palestine.[citation needed]
In early 1947 the British Government announced their desire to terminate the Mandate, and asked the United Nations General Assembly to make recommendations regarding the future of the country.[241] The British Administration declined to accept the responsibility for implementing any solution that wasn't acceptable to both the Jewish and the Arab communities, or to allow other authorities to take over responsibility for public security prior to the termination of its mandate on 15 May 1948.[242]
UN partition and the 1948 Palestine War
 |
| Part of a series on the |
| Nakba |
|---|

On 29 November 1947, the United Nations General Assembly, voting 33 to 13 in favour with 10 abstentions, adopted a resolution, Resolution 181 (II), recommended a partition with Economic Union of Mandatory Palestine to follow the termination of the British Mandate. The plan was to partition Palestine into Independent Arab state alongside a Jewish States, and the Special International Regime for the City of Jerusalem.[243] Jerusalem was to encompass Bethlehem. Zionist leaders (including the Jewish Agency), accepted the plan, while Palestinian Arab leaders rejected it and all independent Muslim and Arab states voted against it.[244][245][246] Almost immediately, sectarian violence erupted and spread, killing hundreds of Arabs, Jews and British over the ensuing months.[citation needed]
The rapid evolution of events precipitated into a Civil War. For four months, under continuous Arab provocation and attack, the Yishuv was usually on the defensive while occasionally retaliating.[247] Arab volunteers of the Arab Liberation Army entered Palestine to fight with the Palestinians, but the April–May offensive of Yishuv forces defeated the Arab forces and Arab Palestinian society collapsed. Some 700,000 Palestinians caught up in the turmoil fled or were driven from their homes.[citation needed]

On 14 May 1948, David Ben-Gurion and the Jewish People's Council declared the establishment of a Jewish state in Eretz Israel (The Land of Israel), to be known as the State of Israel.[248] The neighbouring Arab states intervened to prevent the partition and support the Palestinian Arab population. While Transjordan took control of territory designated for the future Arab State, Syrian, Iraqi and Egyptian expeditionary forces attacked Israel without success. The most intensive battles were waged between the Jordanian and Israeli forces over the control of Jerusalem.[citation needed]
On June 11, a truce was accepted by all parties. Israel used the lull to undertake a large-scale reinforcement of its army. In a series of military operations, during the war it conquered the whole of the Galilee region, both the Lydda and Ramle areas, and the Negev. It also managed to secure, in the Battles of Latrun, a road linking Jerusalem to Israel. However, the neighboring Arab countries signed the 1949 Armistice Agreements that ended the war, and have recognized de facto the new borders of Israel. In this phase, 350,000 more Arab Palestinians fled or were expelled from the conquered areas.[citation needed]
Partition of former Mandatory territory
Following the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, the area allocated to the Palestinian Arabs and the international zone of Jerusalem were occupied by Israel and the neighboring Arab states in accordance with the terms of the 1949 Armistice Agreements. In addition to the UN-partitioned area allotted to the Jewish state, Israel captured and incorporated a further 26% of the British Mandate territory.[citation needed] Jordan retained possession of about 21% of the former Mandate territory. Jerusalem was divided, with Jordan taking the eastern parts, including the Old City, and Israel taking the western parts. In addition, Syria held on to small slivers of the former Mandate territory to the south and east of the Sea of Galilee, which had been allocated in the UN partition plan to the Jewish state.[citation needed] For a description of the massive population movements, Arab and Jewish, at the time of the 1948 war and over the following decades, see Palestinian exodus and Jewish exodus from Arab lands.[citation needed]
Palestinian governorship in Egyptian-controlled Gaza
On the same day that the State of Israel was announced, the Arab League announced that it would set up a single Arab civil administration throughout Palestine,[249][250] and launched an attack on the new Israeli state.
The All-Palestine Government was established by the Arab League on 22 September 1948, during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. It was soon recognized by all Arab League members, except Jordan. Though jurisdiction of the Government was declared to cover the whole of the former Mandatory Palestine, its effective jurisdiction was limited to the Gaza Strip.[251] The Prime Minister of the Gaza-seated administration was named Ahmed Hilmi Pasha, and the President was named Hajj Amin al-Husseini,[252] former chairman of the Arab Higher Committee.
The All-Palestine Government is regarded by some as the first attempt to establish an independent Palestinian state. It was under official Egyptian protection,[251] but on the other hand it had no executive role, but rather mostly political and symbolic.[251] Its importance gradually declined, especially due to relocation of seat of government from Gaza to Cairo following the Israeli invasion in late 1948. Though Gaza Strip returned under Egyptian control later on through the war, the All-Palestine Government remained in-exile in Cairo, managing Gazan affairs from outside.
In 1959, the All-Palestine Government was officially merged into the United Arab Republic, coming under formal Egyptian military administration, with the appointment of Egyptian military administrators in Gaza. Egypt, however, both formally and informally denounced any and all territorial claims to Palestinian territory, in contrast to the government of Transjordan, which declared its annexation of the Palestinian West Bank. The All-Palestine Government's credentials as a bona fide sovereign state were questioned by many, particularly due to the effective reliance upon not only Egyptian military support, but Egyptian political and economic power.
Annexation of the West Bank of Jordan
Shortly after the proclamation of All-Palestine Government in Gaza, the Jericho Conference named King Abdullah I of Transjordan, "King of Arab Palestine".[253] The Congress called for the union of Arab Palestine and Transjordan and Abdullah announced his intention to annex the West Bank. The other Arab League member states opposed Abdullah's plan.
The New Historians, like Avi Shlaim, hold that there was an unwritten secret agreement between King Abdullah of Transjordan and Israeli authorities to partition the territory between themselves, and that this translated into each side limiting their objectives and exercising mutual restraint during the 1948 war.[254]
The presence of a large number of immigrants and refugees from the now dissolved Mandate of Palestine fueled the regional ambitions of King Abdullah I, who sought control over what had been the British Jerusalem and Samaria districts on the west bank of Jordan River. Towards this goal the king granted Jordanian citizenship to all Arab holders of the Palestinian Mandate identity documents in February 1949, and outlawed the terms "Palestinian" and "Transjordanian" from official usage, changing the country's name from the Emirate of Trans-Jordan to the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan.[255] The area east of the river became known as "al-Ḍiffah al-Sharqiyyal", or "The East Bank". In April 1950, with the formal annexation of the positions held by the Jordanian Army since 1948, the area became known as "al-Ḍiffah al-Gharbiyyal" or "The Western Bank".[256] With the formal union of the East and West Banks in 1950, the number of Palestinians in the kingdom rose by another 720,000, of whom 440,000 were West Bank residents and 280,000 were refugees from other areas of the former Mandate then living on the West Bank. Palestinians became the majority in Jordan although most believed their return to what was now the state of Israel was imminent.[257]
Israeli controlled areas
The examples and perspective in this article may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. (October 2012) |
Israel did not retain the administrative structure of the Mandate, redrawing the district borders to roughly parallel the areas of responsibility of its military formations, then infantry brigades.
Six Day War and Yom Kippur War
In the course of the Six Day War in June 1967, Israel captured the rest of the area that had been part of the British Mandate of Palestine, taking the West Bank (including East Jerusalem) from Jordan and the Gaza Strip from Egypt. Following military threats by Egypt and Syria, including Egyptian president Nasser's demand of the UN to remove its peace-keeping troops from the Egyptian-Israeli border, in June 1967 Israeli forces went to action against Egypt, Syria and Jordan. As a result of that war, the Israel Defense Forces conquered the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, the Golan Heights, and the Sinai Peninsula bringing them under military rule. Israel also pushed Arab forces back from East Jerusalem, which Jews had not been permitted to visit during the prior Jordanian rule. East Jerusalem was allegedly[258] annexed by Israel as part of its capital, though this action has not been recognized internationally.[citation needed] Israel also started building settlements on the occupied land.[259]
The United Nation's Security Council passed Resolution 242, promoting the "land for peace" formula, which called for Israeli withdrawal from territories occupied in 1967, in return for the end of all states of belligerency by the aforementioned Arab League nations. Palestinians continued longstanding demands for the destruction of Israel or made a new demand for self-determination in a separate independent Arab state in the West Bank and Gaza Strip similar to but smaller than the original Partition area that Palestinians and the Arab League had rejected for statehood in 1947.[citation needed]
In the course of 1973 Yom Kippur War, military forces of Egypt crossed the Suez canal and Syria to regain the Golan heights. The attacking military forces of Syria were pushed back. After a cease fire, Egyptian President Sadat Anwar Sadat started peace talks with the U.S. and Israel. Israel returned the Sinai Peninsula to Egypt as part of the 1978 Camp David Peace Accords between Egypt and Israel in hopes of establishing a genuine peace.[citation needed]
First Intifada, Oslo Accords and Palestinian Authority
From 1987 to 1993, the First Palestinian Intifada against Israel took place. Attempts at the peace process in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict were made at the Madrid Conference of 1991. As the process progressed, in 1993 the Israelis allowed Chairman and President of the Palestine Liberation Organization Yassir Arafat to return to the region.[citation needed]
Following the historic 1993 Oslo Peace Accords between Palestinians and Israel (the "Oslo Accords"), which gave the Palestinian Arabs limited self-rule in some parts of the occupied territories[260] through the Palestinian Authority, and other detailed negotiations, proposals for a Palestinian state gained momentum. They were soon followed in 1993 by the Israel-Jordan Treaty of Peace. To date, efforts to resolve the conflict have ended in deadlock, and the people of the region, Jews and Arabs, are engaged in a bloody conflict, called variously the "Arab-Israeli conflict" or "Israeli-Palestinian conflict".[citation needed]
Second Intifada and later
After few years of on-and-off negotiations, the Palestinians began an uprising against Israel. This was known as the Al-Aqsa Intifada. The events were highlighted in world media by Palestinian suicide bombings in Israel that killed many civilians, and by Israeli Security Forces full-fledged invasions into civilian areas[261] along with some targeted killings of Palestinian militant leaders and organizers. Israel began building a complex security barrier to block suicide bombers invading into Israel from the West Bank in 2002.[citation needed]
Also in 2002, the Road map for peace calling for the resolution of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict was proposed by a "quartet": the United States, European Union, Russia, and United Nations. U.S. President George W. Bush in a speech on June 24, 2002 called for an independent Palestinian state living side by side with Israel in peace. Bush was the first U.S. President to explicitly call for such a Palestinian state.[citation needed]
Following Israel's unilateral disengagement plan of 2004, it withdrew all settlers and most of the military presence from the Gaza strip, but maintained control of the air space and coast. Israel also dismantled four settlements in northern West Bank in September 2005. Following Israel's withdrawal, Palestinian militia groups fired Qassam rockets into Israel and smuggled weapons and ammunition into Gaza from Egypt. After the kidnap of Israeli soldiers in June 2006, Israel launched a military operation and reentered some parts of the Gaza Strip. Amidst severe criticism, they built the Israeli West Bank barrier.[citation needed]
Following the January 2006 election of the Hamas government, Fatah resistance took the form of street battles that resulted in a victory for Hamas.[261][262] Hamas took over the ministries of the (Fatah) Palestinian Authority and Gaza became a Hamas enclave outside PA control.[citation needed]
As of July 2009, approximately 305,000 Israelis lived in 121 settlements in the West Bank.[263] The 2.4 million[citation needed] West Bank Palestinians (according to Palestinian evaluations) live primarily in four blocs centered in Hebron, Ramallah, Nablus, and Jericho.
Non-member status of State of Palestine
On 23 September 2011, President Mahmoud Abbas on behalf of the Palestine Liberation Organisation submitted an application for membership of Palestine in the United Nations. The campaign, dubbed "Palestine 194",[264] was formally backed by the Arab League in May,[265] and was officially confirmed by the PLO on 26 June.[266] The decision was labelled by the Israeli government as a unilateral step, while the Palestinian government countered that it is essential to overcoming the current impasse. Several other countries, such as Germany and Canada, have also denounced the decision and called for a prompt return to negotiations. Many others, however, such as Norway and Russia, have endorsed the plan, as has Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon, who stated, "UN members are entitled whether to vote for or against the Palestinian statehood recognition at the UN."[267]
In July 2012, it was reported that Hamas Government in Gaza was considering declaring the independence of the Gaza Strip with the help of Egypt.[268] In August 2012, Foreign Minister of the PNA Riyad al-Malki told reporters in Ramallah that PNA would renew effort to upgrade the Palestinian (PLO) status to "full member state" at the U.N. General Assembly on September 27, 2012.[269] By September 2012, with their application for full membership stalled due to the inability of Security Council members to "make a unanimous recommendation", Palestine had decided to pursue an upgrade in status from "observer entity" to "non-member observer state". On November 27, it was announced that the appeal had been officially made, and would be put to a vote in the General Assembly on November 29, where their status upgrade was expected to be supported by a majority of states. In addition to granting Palestine "non-member observer state status", the draft resolution "expresses the hope that the Security Council will consider favourably the application submitted on 23 September 2011 by the State of Palestine for admission to full membership in the United Nations, endorses the two state solution based on the pre-1967 borders, and stresses the need for an immediate resumption of negotiations between the two parties".
On November 29, 2012, in a 138–9 vote (with 41 abstaining), General Assembly resolution 67/19 passed, upgrading Palestine to "non-member observer state" status in the United Nations.[270][271] The new status equates Palestine's with that of the Holy See.The change in status was described by The Independent as "de facto recognition of the sovereign state of Palestine".[272]
The UN has permitted Palestine to title its representative office to the UN as "The Permanent Observer Mission of the State of Palestine to the United Nations",[273] and Palestine has started to re-title its name accordingly on postal stamps, official documents and passports,[271][274] whilst it has instructed its diplomats to officially represent "The State of Palestine", as opposed to the 'Palestine National Authority'.[271] Additionally, on 17 December 2012, UN Chief of Protocol Yeocheol Yoon decided that "the designation of 'State of Palestine' shall be used by the Secretariat in all official United Nations documents",[275] thus recognising the PLO-proclaimed State of Palestine as being sovereign over the territories Palestine and its citizens under international law.
As of February 2013, 131 (67.9%) of the 193 member states of the United Nations have recognised the State of Palestine. Many of the countries that do not recognise the State of Palestine nevertheless recognise the PLO as the 'representative of the Palestinian people'.
Graphical Overview of Palestine's Historical Sovereign Powers

See also
- History of ancient Israel and Judah
- History of Israel
- History of Levant
- History of pottery in the Southern Levant
References
- ^ van Seters, John (1997), "Abraham in History and Tradition", (Yale University Press)
- ^ Tomoo Ishida, History and Historical Writing in Ancient Israel: Studies in Biblical Historiography, BRILL 1999 pp.14-15
- ^ a b Finkelstein and Silberman, Free Press, New York, 2001, 385 pp., ISBN 0-684-86912-8, p 107
- ^ a b Smith, Morton (1999). "The Gentiles in Judaism, 125 BCE - 66 CE". In Horbury, William; Davies, W D; Sturdy, John (eds.). Cambridge History of Judaism, The early Roman period. Vol. 2. p. 210. ISBN 0521243777.
- ^ Parfitt , Tudor (1987) The Jews in Palestine, 1800–1882. Royal Historical Society studies in history (52). Woodbridge: Published for the Royal Historical Society by Boydell.
- ^ "al-Nakba: the Palestinian "Catastrophe"". Al-nakba-history.com. Retrieved 2015-01-12.
- ^ "Benjamin Netanyahu on Palestinian 'right of return': There is no room for maneuver". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 12 January 2015.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|work=(help) - ^ "The settlements are illegal under international law". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 12 January 2015.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|work=(help) - ^ "Myths & Facts: 2008 Gaza War (Operation Cast Lead) (Chapter 24) - Jewish Virtual Library". Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ^ "LIVE UPDATES: Operation Protective Edge, day 24". Haaretz.com. 1 August 2014. Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ^ Galilee, Sea of. (2007). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved August 12, 2007, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online
- ^ "Human Evolution and Neanderthal Man" (PDF). Antiquity Journal.
- ^ Amud. (2007). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved August 12, 2007, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online
- ^ Olson, S. Mapping Human History. Houghton Mifflin, New York (2003). p. 74–75.
- ^ Belfer-Cohen and Bar-Yosef, 2000, pp. 19–38.
- ^ Stearns, 2001, p. 13.
- ^ Harris, 1996, p. 253.
- ^ Gates, 2003, p. 18.
- ^ a b c d e Shahin (2005), p. 4
- ^ Rosen, 1997, pp. 159–161.
- ^ Neil Asher Silberman, Thomas E. Levy, Bonnie L. Wisthoff, Ron E. Tappy, John L. Meloy "Near East" The Oxford Companion to Archaeology. Brian M. Fagan, ed., Oxford University Press 1996.
- ^ Canaan. (2007). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved August 12, 2007, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online.
- ^ Mills, 1990, p. 439.
- ^ "Palestine: Middle Bronze Age". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 2007-08-11.
- ^ Ember, Melvin; Peregrine, Peter Neal, eds. (2001). Encyclopedia of Prehistory. Vol. 8: South and Southwest Asia (1 ed.). Springer. p. 103. ISBN 0-306-46262-1.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ a b Slavik, Diane. 2001. Cities through Time: Daily Life in Ancient and Modern Jerusalem. Geneva, Illinois: Runestone Press, p. 60. ISBN 978-0-8225-3218-7
- ^ Mazar, Benjamin. 1975. The Mountain of the Lord. Garden City, New York: Doubleday & Company, Inc., p. 45. ISBN 0-385-04843-2
- ^ Remains Of Minoan-Style Painting Discovered During Excavations Of Canaanite Palace, ScienceDaily (December 7, 2009) [1]
- ^ William H. Propp "Amarna Letters" The Oxford Companion to the Bible. Bruce M. Metzger and Michael D. Coogan, eds. Oxford University Press Inc. 1993. Oxford Reference Online. Oxford University Press.
- ^ Ilan Ben Zion, ' Egyptian coffin, gold seal with king’s name found in Israel,' The Times of Israel, 9 April 2014.
- ^ a b c d e Niels Peter Lemche. "On the Problems of Reconstructing Pre-Hellenistic Israelite (Palestinian) History". Journal of Hebrew Scriptures. Retrieved 2007-05-10.
- ^ a b c d e Shahin (2005), p. 6
- ^ Carl S. Ehrlich "Philistines" The Oxford Guide to People and Places of the Bible. Ed. Bruce M. Metzger and Michael D. Coogan. Oxford University Press, 2001. Oxford Reference Online. Oxford University Press.
- ^ Philistine. (2007). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved August 12, 2007, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online
- ^ Peter Myers. "The Exodus & the Expulsion of the Hyksos - Archaeology of the Bible" (2010)
- ^ Avraham Faust (2009) "How Did Israel Become a People? The Genesis of Israelite Identity. Biblical Archaeology Review 201: pp. 62-69, 92-94
- ^ Finkelstein and Silberman (2001), p. 107
- ^ Holy Bible. King James version. Ezra, Chapter 9
- ^ "Canaan". Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ^ a b c d e "Facts about Israel:History". Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affaits. Retrieved 2007-05-10.
- ^ Bienkowski, op.cit.
- ^ ""House of David" Restored in Moabite Inscription: A new restoration of a famous inscription reveals another mention of the "House of David" in the ninth century BCE". Jewishhistory.com. Retrieved 2010-08-24.
- ^ Gyémánt, Ladislau (2003). "Historiographic Views on the Settlement of the Jewish Tribes in Canaan". 1/2003. Sacra Scripta: 26–30.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Austel in Grisanti and Howard, 2003, p. 160.
- ^ Schiller, 2009, p. 98.
- ^ Finkelstein, Mazar and Schmidt, 2007, pp. 10–20
- ^ Erlanger, Steven (2005-08-05). "King David's Palace Is Found, Archaeologist Says". The New York Times. Retrieved 2007-05-24.
- ^ Matthew Sturgis, It ain't necessarily so, ISBN 0-7472-4510-X
- ^ Carol A. Redmount, 'Bitter Lives: Israel in and out of Egypt' in The Oxford History of the Biblical Word, ed: Michael D. Coogan, (Oxford University Press: 1999)
- ^ Stager, Lawrence E., "Forging an Identity: The Emergence of Ancient Israel" in Michael Coogan ed. The Oxford History of the Biblical World, Oxford University Press, 2001. p. 92
- ^ M. G. Hasel, "Israel in the Merneptah Stela", BASOR 296, 1994, pp. 54, 56, n. 12.
- ^ Pritchard, Texts p. 321
- ^ Pritchard, Pictures p. 275, 744
- ^ J. Simons, Jerusalem in the Old Testament (1952) p. 175-92
- ^ Encyclopaedia Judaica, vol. 14 pp. 1440–1441
- ^ "Babylon" A Dictionary of the Bible. W. R. F. Browning. Oxford University Press, 1997. Oxford Reference Online. Oxford University Press.
- ^ *Dandamaev, M (1994): "[2]", in E. Yarshater (ed.) Encyclopaedia Iranica vol. 7.
- ^ Drumbrell, WJ (1971): "The Tell el-Maskuta Bowls and the 'Kingdom' of Qedar in the Persian Period", BASOR 203, pp. 33–44.
- ^ Tuell (1991): "The Southern and Eastern Borders of Abar-Nahara", BASOR n. 234, pp. 51–57
- ^ Jona Lendering. "Satrapies". Livius.org. Retrieved 2011-08-16.
- ^ Diana Edelman (November 2005). "Redating the Building of the Second Temple".
- ^ a b c d Palestine. (2007). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved August 12, 2007, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online.
- ^ "Avdat: A Nabatean City in the Negev". Jewish Virtual Library. Retrieved 2007-08-11.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Shahin (2005), p. 7
- ^ "Hellenistic Greece:Alexander the Great". Washington State University. 1996. Retrieved 2007-08-11.
- ^ Free, Joseph P.; Vos, Howard F. (1992). Archaeology and Bible History. Zondervan. ISBN 978-0-310-47961-1., p. 225.
- ^ "Palestine". Britannica. Retrieved 2007-08-14.
- ^ Julie Galambush (2006). "The Reluctant Parting: How the New Testament's Jewish Writers Created a Christian Book". HarperCollins.ca. Retrieved 2007-08-20.
- ^ Dick Doughty (September–October 1994). "Gaza:Contested Crossroads". SaudiAramcoWorld. Retrieved 2007-08-20.
- ^ "Tell Balatah (Shechem or Ancient Nablus)". World Monuments Watch:100 Most Endangered Sites 2006. Archived from the original on 2007-09-27. Retrieved 2007-08-20.
- ^ Lectures on ancient history, Barthold Georg Niebuhr, Marcus Carsten Nicolaus von Niebuhr. Books.google.com. Retrieved 2011-08-16.
- ^ Josephus. Antiquities of the Jews. 13., Perseus Project AJ13.10.1, .
- ^ Encyclopaedic dictionary of the Bible, Volume 5, William George Smith. Books.google.com. Retrieved 2011-08-16.
- ^ Sievers, 142
- ^ "Cambridge History of Judaism". Cambridge.org. p. 210. Retrieved 2011-08-16. "In both the Idumaean and the Ituraean alliances, and in the annexation of Samaria, the Judaeans had taken the leading role. They retained it. The whole political–military–religious league that now united the hill country of Palestine from Dan to Beersheba, whatever it called itself, was directed by, and soon came to be called by others, ‘the Ioudaioi’"
- ^ A History of the Jewish People, edited by Haim Hillel Ben-Sasson, page 226, "The name Judea no longer referred only to...."
- ^ Between Rome and Jerusalem: 300 years of Roman-Judaean relations By Martin Sicker. Books.google.co.uk. Retrieved 2011-08-16.
- ^ "Armenians of Jerusalem Launch Project To Preserve History and Culture". Pr-inside.com. Retrieved 2011-08-16.
- ^ The problem of the Greek sources of Movsēs Xorenacʻi's History of Armenia. Books.google.co.uk. Retrieved 2011-08-16.
- ^ A history of the Jews in Babylonia, Volume 2 By Jacob Neusner p. 351. Books.google.co.uk. Retrieved 2011-08-16.
- ^ Josephus. Antiquities of the Jews. 14., Perseus Project AJ14.5.4, .: "And when he had ordained five councils (συνέδρια), he distributed the nation into the same number of parts. So these councils governed the people; the first was at Jerusalem, the second at Gadara, the third at Amathus, the fourth at Jericho, and the fifth at Sepphoris in Galilee."
- ^ "Josephus uses συνέδριον for the first time in connection with the decree of the Roman governor of Syria, Gabinius (57 BCE), who abolished the constitution and the then existing form of government of Palestine and divided the country into five provinces, at the head of each of which a sanhedrin was placed ("Ant." xiv 5, § 4)." via Jewish Encyclopedia: Sanhedrin:
- ^ "Herod". Concise Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2007-08-11.
- ^ "Introducing Young People to the Protection of Heritage Sites and Historic Cities" (PDF). UNESCO. 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-09-30. Retrieved 2007-08-14.
- ^ "Herodium (Jebel Fureidis) Jordan/Israel". The Princeton Encyclopedia of Classical Sites. Retrieved 2007-08-11.
- ^ http://icarus.umkc.edu/sandbox/perseus/pecs/page.887.a.php
- ^ "Judaea-Palestine". UNRV History: Roman Empire. Retrieved 2007-08-14.
- ^ Josephus. Antiquities of the Jews. 18., Perseus Project AJ18.1.1, . "Cyrenius came himself into Judea, which was now added to the province of Syria"
- ^ H.H. Ben-Sasson, A History of the Jewish People, pp. 247-248: "Consequently, the province of Judea may be regarded as a satellite of Syria, though, in view of the measure of independence left to its governor in domestic affairs, it would be wrong to say that in the Julio-Claudian era Judea was legally part of the province of Syria."
- ^ A History of the Jewish People, H. H. Ben-Sasson editor, 1976, p. 247: "When Judea was converted into a Roman province [in 6 CE, p. 246], Jerusalem ceased to be the administrative capital of the country. The Romans moved the governmental residence and military headquarters to Caesarea. The centre of government was thus removed from Jerusalem, and the administration became increasingly based on inhabitants of the hellenistic cities (Sebaste, Caesarea and others)."
- ^ Köstenberger, Kellum & Quarles 2009, p. 114.
- ^ Maier 1989, p. 124.
- ^ Green, McKnight & Marshall 1992, p. 442.
- ^ Borg, Marcus J. (2006). "The Spirit-Filled Experience of Jesus". In Dunn, James D. G.; McKnight, Scot (eds.). The Historical Jesus in Recent Research. Eisenbrauns. p. 303. ISBN 978-1-57506-100-9.
- ^ Crossan & Watts 1999, pp. 28–29.
- ^ Vermes, Géza (2010). The Nativity: History and Legend. Random House Digital. pp. 81–82. ISBN 978-0-307-49918-9.
- ^ Dunn 2003, p. 324.
- ^ Meier 1991, p. 407.
- ^ Finegan, Jack (1998). Handbook of Biblical Chronology, rev. ed. Hendrickson Publishers. p. 319. ISBN 978-1-56563-143-4.
- [[#cite_ref-FOOTNOTEFor_example,_John_P._Meier_states_that_Jesus'_birth_year_is_''c.''_7/6_BC,'"`UNIQ--ref-00000086-QINU`"'_while_Finegan_favors_''c.''_3/2_BC.'"`UNIQ--ref-00000087-QINU`"'_100-0|^]] For example, John P. Meier states that Jesus' birth year is c. 7/6 BC,[98] while Finegan favors c. 3/2 BC.[99].
- ^ Levine 2006, p. 4.
- ^ Humphreys, Colin J.; Waddington, W.G. (1992). "The Jewish Calendar, a Lunar Eclipse and the Date of Christ's Crucifixion" (PDF). Tyndale Bulletin. 43 (2): 340.
- ^ Köstenberger, Kellum & Quarles 2009, p. 398.
- ^ Mark A. Chancey (2005) Greco-Roman Culture and the Galilee of Jesus Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-84647-1 p 62
- ^ H.H. Ben-Sasson, A History of the Jewish People, Harvard University Press, 1976, ISBN 0-674-39731-2, page 334: "In an effort to wipe out all memory of the bond between the Jews and the land, Hadrian changed the name of the province from Iudaea to Syria-Palestina, a name that became common in non-Jewish literature."
- ^ Ariel Lewin. The archaeology of Ancient Judea and Palestine. Getty Publications, 2005 p. 33. "It seems clear that by choosing a seemingly neutral name - one juxtaposing that of a neighboring province with the revived name of an ancient geographical entity (Palestine), already known from the writings of Herodotus - Hadrian was intending to suppress any connection between the Jewish people and that land." ISBN 0-89236-800-4
- ^ 'The Bar Kokhba War Reconsidered' By Peter Schäfer, p. 33. ISBN 3-16-148076-7
- ^ [3] Roman History, Cassius Dio, book 69 parts 12-15
- ^ a b c d Lehmann, Clayton Miles (Summer 1998). "Palestine: History: 135–337: Syria Palaestina and the Tetrarchy". The On-line Encyclopedia of the Roman Provinces. University of South Dakota. Retrieved 2009-01-06.
- ^ Whealey, J (2008) "Eusebius and the Jewish Authors: His Citation Technique in an Apologetic Context" (Journal of Theological Studies; Vol 59: 359–362)
- ^ Hans Küng,Christianity and world religions: paths of dialogue with Islam, Hinduism, and Buddhism, Orbis Books, 1993 p.124.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Shahin (2005), p. 8
- ^ Shaye I.D. Cohen. "Legitimization Under Constantine". PBS. Retrieved 2007-08-11.
- ^ Schaff's Seven Ecumenical Councils: First Nicaea: Canon VII: "Since custom and ancient tradition have prevailed that the Bishop of Aelia [i.e., Jerusalem] should be honored, let him, saving its due dignity to the Metropolis, have the next place of honor."; "It is very hard to determine just what was the "precedence" granted to the Bishop of Aelia, nor is it clear which is the "metropolis" referred to in the last clause. Most writers, including Hefele, Balsamon, Aristenus and Beveridge consider it to be Cæsarea; while Zonaras thinks Jerusalem to be intended, a view recently adopted and defended by Fuchs; others again suppose it is Antioch that is referred to."
- ^ Thomas A. Idniopulos (1998). "Weathered by Miracles: A History of Palestine From Bonaparte and Muhammad Ali to Ben-Gurion and the Mufti". The New York Times. Retrieved 2007-08-11.
- ^ "Roman Arabia". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2007-08-11.
- ^ H.H. Ben-Sasson, A History of the Jewish People, Harvard University Press, 1976, ISBN 0-674-39731-2, p. 351
- ^ Merrills, A. H., History and Geography in Late Antiquity, Cambridge Studies in Medieval Life and Thought fourth Series, Cambridge University Press, Melbourne, 2005, pp. 242–243
- ^ Horn, Cornelia B.; Robert R. Phenix, Jr. 2008. The Lives of Peter the Iberian, Theodosius of Jerusalem, and the Monk Romanus. Atlanta, Georgia: Society of Biblical Literature, p. lxxxviii. ISBN 978-1-58983-200-8
- ^ a b c Kenneth G. Holum "Palestine" The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium. Ed. Alexander P. Kazhdan. Oxford University Press 1991.
- ^ Glen Warren Bowersock, Peter Robert Lamont Brown, Oleg Grabar (1999) Late Antiquity: A Guide to the Postclassical World Harvard University Press, ISBN 0-674-51173-5 p 553
- ^ Moshe Gil and Ethel Broido (1997) History of Palestine, 634–1099, Translated by Ethel Broido Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-59984-9 p 3
- ^ Jews and Christians in the Holy Land, Gunter Stemberger, 2000
- ^ Browning, Robert. 1978. The Emperor Julian. Berkeley, California: University of California Press, p. 176. ISBN 0-520-03731-6
- ^ Martindale, Jones & Morris (1992), p. 102–104
- ^ "The Emperor Justinian and Jerusalem (527–565 CE)". Snunit.k12.il. Retrieved 2011-08-16.
- ^ Hussey, J. M. 1961. The Byzantine World. New York, New York: Harper & Row, Publishers, p. 25.
- ^ Karen Armstrong. 1997. Jerusalem: One City, Three Faiths. New York, New York: Ballantine Books, p. 229. ISBN 0-345-39168-3
- ^ Ostrogorsky, George. 1969. History of the Byzantine State. New Brunswick, New Jersey: Rutgers University Press, p. 104. ISBN 0-8135-0599-2
- ^ Paul Johnson, A History of the Jews (London 1987)
- ^ A History of Palestine, 634–1099, Moshe Gil, pp. 16–17
- ^ See Muhammad's first revelation
- ^ "Translation of Sahih Bukhari, Book 21, Number 281: "Do not set out on a journey except for three Mosques i.e. Al-Masjid-Al-Haram, the Mosque of Allah's Apostle, and the Mosque of Al-Aqsa, (Mosque of Jerusalem)."". Islamicity.com. Retrieved 2011-08-16.
- ^ Gil, Moshe (February 1997). A History of Palestine, 634–1099. Cambridge University Press. pp. 68–71. ISBN 0-521-59984-9.
- ^ "Caliph Umar'S Address After Jerusalem". Cyberistan.org. Retrieved 2010-08-24.
- ^ The Fight for Jerusalem: Radical Islam, the West, and the Future of the Holy City By Dore Gold, pg. 97
- ^ a b c Shahin, 2005, p. 10.
- ^ http://www.mideastweb.org/caliph2m.gif
- ^ Walid Khalidi (1984). Before Their Diaspora. Institute for Palestine Studies, Washington DC. pp. 27–28. ISBN 0-88728-144-3.
- ^ Haim Gerber (Fall 2003). "Zionism, Orientalism, and the Palestinians". Journal of Palestine Studies. 33 (1). Journal of Palestine Studies: 23–41. doi:10.1525/jps.2003.33.1.23.
- ^ a b James Parkes. "Palestine Under the Caliphs". MidEastWeb. Retrieved 2007-08-20.
- ^ Rizwi Faizer (1998). "The Shape of the Holy: Early Islamic Jerusalem". Rizwi's Bibliography for Medieval Islam. Archived from the original on 2007-06-09. Retrieved 2007-07-14.
- ^ Ahl al-Kitab. (2007). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved August 12, 2007, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online
- ^ a b c d e f g Shahin (2005), p. 11
- ^ M. Cherif Bassiouni (2004). "Islamic Civilization: An Overview". Middle East Institute: The George Camp Keiser Library. Archived from the original on 2007-09-28. Retrieved 2007-08-14.
- ^ Gil, Moshe (February 1997). A History of Palestine, 634–1099. Cambridge University Press. pp. 297–298. ISBN 0-521-59984-9.
- ^ Ghada Hashem Talhami (February 2000). "The Modern History of Islamic Jerusalem: Academic Myths and Propaganda". VII (2). Middle East Policy Council. Archived from the original on 2007-09-27. Retrieved 2007-08-20.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Yaacov Lev (2007). "The Ethics and Practice of Islamic Medieval Charity". 5 (2). History Compass: 603–618.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b c Gil, Moshe (February 1997). A History of Palestine, 634–1099. Cambridge University Press. pp. 279–281. ISBN 0-521-59984-9.
- ^ Palestine Exploration Fund, 1872, p. 167.
- ^ Patrich, 2001, p. 65.
- ^ Shagrir, Ellenblum, Riley-Smith, and Kedar, 2007, p. 22.
- ^ ''Charlemagne and the Early Middle Ages'' by Miriam Greenblatt, p. 29. Books.google.com. Retrieved 2011-08-16.
- ^ Gil, Moshe (February 1997). A History of Palestine, 634–1099. Cambridge University Press. pp. 159 and 285–289. ISBN 0-521-59984-9.
- ^ Heck, Gene W. Charlemagne, Muhammad, and the Arab roots of capitalism. p. 172.
- ^ War And Peace in the Law of Islam by Majid Khadduri, p. 247. Books.google.com. Retrieved 2011-08-16.
- ^ "Egypt: The Fatimid Period 969 - 1771". Arab Net. 2002. Retrieved 2007-08-14.[dead link]
- ^ Norwich 1997, p. 202
- ^ Norwich 1997, p. 203
- ^ Moshe Gil, A History of Palestine (Cambridge, 1992) p. 410; p. 411 n. 61
- ^ Singh, Nagendra. 2002. "International Encyclopedia of Islamic Dynasties"
- ^ Bosworth, Clifford Edmund. 2007. "Historic Cities of the Islamic World
- ^ Holt, pp. 11–14.
- ^ Norwich, pg. 30
- ^ Canduci, pg. 279
- ^ Runciman, Steven. 1951. A History of the Crusades: Volume 1 The First Crusade and the Foundation of the Kingdom of Jerusalem. New York, New York: Cambridge University Press, pp. 279–290. ISBN 0-521-06161-X
- ^ David Nicolle (July 2005). Crusader Castles in the Holy Land 1192–1302. Osprey. ISBN 978-1-84176-827-4.
- ^ "Projects:The Old City of Akko (Acre)". Israeli Antiquities Authority. Retrieved 2007-08-14.
- ^ Frank Heynick, Jews and medicine, An Epic Saga, KTAV Publishing House, Inc., 2002 p. 103, commenting on Maimonidies' decision not to settle there a century later.
- ^ A History of the Crusades: The Impact of the Crusades on the Near East (vol 5), By Kenneth M. Setton, Norman P. Zacour, Harry W. Hazard, Marshall Whithed Baldwin, Robert Lee Wolff, Univ of Wisconsin Press, 1985, ISBN 0-299-09144-9, ISBN 978-0-299-09144-6, pp. 96.
- ^ Sefer HaCharedim Mitzvat Tshuva Chapter 3
- ^ a b c Kenneth Setton, ed. A History of the Crusades, vol. I. University of Pennsylvania Press, 1958
- ^ a b c d e Shahin (2005), p. 12.
- ^ p. 73 in Jonathan Sachs (2005) To heal a fractured world: the ethics of responsibility. London: Continuum (ISBN 978-0-8264-8039-2)
- ^ "Catholic Encyclopedia: Jerusalem (After 1291)". Newadvent.org. Retrieved 2011-08-16.
- ^ Myriam Rosen-Ayalon, ``Between Cairo and Damascus: Rural Life and Urban Economics in the Holy Land During the Ayyuid, Maluk and Ottoman Periods in The Archaeology of Society in the Holy Land edited Thomas Evan Levy, Continuum International Publishing Group, 1998
- ^ a b Walid Khalidi (1984). Before Their Diaspora. Institute for Palestine Studies, Washington DC. pp. 28–29. ISBN 0-88728-144-3.
- ^ Chase, 2003, pp. 104–105.
- ^ Parkes, James (1970) [1949]. "Turkish Territorial Divisions in 1914". Whose Land?: A History of the Peoples of Palestine. Harmondsworth: Penguin Books. p. 187. Retrieved 13 July 2011.
- ^ Gerber, 1998.
- ^ Fuller, Thomas (1639). The historie of the holy warre. Retrieved 28 January 2011.
- ^ Milner, John (1687). A collection of the church-history of Palestine: From the birth of Christ to the beginning of the empire of Diocletian. Retrieved 28 January 2011.
- ^ The London Magazine and Monthly Chronologer. 1751. Retrieved 28 January 2011.
- ^ Salmon, Thomas (1744). Modern history or, the present state of all nations. Vol. 1. London: Printed for T. Longman. T. Osborne. J. Shuckburgh. C. Hitch. S. Austen. And J. Rivington. p. 461. Retrieved 28 January 2011.
- ^ "The Druzes". Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ^ Schlöoch, Alexander, Was There A Feudal System in Ottoman Lebanon and Palestine?, in, Kushner, David, ed., Palestine in the late Ottoman period: political, social, and economic transformation, E.J. Brill, Leiden, the Netherlands, 1986, p. 140
- ^ Napoleon, the Jews and the Sanhedrin, Simon Schwarzfuchs, Oxford University Press, USA, 1984. Books.google.com. Retrieved 2011-08-16.
- ^ Franco, Moise (1973) [1897]. Essai Sur L'histoire Des Israélites De L'empire Ottoman Depuis Les Origines Jusqu'à Nos Jours (in French). Hildesheim: G. Olms. pp. 130–131.
- ^ The Capitulations of the Ottoman Empire and the Question of their Abrogation as it Affects the United States, Lucius Ellsworth Thayer, The American Journal of International Law, Vol. 17, No. 2 (April , 1923), pp. 207-233 [4]
- ^ e.g. American Consuls in the Holy Land, 1832–1914 By Ruth Kark, Hebrew University Magnes Press, 1994, ISBN 0-8143-2523-8, p. 139 [5]
- ^ Biger, Gideon (1981). Where was Palestine? Pre-World War I perception, AREA (Journal of the Institute of British Geographers) Vol 13, No. 2, pp. 153–160.
- ^ The Abrogation of the Turkish Capitulations, Norman Bentwich, Journal of Comparative Legislation and International Law, Third Series, Vol. 5, No. 4 (1923), pp. 182–188 [6]
- ^ Raja Shehadeh, Kluwer Law International, 1997, ISBN 90-411-0618-9, p. 75
- ^ Ambassador Morgenthau's Story, Henry Morgenthau, Cornell University Library 2009, ISBN 1-112-30638-2, Chapter 10, p. 70 [7]
- ^ The Habsburgs and the Jewish Philanthropy in Jerusalem during the Crimean War (1853–6), Yochai Ben-Ghedalia, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, 2009 [8]
- ^ See Jews, Turks, Ottomans, Avigdor Levy (Editor) Syracuse University Press, 2003, ISBN 0-8156-2941-9, p. 109; Christian communities in Jerusalem and the West Bank since 1948, By Daphne Tsimhoni, Praeger, 1993, ISBN 0-275-93921-9, p. xv
- ^ See International law: achievements and prospects, UNESCO, editor Mohammed Bedjaoui, Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, 1991, ISBN 92-3-102716-6, p. 7
- ^ Heikki Palva, Negations in the dialect of es-Salt, Jordan, university of Helsinki, in, Martine Haak, Rudolf de Jong, Kees Versteegh, eds., Approaches to Arabic dialects: A collection of articles presented to Manfred Woidich on the occasion of his sixtieth birthday, Koninklijke Brill NV, The Netherlands, 2004, p. 223
- ^ Heikki Palva, Negations in the dialect of es-Salt, Jordan, university of Helsinki, in, Martine Haak, Rudolf de Jong, Kees Versteegh, eds., Approaches to Arabic dialects: A collection of articles presented to Manfred Woidich on the occasion of his sixtieth birthday, Koninklijke Brill NV, The Netherlands, 2004, pp. 223–224
- ^ a b Gideon Biger, The Boundaries of Modern Palestine, 1840–1947, pp. 13–15. Routledge, 2004. ISBN 0-7146-5654-2
- ^ Jankowski, James P. (1997). Rethinking Nationalism in the Arab Middle East. Columbia University Press. p. 174. ISBN 0231106955.
- ^ Bernard Lewis, "Palestine: On the History and Geography of a Name", International History Review 11 (1980): 1–12
- ^ Porath, 1974, pp. 8–9.
- ^ Haim Gerber (1998) referring to fatwas by two Hanafite Syrian jurists.
- ^ Strawson, John (2010), pp. 25.
- ^ Scharfstein, Sol, Chronicle of Jewish History: From the Patriarchs to the 21st Century, p. 231, Ktav Publishing House (1997), ISBN 0-88125-545-9
- ^ "New Aliyah - Modern Zionist Aliyot (1882–1948)". Jewish Agency for Israel. Retrieved 2008-10-26.
- ^ "The First Aliyah". Jewishvirtuallibrary.org. Retrieved 2009-06-16.
- ^ Mandel, Neville, The Arabs and Zionism before World War I, Berkeley: University of California Press, 1976. (p. xviii)
- ^ Porath, Zipporah, Letters from Jerusalem, 1947–1948, Jerusalem: Association of Americans and Canadians in Israel, 1987 (p. 26)
- ^ "Israeli government site on the Second Aliyah". Moia.gov.il. Retrieved 2010-08-24.
- ^ Baylis Thomas,''How Israel was Won'' (1999) p. 19. Books.google.com. 1999. ISBN 978-0-7391-0064-6. Retrieved 2010-08-24.
- ^ Hughes, 1999, p. 17; p. 97.
- ^ See also Third Battle of Gaza and Battle of Beersheba
- ^ "The Palestine Mandate". Avalon.law.yale.edu. Retrieved 2010-08-24.
- ^ Article 22, The Covenant of the League of Nations and "Mandate for Palestine", Encyclopedia Judaica, Vol. 11, p. 862, Keter Publishing House, Jerusalem, 1972
- ^ see A History of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, By Mark A. Tessler, Indiana University Press, 1994, ISBN 0-253-20873-4, pp. 155–156
- ^ J. B. Barron, ed. (1923). Palestine: Report and General Abstracts of the Census of 1922. Government of Palestine. Table I.
- ^ 'Zionist Aspirations: Dr Weizmann on the Future of Palestine', The Times, Saturday, 8 May 1920; p. 15.
- ^ Gelber, 1997, pp. 6–15.
- ^ Sicker, 1999, p. 164.
- ^ Boundaries Delimitation: Palestine and Trans-Jordan, Yitzhak Gil-Har, Middle Eastern Studies, Vol. 36, No. 1 (January , 2000), pp. 68-81
- ^ See Marjorie M. Whiteman, Digest of International Law, vol. 1, U.S. State Department (Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1963) pp. 650–652
- ^ "The Council for Arab-British Understanding". CAABU. Retrieved 2009-06-16.
- ^ No. 565. — Exchange of Notes * Constituting an Agreement Between the British and French Governments Respecting the Boundary Line Between Syria and Palestine from the Mediterranean to El Hammé, Paris March 7, 1923, p. 7 Border Treaty
- ^ Ingrams, 1972
- ^ "Mandate for Palestine - Interim report of the Mandatory to the LoN/Balfour Declaration text". League of Nations. 1921-07-30. Retrieved 2007-03-08.
- ^ Henry Laurens, [La Question de Palestine] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help), Fayard, Paris 2002 vol.2 p. 101
- ^ Rashid Khalidi, The Iron Cage: The Story of the Palestinian Struggle for Statehood, 2006. Beacon Press. [9].
- ^ see see Uniform and History of the Palestine Police
- ^ Etzel - The Establishment of Irgun.
- ^ "Restraint and Retaliation". Etzel. Retrieved 2010-08-24.
- ^ see for example the incident on 14 March 1937 when Arieh Yitzhaki and Benjamin Zeroni tossed a bomb into the Azur coffee house outside Tel Aviv in Terror Out of Zion, by J. Bowyer Bell, Transaction Publishers, , 1996, ISBN 1-56000-870-9, pp. 35–36.
- ^ "Aljazeera: The history of Palestinian revolts". Web.archive.org. Archived from the original on 2005-12-15. Retrieved 2010-08-24.
- ^ "Why Italian Planes Bombed Tel-Aviv?". Isracast.com. 2009-09-09. Retrieved 2010-08-24.
- ^ How the Palmach was formed (History Central)
- ^ Karl Lenk, The Mauritius Affair, The Boat People of 1940/41, London 1991
- ^ James L. Gelvin, The Israel-Palestine conflict, Cambridge University Press, 2007, p. 120.
- ^ "Land Registration in Palestine before 1948 (Nakba): Table 2 showing Holdings of Large Jewish Lands Owners as of December 31st, 1945, British Mandate: A Survey of Palestine: Volume I - Page 245. Chapter VIII: Land: Section 3. - Palestine Remembered". Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ^ The Rise and fall of the British Empire, By Lawrence James, Macmillan, 1997, ISBN 0-312-16985-X, p. 562
- ^ see Request for a Special Session of the General Assembly on Palestine
- ^ see Rabbi Silver's request regarding the formation of a Jewish militia and the dissolution of the mandate in S/PV.262, Minutes 262nd Meeting of the UN Security Council,5 March 1948
- ^ UNITED NATIONS General Assembly: A/RES/181(II): 29 November 1947: Resolution 181 (II): Future government of Palestine: Retrieved 26 April 2012
- ^ Plascov, Avi (2008). The Palestinian refugees in Jordan 1948-1957. Routledge. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-7146-3120-2. Retrieved 2009-12-11.
- ^ Bovis, H. Eugene (1971). The Jerusalem question, 1917–1968. Hoover Institution Press,U.S. p. 40. ISBN 978-0-8179-3291-6. Retrieved 2009-12-11.
- ^ 6 Arab states, Egypt, Iraq, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Yemen: 4 Moslem states, Afghanistan, Iran, Pakistan, Turkey: Greece, Cuba and India also voted against. See Henry Cattan, The Palestine question, Routledge, London 1988 p. 36
- ^ Benny Morris, 1948. A History of the First Arab-Israeli War, Yale University Press, 2008, p.79.
- ^ Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs: Declaration of Establishment of State of Israel: 14 May 1948: Retrieved 26 April 2012
- ^ Truman, the Jewish Vote, and the Creation of Israel, John Snetsinger, Hoover Press, 1974, ISBN 0-8179-3391-3, p. 107. Books.google.com. 1974. ISBN 978-0-8179-3391-3. Retrieved 2010-08-24.
- ^ see The Middle East Journal, Middle East Institute (Washington, D.C.), 1949, p. 78, October 1): Robert A. Lovett, Acting Secretary of State, announced the U.S. would not recognize the new Arab Government in Palestine, and Foreign relations of the United States, 1948. The Near East, South Asia, and Africa, Volume V, Part 2, p. 1448
- ^ a b c "Palestine, 1948". Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ^ "The Encyclopedia of the Arab-Israeli Conflict". Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ^ See Jericho Declaration, Palestine Post, December 14, 1948, Front page
- ^ Avi Shlaim in Pappe's The Israel/Palestine question, p. 187.
- ^ Carroll, K. B., Business As Usual?: Economic Reform in Jordan, Lexington Books, 2003, p.108
- ^ Lutfiyya, A. M., Baytin: A Jordanian Village. A Study of Social Institutions and Social Change in a Folk Community, Walter de Gruyter, 1966, pp.13-14
- ^ Carroll, p.108
- ^ Ian Lustick, Has Israel Annexed East Jerusalem?
- ^ Ian J. Bickerton 2009, The Arab-Israeli-Conflict: A History. Reaktion Books Ltd, ISBN 9781861895271, p. 106.
- ^ Israel and the Palestinians: Key terms, BBC
- ^ a b Baroud, Ramzy (July 2007). "Gaza: chaos foretold". Le Monde Diplomatique. Retrieved 2009-07-26.
- ^ "No-goodniks and the Palestinian shootout". Asia Times. 2007-01-09. Retrieved 2009-07-26.
- ^ "IDF: More than 300,000 settlers live in West Bank". haaretz.com. Retrieved 9 May 2010.
- ^ Schell, Bernhard (July 31, 2011). "UN will count 194 members if Palestine gets in". InDepthNews. Retrieved 2011-08-01.
- ^ Sawafta, A. (14 July 2011). "Arabs to seek full Palestinian upgrade at UN". Reuters. Thomson Reuters. Retrieved 2011-07-19.
- ^ Staff writers (July 6, 2011). "Arab League Requests Palestinian Statehood from U.N." Palestine News Network. Retrieved 2011-07-19.
- ^ Ashkar, Alaa; Bannoura, Saed (9 September 2011). "UN Secretary-General Supports Full Palestinian Membership". IMEMC News. International Middle East Media Center. Retrieved 2011-09-09.
- ^ "Report of possible Gaza independence stirs debate". Al Arabiya. 31 July 2012. Retrieved 2012-11-26.
- ^ "Palestinians to renew U.N. statehood drive in September". Al Arabiya. August 4, 2012. Retrieved 2012-11-26.
- ^ "A/67/L.28 of 26 November 2012 and A/RES/67/19 of 29 November 2012". Unispal.un.org. Retrieved 2012-12-02.
- ^ a b c Inside Story. "Palestine: What is in a name (change)?". Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ^ "Israel defies UN after vote on Palestine with plans for 3,000 new homes in the West Bank". The Independent. 1 December 2012.
- ^ "Permanent Observer Mission of the State of Palestine to the United Nations". Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ^ "Palestinian Authority officially changes name to 'State of Palestine'". Haaretz.com. 5 January 2013. Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ^ Gharib, Ali (2012-12-20). "U.N. Adds New Name: "State of Palestine"". The Daily Beast. Retrieved 2013-01-10.
External links
- Picturesque Palestine, Sinai and Egypt by Colonel Sir Charles William Wilson, ed. (published 1881–1884) image gallery at New York Public Library
- hWeb - Israel-Palestine in Maps
- Holy land Maps
- Abraham J. Brawer & Shimon Gibson, Palestine, Encyclopedia Judaica
- A map of Palestine from 1475, it is considered one of the earliest printed maps.
- Syria and Palestine from 1920