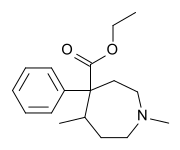
Metethoheptazine
Appearance
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | WY-535 |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H25NO2 |
| Molar mass | 275.392 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Metethoheptazine[1] (WY-535) is an opioid analgesic from the phenazepine family. It was invented in the 1960s.[2]
Metethoheptazine produces similar effects to other opioids, including analgesia, sedation, dizziness and nausea.
Metethoheptazine is not listed as a controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act 1970 in the United States.[3] The Canadian Controlled Drugs and Substances Act specifically excludes the phenazepine opioids from control.
References
- ^ GB Patent 843924
- ^ Walkenstein SS, Corradino RA, Wiser R, Gudmundsen CH. Metabolism of the Non-Narcotic Analgesic, WY-535. Biochemical Pharmacology. 1965 Feb;14:121-8.
- ^ "Conversion Factors for Controlled Substances". U.S. Department of Justice Drug Enforcement Administration. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
