Solar eclipse of May 20, 2012
| Solar eclipse of May 20, 2012 | |
|---|---|
 Composite image taken from Red Bluff, California | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Annular |
| Gamma | 0.4828 |
| Magnitude | 0.9439 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 346 s (5 min 46 s) |
| Coordinates | 49°06′N 176°18′E / 49.1°N 176.3°E |
| Max. width of band | 237 km (147 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| (P1) Partial begin | 20:56:07 |
| (U1) Total begin | 22:06:17 |
| Greatest eclipse | 23:53:54 |
| (U4) Total end | 1:39:11 |
| (P4) Partial end | 2:49:21 |
| References | |
| Saros | 128 (58 of 73) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9535 |
An annular solar eclipse took place on May 20, 2012 (May 21, 2012 in local time in the Eastern Hemisphere), with a magnitude of 0.9439. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.
Visibility
- North America
It was the first annular eclipse in the continental U.S. since the solar eclipse of May 10, 1994 which was also the previous eclipse of this series Solar Saros 128.
- Hong Kong
It was predicted that the antumbra would pass over Hong Kong but due to weather it was not observable.
Photo Gallery
Asia
-
Aichi Prefecture, Japan
-
Kōfu, Japan
-
Aoba-ku, Yokohama, Japan
-
23 wards of Tokyo, Japan
-
Tokyo, Japan
-
Video from Tokyo, Japan
-
Kashima, Ibaraki, Japan
USA
-
Crescent shadows on an outdoor wall in San Francisco, California.
-
Crescent shaped shadows from tree on a wall in San Francisco, California
-
Crescent images from solar eclipse, May 2012 in San Francisco, California
-
Photo taken from San Francisco, California
-
Composite image from Huntington Beach, California
-
From Palm Springs, California, wide angle
-
From Los Osos, California
-
Photo taken from San Juan Capistrano, California at 1:20 UTC
-
80mm refractor, 1:36 UTC, Nevada City, California
-
Near Phoenix, Arizona
-
Eclipse as seen from Flagstaff, Arizona
-
Amateur scientists observing eclipse in Albuquerque, New Mexico.
-
Center line, south shore of Pyramid Lake (Nevada) in Nevada.
-
2012-05-20 Eclipse as seen from Wolfforth, Texas.
-
Partial Solar Eclipse in Salt Lake City, Utah.
-
From Pleasant Grove, Utah
-
East of Ogden, Iowa at 1:25 UTC
-
Minneapolis, Minnesota at 1:27:53 UTC
-
Projection method using 60mm refractor from Medford, Oregon.
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 2011–2014
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
The partial solar eclipses on January 4, 2011 and July 1, 2011 occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2011 to 2014 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
118 Partial in Tromsø, Norway |
June 1, 2011 Partial |
1.21300 | 123 Hinode XRT footage |
November 25, 2011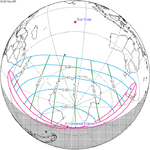 Partial |
−1.05359 | |
128 Annularity in Red Bluff, CA, USA |
May 20, 2012 Annular |
0.48279 | 133 Totality in Mount Carbine, Queensland, Australia |
November 13, 2012 Total |
−0.37189 | |
138 Annularity in Churchills Head, Australia |
May 10, 2013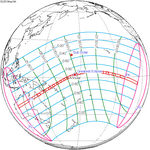 Annular |
−0.26937 | 143 Partial in Libreville, Gabon |
November 3, 2013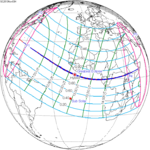 Hybrid |
0.32715 | |
148 Partial in Adelaide, Australia |
April 29, 2014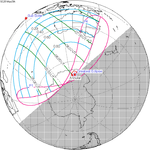 Annular (non-central) |
−0.99996 | 153 Partial in Minneapolis, MN, USA |
October 23, 2014 Partial |
1.09078 | |
Saros 128
This eclipse is a part of Saros series 128, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 73 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on August 29, 984 AD. It contains total eclipses from May 16, 1417 through June 18, 1471; hybrid eclipses from June 28, 1489 through July 31, 1543; and annular eclipses from August 11, 1561 through July 25, 2120. The series ends at member 73 as a partial eclipse on November 1, 2282. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of totality was produced by member 27 at 1 minutes, 45 seconds on June 7, 1453, and the longest duration of annularity was produced by member 48 at 8 minutes, 35 seconds on February 1, 1832. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s descending node of orbit.[2]
| Series members 47–68 occur between 1801 and 2200: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 47 | 48 | 49 |
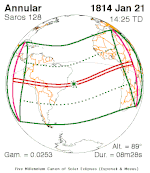 January 21, 1814 |
 February 1, 1832 |
 February 12, 1850 |
| 50 | 51 | 52 |
 February 23, 1868 |
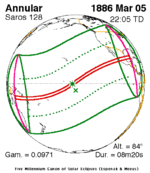 March 5, 1886 |
 March 17, 1904 |
| 53 | 54 | 55 |
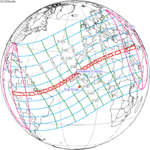 March 28, 1922 |
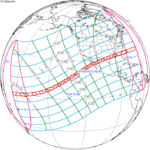 April 7, 1940 |
 April 19, 1958 |
| 56 | 57 | 58 |
 April 29, 1976 |
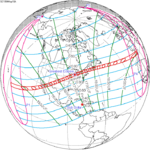 May 10, 1994 |
 May 20, 2012 |
| 59 | 60 | 61 |
 June 1, 2030 |
 June 11, 2048 |
 June 22, 2066 |
| 62 | 63 | 64 |
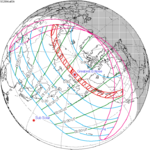 July 3, 2084 |
 July 15, 2102 |
 July 25, 2120 |
| 65 | 66 | 67 |
 August 5, 2138 |
 August 16, 2156 |
 August 27, 2174 |
| 68 | ||
 September 6, 2192 | ||
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.
| 21 eclipse events between May 21, 1993 and May 20, 2069 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| May 20–21 | March 9 | December 25–26 | October 13–14 | August 1–2 |
| 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 | 126 |
 May 21, 1993 |
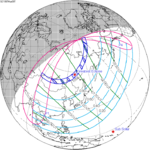 March 9, 1997 |
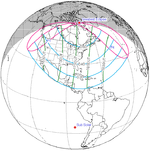 December 25, 2000 |
 October 14, 2004 |
 August 1, 2008 |
| 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 | 136 |
 May 20, 2012 |
 March 9, 2016 |
 December 26, 2019 |
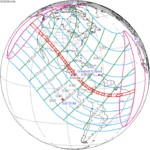 October 14, 2023 |
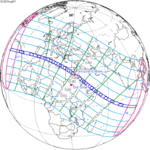 August 2, 2027 |
| 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 | 146 |
 May 21, 2031 |
 March 9, 2035 |
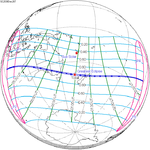 December 26, 2038 |
 October 14, 2042 |
 August 2, 2046 |
| 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 | 156 |
 May 20, 2050 |
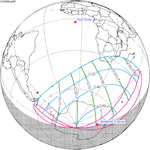 March 9, 2054 |
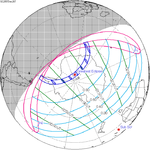 December 26, 2057 |
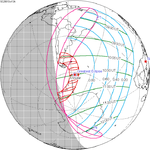 October 13, 2061 |
 August 2, 2065 |
| 158 | ||||
 May 20, 2069 | ||||
Notes
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ "NASA - Catalog of Solar Eclipses of Saros 128". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Closeup map of path
- www.eclipser.ca: Jay Anderson 2012 May 20/21 Annular Solar Eclipse
- NightSkyInfo.com: May 20, 2012 Annular Solar Eclipse
- Photo Gallery from Big Spring TX
External links
- A Partial Solar Eclipse over Texas, APOD 5/22/2012, from 30 km west of Sundown, Texas, the same picture chosen as APOD again on 9/13/2015
- Looking Back at an Eclipsed Earth, APOD 5/30/2012, taken by MTSAT
































