Abortion in the United States
Abortion is legal throughout the United States and its territories, although restrictions and accessibility vary from state to state. Abortion is a controversial and divisive issue in the society, culture and politics of the U.S., and various anti-abortion laws have been in force in each state since at least 1900.
Before the Supreme Court of the United States decisions of Roe v. Wade and Doe v. Bolton decriminalized abortion nationwide in 1973, abortion was already legal in several states, but the decision imposed a uniform framework for state legislation on the subject. It established a minimal period during which abortion is legal (with more or fewer restrictions throughout the pregnancy). That basic framework, modified in Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992), remains nominally in place, although the effective availability of abortion varies significantly from state to state, as many counties have no abortion providers.[1] Planned Parenthood v. Casey held that a law cannot place legal restrictions imposing an undue burden for "the purpose or effect of placing a substantial obstacle in the path of a woman seeking an abortion of a nonviable fetus."[2]
The abortion rate has continuously fallen from a peak in 1980 of 30 per 1,000 women of childbearing age (15–44), to 12 per 1,000 by 2016.[3][4] In 2016, 66% of abortions were performed at 8 weeks or less gestation, and 91% of abortions were performed at 13 weeks or less gestation.[3][4]
The main actors in the abortion debate are often framed as either "pro-choice" or "pro-life", though shades of opinion exist, and most Americans are found to agree with some positions held by both sides.[5] A 2018 Gallup survey found the percentages that were "pro-choice" or "pro-life" were equal (at 48%), but more people considered abortion morally wrong (48%) than morally acceptable (43%). The poll results also indicated that Americans harbor a diverse and shifting set of opinions on the legal status of abortion. The survey found that only 29% of respondents believed abortion should be legal in all circumstances, and 50% of respondents believed that abortion should be legal under certain circumstances.[6] Recent polling results also found that only 34% of Americans were satisfied with abortion laws.[7]
Terminology
The abortion debate most commonly relates to the "induced abortion" of an embryo or fetus at some point in a pregnancy, which is also how the term is used in a legal sense.[8] Some also use the term "elective abortion", which is used in relation to a claim to an unrestricted right of a woman to an abortion, whether or not she chooses to have one. The term elective abortion or voluntary abortion describes the interruption of pregnancy before viability at the request of the woman, but not for medical reasons.[9]
In medical parlance, "abortion" can refer to either miscarriage or abortion until the fetus is viable. After viability, doctors call an abortion a "termination of pregnancy".
History
Rise of anti-abortion legislation

When the United States first became independent, most states applied English common law to abortion. This meant it was not permitted after quickening, or the start of fetal movements, usually felt 15–20 weeks after conception.[11]
Abortion has existed in America since European colonization. The earliest settlers would often encourage abortions before the "quickening" stage in the pregnancy. There were many reasons given for this, including not having resources to bear children. It was not until the late 1800s[clarification needed] when states began to make abortions illegal. One reason given for the legislation was that abortions had been performed with dangerous methods and were often surgical. Because of this,[clarification needed] many states decided to legalize abortions. As technology advanced and abortion methods improved, abortions still remained illegal. Women would resort to illegal unsafe methods, also known as "back alley" abortions. As of 2020[update], some women who live in areas with limited access to abortion clinics resort to "back-alley" abortions.[citation needed]
Abortions became illegal by statute in Britain in 1803 with Lord Ellenborough's Act. Additionally, various anti-abortion statutes began to appear in the United States in the 1820s that codified or expanded common law. In 1821, a Connecticut law targeted apothecaries who sold "poisons" to women for purposes of inducing an abortion, and New York made post-quickening abortions a felony and pre-quickening abortions a misdemeanor in 1829.[12][citation needed] Other legal scholars have pointed out that some of the early laws punished not only the doctor or abortionist, but also the woman who hired them.[13]
A number of other factors likely played a role in the rise of anti-abortion laws. Physicians, who were the leading advocates of abortion criminalization laws, appear to have been motivated at least in part by advances in medical knowledge. Science had discovered that conception inaugurated a more or less continuous process of development, which would produce a new human being if uninterrupted. Moreover, quickening was found to be neither more nor less crucial in the process of gestation than any other step. Many physicians concluded that if society considered it unjustifiable to terminate pregnancy after the fetus had quickened, and if quickening was a relatively unimportant step in the gestation process, then it was just as wrong to terminate a pregnancy before quickening as after quickening.[14] Ideologically, the Hippocratic Oath and the medical mentality of that age to defend the value of human life as an absolute also played a significant role in molding opinions about abortion.[14] Doctors were also influenced by practical reasons to impose anti-abortion laws. For one, abortion providers tended to be untrained and not members of medical societies. In an age where the leading doctors in the nation were attempting to standardize the medical profession, these "irregulars" were considered a nuisance to public health.[15] The more formalized medical profession disliked the "irregulars" because they were competition, often at a cheaper cost.
Despite campaigns to end the practice of abortion, abortifacient advertising was highly effective, though less so across the Atlantic. Contemporary estimates of mid-19th century abortion rates suggest between 20 and 25% of all pregnancies in the United States during that era ended in abortion.[16] This era saw a marked shift in those who were obtaining abortions. Before the start of the 19th century, most abortions were sought by unmarried women who had become pregnant out of wedlock. Out of 54 abortion cases published in American medical journals between 1839 and 1880, over half were sought by married women, and well over 60% of the married women already had at least one child.[17] The sense that married women were now frequently obtaining abortions worried many conservative physicians, who were almost exclusively men. In the post-Civil War era, much of the blame was placed on the burgeoning women's rights movement.
Though the medical profession expressed hostility toward feminism, many feminists of the era were opposed to abortion.[18][19] In The Revolution, operated by Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony, an anonymous contributor signing "A" wrote in 1869 about the subject, arguing that instead of merely attempting to pass a law against abortion, the root cause must also be addressed. Simply passing an anti-abortion law would, the writer stated, "be only mowing off the top of the noxious weed, while the root remains. [...] No matter what the motive, love of ease, or a desire to save from suffering the unborn innocent, the woman is awfully guilty who commits the deed. It will burden her conscience in life, it will burden her soul in death; But oh! thrice guilty is he who drove her to the desperation which impelled her to the crime."[19][20][21][22] To many feminists of this era, abortion was regarded as an undesirable necessity forced upon women by thoughtless men.[23] Even the "free love" wing of the feminist movement refused to advocate for abortion and treated the practice as an example of the hideous extremes to which modern marriage was driving women.[24] Marital rape and the seduction of unmarried women were societal ills which feminists believed caused the need to abort, as men did not respect women's right to abstinence.[24]
However, physicians remained the loudest voice in the anti-abortion debate, and they carried their anti-feminist agenda to state legislatures around the country, advocating not only anti-abortion laws, but also laws against birth control. This movement presaged the modern debate over women's body rights.[25] A campaign was launched against the movement and the use and availability of contraceptives.
Criminalization of abortion accelerated from the late 1860s, through the efforts of concerned legislators, doctors, and the American Medical Association.[26] In 1873, Anthony Comstock created the New York Society for the Suppression of Vice, an institution dedicated to supervising the morality of the public. Later that year, Comstock successfully influenced the United States Congress to pass the Comstock Law, which made it illegal to deliver through the U.S. mail any "obscene, lewd, or lascivious" material. It also prohibited producing or publishing information pertaining to the procurement of abortion or the prevention of conception or venereal disease, even to medical students.[27] The production, publication, importation, and distribution of such materials was suppressed under the Comstock Law as being obscene, and similar prohibitions were passed by 24 of the 37 states.[28]
In 1900, abortion was a felony in every state. Some states included provisions allowing for abortion in limited circumstances, generally to protect the woman's life or to terminate pregnancies arising from rape or incest.[29] Abortions continued to occur, however, and became increasingly available. The American Birth Control League was founded by Margaret Sanger in 1921, which would later become Planned Parenthood Federation of America in 1942.[30][31]
By the 1930s, licensed physicians performed an estimated 800,000 abortions a year.[32]
Sherri Finkbine
One notable case dealt with a woman named Sherri Finkbine. Born in the area of Phoenix, Arizona, Sherri had 4 healthy children. However, during her pregnancy with her 5th child, she had found that the child might have severe deformities.[33] Finkbine had been taking sleeping pills that contained a drug called Thalidomide which was also very popular in several countries.[34] She had later learned that the drug was causing fetal deformities and she wanted to warn the general public. Finkbine strongly wanted an abortion, however the abortion laws of Arizona limited her decision. In Arizona, an abortion could only occur if the mother's life was in danger. She met with a reporter from The Arizona Republic and told her story. While Sherri Finkbine wanted to be kept anonymous, the reporter disregarded this idea. On August 18, 1962, Finkbine traveled to Sweden where she was able to obtain a legal abortion. It was also confirmed that the child would have been very much deformed.[35] Sherri Finkbine's story marks a turning point for women as well as the history of abortion laws occurring in the United States. Sherri Finkbine, unlike many other women was able to afford going overseas to have the abortion. However, for the women who have pregnancies that are actually unintended, they may not be able to afford traveling, leading them to seek more illegal forms of abortion. [citation needed]
Pre-Roe precedents
In 1964, Gerri Santoro of Connecticut died trying to obtain an illegal abortion and her photo became the symbol of an abortion-rights movement. Some women's rights activist groups developed their own skills to provide abortions to women who could not obtain them elsewhere. As an example, in Chicago, a group known as "Jane" operated a floating abortion clinic throughout much of the 1960s. Women seeking the procedure would call a designated number and be given instructions on how to find "Jane".[36]
In 1965, the U.S. Supreme Court case Griswold v. Connecticut struck down one of the remaining contraception Comstock laws in Connecticut and Massachusetts.[37] However, Griswold only applied to marital relationships. Eisenstadt v. Baird (1972) extended its holding to unmarried persons as well.[38] Following the Griswold case, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) issued a medical bulletin accepting a recommendation from six years earlier that clarified that "conception is the implantation of a fertilized ovum";[39] and consequently birth control methods that prevented implantation became classified as contraceptives, not abortifacients.
In 1967, Colorado became the first state to decriminalize abortion in cases of rape, incest, or in which pregnancy would lead to permanent physical disability of the woman. Similar laws were passed in California, Oregon, and North Carolina. In 1970, Hawaii became the first state to legalize abortions on the request of the woman,[40] and New York repealed its 1830 law and allowed abortions up to the 24th week of pregnancy. Similar laws were soon passed in Alaska and Washington. In 1970, Washington held a referendum on legalizing early pregnancy abortions, becoming the first state to legalize abortion through a vote of the people.[41] A law in Washington, D.C., which allowed abortion to protect the life or health of the woman, was challenged in the Supreme Court in 1971 in United States v. Vuitch. The court upheld the law, deeming that "health" meant "psychological and physical well-being", essentially allowing abortion in Washington, D. C. By the end of 1972, 13 states had a law similar to that of Colorado, while Mississippi allowed abortion in cases of rape or incest only and Alabama and Massachusetts allowed abortions only in cases where the woman's physical health was endangered. In order to obtain abortions during this period, women would often travel from a state where abortion was illegal to states where it was legal. The legal position prior to Roe v. Wade was that abortion was illegal in 30 states and legal under certain circumstances in 20 states.[42]
In the late 1960s, a number of organizations were formed to mobilize opinion both against and for the legalization of abortion. In 1966, the National Conference of Catholic Bishops assigned Monsignor James T. McHugh to document efforts to reform abortion laws, and anti-abortion groups began forming in various states in 1967. In 1968, McHugh led an advisory group which became the National Right to Life Committee.[43][44] The forerunner of the NARAL Pro-Choice America was formed in 1969 to oppose restrictions on abortion and expand access to abortion.[45] Following Roe v. Wade, in late 1973, NARAL became the National Abortion Rights Action League.
Roe v. Wade

Prior to Roe v. Wade, 30 states prohibited abortion without exception, 16 states banned abortion except in certain special circumstances (e.g., rape, incest, health threat to mother), 3 states allowed residents to obtain abortions, and New York allowed abortions generally.[46] Early that year, on January 22, 1973, the Supreme Court in Roe v. Wade invalidated all of these laws, and set guidelines for the availability of abortion. Roe established that the right of privacy of a woman to obtain an abortion "must be considered against important state interests in regulation".[47] Roe established a "trimester" (i.e., 12 week) threshold of state interest in the life of the fetus corresponding to its increasing "viability" (likelihood of survival outside the uterus) over the course of a pregnancy, such that states were prohibited from banning abortion early in pregnancy but allowed to impose increasing restrictions or outright bans later in pregnancy.
In deciding Roe v. Wade, the Supreme Court ruled that a Texas statute forbidding abortion except when necessary to save the life of the mother was unconstitutional. The Court arrived at its decision by concluding that the issue of abortion and abortion rights falls under the right to privacy (in the sense of the right of a person not to be encroached by the state). In its opinion, it listed several landmark cases where the court had previously found a right to privacy implied by the Constitution. The Court did not recognize a right to abortion in all cases:
State regulation protective of fetal life after viability thus has both logical and biological justifications. If the State is interested in protecting fetal life after viability, it may go so far as to proscribe abortion during that period, except when it is necessary to preserve the life or health of the mother.[48]
The Court held that a right to privacy existed and included the right to have an abortion. The court found that a mother had a right to abortion until viability, a point to be determined by the abortion doctor. After viability a woman can obtain an abortion for health reasons, which the Court defined broadly to include psychological well-being.
A central issue in the Roe case (and in the wider abortion debate in general) is whether human life or personhood begins at conception, birth, or at some point in between. The Court declined to make an attempt at resolving this issue, noting: "We need not resolve the difficult question of when life begins. When those trained in the respective disciplines of medicine, philosophy, and theology are unable to arrive at any consensus, the judiciary, at this point in the development of man's knowledge, is not in a position to speculate as to the answer." Instead, it chose to point out that historically, under English and American common law and statutes, "the unborn have never been recognized ... as persons in the whole sense", and thus, the fetuses are not legally entitled to the protection afforded by the right to life specifically enumerated in the Fourteenth Amendment. So, rather than asserting that human life begins at any specific point, the court simply declared that the State has a "compelling interest" in protecting "potential life" at the point of viability.
Doe v. Bolton
Under Roe v. Wade, state governments may not prohibit late terminations of pregnancy when "necessary to preserve the life or health of the mother", even if it would cause the demise of a viable fetus.[49] This rule was clarified by the 1973 judicial decision Doe v. Bolton, which specifies "that the medical judgment may be exercised in the light of all factors — physical, emotional, psychological, familial, and the woman's age — relevant to the well-being of the patient".[50][51][52] It is by this provision for the mother's mental health that women in the US legally choose abortion after viability when screenings reveal abnormalities that do not cause a baby to die shortly after birth.[53][54][55][56]
Later judicial decisions
In the 1992 case of Planned Parenthood v. Casey, the Court abandoned Roe's strict trimester framework but maintained its central holding that women have a right to choose to have an abortion before viability.[57] Roe had held that statutes regulating abortion must be subject to "strict scrutiny" — the traditional Supreme Court test for impositions upon fundamental Constitutional rights. Casey instead adopted the lower, undue burden standard for evaluating state abortion restrictions,[58] but re-emphasized the right to abortion as grounded in the general sense of liberty and privacy protected under the constitution: "Constitutional protection of the woman's decision to terminate her pregnancy derives from the Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment. It declares that no State shall 'deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law.' The controlling word in the cases before us is 'liberty'."[59]
The Supreme Court continues to grapple with cases on the subject. On April 18, 2007, it issued a ruling in the case of Gonzales v. Carhart, involving a federal law entitled the Partial-Birth Abortion Ban Act of 2003 which President George W. Bush had signed into law. The law banned intact dilation and extraction, which opponents of abortion rights referred to as "partial-birth abortion", and stipulated that anyone breaking the law would get a prison sentence up to 2.5 years. The United States Supreme Court upheld the 2003 ban by a narrow majority of 5-4, marking the first time the Court has allowed a ban on any type of abortion since 1973. The opinion, which came from justice Anthony Kennedy, was joined by Justices Antonin Scalia, Clarence Thomas, and the two recent appointees, Samuel Alito and Chief Justice John Roberts.
In the case of Whole Woman's Health v. Hellerstedt, the Supreme Court in a 5-3 decision on June 27, 2016 swept away forms of state restrictions on the way abortion clinics can function. The Texas legislature enacted in 2013 restrictions on the delivery of abortions services that created an undue burden for women seeking an abortion by requiring abortion doctors to have difficult-to-obtain "admitting privileges" at a local hospital and by requiring clinics to have costly hospital-grade facilities. The Court struck down these two provisions "facially" from the law at issue—that is, the very words of the provisions were invalid, no matter how they might be applied in any practical situation. According to the Supreme Court, the task of judging whether a law puts an unconstitutional burden on a woman's right to abortion belongs with the courts, and not the legislatures.[60]
The Supreme Court will hear arguments in June Medical Services, LLC v. Gee in the 2019 term, a case resulting from a Louisiana state law that was passed at a similar time as the Texas law at the center of Whole Woman's Health. Like Texas' law, the Louisiana law required certain measures for abortion clinics that, if having gone into effect, would have closed five of the six clinics in the state. The case in Louisiana was put on hold pending the result of Whole Woman's Health, and was retried based on the Supreme Court's decision. While the District Court ruled the law unconstitutional, the Fifth Circuit found that unlike the Texas law, the burden of the Louisiana law passed the tests outlined in Whole Woman's Health, and thus the law was constitutional. The Supreme Court issued an order to suspend enforcement of the law pending further review, and agreed to hear the case in full in October 2019. It will be the first abortion-related case to be heard by President Donald Trump's appointees to the Court, Neil Gorsuch and Bret Kavanaugh.[61]
Current legal status
Federal legislation
Since 1995, led by congressional Republicans, the U.S. House of Representatives and U.S. Senate have moved several times to pass measures banning the procedure of intact dilation and extraction, commonly known as partial birth abortion. Such measures passed twice by wide margins, but President Bill Clinton vetoed those bills in April 1996 and October 1997 on the grounds that they did not include health exceptions. Congressional supporters of the bill argue that a health exception would render the bill unenforceable, since the Doe v. Bolton decision defined "health" in vague terms, justifying any motive for obtaining an abortion. Congress was unsuccessful with subsequent attempts to override the vetoes.
The Born-Alive Infants Protection Act of 2002 ("BAIPA") was enacted August 5, 2002 by an Act of Congress and signed into law by George W. Bush. It asserts the human rights of infants born after a failed attempt to induce abortion. A "born-alive infant" is specified as a "person, human being, child, individual". "Born alive" is defined as the complete expulsion of an infant at any stage of development that has a heartbeat, pulsation of the umbilical cord, breath, or voluntary muscle movement, no matter if the umbilical cord has been cut or if the expulsion of the infant was natural, induced labor, cesarean section, or induced abortion.
On October 2, 2003, with a vote of 281-142, the House approved the Partial-Birth Abortion Ban Act to ban partial-birth abortion, with an exemption in cases of fatal threats to the woman. Through this legislation, a doctor could face up to two years in prison and civil lawsuits for performing such a procedure. A woman undergoing the procedure could not be prosecuted under the measure. On October 21, 2003, the United States Senate passed the bill by a vote of 64-34, with a number of Democrats joining in support. The bill was signed by President George W. Bush on November 5, 2003, but a federal judge blocked its enforcement in several states just a few hours after it became public law. The Supreme Court upheld the nationwide ban on the procedure in the case Gonzales v. Carhart on April 18, 2007, signaling a substantial change in the Court's approach to abortion law.[62] The 5-4 ruling said the Partial Birth Abortion Ban Act does not conflict with previous decisions regarding abortion.
The current judicial interpretation of the U.S. Constitution regarding abortion, following the Supreme Court of the United States's 1973 landmark decision in Roe v. Wade, and subsequent companion decisions, is that abortion is legal but may be restricted by the states to varying degrees. States have passed laws to restrict late-term abortions, require parental notification for minors, and mandate the disclosure of abortion risk information to patients prior to the procedure.[63]
The official report of the U.S. Senate Judiciary Committee, issued in 1983 after extensive hearings on the Human Life Amendment (proposed by Senators Orrin Hatch and Thomas Eagleton), stated that
Thus, the [Judiciary] Committee observes that no significant legal barriers of any kind whatsoever exist today in the United States for a mother to obtain an abortion for any reason during any stage of her pregnancy.[64]
One aspect of the legal abortion regime now in place has been determining when the fetus is "viable" outside the womb as a measure of when the "life" of the fetus is its own (and therefore subject to being protected by the state). In the majority opinion delivered by the court in Roe v. Wade, viability was defined as "potentially able to live outside the mother's womb, albeit with artificial aid. Viability is usually placed at about seven months (28 weeks) but may occur earlier, even at 24 weeks". When the court ruled in 1973, the then-current medical technology suggested that viability could occur as early as 24 weeks. Advances over the past three decades allow survival of some babies born at 22 weeks.[65]
As of 2006[update], the youngest child to survive a premature birth in the United States was a girl born at Kapiolani Medical Center in Honolulu, Hawaii at 21 weeks and 3 days gestation.[66] Because of the split between federal and state law, legal access to abortion continues to vary by state. Geographic availability varies dramatically, with 87 percent of U.S. counties having no abortion provider.[67] Moreover, due to the Hyde Amendment, many state health programs do not cover abortions; currently 17 states (including California, Illinois and New York) offer or require such coverage.[68]
The legality of abortion is frequently a major issue in nomination battles for the U.S. Supreme Court. Nominees typically remain silent on the issue during their hearings, as the issue may come before them as judges.
The Unborn Victims of Violence Act, commonly known as "Laci and Conner's Law" was passed by Congress and signed into law by President Bush on April 1, 2004, allowing two charges to be filed against someone who kills a pregnant mother (one for the mother and one for the fetus). It specifically bans charges against the mother and/or doctor relating to abortion procedures. Nevertheless, it has generated much controversy among pro-abortion rights advocates who view it as a potential step in the direction of banning abortion.
The Pain-Capable Unborn Child Protection Act is a United States Congress bill to ban late-term abortions nationwide after 20 weeks post-fertilization on the basis that the fetus is capable of feeling pain during an abortion at and after that point of pregnancy. The bill was first introduced in Congress in 2013. It successfully passed the House of Representatives in 2013, 2015, and 2017, but has yet to pass the Senate. Opponents of the bill reject the claims made by the bill's supporters regarding fetal development, and argue that such a restriction would endanger women's health.

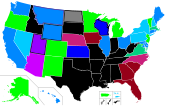
State-by-state legal status
Abortion is legal in all U.S. states, and every state has at least one abortion clinic.[69][70] Abortion is a controversial political issue, and regular attempts to restrict it occur in most states. One such case, originating in Texas, led to the Supreme Court case of Whole Woman's Health v. Hellerstedt (2016) in which several Texas restrictions were struck down.[71]
The issue of minors and abortion is regulated at the state level, and 37 states require some parental involvement, either in the form of parental consent or in the form of parental notification. In certain situations, the parental restrictions can be overridden by a court.[72] Mandatory waiting periods, mandatory ultrasounds and scripted counseling are common abortion regulations. Abortion laws are generally stricter in a conservative Southern states than they are in other parts of the country.
In 2019, New York passed the Reproductive Health Act (RHA), which repealed a pre-Roe provision that banned third-trimester abortions except in cases where the continuation of the pregnancy endangered a pregnant woman's life.[73][74]
Abortion in the Northern Mariana Islands, a United States Commonwealth territory, is illegal.
Alabama House Republicans passed a law on April 30, 2019 that will criminalize abortion if it goes into effect.[75] Dubbed the "Human Life Protection Act", it offers only two exceptions: serious health risk to the mother or a lethal fetal anomaly.[76] It will also make the procedure a Class A felony.[77] Twenty-five male Alabama senators voted to pass the law on May 13.[78] The next day, Alabama governor Kay Ivey signed the bill into law, primarily as a symbolic gesture in hopes of challenging Roe v. Wade in the Supreme Court.[79][80]
Since Alabama introduced the first modern anti-abortion legislation in April 2019, five other states have also adopted abortion laws including Mississippi, Kentucky, Ohio, Georgia and most recently Louisiana on May 30, 2019.[81]
In May 2019, the US Supreme Court upheld an Indiana state law that requires fetuses which were aborted be buried or cremated.[82] In a December 2019 case, the court declined to review a lower court decision which upheld a Kentucky law requiring doctors to perform ultrasounds and show fetal images to patients before abortions.[83]
In response to the coronavirus pandemic
Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, anti-abortion government officials in several American states enacted or attempted to enact restrictions on abortion, characterizing it as a non-essential procedure that can be suspended during the medical emergency.[84] The orders have led to several legal challenges and criticism by human rights groups and several national medical organizations, including the American Medical Association.[85] Legal challenges on behalf of abortion providers, many of which are represented by the American Civil Liberties Union and Planned Parenthood, have successfully stopped most of the orders on a temporary basis.[84]
Qualifying requirements for abortion providers




Qualifying requirements for performing abortions vary from state to state,[86] and are currently being changed in several states by lawmakers who anticipate the possibility that Roe v. Wade may soon be overturned.[87] Currently, New York,[88] Illinois,[89] and Maine[90] allow non-physician health professionals, such as physicians' assistants, nurse practitioners, and certified nurse midwives, acting within their scope of practice, to perform abortion procedures; their laws do not explicitly specify which types of abortions these non-physicians may do. California, Oregon, Montana, Vermont, and New Hampshire allow qualified non-physician health professionals to do first-trimester aspiration abortions and to prescribe drugs for medical abortions. Washington State, New Mexico, Alaska, Maryland, Massachusetts, Connecticut, and New Jersey allow qualified non-physicians to prescribe drugs for medical abortions only.[91] In all other states, only licensed physicians may perform abortions.[92] In 2016, the FDA issued new guidelines recommending that qualified non-physician health-care professionals be allowed to prescribe mifepristone in all states; however, these guidelines are not binding, and states are free to determine their own policies regarding mifepristone.[93]
Statistics
Because reporting of abortions is not mandatory, statistics are of varying reliability. Both the Centers For Disease Control (CDC)[94] and the Guttmacher Institute regularly compile these statistics.[95][96]
File:U.S. abortion rate, 1973-2014, data collected by the Guttmacher Institute.jpg
Number of abortions
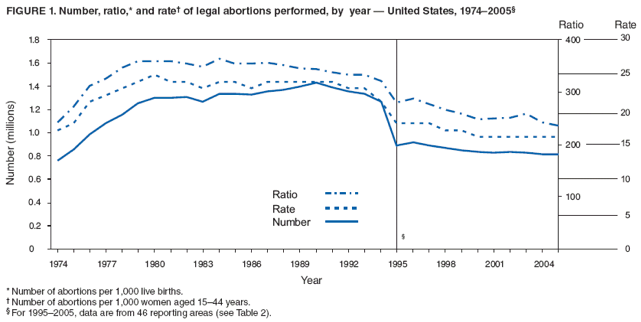
The annual number of legal induced abortions in the US doubled between 1973 and 1979, and peaked in 1990. There was a slow but steady decline throughout the 1990s. Overall, the number of annual abortions decreased by 6% between 2000 and 2009, with temporary spikes in 2002 and 2006.[97]
By 2011, abortion rate in the nation dropped to its lowest point since the Supreme Court legalized the procedure. According to a study performed by Guttmacher Institute, long-acting contraceptive methods had a significant impact in reducing unwanted pregnancies. There were fewer than 17 abortions for every 1,000 women of child-bearing age. That was a 13%-decrease from 2008's numbers and slightly higher than the rate in 1973, when the Supreme Court's Roe v. Wade decision legalized abortion. The study indicated a long-term decline in the abortion rate.[98][99][100][101]
In 2016, the CDC reported 623,471 abortions, a 2% decrease from 636,902 in 2015.[102]
Medical abortions
A Guttmacher Institute survey of abortion providers estimated that early medical abortions accounted for 17% of all non-hospital abortions and slightly over one-quarter of abortions before 9 weeks gestation in the United States in 2008.[103] Medical abortions voluntarily reported to the CDC by 34 reporting areas (excluding Alabama, California, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Hawaii, Illinois, Louisiana, Maryland, Massachusetts, Nebraska, Nevada, New Hampshire, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Vermont, Wisconsin, and Wyoming) and published in its annual abortion surveillance reports have increased every year since the September 28, 2000 FDA approval of mifepristone (RU-486): 1.0% in 2000, 2.9% in 2001, 5.2% in 2002, 7.9% in 2003, 9.3% in 2004, 9.9% in 2005, 10.6% in 2006, 13.1% in 2007, 15.8% in 2008, 17.1% in 2009 (25.2% of those at less than 9 weeks gestation).[104] Medical abortions accounted for 32% of first-trimester abortions at Planned Parenthood clinics in 2008.[105]
Abortion and religion
A majority of abortions are obtained by religiously identified women. According to the Guttmacher Institute, "more than 7 in 10 U.S. women obtaining an abortion report a religious affiliation (37% protestant, 28% Catholic, and 7% other), and 25% attend religious services at least once a month. The abortion rate for protestant women is 15 per 1,000 women, while Catholic women have a slightly higher rate, 20 per 1,000."[106]
Abortions and ethnicity
Abortion rates tend to be higher among minority women in the U.S. In 2000–2001, due to lower access to health care and contraception, the rates among black and Hispanic women were 49 per 1,000 and 33 per 1,000, respectively, vs. 13 per 1,000 among non-Hispanic white women. Note that this figure includes all women of reproductive age, including women that are not pregnant. In other words, these abortion rates reflect the rate at which U.S. women of reproductive age have an abortion each year.[107]
In 2004, the rates of abortion by ethnicity in the U.S. were 50 abortions per 1,000 black women, 28 abortions per 1,000 Hispanic women, and 11 abortions per 1,000 white women.[108][109]
Reasons for abortions
A 1998 study revealed that in 1987 to 1988, women reported the following as their primary reasons for choosing an abortion:[110][111]
| Percentage
of women |
Primary reason for choosing an abortion |
|---|---|
| 25.5% | Want to postpone childbearing |
| 21.3% | Cannot afford a baby |
| 14.1% | Has relationship problem or partner does not want pregnancy |
| 12.2% | Too young; parent(s) or other(s) object to pregnancy |
| 10.8% | Having a child will disrupt education or employment |
| 7.9% | Want no (more) children |
| 3.3% | Risk to fetal health |
| 2.8% | Risk to maternal health |
| 2.1% | Other |
The source of this information takes findings into account from 27 nations including the United States, and therefore, these findings may not be typical for any one nation.
According to a 1987 study that included specific data about late abortions (i. e., abortions "at 16 or more weeks' gestation"),[112] women reported that various reasons contributed to their having a late abortion:
| Percentage
of women |
Reasons contributing to a late abortion |
|---|---|
| 71% | Woman did not recognize she was pregnant or misjudged gestation |
| 48% | Woman had found it hard to make arrangements for an earlier abortion |
| 33% | Woman was afraid to tell her partner or parents |
| 24% | Woman took time to decide to have an abortion |
| 8% | Woman waited for her relationship to change |
| 8% | Someone had earlier pressured woman not to have abortion |
| 6% | Something changed some time after woman became pregnant |
| 6% | Woman did not know timing is important |
| 5% | Woman did not know she could get an abortion |
| 2% | A fetal problem was diagnosed late in pregnancy |
| 11% | Other. |
In 2000, cases of rape or incest accounted for 1% of abortions.[113]
A 2004 study by the Guttmacher Institute reported that women listed the following amongst their reasons for choosing to have an abortion:[111]
| Percentage
of women |
Reason for choosing to have an abortion |
|---|---|
| 74% | Having a baby would dramatically change my life |
| 73% | Cannot afford a baby now |
| 48% | Do not want to be a single mother or having relationship problems |
| 38% | Have completed my childbearing |
| 32% | Not ready for another child |
| 25% | Do not want people to know I had sex or got pregnant |
| 22% | Do not feel mature enough to raise another child |
| 14% | Husband or partner wants me to have an abortion |
| 13% | Possible problems affecting the health of the fetus |
| 12% | Concerns about my health |
| 6% | Parents want me to have an abortion |
| 1% | Was a victim of rape |
| less than .5% | Became pregnant as a result of incest |
A 2008 National Survey of Family Growth (NSFG) shows that rates of unintended pregnancy are highest among Blacks, Hispanics, and women with lower socio-economic status.[114]
- 70% of all pregnancies among Black women were unintended
- 57% of all pregnancies among Hispanic women were unintended
- 42% of all pregnancies among White women were unintended
When women have abortions (by gestational age)
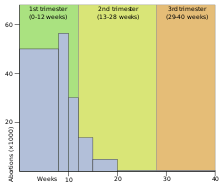
According to the Centers for Disease Control, in 2011, most (64.5%) abortions were performed by ≤8 weeks' gestation, and nearly all (91.4%) were performed by ≤13 weeks' gestation. Few abortions (7.3%) were performed between 14 and 20 weeks' gestation or at ≥21 weeks' gestation (1.4%). From 2002 to 2011, the percentage of all abortions performed at ≤8 weeks' gestation increased 6%. [115]
Safety of abortions
In the US, the risk of death from carrying a child to term is approximately 14 times greater than the risk of death from a legal abortion.[116] The risk of abortion-related mortality increases with gestational age, but remains lower than that of childbirth through at least 21 weeks' gestation.[117][118][119]
Public opinion

Americans have been equally divided on the issue; a May 2018 Gallup poll indicated that 48% of Americans described themselves as "pro-choice" and 48% described themselves as "pro-life". A July 2018 poll indicated that 64% of Americans did not want the Supreme Court to overturn Roe vs. Wade, while 28% did.[120] The same poll found that support for abortion being generally legal was 60% during the first trimester, dropping to 28% in the second trimester, and 13% in the third trimester.[121]
Support for the legalization of abortion has been consistently higher among more educated adults than less educated,[122] and in 2019, 70% of college graduates support abortion being legal in all or most cases, compared to 60% of those with some college, and 54% of those with a high school degree or less.[123]
In January 2013, a majority of Americans believed abortion should be legal in all or most cases, according to a poll by NBC News and The Wall Street Journal.[124] Approximately 70% of respondents in the same poll opposed Roe v. Wade being overturned.[124] A poll by the Pew Research Center yielded similar results.[125] Moreover, 48% of Republicans opposed overturning Roe, compared to 46% who supported overturning it.[125]
Gallup declared in May 2010 that more Americans identifying as "pro-life" is "the new normal", while also noting that there had been no increase in opposition to abortion. It suggested that political polarization may have prompted more Republicans to call themselves "pro-life".[126] The terms "pro-choice" and "pro-life" do not always reflect a political view or fall along a binary; in one Public Religion Research Institute poll, seven in ten Americans described themselves as "pro-choice" while almost two-thirds described themselves as "pro-life". The same poll found that 56% of Americans were in favor of legal access to abortion in all or some cases.[127]
| Date of poll | "Pro-life" | "Pro-choice" | Mixed / neither | Don't know what terms mean | No opinion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016, May 4–8 | 46% | 47% | 3% | 3% | 2% |
| 2015, May 6–10 | 44% | 50% | 3% | 2% | 1% |
| 2014, May 8–11 | 46% | 47% | 3% | 3% | - |
| 2013, May 2–7 | 48% | 45% | 3% | 3% | 2% |
| 2012, May 3–6 | 50% | 41% | 4% | 3% | 3% |
| 2011, May 5–8 | 45% | 49% | 3% | 2% | 2% |
| 2010, March 26–28 | 46% | 45% | 4% | 2% | 3% |
| 2009, November 20–22 | 45% | 48% | 2% | 2% | 3% |
| 2009, May 7–10 | 51% | 42% | - | 0 | 7% |
| 2008, September 5–7 | 43% | 51% | 2% | 1% | 3% |
By gender and age
Pew Research Center polling shows little change in views from 2008 to 2012; modest differences based on gender or age.[128]
(The original article's table also shows by party affiliation, religion, and education level.)
| 2011–2012 | 2009–2010 | 2007–2008 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Legal | Illegal | Don't Know | Legal | Illegal | Don't Know | Legal | Illegal | Don't Know | |
| Total | 53% | 41% | 6% | 48% | 44% | 8% | 54% | 40% | 6% |
| Men | 51% | 43% | 6% | 46% | 46% | 9% | 52% | 42% | 6% |
| Women | 55% | 40% | 5% | 50% | 43% | 7% | 55% | 39% | 5% |
| 18-29 | 53% | 44% | 3% | 50% | 45% | 5% | 52% | 45% | 3% |
| 30-49 | 54% | 42% | 4% | 49% | 43% | 7% | 58% | 38% | 5% |
| 50-64 | 55% | 38% | 7% | 49% | 42% | 9% | 56% | 38% | 6% |
| 65+ | 48% | 43% | 9% | 39% | 49% | 12% | 45% | 44% | 11% |
By educational level
Support for the legalization of abortion is significantly higher among more educated adults than less educated, and has been consistently so for decades.[122] In 2019, 70% of college graduates support abortion being legal in all or most cases, as well as 60% of those with some college education, compared to 54% of those with a high school degree or less.[123]
| 2019 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Educational attainment | Legal in all or most cases | Illegal in all or most cases |
| College grad or more | 70% | 30% |
| Some college | 60% | 39% |
| High school or less | 54% | 44% |
By gender, party, and region
A January 2003 CBS News/The New York Times poll examined whether Americans thought abortion should be legal or not, and found variations in opinion which depended upon party affiliation and the region of the country.[129] The margin of error is +/- 4% for questions answered of the entire sample ("overall" figures) and may be higher for questions asked of subgroups (all other figures).[129]
| Group | Generally available | Available, but with stricter limits than now | Not permitted |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 39% | 38% | 22% |
| Women | 37% | 37% | 24% |
| Men | 40% | 40% | 20% |
| Democrats | 43% | 35% | 21% |
| Republicans | 29% | 41% | 28% |
| Independents | 42% | 38% | 18% |
| Northeasterners | 48% | 31% | 19% |
| Midwesterners | 34% | 40% | 25% |
| Southerners | 33% | 41% | 25% |
| Westerners | 43% | 40% | 16% |
By trimester of pregnancy
A CNN/USA Today/Gallup poll in January 2003 asked about the legality of abortion by trimester, using the question, "Do you think abortion should generally be legal or generally illegal during each of the following stages of pregnancy?"[130] This same question was also asked by Gallup in March 2000 and July 1996.[131][132] Polls indicates general support of legal abortion during the first trimester, although support drops dramatically for abortion during the second and third trimester.
Since the 2011 poll, support for legal abortion during the first trimester has declined.
| 2018 Poll | 2012 Poll | 2011 Poll | 2003 Poll | 2000 Poll | 1996 Poll | |||||||
| Legal | Illegal | Legal | Illegal | Legal | Illegal | Legal | Illegal | Legal | Illegal | Legal | Illegal | |
| First trimester | 60% | 34% | 61% | 31% | 62% | 29% | 66% | 35% | 66% | 31% | 64% | 30% |
| Second trimester | 28% | 65% | 27% | 64% | 24% | 71% | 25% | 68% | 24% | 69% | 26% | 65% |
| Third trimester | 13% | 81% | 14% | 80% | 10% | 86% | 10% | 84% | 8% | 86% | 13% | 82% |
By circumstance or reasons
According to Gallup's long-time polling on abortion, the majority of Americans are neither strictly "pro-life" or "pro-choice"; it depends upon the circumstances of the pregnancy. Gallup polling from 1996 to 2009 consistently reveals that when asked the question, "Do you think abortions should be legal under any circumstances, legal only under certain circumstances, or illegal in all circumstances?", Americans repeatedly answer 'legal only under certain circumstances'. According to the poll, in any given year 48-57% say legal only under certain circumstances (for 2009, 57%), 21-34% say legal under any circumstances (for 2009, 21%), and 13-19% illegal in all circumstances (for 2009, 18%), with 1-7% having no opinion (for 2009, 4%).[131]
"Do you think abortions should be legal under any circumstances, legal only under certain circumstances, or illegal in all circumstances?"
| Legal under any circumstances | Legal only under certain circumstances | Illegal in all circumstances | No opinion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 May 1–10 | 29% | 50% | 18% | 2% |
| 2017 May 3–7 | 29% | 50% | 18% | 3% |
| 2016 May 4–8 | 29% | 50% | 19% | 2% |
| 2015 May 6–10 | 29% | 51% | 19% | 1% |
| 2014 May 8–11 | 28% | 50% | 21% | 2% |
| 2013 May 2–7 | 26% | 52% | 20% | 2% |
| 2012 Dec 27-30 | 28% | 52% | 18% | 3% |
| 2012 May 3–6 | 25% | 52% | 20% | 3% |
| 2011 Jul 15-17 | 26% | 51% | 20% | 3% |
| 2011 June 9–12 | 26% | 52% | 21% | 2% |
| 2011 May 5–8 | 27% | 49% | 22% | 3% |
| 2009 Jul 17-19 | 21% | 57% | 18% | 4% |
| 2009 May 7–10 | 22% | 53% | 23% | 2% |
| 2008 May 8–11 | 28% | 54% | 18% | 2% |
| 2007 May 10–13 | 26% | 55% | 17% | 1% |
| 2006 May 8–11 | 30% | 53% | 15% | 2% |
According to the aforementioned poll,[131] Americans differ drastically based upon situation of the pregnancy, suggesting they do not support unconditional abortions. Based on two separate polls taken May 19–21, 2003, of 505 and 509 respondents respectively, Americans stated their approval for abortion under these various circumstances:
| Poll Criteria | Total | Poll A | Poll B |
|---|---|---|---|
| When the woman's life is endangered | 78% | 82% | 75% |
| When the pregnancy was caused by rape or incest | 65% | 72% | 59% |
| When the child would be born with a life-threatening illness | 54% | 60% | 48% |
| When the child would be born mentally disabled | 44% | 50% | 38% |
| When the woman does not want the child for any reason | 32% | 41% | 24% |
Another separate trio of polls taken by Gallup in 2003, 2000, and 1996,[131] revealed public support for abortion as follows for the given criteria:
| Poll criteria | 2003 Poll | 2000 Poll | 1996 Poll |
|---|---|---|---|
| When the woman's life is endangered | 85% | 84% | 88% |
| When the woman's physical health is endangered | 77% | 81% | 82% |
| When the pregnancy was caused by rape or incest | 76% | 78% | 77% |
| When the woman's mental health is endangered | 63% | 64% | 66% |
| When there is evidence that the baby may be physically impaired | 56% | 53% | 53% |
| When there is evidence that the baby may be mentally impaired | 55% | 53% | 54% |
| When the woman or family cannot afford to raise the child | 35% | 34% | 32% |
Gallup furthermore established public support for many issues supported by the anti-abortion community and opposed by the abortion rights community:[131]
| Legislation | 2003 Poll | 2000 Poll | 1996 Poll |
|---|---|---|---|
| A law requiring doctors to inform patients about alternatives to abortion before performing the procedure | 88% | 86% | 86% |
| A law requiring women seeking abortions to wait 24 hours before having the procedure done | 78% | 74% | 73% |
| Legislation | 2005 Poll | 2003 Poll | 1996 Poll | 1992 Poll |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A law requiring women under 18 to get parental consent for any abortion | 69% | 73% | 74% | 70% |
| A law requiring that the husband of a married woman be notified if she decides to have an abortion | 64% | 72% | 70% | 73% |
An October 2007 CBS News poll explored under what circumstances Americans believe abortion should be allowed, asking the question, "What is your personal feeling about abortion?" The results were as follows:[130]
| Permitted in all cases | Permitted, but subject to greater restrictions than it is now | Only in cases such as rape, incest, or to save the woman's life | Only permitted to save the woman's life | Never | Unsure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26% | 16% | 34% | 16% | 4% | 4% |
Additional polls

- A June 2000 Los Angeles Times survey found that, although 57% of polltakers considered abortion to be murder, half of that 57% believed in allowing women access to abortion. The survey also found that, overall, 65% of respondents did not believe abortion should be legal after the first trimester, including 72% of women and 58% of men. Further, the survey found that 85% of Americans polled supported abortion in cases of risk to a woman's physical health, 54% if the woman's mental health was at risk, and 66% if a congenital abnormality was detected in the fetus.[134]
- A July 2002 Public Agenda poll found that 44% of men and 42% of women thought that "abortion should be generally available to those who want it", 34% of men and 35% of women thought that "abortion should be available, but under stricter than limits it is now", and 21% of men and 22% of women thought that "abortion should not be permitted".[135]
- A January 2003 ABC News/The Washington Post poll also examined attitudes towards abortion by gender. In answer to the question, "On the subject of abortion, do you think abortion should be legal in all cases, legal in most cases, illegal in most cases or illegal in all cases?", 25% of women responded that it should be legal in "all cases", 33% that it should be legal in "most cases", 23% that it should be illegal in "most cases", and 17% that it should be illegal in "all cases". 20% of men thought it should be legal in "all cases", 34% legal in "most cases", 27% illegal in "most cases", and 17% illegal in "all cases".[135]
- Most Fox News viewers favor both parental notification as well as parental consent, when a minor seeks an abortion. A Fox News poll in 2005 found that 78% of people favor a notification requirement, and 72% favor a consent requirement.[136]
- An April 2006 Harris poll on Roe v. Wade, asked, "In 1973, the U.S. Supreme Court decided that states' laws which made it illegal for a woman to have an abortion up to three months of pregnancy were unconstitutional, and that the decision on whether a woman should have an abortion up to three months of pregnancy should be left to the woman and her doctor to decide. In general, do you favor or oppose this part of the U.S. Supreme Court decision making abortions up to three months of pregnancy legal?", to which 49% of respondents indicated favor while 47% indicated opposition. The Harris organization has concluded from this poll that, "49 percent now support Roe vs. Wade".[137]
- Two polls were released in May 2007 asking Americans "With respect to the abortion issue, would you consider yourself to be pro-choice or pro-life?" May 4–6, a CNN poll found 45% said "pro-choice" and 50% said pro-life.[138] Within the following week, a Gallup poll found 50% responding "pro-choice" and 44% pro-life.[139]
- In 2011, a poll conducted by the Public Religion Research Institute found that 43% of respondents identified themselves as both "pro-life" and "pro-choice".[140]
"Partial birth abortion"
"Partial-Birth abortion" is nomenclature for a procedure called intact dilation and extraction generally used by those who oppose the procedure. A Rasmussen Reports poll four days after the Supreme Court's opinion in Gonzales v. Carhart found that 40% of respondents "knew the ruling allowed states to place some restrictions on specific abortion procedures." Of those who knew of the decision, 56% agreed with the decision and 32% were opposed.[141] An ABC poll from 2003 found that 62% of respondents thought partial-birth abortion should be illegal; a similar number of respondents wanted an exception "if it would prevent a serious threat to the woman's health".
Gallup has repeatedly queried the American public on this issue, as seen on its Abortion page:[131]
| Legislation | 2003 | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 | 1999 | 1998 | 1997 | 1996 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A law which would make it illegal to perform a specific abortion procedure conducted in the last six months (or second and/or third trimester) of pregnancy known by some opponents as a partial birth abortion, except in cases necessary to save the life of the mother | 70% | 63% | 66% | 64% | 61% | 61% | 55% | 57% |
Abortion financing

Navy blue: Medicaid covers medically necessary abortion for low-income women through legislation
Royal blue: Medicaid covers medically necessary abortions for low-income women under court order
Gray: Medicaid denies abortion coverage for low-income women except for cases of rape, incest, or life endangerment.
The abortion debate has also been extended to the question of who pays the medical costs of the procedure, with some states using the mechanism as a way of reducing the number of abortions. The cost of an abortion varies depending on factors such as location, facility, timing, and type of procedure. In 2005, a non-hospital abortion at 10 weeks' gestation ranged from $90 to $1,800 (average: $430), whereas an abortion at 20 weeks' gestation ranged from $350 to $4,520 (average: $1,260). Costs are higher for a medical abortion than a first-trimester surgical abortion.
Medicaid
The Hyde Amendment is a federal legislative provision barring the use of federal Medicaid funds to pay for abortions except for rape and incest.[142] The provision, in various forms, was in response to Roe v. Wade, and has been routinely attached to annual appropriations bills since 1976, and represented the first major legislative success by the pro-life movement. The law requires that states cover abortions under Medicaid in the event of rape, incest, and life endangerment. Based on the federal law:
- 32 states and D. C. fund abortions through Medicaid only in the cases of rape, incest, or life endangerment. SD covers abortions only in the cases of life endangerment, which does not comply with federal requirements under the Hyde Amendment. IN, UT, and WI have expanded coverage to women whose physical health is jeopardized, and IA, MS, UT, and VA also include fetal abnormality cases.
- 17 states (AK, AZ, CA, CT, HI, IL, MD, MA, MN, MT, NJ, NM, NY, OR, VT, WA, WV) use their own funds to cover all or most "medically necessary" abortions sought by low-income women under Medicaid, 12 of which are required by State court orders to do so.[143]
Private insurance
- 5 states (ID, KY, MO, ND, OK) restrict insurance coverage of abortion services in private plans: OK limits coverage to life endangerment, rape or incest circumstances; and the other four states limit coverage to cases of life endangerment.
- 11 states (CO, KY, MA, MS, NE, ND, OH, PA, RI, SC, VA) restrict abortion coverage in insurance plans for public employees, with CO and KY restricting insurance coverage of abortion under any circumstances.
- U.S. laws also ban federal funding of abortions for federal employees and their dependents, Native Americans covered by the Indian Health Service, military personnel and their dependents, and women with disabilities covered by Medicare.[144]
Under this policy, US federal funding to NGOs that provide abortion is not permitted.
Positions of U.S. political parties
Though members of both major political parties come down on either side of the issue, the Republican Party is often seen as being anti-abortion, since the official party platform opposes abortion and considers unborn children to have an inherent right to life. Republicans for Choice represents the minority of that party. In 2006, pollsters found that 9% of Republicans favor the availability of abortion in most circumstances.[145] Of Republican National Convention delegates in 2004, 13% believed that abortion should be generally available, and 38% believed that it should not be permitted. The same poll showed that 17% of all Republican voters believed that abortion should be generally available to those who want it, while 38% believed that it should not be permitted.[146]
The Democratic Party platform considers abortion to be a woman's right. Democrats for Life of America represents the minority of that party. In 2006, pollsters found that 74% of Democrats favor the availability of abortion in most circumstances.[145] However, a Zogby International poll in 2004 found that 43% of all Democrats believed that abortion "destroys a human life, and is manslaughter".[147] Of Democratic National Convention delegates in 2004, 75% believed that abortion should be generally available, and 2% believed that abortion should not be permitted. The same poll showed that 49% of all Democratic voters believed that abortion should be generally available to those who want it, while 13% believed that it should not be permitted.[148]
The Green Party of the United States supports legal abortion as a woman's right.
The Libertarian Party platform (2012) states that "government should be kept out of the matter, leaving the question to each person for their conscientious consideration".[149] Abortion is a contentious issue among Libertarians, and the Maryland-based organization Libertarians for Life opposes the legality of abortion in most circumstances.
The issue of abortion has become deeply politicized: in 2002, 84% of state Democratic platforms supported the right to having an abortion while 88% of state Republican platforms opposed it. This divergence also led to Christian Right organizations like Christian Voice, Christian Coalition and Moral Majority having an increasingly strong role in the Republican Party. This opposition has been extended under the Foreign Assistance Act: in 1973 Jesse Helms introduced an amendment banning the use of aid money to promote abortion overseas, and in 1984 the Mexico City Policy prohibited financial support to any overseas organization that performed or promoted abortions. The "Mexico City Policy" was revoked by President Bill Clinton and subsequently reinstated by President George W. Bush. President Barack Obama overruled this policy by Executive Order on January 23, 2009,[citation needed] and it was reinstated on January 23, 2017, by President Donald Trump.
Effects of legalization

The risk of death due to legal abortion has fallen considerably since legalization in 1973, due to increased physician skills, improved medical technology, and earlier termination of pregnancy.[150] From 1940 through 1970, deaths of pregnant women during abortion fell from nearly 1,500 to a little over 100.[150] According to the Centers for Disease Control, the number of women who died in 1972 from illegal abortion was thirty-nine.[151]
The Roe effect is an hypothesis which suggests that since supporters of abortion rights cause the erosion of their own political base by having fewer children, the practice of abortion will eventually lead to the restriction or illegalization of abortion. The legalized abortion and crime effect is another controversial theory that posits legal abortion reduces crime, because unwanted children are more likely to become criminals.
Since Roe v. Wade, there have been numerous attempts to reverse the decision. In the 2011 election season, Mississippi placed an amendment on the ballot that redefine how the state viewed abortion. The personhood amendment defined personhood as "every human being from the moment of fertilization, cloning or the functional equivalent thereof". If passed, it would have been illegal to get an abortion in the state.[152]
On July 11, 2012, a Mississippi federal judge ordered an extension of his temporary order to allow the state's only abortion clinic to stay open. The order will stay in place until U.S. District Judge Daniel Porter Jordan III can review newly drafted rules on how the Mississippi Department of Health will administer a new abortion law. The law in question came into effect on July 1, 2012.[153]
According to a 2019 study, if Roe v. Wade is reversed and abortion bans are implemented in trigger law states and states considered highly likely to ban abortion, the increases in travel distance are estimated to prevent 93,546 to 143,561 women from accessing abortion care.[154]
Unintended live birth
Although it is uncommon, women sometimes give birth in spite of an attempted abortion.[155][156][157][158][159][160][161] Reporting of livebirth after attempted abortion may not be consistent from state to state, but 38 were recorded in one study in upstate New York in the two-and-a-half years before Roe v. Wade.[162] Under the Born-Alive Infants Protection Act of 2002, medical staff must report live birth if they observe any breathing, heartbeat, umbilical cord pulsation, or confirmed voluntary muscle movement, regardless of whether the born-alive is non-viable ex utero in the long term because of birth defects, and regardless of gestational age, including gestational ages which are too early for long-term viability ex utero.[163][164][165][166][167]
See also
- Abortion and religion
- Abortion by country
- Anti-abortion violence in the United States
- Catholic Church and abortion in the United States
- Feminism in the United States
- Reproductive rights
- Types of abortion restrictions in the United States
- War on Women
- Notable cases
- Becky Bell, an American teenage girl who died as a result of an unsafe abortion in 1988.
- Sherri Finkbine, an actress who had difficulty seeking an abortion for her Thalidomide deformed baby.
- Gerardo Flores, convicted in 2005 on two counts of capital murder for giving his girlfriend, who was carrying twins, an at-home abortion.
- Rosie Jimenez, an American woman who died the first recorded death due to an illegal abortion after federal Medicaid funds for abortions were removed by the Hyde Amendment.
- Gerri Santoro, an American woman who died because of an illegal abortion in 1964.
References
- ^ Alesha Doan (2007). Opposition and Intimidation: The Abortion Wars and Strategies of Political Harassment. University of Michigan Press. p. 57. ISBN 9780472069750.
- ^ Casey, 505 U.S. at 877.
- ^ a b Iati, Marisa (November 27, 2019). "Birthrates in the U.S. are falling. Abortions have also hit an all-time low". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on December 1, 2019. Retrieved January 18, 2020.
In 2016, there were 11.6 abortions per 1,000 women, ... Almost two-thirds of abortions in 2016 were performed at or before eight weeks of gestation, and 91 percent were performed at or before 13 weeks.
- ^ a b Jatlaoui, Tara C.; Eckhaus, Lindsay; Mandel, Michele G.; Nguyen, Antoinette; Oduyebo, Titilope; Petersen, Emily; Whiteman, Maura K. (November 29, 2019). "Abortion Surveillance — United States, 2016". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 68 (11): 1–41. doi:10.15585/mmwr.ss6811a1. PMID 31774741. Archived from the original on November 29, 2019. Retrieved January 18, 2020.
Among these 48 reporting areas, the abortion rate for 2016 was 11.6 abortions per 1,000 women aged 15–44 years, ... In 2016, almost two-thirds (65.5%) of abortions were performed at ≤8 weeks' gestation, and nearly all (91.0%) were performed at ≤13 weeks' gestation.
- ^ Saad, Lydia (August 8, 2011). "Plenty of Common Ground Found in Abortion Debate". Gallup.com. Retrieved August 8, 2013.
- ^ Jeffrey Jones (June 11, 2018). "U.S. Abortion Attitudes Remain Closely Divided". Gallup.
- ^ "Abortion | Gallup Historical Trends". Gallup.com. June 22, 2007. Retrieved August 10, 2014.
- ^ According to the Supreme Court's decision in Roe v. Wade:
(a) For the stage prior to approximately the end of the first trimester, the abortion decision and its effectuation must be left to the medical judgment of the pregnant woman's attending physician.
(b) For the stage subsequent to approximately the end of the first trimester, the State, in promoting its interest in the health of the mother, may, if it chooses, regulate the abortion procedure in ways that are reasonably related to maternal health.
(c) For the stage subsequent to viability, the State in promoting its interest in the potentiality of human life may, if it chooses, regulate, and even proscribe, abortion except where it is necessary, in appropriate medical judgment, for the preservation of the life or health of the mother.
Likewise, Black's Law Dictionary defines abortion as "knowing destruction" or "intentional expulsion or removal".
- ^ Watson, Katie (December 20, 2019). "Why We Should Stop Using the Term "Elective Abortion"". AMA Journal of Ethics. 20 (12): 1175–1180. doi:10.1001/amajethics.2018.1175. PMID 30585581.
- ^ Linton, P. B. (1989). "Roe v. Wade and the history of abortion regulation". American Journal of Law & Medicine. Vol. 15, no. 2–3. pp. 227–33. PMID 2690604.
- ^ Levene, Malcolm et al. Essentials of Neonatal Medicine (Blackwell 2000), page 8. Retrieved February 15, 2007.
- ^ Buell, Samuel (1991). "Criminal Abortion Revisited". New York University Law Review. 66:1774 (6): 1774–831. PMID 11652642 – via duke.edu.
- ^ Alford, Suzanne M. (2003). "Is Self-Abortion a Fundamental Right?". Duke Law Journal. 52 (5): 1011–29. JSTOR 1373127. PMID 12964572. Archived from the original on 2019-01-22. Retrieved 2007-01-21.
- ^ a b James C. Mohr (1978). Abortion in America: The Origins and Evolution of National Policy. Oxford University Press. pp. 35–36. ISBN 978-0195026160.
- ^ James C. Mohr (1978). Abortion in America: The Origins and Evolution of National Policy. Oxford University Press. p. 34. ISBN 978-0195026160.
- ^ James C. Mohr (1978). Abortion in America: The Origins and Evolution of National Policy. Oxford University Press. pp. 76–82. ISBN 978-0195026160.
- ^ James C. Mohr (1978). Abortion in America: The Origins and Evolution of National Policy. Oxford University Press. pp. 100–101. ISBN 978-0195026160.
- ^ Gordon, Sarah Barringer. "Law and Everyday Death: Infanticide and the Backlash against Woman's Rights after the Civil War." Lives of the Law. Austin Sarat, Lawrence Douglas, and Martha Umphrey, Editors. (University of Michigan Press 2006) p. 67
- ^ a b Schiff, Stacy. "Desperately Seeking Susan." October 13, 2006, The New York Times. Retrieved February 5, 2009.
- ^ "Marriage and Maternity". The Revolution. Susan B. Anthony. July 8, 1869. Retrieved April 21, 2009.
- ^ Susan B. Anthony, "Marriage and Maternity", Archived October 5, 2011, at the Wayback Machine The Revolution (July 8, 1869), via University Honors Program, Syracuse University.
- ^ Federer, William. American Minute, page 81 (Amerisearch 2003).
- ^ James C. Mohr (1978). Abortion in America: The Origins and Evolution of National Policy. Oxford University Press. p. 110. ISBN 978-0195026160.
- ^ a b James C. Mohr (1978). Abortion in America: The Origins and Evolution of National Policy. Oxford University Press. p. 112. ISBN 978-0195026160.
- ^ Hartmann, B (1997). "Population control I: Birth of an ideology". International Journal of Health Services. 27 (3): 523–40. doi:10.2190/bl3n-xajx-0yqb-vqbx. PMID 9285280.
- ^ Lewis, Jone Johnson. "Abortion History: A History of Abortion in the United States". Women's History section of About.com. About.com. Retrieved July 7, 2006.
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/anthonycomstockh00bennuoft#page/1017/mode/1up Anthony Comstock: His Career of Cruelty and Crime A Chapter from "Champions of the Church". DeRobigne Mortimer Bennett. 1878.
- ^ Kevles, Daniel J. (July 22, 2001). "The Secret History of Birth Control". The New York Times. Retrieved October 21, 2006.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ "A Political, Public & Moral Look at Abortion". New York University. New York University. February 28, 2006. Retrieved February 16, 2016.
- ^ Kathryn Cullen-DuPont (August 1, 2000). Encyclopedia of women's history in America. Infobase Publishing. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-8160-4100-8. Retrieved November 28, 2011.
- ^ "American Rhetoric: Margaret Sanger—The Morality of Birth Control". americanrhetoric.com. Retrieved August 8, 2015.
- ^ Boyer, Paul S., ed. (2006). The Oxford companion to United States history. Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-19-508209-8.
- ^ "Sherri Finkbine's Abortion: Its Meaning 50 Years Later". Planned Parenthood Advocates of Arizona. August 15, 2012. Retrieved December 2, 2017.
- ^ Braun, Whitny (December 29, 2015). "Thalidomide: The Connection Between a Statue in Trafalgar Square, a 1960s Children's Show Host and the Abortion Debate". Huffington Post. Retrieved December 2, 2017.
- ^ "Click - Debating Reproductive Rights - Reproductive Rights and Feminism, History of Abortion Battle, History of Abortion Debate, Roe v. Wade and Feminists". www.cliohistory.org. Retrieved December 2, 2017.
- ^ Johnson, Linnea. "Something Real: Jane and Me. Memories and Exhortations of a Feminist Ex-Abortionist". CWLU Herstory Project. Archived from the original on July 25, 2011. Retrieved May 23, 2010.
- ^ Griswold v. Connecticut, 381 U.S. 479 (1965).
- ^ Eisenstadt v. Baird, 405 U.S. 438 (1972).
- ^ American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Terminology Bulletin. Terms Used in Reference to the Fetus. No. 1. Philadelphia: Davis, September 1965.
- ^ "Medicine: Abortion on Request". Time. March 9, 1970. Retrieved October 15, 2012. (subscription required)
- ^ "Abortion Reform in Washington State - HistoryLink.org". www.historylink.org. Retrieved October 9, 2017.
- ^ Kliff, Sarah (January 22, 2013). "CHARTS: How Roe v. Wade changed abortion rights". The Washington Post.
- ^ Cassidy, Keith (1995). "The Right to Life Movement". In Donald T. Critchlow (ed.). The Politics of Abortion and Birth Control in Historical Perspective. Issues in Policy History. Penn State Press. p. 140. ISBN 9780271015705.
- ^ Staggenborg, Suzanne (1994). The Pro-Choice Movement: Organization and Activism in the Abortion Conflict. Oxford University Press. p. 35. ISBN 9780195089257.
- ^ "Content Module Example Page".
- ^ Lessons from Before Roe: Will Past be Prologue? The Guttmacher Policy Review, Vol. 6 Iss. 1, March 1, 2003. Retrieved January 11, 2017.
- ^ Roe v. Wade, 410 U.S. 113, 154 (1973) "We, therefore, conclude that the right of personal privacy includes the abortion decision, but that this right is not unqualified, and must be considered against important state interests in regulation."
- ^ Roe v. Wade, 410 U.S. 113[permanent dead link] (1972). Findlaw.com. Retrieved April 14, 2011.
- ^ Roe v. Wade, 410 U.S. 113, 164 (1973) ("If the State is interested in protecting fetal life after viability, it may go so far as to proscribe abortion during [the third trimester], except when it is necessary to preserve the life or health of the mother.")
- ^ Doe v. Bolton, 410 U.S. 179, 192 (1973)
- ^ "Frontline / Abortion Wars / Roe v Wade and Beyond". www.pbs.org. Retrieved October 5, 2015.
- ^ "The Right to Choose at 25: Looking Back and Ahead". www.aclu.org. Retrieved October 5, 2015.
- ^ Dailard, Cynthia (June 1999). "Issues and Implications, Abortion Restrictions and the Drive for Mental Health Parity: A Conflict in Values?". The Guttmacher Report on Public Policy. 2 (3). Retrieved October 2, 2015.
- ^ Palley, Marian Lief and Howard (2014). The Politics of Women's Health Care in the US. New York and London: Palgrave Pivot. p. 74. ISBN 9781137008633. Retrieved October 5, 2015.
- ^ "Abortion after the First Trimester in the United States" (PDF). Planned Parenthood. February 2014. Retrieved October 5, 2015.
- ^ "Fetal Viability And Late-Term Abortion: The Facts And The Law". www.democraticunderground.com. Retrieved October 5, 2015.
- ^ Planned Parenthood v. Casey, 505 U.S. 833, 878 (1992)
- ^ Planned Parenthood v. Casey, 505 U.S. 833, 878 (1992) ("(a) To protect the central right recognized by Roe v. Wade while at the same time accommodating the State's profound interest in potential life, we will employ the undue burden analysis as explained in this opinion. An undue burden exists, and therefore, a provision of law is invalid, if its purpose or effect is to place a substantial obstacle in the path of a woman seeking an abortion before the fetus attains viability.")
- ^ Planned Parenthood v. Casey, 505 U.S. 833, 846 (1992)
- ^ Denniston, Lyle (June 27, 2016). "Whole Woman's Health v. Hellerstedt - Opinion analysis: Abortion rights reemerge strongly". SCOTUSblog. Retrieved June 29, 2016.
- ^ Barnes, Robert (October 4, 2019). "Supreme Court to review ruling on Louisiana abortion law". The Washington Post. Retrieved October 4, 2019.
- ^ Greenhouse, Linda (April 19, 2007). "Justices Back Ban on Method of Abortion". The New York Times. Retrieved January 3, 2010.
- ^ Interactive maps comparing U.S. abortion restrictions by state, LawServer
- ^ Report, Committee on the Judiciary, U.S. Senate, on Senate Joint Resolution 3, 98th Congress, 98-149, June 7, 1983, p. 6.
- ^ "Perinatal Management of Extreme Preterm Birth before 27 weeks of gestation A Framework for Practice" (PDF). British Association of Perinatal Medicine. October 2019. Retrieved December 4, 2019.
- ^ Baptist Hospital of Miami, Fact Sheet at the Wayback Machine (archived March 26, 2009). (archived from the original on March 26, 2009)
- ^ "Access to Abortion" (PDF). National Abortion Federation. 2003. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 19, 2007. Retrieved June 17, 2007.
- ^ ""Public Funding for Abortion" (map)" (PDF). Retrieved August 8, 2013.
- ^ "Using Abortion Pills for Safe Abortion in the USA. Self-Managed Abortion; Safe and Supported (SASS). — Women Help Women Consultation". Consult.womenhelp.org. January 12, 2017. Retrieved July 21, 2017.
- ^ Politics (February 10, 2017). "Here's how many abortion clinics are in each state". Business Insider. Retrieved July 21, 2017.
- ^ "Strict Texas abortion law struck down". BBC News. June 27, 2016 – via www.bbc.com.
- ^ "Parental Involvement in Minors' Abortions". March 14, 2016.
- ^ "New York Dems Flex Muscles, Pass Reproductive Health Act". CBSNewYork. January 22, 2019.
- ^ Russo, Amy (January 23, 2019). "Andrew Cuomo Signs Abortion Bill Into Law, Codifying Roe v. Wade". Huffington Post.
- ^ Stracqualursi, Veronica (May 1, 2019). "Alabama House passes bill that would make abortion a felony". CNN. Retrieved May 2, 2019.
- ^ Elliott, Debbie (May 1, 2019). "Alabama Lawmakers Move To Outlaw Abortion In Challenge To Roe V. Wade". NPR.org. Retrieved May 6, 2019.
- ^ Smith, Kate (May 13, 2019). "Ahead of Alabama abortion bill debate, Lieutenant Governor fights against rape and incest exceptions". CBS News. Retrieved May 14, 2019.
- ^ Garrand, Danielle (May 15, 2019). "Alabama just criminalized abortions – and every single yes vote was cast by a white man". CBS News. Retrieved May 15, 2019.
- ^ Kelly, Caroline (May 15, 2019). "Alabama governor signs nation's most restrictive anti-abortion bill into law". CNN. Retrieved May 15, 2019.
- ^ Rambaran, Vandana (May 15, 2019). "Alabama 'has gone too far' with 'extreme' abortion bill, Pat Robertson says". Fox News. Retrieved May 15, 2019.
- ^ "Louisiana's Democratic governor signs abortion ban into law". Associated Press. NBC News. May 30, 2019. Retrieved August 27, 2019.
- ^ "Supreme Court Upholds Indiana Provision Mandating Fetal Burial or Cremation".
- ^ "Supreme Court declines to hear Kentucky ultrasound law". December 9, 2019.
- ^ a b Gold, Hannah (April 7, 2020). "Every State That's Tried to Ban Abortion Over the Coronavirus". The Cut. Retrieved April 7, 2020.
- ^ "In Texas, Oklahoma, Women Turned Away Because Of Coronavirus Abortion Bans". NPR.org. Retrieved April 8, 2020.
- ^ Advancing access to abortion care. ANSIRH (January 24, 2013). Retrieved on 2015-04-12.
- ^ North, Anna (June 12, 2019). "While some states try to ban abortion, these states are expanding access". Vox.
- ^ Burke, Michael (January 22, 2019). "New York passes bill expanding abortion access". TheHill.
- ^ Caroline Kelly. "Illinois governor signs sweeping abortion protection bill into law". CNN.
- ^ "Maine expands list of abortion providers". Associated Press. June 10, 2019. Archived from the original on June 11, 2019. Retrieved September 19, 2019.
Maine is making it easier to get an abortion with the governor's signing of a bill Monday to allow medical professionals who are not doctors to perform the procedure. The bill, which Democratic Gov. Janet Mills introduced herself, will go into effect 90 days after the Legislature adjourns, which is expected in mid-June. Maine is now set to allow nurse practitioners, physician assistants and certified nurse-midwives to provide abortion medication and perform in-clinic abortions, which typically involve suction. ... Maine will be the second state after California with a law allowing non-doctors to perform in-clinic abortions, according to Maine's Office of Policy and Legal Analysis.
- ^ "Study: Abortions Are Safe When Performed By Nurse Practitioners, Physician Assistants, Certified Nurse Midwives". Retrieved January 25, 2017.
- ^ Technically, Colorado, Kansas, and West Virginia do not have laws forbidding non-physicians from doing abortions, but liability issues effectively prevent non-physicians from doing them in these states.
- ^ "FDA relaxes guidelines for abortion pill - The Portland Press Herald". March 30, 2016. Retrieved January 25, 2017.
- ^ "CDCs Abortion Surveillance System FAQs". Center for Disease Control and Prevention. November 21, 2012. Retrieved August 8, 2013.
- ^ Jones, Rachel K.; Kooistra, Kathryn (March 2011). "Abortion Incidence and Access to Services in the United States, 2008" (PDF). Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health. 43 (1): 41–50. doi:10.1363/4304111. PMID 21388504. Retrieved December 8, 2017.
- ^ Jones, Rachel K.; Jerman, Jenna (March 2011). "Abortion Incidence and Service Availability in the United States, 2014" (PDF). Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health. 49 (1): 17–27. doi:10.1363/psrh.12015. PMC 5487028. PMID 28094905. Retrieved December 8, 2017.
- ^ D. Elam-Evans, Ph.D., Laurie (2003). "Abortion Surveillance --- United States, 2000". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Surveillance Summaries (Washington, D.C. : 2002). 52 (12). Center for Disease Control: 1–32. PMID 14647014. Retrieved October 2, 2013.
- ^ Somashekhar, Sandhya (February 2, 2014). "Study: Abortion rate at lowest point since 1973". Washington Post. Retrieved February 3, 2014.
- ^ Moon, Angela (February 2, 2014). "U.S. abortion rate hits lowest level since 1973: study". Reuters. Retrieved February 3, 2014.
- ^ Bassett, Laura (February 2, 2014). "U.S. Abortion Rate Hits Lowest Point Since 1973". Huffington Post. Retrieved February 3, 2014.
- ^ Jayson, Sharon (February 2, 2014). "Abortion rate at lowest level since 1973". USA Today. Retrieved February 3, 2014.
- ^ Jatlaoui, TC; Eckhaus, L; Mandel, MG; Nguyen, A; Oduyebo, T; Petersen, Emily; Whiteman, MK (November 29, 2019). "Abortion Surveillance — United States, 2016". MMWR. Surveillance Summaries. 68 (11): 1–41. doi:10.15585/mmwr.ss6811a1. ISSN 1546-0738. PMID 31774741.
- ^ Jones, Rachel K.; Kooistra, Kathryn (March 2011). "Abortion incidence and access to services in the United States, 2008" (PDF). Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health. 43 (1): 41–50. doi:10.1363/4304111. PMID 21388504. 94% of non-hospital medical abortions used mifepristone and misoprostol—6% used methotrexate and misoprostol—in the United States in 2008.
- ^ Pazol, Karen; Creanga, Andreea A.; Zane, Suzanne B.; Burley, Kim D.; Jamieson, Denise J; Division of Reproductive Health (November 23, 2012). "Abortion surveillance - United States, 2009" (PDF). MMWR Surveillance Summaries. 61 (8): 1–44. PMID 23169413.
- ^ Fjerstad, Mary; Trussell, James; Sivin, Irving; Lichtenberg, E. Steve; Cullins, Vanessa (July 9, 2009). "Rates of serious infection after changes in regimens for medical abortion". New England Journal of Medicine. 361 (2): 145–151. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0809146. PMC 3568698. PMID 19587339.
- ^ Jones, Rachel K (June 2011). "Changes in Abortion Rates Between 2000 and 2008 and Lifetime Incidence of Abortion". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 117 (6): 1358–1366. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e31821c405e. PMID 21606746.
- ^ Guttmacher.org"Get "In the Know": Questions About Pregnancy, Contraception and Abortion". Archived from the original on March 11, 2008. Retrieved April 26, 2007.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Abortion Rate Falls, But Not Equally for All Women, Time magazine, September 23, 2008
- ^ Abortion and Women of Color: The Bigger Picture, Guttmacher Policy Review, Volume 11, Issue 3
- ^ Bankole, Akinrinola; Singh, Susheela; Haas, Taylor (1998). "Reasons Why Women Have Induced Abortions: Evidence from 27 Countries". International Family Planning Perspectives. 24 (3): 117–27, 152. doi:10.2307/3038208. JSTOR 3038208.
- ^ a b Finer, Lawrence B.; Frohwirth, Lori F.; Dauphinee, Lindsay A.; Singh, Susheela; Moore, Ann M. (September 2005). "Reasons U.S. Women Have Abortions: Quantitative and Qualitative Perspectives" (PDF). Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health. 37 (3): 110–8. doi:10.1111/j.1931-2393.2005.tb00045.x. JSTOR 3650599. PMID 16150658.
- ^ Torres, Aida; Forrest, Jacqueline Darroch (Jul–Aug 1988). "Why Do Women Have Abortions?". Family Planning Perspectives. 20 (4): 169–76. doi:10.2307/2135792. JSTOR 2135792. PMID 3243347. S2CID 25224865.
Some 42 facilities were originally invited to participate in the study; these include six at which a relatively large number of late abortions (those at 16 or more weeks' gestation) were performed.
- ^ "Induced Abortion Facts in Brief" (2002) (13,000 out of 1.31 million abortions in 2000 were on account of rape or incest). Retrieved via InfoPlease January 7, 2007. Adapted from "Alan Guttmacher Institute, Induced Abortion, Facts in Brief, 2002". Facts in Brief Archived October 13, 2007, at the Wayback Machine from Guttmacher Institute does not include the 13 000 statistic though, nor does the 2003 version.
- ^ Dehlendorf, Christine; Lisa Harris (October 1, 2013). "Disparities in Abortion Rates: A Public Health Approach". American Journal of Public Health. 103 (10): 1772–1779. doi:10.2105/ajph.2013.301339. PMC 3780732. PMID 23948010.
- ^ "Abortion Surveillance — United States, 2011". Retrieved January 25, 2017.
- ^ Raymond, E. G.; Grimes, D. A. (2012). "The Comparative Safety of Legal Induced Abortion and Childbirth in the United States". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 119 (2, Part 1): 215–219. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e31823fe923. PMID 22270271.
...The pregnancy-associated mortality rate among women who delivered live neonates was 8.8 deaths per 100,000 live births. The mortality rate related to induced abortion was 0.6 deaths per 100,000 abortions...The risk of death associated with childbirth is approximately 14 times higher than that with abortion.
- ^ Bartlett LA; Berg CJ; Shulman HB; et al. (April 2004). "Risk factors for legal induced abortion-related mortality in the United States". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 103 (4): 729–37. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000116260.81570.60. PMID 15051566.
- ^ Trupin, Suzanne (May 27, 2010). "Elective Abortion". eMedicine. Archived from the original on December 14, 2004. Retrieved June 1, 2010.
At every gestational age, elective abortion is safer for the mother than carrying a pregnancy to term.
- ^ Pittman, Genevra (January 23, 2012). "Abortion safer than giving birth: study". Reuters. Archived from the original on February 6, 2012. Retrieved February 4, 2012.
- ^ "Gallup: Abortion". Gallup poll. June 22, 2007.
- ^ "Trimesters Still Key to U.S. Abortion Views". June 13, 2018.
- ^ a b Saad, Lydia (April 28, 2010). "Education Trumps Gender in Predicting Support for Abortion - College-educated adults -- and especially college-educated women -- most supportive". Gallop. Archived from the original on September 16, 2017. Retrieved January 5, 2020.
Educational achievement is much more important than gender in determining support for broadly legal abortion, with college-educated adults -- and especially college-educated women -- the most supportive. This has been the case since the 1970s. Gallup's long-term abortion question -- instituted two years after the 1973 Roe v. Wade ruling gave sweeping constitutional protection to abortion -- asks Americans to say whether they believe abortion should be "legal under any circumstances," "legal only under certain circumstances," or "illegal in all circumstances."
- ^ a b "Public Opinion on Abortion - Views on abortion, 1995-2019". Pew Research Center. August 29, 2019. Archived from the original on September 19, 2019. Retrieved January 5, 2020.
Seven-in-ten college graduates (70%) say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, as do 60% of those with some college education. A slim majority of those with a high school degree or less education share this opinion: 54% say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, while 44% say it should be illegal in all or most cases.
- ^ a b Murray, Mark (January 21, 2013). "NBC/WSJ poll: Majority, for first time, want abortion to be legal". NBC News. Retrieved August 8, 2013.
- ^ a b "Roe v. Wade at 40: Most Oppose Overturning Abortion Decision". January 16, 2013.
- ^ Saad, Lydia (May 14, 2010). "The New Normal on Abortion: Americans More "Pro-Life"". Gallup. Retrieved August 8, 2013.
- ^ "Committed to Availability, Conflicted about Morality: What the Millennial Generation Tells Us about the Future of the Abortion Debate and the Culture Wars". Public Religion Research Institute. June 9, 2011.
- ^ "Abortion views table 2008–2012". Pew Research Center for the People & the Press. April 25, 2012. Retrieved August 8, 2013.
- ^ a b "Poll: Strong Support For Abortion Rights" (January 22, 2003). CBS News. Retrieved January 11, 2007.
- ^ a b The Polling Report. (2008). Retrieved September 10, 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f "Abortion". Gallup Poll. Gallup.com. June 22, 2007. p. 2. Archived from the original on May 13, 2010. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
- ^ See Saad, "Americans Walk the Middle Road on Abortion", The Gallup Poll Monthly (April 2000); "Gallup Poll Topics". Archived from the original on June 3, 2008. Retrieved August 25, 2016. from Florida Right to Life. Retrieved January 12, 2007.
- ^ "Abortion". Gallup.com. June 22, 2007. Retrieved August 8, 2013.
- ^ Rubin, Allisa J. (June 18, 2000). "Americans Narrowing Support for Abortion." Los Angeles Times. Retrieved January 11, 2007.
- ^ a b Public Agenda Online. (2006). Men and women hold similar views on the legality of abortion
- ^ FOX News/Opinion Dynamics Poll. April 25–26, 2005: "Do you think a female under age 18 should be required by state law to notify at least one parent or guardian before having an abortion?" 78% yes, 17% no. "Do you think a female under age 18 should be required by state law to get permission or consent from at least one parent or guardian before having an abortion?" 72% yes, 22% no.
- ^ Harris Interactive, (May 4, 2006). "Support for Roe vs. Wade Declines to Lowest Level Ever." Retrieved 2007-01-04. Pro-life activists have disputed whether the Harris poll question is a valid measure of public opinion about Roe's overall decision, because the question focuses only on the first three months of pregnancy. See Franz, Wanda. "The Continuing Confusion About Roe v. Wade" Archived May 12, 2008, at the Wayback Machine, NRL News (June 2007). Also see Adamek, Raymond. "Abortion Polls", Public Opinion Quarterly, Vol. 42, No. 3 (Autumn, 1978), pp. 411–413.
- ^ CNN Opinion Research Poll, (May 9, 2007). Retrieved 2007-05-27.
- ^ "Abortion" The Gallup Poll (May 21, 2007) Retrieved May 28, 2007.
- ^ "Moving Beyond "Pro-Choice" and "Pro-Life" - PRRI". Retrieved January 25, 2017.
- ^ Most Who Know of Decision Agree With Supreme Court on Partial Birth Abortion Archived 2007-04-27 at the Wayback Machine Rasmussen Reports. April 22, 2007. Retrieved on April 26, 2007
- ^ "The Hyde Amendment" (PDF). National Committee for a Human Life Amendment. April 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 16, 2009. Retrieved January 23, 2009. text and history
- ^ Francis Roberta W. "Frequently Asked Questions". Equal Rights Amendment. Alice Paul Institute. Archived from the original on April 17, 2009. Retrieved September 13, 2009.
- ^ "Women's Health Policy Facts" (PDF). The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 25, 2009. Retrieved January 2, 2009.
- ^ a b Archived June 3, 2008, at the Wayback Machine (archived from the original on June 3, 2008)
- ^ "The New York Times/CBS News Poll 2004 Republican National Delegate Survey (Q29)" (PDF). The New York Times.
- ^ "New National Abortion Poll Shows Majority of Americans are Pro-Life". Zogby International. January 16, 2004. Archived from the original on December 5, 2004. Retrieved June 29, 2011.
- ^ "The New York Times/CBS News Poll 2004 Democratic National Delegate Survey (Q29)" (PDF). The New York Times.
- ^ National Platform of the Libertarian Party, 1.4 Abortion, adopted in Convention, May 2012.
- ^ a b Coble, Yank D. (1992). "Induced Termination of Pregnancy Before and After Roe v Wade: Trends in the Mortality and Morbidity of Women". JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association. 268 (22): 3231. doi:10.1001/jama.1992.03490220075032.
- ^ Strauss, Lilo T.; Herndon, Joy; Chang, Jeani; Parker, Wilda Y.; Bowens, Sonya V.; Zane, Suzanne B.; Berg, Cynthia J.; Berg, CJ (2004). "Abortion surveillance--United States, 2001". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 53 (9): 1–32. PMID 15562258.
- ^ "Mississippi 'Personhood' Amendment Vote Fails". Huffington Post. November 8, 2011.
- ^ Phillips, Rich. "Judge lets Mississippi's only abortion clinic stay open -- for now". CNN.
- ^ Myers, Caitlin; Jones, Rachel; Upadhyay, Ushma (July 31, 2019). "Predicted changes in abortion access and incidence in a post-Roe world". Contraception. 100 (5): 367–373. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2019.07.139. ISSN 0010-7824. PMID 31376381.
- ^ "Termination of Pregnancy for Fetal Abnormality" (PDF). Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists: 30. May 2010. Retrieved October 26, 2015.
Live birth following medical termination of pregnancy before 21+6 weeks of gestation is very uncommon. Nevertheless, women and their partners should be counselled about this unlikely possibility and staff should be trained to deal with this eventuality. Instances of recorded live birth and survival increase as gestation at birth extends from 22 weeks. In accordance with prior RCOG guidance, feticide should be routinely offered from 21+6 weeks of gestation.Where the fetal abnormality is not compatible with survival, termination of pregnancy without prior feticide may be preferred by some women. In such cases, delivery management should be discussed and planned with the parents and all health professionals involved and a written care plan agreed before termination takes place. Where the fetal abnormality is not lethal and termination of pregnancy is being undertaken after 22 weeks of gestation, failure to perform feticide could result in live birth and survival, an outcome that contradicts the intention of the abortion. In such situations, the child should receive the neonatal support and intensive care that is in the child's best interest and its condition managed within published guidance for neonatal practice.
- ^ Hollander, D. (May 2004). "For Second-Trimester Abortion, Women Given Misoprostol Vaginally Report the Greatest Satisfaction". Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health. 36 (3): 133. doi:10.1111/j.1931-2393.2004.tb00203.x. Retrieved October 26, 2015.
...Additionally, a significantly higher proportion of women in the vaginal misoprostol group, and a marginally higher proportion of those in the oral misoprostol group, than of those in the intra-amniotic prostaglandin group had a live birth (20%, 15% and 5%, respectively)....
- ^ Hopper, Tristin (February 1, 2013). "Birth of a legal quandry[sic]: Live-birth abortions a perilous grey zone in Canada's criminal code". National Post. Retrieved October 26, 2015.
- ^ Vellacott, Maurice (January 23, 2013). "Letter to RCMP Commissioner Rob Paulson". www.straight.com. Archived from the original (Letter) on January 31, 2013. Retrieved October 26, 2015.
- ^ The Associated Press (February 7, 2009). "Doctor loses license over live-birth abortion". New York Daily News. Retrieved October 26, 2015.
- ^ Jeffries, Liz (August 2, 1981). "Abortion". The Philadelphia Inquirer. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 9, 1981. Retrieved October 26, 2015.
- ^ Wyldes (May 2007). "Termination of pregnancy for fetal anomaly: a population-based study 1995 to 2004". BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology. 114 (5): 639–642. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2007.01279.x. PMID 17355269.
- ^ Stroh, G. (September 1, 1976). "Reported live births following induced abortion: two and one-half years' experience in Upstate New York". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 126 (1): 83–90. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(76)90469-5. PMID 961751.
- ^ "House Report 107-186 - BORN-ALIVE INFANTS PROTECTION ACT OF 2001". Retrieved January 25, 2017.
- ^ Pear, Robert (April 23, 2005). "New Attention for 2002 Law on Survivors of Abortion". The New York Times. Retrieved October 26, 2015.
- ^ Diedrich, J.; Drey, E. (January 2010). "Clinical Guidelines: Induction of fetal demise before abortion" (PDF). Contraception. 81 (6): 462–73. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2010.01.018. PMID 20472112. Retrieved October 26, 2015.
- ^ Jansen, Robert (1990). "Unfinished Feticide". Journal of Medical Ethics. 16 (2): 61–65. doi:10.1136/jme.16.2.61. PMC 1375929. PMID 2195170. Retrieved October 26, 2015.
- ^ Sfakianaki, Anna K. (February 1, 2014). "Potassium Chloride-Induced Fetal Demise: A Retrospective Cohort Study of Efficacy and Safety". Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine. 33 (2): 337–341. doi:10.7863/ultra.33.2.337. PMID 24449738. Archived from the original on October 28, 2015. Retrieved October 26, 2015.
Further reading
- Reagan, Leslie J. (1997). When Abortion Was a Crime: Women, Medicine, and Law in the United States, 1867–1973. Berkeley, Calif.: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-08848-4.
- Rowland, Debran (2004). The Boundaries of Her Body: The Troubling History of Women's Rights in America. Naperville, Ill.: Sphinx Publishing. ISBN 1-57248-368-7.
- Shimabukuro, Jon O. (December 7, 2018). "Abortion: Judicial History and Legislative Response" (PDF). Washington, DC: Congressional Research Service.
- Weingarten, Karen (2014). Abortion in the American Imagination: Before Life and Choice, 1880–1940. New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press. ISBN 978-0-8135-6530-9.
External links
- Abortion pill access
- Full Text of Roe v. Wade Decision
- Interactive maps comparing U.S. abortion restrictions by state
- Number of Abortions - Abortion Counters
- For Many Women, The Nearest Abortion Provider Is Hundreds Of Miles Away - Includes map showing distance to nearest abortion clinic
- Towards a compromise solution brief essay