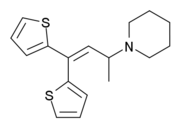
Piperidylthiambutene
Appearance
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H21NS2 |
| Molar mass | 303.485 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 188 to 189 °C (370 to 372 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Piperidylthiambutene (Piperidinohton) is an opioid analgesic drug from the thiambutene family, which has around the same potency as morphine.[1][2][3] If sold / was obtained for the purpose of human consumption it could be considered a controlled substance analogue in some countries such as the USA, Australia and New Zealand, but is legal in the rest of the world.
References
- ^ Adamson DW, Green AF. A new series of analgesics. Nature. 1950 Jan 21;165(4186):122. doi:10.1038/165122a0 PMID 15409854
- ^ Adamson DW, Duffin WM, Green AF. Dithienylbutylamines as analgesics. Nature. 1951 Jan 27;167(4239):153-4. doi:10.1038/167153b0 PMID 14806409
- ^ Green AF. Analgesic and other properties of 3: 3-dithienylalkenylamines. British Journal of Pharmacology and Chemotherapy. 1953 Mar;8(1):2-9. PMID 13066683
