Telephone numbers in the Netherlands
| Location | |
|---|---|
| Country | Netherlands |
| Continent | Europe |
| Access codes | |
| Country code | +31 |
| International access | 00 |
| Long-distance | 0 |
Telephone numbers in the Netherlands are administered by the Ministry of Economic Affairs, Agriculture and Innovation of the Netherlands and may be grouped into three general categories: geographical numbers, non-geographical numbers, and numbers for public services.
Geographical telephone numbers are sequences of 9 digits (0-9) and consist of an area code of two or three digits and a subscriber number of seven or six digits, respectively. When dialled within the country, the number must be prefixed with the trunk access code 0, identifying a destination telephone line in the Dutch telephone network.
Non-geographical numbers have no fixed length, but also required the dialling of the trunk access code (0). They are used for mobile telephone networks and other designated service types, such as toll-free dialling, Internet access, voice over IP, restricted audiences, and information resources.
In addition, special service numbers exist for emergency response, directory assistance, and other services by the public authorities.
Numbering plan
The telephone numbering plan of the Netherlands is divided into geographical, non-geographical, and special public resource telephone numbers. The dial plan prescribes that within the country dialling both geographical and non-geographical numbers requires a national network access code, which is the digit 0. The following list includes this national trunk access digit when it must be dialled before the number.
| Access digits | Description |
|---|---|
| 01x(x) to 05x(x) | Geographical area codes |
| 061 to 065 | Mobile phones |
| 066 | Mobile pagers |
| 0670 to 0675 | Videotex |
| 0676 | Internet access number |
| 068 | Mobile phones |
| 07x | Geographical area codes |
| 0800 | Toll free number |
| 082 | Virtual private networks |
| 084 | Location independent, premium rate (used mostly for fax-to-email and voicemail services) |
| 085 | Location independent, basic rate (for private use) VoIP telephony |
| 087 | Location independent, premium rate |
| 088 | Location independent, basic rate (for companies) |
| 091 | VoIP telephony |
| 097 | Location independent, machine to machine |
| 0900 | Premium rate, information |
| 0906 | Premium rate, adult content |
| 0909 | Premium rate, entertainment |
| 112 | Emergency services |
| 14xx(xx) | Public authorities, where xxxx is the two-, three- or four-digit area-code of the municipality |
| 16xx | Carrier select prefixes |
| 18xx | Number information |
066, 084 and 087 are often used by scammers, because they are easy and cheap to register and make identification very hard.[citation needed]
Previously, 06-0, 06-1000 and 06-4 were used for toll-free numbers, 06-8 for shared cost, 06-9 for premium rate, and other 06-numbers for mobile numbers. 0011 and later 06-11 was used for emergency services before this changed to 112. 09 was used as the international access code before this changed to 00.
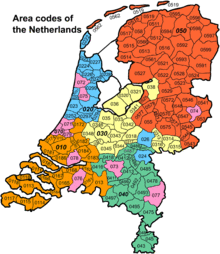
Geographical telephone numbers
Since the reorganization of the telephone system in 1995, Dutch geographical numbers consist of 9 digits. The numbering plan implements a system of area codes. An area code consists of two or three digits. The larger cities and areas have two digits with a subscriber number of seven digits, permitting more local numbers. Smaller areas use three digits with a six-digit subscriber number.
Geographic numbers are allocated in blocks to telecommunications providers. However, a telephone number from a block allocated to a certain provider may no longer be serviced by the original assignee due to number portability; subscribers who switch providers can take their number with them.
When dialled within the Netherlands, the domestic trunk access code 0 must be dialled before the telephone number, extending the dialling sequence to 10 digits.
Before the 1995 reorganization, area codes were restricted to towns. This was lifted and multiple towns may now share an area code. The following table lists only one town for each area code, and it includes the trunk access code (0).
Non-geographical telephone numbers
The non-geographic numbers do not have a prescribed fixed number of digits, but are usually kept as short as possible. Mobile telephone numbers, however, always have 9 digits, just like geographic numbers.
The non-geographical telephone number categories are, including the trunk access code:
- 06: mobile telephone operators,
- 0800: free service numbers,
- 084, 085: used for VoIP
- 087: voicemail and virtual private numbers
- 088: large companies with more than one address
- 0970: machine to machine communication, numbers are 8 digits long
- 0979: machine to machine communication, numbers have no fixed length and are reserved for network internal usage
- 0900: paid information services
- 0906: adult lines
- 0909: entertainment
Toll-free numbers (0800) can always be dialled for free, even from (public) payphones; other numbers starting with 08 are not free.
Public resources
The emergency number is 112. GSM mobile phones may accept different numbers, such as 999, 000 or 911, depending on the firmware. Additionally, calls to 911 are forwarded to 112 (in the Caribbean Netherlands, this is reversed - 112 redirects to 911 in that case).
Directory assistance is available from several commercial providers, on 18xx (e.g., 1888 from KPN).
Caribbean Netherlands
The islands of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba, which form the Caribbean Netherlands after the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles, retained the numbering plan of the Netherlands Antilles using country code +599, followed by 7, 3 or 4 for Bonaire, Sint Eustatius or Saba, respectively. Calls between the European Netherlands and Caribbean Netherlands are billed as international calls.
See also
- Communications in the Netherlands
- Telephone numbers in Aruba
- Telephone numbers in Sint Maarten (NANP)
External links
- The Ministry of Economic Affairs, Agriculture and Innovation is responsible for the Dutch Numbering plan.
- The Authority for Consumers & Markets (ACM ) manages the available telephone and other numbers and assigns these to telecommunication companies, as well as being the regulatory body governing telecommunications providers in The Netherlands.
- De Telefoongids KPN telephone directory, combined white pages and yellow pages
