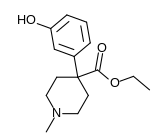
Hydroxypethidine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.738 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H21NO3 |
| Molar mass | 263.337 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Hydroxypethidine (Bemidone) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of the more commonly used pethidine (meperidine). Hydroxypethidine is slightly more potent than meperidine as an analgesic, 1.5x meperidine in potency,[1] and it also has NMDA antagonist properties like its close relative ketobemidone.[2]
Hydroxypethidine has similar effects to other opioids, and produces analgesia, sedation and euphoria. Side effects can include itching, nausea and potentially serious respiratory depression which can be life-threatening.
Hydroxypethidine is under international control under the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs 1961 and therefore controlled like morphine in most countries; in the United States it is a Schedule I Narcotic controlled substance with an ACSCN of 9627 and a 2014 annual aggregate manufacturing quota of 2 grams. The salt in use is the hydrochloride, with a free base conversion ratio of 0.878. [3]
See also
References
- ^ Beckett AH, Casy AF (February 1965). "Analgesics and their antagonists: biochemical aspects and structure-activity relationships". Progress in Medicinal Chemistry. 4: 171–218. doi:10.1016/s0079-6468(08)70169-3. PMID 5319798.
- ^ Harris I (1949). "The addiction liability of some analogues of meperidine". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 97 (2): 182–190.
- ^ "Conversion Factors for Controlled Substances". Diversion Control Division. Drug Enforcement Administration, U.S. Department of Justice.
