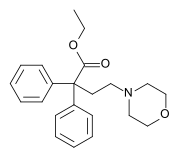
Dioxaphetyl butyrate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Amidalgon, Spasmoxal |
| Routes of administration | Oral, Other ROA Unknown |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.731 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H27NO3 |
| Molar mass | 353.45 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Dioxaphetyl butyrate (INN; trade names Amidalgon, Spasmoxal) is an opioid analgesic which is a diphenylacetic acid derivative, related to other open-chain opioid drugs such as dextropropoxyphene, levacetylmethadol (LAAM), lefetamine and dimenoxadol.
It produces similar effects to other opioids, including dependence, euphoria, analgesia, sedation, constipation, dizziness and nausea.
In the United States it is a Schedule I Narcotic controlled substance with an ACSCN of 9621 and a 2013 annual aggregrate manufacturing quota of zero.
References
