Solar eclipse of January 6, 2019
| Solar eclipse of January 6, 2019 | |
|---|---|
 From Nakhodka, Russia | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | 1.1417 |
| Magnitude | 0.7145 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 67°24′N 153°36′E / 67.4°N 153.6°E |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 1:42:38 |
| References | |
| Saros | 122 (58 of 70) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9550 |

The solar eclipse of January 6, 2019 was a partial solar eclipse that was visible in East Asia and North Pacific.
Visibility
The maximal phase (71%) of the partial eclipse was recorded in Sakha Republic (Russia).
The eclipse was observed in Japan, Russian Far East, North and South Korea, eastern China, eastern Mongolia and on the north-west of Alaska.
Gallery
-
Jinan, China, 00:18 UTC
-
Bohyeonsan, South Korea, 00:47 UTC
-
Aichi Prefecture, Japan, 01:00 UTC
Related eclipses
Eclipses of 2019
- A partial solar eclipse on January 6.
- A total lunar eclipse on January 21.
- A total solar eclipse on July 2.
- A partial lunar eclipse on July 16.
- An annular solar eclipse on December 26.
Tzolkinex
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of November 25, 2011
- Followed: Solar eclipse of February 17, 2026
Half-Saros cycle
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of December 31, 2009
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of January 12, 2028
Tritos
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of February 7, 2008
- Followed: Solar eclipse of December 5, 2029
Solar Saros 122
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of December 25, 2000
- Followed: Solar eclipse of January 16, 2037
Inex
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of January 26, 1990
- Followed: Solar eclipse of December 16, 2047
Triad
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of March 7, 1932
- Followed: Solar eclipse of November 6, 2105
Solar eclipses of 2018–2021
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
The partial solar eclipses on February 15, 2018 and August 11, 2018 occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2018 to 2021 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
117 Partial in Melbourne, Australia |
July 13, 2018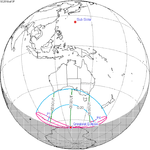 Partial |
−1.35423 | 122 Partial in Nakhodka, Russia |
January 6, 2019 Partial |
1.14174 | |
127 Totality in La Serena, Chile |
July 2, 2019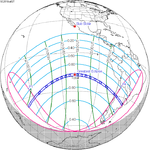 Total |
−0.64656 | 132 Annularity in Jaffna, Sri Lanka |
December 26, 2019 Annular |
0.41351 | |
137 Annularity in Beigang, Yunlin, Taiwan |
June 21, 2020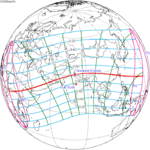 Annular |
0.12090 | 142 Totality in Gorbea, Chile |
December 14, 2020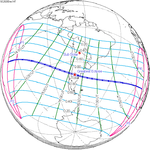 Total |
−0.29394 | |
147 Partial in Halifax, Canada |
June 10, 2021 Annular |
0.91516 | 152 From HMS Protector off South Georgia |
December 4, 2021 Total |
−0.95261 | |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.
| 22 eclipse events between June 1, 2011 and October 24, 2098 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| May 31–June 1 | March 19–20 | January 5–6 | October 24–25 | August 12–13 |
| 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 | 126 |
 June 1, 2011 |
 March 20, 2015 |
 January 6, 2019 |
 October 25, 2022 |
 August 12, 2026 |
| 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 | 136 |
 June 1, 2030 |
 March 20, 2034 |
 January 5, 2038 |
 October 25, 2041 |
 August 12, 2045 |
| 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 | 146 |
 May 31, 2049 |
 March 20, 2053 |
 January 5, 2057 |
 October 24, 2060 |
 August 12, 2064 |
| 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 | 156 |
 May 31, 2068 |
 March 19, 2072 |
 January 6, 2076 |
 October 24, 2079 |
 August 13, 2083 |
| 158 | 160 | 162 | 164 | |
 June 1, 2087 |
 October 24, 2098 | |||
References
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.







