Solar eclipse of November 3, 2013
| Solar eclipse of November 3, 2013 | |
|---|---|
Partial from Libreville, Gabon | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Hybrid |
| Gamma | 0.3272 |
| Magnitude | 1.0159 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 100 s (1 min 40 s) |
| Coordinates | 3°30′N 11°42′W / 3.5°N 11.7°W |
| Max. width of band | 58 km (36 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| (P1) Partial begin | 10:04:34 |
| (U1) Total begin | 11:05:17 |
| Greatest eclipse | 12:47:36 |
| (U4) Total end | 14:27:42 |
| (P4) Partial end | 15:28:21 |
| References | |
| Saros | 143 (23 of 72) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9538 |
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node on 3 November 2013. It was a hybrid eclipse of the Sun with a magnitude of 1.0159, with a small portion over the western Atlantic Ocean at sunrise as an annular eclipse, and the rest of the path as a narrow total solar eclipse. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A hybrid solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's in sunrise and sunset, but at Greatest Eclipse the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's.
In this particular case the eclipse path starts out as annular. Further down the track it changes to total and then back to annular before the path ends.
It was the 23rd eclipse of the 143rd Saros cycle, which began with a partial eclipse on March 7, 1617 and will conclude with a partial eclipse on April 23, 2897.
This hybrid solar eclipse started annular solar eclipse and ended total solar eclipse.
Viewing
Totality was visible from the northern Atlantic Ocean (east of Florida) to Africa (Gabon (landfall), R. Congo, DR Congo, Uganda, South Sudan, Kenya, Ethiopia, Somalia), with a maximum duration of totality of 1 minute and 39 seconds, visible from the Atlantic Ocean south of Ivory Coast and Ghana.[1]
Places with partial darkening were the Eastern coast of North America, southern Greenland, Bermuda, the Caribbean islands, Costa Rica, Panama, Northern South America, almost all the African continent, the Iberian Peninsula, Italy, Greece, Malta, Southern Russia, the Caucasus, Turkey and the Middle East.
This solar eclipse happened simultaneously with the 2013 Abu Dhabi Grand Prix, and it was possible to observe a partial solar eclipse in Abu Dhabi before the sunset while the F1 race took place, as shown briefly during its broadcast.[2]
From space
Photo gallery
-
Wind angle view in Agüimes, Las Palmas during the eclipse
-
Simulated eclipse offshore Monrovia, Liberia at 12:34 UTC, 13 minutes before totality
-
An eclipse monument in Pakwach, Uganda
-
From Ottawa, Canada at sunrise, 11:24 UTC
-
From Liberty State Park, New Jersey at sunrise, 11:37 UTC
-
From Arlington, Virginia at sunrise, 11:40 UTC
-
From Melbourne, Florida at sunrise, 11:45 UTC
-
Partial from Las Palmas, Canary Islands, 12:01 UTC
-
Partial from Tétouan, Morocco, 12:27 UTC
-
Partial from Bayeux, Brazil, 12:35 UTC
-
Partial from Lake Turkana, Kenya, 13:54 UTC
-
From Triolet, Mauritius at sunset, 14:18 UTC
-
From Bunia, DR Congo at greatest eclipse, 14:22 UTC
-
From Addis Ababa, Ethiopia at sunset, 14:50 UTC
Related eclipses
Eclipses of 2013
- A partial lunar eclipse on April 25.
- An annular solar eclipse on May 10.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on May 25.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on October 18.
- A hybrid solar eclipse on November 3.
Solar eclipses 2011–2014
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[3]
The partial solar eclipses on January 4, 2011 and July 1, 2011 occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2011 to 2014 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
118 Partial in Tromsø, Norway |
June 1, 2011 Partial |
1.21300 | 123 Hinode XRT footage |
November 25, 2011 Partial |
−1.05359 | |
128 Annularity in Red Bluff, CA, USA |
May 20, 2012 Annular |
0.48279 | 133 Totality in Mount Carbine, Queensland, Australia |
November 13, 2012 Total |
−0.37189 | |
138 Annularity in Churchills Head, Australia |
May 10, 2013 Annular |
−0.26937 | 143 Partial in Libreville, Gabon |
November 3, 2013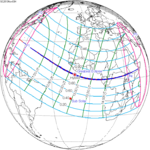 Hybrid |
0.32715 | |
148 Partial in Adelaide, Australia |
April 29, 2014 Annular (non-central) |
−0.99996 | 153 Partial in Minneapolis, MN, USA |
October 23, 2014 Partial |
1.09078 | |
Saros 143
This eclipse is a part of Saros series 143, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 72 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on March 7, 1617. It contains total eclipses from June 24, 1797 through October 24, 1995; hybrid eclipses from November 3, 2013 through December 6, 2067; and annular eclipses from December 16, 2085 through September 16, 2536. The series ends at member 72 as a partial eclipse on April 23, 2897. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of totality was produced by member 16 at 3 minutes, 50 seconds on August 19, 1887, and the longest duration of annularity will be produced by member 51 at 4 minutes, 54 seconds on September 6, 2518. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit.[4]
| Series members 12–33 occur between 1801 and 2200: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 12 | 13 | 14 |
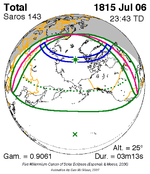 July 6, 1815 |
 July 17, 1833 |
 July 28, 1851 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 |
 August 7, 1869 |
 August 19, 1887 |
 August 30, 1905 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 |
 September 10, 1923 |
 September 21, 1941 |
 October 2, 1959 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 |
 October 12, 1977 |
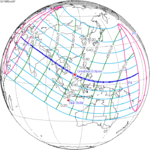 October 24, 1995 |
 November 3, 2013 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 |
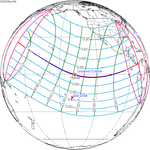 November 14, 2031 |
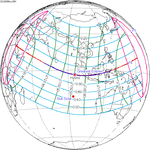 November 25, 2049 |
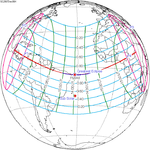 December 6, 2067 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 |
 December 16, 2085 |
 December 29, 2103 |
 January 8, 2122 |
| 30 | 31 | 32 |
 January 20, 2140 |
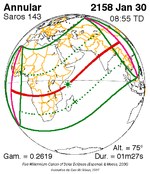 January 30, 2158 |
 February 10, 2176 |
| 33 | ||
 February 21, 2194 | ||
Inex series
This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Inex series members between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
 January 3, 1927 (Saros 140) |
 December 14, 1955 (Saros 141) |
 November 22, 1984 (Saros 142) |
 November 3, 2013 (Saros 143) |
 October 14, 2042 (Saros 144) |
 September 23, 2071 (Saros 145) |
 September 4, 2100 (Saros 146) |
||
Tritos series
This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1901 and 2100 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 September 9, 1904 (Saros 133) |
 August 10, 1915 (Saros 134) |
 July 9, 1926 (Saros 135) | |
 June 8, 1937 (Saros 136) |
 May 9, 1948 (Saros 137) |
 April 8, 1959 (Saros 138) | |
 March 7, 1970 (Saros 139) |
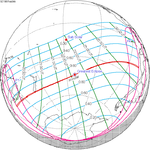 February 4, 1981 (Saros 140) |
 January 4, 1992 (Saros 141) | |
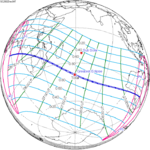 December 4, 2002 (Saros 142) |
 November 3, 2013 (Saros 143) |
 October 2, 2024 (Saros 144) | |
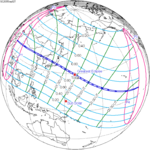 September 2, 2035 (Saros 145) |
 August 2, 2046 (Saros 146) |
 July 1, 2057 (Saros 147) | |
 May 31, 2068 (Saros 148) |
 May 1, 2079 (Saros 149) |
 March 31, 2090 (Saros 150) | |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| 20 eclipse events between June 10, 1964 and August 21, 2036 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| June 10–11 | March 28–29 | January 14–16 | November 3 | August 21–22 |
| 117 | 119 | 121 | 123 | 125 |
 June 10, 1964 |
 March 28, 1968 |
 January 16, 1972 |
 November 3, 1975 |
 August 22, 1979 |
| 127 | 129 | 131 | 133 | 135 |
 June 11, 1983 |
 March 29, 1987 |
 January 15, 1991 |
 November 3, 1994 |
 August 22, 1998 |
| 137 | 139 | 141 | 143 | 145 |
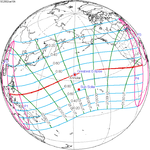 June 10, 2002 |
 March 29, 2006 |
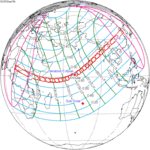 January 15, 2010 |
 November 3, 2013 |
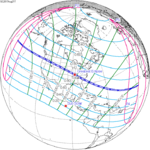 August 21, 2017 |
| 147 | 149 | 151 | 153 | 155 |
 June 10, 2021 |
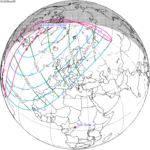 March 29, 2025 |
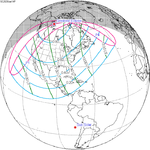 January 14, 2029 |
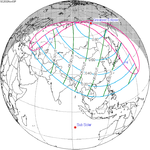 November 3, 2032 |
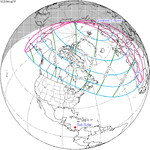 August 21, 2036 |
Notes
References
- ^ Hybrid Solar Eclipse of 2013 Nov 03 NASA
- ^ "Rare 'hybrid' eclipse sweeps across the globe plunging parts of Europe, Africa and US into darkness". Belfast Telegraph. November 3, 2013. Retrieved November 4, 2013.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ "NASA - Catalog of Solar Eclipses of Saros 143". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Eclipse Over New York (partial), APOD 11/4/2013
- Eclipse at 44,000 Feet, APOD 11/7/2013, totality above Atlantic Ocean, 600 miles southeast of Bermuda
- Solar Eclipse from Uganda, APOD 11/8/2013, totality from Pokwero, Nebbi District, Northern Region, Uganda
- An Active Sun During a Total Eclipse, APOD 11/11/2013, combination of Sun in ultraviolet light recorded by the SWAP instrument aboard PROBA2, total eclipse from Gabon, and solar corona taken by LASCO instrument aboard SOHO



















