Canadian Prairies
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2014) |
The Canadian Prairies is a region in Western Canada, which may correspond to several different definitions, natural or political. The region comprises the Canadian portion of the Great Plains, and notably, the Prairie provinces or simply the Prairies comprise the provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba, as they are partially covered by prairie (grasslands), mostly in the southern regions of each province. In a more restricted sense, the term may also refer only to the areas of those provinces covered by prairie; their portions of the physiographic region known as the Interior Plains. Prairie also covers portions of northeastern British Columbia, though that province is typically not included in the region in a political sense.[citation needed]
Definitions
The prairies in Canada are a temperate grasslands and shrublands biome, within the prairie ecoregion of Canada and consists of Northern mixed grasslands in Alberta, Saskatchewan, and southern Manitoba. Northern short grasslands in southeastern Alberta and southwestern Saskatchewan. Northern tall grasslands in southern Manitoba, and Aspen parkland, which covers central Alberta, central Saskatchewan, and southern Manitoba.[1] The Prairie starts from north of Edmonton, it covers the three provinces in a southward-slanting line east to the Manitoba-Minnesota border.[2] Alberta has the most land classified as Prairie, while Manitoba has the least, as the Boreal Forest begins at a lower latitude in Manitoba than in Alberta.
Main climates


According to the Köppen climate classification the Canadian prairies generally experience dry semi-arid climates (Köppen Bsk) in the brown soil regions, and somewhat dry Humid Continental climates (Köppen Dfb) in the outer dark brown and black soil areas. The Canadian prairies typically experience about 12 to 15 in (300 to 380 mm) of annual precipitation in the semi-arid areas while they experience 16 to 20 in (410 to 510 mm) in the continental regions. The area is also prone to thunderstorms in the spring and summer. Some of these storms, especially further south, are strong enough for tornadoes.
| City | Province | July | January | Annual precipitation | Plant hardiness zone | Average growing season (in days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lethbridge[4] | AB | 26 °C/10 °C (79 °F/50 °F) | 0 °C/-12 °C (32 °F/10 °F) | 380 mm (14.9 in) | 4B | 119 |
| Calgary[5] | AB | 23 °C/9 °C (73 °F/48 °F) | -1 °C/-13 °C (30 °F/9 °F) | 419 mm (16.4 in) | 4A | 117 |
| Medicine Hat[6] | AB | 28 °C/12 °C (82 °F/54 °F) | -5 °C/-16 °C (23 °F/3 °F) | 323 mm (12.7 in) | 4B | 134 |
| Edmonton[7] | AB | 23 °C/12 °C (73 °F/54 °F) | -6 °C/-15 °C (21 °F/5 °F) | 456 mm (17.9 in) | 4A | 135 |
| Grande Prairie[8] | AB | 23 °C/10 °C (73 °F/50 °F) | -8 °C/-19 °C (18 °F/-2 °F) | 445 mm (17.5 in) | 3B | 117 |
| Regina[9] | SK | 26 °C/12 °C (79 °F/54 °F) | -9 °C/-20 °C (16 °F/-4 °F) | 390 mm (15.3 in) | 3B | 119 |
| Saskatoon[10] | SK | 25 °C/12 °C (77 °F/54 °F) | -10 °C/-21 °C (14 °F/-9 °F) | 354 mm (13.8 in) | 3B | 117 |
| Prince Albert[11] | SK | 24 °C/12 °C (75 °F/54 °F) | -11 °C/-23 °C (12 °F/-9 °F) | 428 mm (16.8 in) | 3A | 108 |
| Brandon[12] | MB | 25 °C/11 °C (77 °F/54 °F) | -11 °C/-22 °C (12 °F/-11 °F) | 474 mm (18.6 in) | 3B | 119 |
| Winnipeg[13] | MB | 25 °C/12 °C (77 °F/55 °F) | -11 °C/-21 °C (12 °F/-6 °F) | 521 mm (20.5 in) | 4A | 121 |
Physical geography
Although the Prairie Provinces region is named for the prairies located within Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba, the physical geography of the three provinces is quite diverse, consisting of portions of the Canadian Shield, the Western Cordillera and the Canadian Interior Plains. The plains comprise both prairies and forests while, with the exception of Arctic tundra along the Hudson Bay, the shield is predominantly forested.

Prairies

Three main grassland types occur in the Canadian prairies: tallgrass prairie, mixed grass prairie, and fescue prairie (or using the WWF terminology, northern tall grasslands, northern mixed grasslands, and northern short grasslands). Each has a unique geographic distribution and characteristic mix of plant species. All but a fraction of one percent of the tallgrass prairie has been converted to cropland. What remains occurs on the 6,000 km2 (2,300 sq mi) plain centred in the Red River Valley in Manitoba. Mixed prairie is more common and is part of the dry interior plains that extend from Canada south to the U.S. state of Texas. More than half of the remaining native grassland in the Canadian prairies is mixed. Though widespread in southern Saskatchewan and southeastern Alberta, because of extensive cattle grazing, it is estimated that only 24% of the original mixed prairie grassland remains.[citation needed] Fescue prairie occurs in the moister regions, occupying the northern extent of the prairies in central and southwestern Alberta and west-central Saskatchewan.[14]
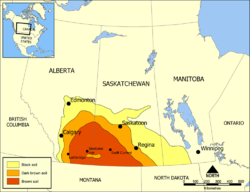
The southwestern Canadian prairies, supporting brown and black soil types, are semi-arid and highly prone to frequent and severe droughts. The zones around the cities of Regina and immediately east of Calgary are also very dry. Most heavy precipitation quickly dissipates by the time it passes Cheadle on its way heading east. In an average year, southern Saskatchewan receives between 30–51 cm (12–20 in) of precipitation, with the majority falling between April and June. Frost from October to April (and sometimes even early May) limits the growing season for certain crops.
The eastern section of the Canadian prairies in Manitoba is well watered with several large lakes such as Lake Winnipeg and several large rivers. The area also gets reasonable amounts of precipitation. The middle sections of Alberta and Saskatchewan are also wetter than the south and have better farmland, despite having a shorter frost-free season.[citation needed] The areas around Edmonton and Saskatoon are especially notable as good farmland. Both lie in the northern area of the Palliser's Triangle, and are within aspen parkland a transitional prairie ecozone.[1][2]
Further north, the area becomes too cold for most agriculture besides wild rice operations and sheep raising, and it is dominated by boreal forest. The Peace Region in northwestern Alberta is an exception, however. It lies north of the 55th Parallel and is warm and dry enough to support extensive farming. Aspen parkland covers the area; The long daylight hours in this region during the summer are an asset despite having an even shorter growing season than central Alberta. In fact, agriculture plays a major economic role in the Peace Region.
Demographics
Template:Canadian Prairies census metropolitan areas In the Canada 2011 Census, the Canadian prairie provinces had a population of 5,886,906, consisting of 3,645,257 in Alberta, 1,208,268 in Manitoba, and 1,033,381 in Saskatchewan, up 8.9% from 5,406,908 in 2006.[15] The three provinces have a combined area of 1,780,650.6 km2 (687,513.0 sq mi), consisting of 640,081.87 km2 (247,136.99 sq mi) in Alberta, 552,329.52 km2 (213,255.62 sq mi) in Manitoba, and 588,239.21 km2 (227,120.43 sq mi) in Saskatchewan.[15]

Growth
Some of the prairie region of Canada has seen rapid growth from a boom in oil production since the mid-20th century.[16] According to StatsCanada, the prairie provinces had a population of 5,886,906 in 2011. In 2016, the population had grown by 14.6% to 6,748,280.[17]
Economy
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2013) |

Primary industries include agriculture (wheat, barley, canola, brassica, oats), and cattle and sheep ranching. Also, natural resources such as oil sands (Fort McMurray, Alberta) and other forms of oil production can be found on the plains. Secondary industries consist of the refinement of oils and agriculture processing.
Culture and politics

The Prairies are distinguished from the rest of Canada by cultural and political traits. The oldest influence on Prairie culture are the First Nations, who have lived in the area for millennia. The first Europeans to see the Prairies were fur traders and explorers from eastern Canada (mainly present-day Quebec) and Great Britain via Hudson Bay. They gave rise to the Métis, working class "children of the fur trade." Not until the Canadian Pacific Railway was built did widespread agricultural settlement occur. During their settlement, the prairies were settled in distinct ethnic block settlements giving certain areas distinctively Ukrainian, German, French, or Scandinavian Canadian cultures.
Some areas also developed cultures around their main economic activity. For example, southern Alberta is renowned for its cowboy culture, which developed when real open range ranching was practised in the 1880s. Canada's first rodeo, the Raymond Stampede, was established in 1902. These influences are also evident in the music of Canada's Prairie Provinces. This can be attributed partially to the massive influx of American settlers who began to migrate to Alberta (and to a lesser extent, Saskatchewan) in the late 1880s because of the lack of available land in the United States.
The Prairie Provinces have given rise to the "prairie protest" movements, such as the Winnipeg General Strike of 1919, the first general strike in Canadian history. These political movements (both of the left and right) tend to feed off of well established feelings of Western alienation, and each one represents a distinct challenge to the perceived Central Canadian elite.
The Prairies continue to have a wide range of political representation. While the Conservative Party of Canada has widespread support throughout the region, the New Democratic Party holds seats at the provincial level in all three provinces, forming the government in one, as well as holding seats at the federal level in all three provinces. The Liberal Party of Canada presently holds federal seats in urban areas of Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba, while the Alberta Liberal Party holds a provincial seat in Alberta and the Manitoba Liberal Party holds a seat in Manitoba.
See also
- List of regions of Canada
- Dominion Land Survey
- Natural Resources Acts
- Terrestrial ecozone
- High Plains (United States)
- Llano Estacado
- Shortgrass prairie
- Corner Gas – TV show featuring the sparseness of the plains as a major theme
References
- ^ a b "Prairies Ecozone". Ecological Framework of Canada. Government of Canada. Archived from the original on 2 June 2016. Retrieved 23 May 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Wide open spaces, but for how long?". The Royal Canadian Geographical Society. The Royal Canadian Geographical Society. Archived from the original on 3 April 2016. Retrieved 23 May 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Canada's Plant Hardiness". Canada's Plant Hardiness. Natural Resources Canada. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Lethbridge A, Alberta". Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010. Environment Canada. Archived from the original on 12 May 2014. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Canadian Climate Normals 1981-2010 Station Data Calgary International Airport". Environment Canada. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 15 July 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Medicine Hat A, Alberta". Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010 Medicine Hat. Environment Canada. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 14 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Edmonton City Centre Airport". Canadian Climate Normals 1981−2010. Environment Canada. August 19, 2013. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved September 10, 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Grande Prairie A". Canadian Climate Normals 1981−2010. Environment Canada. Archived from the original on May 14, 2014. Retrieved May 14, 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Regina International Airport". Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010. Environment Canada. Archived from the original on 12 May 2014. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Saskatoon Diefenbaker International Airport". Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010. Environment Canada. Archived from the original on May 13, 2014. Retrieved May 12, 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Prince Albert A". Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010. Environment Canada. Archived from the original on May 14, 2014. Retrieved May 14, 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Brandon CDA, Manitoba". Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010. Environment Canada. Archived from the original on 8 May 2014. Retrieved 7 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Winnipeg Richardson International Airport". Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010. Environment Canada. Archived from the original on February 11, 2015. Retrieved May 7, 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Prairie Grasslands and Parkland". Archived from the original on 2010-05-27.
- ^ a b "Population and dwelling counts, for Canada, provinces and territories, 2011 and 2006 censuses". Statistics Canada. 2012-01-24. Archived from the original on 2014-03-07. Retrieved 2012-03-17.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Atlantic unemployment tonic: oil sands". Archived from the original on 2008-10-20.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2017-05-04. Retrieved 2017-05-04.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
Further reading
- Alberta Encyclopedia Online (2005)
- Archer, John H. Saskatchewan: A History (1980)
- Barnhart, Gordon L., ed. Saskatchewan Premiers of the Twentieth Century. (2004). 418 pp.
- Bennett, John W. and Seena B. Kohl. Settling the Canadian-American West, 1890-1915: Pioneer Adaptation and Community Building. An Anthropological History. (1995). 311 pp. online edition
- Danysk, Cecilia. Hired Hands: Labour and the Development of Prairie Agriculture, 1880–1930. (1995). 231 pp.
- Emery, George. The Methodist Church on the Prairies, 1896–1914. McGill-Queen's U. Press, 2001. 259 pp.
- The Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan: A Living Legacy. U. of Regina Canadian Plains Research Center, 2005. online 1071pp in print edition
- Fairbanks, C. and S.B. Sundberg. Farm Women on the Prairie Frontier. (1983)
- Friesen, Gerald (1987), The Canadian prairies: a history, University of Toronto Press, ISBN 0-8020-6648-8
- Hodgson, Heather, ed. Saskatchewan Writers: Lives Past and Present. Regina: Canadian Plains Research Center, 2004. 247 pp.
- Jones, David C. Empire of Dust: Settling and Abandoning the Prairie Dry Belt. (1987) 316 pp.
- Keahey, Deborah. Making It Home: Place in Canadian Prairie Literature. (1998). 178 pp.
- Kononenko, Natalie "Vernacular religion on the prairies: negotiating a place for the unquiet dead," Canadian Slavonic Papers 60, no. 1-2 (2018)
- Langford, N. "Childbirth on the Canadian Prairies 1880-1930." Journal of Historical Sociology, 1995. Vol. 8, No. 3, pp. 278–302.
- Langford, Nanci Louise. "First Generation and Lasting Impressions: The Gendered Identities of Prairie Homestead Women." PhD dissertation U. of Alberta 1994. 229 pp. DAI 1995 56(4): 1544-A. DANN95214 Fulltext: ProQuest Dissertations & Theses
- Laycock, David. Populism and Democratic Thought in the Canadian Prairies, 1910 to 1945. (1990). 369 pp.
- Melnyk, George. The Literary History of Alberta, Vol. 1: From Writing-on-Stone to World War Two. U. of Alberta Press, 1998. 240 pp.
- Morton, Arthur S. and Chester Martin, History of prairie settlement (1938) 511pp
- Morton, W. L. Manitoba, a History University of Toronto Press, 1957 online edition
- Norrie, K. H. "The Rate of Settlement of the Canadian Prairies, 1870–1911", Journal of Economic History, Vol. 35, No. 2 (Jun., 1975), pp. 410–427 in JSTOR; statistical models
- Palmer, Howard. The Settlement of the West (1977) online edition
- Pitsula, James M. "Disparate Duo" Beaver 2005 85(4): 14–24, a comparison of Saskatchewan and Alberta, Fulltext in EBSCO
- Rollings-Magnusson, Sandra. "Canada's Most Wanted: Pioneer Women on the Western Prairies". Canadian Review of Sociology and Anthropology 2000 37(2): 223–238. ISSN 0008-4948 Fulltext: Ebsco
- Swyripa, Frances. Storied Landscapes: Ethno-Religious Identity and the Canadian Prairies (University of Manitoba Press, 2010) 296 pp. ISBN 978-0-88755-720-0.
- Thompson, John Herd. Forging the Prairie West (1998).
- Wardhaugh, Robert A. Mackenzie King and the Prairie West (2000). 328 pp.
- Waiser, Bill, and John Perret. Saskatchewan: A New History (2005).
Historiography
- Francis, R. Douglas. "In search of a prairie myth: A survey of the intellectual and cultural historiography of prairie Canada." Journal of Canadian Studies/Revue d'Études Canadiennes 24#3 (1989): 44+ online
- Ingles, Ernie B (2009), Peel's Bibliography of the Canadian Prairies to 1953, University of Toronto Press, ISBN 0-8020-4825-0
- Wardhaugh, Robert A., ed. Toward Defining the Prairies: Region, Culture, and History. (2001). 234 pp.
- Wardhaugh, Robert; Calder, Alison (2005), History, literature, and the writing of the Canadian Prairies, University of Manitoba Press, ISBN 0-88755-682-5 310 pp.
External links
 Media related to Canadian Prairies at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Canadian Prairies at Wikimedia Commons
